abf6114c1dab87c8e4c4888091203b3d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 Z 39. 50 and Cryptography ZIG July 13 th 2000 Poul Henrik Jørgensen, mailto: phj@dbc. dk DBC www. dbc. dk ZIG July 2000 Crypto Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC
Z 39. 50 and Cryptography ZIG July 13 th 2000 Poul Henrik Jørgensen, mailto: phj@dbc. dk DBC www. dbc. dk ZIG July 2000 Crypto Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC
 Is Cryptography Relevant to Z 39. 50? ¨ Authentication: identify users (and servers) internally. ¨ Confidentiality: keep searches, responses (and users) secret to from others. ¨ Integrity: prevent tampering with searches and responses. ¨ Non-repudiation: prove the transactions. ZIG July 2000 Crypto Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC 2
Is Cryptography Relevant to Z 39. 50? ¨ Authentication: identify users (and servers) internally. ¨ Confidentiality: keep searches, responses (and users) secret to from others. ¨ Integrity: prevent tampering with searches and responses. ¨ Non-repudiation: prove the transactions. ZIG July 2000 Crypto Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC 2
 Security Threats ¨ Spoofing: Masquerading as one of the parties. ¨ Eavesdropping: Snooping on traffic between parties. ¨ Tampering: Forgery or modification of messages. ¨ Repudiation: Denying the transaction. ZIG July 2000 Crypto Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC 3
Security Threats ¨ Spoofing: Masquerading as one of the parties. ¨ Eavesdropping: Snooping on traffic between parties. ¨ Tampering: Forgery or modification of messages. ¨ Repudiation: Denying the transaction. ZIG July 2000 Crypto Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC 3
 Symmetric Encryption ¨ A single common encryption key is used to encode and decode messages ¨ Both sender and receiver must know the common key ¨ The common key need to be exchanged beforehand by some other secure method ¨ Symmetric encryption is simple and fast ¨ But - key management is impractical with large number of senders and receivers! ZIG July 2000 Crypto Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC 4
Symmetric Encryption ¨ A single common encryption key is used to encode and decode messages ¨ Both sender and receiver must know the common key ¨ The common key need to be exchanged beforehand by some other secure method ¨ Symmetric encryption is simple and fast ¨ But - key management is impractical with large number of senders and receivers! ZIG July 2000 Crypto Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC 4
 Public-key Cryptography ¨ Public-key (PK) encryption algorithms use pairs of matched (asymmetric) keys for encryption and decryption. ¨ Each user has a Public key and a corresponding Private (secret) key ¨ Public-key cryptography is used to exchange symmetric keys securely. ¨ Public-keys are also used to validate digital signatures. ZIG July 2000 Crypto Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC 5
Public-key Cryptography ¨ Public-key (PK) encryption algorithms use pairs of matched (asymmetric) keys for encryption and decryption. ¨ Each user has a Public key and a corresponding Private (secret) key ¨ Public-key cryptography is used to exchange symmetric keys securely. ¨ Public-keys are also used to validate digital signatures. ZIG July 2000 Crypto Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC 5
 Public-key Usage ¨ Alice creates a new symmetric session-key. ¨ Alice encrypts the session-key by means of Bob’s public key. ¨ Alice transmits the encrypted message containing the session-key to Bob. ¨ Bob decrypts Alice’s message with the session-key by means of his private key. ¨ Alice and Bob both encrypt and decrypt subsequent messages by means of the session-key. ZIG July 2000 Crypto Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC 6
Public-key Usage ¨ Alice creates a new symmetric session-key. ¨ Alice encrypts the session-key by means of Bob’s public key. ¨ Alice transmits the encrypted message containing the session-key to Bob. ¨ Bob decrypts Alice’s message with the session-key by means of his private key. ¨ Alice and Bob both encrypt and decrypt subsequent messages by means of the session-key. ZIG July 2000 Crypto Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC 6
 Digital Signatures and Certificates ¨ Sender”sign” messages by means of his private secret key. ¨ Recipient verify the senders signature by means of the senders public key. ¨ The senders identity is certified by means of a”Certificate” which is digitally signed by a trusted third party. ZIG July 2000 Crypto Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC 7
Digital Signatures and Certificates ¨ Sender”sign” messages by means of his private secret key. ¨ Recipient verify the senders signature by means of the senders public key. ¨ The senders identity is certified by means of a”Certificate” which is digitally signed by a trusted third party. ZIG July 2000 Crypto Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC 7
 Secure Socket Layer (SSL) ¨ SSL is a communication layer on top of TCP/IP ¨ SSL is supported by current browsers ¨ Browser request a copy of a HTTPS servers’ certificate ¨ Browser verify identity of the server by checking the certificate and the digital signature ¨ Browser create a symmetric session key ZIG July 2000 Crypto Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC 8
Secure Socket Layer (SSL) ¨ SSL is a communication layer on top of TCP/IP ¨ SSL is supported by current browsers ¨ Browser request a copy of a HTTPS servers’ certificate ¨ Browser verify identity of the server by checking the certificate and the digital signature ¨ Browser create a symmetric session key ZIG July 2000 Crypto Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC 8
 Secure Socket Layer cont. ¨ Browser encrypt the session key by means of the HTTP servers public key and transmits the session key to the server ¨ Session data is encrypted and decrypted both ways at both ends by means of the symmetric session key ¨ http: //developer. netscape. com/tech/security/ssl/howitworks. html ZIG July 2000 Crypto Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC 9
Secure Socket Layer cont. ¨ Browser encrypt the session key by means of the HTTP servers public key and transmits the session key to the server ¨ Session data is encrypted and decrypted both ways at both ends by means of the symmetric session key ¨ http: //developer. netscape. com/tech/security/ssl/howitworks. html ZIG July 2000 Crypto Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC 9
 Z 39. 50 and Symmetric Keys ¨ A new Z 39. 50 Init Request option may specify use of a symmetric encryption algorithm within a Z 39. 50 session ¨ Symmetric encryption key must be exchanged outside of the Z 39. 50 protocol, e. g. based on a predefined user password ¨ Only Z 39. 50 user data is encrypted – not protocol elements ZIG July 2000 Crypto Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC 10
Z 39. 50 and Symmetric Keys ¨ A new Z 39. 50 Init Request option may specify use of a symmetric encryption algorithm within a Z 39. 50 session ¨ Symmetric encryption key must be exchanged outside of the Z 39. 50 protocol, e. g. based on a predefined user password ¨ Only Z 39. 50 user data is encrypted – not protocol elements ZIG July 2000 Crypto Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC 10
 Z 39. 50 and Symmetric Keys cont. ¨ Encryption and decryption must be handled by Z 39. 50 server and client applications. ¨ This solution require limited changes to Z 39. 50 toolkits in order to handle a new Init Request option. ¨ Z 39. 50 servers and clients must be modified to encrypt- and decrypt data via passwords or other symmetric keys. ZIG July 2000 Crypto Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC 11
Z 39. 50 and Symmetric Keys cont. ¨ Encryption and decryption must be handled by Z 39. 50 server and client applications. ¨ This solution require limited changes to Z 39. 50 toolkits in order to handle a new Init Request option. ¨ Z 39. 50 servers and clients must be modified to encrypt- and decrypt data via passwords or other symmetric keys. ZIG July 2000 Crypto Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC 11
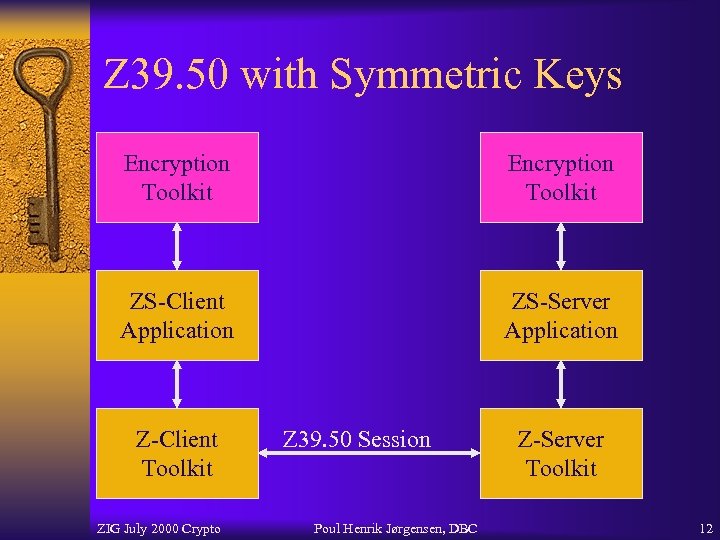 Z 39. 50 with Symmetric Keys Encryption Toolkit ZS-Client Application ZS-Server Application Z-Client Toolkit ZIG July 2000 Crypto Z 39. 50 Session Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC Z-Server Toolkit 12
Z 39. 50 with Symmetric Keys Encryption Toolkit ZS-Client Application ZS-Server Application Z-Client Toolkit ZIG July 2000 Crypto Z 39. 50 Session Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC Z-Server Toolkit 12
 Z 39. 50 and SSL ¨ Z 39. 50 over SSL offers a complete security solution ¨ Transparent to Z 39. 50 server and z-client applications ¨ Require no changes to the Z 39. 50 protocol ¨ Require a compatible Z 39. 50 toolkit on both zserver and z-client that utilise a SSL library ¨ May require key certificates on Z 39. 50 server ZIG July 2000 Crypto Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC 13
Z 39. 50 and SSL ¨ Z 39. 50 over SSL offers a complete security solution ¨ Transparent to Z 39. 50 server and z-client applications ¨ Require no changes to the Z 39. 50 protocol ¨ Require a compatible Z 39. 50 toolkit on both zserver and z-client that utilise a SSL library ¨ May require key certificates on Z 39. 50 server ZIG July 2000 Crypto Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC 13
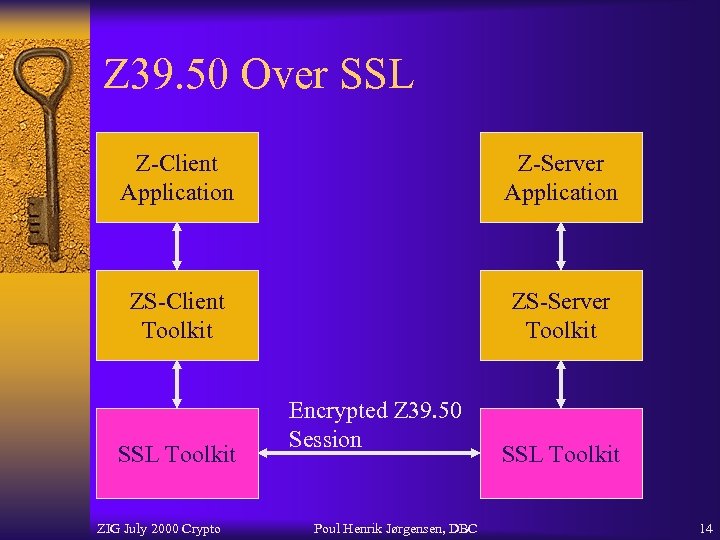 Z 39. 50 Over SSL Z-Client Application Z-Server Application ZS-Client Toolkit ZS-Server Toolkit SSL Toolkit ZIG July 2000 Crypto Encrypted Z 39. 50 Session Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC SSL Toolkit 14
Z 39. 50 Over SSL Z-Client Application Z-Server Application ZS-Client Toolkit ZS-Server Toolkit SSL Toolkit ZIG July 2000 Crypto Encrypted Z 39. 50 Session Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC SSL Toolkit 14
 Summary ¨ Security is primarily relevant to identify Z 39. 50 users ¨ Confidentiality of queries and presented data may also be an issue ¨ SSL require Z 39. 50 SRPM toolkits to utilise SSL libraries, but is transparent to z-servers and clients ¨ Simple symmetric keys may require modifications to Z 39. 50 protocol and to z-servers and clients www. portia. dk/zigjuly 2000/z 3950 crypto. htm ZIG July 2000 Crypto Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC 15
Summary ¨ Security is primarily relevant to identify Z 39. 50 users ¨ Confidentiality of queries and presented data may also be an issue ¨ SSL require Z 39. 50 SRPM toolkits to utilise SSL libraries, but is transparent to z-servers and clients ¨ Simple symmetric keys may require modifications to Z 39. 50 protocol and to z-servers and clients www. portia. dk/zigjuly 2000/z 3950 crypto. htm ZIG July 2000 Crypto Poul Henrik Jørgensen, DBC 15


