654f213bb737e0e033b8e79868fb98cd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 87

Youth and Family Crisis Assessment Presented by:

Meet the Presenters l l Jill Chaffee, MSW, jillchaffee@nwpass. com Himanshu Agrawal, M. D. , himanshu@nwpass. com Angela Fredrickson, LCSW, angela@nwpass. com David Swenson, Ph. D, david@nwpass. com

Why you should care: l l Law enforcement Social Worker Tax Payer Family Member/Advocate

Goals of today: Learn tools and methodology to complete a crisis assessment The Four P concept Understanding and appreciating the role of mental illness in crisis situations Evaluate, manage, and document risk

Overview of Western Region Grant • Certifying counties (DHS 34) • Training • Stabilization services

Goals of the grant Reduce inappropriate/unnecessary restriction of rights by using more restrictive placement than needed Improve access to community based least restrictive options

Goals of Emergency Services/Crisis Program (DHS 34) 1. Quality of Service Ø client centered Ø utilizing least restrictive options Ø community-based Ø ensuring consumer satisfaction (client, family, law enforcement, social worker, community partners)

Goals of Emergency Services/Crisis Program (DHS 34) 2. Efficiency Ø understanding the costs and benefits of the program Ø understanding pro-active planning for crisis Ø understanding a crisis before it becomes a crisis Ø fewer and fewer hospital and beds are available

Goals of Emergency Services/Crisis Program (DHS 34) 3. Outcomes Expected Ø avoid unnecessary hospitalizations Ø engage in evidence-based best practices by law enforcement teaming with mental health Ø state budget requires this consultation Ø serve clients in the community Ø preserve families

Goals of Emergency Services/Crisis Program (DHS 34) 4. Risk Management Ø philosophy Ø shared risk Ø documentation Ø risk taking, creative thinking, and problem solving
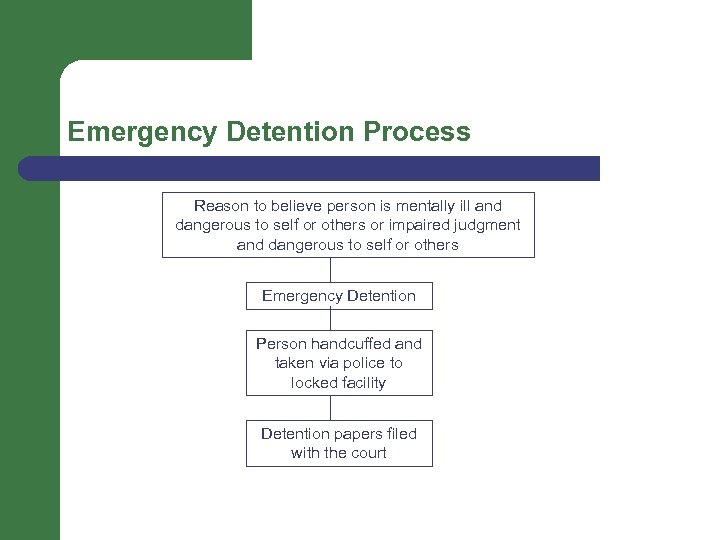
Emergency Detention Process Reason to believe person is mentally ill and dangerous to self or others or impaired judgment and dangerous to self or others Emergency Detention Person handcuffed and taken via police to locked facility Detention papers filed with the court
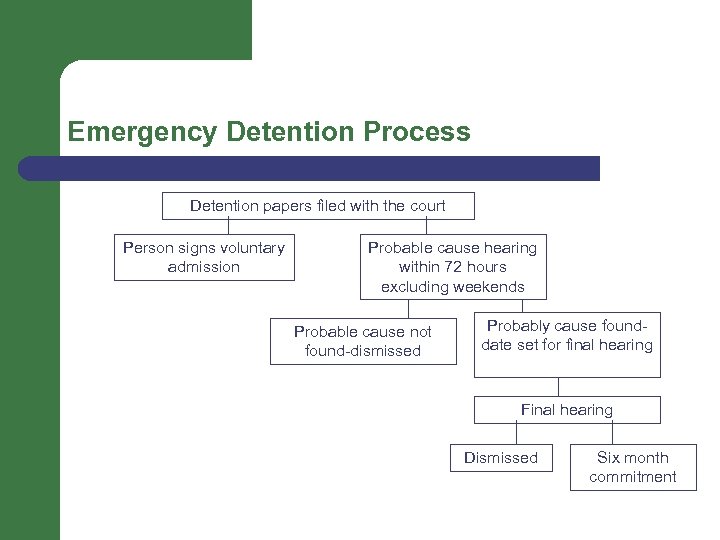
Emergency Detention Process Detention papers filed with the court Person signs voluntary admission Probable cause hearing within 72 hours excluding weekends Probable cause not found-dismissed Probably cause founddate set for final hearing Final hearing Dismissed Six month commitment

No matter how big the problem, don’t rush to solve it. Check with others, sit on it awhile and see what develops.

Interviewing-Overview Building Rapport Assessor Behavior Intervention Don’ts Basic Crisis Strategies Validate Emotions Assessment Tools

Build Rapport • take an interest in the child/adolescent • ask about what he/she likes to do, collect, music interest etc. • find things you have in common • acknowledge his/her achievements

Assessor Behavior • be calm • be respectful even when they are not • have a few clear rules • give clear, direct, simple messages • be consistent • avoid confrontations in front of others • start fresh every day • give choices • use positive reinforcers whenever possible • don’t sweat the small stuff

Intervention DON’T’S Ø DON’T ignore, minimize or joke about life threatening statements Ø DON’T be afraid to inquire about or discuss whether they have considered violence Ø DON’T be judgmental (e. g. , it’s wrong, a sin, etc. ) Ø DON’T act shocked, repulsed, rejecting Ø DON’T call the bluff or challenge to do it Ø DON’T analyze or over-interpret motives Ø DON’T try to argue them out of it Ø DON’T moralize or give advice Ø DON’T promise to keep the violence intention or discussion secret Ø DON’T give up just because they don’t want to talk

Basic Crisis Strategies for Youth and Families • Explore the current problem Øidentify the Precipitating Factors of the crisis Østay present focused – parents and youth Øavoid historical factors

Basic Crisis Strategies for Youth and Families • Pay attention to affect rather than content of the statement Øfocus on the actual suicidal thought Øfocus on the emotions related to the thought Øavoid getting swept away with the other details

Basic Crisis Strategies for Youth and Families Immediate Problem Solving Ø remain present-focused Ø guide parents and youth to find ways to tolerate the affect generated by the Precipitating Factors

Basic Crisis Strategies for Youth and Families Obtain a commitment to a plan of action Ø a series of steps that will help all parties get through the crisis by tolerating it and not engaging in self-harm/suicide/harm to others Ø trouble shooting Ø include a plan for follow-up

Validate Emotions Validation is a way to let people know that their emotions/actions/thoughts make sense given what they have experienced in life. Validation does not equal agreement. Validation is about letting others know you hear them and understand what they are trying to communicate. Try to avoid the “but’s”

Assessment Tools (handouts) Suicide checklist Specific risk factors for suicide
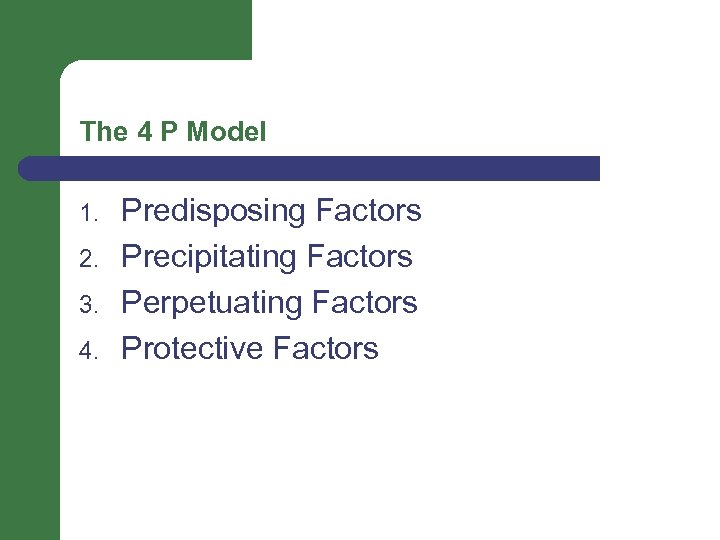
The 4 P Model 1. 2. 3. 4. Predisposing Factors Precipitating Factors Perpetuating Factors Protective Factors
Family history C c on e o pti n
Family history n n Co o pti Bir th ce In-utero exposure
Medical Hx TBI, Sz, DM, Hep C etc Family history n Co ce o pti n Bir In-utero exposure th
Medical Hx TBI, Sz, DM, Hep C etc Family history C on ce o pti n Bir In-utero exposure th Drugs
Medical Hx TBI, Sz, DM, Hep C etc Family history n ce on C o pti In-utero exposure Bir th Drugs

Definitions of the 4 P’s 1. Predisposing Factors-factors or conditions that render an individual vulnerable to disease or disorder 2. Precipitating Factors-an element that causes or contributes to the occurrence of a disorder or problem 3. Perpetuating Factors-factors that cause to continue the situation or condition indefinitely 4. Protective Factors-factors serving or intending to protect the person or improve the situation

Biological Predisposing Factors Psychological Social Biological Precipitating Factors Psychological Social Biological Perpetuating Factors Psychological Social Biological Protective Factors Psychological Social
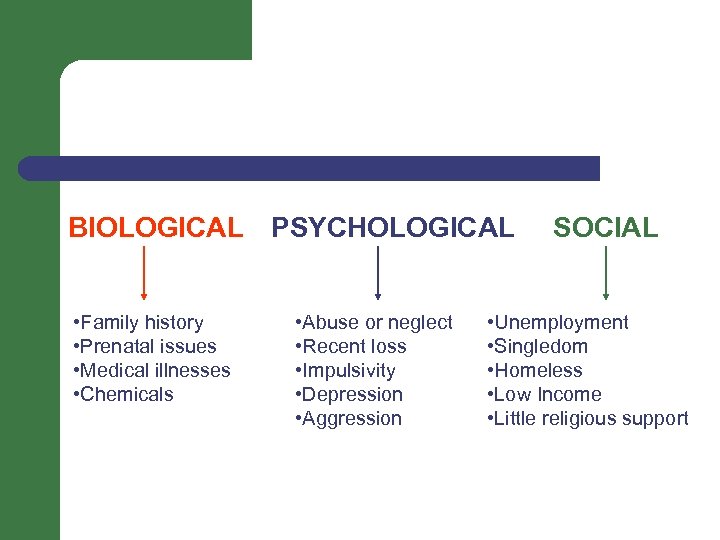
BIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGICAL • Family history • Prenatal issues • Medical illnesses • Chemicals • Abuse or neglect • Recent loss • Impulsivity • Depression • Aggression SOCIAL • Unemployment • Singledom • Homeless • Low Income • Little religious support

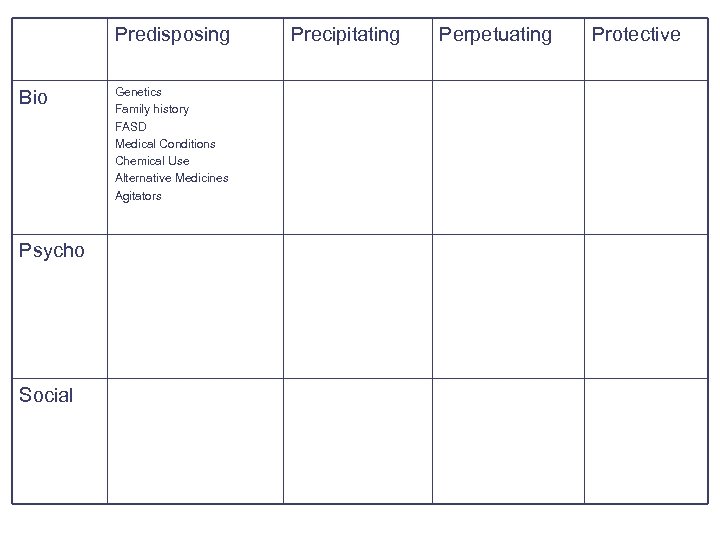
4 P Tool Predisposing Bio Psycho Social Precipitating Perpetuating Protective

Predisposing Biological Factors: Relatively stable factors that increase vulnerability l l Genetics/Family History Exposure to chemicals during pregnancy – Alcohol (FASD) Early age of onset Medical Conditions – Seizures – Traumatic Brain Injury – Mental Retardation – Diabetes – Developmental Disorders, Autism Spectrum Disorders – Sleep Deprivation

Predisposing Biological Factors: Factors that increase vulnerability to a condition l l l Chemical Use Alternative medicine Agitators – Adderall, Ritalin, Cocaine, Meth, Steroids, Alcohol, Antipsychotics – Withdrawal from-Benzo’s, Alcohol, Opiates, Cocaine, Paxil, Effexor
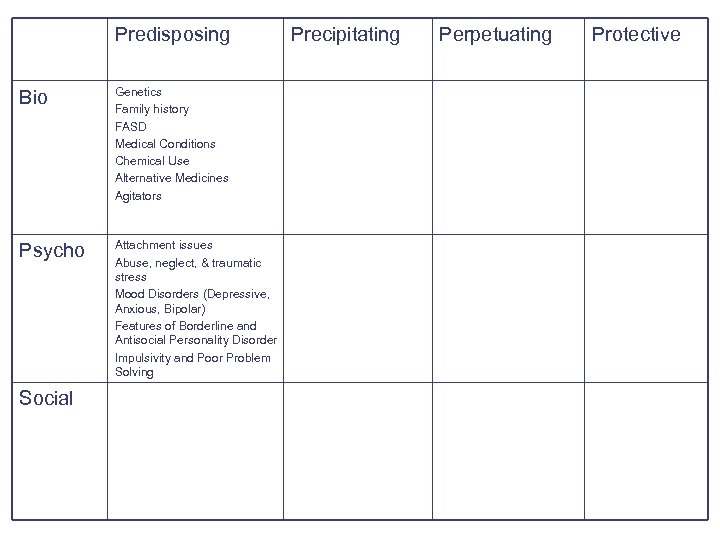
Predisposing Bio Psycho Social Genetics Family history FASD Medical Conditions Chemical Use Alternative Medicines Agitators Precipitating Perpetuating Protective

Predisposing Psychological Factors: Relatively stable factors that increase vulnerability l l l Attachment issues Abuse, neglect, & traumatic stress Mood Disorders (Depressive, Anxious, Bipolar) Features of Borderline and Antisocial Personality Disorders Impulsivity and poor problem solving (interpersonal)

Attachment, Abuse, and Mental Health Attachment difficulties and abuse history often go hand in hand often are present for those with mental illness. Comorbidity of mental disorders is the rule rather than the exception among adolescents 90% of individuals who completed suicide were found to have a diagnosable mental health issue To further complicate matters, such disorders look very different in children and adolescents as compared to adults.

Depression in children and adolescents l Symptoms unique or especially important to teen/child depression – – – Sadness is often replaced by irritability and anger Risk-taking and/or acting out behavior Isolation from friends Drop in school performance Vague body complaints

Personality Disorders and Adolescence l Personality is still developing in adolescence – l l Characteristics of personality disorder are still identified in adolescents The current review of the literature shows Personality Disorders are as great a risk factor for suicide as depression and schizophrenia. The combination of such personality patterns and a tendency for impulsive aggression raises risk.

Impulsivity l l l Research shows that completed suicides are often impulsive acts by adolescents – only 25% show evidence of planning. Studies show a great deal of ambivalence in terms of intent to die in adolescents who attempt suicide. Aggression with impulsivity has been linked to suicidal behaviors in children and adolescents.
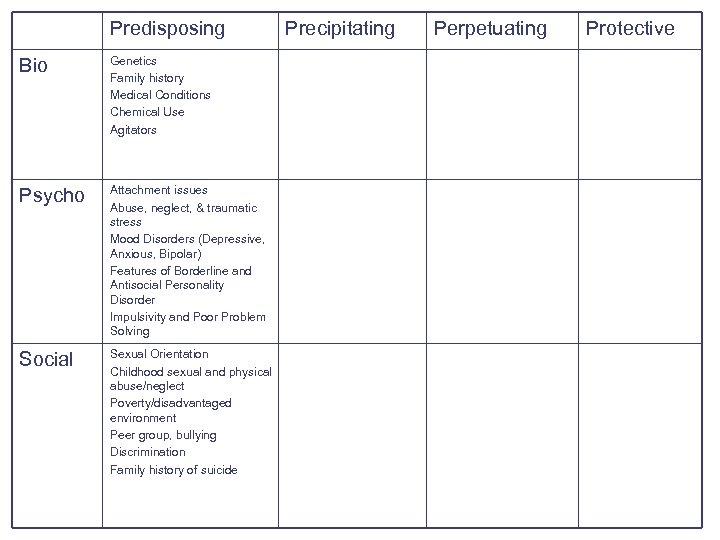
Predisposing Bio Genetics Family history FASD Medical Conditions Chemical Use Alternative Medicines Agitators Psycho Attachment issues Abuse, neglect, & traumatic stress Mood Disorders (Depressive, Anxious, Bipolar) Features of Borderline and Antisocial Personality Disorder Impulsivity and Poor Problem Solving Social Precipitating Perpetuating Protective

Predisposing Social Factors: Factors that increase vulnerability to a condition Sexual Orientation Childhood sexual and physical abuse/neglect Poverty/disadvantaged environment Peer group, bullying Family conflict/functioning Unemployment Discrimination Family history of suicide

Predisposing Social Factors: Factors that increase vulnerability to a condition l l In most cases a predisposing factor alone is not enough to initiate a crisis. Available data are mixed regarding the impact of socioeconomic status and the effect of family stress. – l Suicidal ideation has been associated with presence of parental mental illness, low levels of parental emotional support and low levels of emotion expression within the home. Family history of suicidal behavior significantly increases risk – – 5 times more likely in offspring of mothers who have completed suicide 2 times more common in offspring of fathers who have completed suicide.
Predisposing Bio Genetics Family history Medical Conditions Chemical Use Agitators Psycho Attachment issues Abuse, neglect, & traumatic stress Mood Disorders (Depressive, Anxious, Bipolar) Features of Borderline and Antisocial Personality Disorder Impulsivity and Poor Problem Solving Social Sexual Orientation Childhood sexual and physical abuse/neglect Poverty/disadvantaged environment Peer group, bullying Discrimination Family history of suicide Precipitating Perpetuating Protective
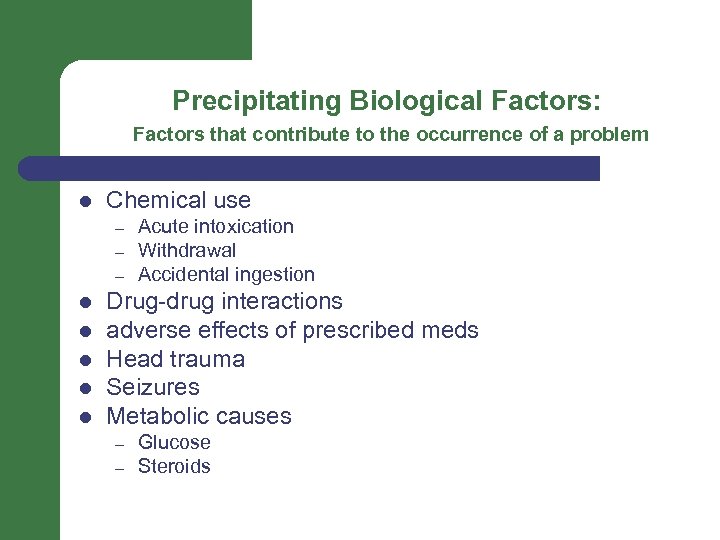
Precipitating Biological Factors: Factors that contribute to the occurrence of a problem l Chemical use – – – l l l Acute intoxication Withdrawal Accidental ingestion Drug-drug interactions adverse effects of prescribed meds Head trauma Seizures Metabolic causes – – Glucose Steroids
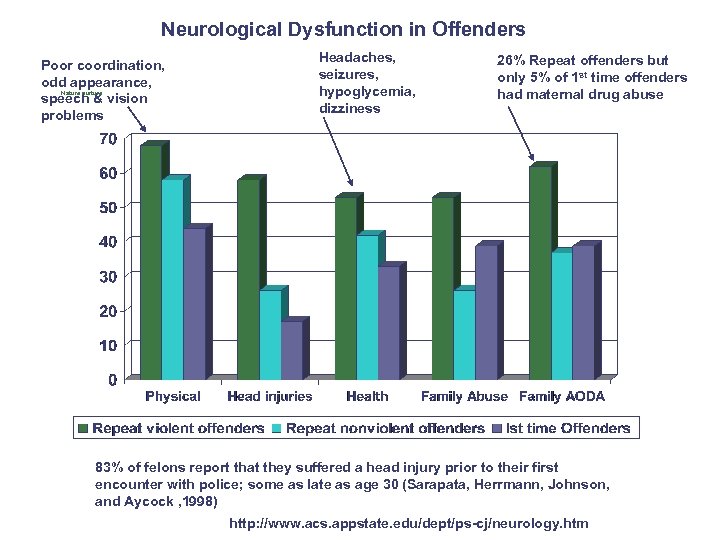
Neurological Dysfunction in Offenders Poor coordination, odd appearance, Nature nurture speech & vision problems Headaches, seizures, hypoglycemia, dizziness 26% Repeat offenders but only 5% of 1 st time offenders had maternal drug abuse 83% of felons report that they suffered a head injury prior to their first encounter with police; some as late as age 30 (Sarapata, Herrmann, Johnson, and Aycock , 1998) http: //www. acs. appstate. edu/dept/ps-cj/neurology. htm

Medication Risks • • • time to reach therapeutic levels interaction effects with illicit drugs side effects & toxicity dietary restriction with MAOI hoarding drugs for overdose

Medication Risks • substance abuse or relapse • selling medications • defiance & noncompliance • may require close medical supervision • only for symptomatic treatment
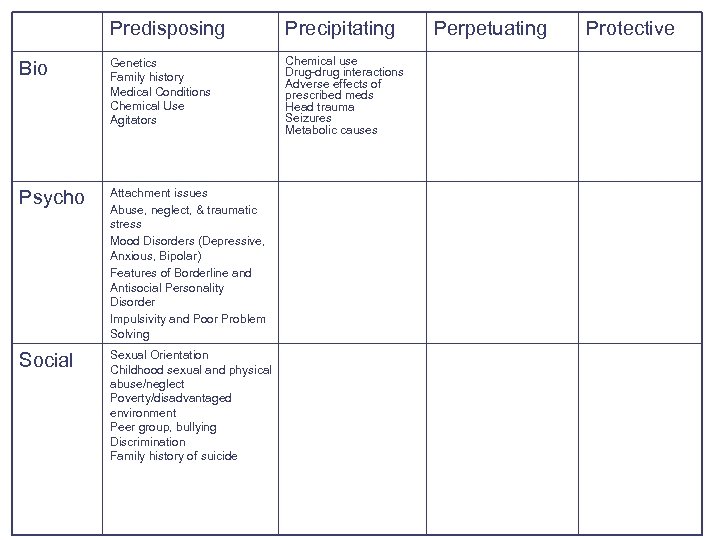
Predisposing Precipitating Bio Genetics Family history Medical Conditions Chemical Use Agitators Chemical use Drug-drug interactions Adverse effects of prescribed meds Head trauma Seizures Metabolic causes Psycho Attachment issues Abuse, neglect, & traumatic stress Mood Disorders (Depressive, Anxious, Bipolar) Features of Borderline and Antisocial Personality Disorder Impulsivity and Poor Problem Solving Social Sexual Orientation Childhood sexual and physical abuse/neglect Poverty/disadvantaged environment Peer group, bullying Discrimination Family history of suicide Perpetuating Protective

Precipitating Psychological Factors: Events, cognitive & emotional triggers l l Interpersonal Conflict and Separations Previous Suicide Attempt – – l Substance use – l The best predictor future suicidal behavior is past suicidal behavior Also the single most important predictor of future completed suicide. Found in great frequency among youth who attempt suicide and is a strong risk factor. Poor problem solving and impulsive decision making

Factors in choice of methods used in adolescent suicide attempts Ø Availability/accessibility Ø Ø Ø Most common method in US regardless of race, gender, age is firearms. Suicide probability increases fivefold when a firearm is kept in the home One study suggested availability of guns contributed more risk than psychopathology Socio-cultural acceptance Familiarity with use Social or behavior suggestion

Factors in choice of methods used in adolescent suicide attempts Saliency – suggestion by publicity, news, drama Ø The magnitude of suicide increase in in direct proportion to the amount, duration, prominence of media coverage of an event Personal, symbolic meaning of the act or setting Intentionality and rescue-ability Ø The greater the intent, the higher level of lethality of method Ø However, lethality does not always match the intent
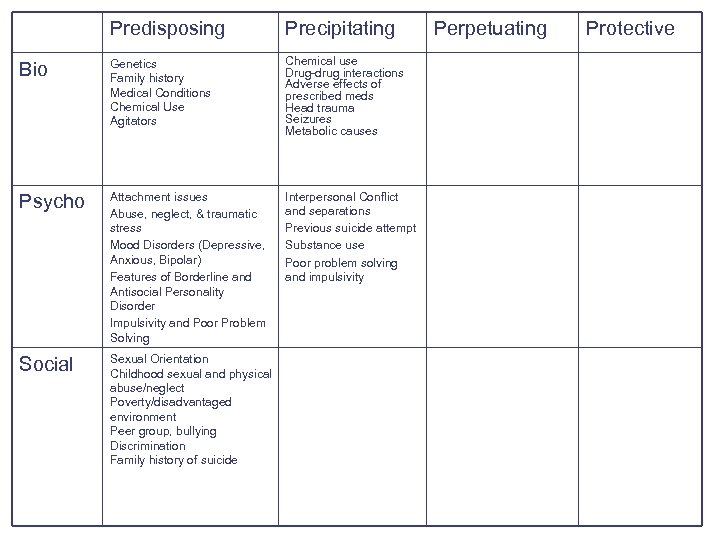
Predisposing Precipitating Bio Genetics Family history Medical Conditions Chemical Use Agitators Chemical use Drug-drug interactions Adverse effects of prescribed meds Head trauma Seizures Metabolic causes Psycho Attachment issues Abuse, neglect, & traumatic stress Mood Disorders (Depressive, Anxious, Bipolar) Features of Borderline and Antisocial Personality Disorder Impulsivity and Poor Problem Solving Interpersonal Conflict and separations Previous suicide attempt Substance use Poor problem solving and impulsivity Social Sexual Orientation Childhood sexual and physical abuse/neglect Poverty/disadvantaged environment Peer group, bullying Discrimination Family history of suicide Perpetuating Protective

Precipitating Social Factors: Factors that contribute to the occurrence of a problem Losses – most importantly interpersonal losses Ø breakup of a romantic relationship, divorce, relative or friend death, disciplinary crisis, humiliation, arguments Arrest/Legal problems Friend has attempted/completed suicide Academic Difficulties Coming out and disclosure Parental job loss Residence change Change in family membership

Precipitating Social Factors l l l Studies show an increase in suicide attempts in individuals who have suicide attempts/completions in their social networks. Adolescents are at highest risk of experiencing suicide clusters. Adolescents are highly susceptible to suggestion and imitative behavior – – A primary mode for learning for this age group Essentially, it is a teen’s job to learn about social behavior and identity.
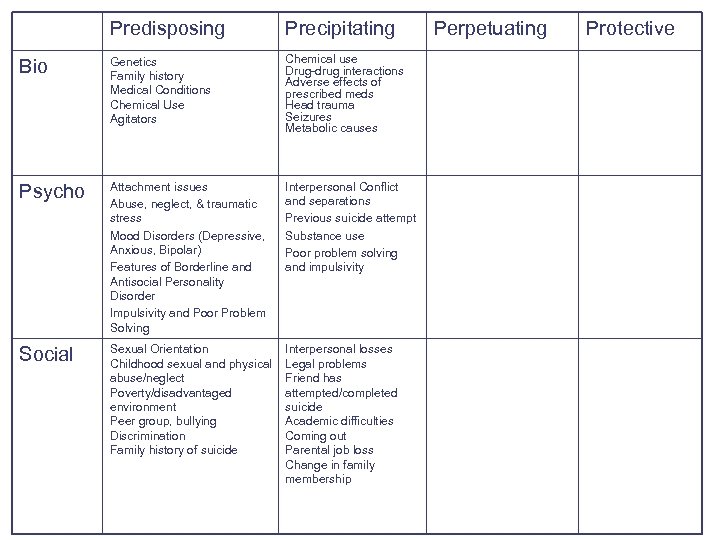
Predisposing Precipitating Bio Genetics Family history Medical Conditions Chemical Use Agitators Chemical use Drug-drug interactions Adverse effects of prescribed meds Head trauma Seizures Metabolic causes Psycho Attachment issues Abuse, neglect, & traumatic stress Mood Disorders (Depressive, Anxious, Bipolar) Features of Borderline and Antisocial Personality Disorder Impulsivity and Poor Problem Solving Interpersonal Conflict and separations Previous suicide attempt Substance use Poor problem solving and impulsivity Social Sexual Orientation Childhood sexual and physical abuse/neglect Poverty/disadvantaged environment Peer group, bullying Discrimination Family history of suicide Interpersonal losses Legal problems Friend has attempted/completed suicide Academic difficulties Coming out Parental job loss Change in family membership Perpetuating Protective

Perpetuating Biological Factors: Factors that maintain the behavior or prevent resolution l Poorly controlled medical conditions – – l l Diabetes Cushing’s disease/ Addison’s disease Thyroid and parathyroid conditions Seizures Ongoing drug use Chronic sleep deprivation Chronic pain (incl fibromyalgia ) Painful/debilitating diseases (arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis, psoriasis, etc).
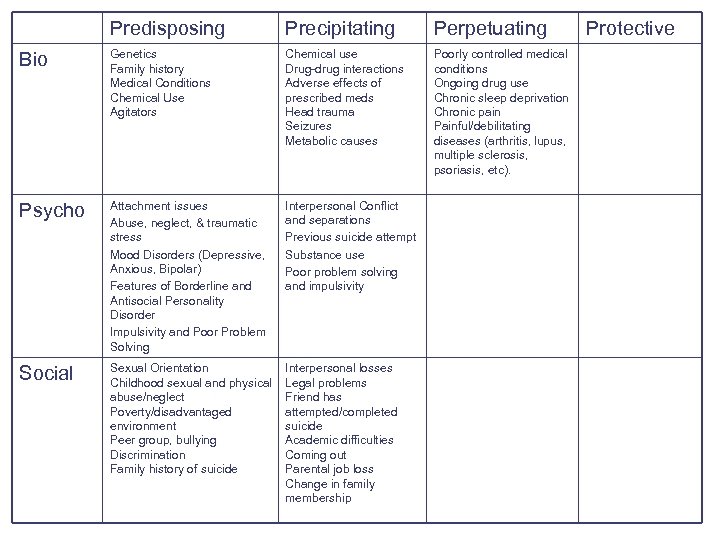
Predisposing Precipitating Perpetuating Bio Genetics Family history Medical Conditions Chemical Use Agitators Chemical use Drug-drug interactions Adverse effects of prescribed meds Head trauma Seizures Metabolic causes Poorly controlled medical conditions Ongoing drug use Chronic sleep deprivation Chronic pain Painful/debilitating diseases (arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis, psoriasis, etc). Psycho Attachment issues Abuse, neglect, & traumatic stress Mood Disorders (Depressive, Anxious, Bipolar) Features of Borderline and Antisocial Personality Disorder Impulsivity and Poor Problem Solving Interpersonal Conflict and separations Previous suicide attempt Substance use Poor problem solving and impulsivity Social Sexual Orientation Childhood sexual and physical abuse/neglect Poverty/disadvantaged environment Peer group, bullying Discrimination Family history of suicide Interpersonal losses Legal problems Friend has attempted/completed suicide Academic difficulties Coming out Parental job loss Change in family membership Protective

Perpetuating Psychological Factors: Factors that maintain the behavior or prevent resolution l l The continuation of both psychological and social predisposing factors Continuation and reinforcement of poor problem solving Mental Health Disorders Lack of healthy intervention for child/family
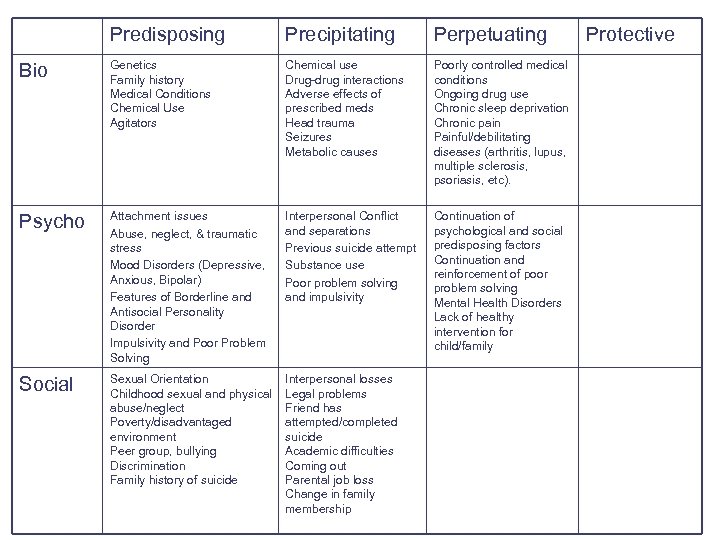
Predisposing Precipitating Perpetuating Bio Genetics Family history Medical Conditions Chemical Use Agitators Chemical use Drug-drug interactions Adverse effects of prescribed meds Head trauma Seizures Metabolic causes Poorly controlled medical conditions Ongoing drug use Chronic sleep deprivation Chronic pain Painful/debilitating diseases (arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis, psoriasis, etc). Psycho Attachment issues Abuse, neglect, & traumatic stress Mood Disorders (Depressive, Anxious, Bipolar) Features of Borderline and Antisocial Personality Disorder Impulsivity and Poor Problem Solving Interpersonal Conflict and separations Previous suicide attempt Substance use Poor problem solving and impulsivity Continuation of psychological and social predisposing factors Continuation and reinforcement of poor problem solving Mental Health Disorders Lack of healthy intervention for child/family Social Sexual Orientation Childhood sexual and physical abuse/neglect Poverty/disadvantaged environment Peer group, bullying Discrimination Family history of suicide Interpersonal losses Legal problems Friend has attempted/completed suicide Academic difficulties Coming out Parental job loss Change in family membership Protective

Perpetuating Social Factors: Factors that maintain the behavior or prevent resolution Continuation of precipitating factors Parental Mental Disorders/Substance use Abuse/neglect Poor parent-child communication Øchild views parent as uncaring and/or overprotective Social isolation Mistrust of helping-professionals, stigma
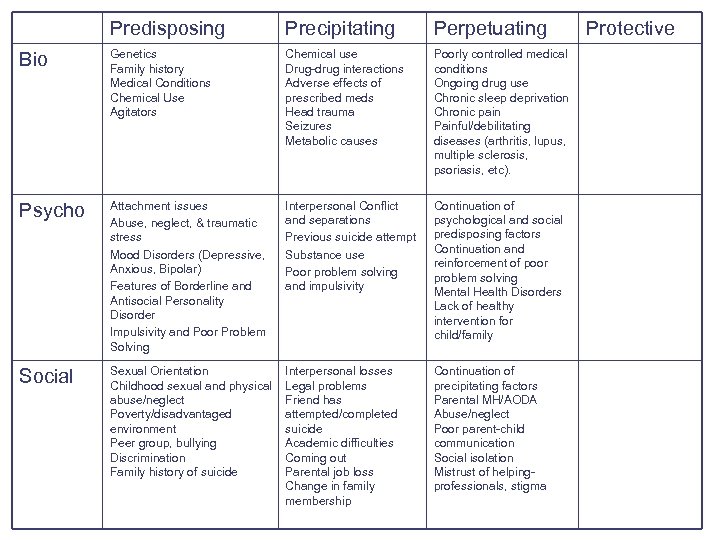
Predisposing Precipitating Perpetuating Bio Genetics Family history Medical Conditions Chemical Use Agitators Chemical use Drug-drug interactions Adverse effects of prescribed meds Head trauma Seizures Metabolic causes Poorly controlled medical conditions Ongoing drug use Chronic sleep deprivation Chronic pain Painful/debilitating diseases (arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis, psoriasis, etc). Psycho Attachment issues Abuse, neglect, & traumatic stress Mood Disorders (Depressive, Anxious, Bipolar) Features of Borderline and Antisocial Personality Disorder Impulsivity and Poor Problem Solving Interpersonal Conflict and separations Previous suicide attempt Substance use Poor problem solving and impulsivity Continuation of psychological and social predisposing factors Continuation and reinforcement of poor problem solving Mental Health Disorders Lack of healthy intervention for child/family Social Sexual Orientation Childhood sexual and physical abuse/neglect Poverty/disadvantaged environment Peer group, bullying Discrimination Family history of suicide Interpersonal losses Legal problems Friend has attempted/completed suicide Academic difficulties Coming out Parental job loss Change in family membership Continuation of precipitating factors Parental MH/AODA Abuse/neglect Poor parent-child communication Social isolation Mistrust of helpingprofessionals, stigma Protective

Protective Biological Factors: Factors that protect the person, prevent further deterioration, or improve the situation l l Healthy living (nutrition, sleep, exercise, stress management) Positives – – No drug use No exposure to chemicals in uterus No schizophrenia or bipolar in family No traumatic brain injury
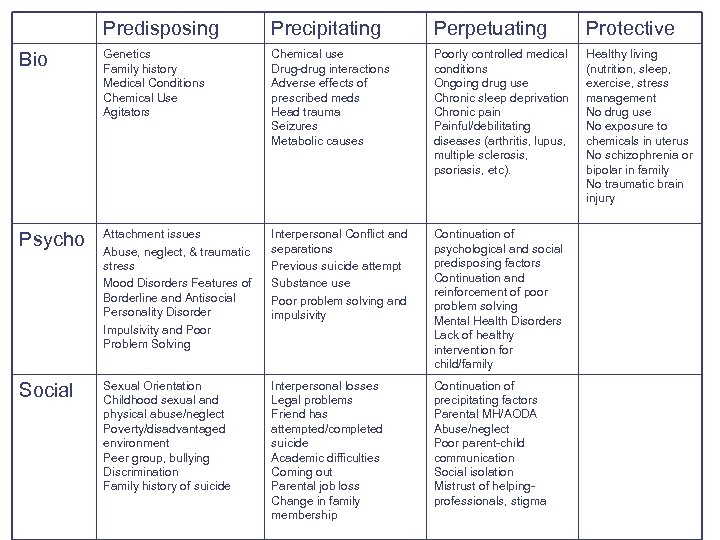
Predisposing Precipitating Perpetuating Protective Bio Genetics Family history Medical Conditions Chemical Use Agitators Chemical use Drug-drug interactions Adverse effects of prescribed meds Head trauma Seizures Metabolic causes Poorly controlled medical conditions Ongoing drug use Chronic sleep deprivation Chronic pain Painful/debilitating diseases (arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis, psoriasis, etc). Healthy living (nutrition, sleep, exercise, stress management No drug use No exposure to chemicals in uterus No schizophrenia or bipolar in family No traumatic brain injury Psycho Attachment issues Abuse, neglect, & traumatic stress Mood Disorders Features of Borderline and Antisocial Personality Disorder Impulsivity and Poor Problem Solving Interpersonal Conflict and separations Previous suicide attempt Substance use Poor problem solving and impulsivity Continuation of psychological and social predisposing factors Continuation and reinforcement of poor problem solving Mental Health Disorders Lack of healthy intervention for child/family Social Sexual Orientation Childhood sexual and physical abuse/neglect Poverty/disadvantaged environment Peer group, bullying Discrimination Family history of suicide Interpersonal losses Legal problems Friend has attempted/completed suicide Academic difficulties Coming out Parental job loss Change in family membership Continuation of precipitating factors Parental MH/AODA Abuse/neglect Poor parent-child communication Social isolation Mistrust of helpingprofessionals, stigma

Protective Psychological Factors: Factors that protect the person, prevent further deterioration, or improve the situation Cultural/Religious Beliefs Ongoing access to effective mental health/substance use treatment Skills in problem solving, interpersonal communication, emotional regulation, and distress tolerance
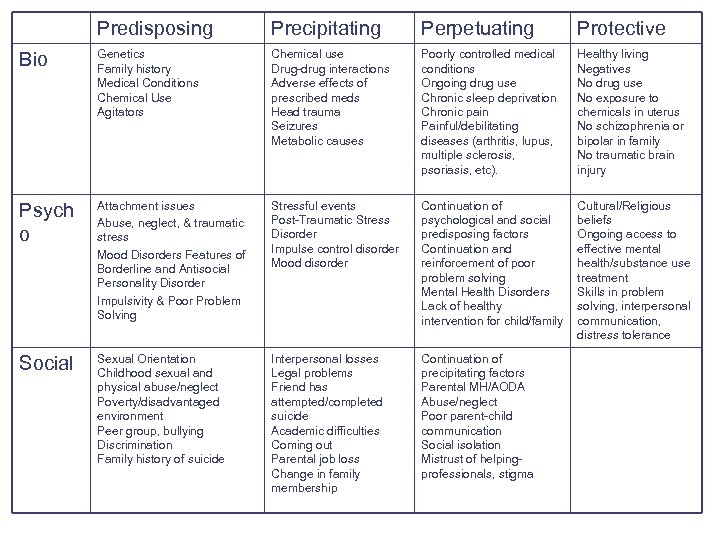
Predisposing Precipitating Perpetuating Protective Bio Genetics Family history Medical Conditions Chemical Use Agitators Chemical use Drug-drug interactions Adverse effects of prescribed meds Head trauma Seizures Metabolic causes Poorly controlled medical conditions Ongoing drug use Chronic sleep deprivation Chronic pain Painful/debilitating diseases (arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis, psoriasis, etc). Healthy living Negatives No drug use No exposure to chemicals in uterus No schizophrenia or bipolar in family No traumatic brain injury Psych o Attachment issues Abuse, neglect, & traumatic stress Mood Disorders Features of Borderline and Antisocial Personality Disorder Impulsivity & Poor Problem Solving Stressful events Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Impulse control disorder Mood disorder Continuation of psychological and social predisposing factors Continuation and reinforcement of poor problem solving Mental Health Disorders Lack of healthy intervention for child/family Cultural/Religious beliefs Ongoing access to effective mental health/substance use treatment Skills in problem solving, interpersonal communication, distress tolerance Social Sexual Orientation Childhood sexual and physical abuse/neglect Poverty/disadvantaged environment Peer group, bullying Discrimination Family history of suicide Interpersonal losses Legal problems Friend has attempted/completed suicide Academic difficulties Coming out Parental job loss Change in family membership Continuation of precipitating factors Parental MH/AODA Abuse/neglect Poor parent-child communication Social isolation Mistrust of helpingprofessionals, stigma

Protective Social Factors: Factors that protect the person, prevent further deterioration, or improve the situation Existence of even one positive adult relationship Engagement in effective mental health treatment Limited access to means for violence Educated caregiver within the home Stability within the family School based resources Community involvement
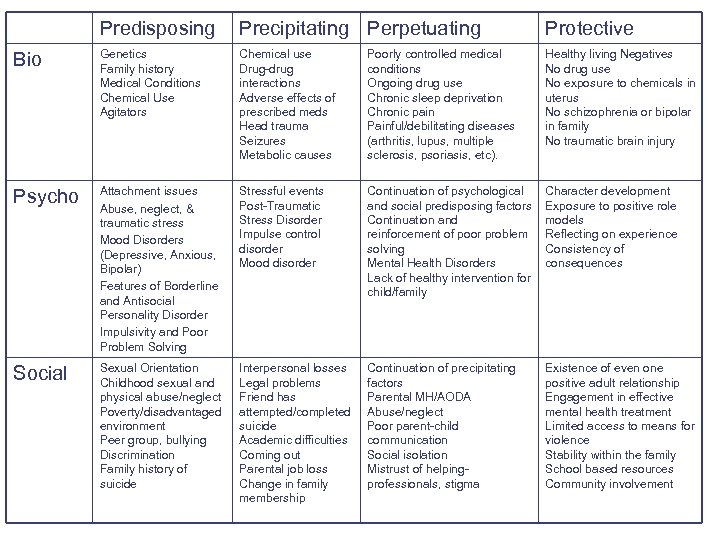
Predisposing Precipitating Perpetuating Protective Bio Genetics Family history Medical Conditions Chemical Use Agitators Chemical use Drug-drug interactions Adverse effects of prescribed meds Head trauma Seizures Metabolic causes Poorly controlled medical conditions Ongoing drug use Chronic sleep deprivation Chronic pain Painful/debilitating diseases (arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis, psoriasis, etc). Healthy living Negatives No drug use No exposure to chemicals in uterus No schizophrenia or bipolar in family No traumatic brain injury Psycho Attachment issues Abuse, neglect, & traumatic stress Mood Disorders (Depressive, Anxious, Bipolar) Features of Borderline and Antisocial Personality Disorder Impulsivity and Poor Problem Solving Stressful events Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Impulse control disorder Mood disorder Continuation of psychological and social predisposing factors Continuation and reinforcement of poor problem solving Mental Health Disorders Lack of healthy intervention for child/family Character development Exposure to positive role models Reflecting on experience Consistency of consequences Social Sexual Orientation Childhood sexual and physical abuse/neglect Poverty/disadvantaged environment Peer group, bullying Discrimination Family history of suicide Interpersonal losses Legal problems Friend has attempted/completed suicide Academic difficulties Coming out Parental job loss Change in family membership Continuation of precipitating factors Parental MH/AODA Abuse/neglect Poor parent-child communication Social isolation Mistrust of helpingprofessionals, stigma Existence of even one positive adult relationship Engagement in effective mental health treatment Limited access to means for violence Stability within the family School based resources Community involvement

Case Example: Internalizing Behavior Clients name is Janny is a 13 -year-old female. This worker spoke to Janny at the local police department. Janny went to the Dells on a field trip for school today. Janny stated that her “ex-friend” called her stupid and she got angry at that. On the bus ride home she took her cousin’s swimsuit and tied it around her neck. Janny stated, “I must have done it really well”, because her friends near her could not get it untied. Janny explained that her friends began crying and that’s when the teacher came back and had to cut it off her neck. Janny expressed she has thought a lot about suicide lately, but stated that she does not know why she did that today. Janny commented that if one bad thing happens, she starts a whole lot of negative thinking and that becomes all she can think about. Janny felt that this incident was not planned, but just happened because she got angry.

Janny listed other current stressors in her life. Janny stated that she is moving with her mom to another, more expensive apartment and she is worried they will not be able to afford it. Janny is supposed to go to her dad’s for one month, but she does not want to. She is agreeing to go because he threatens her with taking away child support from her mom. Her mom is already depressed and doesn’t need the extra stress from her alcoholic father. Janny stated that she has gained a lot of weight recently and has also had a hard time sleeping. She was told this could be from a thyroid condition that she has, or it could be her depression. Janny recalls she has been out of her thyroid medicine for several weeks now. Janny is diagnosed with depression and is seeing Jenn Smith and Dr. Hyde from ABC Clinic in Town. Janny stated that she gets along well with her therapist and she is taking 20 mg Prozac as prescribed. Janny continues to suffer from many symptoms of depression and feels like the medications are not working. Janny relayed that she is not currently suicidal. Janny stated that today she did feel like she wanted to die, but not as much now. Janny stated that she has had suicidal thoughts since 3 rd grade, but the past three – four months they have been getting worse. Janny stated that she thinks about suicide a lot, but doesn’t always want to do it. Janny states that she has looked up a website on ways to commit suicide and stated that “it was weird”. Janny stated that she has also read a book on depression and this worker believes she has good insight into her illness.

Janny stated that she does not have a plan for suicide. Janny stated that she hung herself from a shower stall at school three months ago, but the sweater she used ripped and wasn’t strong enough. Janny also reports she has cut her forearms ‘a gazillion times’ since age 8 or 9, but doesn’t know why she does it. Janny stated that she went to an assessment center because of that and does not want to go back. Janny works at Burger King and enjoys that. She also enjoys smoking pot. Janny stated that she also enjoys reading, walking, horseback riding, baby-sitting and animals. Janny stated that she listens to music to cope with feelings. Janny is looking forward to the County Fair because she is submitting a recipe. Janny is also looking forward to summer and sleeping in. When asked if there was anything she would miss if she weren’t around, Janny listed many things and stated, “I guess I would miss life… I can’t believe I did that today. ” Janny stated that she would feel safe tonight and recognizes that certain things trigger negative feelings. Janny stated that she would ask for help when these negative and suicidal feelings come back. Janny stated that she would read, jog around the block or call the crisis line if she began to feel bad again. This worker was very familiar with Janny from a previous position and believes to have a good rapport with Janny was cooperative. Janny’s mood was stable and even elevated throughout assessment. Janny was not visibly sad in any way, but instead smiling and joking around.
Predisposing Bio Psycho Social Precipitating Perpetuating Protective

Case Example: Development of antisocial and psychopathic behavior

Case Example: Antisocial Personality What happens to nice kids… …That makes them go bad?

Hard core: antisocial & psychopathic personality (PCL-R) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. Glibness/superficial charm (1) Grandiose sense of self-worth (1) Pathological lying (1) Cunning/manipulative (1) Lack of remorse or guilt (1) Shallow affect (1) Callous/lack of empathy (1) Failure to accept responsibility for own actions (1) Need for stimulation/proneness to boredom (2) Parasitic lifestyle (2) Poor behavioral controls (2) Early behavior problems (2) Lack of realistic, long-term plans (2) Impulsivity (2) Irresponsibility (2) Juvenile delinquency (2) Factor 1: Callous emotional and interpersonal detachment; affective impairment Revocation of conditional release (2) Promiscuous sexual behavior (T) Factor 2: Chronic and socially deviant antisocial Many short-term relationships (T) behaviors & lifestyle Criminal versatility (Hare, 1986) (T) ?

Common progression of mental disorders toward disruptive behavior Mood Disorder • • Irritability Mood swings Unpredictable Reactive • Anxious • Difficult to console • Easily frustrated • Highly sensitive • • • Recklessness Self-injury Depression Suicidal gestures Threats to others

ADHD Mood Disorder • • • Inattention Carelessness Not listen Failure to finish forgetful • • Irritability Mood swings Unpredictable Reactive • Hyperactivity • Excessively run & climb • Fidget & motion • Can’t sit still • • Anxious Difficult to console Easily frustrated Highly sensitive • • • Impulsivity Blurts out Interrupts Not wait turns Recklessness Self-injury Depression Suicidal gestures Threats to others

• Loses temper • Argues with adults • Defies rules ADHD Mood Disorder • • • Annoying • Angry • Blames others • Spiteful & • Easily annoyed vindictive • • • Oppositional Defiant Disorder • Hyperactivity • Excessively run & climb • Fidget & motion • Can’t sit still Inattention Carelessness Not listen Failure to finish forgetful Irritability Mood swings Unpredictable Reactive • • Anxious Difficult to console Easily frustrated Highly sensitive • • • Impulsivity Blurts out Interrupts Not wait turns Recklessness Self-injury Depression Suicidal gestures Threats to others
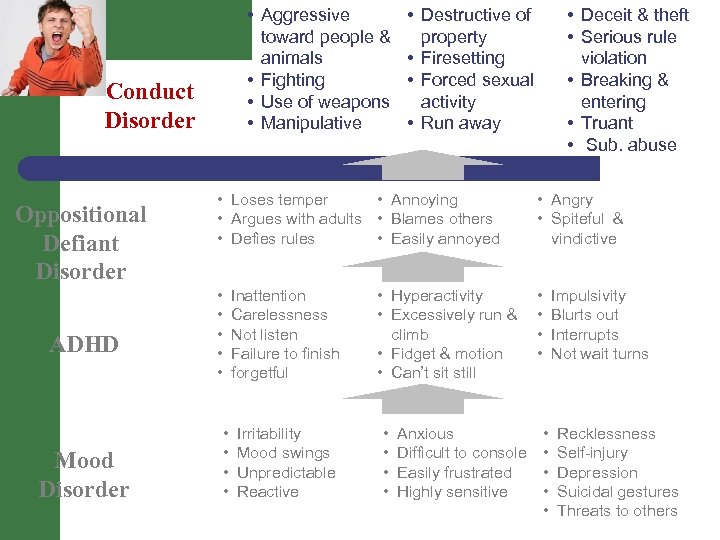
• Aggressive toward people & animals • Fighting • Use of weapons • Manipulative Conduct Disorder Oppositional Defiant Disorder ADHD Mood Disorder • Destructive of property • Firesetting • Forced sexual activity • Run away • Deceit & theft • Serious rule violation • Breaking & entering • Truant • Sub. abuse • Loses temper • Annoying • Argues with adults • Blames others • Defies rules • Easily annoyed • Angry • Spiteful & vindictive • • • Inattention Carelessness Not listen Failure to finish forgetful • • Irritability Mood swings Unpredictable Reactive • Hyperactivity • Excessively run & climb • Fidget & motion • Can’t sit still • • Anxious Difficult to console Easily frustrated Highly sensitive Impulsivity Blurts out Interrupts Not wait turns • • • Recklessness Self-injury Depression Suicidal gestures Threats to others
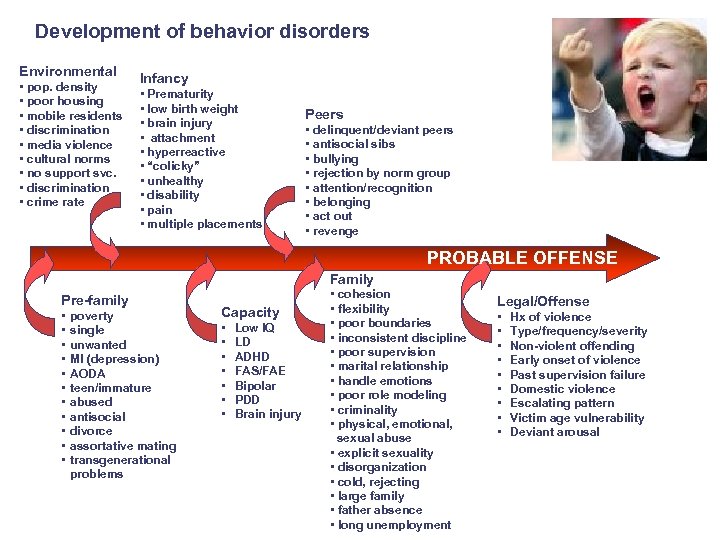
Development of behavior disorders Environmental • pop. density • poor housing • mobile residents • discrimination • media violence • cultural norms • no support svc. • discrimination • crime rate Infancy • Prematurity • low birth weight • brain injury • attachment • hyperreactive • “colicky” • unhealthy • disability • pain • multiple placements Peers • delinquent/deviant peers • antisocial sibs • bullying • rejection by norm group • attention/recognition • belonging • act out • revenge PROBABLE OFFENSE Family Pre-family • • • poverty single unwanted MI (depression) AODA teen/immature abused antisocial divorce assortative mating transgenerational problems Capacity • • Low IQ LD ADHD FAS/FAE Bipolar PDD Brain injury • cohesion • flexibility • poor boundaries • inconsistent discipline • poor supervision • marital relationship • handle emotions • poor role modeling • criminality • physical, emotional, sexual abuse • explicit sexuality • disorganization • cold, rejecting • large family • father absence • long unemployment Legal/Offense • • • Hx of violence Type/frequency/severity Non-violent offending Early onset of violence Past supervision failure Domestic violence Escalating pattern Victim age vulnerability Deviant arousal

Meet the psychopath…. Ø parental alcohol abuse & paternal abandonment Ø exposure to father beating brother to death Ø multiple head injuries from parental abuse, fighting, recklessness Ø learning disabilities Ø peer teasing & rejection; introverted & shy as a child; charming as adult Ø compulsive gambling Ø tortured & killed animals, first murder age 14, claimed 200 people Richard Kuklinsky (The “Iceman”)


Small Groups Describe afternoon process Ø Ø review scenario locate 4 Ps locate Bio, Psycho, Social of 4 Ps complete Assessment Process focused Large group review

Before you leave Fill out training feedback form Ø any suggestions for spring training Pick up CEU and/or participation certificate Check out

When struggling enlarge the field Don’t try to do everything on your own– use teamwork for interventions, sharing, support, feedback, debriefing, etc…

Thank you
654f213bb737e0e033b8e79868fb98cd.ppt