7044da58f22c405cd48ef05bb4de728b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 XTP Changes in 2. 57 SAXESS 5. 0. 0 Speaker Title Sebastian. Tomac@omxgroup. com XTP Changes in 2. 57 Version 1. 0
XTP Changes in 2. 57 SAXESS 5. 0. 0 Speaker Title Sebastian. Tomac@omxgroup. com XTP Changes in 2. 57 Version 1. 0
 Areas • Transaction and data changes – Overview Price Checks and Circuit Breakers – Reference Prices – Circuit Breakers – Revised validation of Price Checks – Mid-price matching – Trade Action and Cancellation of Trade Report External – Deferred trades in Average Price – Turnover List Structure Revision – Trade id – Other data – Certified Advisor • Documentation 2
Areas • Transaction and data changes – Overview Price Checks and Circuit Breakers – Reference Prices – Circuit Breakers – Revised validation of Price Checks – Mid-price matching – Trade Action and Cancellation of Trade Report External – Deferred trades in Average Price – Turnover List Structure Revision – Trade id – Other data – Certified Advisor • Documentation 2
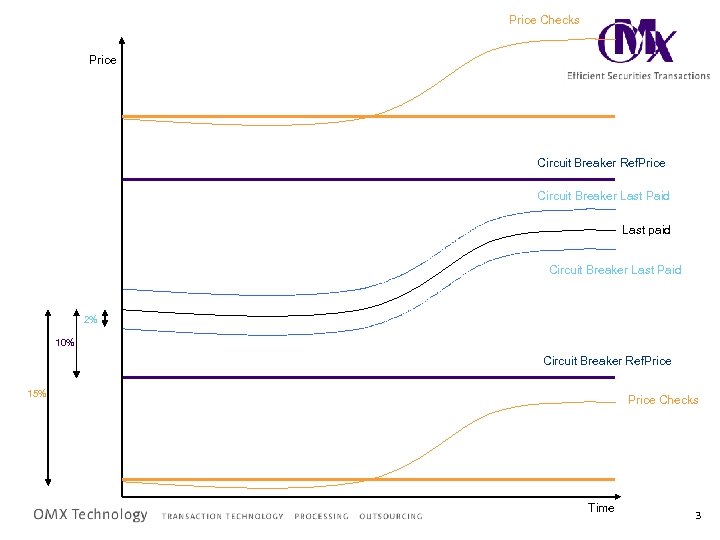 Price Checks Price Circuit Breaker Ref. Price Circuit Breaker Last Paid Last paid Circuit Breaker Last Paid 2% 10% Circuit Breaker Ref. Price 15% Price Checks Time 3
Price Checks Price Circuit Breaker Ref. Price Circuit Breaker Last Paid Last paid Circuit Breaker Last Paid 2% 10% Circuit Breaker Ref. Price 15% Price Checks Time 3
 Reference Prices Why: • The reference price is used by both Price Checks and Circuit Breakers. Design/Implementation: • The TID_MC_Orderbook. Refprices contains the Reference price. • The Price check/circuit breaker price update method is mandatory – Last Paid or explicitly disseminated FID_MC_Orderbook. Refprices. 4
Reference Prices Why: • The reference price is used by both Price Checks and Circuit Breakers. Design/Implementation: • The TID_MC_Orderbook. Refprices contains the Reference price. • The Price check/circuit breaker price update method is mandatory – Last Paid or explicitly disseminated FID_MC_Orderbook. Refprices. 4
 Revised validation of Price Checks Why: • Price checks of orders with last paid as reference price • Price checks of orders with relative price updates. Design/Implementation: • The price checks have been moved to the central system. Hence an order that i rejected due to a price check result in a TID_UC_Error. Msg. • Intraday changed limits are disseminated in TID_MC_Orderbook. Ref. Prices/FID_Orderbook. Price. Ch ecks. • TID_MC_Orderbook. Ref. Prices/FID_Base. Data. Chg/Ope ration code indicates intraday insert/update/delete of a orderbook price check. 5
Revised validation of Price Checks Why: • Price checks of orders with last paid as reference price • Price checks of orders with relative price updates. Design/Implementation: • The price checks have been moved to the central system. Hence an order that i rejected due to a price check result in a TID_UC_Error. Msg. • Intraday changed limits are disseminated in TID_MC_Orderbook. Ref. Prices/FID_Orderbook. Price. Ch ecks. • TID_MC_Orderbook. Ref. Prices/FID_Base. Data. Chg/Ope ration code indicates intraday insert/update/delete of a orderbook price check. 5
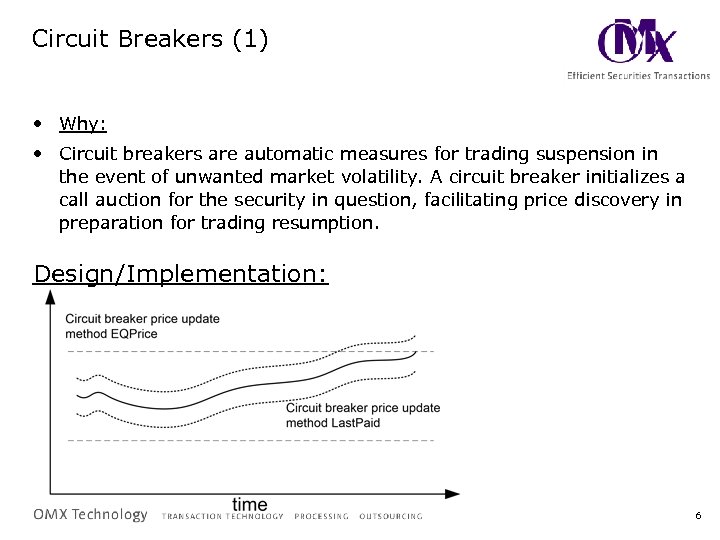 Circuit Breakers (1) • Why: • Circuit breakers are automatic measures for trading suspension in the event of unwanted market volatility. A circuit breaker initializes a call auction for the security in question, facilitating price discovery in preparation for trading resumption. Design/Implementation: 6
Circuit Breakers (1) • Why: • Circuit breakers are automatic measures for trading suspension in the event of unwanted market volatility. A circuit breaker initializes a call auction for the security in question, facilitating price discovery in preparation for trading resumption. Design/Implementation: 6
 Circuit Breakers (2) Price update method Reference Price • Based on a Reference price – Reference Price: - equilibrium price from last call auction - a call auction can be the morning call auction, a call auction that occurs during the continuous trading or an evening call auction - if no equilibrium price was formed in the morning call auction, the previous day’s closing price will be used as a reference price • Breach of a static circuit breaker will lead to a trading interruption and a call auction where a new equilibrium price will be formed 7
Circuit Breakers (2) Price update method Reference Price • Based on a Reference price – Reference Price: - equilibrium price from last call auction - a call auction can be the morning call auction, a call auction that occurs during the continuous trading or an evening call auction - if no equilibrium price was formed in the morning call auction, the previous day’s closing price will be used as a reference price • Breach of a static circuit breaker will lead to a trading interruption and a call auction where a new equilibrium price will be formed 7
 Circuit Breakers (3) Price update method Last Paid • As a reference price the last paid price will be used • Active only during continuous trading • Breach will lead to a trading interruption and call auction, where a new reference price for the static circuit breaker will be formed 8
Circuit Breakers (3) Price update method Last Paid • As a reference price the last paid price will be used • Active only during continuous trading • Breach will lead to a trading interruption and call auction, where a new reference price for the static circuit breaker will be formed 8
 Circuit Breakers (4) Design/Implementation: • TID_Qry. Sub. Market FID_Submarket. Circuit. Breaker contains the submarket circuit breaker limits. One FID per Circuit breaker price update method. • FID_MC_Orderbook. Circuit. Breaker contains intraday changes of the orderbook circuit breaker limits. • The Circuit breaker price update method what price is used as reference – Last Paid (FID_MC_Trade/updates last paid) or as explicitly disseminated FID_MC_Orderbook. Refprices. • More than one circuit breaker may be active during continues trading. 9
Circuit Breakers (4) Design/Implementation: • TID_Qry. Sub. Market FID_Submarket. Circuit. Breaker contains the submarket circuit breaker limits. One FID per Circuit breaker price update method. • FID_MC_Orderbook. Circuit. Breaker contains intraday changes of the orderbook circuit breaker limits. • The Circuit breaker price update method what price is used as reference – Last Paid (FID_MC_Trade/updates last paid) or as explicitly disseminated FID_MC_Orderbook. Refprices. • More than one circuit breaker may be active during continues trading. 9
 Circuit Breakers (5) Design/Implementation: • A Circuit breaker call is indicated by Call purpose Circuit. Breaker. • Orders deleted due to a circuit breaker will have Order delete reason circuit breaker. 10
Circuit Breakers (5) Design/Implementation: • A Circuit breaker call is indicated by Call purpose Circuit. Breaker. • Orders deleted due to a circuit breaker will have Order delete reason circuit breaker. 10
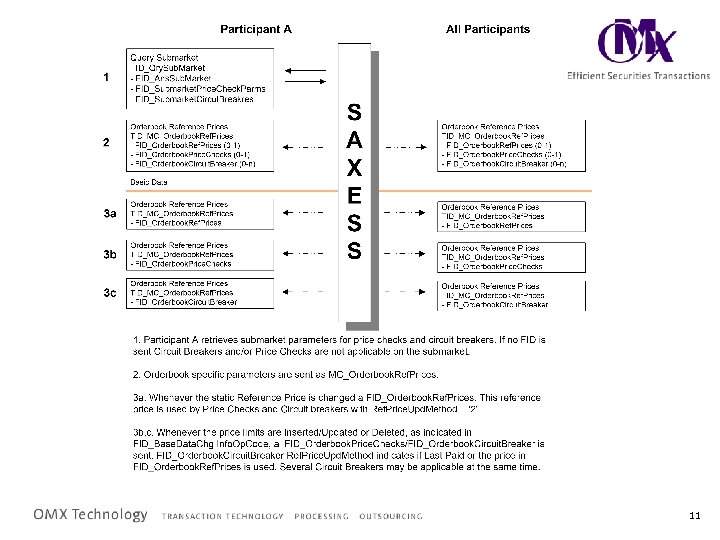 11
11
 Mid-price matching (1) • Continuous Midprice matching – each trade in the Midprice orderbook will be executed at the round lot spread Midprice in the order book • Midprice matching possible also at scheduled occasions (Auctions) – a submarket event will trigger matching • Midprice is (best bid + best ask)/2 • Midprice orders are fully anonymous & hidden (cannot be seen by other trading participants) • Midprice order criteria's – Match multiple = Midprice lot size – Total volume = multiple of the Midprice lot size • Midprice spread – Percentage from the bid side price 12
Mid-price matching (1) • Continuous Midprice matching – each trade in the Midprice orderbook will be executed at the round lot spread Midprice in the order book • Midprice matching possible also at scheduled occasions (Auctions) – a submarket event will trigger matching • Midprice is (best bid + best ask)/2 • Midprice orders are fully anonymous & hidden (cannot be seen by other trading participants) • Midprice order criteria's – Match multiple = Midprice lot size – Total volume = multiple of the Midprice lot size • Midprice spread – Percentage from the bid side price 12
 Mid-price matching (2) Design/Implementation: • FID_Ans. Sub. Market and FID_Ans. Orderbook contains; – Midprice matching – Maximum midprice spread. • FID_Ans. Orderbook contains; – Midprice auction – Midprice allotment • FID_MC_Sub. Mkt. Event Submarket event type indicates a scheduled mid-price matching. 13
Mid-price matching (2) Design/Implementation: • FID_Ans. Sub. Market and FID_Ans. Orderbook contains; – Midprice matching – Maximum midprice spread. • FID_Ans. Orderbook contains; – Midprice auction – Midprice allotment • FID_MC_Sub. Mkt. Event Submarket event type indicates a scheduled mid-price matching. 13
 Cancellation of Trade Report External • Why: • Enable cancellation of trade report external Design/Implementation: • External trade report maybe cancelled with TID_Trade. Report. External. Cancel. Upon cancellation a TID_UC_Trade. Report. External. Cancel is sent. Originator indicates by user or system. • Timestamp, trade report is used as key. 14
Cancellation of Trade Report External • Why: • Enable cancellation of trade report external Design/Implementation: • External trade report maybe cancelled with TID_Trade. Report. External. Cancel. Upon cancellation a TID_UC_Trade. Report. External. Cancel is sent. Originator indicates by user or system. • Timestamp, trade report is used as key. 14
 Trade Action Why: • Generic XTP transactions for operating on Trades. Design/Implementation: • The TID_External. Trade. Cancel has been replaced by TID_Trade. Action with Trade action code “Cancel trade”. 15
Trade Action Why: • Generic XTP transactions for operating on Trades. Design/Implementation: • The TID_External. Trade. Cancel has been replaced by TID_Trade. Action with Trade action code “Cancel trade”. 15
 Deferred trades in Average Price Why: • At the time of trade the trade information is not available on the multicast flow for deferred trades. Information systems that provide real time calculation of the average price needs the Trade price at the time of trade. Design/Implementation: • TID_MC_Average. Price is disseminated whenever a trade notification is sent for a trade that updated average price is created or cancelled. Only sent to information systems. 16
Deferred trades in Average Price Why: • At the time of trade the trade information is not available on the multicast flow for deferred trades. Information systems that provide real time calculation of the average price needs the Trade price at the time of trade. Design/Implementation: • TID_MC_Average. Price is disseminated whenever a trade notification is sent for a trade that updated average price is created or cancelled. Only sent to information systems. 16
 Turnover List Structure Revision Why: • A turnover list heading may to belong to several lists. Design/Implementation: • TID_Qry. Turnover. List. Heading for two different lists may yield responses with duplicate Turnover list id. 17
Turnover List Structure Revision Why: • A turnover list heading may to belong to several lists. Design/Implementation: • TID_Qry. Turnover. List. Heading for two different lists may yield responses with duplicate Turnover list id. 17
 Trade Id (1) Why: • Provide protocol wide unique Trade identifier. Design/Implementation: • Trade. Id is a system unique Trade identifier • Trade. Id is unique over several trading days. • Trade. Id is a valid Clearing Reference for the Trade. 18
Trade Id (1) Why: • Provide protocol wide unique Trade identifier. Design/Implementation: • Trade. Id is a system unique Trade identifier • Trade. Id is unique over several trading days. • Trade. Id is a valid Clearing Reference for the Trade. 18
 Trade Id (2) • Old way (still valid) • Trade. No unique per trading day. – Used to identify a published Trade • Trade. Notification. No unique until trade publication. – Used to identify a deferred not yet published Trade • To identify for a Trade over several trading days a key has to be constructed by combining Orderbook. Id, Time and Trade. No. 19
Trade Id (2) • Old way (still valid) • Trade. No unique per trading day. – Used to identify a published Trade • Trade. Notification. No unique until trade publication. – Used to identify a deferred not yet published Trade • To identify for a Trade over several trading days a key has to be constructed by combining Orderbook. Id, Time and Trade. No. 19
 Other data Design/Implementation: • TID_Qry. Orderbooks/FID_Ans. Orderbook – Certified advisor. • TID_Qry. Instrument/FID_Bonds – Yearly Coupon Frequency – First Installment Date • TID_Qry. Trades and TID_UC_Trade – user name 20
Other data Design/Implementation: • TID_Qry. Orderbooks/FID_Ans. Orderbook – Certified advisor. • TID_Qry. Instrument/FID_Bonds – Yearly Coupon Frequency – First Installment Date • TID_Qry. Trades and TID_UC_Trade – user name 20
 Documentation • XTP chapter reorganization. • Appendix Trade Reporting Flow has been updated with TID_Trade. Report. External and TID_Trade. Report. External. Cancel example. • XTP specification available as XML Schema. 21
Documentation • XTP chapter reorganization. • Appendix Trade Reporting Flow has been updated with TID_Trade. Report. External and TID_Trade. Report. External. Cancel example. • XTP specification available as XML Schema. 21
 Questions? Help us get better… • What are you missing in the protocol? • How may we improve the support? • What are unclear in the documentation? Sebastian. tomac@omxgroup. com
Questions? Help us get better… • What are you missing in the protocol? • How may we improve the support? • What are unclear in the documentation? Sebastian. tomac@omxgroup. com


