86ab4aa03cf888ef1e6d2a9babcc358b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 XPATH http: //www. zvon. org/xxl/XPath. Tutorial/Ge neral/examples. html
XPATH http: //www. zvon. org/xxl/XPath. Tutorial/Ge neral/examples. html
 • XPath syntax is similar to file system. If the path starts with the slash / , then it represents an absolute path to the required element. • /AAA (Select the root element AAA) •
• XPath syntax is similar to file system. If the path starts with the slash / , then it represents an absolute path to the required element. • /AAA (Select the root element AAA) •
 • /AAA/CCC • Select all elements CCC which are children of the root element AAA •
• /AAA/CCC • Select all elements CCC which are children of the root element AAA •
 • /AAA/DDD/BBB • Select all elements BBB which are children of DDD which are children of the root element AAA •
• /AAA/DDD/BBB • Select all elements BBB which are children of DDD which are children of the root element AAA •
 • If the path starts with // then all elements in the document which fulfill following criteria are selected. • //BBB • Select all elements BBB •
• If the path starts with // then all elements in the document which fulfill following criteria are selected. • //BBB • Select all elements BBB •
 • //DDD/BBB • Select all elements BBB which are children of DDD •
• //DDD/BBB • Select all elements BBB which are children of DDD •
 • The star * selects all elements located by preceeding path /AAA/CCC/DDD/* • Select all elements enclosed by elements /AAA/CCC/DDD •
• The star * selects all elements located by preceeding path /AAA/CCC/DDD/* • Select all elements enclosed by elements /AAA/CCC/DDD •
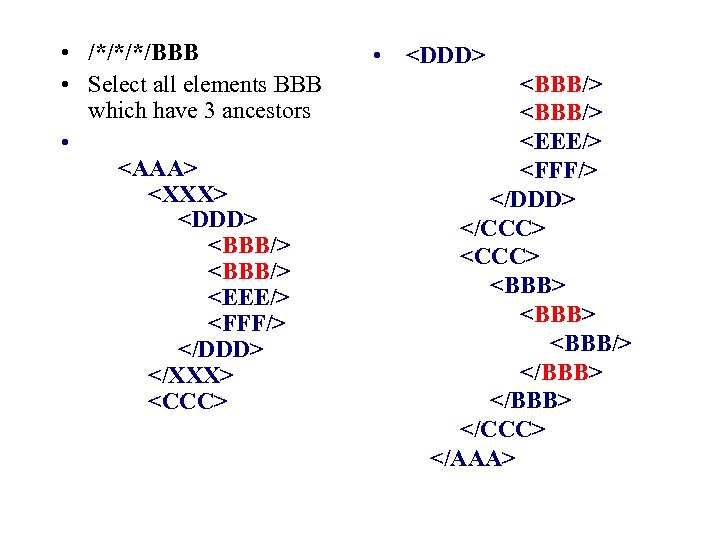 • /*/*/*/BBB • Select all elements BBB which have 3 ancestors •
• /*/*/*/BBB • Select all elements BBB which have 3 ancestors •
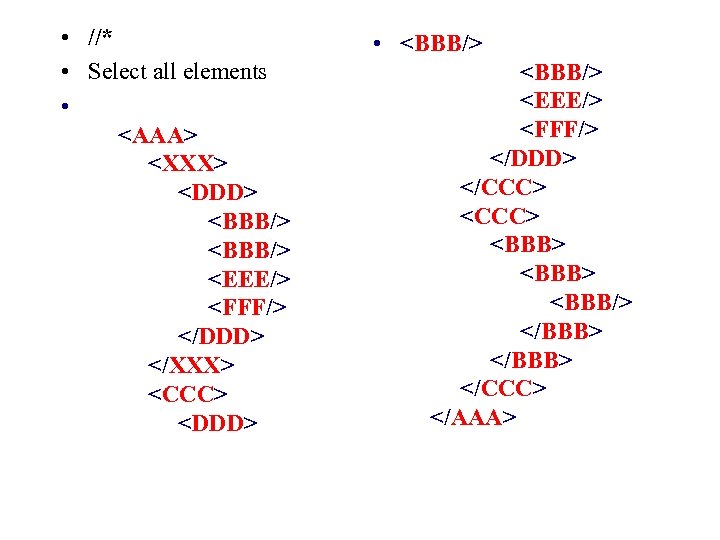 • //* • Select all elements •
• //* • Select all elements •
 • Expression in square brackets can further specify an element. A number in the brackets gives the position of the element in the selected set. The function last() selects the last element in the selection. /AAA/BBB[1] • Select the first BBB child of element AAA •
• Expression in square brackets can further specify an element. A number in the brackets gives the position of the element in the selected set. The function last() selects the last element in the selection. /AAA/BBB[1] • Select the first BBB child of element AAA •
![• /AAA/BBB[last()] • Select the last BBB child of element AAA • <AAA> • /AAA/BBB[last()] • Select the last BBB child of element AAA • <AAA>](https://present5.com/presentation/86ab4aa03cf888ef1e6d2a9babcc358b/image-11.jpg) • /AAA/BBB[last()] • Select the last BBB child of element AAA •
• /AAA/BBB[last()] • Select the last BBB child of element AAA •
 • Attributes are specified by @ prefix. • //@id • Select all attributes @id •
• Attributes are specified by @ prefix. • //@id • Select all attributes @id •
![• //BBB[@id] • Select BBB elements which have attribute id • <AAA> <BBB • //BBB[@id] • Select BBB elements which have attribute id • <AAA> <BBB](https://present5.com/presentation/86ab4aa03cf888ef1e6d2a9babcc358b/image-13.jpg) • //BBB[@id] • Select BBB elements which have attribute id •
• //BBB[@id] • Select BBB elements which have attribute id •
![• //BBB[@name] • Select BBB elements which have attribute name • <AAA> <BBB • //BBB[@name] • Select BBB elements which have attribute name • <AAA> <BBB](https://present5.com/presentation/86ab4aa03cf888ef1e6d2a9babcc358b/image-14.jpg) • //BBB[@name] • Select BBB elements which have attribute name •
• //BBB[@name] • Select BBB elements which have attribute name •
![• //BBB[@*] • Select BBB elements which have any attribute • <AAA> <BBB • //BBB[@*] • Select BBB elements which have any attribute • <AAA> <BBB](https://present5.com/presentation/86ab4aa03cf888ef1e6d2a9babcc358b/image-15.jpg) • //BBB[@*] • Select BBB elements which have any attribute •
• //BBB[@*] • Select BBB elements which have any attribute •
![• //BBB[not(@*)] • Select BBB elements without an attribute • <AAA> <BBB id • //BBB[not(@*)] • Select BBB elements without an attribute • <AAA> <BBB id](https://present5.com/presentation/86ab4aa03cf888ef1e6d2a9babcc358b/image-16.jpg) • //BBB[not(@*)] • Select BBB elements without an attribute •
• //BBB[not(@*)] • Select BBB elements without an attribute •
![• Values of attributes can be used as selection criteria. . //BBB[@id='b 1'] • Values of attributes can be used as selection criteria. . //BBB[@id='b 1']](https://present5.com/presentation/86ab4aa03cf888ef1e6d2a9babcc358b/image-17.jpg) • Values of attributes can be used as selection criteria. . //BBB[@id='b 1'] • Select BBB elements which have attribute id with value b 1 •
• Values of attributes can be used as selection criteria. . //BBB[@id='b 1'] • Select BBB elements which have attribute id with value b 1 •
![• //BBB[@name='bbb'] • Select BBB elements which have attribute name with value 'bbb' • //BBB[@name='bbb'] • Select BBB elements which have attribute name with value 'bbb'](https://present5.com/presentation/86ab4aa03cf888ef1e6d2a9babcc358b/image-18.jpg) • //BBB[@name='bbb'] • Select BBB elements which have attribute name with value 'bbb' •
• //BBB[@name='bbb'] • Select BBB elements which have attribute name with value 'bbb' •
 • Normalized-space removes leading and starting spaces and replaces sequences of whitespace characters by a single space • //BBB[normalize-space(@name)='bbb'] • Select BBB elements which have attribute name with value bbb, leading and trailing spaces are removed before comparison •
• Normalized-space removes leading and starting spaces and replaces sequences of whitespace characters by a single space • //BBB[normalize-space(@name)='bbb'] • Select BBB elements which have attribute name with value bbb, leading and trailing spaces are removed before comparison •
![• Function count() counts the number of selected elements • //*[count(BBB)=2] • Select • Function count() counts the number of selected elements • //*[count(BBB)=2] • Select](https://present5.com/presentation/86ab4aa03cf888ef1e6d2a9babcc358b/image-20.jpg) • Function count() counts the number of selected elements • //*[count(BBB)=2] • Select elements which have two children BBB •
• Function count() counts the number of selected elements • //*[count(BBB)=2] • Select elements which have two children BBB •
![• //*[count(*)=2] • Select elements which have 2 children • <AAA> <CCC> <BBB/> • //*[count(*)=2] • Select elements which have 2 children • <AAA> <CCC> <BBB/>](https://present5.com/presentation/86ab4aa03cf888ef1e6d2a9babcc358b/image-21.jpg) • //*[count(*)=2] • Select elements which have 2 children •
• //*[count(*)=2] • Select elements which have 2 children •
![• //*[count(*)=3] • Select elements which have 3 children • <AAA> <CCC> <BBB/> • //*[count(*)=3] • Select elements which have 3 children • <AAA> <CCC> <BBB/>](https://present5.com/presentation/86ab4aa03cf888ef1e6d2a9babcc358b/image-22.jpg) • //*[count(*)=3] • Select elements which have 3 children •
• //*[count(*)=3] • Select elements which have 3 children •
![• //*[name()='BBB'] • Select all elements with name BBB, equivalent with //BBB • • //*[name()='BBB'] • Select all elements with name BBB, equivalent with //BBB •](https://present5.com/presentation/86ab4aa03cf888ef1e6d2a9babcc358b/image-23.jpg) • //*[name()='BBB'] • Select all elements with name BBB, equivalent with //BBB •
• //*[name()='BBB'] • Select all elements with name BBB, equivalent with //BBB •
![• //*[starts-with(name(), 'B')] • Select all elements name of which starts with letter • //*[starts-with(name(), 'B')] • Select all elements name of which starts with letter](https://present5.com/presentation/86ab4aa03cf888ef1e6d2a9babcc358b/image-24.jpg) • //*[starts-with(name(), 'B')] • Select all elements name of which starts with letter B •
• //*[starts-with(name(), 'B')] • Select all elements name of which starts with letter B •
![• //*[contains(name(), 'C')] • Select all elements name of which contain letter C • //*[contains(name(), 'C')] • Select all elements name of which contain letter C](https://present5.com/presentation/86ab4aa03cf888ef1e6d2a9babcc358b/image-25.jpg) • //*[contains(name(), 'C')] • Select all elements name of which contain letter C •
• //*[contains(name(), 'C')] • Select all elements name of which contain letter C •
![• //*[string-length(name()) = 3] • Select elements with three-letter name • <AAA> <Q/> • //*[string-length(name()) = 3] • Select elements with three-letter name • <AAA> <Q/>](https://present5.com/presentation/86ab4aa03cf888ef1e6d2a9babcc358b/image-26.jpg) • //*[string-length(name()) = 3] • Select elements with three-letter name •
• //*[string-length(name()) = 3] • Select elements with three-letter name •
![• //*[string-length(name()) < 3] • Select elements name of which has one or • //*[string-length(name()) < 3] • Select elements name of which has one or](https://present5.com/presentation/86ab4aa03cf888ef1e6d2a9babcc358b/image-27.jpg) • //*[string-length(name()) < 3] • Select elements name of which has one or two characters •
• //*[string-length(name()) < 3] • Select elements name of which has one or two characters •
![• //*[string-length(name()) > 3] • Select elements with name longer than three characters • //*[string-length(name()) > 3] • Select elements with name longer than three characters](https://present5.com/presentation/86ab4aa03cf888ef1e6d2a9babcc358b/image-28.jpg) • //*[string-length(name()) > 3] • Select elements with name longer than three characters •
• //*[string-length(name()) > 3] • Select elements with name longer than three characters •
 • Several paths can be combined with | separator. //CCC | //BBB • Select all elements CCC and BBB •
• Several paths can be combined with | separator. //CCC | //BBB • Select all elements CCC and BBB •
 • /AAA/EEE | //BBB • Select all elements BBB and elements EEE which are children of root element AAA •
• /AAA/EEE | //BBB • Select all elements BBB and elements EEE which are children of root element AAA •
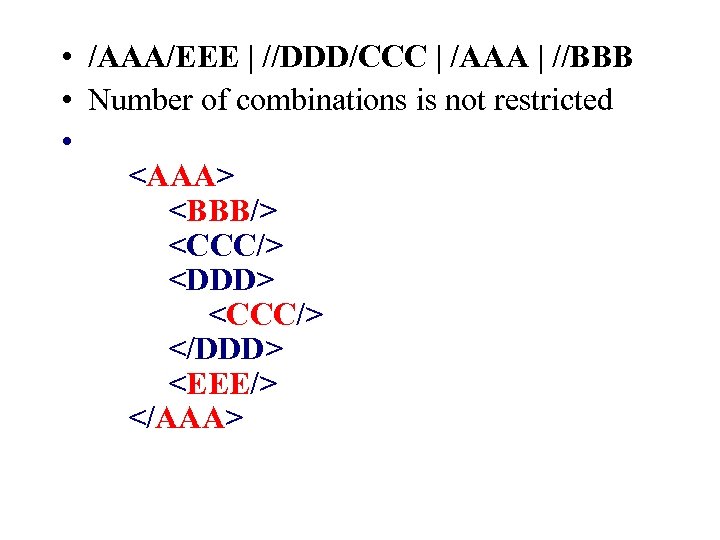 • /AAA/EEE | //DDD/CCC | /AAA | //BBB • Number of combinations is not restricted •
• /AAA/EEE | //DDD/CCC | /AAA | //BBB • Number of combinations is not restricted •
 • The child axis contains the children of the context node. The child axis is the default axis and it can be omitted. /AAA • Equivalent of /child: : AAA •
• The child axis contains the children of the context node. The child axis is the default axis and it can be omitted. /AAA • Equivalent of /child: : AAA •
 • /AAA/BBB • Equivalent of /child: : AAA/child: : BBB •
• /AAA/BBB • Equivalent of /child: : AAA/child: : BBB •
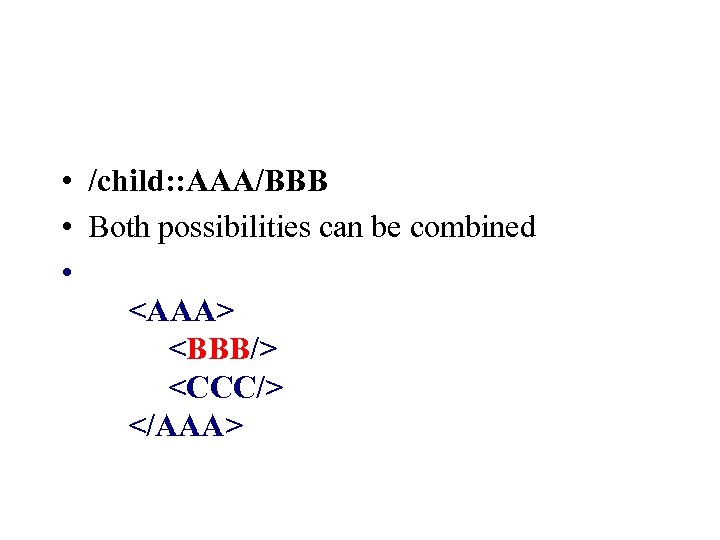 • /child: : AAA/BBB • Both possibilities can be combined •
• /child: : AAA/BBB • Both possibilities can be combined •
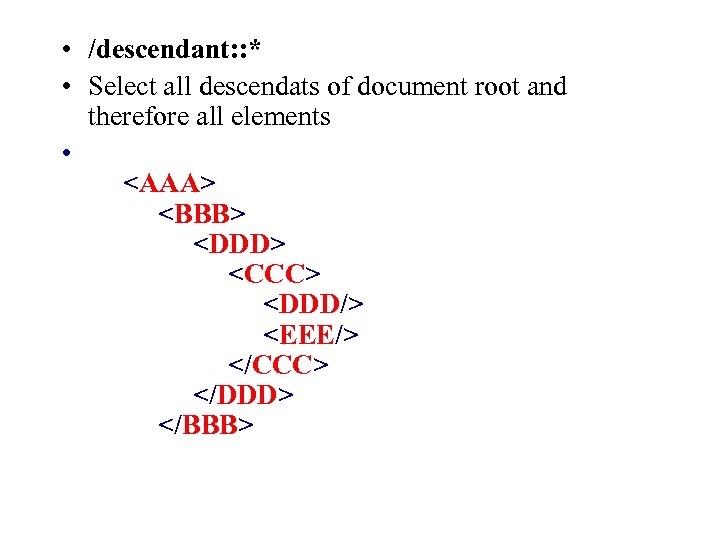 • /descendant: : * • Select all descendats of document root and therefore all elements •
• /descendant: : * • Select all descendats of document root and therefore all elements •
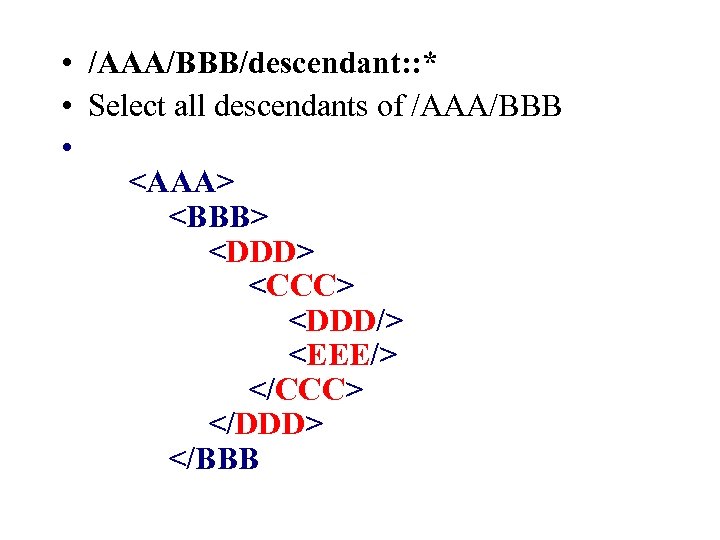 • /AAA/BBB/descendant: : * • Select all descendants of /AAA/BBB •
• /AAA/BBB/descendant: : * • Select all descendants of /AAA/BBB •
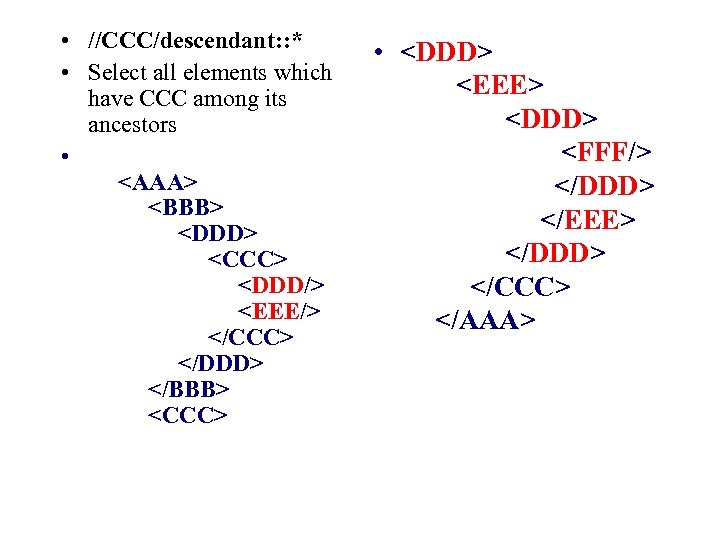 • //CCC/descendant: : * • Select all elements which have CCC among its ancestors •
• //CCC/descendant: : * • Select all elements which have CCC among its ancestors •
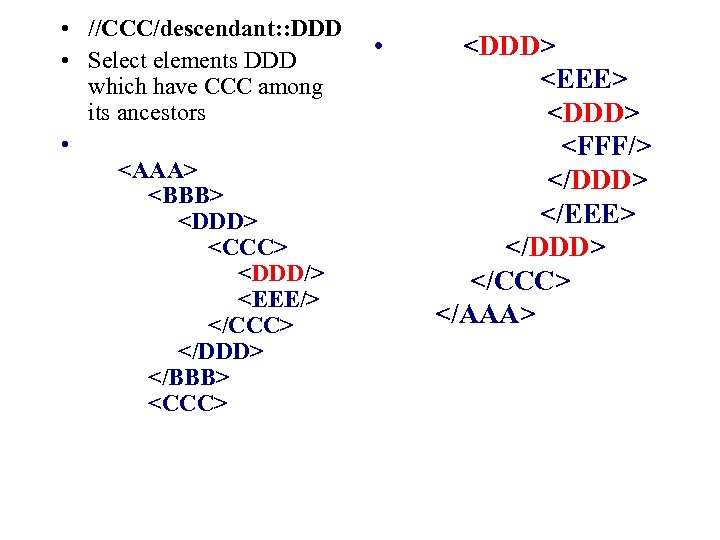 • //CCC/descendant: : DDD • Select elements DDD which have CCC among its ancestors •
• //CCC/descendant: : DDD • Select elements DDD which have CCC among its ancestors •
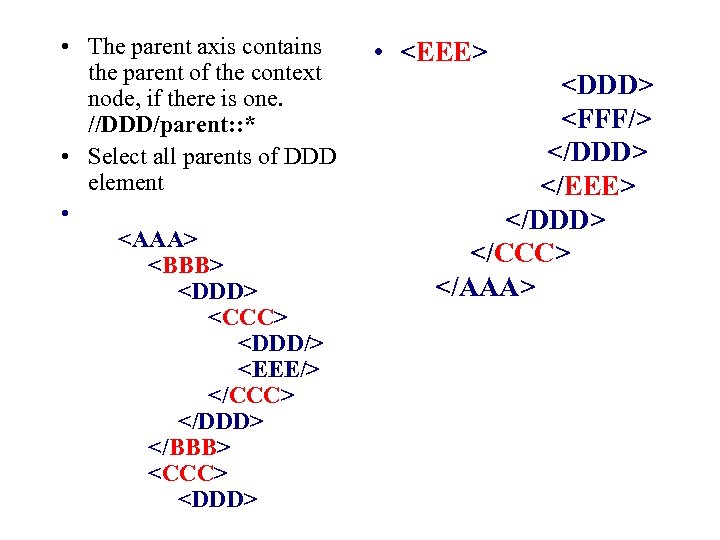 • The parent axis contains the parent of the context node, if there is one. //DDD/parent: : * • Select all parents of DDD element •
• The parent axis contains the parent of the context node, if there is one. //DDD/parent: : * • Select all parents of DDD element •


