a20abd2791930f427e14a63a65688e15.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science B 2 B MARKETPLACES AND E -PROCUREMENT Y. NARAHARI Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science Bangalore - 560 012 hari@csa. iisc. ernet. in http: //www. csa. iisc. ernet. in
Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science B 2 B MARKETPLACES AND E -PROCUREMENT Y. NARAHARI Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science Bangalore - 560 012 hari@csa. iisc. ernet. in http: //www. csa. iisc. ernet. in
 Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science OBJECTIVES OF THE TALK w To bring out and understand the "important" role of electronic marketplaces in supply chain management w To understand "critical" design and implementation issues of E-marketplaces w To understand the issues in Eprocurement
Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science OBJECTIVES OF THE TALK w To bring out and understand the "important" role of electronic marketplaces in supply chain management w To understand "critical" design and implementation issues of E-marketplaces w To understand the issues in Eprocurement
 Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science OUTLINE OF THE TALK w Introduction w How do they add value? w Design Issues w E-Procurement
Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science OUTLINE OF THE TALK w Introduction w How do they add value? w Design Issues w E-Procurement
 Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science ELECTRONIC MARKETS w E-marketplaces are emerging to serve each point of every industry's supply chain w E-markets are highly collaborative EBusiness models that organize complex business processes between multiple participants into a virtual commerce community
Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science ELECTRONIC MARKETS w E-marketplaces are emerging to serve each point of every industry's supply chain w E-markets are highly collaborative EBusiness models that organize complex business processes between multiple participants into a virtual commerce community
 Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science E-MARKETPLACES : VALUE CREATION w efficient transactional processes w new business relationships w new business models w new businesses
Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science E-MARKETPLACES : VALUE CREATION w efficient transactional processes w new business relationships w new business models w new businesses
 Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science E-MARKETPLACES: CATEGORIES w Horizontal w Vertical w Private (sell side, buy side) w Public
Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science E-MARKETPLACES: CATEGORIES w Horizontal w Vertical w Private (sell side, buy side) w Public
 Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science EMERGENCE OF E-MARKETS w w Alliance of IBM - i 2 - Ariba Alliance of GM - Ford - Chrysler Alliance of my. SAP- Commerce One - Oracle chemdex, plasticsnet, e-steel, paperexchange, metalsite, capacityweb, mro, bandx, logisticsweb, etc. w In India: Indiamarkets. com, e. Bizchem. com, Autoexchanges
Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science EMERGENCE OF E-MARKETS w w Alliance of IBM - i 2 - Ariba Alliance of GM - Ford - Chrysler Alliance of my. SAP- Commerce One - Oracle chemdex, plasticsnet, e-steel, paperexchange, metalsite, capacityweb, mro, bandx, logisticsweb, etc. w In India: Indiamarkets. com, e. Bizchem. com, Autoexchanges
 Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science E-MARKETPLACES: A TAXONOMY What is Bought How it is bought Operating Systematic sourcing Spot sourcing Manufg MRO HUBS CATALOG HUBS YIELD EXCHANGES MANAGERS
Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science E-MARKETPLACES: A TAXONOMY What is Bought How it is bought Operating Systematic sourcing Spot sourcing Manufg MRO HUBS CATALOG HUBS YIELD EXCHANGES MANAGERS
 Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science BENEFITS TO BUSINESSES w Extend the presence and reach of a company w Facilitate doing business with anyone, anytime, anywhere w Aggregation of content and facilitation of workflow lead to significant reduction in transaction costs w Cycle times are reduced and deliveries are quicker w Improves relationship with trading partners w market efficiencies n n Better inventory management Better visibility leading to predictability
Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science BENEFITS TO BUSINESSES w Extend the presence and reach of a company w Facilitate doing business with anyone, anytime, anywhere w Aggregation of content and facilitation of workflow lead to significant reduction in transaction costs w Cycle times are reduced and deliveries are quicker w Improves relationship with trading partners w market efficiencies n n Better inventory management Better visibility leading to predictability
 Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science BENEFITS TO BUYERS w Aggregation of multiple suppliers w Direct access to suppliers and through dynamic pricing w Location and tracking of new suppliers w Provides more negotiating power w Leads to quick response buyers
Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science BENEFITS TO BUYERS w Aggregation of multiple suppliers w Direct access to suppliers and through dynamic pricing w Location and tracking of new suppliers w Provides more negotiating power w Leads to quick response buyers
 Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science BENEFITS TO SUPPLIERS w Provides reach to vast, untapped global markets w True value of products can be realized through aggregation and participation of buyers w Enables to support JIT practices w Leads to quick response suppliers
Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science BENEFITS TO SUPPLIERS w Provides reach to vast, untapped global markets w True value of products can be realized through aggregation and participation of buyers w Enables to support JIT practices w Leads to quick response suppliers
 Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science E-MARKETS: DESIGN ISSUES w NEGOTIATIONS n n n Distributed Negotiations Integrative Negotiations Auctions w DESIGN OF USER INTERFACES
Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science E-MARKETS: DESIGN ISSUES w NEGOTIATIONS n n n Distributed Negotiations Integrative Negotiations Auctions w DESIGN OF USER INTERFACES
 Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science E-MARKETS: DESIGN ISSUES ALGORITHMS w Buyer Aggregation w Supplier Aggregation w Demand Aggregation w Buyer-Seller Matching w Dynamic Pricing w Multi-Attribute Auctions w Combinatorial Auctions
Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science E-MARKETS: DESIGN ISSUES ALGORITHMS w Buyer Aggregation w Supplier Aggregation w Demand Aggregation w Buyer-Seller Matching w Dynamic Pricing w Multi-Attribute Auctions w Combinatorial Auctions
 Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science EXAMPLE OF A MARKET ALGORITHM w 3 BUYERS and 4 SUPPLIERS n n n Buyer X : (50 A, 10 B) Buyer Y : (20 B, 30 C) Buyer Z : (40 A, 20 C, 10 D) w BUNDLING n n n Bundle 1: (90 A) Bundle 2: (30 B, 50 C) Bundle 3: (10 D) Negotiated contract Sealed bid auction Dynamic auction
Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science EXAMPLE OF A MARKET ALGORITHM w 3 BUYERS and 4 SUPPLIERS n n n Buyer X : (50 A, 10 B) Buyer Y : (20 B, 30 C) Buyer Z : (40 A, 20 C, 10 D) w BUNDLING n n n Bundle 1: (90 A) Bundle 2: (30 B, 50 C) Bundle 3: (10 D) Negotiated contract Sealed bid auction Dynamic auction
 Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science EXAMPLE OF A MARKET ALGORITHM w Sealed Bid Combinatorial Auction n n Supplier P : (10 B, 10 C, p) Supplier Q : (30 B, q) Supplier R : (50 C, r) Supplier S : (20 B, 50 C, s) w An optimization algorithm decides the best bids and handpicks the optimal subset of bids, based on cost, delivery times, etc.
Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science EXAMPLE OF A MARKET ALGORITHM w Sealed Bid Combinatorial Auction n n Supplier P : (10 B, 10 C, p) Supplier Q : (30 B, q) Supplier R : (50 C, r) Supplier S : (20 B, 50 C, s) w An optimization algorithm decides the best bids and handpicks the optimal subset of bids, based on cost, delivery times, etc.
 Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science E-MARKETS: DESIGN ISSUES n TECHNOLOGY Authentication and security l Electronic payment l Software architecture l Distributed objects l Agents and mobility l Scalability l Interoperability l
Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science E-MARKETS: DESIGN ISSUES n TECHNOLOGY Authentication and security l Electronic payment l Software architecture l Distributed objects l Agents and mobility l Scalability l Interoperability l
 Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science E-MARKETS: DESIGN ISSUES w INTEGRATION n n n with existing best practices with existing business processes with existing catalogs with ERP software with the backend with other E-markets
Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science E-MARKETS: DESIGN ISSUES w INTEGRATION n n n with existing best practices with existing business processes with existing catalogs with ERP software with the backend with other E-markets
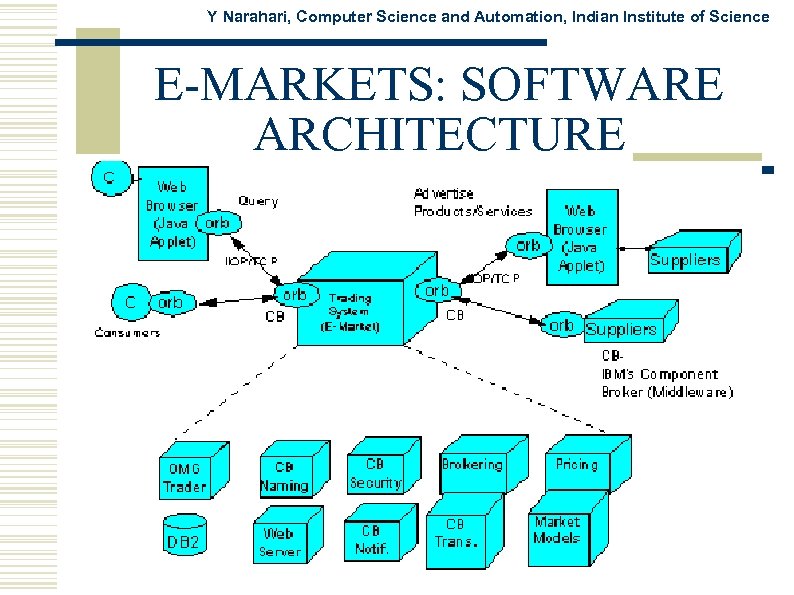 Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science E-MARKETS: SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE
Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science E-MARKETS: SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE
 Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science E-PROCUREMENT w All activities involved in obtaining materials and services and managing their inflow into an organization toward the enduser w Basic steps: n n n Information Negotiation Settlement
Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science E-PROCUREMENT w All activities involved in obtaining materials and services and managing their inflow into an organization toward the enduser w Basic steps: n n n Information Negotiation Settlement
 Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science EMERGENCE OF E-PROCUREMENT w Electronic catalogs w Internet search engines w Web-EDI w On-line auctions and bidding w Advances in E-commerce
Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science EMERGENCE OF E-PROCUREMENT w Electronic catalogs w Internet search engines w Web-EDI w On-line auctions and bidding w Advances in E-commerce
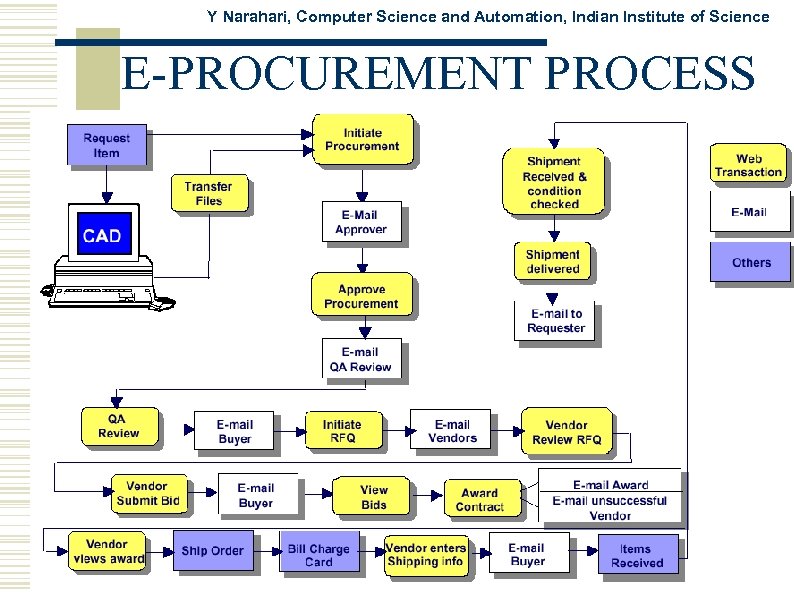 Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science E-PROCUREMENT PROCESS
Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science E-PROCUREMENT PROCESS
 Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science BEST PRACTICE E-PROCUREMENT SYSTEMS w Dell online (Ariba Buyer) w Cisco w Enron corporation (my. SAP and Commerce One) w Lockheed Martin (my. SAP) w GE capital (i 2 Buyside solution) w Defense Logistics Agency w Lawrence Livermore Laboratories
Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science BEST PRACTICE E-PROCUREMENT SYSTEMS w Dell online (Ariba Buyer) w Cisco w Enron corporation (my. SAP and Commerce One) w Lockheed Martin (my. SAP) w GE capital (i 2 Buyside solution) w Defense Logistics Agency w Lawrence Livermore Laboratories
 Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science E-PROCUREMENT: VALUE ADDITIONS w Demand aggregation w Bundling and supplier aggregation w Optimal vendor selection w Innovative dynamic auctions w Multi-attribute decision support
Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science E-PROCUREMENT: VALUE ADDITIONS w Demand aggregation w Bundling and supplier aggregation w Optimal vendor selection w Innovative dynamic auctions w Multi-attribute decision support
 Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science CONCLUSIONS w E-markets are key to faster and more efficient trade w E-markets have a positive influence all through the supply chain w There are challenging technical and technological issues in setting up and operating E-markets w E-procurement has emerged in a big way
Y Narahari, Computer Science and Automation, Indian Institute of Science CONCLUSIONS w E-markets are key to faster and more efficient trade w E-markets have a positive influence all through the supply chain w There are challenging technical and technological issues in setting up and operating E-markets w E-procurement has emerged in a big way


