d9f2b682f89849afcd01307024b5d067.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

Z 39. 50, RDF and the Web ZIG Tutorial August 1999 Poul Henrik Jørgensen, Danish Library Centre, www. dbc. dk ZIG 1999 -08 -10 Z 39. 50 & Web / DBC-PHJ

Contents n n n WWW Benefits and Limitations Z 39. 50 Benefits and Limitations Resource Description Framework, RDF ZIG 1999 -08 -10 Z 39. 50 & Web / DBC-PHJ 2

Web Harvesters n n Web Harvesters follow links to find HTML documents on selected Web Servers Fetches documents and extracts words from the text Meta tags are (sometimes) ignored Maintains databases of words with URLs of corresponding Web pages ZIG 1999 -08 -10 Z 39. 50 & Web / DBC-PHJ 3

Web Search Overview n n Displays search-form in a Web browser Search-words are submitted to indexdatabase List of Web pages with hyperlinks is returned to Web browser User clicks on URLs to fetch original HTML documents from the source ZIG 1999 -08 -10 Z 39. 50 & Web / DBC-PHJ 4
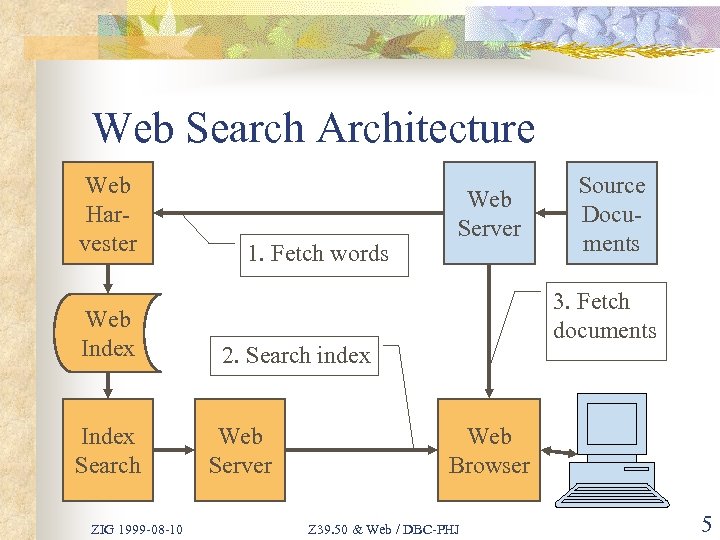
Web Search Architecture Web Harvester Web Index Search ZIG 1999 -08 -10 1. Fetch words Web Server 3. Fetch documents 2. Search index Web Server Source Documents Web Browser Z 39. 50 & Web / DBC-PHJ 5
Web Search Example ZIG 1999 -08 -10 Z 39. 50 & Web / DBC-PHJ 6

Web Search Benefits and Issues n n n Utilize standard Web browsers Returns many URLs to Web pages Information within databases is ignored Tied to special search forms Imprecise search on free-text words Limited control over presentation formats ZIG 1999 -08 -10 Z 39. 50 & Web / DBC-PHJ 7

Z 39. 50 Overview n n Z 39. 50 Targets (Z-Servers) share a standard system interface to Z 39. 50 Origins (Z-Clients) Z-Clients support specialised user interfaces Z-Clients submit metadata Search- and Present requests etc. to Z-Servers Z 39. 50 search metadata and retrieve information from databases ZIG 1999 -08 -10 Z 39. 50 & Web / DBC-PHJ 8
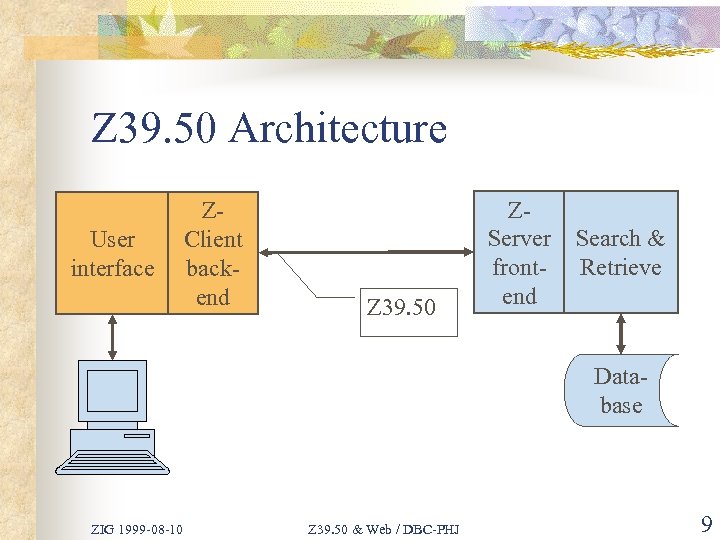
Z 39. 50 Architecture User interface ZClient backend Z 39. 50 ZServer frontend Search & Retrieve Database ZIG 1999 -08 -10 Z 39. 50 & Web / DBC-PHJ 9
Z 39. 50 Example ZIG 1999 -08 -10 Z 39. 50 & Web / DBC-PHJ 10
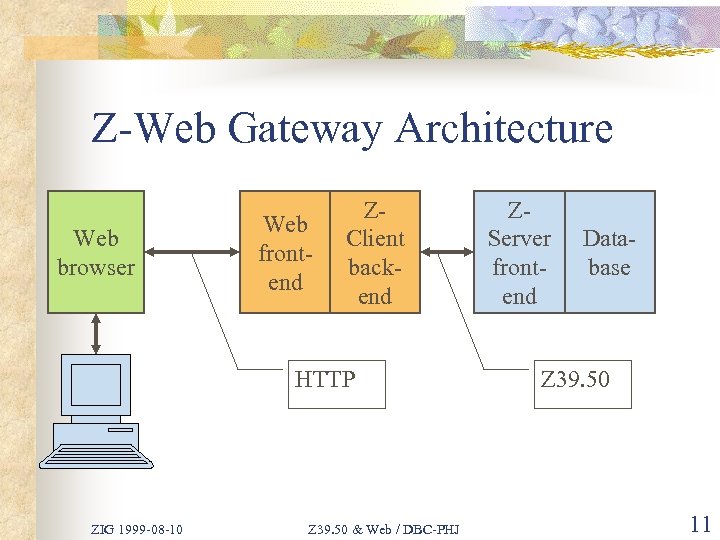
Z-Web Gateway Architecture Web browser Web frontend ZClient backend HTTP ZIG 1999 -08 -10 Z 39. 50 & Web / DBC-PHJ ZServer frontend Database Z 39. 50 11

Z 39. 50 Benefits and Issues n n n Precise searching with metadata attributes Z 39. 50 includes Extended Services to retrieve, order and update information. Information systems require standard ZServer front-ends Require speciel Z-Clients Standard system interface between ZClients and Servers ZIG 1999 -08 -10 Z 39. 50 & Web / DBC-PHJ 12

RDF Overview n n n Resource Description Framework Developed by W 3 C from PICS General information model based on Directed Labeled Graphs (DLG) – and NIAM Serilization and Schema based on XML Namespace defines vocabularies Document Object Model (DOM) as API ZIG 1999 -08 -10 Z 39. 50 & Web / DBC-PHJ 13

RDF Elements n n n An RDF Resource is an instance of one or more Classes Resources have Properties A Class may be a Subclass of another Class Properties are values or Relations to other Resources Statements: Resource (Subject) + Property (Predicate) + Value (Object) ZIG 1999 -08 -10 Z 39. 50 & Web / DBC-PHJ 14

RDF Statement n n n Poul Henrik Jørgensen (Value) is the creator (Property) of the resource http: //neptun. dbc. dk/efila/documents/zigmar 1999/zigmarch 1999 b. htm (Subject). Ref. : http: //www. w 3. org/TR/REC-rdf-syntax/ ZIG 1999 -08 -10 Z 39. 50 & Web / DBC-PHJ 15

RDF XML Syntax <? xml version="1. 0" ? > - <RDF xmlns=http: //www. w 3. org/1999/02/22 -rdf-syntax-ns# xmlns: s="http: //description. org/schema/"> <Description about= "http: //neptun. dbc. dk/efila/documents/zigmar 1999/zigmarch 1999 b. ht” > <s: Creator>Poul Henrik Jørgensen</s: Creator> </Description> </RDF> ZIG 1999 -08 -10 Z 39. 50 & Web / DBC-PHJ 16

Possible RDF and Z 39. 50 Synergy n n Z 39. 50 Services Z 39. 50/HTTP Profile: n n HTTP transmission protocol XML Transfer Syntax XML Namespace as search attributes XSL based Query Language (XQL) ZIG 1999 -08 -10 Z 39. 50 & Web / DBC-PHJ 17
![XQL Example <xsl: for-each select = "book[publisher/name = 'Addison-Wesley'] /author"> <xsl: value-of /> </xsl: XQL Example <xsl: for-each select = "book[publisher/name = 'Addison-Wesley'] /author"> <xsl: value-of /> </xsl:](https://present5.com/presentation/d9f2b682f89849afcd01307024b5d067/image-18.jpg)
XQL Example <xsl: for-each select = "book[publisher/name = 'Addison-Wesley'] /author"> <xsl: value-of /> </xsl: for-each> http: //www. w 3. org/Tand. S/QL/QL 98/pp/xql. html ZIG 1999 -08 -10 Z 39. 50 & Web / DBC-PHJ 18
Summary n Web Search engines have two drawbacks: n n No standard interface (human or otherwise) No standard service models RDF offers general method to describe objects and relationships (i. e. Metadata) Z 39. 50/HTTP + XMLNS + RDF + DOM + XQL may be a winning combination ZIG 1999 -08 -10 Z 39. 50 & Web / DBC-PHJ 19
d9f2b682f89849afcd01307024b5d067.ppt