d848e72b264ca43a4521f66e0c368092.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

ZERO CARBON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENTS IN THE UK AND POTENTIAL CHALLENGES TO THE CODE FOR SUSTAINABLE HOMES MUHAMMAD RIAZ AKBAR Prof. Neil Hewitt Prof. George Heaney Dr. Lay Cheng Lim University of Ulster, UK

CONTENTS • Introduction / Background • Climate Change/Impacts • Code for Sustainable Homes (CSH) • Challenges to the Code • • • Technical Legal and Regulatory Economic Social and Cultural Delivery Capacity High rise development • A Research Approach for Multi-Storey High Density Developments • Research Methodology • Conclusion / Way Forward Muhammad Riaz Akbar
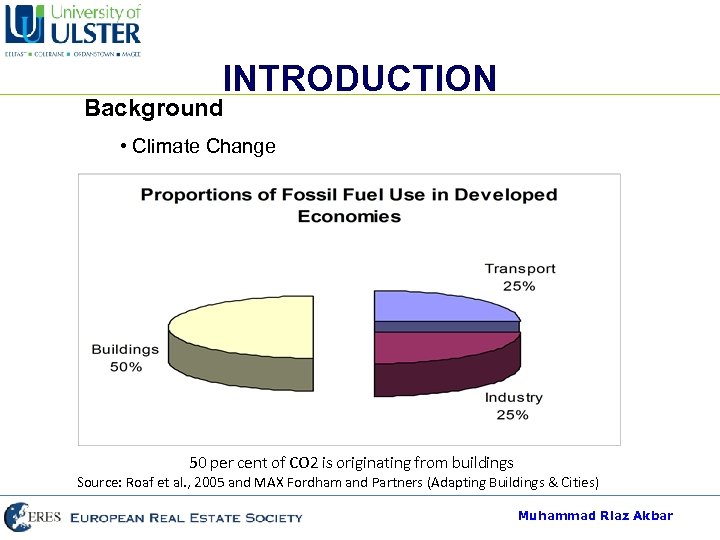
INTRODUCTION Background • Climate Change • • CO 2 Concentration 18% increase in CO 2 mean annual concentration, from 315. 98 to 372. 95 ppmv IPCC (2001) “most of the warming observed over the last 50 years is attributable to human activities” UKCIP 2 to 3. 5 ºC by the 2080 s Rising Temperature 50 per cent of CO 2 is originating from buildings Source: Roaf et al. , 2005 and MAX Fordham and Partners (Adapting Buildings & Cities) Muhammad Riaz Akbar
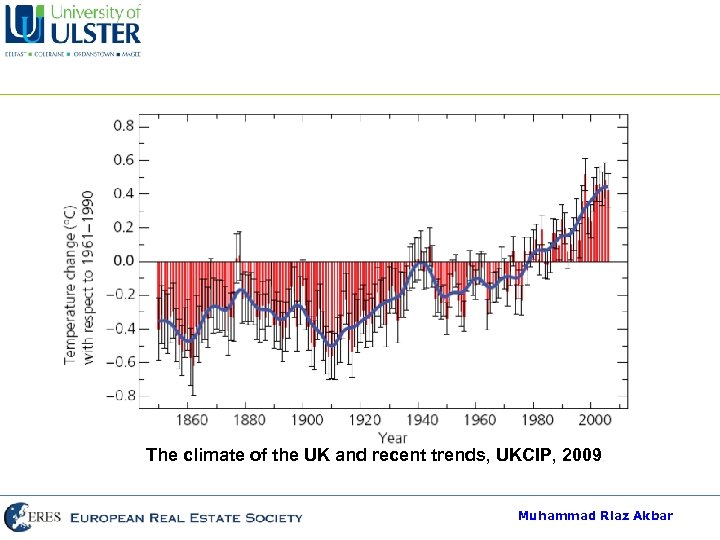
The climate of the UK and recent trends, UKCIP, 2009 Muhammad Riaz Akbar
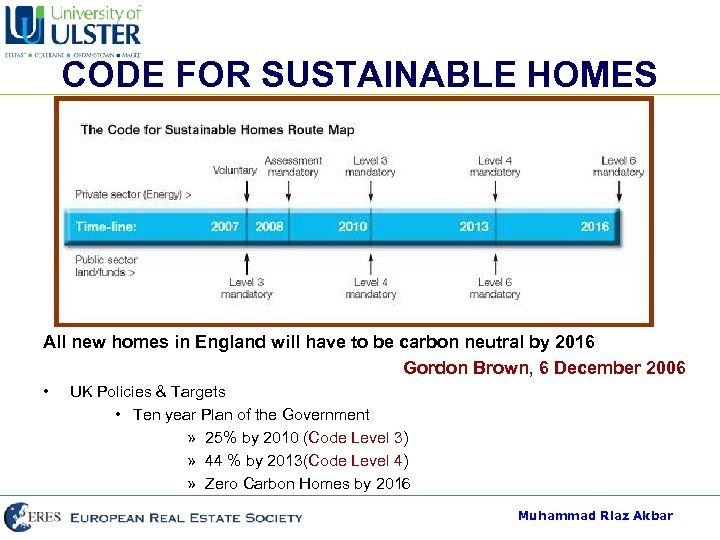
CODE FOR SUSTAINABLE HOMES All new homes in England will have to be carbon neutral by 2016 Gordon Brown, 6 December 2006 • UK Policies & Targets • Ten year Plan of the Government » 25% by 2010 (Code Level 3) » 44 % by 2013(Code Level 4) » Zero Carbon Homes by 2016 Muhammad Riaz Akbar

CODE FOR SUSTAINABLE HOMES (Contd. ) Eco. Homes CSH Muhammad Riaz Akbar
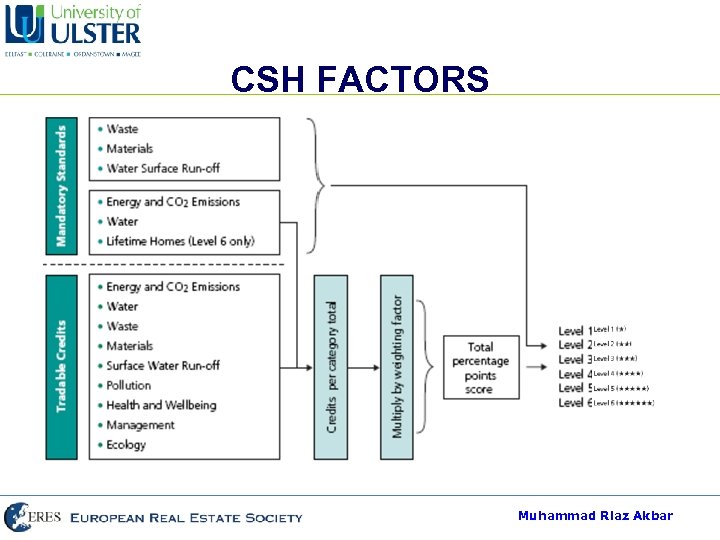
CSH FACTORS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Energy and CO 2 Emissions Water Materials Surface Water Run-off Waste Pollution Heath and Wellbeing Management Ecology Muhammad Riaz Akbar

CHALLENGES TO CSH 1. Technical Challenges 2. Legal and Regulatory Challenges 3. Economic / Financial Challenges 4. Social / Cultural Challenges 5. 1. Technical Capacity Challenges • Post Occupational Assessment 2. Legal. Size. Regulatory • Limiting & & Type of Technologies • Voluntary Nature • Private wires & Financial 3. Economic • Single of Energy Supply • Origin Policy • Increased. Definition Cost • Un-Clear & Cultural • Local 27 -43% Source Energy 4. Social in the absence of WT • • Large glazing areas 5. Delivery Capacity • MVHR (Sigma House Experience) • Lack of Skilled HR • Capacity of Existing Professionals Multi-Storey Developments • Institutional Capacity and Overlapping of Functions) ? Multi-Storey High Density Developments Muhammad Riaz Akbar
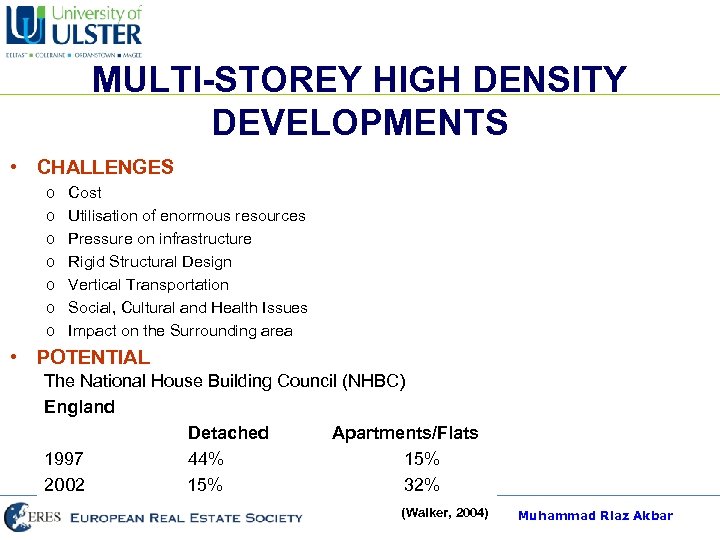
MULTI-STOREY HIGH DENSITY DEVELOPMENTS • CHALLENGES o o o o Cost Utilisation of enormous resources Pressure on infrastructure Rigid Structural Design Vertical Transportation Social, Cultural and Health Issues Impact on the Surrounding area • POTENTIAL The National House Building Council (NHBC) o Land o Cost England o Location and Accessibility Detached Apartments/Flats o Optimum utilisation of infrastructure 1997 44% 15% 2002 15% 32% (Walker, 2004) Muhammad Riaz Akbar
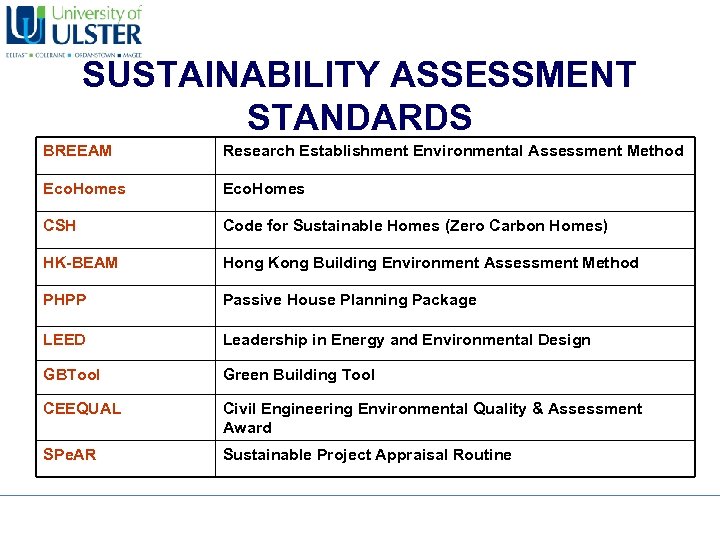
SUSTAINABILITY ASSESSMENT STANDARDS BREEAM Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method Eco. Homes CSH Code for Sustainable Homes (Zero Carbon Homes) HK-BEAM Hong Kong Building Environment Assessment Method PHPP Passive House Planning Package LEED Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design GBTool Green Building Tool CEEQUAL Civil Engineering Environmental Quality & Assessment Award SPe. AR Sustainable Project Appraisal Routine

MOVING TOWARDS MORE SUSTAINABLE MULTI-STOREY HIGH DENSITY ZERO CARBON DEVELOPMENTS
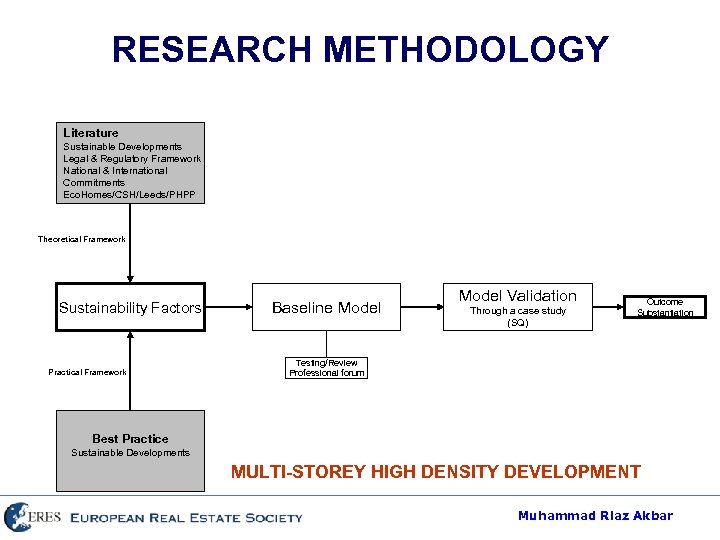
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY Literature Sustainable Developments Legal & Regulatory Framework National & International Commitments Eco. Homes/CSH/Leeds/PHPP Theoretical Framework Sustainability Factors Practical Framework Baseline Model Validation Through a case study (SQ) Outcome Substantiation Testing/Review Professional forum Best Practice Sustainable Developments MULTI-STOREY HIGH DENSITY DEVELOPMENT Muhammad Riaz Akbar
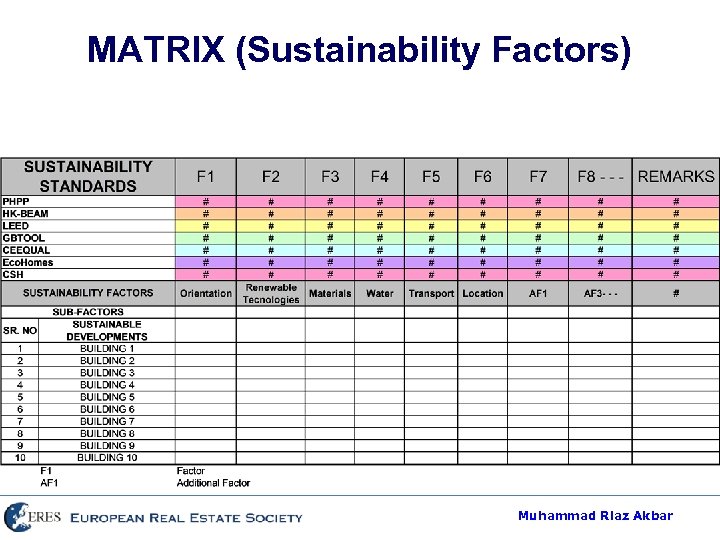
MATRIX (Sustainability Factors) Muhammad Riaz Akbar
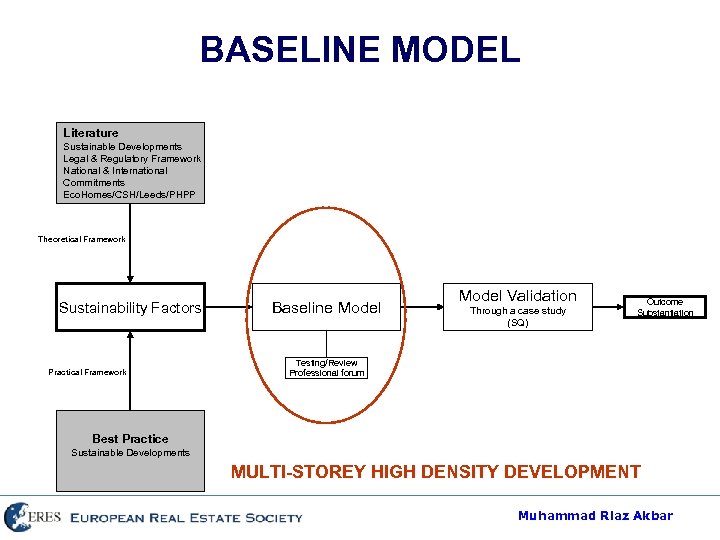
BASELINE MODEL Literature Sustainable Developments Legal & Regulatory Framework National & International Commitments Eco. Homes/CSH/Leeds/PHPP Theoretical Framework Sustainability Factors Practical Framework Baseline Model Validation Through a case study (SQ) Outcome Substantiation Testing/Review Professional forum Best Practice Sustainable Developments MULTI-STOREY HIGH DENSITY DEVELOPMENT Muhammad Riaz Akbar

MODEL TESTING / REVIEW • CEni forum • 50 Professional Experts (Developers, Policy maker, Academia, Property Professionals (engineers/architects/planner), Experts (PHPP/Eco. Homes/CSH) ) Muhammad Riaz Akbar
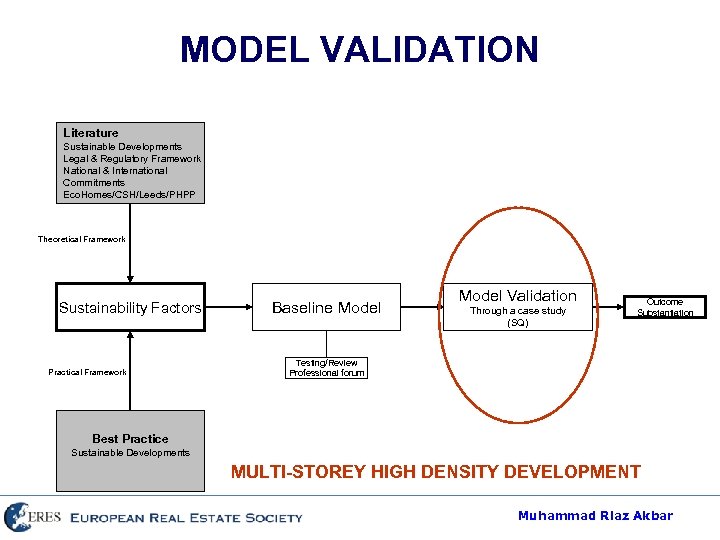
MODEL VALIDATION Literature Sustainable Developments Legal & Regulatory Framework National & International Commitments Eco. Homes/CSH/Leeds/PHPP Theoretical Framework Sustainability Factors Practical Framework Baseline Model Validation Through a case study (SQ) Outcome Substantiation Testing/Review Professional forum Best Practice Sustainable Developments MULTI-STOREY HIGH DENSITY DEVELOPMENT Muhammad Riaz Akbar
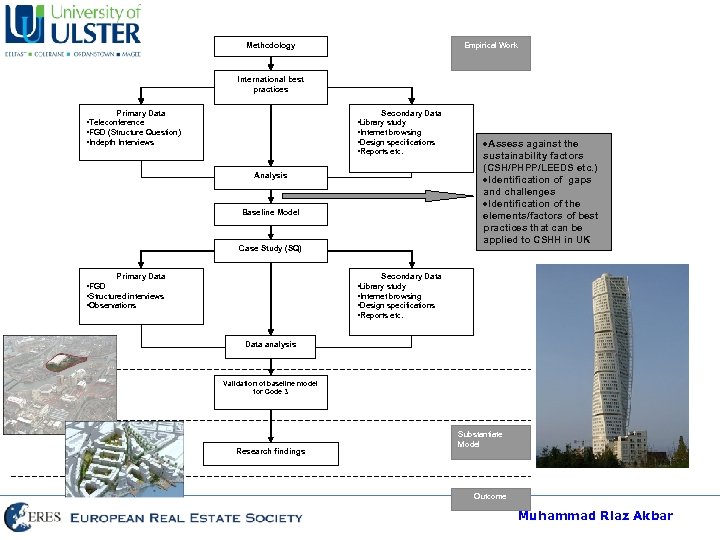
Empirical Work Methodology International best practices Secondary Data Primary Data • Library study • Internet browsing • Design specifications • Reports etc. • Teleconference • FGD (Structure Question) • Indepth Interviews Analysis Baseline Model Case Study (SQ) Primary Data Assess against the sustainability factors (CSH/PHPP/LEEDS etc. ) Identification of gaps and challenges Identification of the elements/factors of best practices that can be applied to CSHH in UK Secondary Data • FGD • Structured interviews • Observations • Library study • Internet browsing • Design specifications • Reports etc. Data analysis Validation of baseline model for Code 3 Research findings Substantiate Model Outcome Muhammad Riaz Akbar
CONCLUSION Summary • • Introduction post occupational assessment Consideration of origin and capacity of private wire for energy supply from renewable source Best combination renewable technologies, integration of renewable energy with the whole system Introduction of a renewable heat tarrif complimentary to that existing for renewable electricity and role of feed in tarrifs in general to offset the initial and running costs of renewables Definition of Zero Carbon Homes Introduction of carbon reduction credits at a single dwelling level Capacity enhancement etc. • • Location Thermal Mass Embodied Energy Impact on the infrastructure and surrounding developments Muhammad Riaz Akbar
CONCLUSION WAY FORWARD CSHH Muhammad Riaz Akbar

THANK YOU Questions/Suggestions Muhammad Riaz Akbar
d848e72b264ca43a4521f66e0c368092.ppt