ea53f36651d643c0ad51498a63f918e7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 61

Zareh. F. MD

Asymptomatic bacteriuria n n n n Colony count more than 10000 No symptom incidence 6% 25 -40% Progress to pyelonephritis. Treatment reduces this 10 -fold Ampicillin or nitrofurantoin 10 -14 days U/c one week following therapy 30% of infection recure n

cystitis n n n . Symptomatic bacteriuria without flank pain or fever Diagnosis and treatment as ASB With sterile urine chlamydia trachomatis suspected

pyelonephritis n n n . 1 -3% of pregnant women Febrile patient , chills, urgency, dysuria, nausea, vomiting Right sided, bilateral Bacterial endotoxins Macrophage cytokines Preterm labor
Recurrent pyelonephritis n n n . 10 -18% of patient Nitrofurantoin 100/night u/c every month Treatment: 10 -day course of antibiotics Ivp 3 months postpartum
Urinary calculi n n n n 1/1000 pregnancies Increase uti to 20 -45% Suppressive nitrofurantoin therapy u/c monthly Infection treated aggressively Sonography 60% Single view Ivp 96%(50 mrad( with persisted obstruction ureteral stent or percutaneous nephrostomy is required.
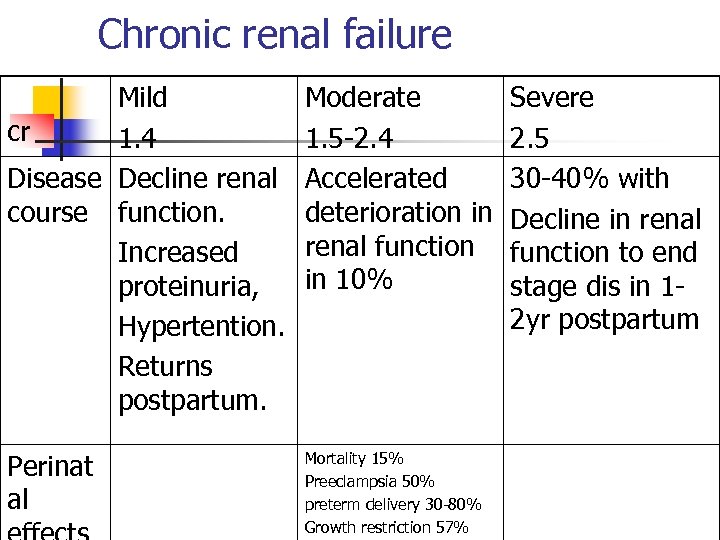
Chronic renal failure Mild cr 1. 4 Disease Decline renal course function. Increased proteinuria, Hypertention. Returns postpartum. Moderate 1. 5 -2. 4 Accelerated deterioration in renal function in 10% Perinat al Mortality 15% Preeclampsia 50% preterm delivery 30 -80% Growth restriction 57% Severe 2. 5 30 -40% with Decline in renal function to end stage dis in 12 yr postpartum

Dialysis n n The goal of dialysis is BUN at 5060 mg/dl Risk of fetal demise is BUN above 80 mg/dl Peritoneal dialysis is superior for minimize fluid shift and does not required anticoagulation Mg-so 4 can be added(serum level 5 meq/l).

Renal transplantation n Avoid of pregnancy for 2 years n n Complications : n n n . With dose of prednisone 15 mg/day , azathioprine 2 mg/kg/day Preeclampsia Infection (cmv, herpes, hepatitis, uti) Parathyroid dysfunction, preterm birth Prematurity 45 -60% and 20% of this babies are IUGR PROM Pregnancy outcome successful 80 -90%

Neurologic disorders n Tension headache n Migaine n Epilepsy n Subarachnoid hemorrhage n Pseudotumor cerebri

Migrain headache n Common, 15% first in pregnancy n R/O B. tumor, stroke, epilepsy n Menstrual migrain, 64% improvement in pregnancy Cerebral artery vasoconstraction n 3 -6 fold ischemic stroke n

treatment Aspirin , acetaminophen with or without caffeine n narcotics, n Phenothiazine n Sumatriptan succinate (Imitrex) n Ergotamin(vasoconstrictor) § NSAIDs should be avoided in 3 th trimester. n

Epilepsy in pregnancy n No change 46% n Reduction 20% n Increase 34%

Factors that increase the frequency of seizure Discontinuation of medication For belief that it harms the fetus n Inability to ingest medication For nausea and vomiting n Sub therapeutic drug level Expanding maternal vascular volume n Lowering of the seizure threshold By sleep deprivation and stress n

druges For many anticonvulsant drugs, the benefit of preventing seizures outweighs any potential risks to the fetus The Druges should be avoided n n fetal factors play a role for fetal hydantoin syn n Valproic acid befor 8 w Trimetadione Epoxide hydrolase deficiency Birth defects increases 3% to 7%

management n n n n Lowest medication Minimized stressors Multivitamin , folate Vit K Sonography During labor antiseizure medication Pain relief n Pain hvt resp. alkalosis sz. threshold

diagnosis n CT scan n CSF exam n angiography
M. S n n n Multifocal demyelinating dis of CNS white matter Characterized by : chronic inflammation, selective demyelination, scarring Etiology: unknown, virus-triggered autoimmune phenomen

pregnancy n n n n UTI Constipation Fatigue Morbidity problem With paraplegia or quadriplegia at risk for precipitous delivery Lesion at or above T 6 are at risk for autonomic dysreflexia Flares are common during the first 3 postpartum months

Spinal cord injury n n Generally tolerate pregnancy well Bowel dysfunction Pressure necrosis UTI
Lesion location n Below T 10 -11 feel ut. Cont normally n Above not feel “ n “ Above T 6 hyperreflexia risk of autonomic

hyperreflexia n n n Stimuli: labor, urethral catheterization , cervical or rectal exam nerve impulses enter the cord initiate focal segmental reflexes that not inhibited by higher center stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system Symptoms: pilomotor erection , excessive sweating , facial flushing , dilated pupils , severe headache , paroxysmal hypertension , bradycardia Prevention: epidural anesthesia

Endocrine disorders

Thyroid disease n Thyroid in pregnancy: modest thyroid enlargement TSH , TRH TBG ( total T 3, T 4 ) free T 4, T 3 in early pregnancy HCG free. T 4

Maternal hypothyroidism n n n n free. T 4 , TSH Excessive fatigue Dry skin Cold intolerance Constipation Bradycardia irritability Myxedema (rare (

complications n n n n Infertility Miscarriage Abruptio Preeclampsia IUGR Fetal demise Post partum hemorrhage Heart failure

Subclinical Hypothyroism n n T 4 , TSH (>10 mu/ml) Asymptomatic 5% of women in reproductive age Complication: pregnancy induced hypertension preterm delivery low IQ in children

Maternal hyperthyroidism 1/500 pregnancy

causes n n n Graves disease (most common) T. S. Is binds to thyroid follicle cell TSH receptor Acute and subacute thyroiditis Toxic nodular goiter Toxic adenoma GTD

diagnosis n n n Symptoms: Shortness of breath Palpitation Heat intolerance Weight loss Poor weight gain Increase bowel frequency

diagnosis n n n Laboratory Free T 4 free. T 3 3 -5% TSH Auto antibodies confirm the autoimmune nature and fetal implication

treatment n Medical PTU 300 -450 mg folowed 50 -300 mg daily Methimazole n Sugary n Radioactive sodium iodine

Drug adverse reaction PTU n n n Skin rash (2 -8%) Bronchospasm Drug fever Hepatitis Oral ulcer Agranulocyopenia Metimazole n Aplasia cutis

Breast feeding PTU is preferable because more strongly bounds to plasma protein

B blockers n Propranolol 20 -40 mg 3 times/day n Reduces sympathetic like syndrome n Inhibitory effect of T 4 T 3

Surgery n If PTU necessary >300 mg/day

radiation n Contrindicated in pregnancy

Hyperthyroid complication on pregnancy n n n Preeclampsia Preterm delivery Fetal demise Growth restriction Fetal or neonate thyroid dysfunction

Fetal thyroid function n n Hormon activity by the end of 1 th trimester and gradually increases T 3 -T 4 CROSS THE PLACENTA MINIMALLY TSIs cross the placenta easily Thyroid H deficiency during fetal development and 2 y after birth irreversible brain damage

Dermatologic diseases

Physiologic changes n n n Hyperpigmentation Vascular change: spider angioma , palmar erythema , venous varicosities , Hair: growing/resting Telogen efflovium 1 -4 month postpartum

Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy n n 2 th most common cause of jaundice in pregnant Increases : n n n n bile salt alk. ph SGOT SGPT Bill recurrence 50% Fetal outcome
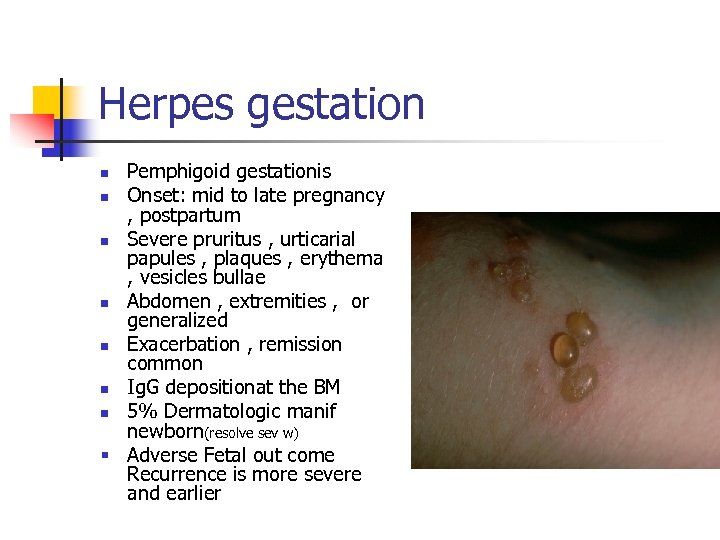
Herpes gestation Pemphigoid gestationis n Onset: mid to late pregnancy , postpartum n Severe pruritus , urticarial papules , plaques , erythema , vesicles bullae n Abdomen , extremities , or generalized n Exacerbation , remission common n Ig. G depositionat the BM n 5% Dermatologic manif newborn(resolve sev w) § Adverse Fetal out come Recurrence is more severe and earlier n
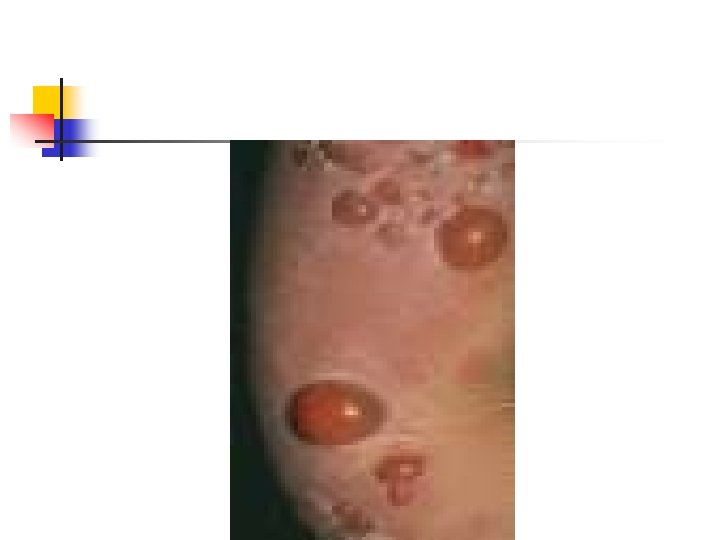

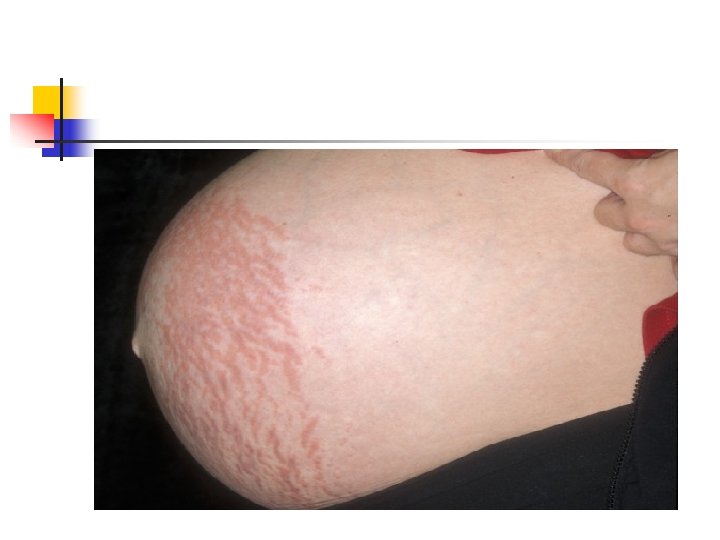
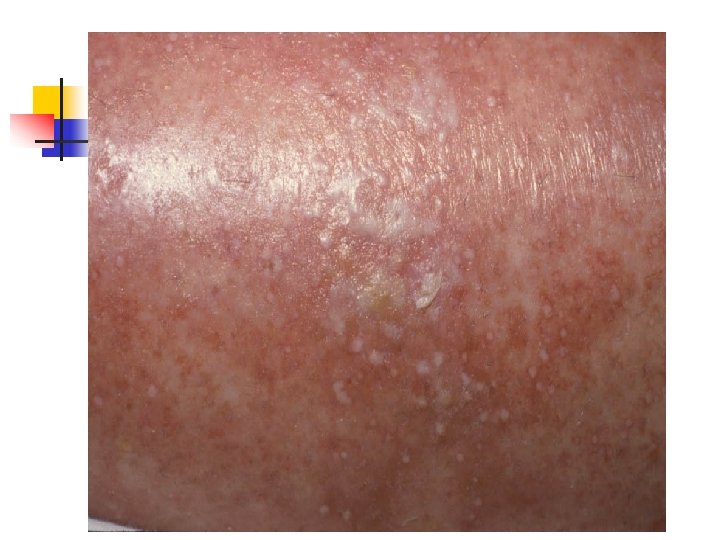
Pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy(PUPPP) n n n n Most common dermatosis of pregnancy 1% Late preg Not recur Generalize , patchy Abd , buttocks , thigh , arm Absence of Ab or complement deposition Perinatal morbidity no increase
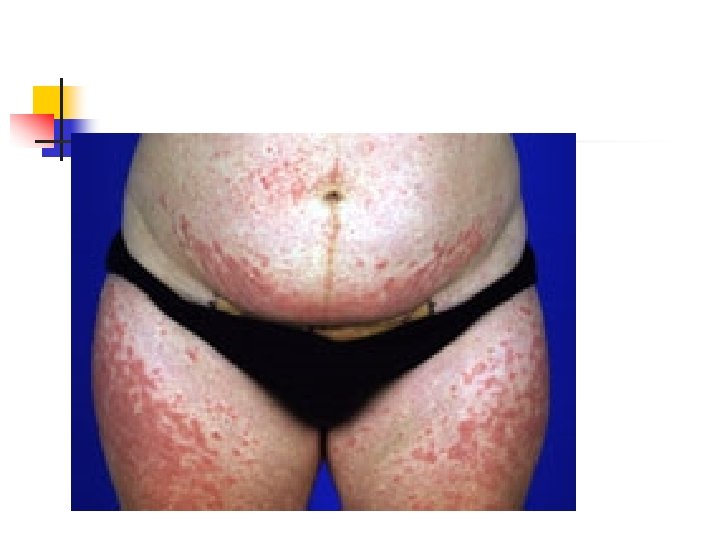
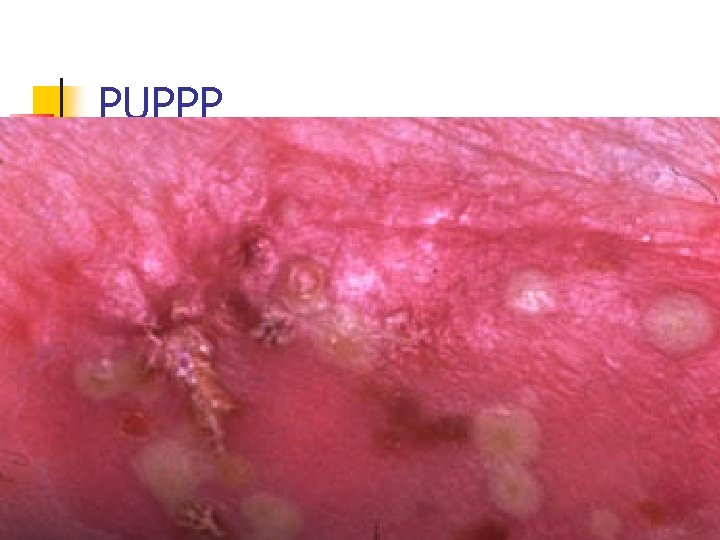
PUPPP
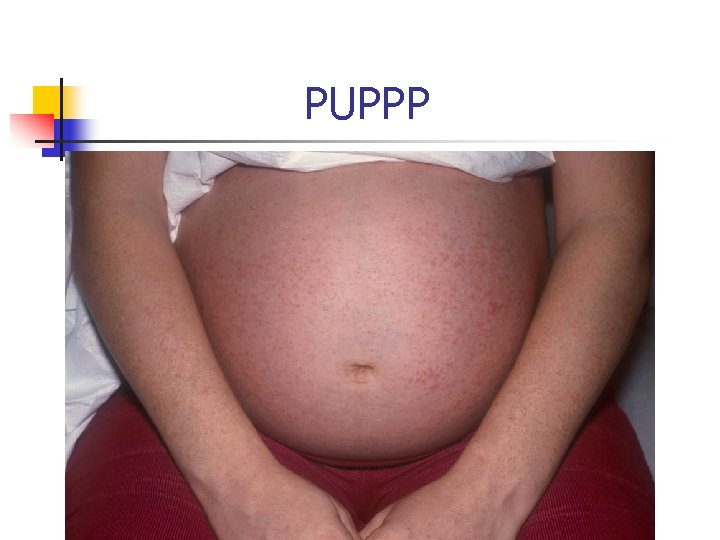
PUPPP

treatment n Antipruritics and topical steroids n Oral steroid may in severe case

Impetigo herpetiform n n n n Pustural psoriasis Late preg Intertrigiginous surface ( extend to involves entire skin and mucosa membrane) Erythematous patches surounded by sterile pustule Fever , malaise , GI distress , hypocalcemia Maternal sepsis is not uncommon Perinatal morbidity , mortality
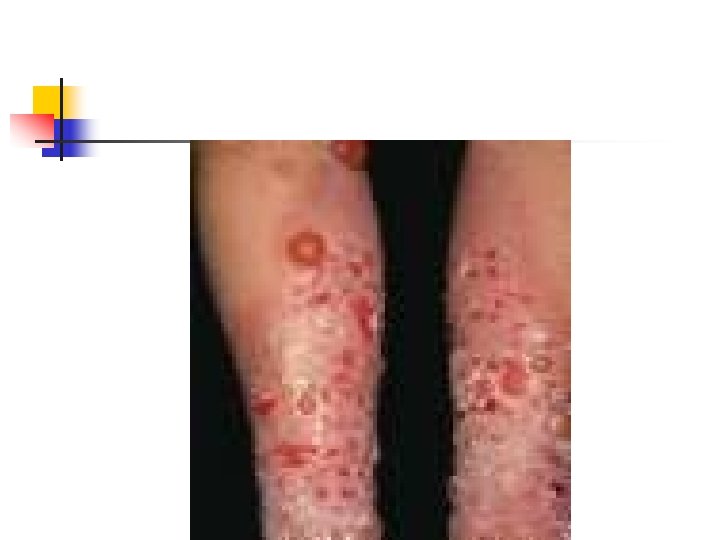
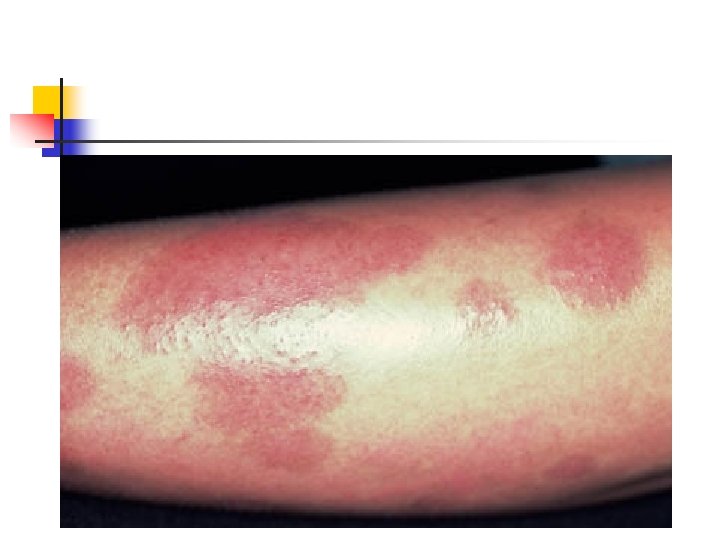

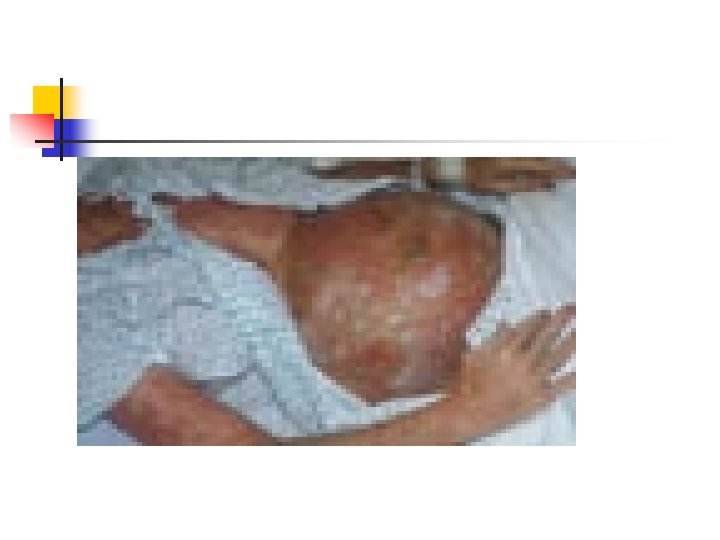

treatment n n n Treatment is supportive Maintenance of fluid and electrolyte balance Correction of hypocalcemia Antibiotic therapy Steroid? Delivery is not necessarily accompanied by resolution




ea53f36651d643c0ad51498a63f918e7.ppt