c27a1a7afd543bb9a78bfd9fc80b4f76.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50
 Year End Review New Year Preview January 20, 2016
Year End Review New Year Preview January 20, 2016
 Welcome! 2
Welcome! 2
 Leadership in Action
Leadership in Action
 The Action Group Board of Directors Nathan Moracco Assistant Commissioner Human Services Deidre Serum Sr. Director of Employee Benefits Rewards Team / HR Jon Born Director, Health and Welfare Benefits 4 Ken Horstman Director, Benefits and Compensation Human Resources Karen Chapin* Health Programs Manager Jon Schloemer Benefits Manager Gretchen Lennon* Benefits Manager
The Action Group Board of Directors Nathan Moracco Assistant Commissioner Human Services Deidre Serum Sr. Director of Employee Benefits Rewards Team / HR Jon Born Director, Health and Welfare Benefits 4 Ken Horstman Director, Benefits and Compensation Human Resources Karen Chapin* Health Programs Manager Jon Schloemer Benefits Manager Gretchen Lennon* Benefits Manager
 Our Members 5
Our Members 5
 The Action Group Value Proposition We understand address top-of-mind business concerns related to health care: • Cost pressures • Workplace and community health • Legislative burdens • Ineffective, confusing, expensive care delivery • Value of providing related benefits • Vendor performance We help purchasers take action that will lead to: • More affordable and predictable health care costs • Improved quality of care and services • Enhanced employee satisfaction with benefit offerings • Improved and new policies and programs that drive the system 6
The Action Group Value Proposition We understand address top-of-mind business concerns related to health care: • Cost pressures • Workplace and community health • Legislative burdens • Ineffective, confusing, expensive care delivery • Value of providing related benefits • Vendor performance We help purchasers take action that will lead to: • More affordable and predictable health care costs • Improved quality of care and services • Enhanced employee satisfaction with benefit offerings • Improved and new policies and programs that drive the system 6
 The Year in Review 2015 Highlights
The Year in Review 2015 Highlights
 Minnesota Bridges to Excellence MNBTE 8
Minnesota Bridges to Excellence MNBTE 8
 9
9

 Care Delivery Learning Network 11
Care Delivery Learning Network 11
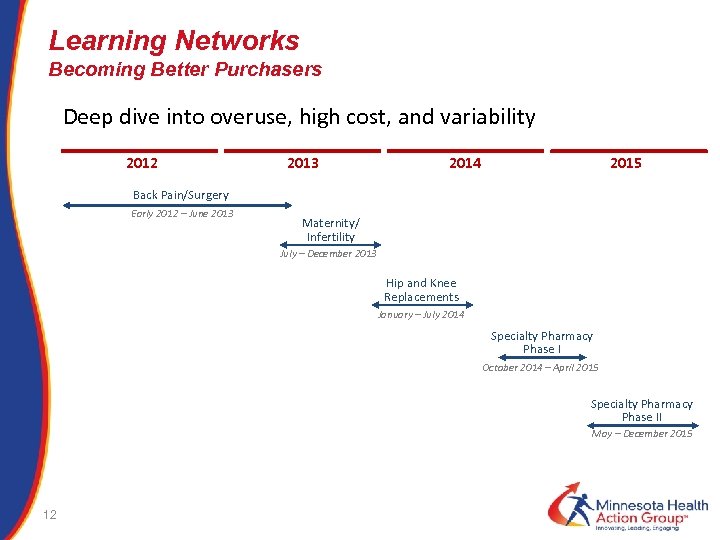 Learning Networks Becoming Better Purchasers Deep dive into overuse, high cost, and variability 2012 2013 2014 2015 Back Pain/Surgery Early 2012 – June 2013 Maternity/ Infertility July – December 2013 Hip and Knee Replacements January – July 2014 Specialty Pharmacy Phase I October 2014 – April 2015 Specialty Pharmacy Phase II May – December 2015 12
Learning Networks Becoming Better Purchasers Deep dive into overuse, high cost, and variability 2012 2013 2014 2015 Back Pain/Surgery Early 2012 – June 2013 Maternity/ Infertility July – December 2013 Hip and Knee Replacements January – July 2014 Specialty Pharmacy Phase I October 2014 – April 2015 Specialty Pharmacy Phase II May – December 2015 12
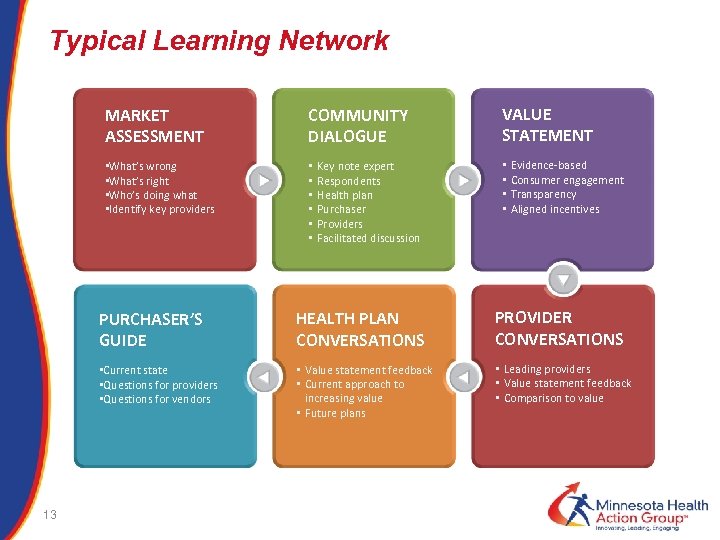 Typical Learning Network MARKET ASSESSMENT COMMUNITY DIALOGUE • What’s wrong • What’s right • Who’s doing what • Identify key providers • • • Key note expert Respondents Health plan Purchaser Providers Facilitated discussion VALUE STATEMENT • • Evidence-based Consumer engagement Transparency Aligned incentives PURCHASER’S GUIDE PROVIDER CONVERSATIONS • Current state • Questions for providers • Questions for vendors 13 HEALTH PLAN CONVERSATIONS • Value statement feedback • Current approach to increasing value • Future plans • Leading providers • Value statement feedback • Comparison to value
Typical Learning Network MARKET ASSESSMENT COMMUNITY DIALOGUE • What’s wrong • What’s right • Who’s doing what • Identify key providers • • • Key note expert Respondents Health plan Purchaser Providers Facilitated discussion VALUE STATEMENT • • Evidence-based Consumer engagement Transparency Aligned incentives PURCHASER’S GUIDE PROVIDER CONVERSATIONS • Current state • Questions for providers • Questions for vendors 13 HEALTH PLAN CONVERSATIONS • Value statement feedback • Current approach to increasing value • Future plans • Leading providers • Value statement feedback • Comparison to value
 Why the Specialty Pharmacy Learning Network is different © Minnesota Health Action Group; confidential – do not copy or distribute without permission
Why the Specialty Pharmacy Learning Network is different © Minnesota Health Action Group; confidential – do not copy or distribute without permission
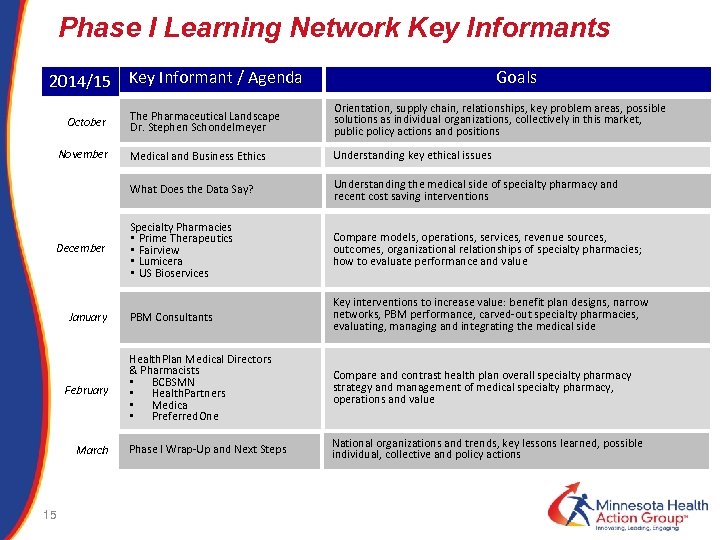 Phase I Learning Network Key Informants 2014/15 Key Informant / Agenda Goals November December January February March 15 Orientation, supply chain, relationships, key problem areas, possible solutions as individual organizations, collectively in this market, public policy actions and positions Medical and Business Ethics Understanding key ethical issues What Does the Data Say? October The Pharmaceutical Landscape Dr. Stephen Schondelmeyer Understanding the medical side of specialty pharmacy and recent cost saving interventions Specialty Pharmacies • Prime Therapeutics • Fairview • Lumicera • US Bioservices Compare models, operations, services, revenue sources, outcomes, organizational relationships of specialty pharmacies; how to evaluate performance and value PBM Consultants Key interventions to increase value: benefit plan designs, narrow networks, PBM performance, carved-out specialty pharmacies, evaluating, managing and integrating the medical side Health. Plan Medical Directors & Pharmacists • BCBSMN • Health. Partners • Medica • Preferred. One Compare and contrast health plan overall specialty pharmacy strategy and management of medical specialty pharmacy, operations and value Phase I Wrap-Up and Next Steps National organizations and trends, key lessons learned, possible individual, collective and policy actions
Phase I Learning Network Key Informants 2014/15 Key Informant / Agenda Goals November December January February March 15 Orientation, supply chain, relationships, key problem areas, possible solutions as individual organizations, collectively in this market, public policy actions and positions Medical and Business Ethics Understanding key ethical issues What Does the Data Say? October The Pharmaceutical Landscape Dr. Stephen Schondelmeyer Understanding the medical side of specialty pharmacy and recent cost saving interventions Specialty Pharmacies • Prime Therapeutics • Fairview • Lumicera • US Bioservices Compare models, operations, services, revenue sources, outcomes, organizational relationships of specialty pharmacies; how to evaluate performance and value PBM Consultants Key interventions to increase value: benefit plan designs, narrow networks, PBM performance, carved-out specialty pharmacies, evaluating, managing and integrating the medical side Health. Plan Medical Directors & Pharmacists • BCBSMN • Health. Partners • Medica • Preferred. One Compare and contrast health plan overall specialty pharmacy strategy and management of medical specialty pharmacy, operations and value Phase I Wrap-Up and Next Steps National organizations and trends, key lessons learned, possible individual, collective and policy actions
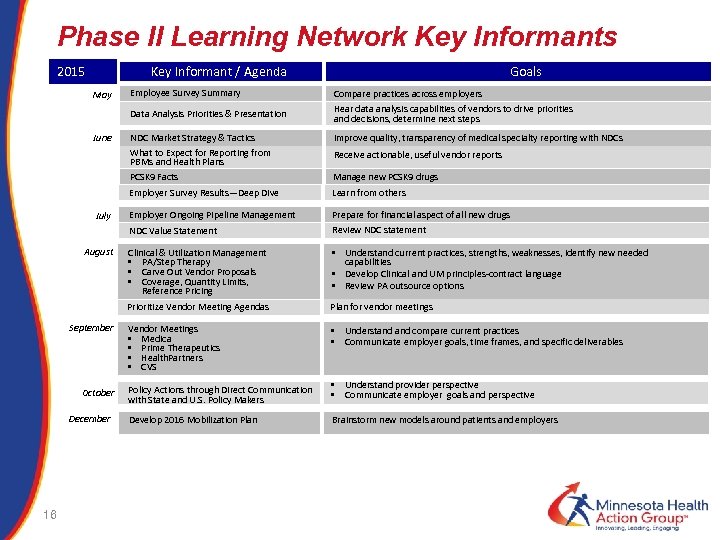 Phase II Learning Network Key Informants 2015 Key Informant / Agenda Goals July Compare practices across employers Hear data analysis capabilities of vendors to drive priorities and decisions, determine next steps NDC Market Strategy & Tactics What to Expect for Reporting from PBMs and Health Plans PCSK 9 Facts Improve quality, transparency of medical specialty reporting with NDCs Manage new PCSK 9 drugs Employer Survey Results—Deep Dive June Employee Survey Summary Data Analysis Priorities & Presentation May Learn from others Employer Ongoing Pipeline Management Prepare for financial aspect of all new drugs Review NDC statement NDC Value Statement August Receive actionable, useful vendor reports Clinical & Utilization Management • PA/Step Therapy • Carve Out Vendor Proposals • Coverage, Quantity Limits, Reference Pricing • Understand current practices, strengths, weaknesses, identify new needed capabilities • Develop Clinical and UM principles-contract language • Review PA outsource options Prioritize Vendor Meeting Agendas Plan for vendor meetings Vendor Meetings • Medica • Prime Therapeutics • Health. Partners • CVS • Understand compare current practices • Communicate employer goals, time frames, and specific deliverables September October December 16 Policy Actions through Direct Communication with State and U. S. Policy Makers Develop 2016 Mobilization Plan • Understand provider perspective • Communicate employer goals and perspective Brainstorm new models around patients and employers
Phase II Learning Network Key Informants 2015 Key Informant / Agenda Goals July Compare practices across employers Hear data analysis capabilities of vendors to drive priorities and decisions, determine next steps NDC Market Strategy & Tactics What to Expect for Reporting from PBMs and Health Plans PCSK 9 Facts Improve quality, transparency of medical specialty reporting with NDCs Manage new PCSK 9 drugs Employer Survey Results—Deep Dive June Employee Survey Summary Data Analysis Priorities & Presentation May Learn from others Employer Ongoing Pipeline Management Prepare for financial aspect of all new drugs Review NDC statement NDC Value Statement August Receive actionable, useful vendor reports Clinical & Utilization Management • PA/Step Therapy • Carve Out Vendor Proposals • Coverage, Quantity Limits, Reference Pricing • Understand current practices, strengths, weaknesses, identify new needed capabilities • Develop Clinical and UM principles-contract language • Review PA outsource options Prioritize Vendor Meeting Agendas Plan for vendor meetings Vendor Meetings • Medica • Prime Therapeutics • Health. Partners • CVS • Understand compare current practices • Communicate employer goals, time frames, and specific deliverables September October December 16 Policy Actions through Direct Communication with State and U. S. Policy Makers Develop 2016 Mobilization Plan • Understand provider perspective • Communicate employer goals and perspective Brainstorm new models around patients and employers
 Annual Employer Benefits Survey 2015 17
Annual Employer Benefits Survey 2015 17
 Minnesota Health Action Group Survey • The only resource that provides comprehensive health benefit benchmarks from Minnesota employers; designed by employers. • Deliverables – The report from survey responses compares and summarizes participant views on: • • • 18 Health benefit planning and goals Medical plan costs and contribution rates Local health plans Prescription drug coverage and costs Health improvement solutions Incentives Other services and vendors − strategies and tactics Retiree medical benefits Eligibility Thoughts on how to improve the health care system and health reform
Minnesota Health Action Group Survey • The only resource that provides comprehensive health benefit benchmarks from Minnesota employers; designed by employers. • Deliverables – The report from survey responses compares and summarizes participant views on: • • • 18 Health benefit planning and goals Medical plan costs and contribution rates Local health plans Prescription drug coverage and costs Health improvement solutions Incentives Other services and vendors − strategies and tactics Retiree medical benefits Eligibility Thoughts on how to improve the health care system and health reform
 Survey participant organizations 19
Survey participant organizations 19
 Executive Summary • Minnesota is slightly higher on health care costs when compared to national averages • Action Group members outperform non-members on cost • Virtually all employers surveyed offer incentives for wellness programs (94%, versus 56% nationally) • Companies are sticking with their health plans, despite average satisfaction • No overwhelmingly consistent cost-savings strategies. Lots of tactics. Lots of vendors. Neutral ratings • Worried about reporting and tax burdens of ACA 20
Executive Summary • Minnesota is slightly higher on health care costs when compared to national averages • Action Group members outperform non-members on cost • Virtually all employers surveyed offer incentives for wellness programs (94%, versus 56% nationally) • Companies are sticking with their health plans, despite average satisfaction • No overwhelmingly consistent cost-savings strategies. Lots of tactics. Lots of vendors. Neutral ratings • Worried about reporting and tax burdens of ACA 20
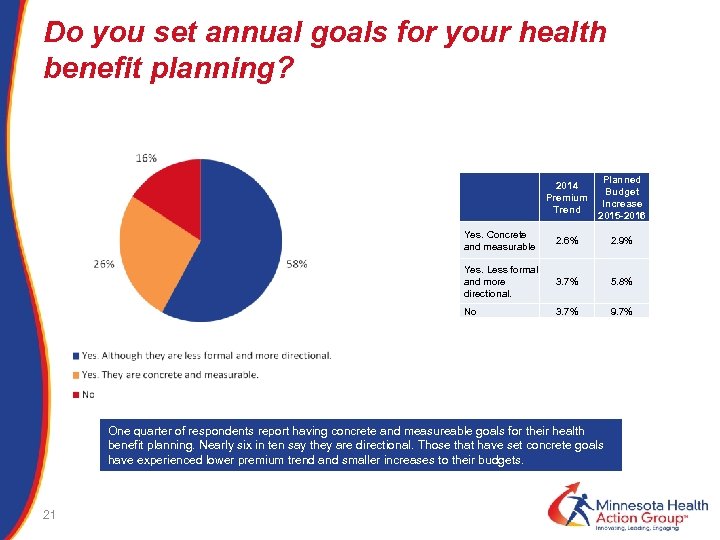 Do you set annual goals for your health benefit planning? 2014 Premium Trend Yes. Concrete and measurable 2. 6% 2. 9% Yes. Less formal and more directional. 3. 7% 5. 8% No Planned Budget Increase 2015 -2016 3. 7% 9. 7% One quarter of respondents report having concrete and measureable goals for their health benefit planning. Nearly six in ten say they are directional. Those that have set concrete goals have experienced lower premium trend and smaller increases to their budgets. 21
Do you set annual goals for your health benefit planning? 2014 Premium Trend Yes. Concrete and measurable 2. 6% 2. 9% Yes. Less formal and more directional. 3. 7% 5. 8% No Planned Budget Increase 2015 -2016 3. 7% 9. 7% One quarter of respondents report having concrete and measureable goals for their health benefit planning. Nearly six in ten say they are directional. Those that have set concrete goals have experienced lower premium trend and smaller increases to their budgets. 21
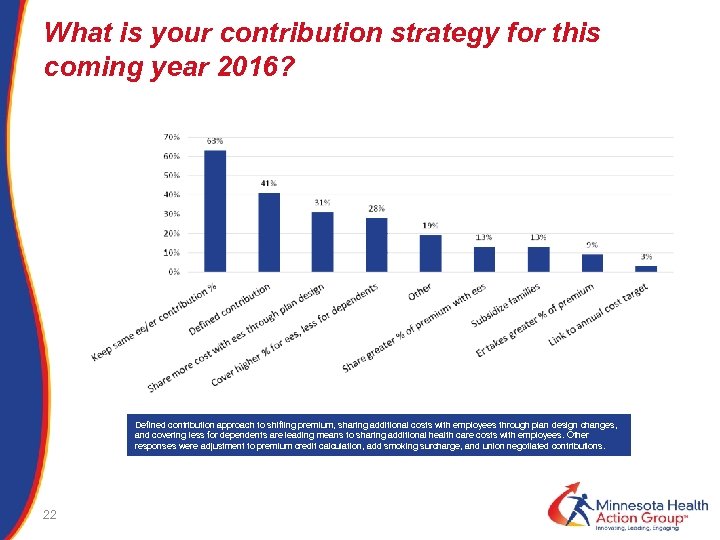 What is your contribution strategy for this coming year 2016? Defined contribution approach to shifting premium, sharing additional costs with employees through plan design changes, and covering less for dependents are leading means to sharing additional health care costs with employees. Other responses were adjustment to premium credit calculation, add smoking surcharge, and union negotiated contributions. 22
What is your contribution strategy for this coming year 2016? Defined contribution approach to shifting premium, sharing additional costs with employees through plan design changes, and covering less for dependents are leading means to sharing additional health care costs with employees. Other responses were adjustment to premium credit calculation, add smoking surcharge, and union negotiated contributions. 22
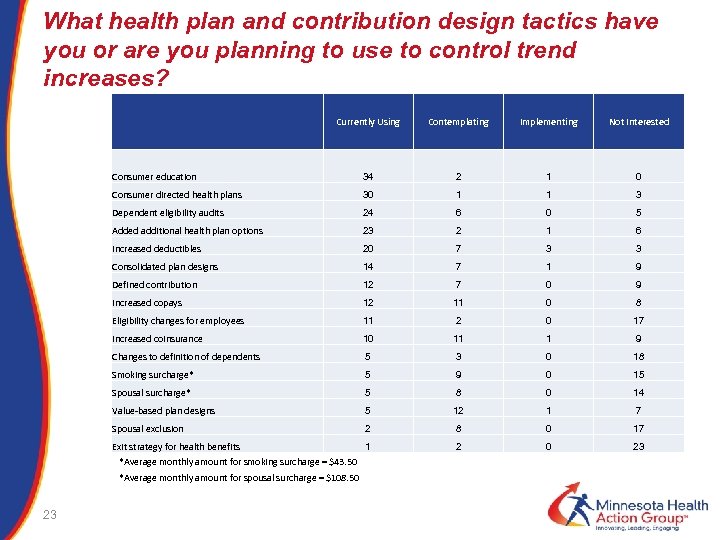 What health plan and contribution design tactics have you or are you planning to use to control trend increases? Currently Using Contemplating Implementing Not Interested Consumer education 34 2 1 0 Consumer directed health plans 30 1 1 3 Dependent eligibility audits 24 6 0 5 Added additional health plan options 23 2 1 6 Increased deductibles 20 7 3 3 Consolidated plan designs 14 7 1 9 12 7 0 9 12 11 0 8 Eligibility changes for employees 11 2 0 17 Increased coinsurance 10 11 1 9 Changes to definition of dependents 5 3 0 18 Smoking surcharge* 5 9 0 15 Spousal surcharge* 5 8 0 14 Value-based plan designs 5 12 1 7 Spousal exclusion 2 8 0 17 Exit strategy for health benefits 1 2 0 23 Defined contribution Increased copays *Average monthly amount for smoking surcharge = $43. 50 *Average monthly amount for spousal surcharge = $108. 50 23
What health plan and contribution design tactics have you or are you planning to use to control trend increases? Currently Using Contemplating Implementing Not Interested Consumer education 34 2 1 0 Consumer directed health plans 30 1 1 3 Dependent eligibility audits 24 6 0 5 Added additional health plan options 23 2 1 6 Increased deductibles 20 7 3 3 Consolidated plan designs 14 7 1 9 12 7 0 9 12 11 0 8 Eligibility changes for employees 11 2 0 17 Increased coinsurance 10 11 1 9 Changes to definition of dependents 5 3 0 18 Smoking surcharge* 5 9 0 15 Spousal surcharge* 5 8 0 14 Value-based plan designs 5 12 1 7 Spousal exclusion 2 8 0 17 Exit strategy for health benefits 1 2 0 23 Defined contribution Increased copays *Average monthly amount for smoking surcharge = $43. 50 *Average monthly amount for spousal surcharge = $108. 50 23
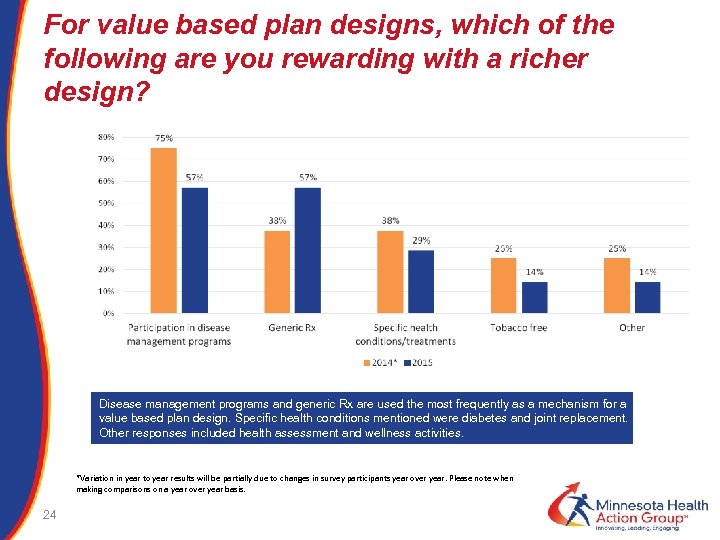 For value based plan designs, which of the following are you rewarding with a richer design? Disease management programs and generic Rx are used the most frequently as a mechanism for a value based plan design. Specific health conditions mentioned were diabetes and joint replacement. Other responses included health assessment and wellness activities. *Variation in year to year results will be partially due to changes in survey participants year over year. Please note when making comparisons on a year over year basis. 24
For value based plan designs, which of the following are you rewarding with a richer design? Disease management programs and generic Rx are used the most frequently as a mechanism for a value based plan design. Specific health conditions mentioned were diabetes and joint replacement. Other responses included health assessment and wellness activities. *Variation in year to year results will be partially due to changes in survey participants year over year. Please note when making comparisons on a year over year basis. 24
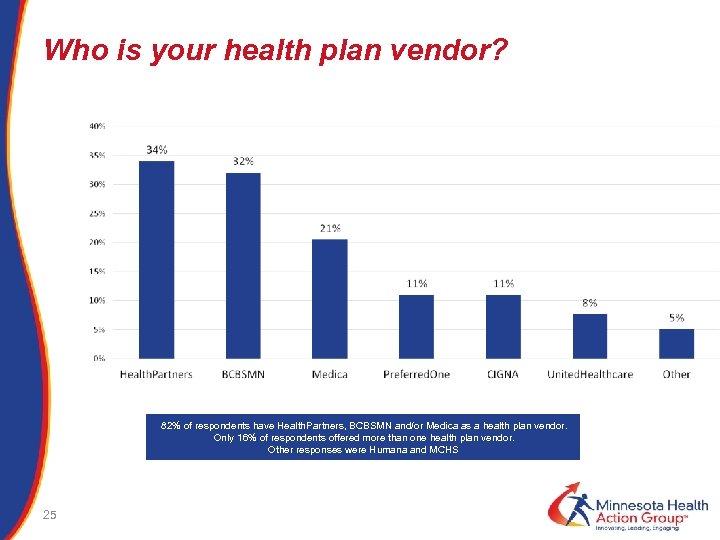 Who is your health plan vendor? 82% of respondents have Health. Partners, BCBSMN and/or Medica as a health plan vendor. Only 16% of respondents offered more than one health plan vendor. Other responses were Humana and MCHS 25
Who is your health plan vendor? 82% of respondents have Health. Partners, BCBSMN and/or Medica as a health plan vendor. Only 16% of respondents offered more than one health plan vendor. Other responses were Humana and MCHS 25
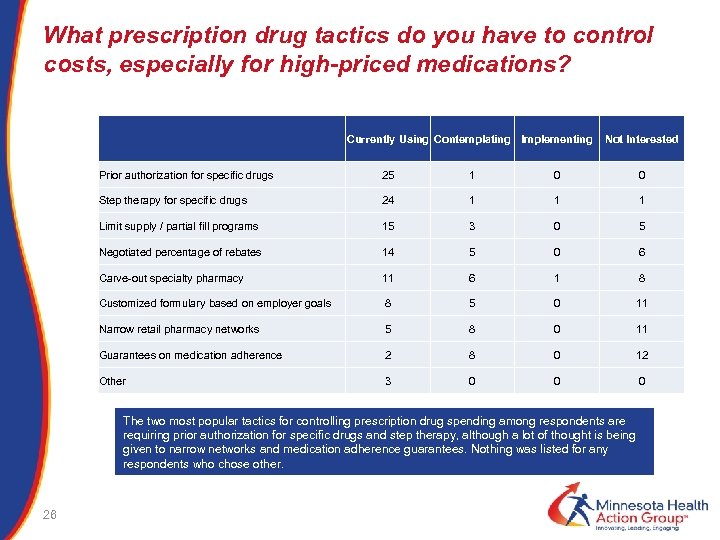 What prescription drug tactics do you have to control costs, especially for high-priced medications? Currently Using Contemplating Implementing Not Interested Prior authorization for specific drugs 25 1 0 0 Step therapy for specific drugs 24 1 1 1 Limit supply / partial fill programs 15 3 0 5 Negotiated percentage of rebates 14 5 0 6 11 6 1 8 Customized formulary based on employer goals 8 5 0 11 Narrow retail pharmacy networks 5 8 0 11 Guarantees on medication adherence 2 8 0 12 Other 3 0 0 0 Carve-out specialty pharmacy The two most popular tactics for controlling prescription drug spending among respondents are requiring prior authorization for specific drugs and step therapy, although a lot of thought is being given to narrow networks and medication adherence guarantees. Nothing was listed for any respondents who chose other. 26
What prescription drug tactics do you have to control costs, especially for high-priced medications? Currently Using Contemplating Implementing Not Interested Prior authorization for specific drugs 25 1 0 0 Step therapy for specific drugs 24 1 1 1 Limit supply / partial fill programs 15 3 0 5 Negotiated percentage of rebates 14 5 0 6 11 6 1 8 Customized formulary based on employer goals 8 5 0 11 Narrow retail pharmacy networks 5 8 0 11 Guarantees on medication adherence 2 8 0 12 Other 3 0 0 0 Carve-out specialty pharmacy The two most popular tactics for controlling prescription drug spending among respondents are requiring prior authorization for specific drugs and step therapy, although a lot of thought is being given to narrow networks and medication adherence guarantees. Nothing was listed for any respondents who chose other. 26
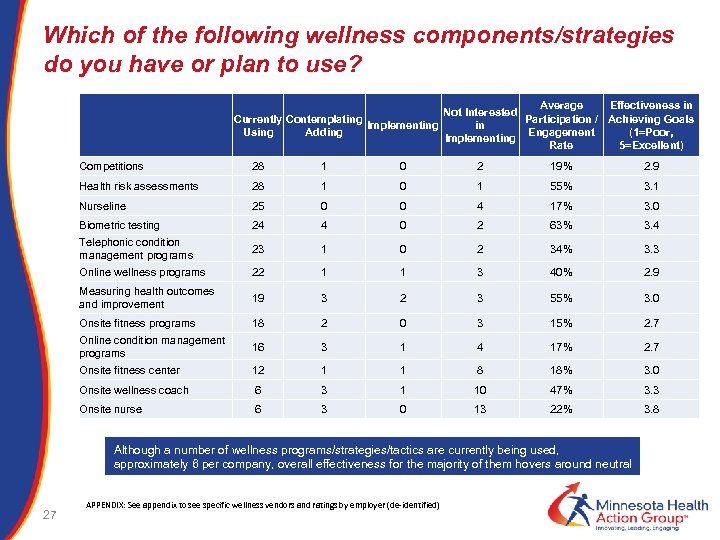 Which of the following wellness components/strategies do you have or plan to use? Currently Contemplating Implementing Using Adding Average Effectiveness in Not Interested Participation / Achieving Goals in Engagement (1=Poor, Implementing Rate 5=Excellent) Competitions 28 1 0 2 19% 2. 9 Health risk assessments 28 1 0 1 55% 3. 1 Nurseline 25 0 0 4 17% 3. 0 Biometric testing 24 4 0 2 63% 3. 4 Telephonic condition management programs 23 1 0 2 34% 3. 3 Online wellness programs 22 1 3 40% 2. 9 Measuring health outcomes and improvement 1 19 3 2 3 55% 3. 0 Onsite fitness programs 18 2 0 3 15% 2. 7 Online condition management programs 16 3 1 4 17% 2. 7 Onsite fitness center 12 1 1 8 18% 3. 0 Onsite wellness coach 6 3 1 10 47% 3. 3 Onsite nurse 6 3 0 13 22% 3. 8 Although a number of wellness programs/strategies/tactics are currently being used, approximately 6 per company, overall effectiveness for the majority of them hovers around neutral 27 APPENDIX: See appendix to see specific wellness vendors and ratings by employer (de-identified)
Which of the following wellness components/strategies do you have or plan to use? Currently Contemplating Implementing Using Adding Average Effectiveness in Not Interested Participation / Achieving Goals in Engagement (1=Poor, Implementing Rate 5=Excellent) Competitions 28 1 0 2 19% 2. 9 Health risk assessments 28 1 0 1 55% 3. 1 Nurseline 25 0 0 4 17% 3. 0 Biometric testing 24 4 0 2 63% 3. 4 Telephonic condition management programs 23 1 0 2 34% 3. 3 Online wellness programs 22 1 3 40% 2. 9 Measuring health outcomes and improvement 1 19 3 2 3 55% 3. 0 Onsite fitness programs 18 2 0 3 15% 2. 7 Online condition management programs 16 3 1 4 17% 2. 7 Onsite fitness center 12 1 1 8 18% 3. 0 Onsite wellness coach 6 3 1 10 47% 3. 3 Onsite nurse 6 3 0 13 22% 3. 8 Although a number of wellness programs/strategies/tactics are currently being used, approximately 6 per company, overall effectiveness for the majority of them hovers around neutral 27 APPENDIX: See appendix to see specific wellness vendors and ratings by employer (de-identified)
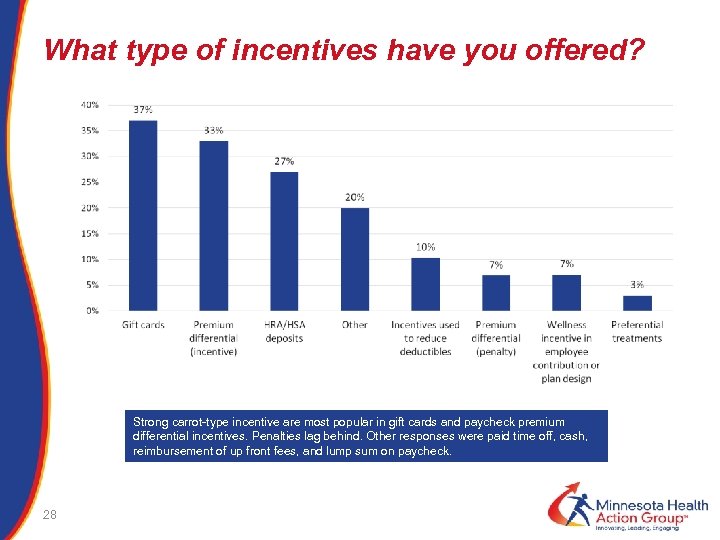 What type of incentives have you offered? Strong carrot-type incentive are most popular in gift cards and paycheck premium differential incentives. Penalties lag behind. Other responses were paid time off, cash, reimbursement of up front fees, and lump sum on paycheck. 28
What type of incentives have you offered? Strong carrot-type incentive are most popular in gift cards and paycheck premium differential incentives. Penalties lag behind. Other responses were paid time off, cash, reimbursement of up front fees, and lump sum on paycheck. 28
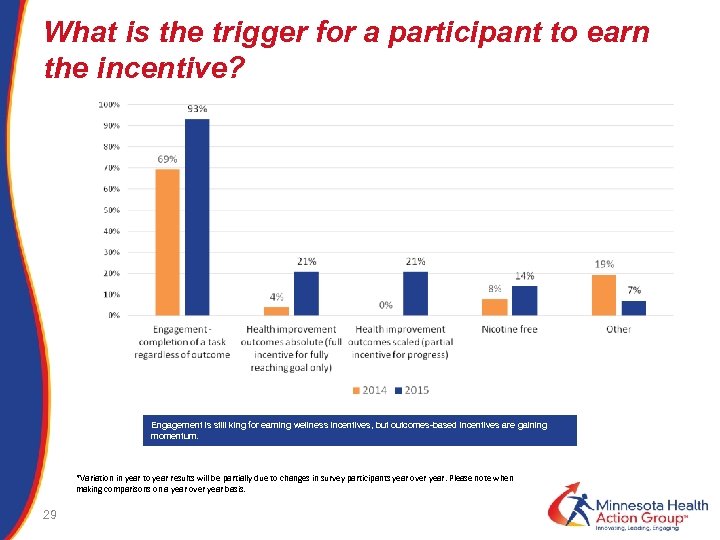 What is the trigger for a participant to earn the incentive? Engagement is still king for earning wellness incentives, but outcomes-based incentives are gaining momentum. *Variation in year to year results will be partially due to changes in survey participants year over year. Please note when making comparisons on a year over year basis. 29
What is the trigger for a participant to earn the incentive? Engagement is still king for earning wellness incentives, but outcomes-based incentives are gaining momentum. *Variation in year to year results will be partially due to changes in survey participants year over year. Please note when making comparisons on a year over year basis. 29
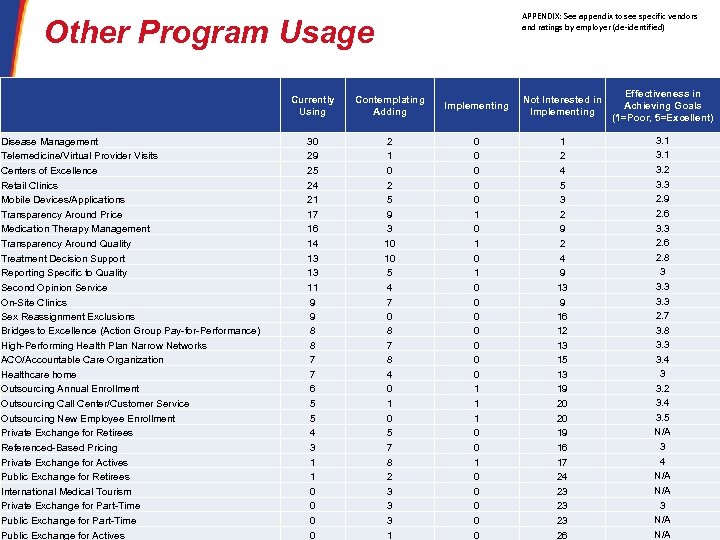 APPENDIX: See appendix to see specific vendors and ratings by employer (de-identified) Other Program Usage Currently Using Disease Management Telemedicine/Virtual Provider Visits Centers of Excellence Retail Clinics Mobile Devices/Applications Transparency Around Price Medication Therapy Management Transparency Around Quality Treatment Decision Support Reporting Specific to Quality Second Opinion Service On-Site Clinics Sex Reassignment Exclusions Bridges to Excellence (Action Group Pay-for-Performance) High-Performing Health Plan Narrow Networks ACO/Accountable Care Organization Healthcare home Outsourcing Annual Enrollment Outsourcing Call Center/Customer Service Outsourcing New Employee Enrollment Private Exchange for Retirees Referenced-Based Pricing Private Exchange for Actives Public Exchange for Retirees International Medical Tourism Private Exchange for Part-Time 30 Public Exchange for Part-Time Public Exchange for Actives Contemplating Adding Implementing Not Interested in Implementing 30 29 25 24 21 17 16 14 13 13 11 9 9 8 8 7 7 6 5 5 4 3 1 1 0 0 2 1 0 2 5 9 3 10 10 5 4 7 0 8 7 8 4 0 1 0 5 7 8 2 3 3 3 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 2 4 5 3 2 9 2 4 9 13 9 16 12 13 15 13 19 20 20 19 16 17 24 23 23 23 26 Effectiveness in Achieving Goals (1=Poor, 5=Excellent) 3. 1 3. 2 3. 3 2. 9 2. 6 3. 3 2. 6 2. 8 3 3. 3 2. 7 3. 8 3. 3 3. 4 3 3. 2 3. 4 3. 5 N/A 3 4 N/A 3 N/A
APPENDIX: See appendix to see specific vendors and ratings by employer (de-identified) Other Program Usage Currently Using Disease Management Telemedicine/Virtual Provider Visits Centers of Excellence Retail Clinics Mobile Devices/Applications Transparency Around Price Medication Therapy Management Transparency Around Quality Treatment Decision Support Reporting Specific to Quality Second Opinion Service On-Site Clinics Sex Reassignment Exclusions Bridges to Excellence (Action Group Pay-for-Performance) High-Performing Health Plan Narrow Networks ACO/Accountable Care Organization Healthcare home Outsourcing Annual Enrollment Outsourcing Call Center/Customer Service Outsourcing New Employee Enrollment Private Exchange for Retirees Referenced-Based Pricing Private Exchange for Actives Public Exchange for Retirees International Medical Tourism Private Exchange for Part-Time 30 Public Exchange for Part-Time Public Exchange for Actives Contemplating Adding Implementing Not Interested in Implementing 30 29 25 24 21 17 16 14 13 13 11 9 9 8 8 7 7 6 5 5 4 3 1 1 0 0 2 1 0 2 5 9 3 10 10 5 4 7 0 8 7 8 4 0 1 0 5 7 8 2 3 3 3 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 2 4 5 3 2 9 2 4 9 13 9 16 12 13 15 13 19 20 20 19 16 17 24 23 23 23 26 Effectiveness in Achieving Goals (1=Poor, 5=Excellent) 3. 1 3. 2 3. 3 2. 9 2. 6 3. 3 2. 6 2. 8 3 3. 3 2. 7 3. 8 3. 3 3. 4 3 3. 2 3. 4 3. 5 N/A 3 4 N/A 3 N/A
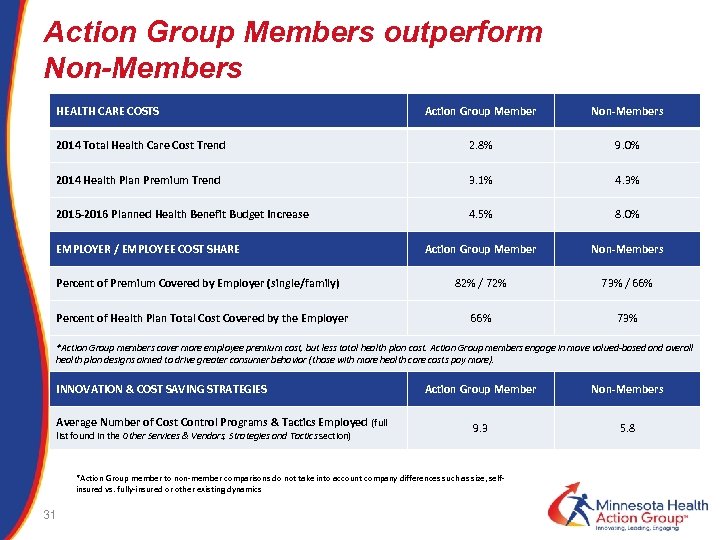 Action Group Members outperform Non-Members HEALTH CARE COSTS Action Group Member Non-Members 2014 Total Health Care Cost Trend 2. 8% 9. 0% 2014 Health Plan Premium Trend 3. 1% 4. 3% 2015 -2016 Planned Health Benefit Budget Increase 4. 5% 8. 0% Action Group Member Non-Members 82% / 72% 73% / 66% 73% EMPLOYER / EMPLOYEE COST SHARE Percent of Premium Covered by Employer (single/family) Percent of Health Plan Total Cost Covered by the Employer *Action Group members cover more employee premium cost, but less total health plan cost. Action Group members engage in move valued-based and overall health plan designs aimed to drive greater consumer behavior (those with more health care costs pay more). INNOVATION & COST SAVING STRATEGIES Average Number of Cost Control Programs & Tactics Employed (full list found in the Other Services & Vendors, Strategies and Tactics section) Action Group Member Non-Members 9. 3 5. 8 *Action Group member to non-member comparisons do not take into account company differences such as size, selfinsured vs. fully-insured or other existing dynamics 31
Action Group Members outperform Non-Members HEALTH CARE COSTS Action Group Member Non-Members 2014 Total Health Care Cost Trend 2. 8% 9. 0% 2014 Health Plan Premium Trend 3. 1% 4. 3% 2015 -2016 Planned Health Benefit Budget Increase 4. 5% 8. 0% Action Group Member Non-Members 82% / 72% 73% / 66% 73% EMPLOYER / EMPLOYEE COST SHARE Percent of Premium Covered by Employer (single/family) Percent of Health Plan Total Cost Covered by the Employer *Action Group members cover more employee premium cost, but less total health plan cost. Action Group members engage in move valued-based and overall health plan designs aimed to drive greater consumer behavior (those with more health care costs pay more). INNOVATION & COST SAVING STRATEGIES Average Number of Cost Control Programs & Tactics Employed (full list found in the Other Services & Vendors, Strategies and Tactics section) Action Group Member Non-Members 9. 3 5. 8 *Action Group member to non-member comparisons do not take into account company differences such as size, selfinsured vs. fully-insured or other existing dynamics 31
 Issues, Workgroups and Meetings 2015 32
Issues, Workgroups and Meetings 2015 32
 Influence and reach of The Action Group
Influence and reach of The Action Group
 Issues, Workgroups and Meetings 2015 § § § § 34 Eighth Annual Leadership Summit All Payer Claims Database MNBTE Recognition Event Specialty Pharmacy Learning Network Health Care Financing Taskforce National Diabetes Prevention Program Choosing Wisely Campaign Prior Authorization Legislation End of Life Care and Advanced Directives Cadillac Tax Payment Reform MNBTE Guiding Coalition MNBTE Champions Best Practices
Issues, Workgroups and Meetings 2015 § § § § 34 Eighth Annual Leadership Summit All Payer Claims Database MNBTE Recognition Event Specialty Pharmacy Learning Network Health Care Financing Taskforce National Diabetes Prevention Program Choosing Wisely Campaign Prior Authorization Legislation End of Life Care and Advanced Directives Cadillac Tax Payment Reform MNBTE Guiding Coalition MNBTE Champions Best Practices
 A Look Ahead 2016 Highlights
A Look Ahead 2016 Highlights
 Programs and Initiatives § Minnesota Bridges to Excellence § Employer Benefits Survey – Launch Feb 8: Due Feb 24 § Specialty Pharmacy Action Network – First Meeting Feb 16 § § § 36 Open Notes Advanced Directives, Palliative and End of Life Care Health Care Innovation Payment Reform National Diabetes Prevention Program Health Literacy
Programs and Initiatives § Minnesota Bridges to Excellence § Employer Benefits Survey – Launch Feb 8: Due Feb 24 § Specialty Pharmacy Action Network – First Meeting Feb 16 § § § 36 Open Notes Advanced Directives, Palliative and End of Life Care Health Care Innovation Payment Reform National Diabetes Prevention Program Health Literacy
 Specialty Pharmacy Key Informants Phase I §Stephen Schondelmeyer – U of MN §Katerina Glac – University of St. Thomas §Donald Brunquell – Children’s Hospital §Corey Belken, Shannon Ambrose – Artemetrx §Pete Wickersham – Prime. Therapeutics §Tim Affeldt - Fairview Specialty Pharmacy §Alan Van Amber – Lumicera/Navitus §Kevin James – USBioservices §Brian Bullock, Shawn Patterson – Burchfield §Kevin Host – PSG Consulting §Bill Gerardi MD – BCBSMN §Charles Fazio, Rick Bruzek – Health. Partners §Howard Epstein, Al Heaton - Preferred. One §Jana Johnson, Jim Hartert - Medica §Brian Klepper – NBCH 37 Phase II §Corey Beklen, Shannon Ambrose, Brenda Motheral – Artemetrx §Brian Burchfield, Shawn Patterson – Burchfield §Sara Drale – MN Medicaid §Rick Bruzek, Christine Strahl – Health. Partners §Jana Johnson, Jim Hartert - Medica §Ray Mc. Mahon - Prime. Therapeutics §Rick Bruzek, Kevin Ronnenberg – Health. Partners §Surya Singh, CVS §Ed Greeno, Marie Brown – UMP §Kyle Skiermont - FVSP §John Rother - NCHC §Megan Sharp – Office of Amy Klobuchar §Samantha Mills – Office of Al Franken §Holly Iverson, Randy Chun, MN House of Representatives §Howard Epstein, Al Heaton - Preferred. One §Alan Van Amber, Laura Jester - Navitus
Specialty Pharmacy Key Informants Phase I §Stephen Schondelmeyer – U of MN §Katerina Glac – University of St. Thomas §Donald Brunquell – Children’s Hospital §Corey Belken, Shannon Ambrose – Artemetrx §Pete Wickersham – Prime. Therapeutics §Tim Affeldt - Fairview Specialty Pharmacy §Alan Van Amber – Lumicera/Navitus §Kevin James – USBioservices §Brian Bullock, Shawn Patterson – Burchfield §Kevin Host – PSG Consulting §Bill Gerardi MD – BCBSMN §Charles Fazio, Rick Bruzek – Health. Partners §Howard Epstein, Al Heaton - Preferred. One §Jana Johnson, Jim Hartert - Medica §Brian Klepper – NBCH 37 Phase II §Corey Beklen, Shannon Ambrose, Brenda Motheral – Artemetrx §Brian Burchfield, Shawn Patterson – Burchfield §Sara Drale – MN Medicaid §Rick Bruzek, Christine Strahl – Health. Partners §Jana Johnson, Jim Hartert - Medica §Ray Mc. Mahon - Prime. Therapeutics §Rick Bruzek, Kevin Ronnenberg – Health. Partners §Surya Singh, CVS §Ed Greeno, Marie Brown – UMP §Kyle Skiermont - FVSP §John Rother - NCHC §Megan Sharp – Office of Amy Klobuchar §Samantha Mills – Office of Al Franken §Holly Iverson, Randy Chun, MN House of Representatives §Howard Epstein, Al Heaton - Preferred. One §Alan Van Amber, Laura Jester - Navitus
 Findings, Surprises and Conclusions that Shape 2016 Action Network Agenda • • • Magnitude of spend on outpatient drugs is higher than expected; more than PBM costs – PBM traditional (non-specialty) + – PBM specialty + – Medical traditional (non-specialty) No current single vendor meets all the employer or consumer needs – Health plans lack pharmacy expertise and data of PBMs – PBMs lack relationship to providers – Specialty pharmacies serve as vendors to PBM, not employer or consumer NDCs are cornerstone of all medical specialty activities; necessary for – PA, step therapy and clinical management – Rebates – Granular and accurate reporting of costs and utilization – Quality measurement and management of providers Variation among health plans’ transparency, price, knowledge and capabilities; medical management is piecemeal if it exists Employers not at the table when decisions are made by PBMs or health plans; on the side lines (menu) Understanding “long arm” of manufacturers: hubs, coupons, rebates, patient support/assistance programs, paying premiums for insurance on ACA exchanges “Silver bullet” site of care approach, moving patients, is short sighted; need provider re-contracting, pricing parity Conflict of interest between PBMs and owned specialty pharmacies; especially problematic if exclusive No current, standard method to establish value of drugs Cost Effectiveness, not used to determine drug prices • • • 38
Findings, Surprises and Conclusions that Shape 2016 Action Network Agenda • • • Magnitude of spend on outpatient drugs is higher than expected; more than PBM costs – PBM traditional (non-specialty) + – PBM specialty + – Medical traditional (non-specialty) No current single vendor meets all the employer or consumer needs – Health plans lack pharmacy expertise and data of PBMs – PBMs lack relationship to providers – Specialty pharmacies serve as vendors to PBM, not employer or consumer NDCs are cornerstone of all medical specialty activities; necessary for – PA, step therapy and clinical management – Rebates – Granular and accurate reporting of costs and utilization – Quality measurement and management of providers Variation among health plans’ transparency, price, knowledge and capabilities; medical management is piecemeal if it exists Employers not at the table when decisions are made by PBMs or health plans; on the side lines (menu) Understanding “long arm” of manufacturers: hubs, coupons, rebates, patient support/assistance programs, paying premiums for insurance on ACA exchanges “Silver bullet” site of care approach, moving patients, is short sighted; need provider re-contracting, pricing parity Conflict of interest between PBMs and owned specialty pharmacies; especially problematic if exclusive No current, standard method to establish value of drugs Cost Effectiveness, not used to determine drug prices • • • 38
 2016 SPRx Action Network Goals 1. 2. 3. 4. NDC Codes on Medical Claims Cost of Site of Care Management Pipeline Management Standard Expectations of Vendors and Providers 5. Senior Management and Employee Communications 6. Policy Actions 7. New Model Development 39
2016 SPRx Action Network Goals 1. 2. 3. 4. NDC Codes on Medical Claims Cost of Site of Care Management Pipeline Management Standard Expectations of Vendors and Providers 5. Senior Management and Employee Communications 6. Policy Actions 7. New Model Development 39
 2016 SPRx Action Network Deliverables • Tools, Checklists and Guides for vendor (PBM and health plan) expectations • RFPs • Contracts, definitions, terms • SPDs • Assessment and Evaluation – Drug price transparency tools – Pipeline management – Media • Initiatives – NDCs, cost of site of care expectations – Specialty pharmacy direct relationship – New care models 40
2016 SPRx Action Network Deliverables • Tools, Checklists and Guides for vendor (PBM and health plan) expectations • RFPs • Contracts, definitions, terms • SPDs • Assessment and Evaluation – Drug price transparency tools – Pipeline management – Media • Initiatives – NDCs, cost of site of care expectations – Specialty pharmacy direct relationship – New care models 40
 41
41
 What is Open. Notes? • Patients invited to review their providers’ notes of visit by email or text through secure patient portals after a visit • • Not a specific vendor product or software. • • • 42 Started with a research and demonstration project in 2010 – 100 PCPs and 20, 000 patients – Boston (BIDMC), rural Pennsylvania (Geisinger), and the Seattle inner city (Harborview) Multiple providers now implemented with state-wide adoption in Oregon Ambulatory visits only but pilots for inpatient, ER and elsewhere Good notes include: – Patient history – Physical exam findings – Lab and x-ray – Assessment and diagnoses – Plan for next steps 42
What is Open. Notes? • Patients invited to review their providers’ notes of visit by email or text through secure patient portals after a visit • • Not a specific vendor product or software. • • • 42 Started with a research and demonstration project in 2010 – 100 PCPs and 20, 000 patients – Boston (BIDMC), rural Pennsylvania (Geisinger), and the Seattle inner city (Harborview) Multiple providers now implemented with state-wide adoption in Oregon Ambulatory visits only but pilots for inpatient, ER and elsewhere Good notes include: – Patient history – Physical exam findings – Lab and x-ray – Assessment and diagnoses – Plan for next steps 42
 Office Note Example History: XXXXX is a 64 y. o. male who comes into clinic with a chief complaint of pain at the right posterior heel. Pain has been present for several months. Pain is described as aching and burning. It is aggravated by day to day activities and specifically long drives. It does not hurt with activity, including running and long hikes. Sometimes it will be sore first thing in the morning. It is unchanged recently. History of injury: none known Past medical history: I have reviewed and confirmed the past medical history in the chart. Medications: reviewed medication list in the chart Allergies: reviewed allergy section in the chart Review of Systems: Review of all other systems is negative Exam: Patient is alert and oriented x 3, in no apparent distress. BP 131/87 mm. Hg | Pulse 52 | Wt 89. 812 kg (198 lb) Musculoskeletal: soft tissue swelling noted over the posterior medial heel with palpable bursa only painful over the superior calcaneal process, and not where it overlies the soft tissue. , tenderness at Achilles tendon insertion Vascular: normal pulses, normal capillary refill and warm Neuro: intact Derm: Mild swelling at the bursa site. X-ray: Ill defined enthesiophyte noted at the achilles insertion. Soft tissue swelling over the medial aspect of the calcaneal process seen. No fractures or other issues noted. Assessment: Chronic bursitis right heel Plan: 1. Discussed pathology and biomechanical findings in detail with patient. Conservative options include; doing nothing, shoe gear modifications, shoe inserts, physical therapy, local injection, casting, oral anti-inflammatories and avoiding all aggravating activities. Surgical options discussed. Patient elects for contrast soaks, RICE, and continued diclofinac gel at this time. 4 43 2. Return to clinic to discuss efficacy of treatment or on an as needed basis.
Office Note Example History: XXXXX is a 64 y. o. male who comes into clinic with a chief complaint of pain at the right posterior heel. Pain has been present for several months. Pain is described as aching and burning. It is aggravated by day to day activities and specifically long drives. It does not hurt with activity, including running and long hikes. Sometimes it will be sore first thing in the morning. It is unchanged recently. History of injury: none known Past medical history: I have reviewed and confirmed the past medical history in the chart. Medications: reviewed medication list in the chart Allergies: reviewed allergy section in the chart Review of Systems: Review of all other systems is negative Exam: Patient is alert and oriented x 3, in no apparent distress. BP 131/87 mm. Hg | Pulse 52 | Wt 89. 812 kg (198 lb) Musculoskeletal: soft tissue swelling noted over the posterior medial heel with palpable bursa only painful over the superior calcaneal process, and not where it overlies the soft tissue. , tenderness at Achilles tendon insertion Vascular: normal pulses, normal capillary refill and warm Neuro: intact Derm: Mild swelling at the bursa site. X-ray: Ill defined enthesiophyte noted at the achilles insertion. Soft tissue swelling over the medial aspect of the calcaneal process seen. No fractures or other issues noted. Assessment: Chronic bursitis right heel Plan: 1. Discussed pathology and biomechanical findings in detail with patient. Conservative options include; doing nothing, shoe gear modifications, shoe inserts, physical therapy, local injection, casting, oral anti-inflammatories and avoiding all aggravating activities. Surgical options discussed. Patient elects for contrast soaks, RICE, and continued diclofinac gel at this time. 4 43 2. Return to clinic to discuss efficacy of treatment or on an as needed basis.
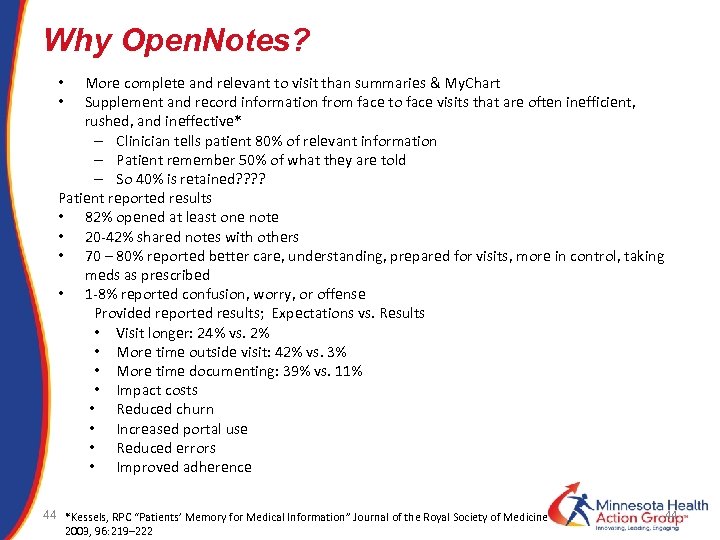 Why Open. Notes? More complete and relevant to visit than summaries & My. Chart Supplement and record information from face to face visits that are often inefficient, rushed, and ineffective* – Clinician tells patient 80% of relevant information – Patient remember 50% of what they are told – So 40% is retained? ? Patient reported results • 82% opened at least one note • 20 -42% shared notes with others • 70 – 80% reported better care, understanding, prepared for visits, more in control, taking meds as prescribed • 1 -8% reported confusion, worry, or offense Provided reported results; Expectations vs. Results • Visit longer: 24% vs. 2% • More time outside visit: 42% vs. 3% • More time documenting: 39% vs. 11% • Impact costs • Reduced churn • Increased portal use • Reduced errors • Improved adherence • • 44 *Kessels, RPC “Patients’ Memory for Medical Information” Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine 2003, 96: 219– 222 44
Why Open. Notes? More complete and relevant to visit than summaries & My. Chart Supplement and record information from face to face visits that are often inefficient, rushed, and ineffective* – Clinician tells patient 80% of relevant information – Patient remember 50% of what they are told – So 40% is retained? ? Patient reported results • 82% opened at least one note • 20 -42% shared notes with others • 70 – 80% reported better care, understanding, prepared for visits, more in control, taking meds as prescribed • 1 -8% reported confusion, worry, or offense Provided reported results; Expectations vs. Results • Visit longer: 24% vs. 2% • More time outside visit: 42% vs. 3% • More time documenting: 39% vs. 11% • Impact costs • Reduced churn • Increased portal use • Reduced errors • Improved adherence • • 44 *Kessels, RPC “Patients’ Memory for Medical Information” Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine 2003, 96: 219– 222 44
 What’s Next • 12/2015 Four Foundations announce $10 million in grants to Open. Notes for dissemination, innovation and research • Strategic partnership discussions underway with multiple organizations to encourage voluntary spread • Multiple consortiums to be launched; MN, WI considering • Vendor capabilities to be assessed. Epic and Cerner can implement Open. Notes. Working with other vendors on their capabilities • Support materials available • Seeking employers to join the movement; become a champion for open notes 46 46
What’s Next • 12/2015 Four Foundations announce $10 million in grants to Open. Notes for dissemination, innovation and research • Strategic partnership discussions underway with multiple organizations to encourage voluntary spread • Multiple consortiums to be launched; MN, WI considering • Vendor capabilities to be assessed. Epic and Cerner can implement Open. Notes. Working with other vendors on their capabilities • Support materials available • Seeking employers to join the movement; become a champion for open notes 46 46
 March 15, 2016 Minnesota Kick Off MN Health Action Group & MAPS (Minnesota Alliance for Patient Safety) • • 47 Invitees: – Health system CIOs and Chief Medical Information Officers – Community clinics – Medical and Hospital Associations – Minnesota Alliance for Patient Safety – Epic – Employers Agenda – Convince MN providers to adopt – John Santa and Open. Notes staff present what, why, how – Employers advocate for implementation ASAP • Providers to encourage engaged patients and adopt Open. Notes ASAP • Reported measures of provider Open. Notes utilization • Other 47
March 15, 2016 Minnesota Kick Off MN Health Action Group & MAPS (Minnesota Alliance for Patient Safety) • • 47 Invitees: – Health system CIOs and Chief Medical Information Officers – Community clinics – Medical and Hospital Associations – Minnesota Alliance for Patient Safety – Epic – Employers Agenda – Convince MN providers to adopt – John Santa and Open. Notes staff present what, why, how – Employers advocate for implementation ASAP • Providers to encourage engaged patients and adopt Open. Notes ASAP • Reported measures of provider Open. Notes utilization • Other 47
 Ongoing Meetings and Outreach § 9 th Annual Leadership Summit – April 22 Turning Vision Into Action § § § § 48 Member Meetings Community Dialogue Weekly Express Monthly Members Only fyi Social Media Outreach Additional Toolkits Consumer Engagement Resources
Ongoing Meetings and Outreach § 9 th Annual Leadership Summit – April 22 Turning Vision Into Action § § § § 48 Member Meetings Community Dialogue Weekly Express Monthly Members Only fyi Social Media Outreach Additional Toolkits Consumer Engagement Resources
 Doing together what no single organization can do alone Affordable, predictable health care costs Improved health and health care quality Policies and programs that work for all Employee satisfaction and accountability
Doing together what no single organization can do alone Affordable, predictable health care costs Improved health and health care quality Policies and programs that work for all Employee satisfaction and accountability
 A powerful force for positive change The Action Group is the only Minnesota organization whose sole purpose is to align and represent the collective voice of those who pay the bill for health care – employers, public purchasers and individuals. We drive innovation, collaboration and engagement in ways that improve health and ensure the economic vitality of all Minnesota communities.
A powerful force for positive change The Action Group is the only Minnesota organization whose sole purpose is to align and represent the collective voice of those who pay the bill for health care – employers, public purchasers and individuals. We drive innovation, collaboration and engagement in ways that improve health and ensure the economic vitality of all Minnesota communities.


