4eee1313e8f86a21791a38c1b0e80b84.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Z 39 Server Digi. Tool Version 3. 0
Z 39 Server Digi. Tool Version 3. 0
 z 39 SERVER Main Topics z 39 server architecture z 39 server services z 39 server configuration Defining a new base for z 39 server Z 39 Server 2
z 39 SERVER Main Topics z 39 server architecture z 39 server services z 39 server configuration Defining a new base for z 39 server Z 39 Server 2
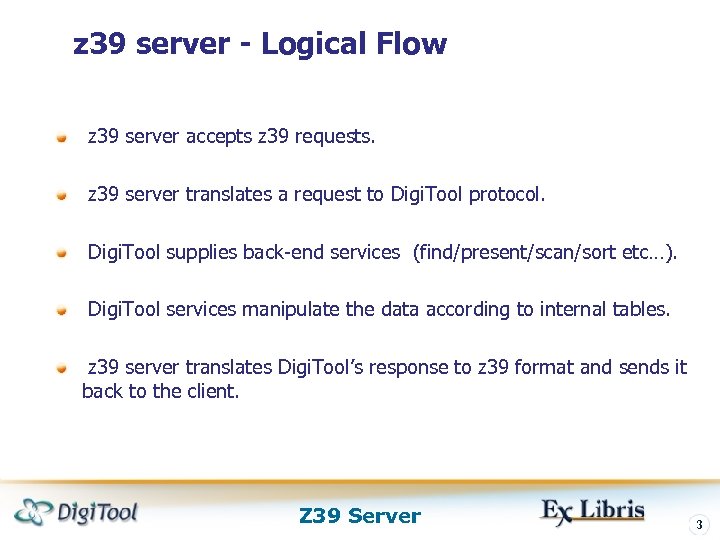 z 39 server - Logical Flow z 39 server accepts z 39 requests. z 39 server translates a request to Digi. Tool protocol. Digi. Tool supplies back-end services (find/present/scan/sort etc…). Digi. Tool services manipulate the data according to internal tables. z 39 server translates Digi. Tool’s response to z 39 format and sends it back to the client. Z 39 Server 3
z 39 server - Logical Flow z 39 server accepts z 39 requests. z 39 server translates a request to Digi. Tool protocol. Digi. Tool supplies back-end services (find/present/scan/sort etc…). Digi. Tool services manipulate the data according to internal tables. z 39 server translates Digi. Tool’s response to z 39 format and sends it back to the client. Z 39 Server 3
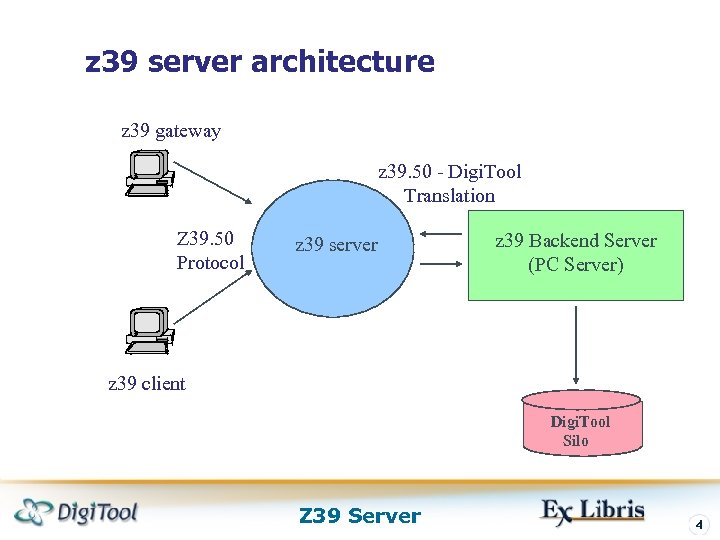 z 39 server architecture z 39 gateway z 39. 50 - Digi. Tool Translation Z 39. 50 Protocol z 39 server z 39 Backend Server (PC Server) z 39 client Digi. Tool Silo Z 39 Server 4
z 39 server architecture z 39 gateway z 39. 50 - Digi. Tool Translation Z 39. 50 Protocol z 39 server z 39 Backend Server (PC Server) z 39 client Digi. Tool Silo Z 39 Server 4
 Overview z 39 server gets a request from z 39. 50 client, performs the request in your local databases and returns the response to the calling z 39. 50 client. z 39 server implements the following z 39. 50 services: Init, Search, Sort, Present, Scan, Z 39 Server 5
Overview z 39 server gets a request from z 39. 50 client, performs the request in your local databases and returns the response to the calling z 39. 50 client. z 39 server implements the following z 39. 50 services: Init, Search, Sort, Present, Scan, Z 39 Server 5
 Overview Init service: z 39 server gets the Init. Request message from the z 39 client. If the message contains user name and password, z 39 server stores them. (They will be used for access to your local database; by default user name z 39 and password z 39 will be used). Z 39 Server 6
Overview Init service: z 39 server gets the Init. Request message from the z 39 client. If the message contains user name and password, z 39 server stores them. (They will be used for access to your local database; by default user name z 39 and password z 39 will be used). Z 39 Server 6
 Overview Search service: z 39 server gets the Search. Request message from the z 39 client. The message contains the database name, the z 39 search query and the result set name. z 39 server translates the z 39 query to an Digi. Tool CCL query, searches the database and creates a result set with a given name. z 39 server sends a Search. Response message to the client. This message contains the number of hits. If an error occurred, the message contains error indication. Z 39 Server 7
Overview Search service: z 39 server gets the Search. Request message from the z 39 client. The message contains the database name, the z 39 search query and the result set name. z 39 server translates the z 39 query to an Digi. Tool CCL query, searches the database and creates a result set with a given name. z 39 server sends a Search. Response message to the client. This message contains the number of hits. If an error occurred, the message contains error indication. Z 39 Server 7
 Overview Scan service: z 39 server gets a Scan. Request message from z 39 client. This message contains database name and z 39 scan query. z 39 server translates a z 39 scan query to an Digi. Tool query and scans the database. z 39 server sends a Scan. Response message to the client. The message contains the scan entries. If an error occurred, the message contains error indication. Z 39 Server 8
Overview Scan service: z 39 server gets a Scan. Request message from z 39 client. This message contains database name and z 39 scan query. z 39 server translates a z 39 scan query to an Digi. Tool query and scans the database. z 39 server sends a Scan. Response message to the client. The message contains the scan entries. If an error occurred, the message contains error indication. Z 39 Server 8
 Overview Sort service: z 39 server gets a Sort. Request message from the z 39 client. The message contains database name, z 39 sort query and result set name. z 39 server translates the z 39 query to an Digi. Tool query and performs a sort of the given set. z 39 server sends a Sort. Response message to the client. The message contains success/failure indication. Z 39 Server 9
Overview Sort service: z 39 server gets a Sort. Request message from the z 39 client. The message contains database name, z 39 sort query and result set name. z 39 server translates the z 39 query to an Digi. Tool query and performs a sort of the given set. z 39 server sends a Sort. Response message to the client. The message contains success/failure indication. Z 39 Server 9
 Overview Present service: z 39 server gets a Present. Request from the z 39 client. The message contains database name, result set name, number of first record to retrieve, total number of records to retrieve and optional record format (USMARC, XML, SUTRS, MAB). z 39 server retrieves the requested records and sends a Present. Response message to the client. The message contains the retrieved records in the requested format. If an error occurred, the message contains error indication. Z 39 Server 10
Overview Present service: z 39 server gets a Present. Request from the z 39 client. The message contains database name, result set name, number of first record to retrieve, total number of records to retrieve and optional record format (USMARC, XML, SUTRS, MAB). z 39 server retrieves the requested records and sends a Present. Response message to the client. The message contains the retrieved records in the requested format. If an error occurred, the message contains error indication. Z 39 Server 10
 Overview All the processing is done using the pc_server. z 39 server receives a request from a client. It translates the request from ‘z 39 language’ to ‘Digi. Tool language’ and passes the translated request to the pc_server. The pc_server executes the request and passes the response to the z 39 server. The z 39 server translates the response from ‘Digi. Tool language’ to ‘z 39 language’ and sends it to the client. Z 39 Server 11
Overview All the processing is done using the pc_server. z 39 server receives a request from a client. It translates the request from ‘z 39 language’ to ‘Digi. Tool language’ and passes the translated request to the pc_server. The pc_server executes the request and passes the response to the z 39 server. The z 39 server translates the response from ‘Digi. Tool language’ to ‘z 39 language’ and sends it to the client. Z 39 Server 11
 z 39 server - Present Service The records may be returned in the following formats: USMARC, UNIMARC, XML, SUTRS, and MAB. If local database contains USMARC record – the records can be returned in USMARC, if local database is in UNIMARC – the records can be returned in UNIMARC, if local database is in MAB - the records can be returned in MAB. Z 39 Server 12
z 39 server - Present Service The records may be returned in the following formats: USMARC, UNIMARC, XML, SUTRS, and MAB. If local database contains USMARC record – the records can be returned in USMARC, if local database is in UNIMARC – the records can be returned in UNIMARC, if local database is in MAB - the records can be returned in MAB. Z 39 Server 12
 z 39 server Configuration The configuration files of the z 39 server are under the dtle_tab/z 39 server directory: There are 3 types of files: 1. z 39 server. conf general z 39 server parameters 2. z 39 server
z 39 server Configuration The configuration files of the z 39 server are under the dtle_tab/z 39 server directory: There are 3 types of files: 1. z 39 server. conf general z 39 server parameters 2. z 39 server
 z 39 server Configuration 1. z 39 server. conf The file contains general settings for the z 39 server. Each setting should be defined in a separate line. There are mandatory settings and optional settings: The settings of the pc_server are mandatory: Syntax: hostname
z 39 server Configuration 1. z 39 server. conf The file contains general settings for the z 39 server. Each setting should be defined in a separate line. There are mandatory settings and optional settings: The settings of the pc_server are mandatory: Syntax: hostname
 z 39 server Configuration z 39 server. conf The following setting is optional: log record indication Syntax: marclog
z 39 server Configuration z 39 server. conf The following setting is optional: log record indication Syntax: marclog
 z 39 server Configuration 2. z 39 server.
z 39 server Configuration 2. z 39 server.
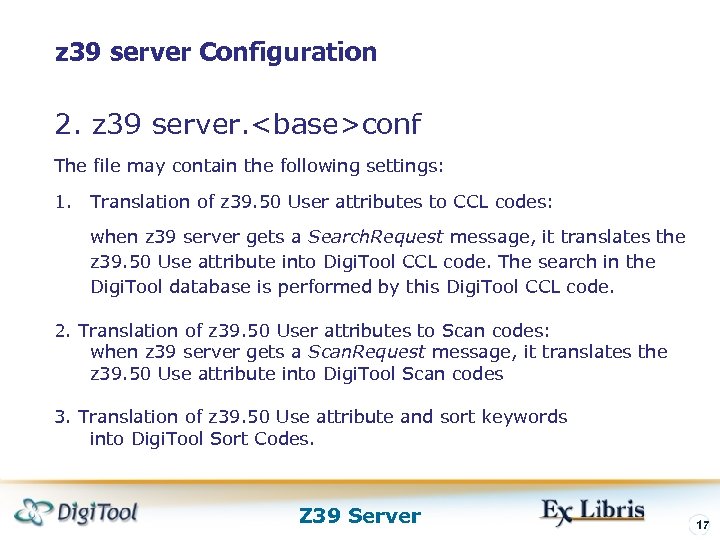 z 39 server Configuration 2. z 39 server.
z 39 server Configuration 2. z 39 server.
 z 39 server User Authentication Init. Request has an optional parameter: id. Authentication. This parameter contains user and password. If the id. Authentication parameter in Init. Request is not empty, z 39 server passes the received user and password to pc_server. If id. Authentication is empty, z 39 server passes user = “z 39” and password = “z 39” to pc_server authenticates the user as a regular Digi. Tool user. The user must have z 39. 50 user permissions for the requested collection. The permissions are defined in the staff privileges portion of the Meditor. Z 39 Server 18
z 39 server User Authentication Init. Request has an optional parameter: id. Authentication. This parameter contains user and password. If the id. Authentication parameter in Init. Request is not empty, z 39 server passes the received user and password to pc_server. If id. Authentication is empty, z 39 server passes user = “z 39” and password = “z 39” to pc_server authenticates the user as a regular Digi. Tool user. The user must have z 39. 50 user permissions for the requested collection. The permissions are defined in the staff privileges portion of the Meditor. Z 39 Server 18
 z 39 server User Authentication This mechanism permits the administrator to grant access to a collection to all users or to specified users only. To grant access to all users: assign to the “z 39” user “z 39. 50 users permissions” to the collection. z 39. 50 clients connecting to our z 39 server must send empty id. Authentication in Init Request. To grant access to specified users: assign to specified users “z 39. 50 users permissions” for the collection. z 39. 50 clients connecting to your z 39 server must send this user name and password in id. Authentication in Init Request. Z 39 Server 19
z 39 server User Authentication This mechanism permits the administrator to grant access to a collection to all users or to specified users only. To grant access to all users: assign to the “z 39” user “z 39. 50 users permissions” to the collection. z 39. 50 clients connecting to our z 39 server must send empty id. Authentication in Init Request. To grant access to specified users: assign to specified users “z 39. 50 users permissions” for the collection. z 39. 50 clients connecting to your z 39 server must send this user name and password in id. Authentication in Init Request. Z 39 Server 19
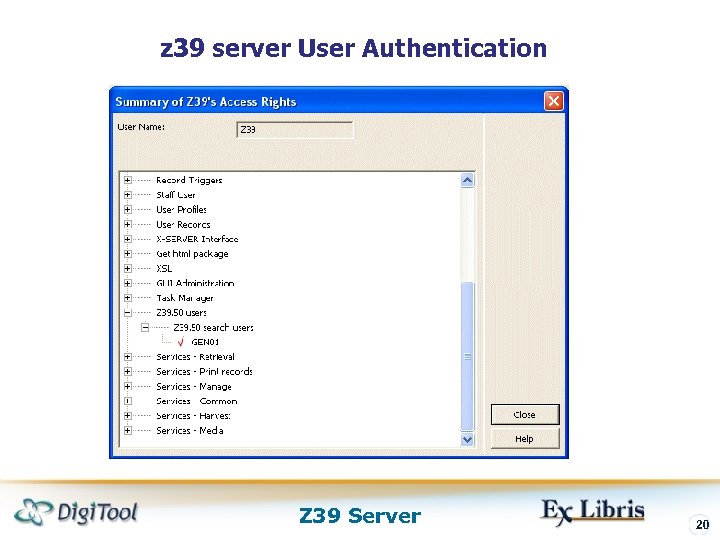 z 39 server User Authentication Z 39 Server 20
z 39 server User Authentication Z 39 Server 20
 z 39 server Configuration How to add a new Base for z 39 server Enter any collection environment (For example, dlib GEN 01). Enter util/n/2 Use the menu options to edit z 39 server configuration. To define new base, choose option ‘ 1. Add base’. Then enter base name. The name will be translated into upper case and the file dtle_tab/z 39 server_
z 39 server Configuration How to add a new Base for z 39 server Enter any collection environment (For example, dlib GEN 01). Enter util/n/2 Use the menu options to edit z 39 server configuration. To define new base, choose option ‘ 1. Add base’. Then enter base name. The name will be translated into upper case and the file dtle_tab/z 39 server_
 Thank you! www. exlibrisgroup. com Z 39 Server 22
Thank you! www. exlibrisgroup. com Z 39 Server 22


