d45051ac0d60c53469d3d350060c21bd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 63

蛋白質體學 Proteomics 2010 Solid-Phase Peptide Synthesis (SPPS) and Applications of Synthetic Peptides 陳威戎
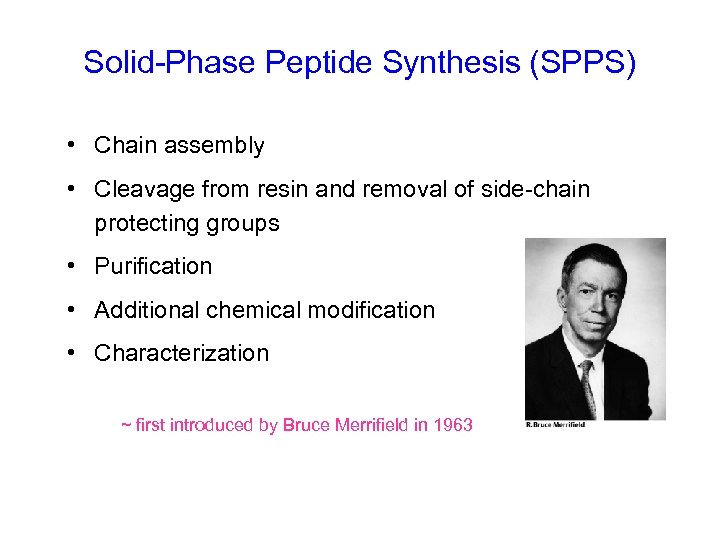
Solid-Phase Peptide Synthesis (SPPS) • Chain assembly • Cleavage from resin and removal of side-chain protecting groups • Purification • Additional chemical modification • Characterization ~ first introduced by Bruce Merrifield in 1963
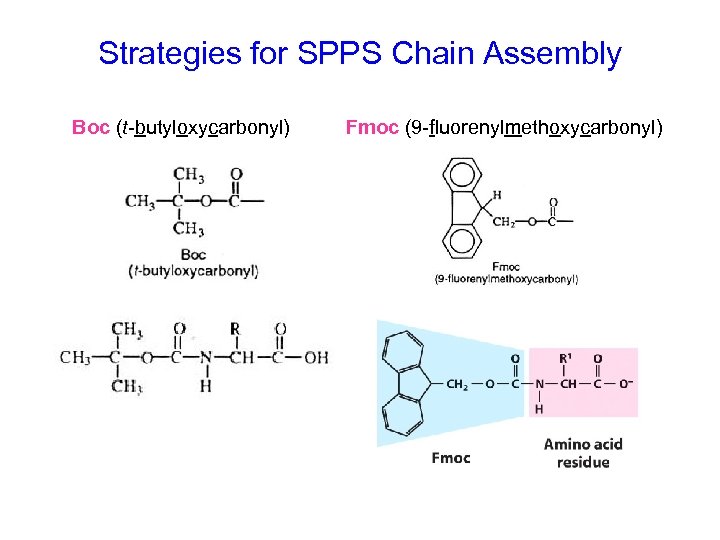
Strategies for SPPS Chain Assembly Boc (t-butyloxycarbonyl) Fmoc (9 -fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl)
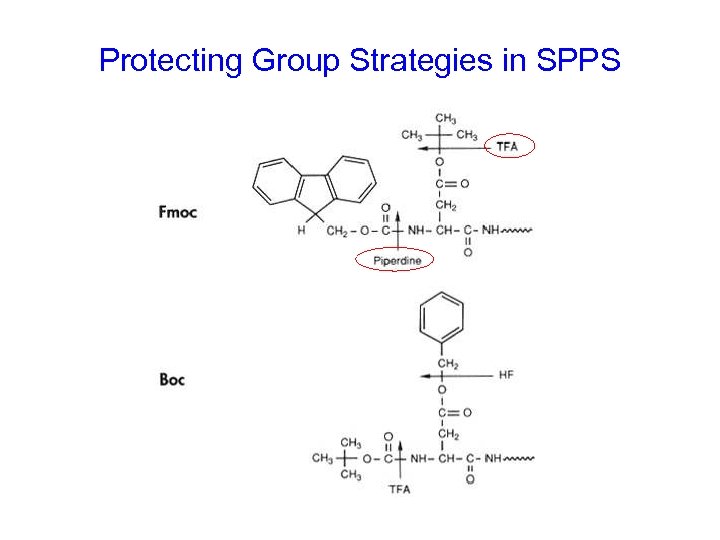
Protecting Group Strategies in SPPS
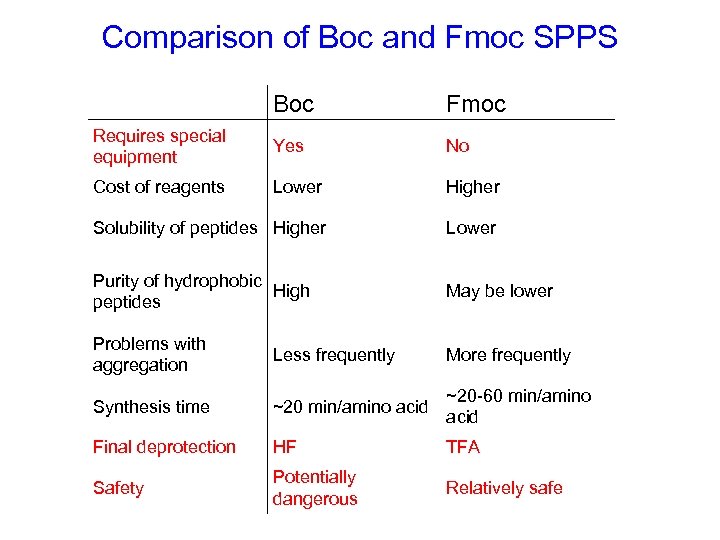
Comparison of Boc and Fmoc SPPS Boc Fmoc Requires special equipment Yes No Cost of reagents Lower Higher Solubility of peptides Higher Lower Purity of hydrophobic High peptides May be lower Problems with aggregation Less frequently More frequently Synthesis time ~20 min/amino acid ~20 -60 min/amino acid Final deprotection HF TFA Safety Potentially dangerous Relatively safe

Solid Support - Resin • Resin for SPPS: polystyrene bead with 1% divinyl-benzene, a cross-linking agent. • Dry resin beads: 40 -100 microns, 100 -200 or 200 -400 mesh • When in contact with solvents, the beads swell to approximately 10 times their dry volume. • Macroscopically, the resin appears as an insoluble solid support. However, on the molecular level the resin is “in solution” or fully solvated. • This solvation enhances coupling of the peptide resin with the protected amino acids.
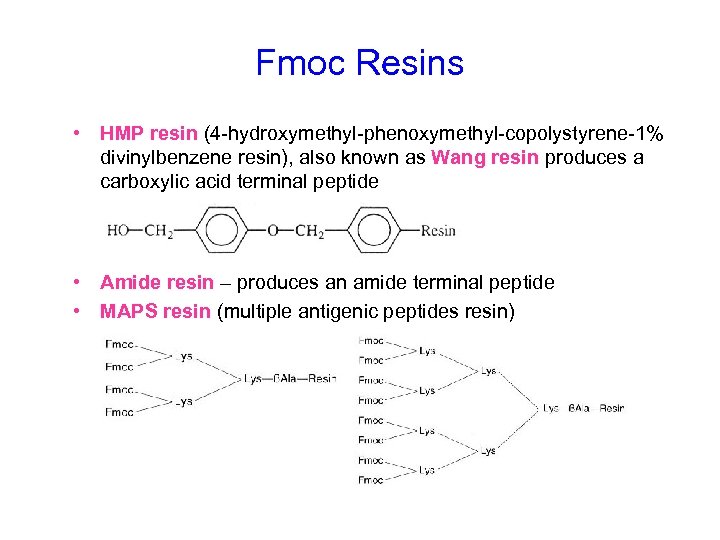
Fmoc Resins • HMP resin (4 -hydroxymethyl-phenoxymethyl-copolystyrene-1% divinylbenzene resin), also known as Wang resin produces a carboxylic acid terminal peptide • Amide resin – produces an amide terminal peptide • MAPS resin (multiple antigenic peptides resin)
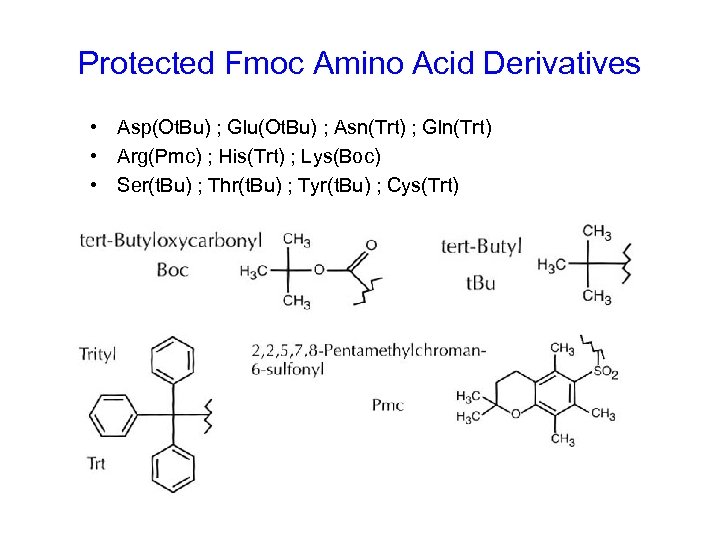
Protected Fmoc Amino Acid Derivatives • Asp(Ot. Bu) ; Glu(Ot. Bu) ; Asn(Trt) ; Gln(Trt) • Arg(Pmc) ; His(Trt) ; Lys(Boc) • Ser(t. Bu) ; Thr(t. Bu) ; Tyr(t. Bu) ; Cys(Trt)
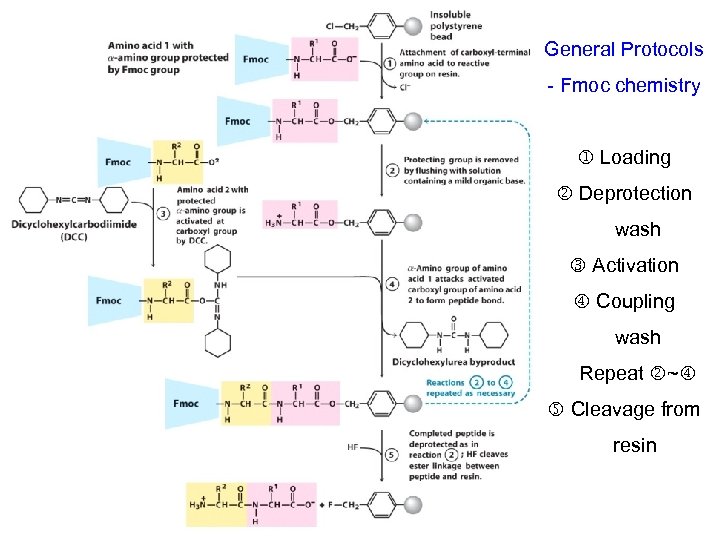
General Protocols - Fmoc chemistry Loading Deprotection wash Activation Coupling wash Repeat ~ Cleavage from resin
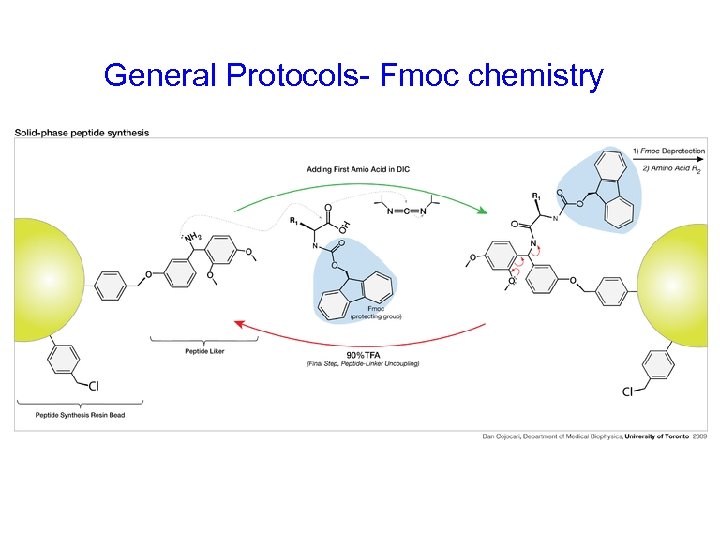
General Protocols- Fmoc chemistry
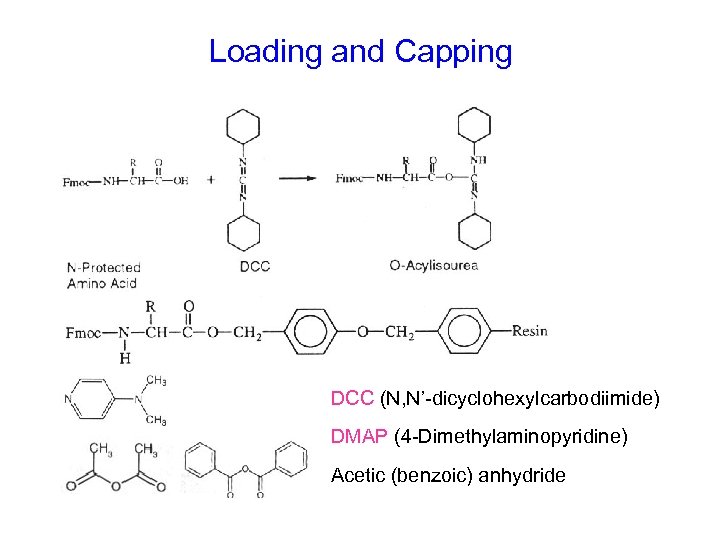
Loading and Capping DCC (N, N’-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide) DMAP (4 -Dimethylaminopyridine) Acetic (benzoic) anhydride
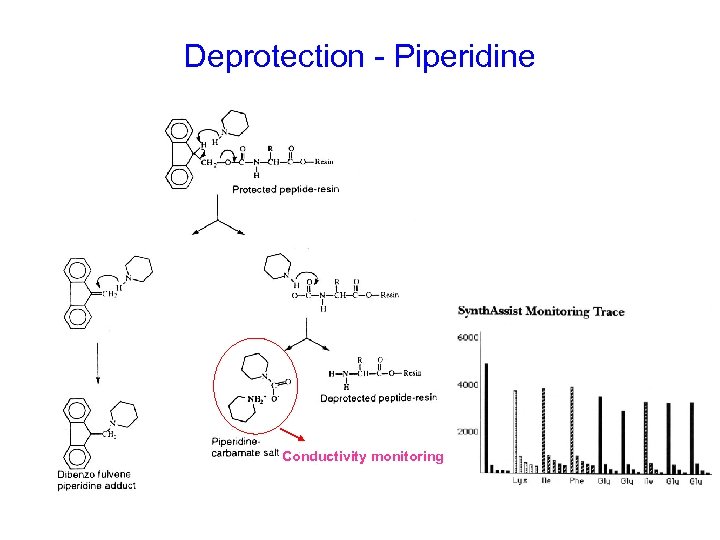
Deprotection - Piperidine Conductivity monitoring
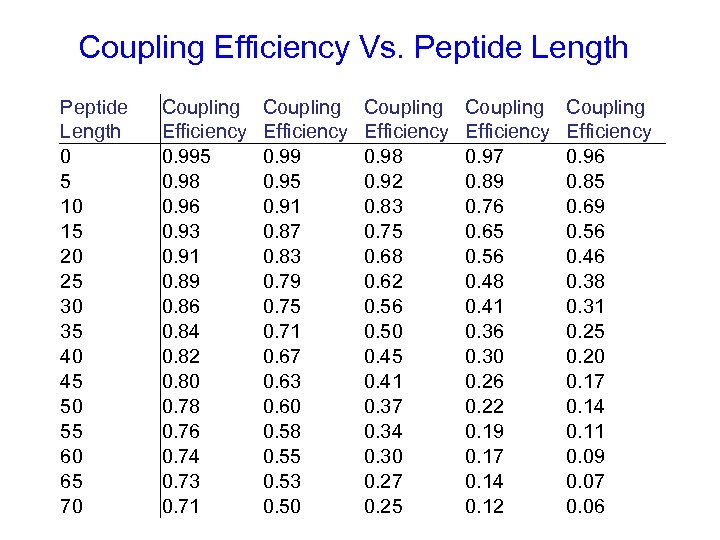
Coupling Efficiency Vs. Peptide Length 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 Coupling Efficiency 0. 995 0. 98 0. 96 0. 93 0. 91 0. 89 0. 86 0. 84 0. 82 0. 80 0. 78 0. 76 0. 74 0. 73 0. 71 Coupling Efficiency 0. 99 0. 95 0. 91 0. 87 0. 83 0. 79 0. 75 0. 71 0. 67 0. 63 0. 60 0. 58 0. 55 0. 53 0. 50 Coupling Efficiency 0. 98 0. 92 0. 83 0. 75 0. 68 0. 62 0. 56 0. 50 0. 45 0. 41 0. 37 0. 34 0. 30 0. 27 0. 25 Coupling Efficiency 0. 97 0. 89 0. 76 0. 65 0. 56 0. 48 0. 41 0. 36 0. 30 0. 26 0. 22 0. 19 0. 17 0. 14 0. 12 Coupling Efficiency 0. 96 0. 85 0. 69 0. 56 0. 46 0. 38 0. 31 0. 25 0. 20 0. 17 0. 14 0. 11 0. 09 0. 07 0. 06
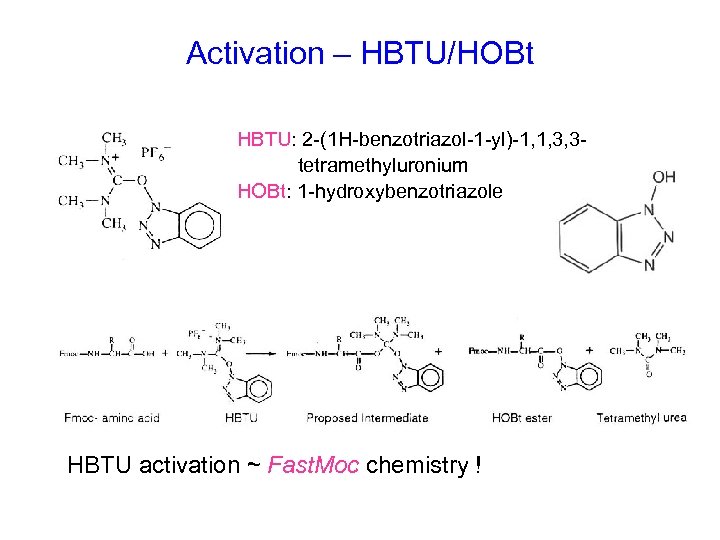
Activation – HBTU/HOBt HBTU: 2 -(1 H-benzotriazol-1 -yl)-1, 1, 3, 3 tetramethyluronium HOBt: 1 -hydroxybenzotriazole HBTU activation ~ Fast. Moc chemistry !
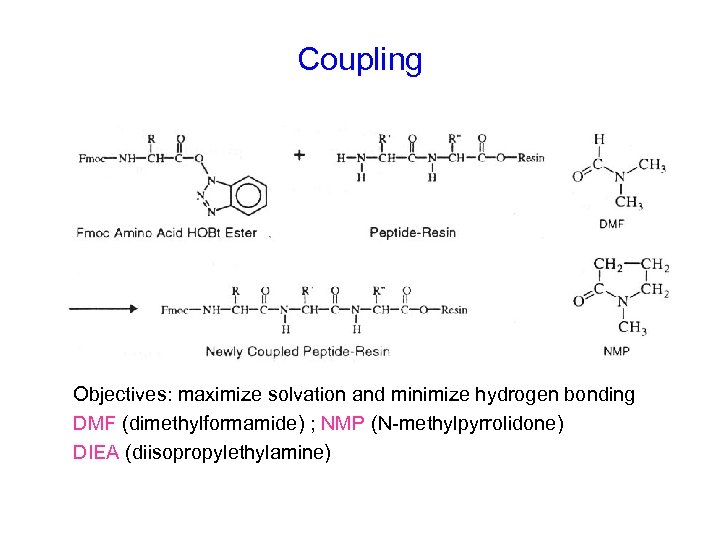
Coupling Objectives: maximize solvation and minimize hydrogen bonding DMF (dimethylformamide) ; NMP (N-methylpyrrolidone) DIEA (diisopropylethylamine)
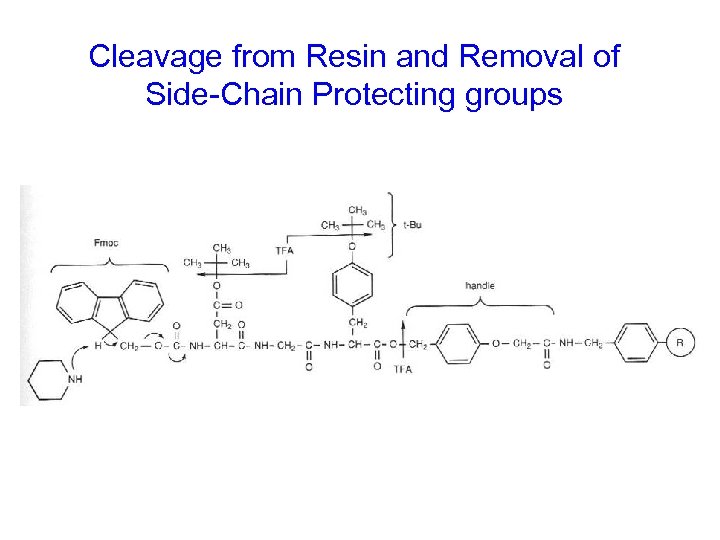
Cleavage from Resin and Removal of Side-Chain Protecting groups
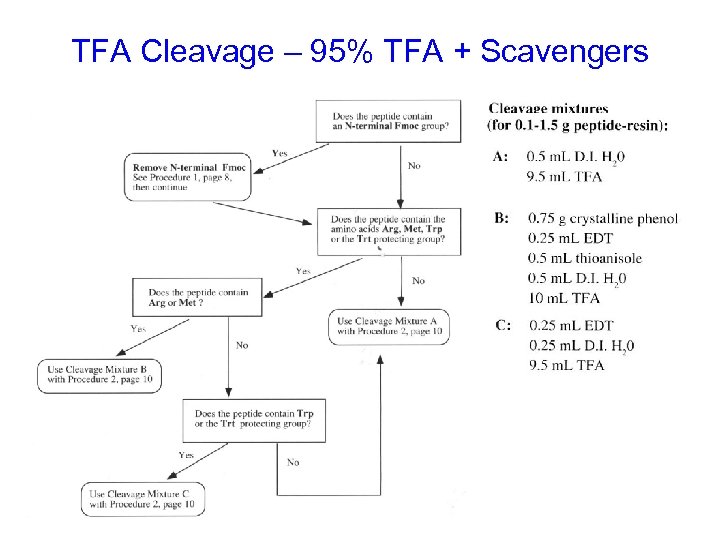
TFA Cleavage – 95% TFA + Scavengers
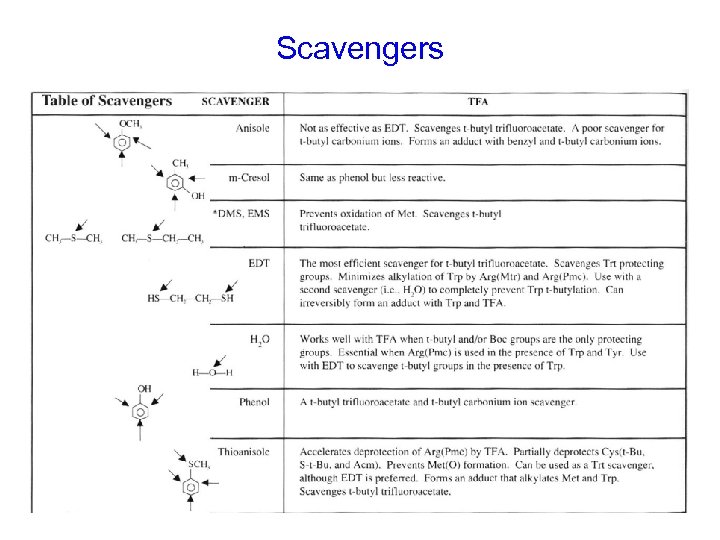
Scavengers
Purification • Filtration and DCM wash • Concentration by Rotavapor • Ether extraction • Lyophilization • Purification by HPLC

Additional Chemical Modification • Disulfide bond formation • Phosphorylation • Biotinylation • Farnesylation • Glycosylation • C- and N-terminal modification • Chromophore and fluorophore labelling

How to Choose Peptide Solvents • Peptides with a net positive charge: (1) H 2 O alone (2) gently shake / warm up to 30 o. C (3) 10% HOAc • Peptides with a net negative charge: (1) H 2 O or HOAc (2) NH 4 HCO 3 • Peptides with a net zero charge: (1) H 2 O, HOAc, warming and shaking (2) 6 M guanidine-HCl, TFA, HCOOH (3) Me. OH, isopropanol, acetonitrile
Characterization • Purity analysis by HPLC • Amino acid composition analysis by precolumn PITC derivatization on a Pico. Tag HPLC system • Determination of peptide molecular weight by mass spectrometry
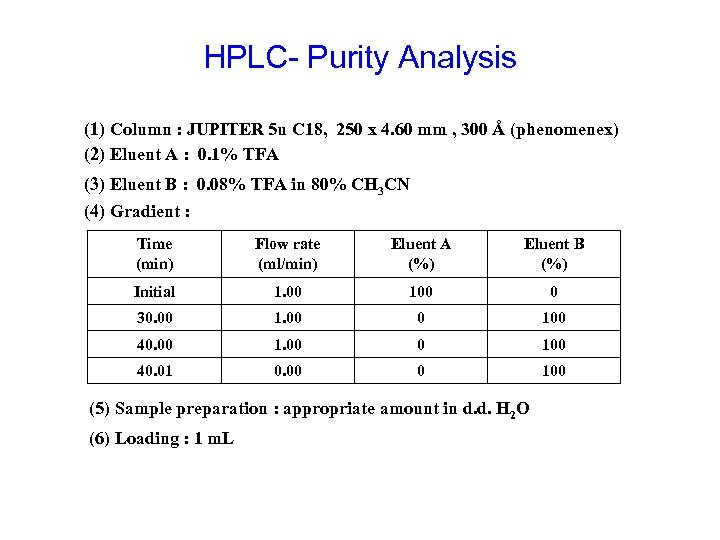
HPLC- Purity Analysis (1) Column : JUPITER 5 u C 18, 250 x 4. 60 mm , 300 Å (phenomenex) (2) Eluent A : 0. 1% TFA (3) Eluent B : 0. 08% TFA in 80% CH 3 CN (4) Gradient : Time (min) Flow rate (ml/min) Eluent A (%) Eluent B (%) Initial 1. 00 100 0 30. 00 1. 00 0 100 40. 01 0. 00 0 100 (5) Sample preparation : appropriate amount in d. d. H 2 O (6) Loading : 1 m. L
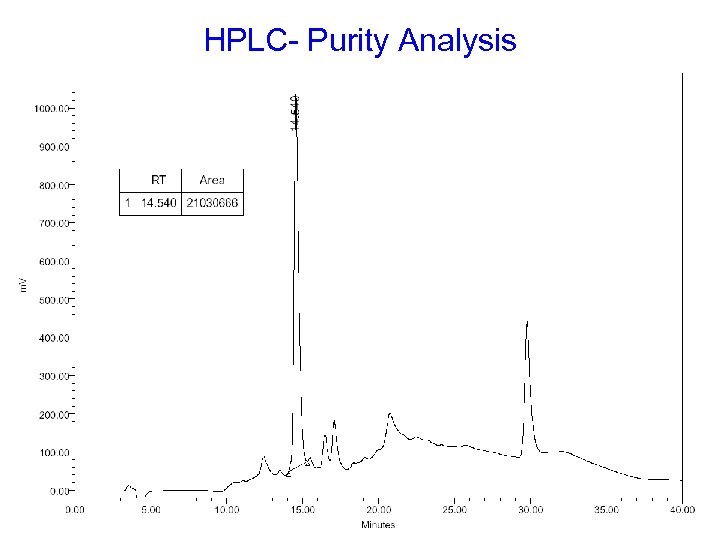
HPLC- Purity Analysis
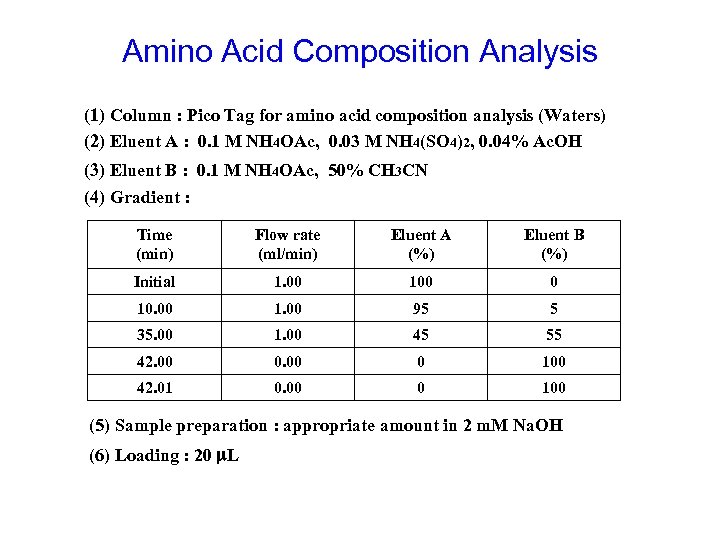
Amino Acid Composition Analysis (1) Column : Pico Tag for amino acid composition analysis (Waters) (2) Eluent A : 0. 1 M NH 4 OAc, 0. 03 M NH 4(SO 4)2, 0. 04% Ac. OH (3) Eluent B : 0. 1 M NH 4 OAc, 50% CH 3 CN (4) Gradient : Time (min) Flow rate (ml/min) Eluent A (%) Eluent B (%) Initial 1. 00 100 0 10. 00 1. 00 95 5 35. 00 1. 00 45 55 42. 00 0 100 42. 01 0. 00 0 100 (5) Sample preparation : appropriate amount in 2 m. M Na. OH (6) Loading : 20 m. L
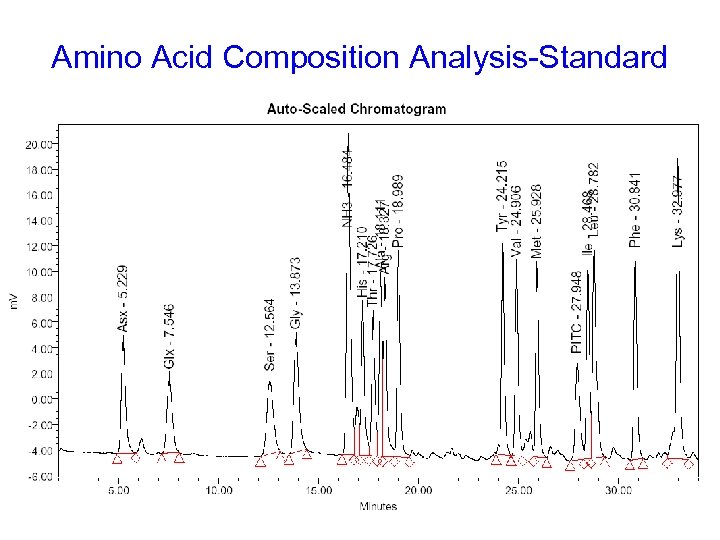
Amino Acid Composition Analysis-Standard
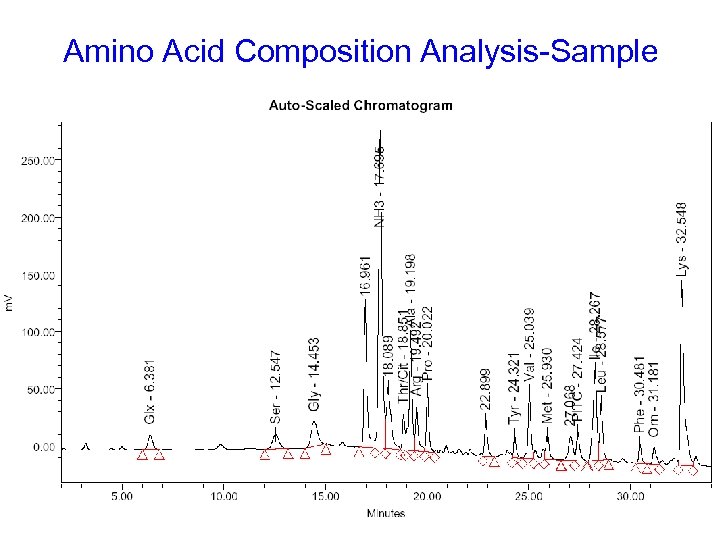
Amino Acid Composition Analysis-Sample
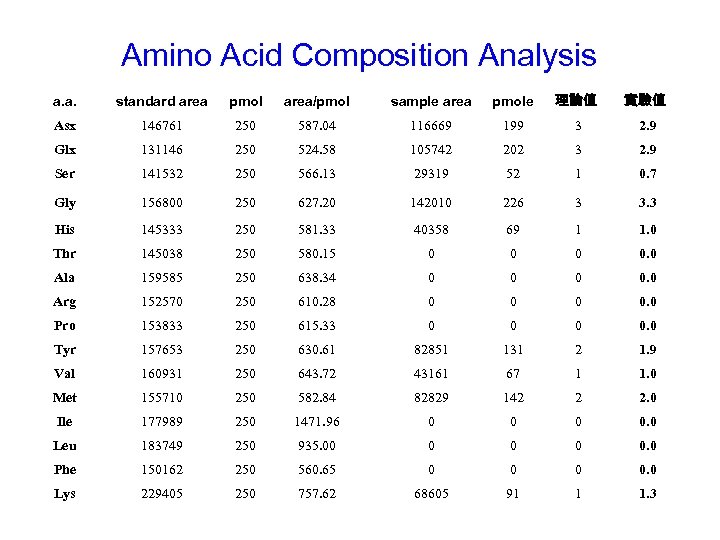
Amino Acid Composition Analysis a. a. standard area pmol area/pmol sample area pmole 理論值 實驗值 Asx 146761 250 587. 04 116669 199 3 2. 9 Glx 131146 250 524. 58 105742 202 3 2. 9 Ser 141532 250 566. 13 29319 52 1 0. 7 Gly 156800 250 627. 20 142010 226 3 3. 3 His 145333 250 581. 33 40358 69 1 1. 0 Thr 145038 250 580. 15 0 0. 0 Ala 159585 250 638. 34 0 0. 0 Arg 152570 250 610. 28 0 0. 0 Pro 153833 250 615. 33 0 0. 0 Tyr 157653 250 630. 61 82851 131 2 1. 9 Val 160931 250 643. 72 43161 67 1 1. 0 Met 155710 250 582. 84 82829 142 2 2. 0 Ile 177989 250 1471. 96 0 0. 0 Leu 183749 250 935. 00 0 0. 0 Phe 150162 250 560. 65 0 0. 0 Lys 229405 250 757. 62 68605 91 1 1. 3

ABI 433 A Peptide Synthesizer
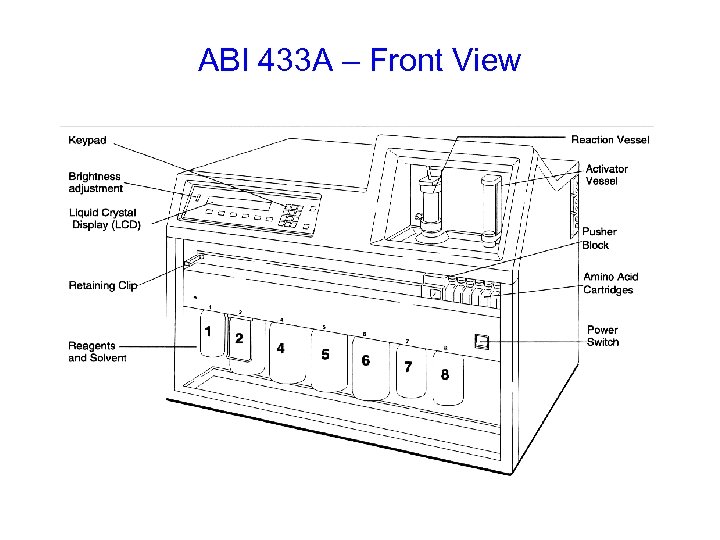
ABI 433 A – Front View
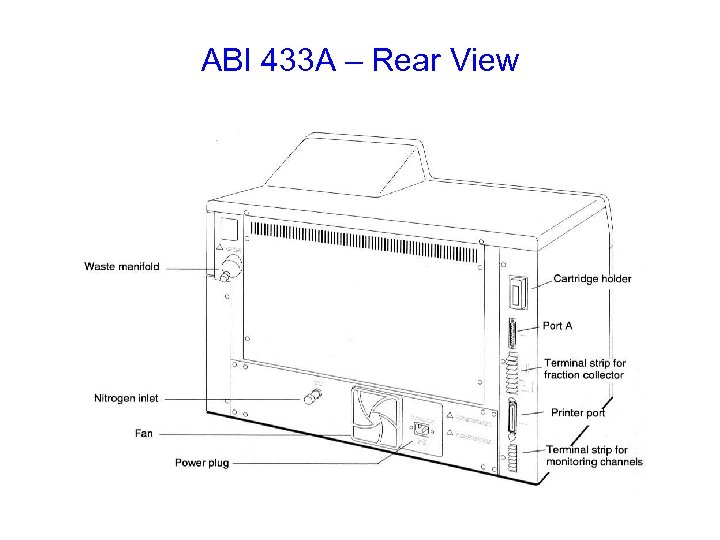
ABI 433 A – Rear View
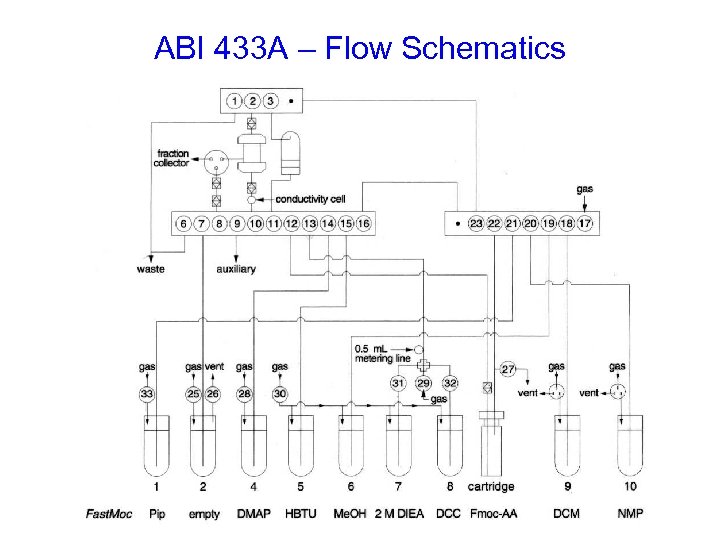
ABI 433 A – Flow Schematics

PS 3 Peptide Synthesizer - PTI PS 3 - a lot cheaper and easier to use! - Simple and fast cycle time under 40 mins/coupling - Variety of coupling techniques - Zero-dead-volume fluid valve system - Self diagnostic program - Higher productivity up to 45 couplings automatically 3 different peptides sequentially

Symphony Peptide Synthesizer - PTI Symphony/Multiplex 12 -channel solidphase synthesizer - Fast multiplex operation operate 12 -channel simultaneously - Patented multiplexing matrix valve - Lower coupling reagent cost - Variable scales: 0. 005 -0. 35 mmol - Automated cleavage - Easily customized protocols - Extreme versatility

Microwave Peptide Synthesizer - CEM Odyssey System on a Discover platform World’s first microwave peptide synthesizer wins 2004 R&D 100 Award! -Significantly increased reaction rates cycle time less than 10 mins - Better product purity and yield - Overcoming chain aggregation - Automated cleavage within 15 mins - Lower cost: cheaper reagents - Useful on multiple programmable scale - Greater flexibility

Pep. Sy Peptide Synthesizer - Zinsser Parallel synthesis of peptide libraries in 96 -well plate format. - 9 independent 96 -well reactor stations - 864 peptides in 30 h, 10 mer, ~ 1 mg each - Dispensing pen for each a. a. - no washes or flushes needed - speeds up synthesis - no cross contamination - Bar code check for every step - Software-assisted library design

Applications of Synthetic Peptides • Peptide Vaccine • Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs) ~ Host-Defense Peptides (HDPs) • Peptide Array (Peptide Chips) • Stimulus-Responsive Peptides

Peptide Vaccine
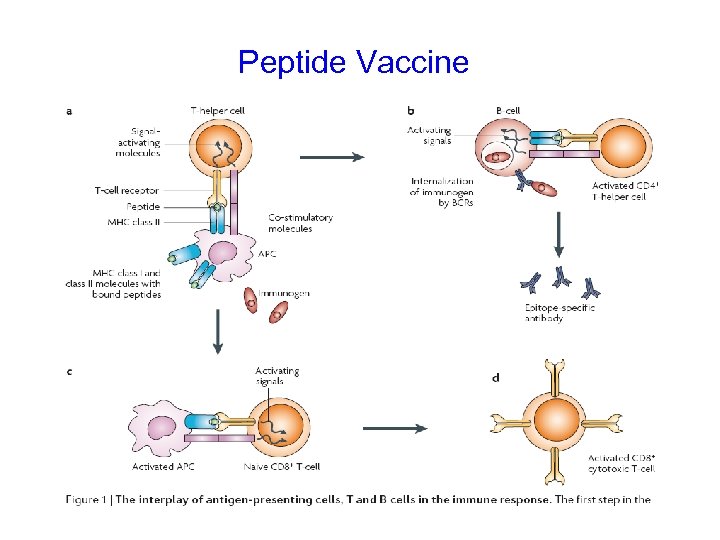
Peptide Vaccine

Peptide Vaccine

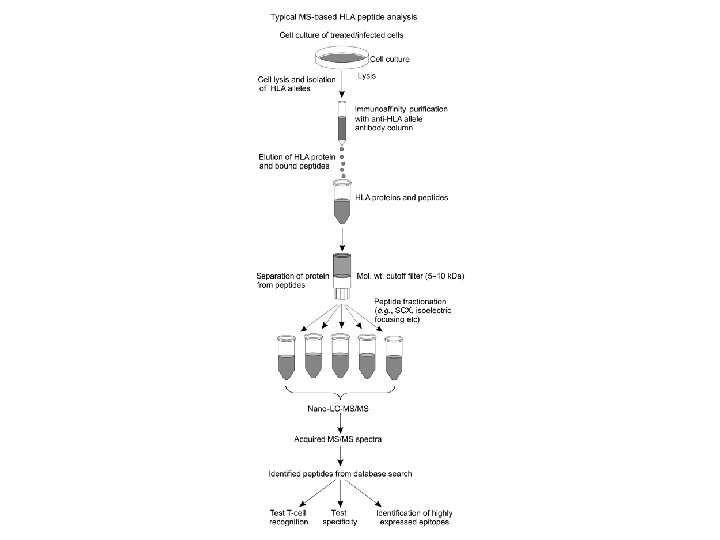


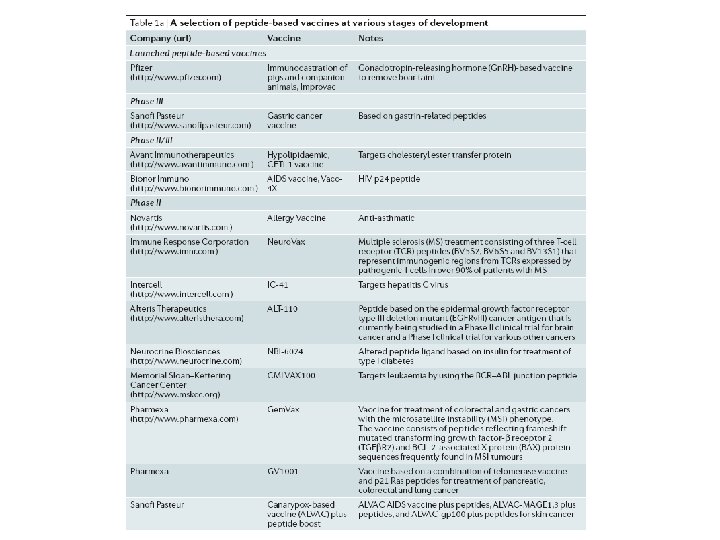

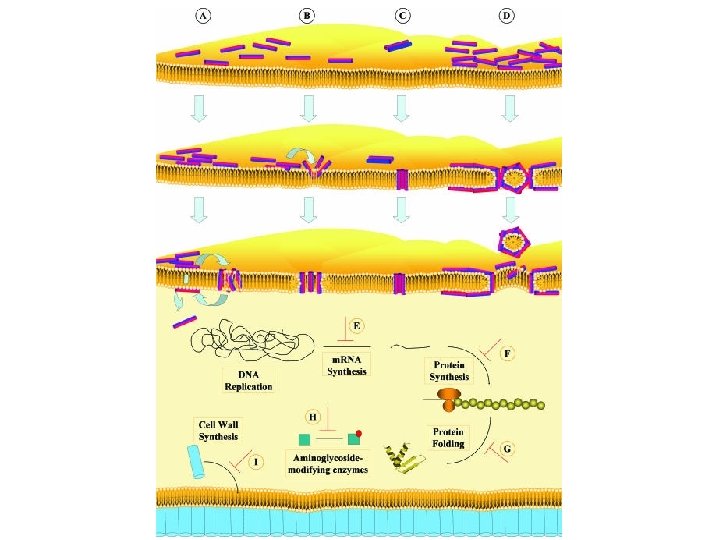
Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs) ~ Host-Defense Peptides (HDPs)

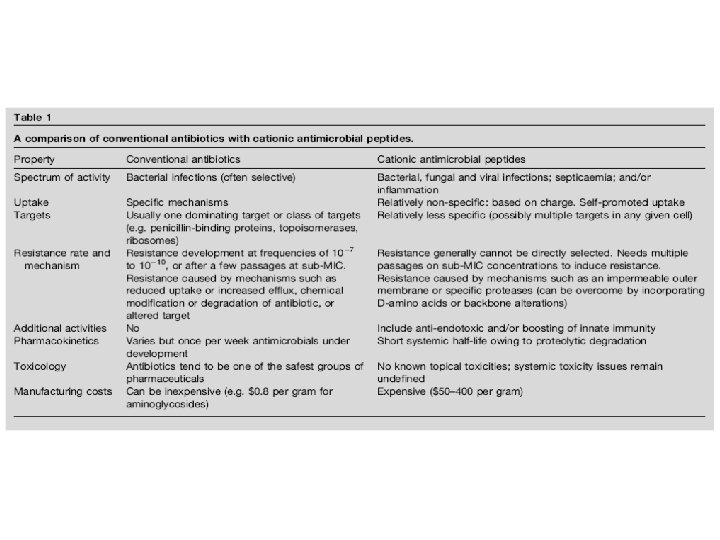
Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs) ~ Host-Defense Peptides (HDPs)





Peptide Array (Peptide Chips)
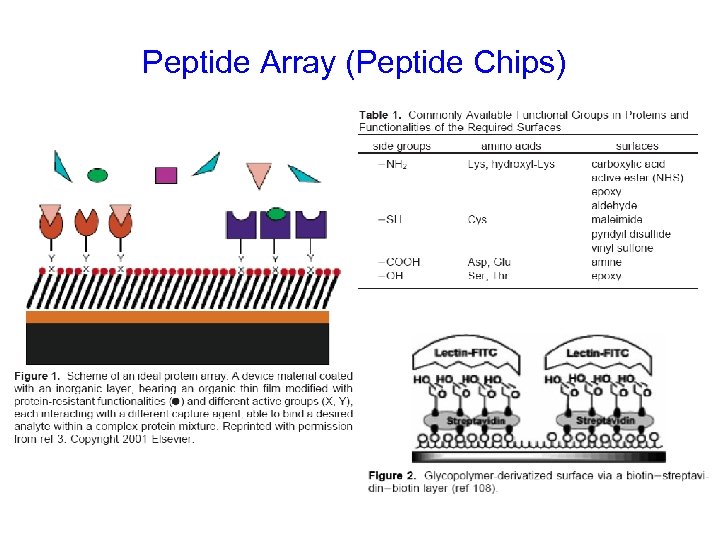
Peptide Array (Peptide Chips)
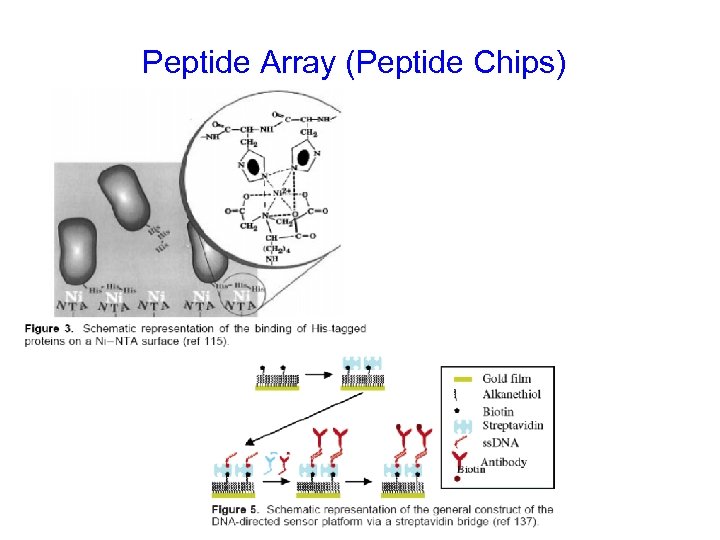
Peptide Array (Peptide Chips)
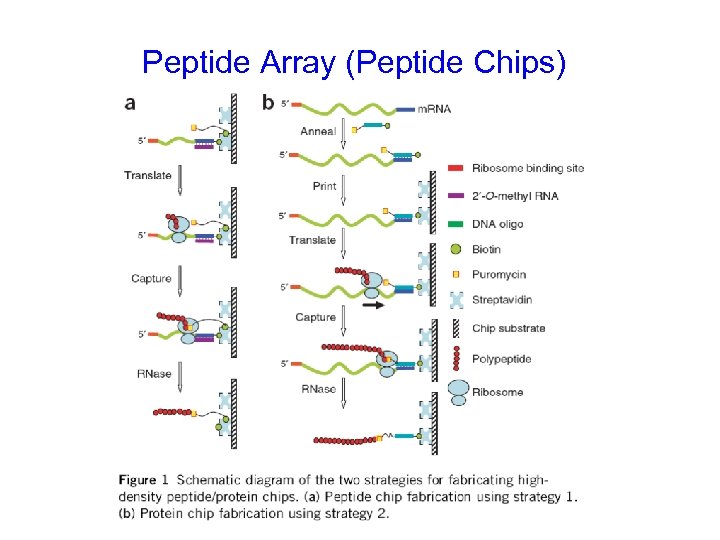
Peptide Array (Peptide Chips)
Stimulus-Responsive Peptides
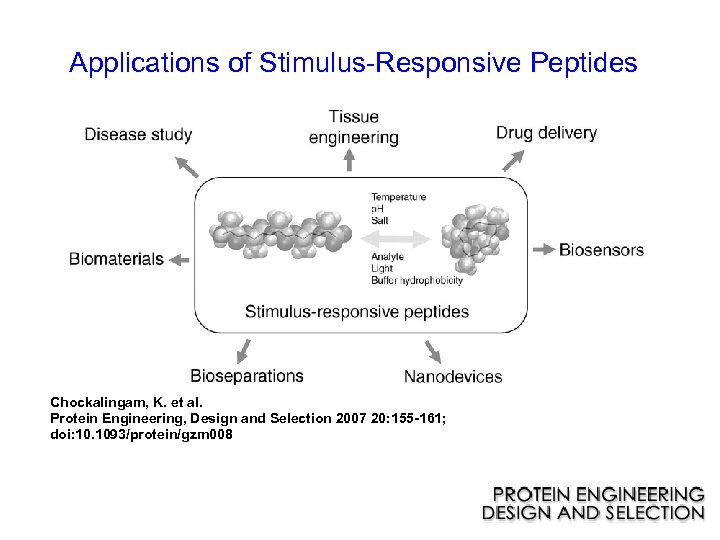
Applications of Stimulus-Responsive Peptides Chockalingam, K. et al. Protein Engineering, Design and Selection 2007 20: 155 -161; doi: 10. 1093/protein/gzm 008
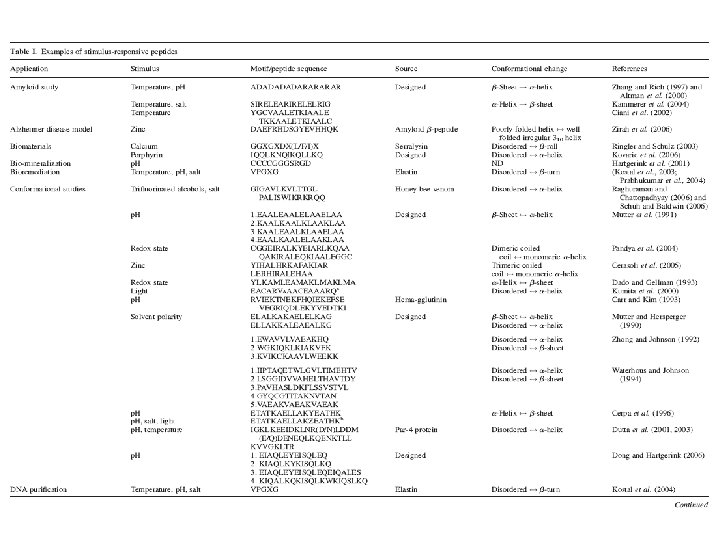

d45051ac0d60c53469d3d350060c21bd.ppt