b32688bc334869fd89f7e6de35ad205f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 XP (not Microsoft) e. Xtreme Programming Can KOMAR can. komar@boun. edu. tr 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming
XP (not Microsoft) e. Xtreme Programming Can KOMAR can. komar@boun. edu. tr 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming
 Contents Introduction n Why XP? n Values of XP n Overview of XP n Practices of XP n Discussion n 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 2
Contents Introduction n Why XP? n Values of XP n Overview of XP n Practices of XP n Discussion n 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 2
 What is XP? XP is a specific instantiation of an agile process n XP combines best practices in a different way n XP is a different approach to development n XP provides a core process model n XP is not intended to be a complete framework n 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 3
What is XP? XP is a specific instantiation of an agile process n XP combines best practices in a different way n XP is a different approach to development n XP provides a core process model n XP is not intended to be a complete framework n 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 3
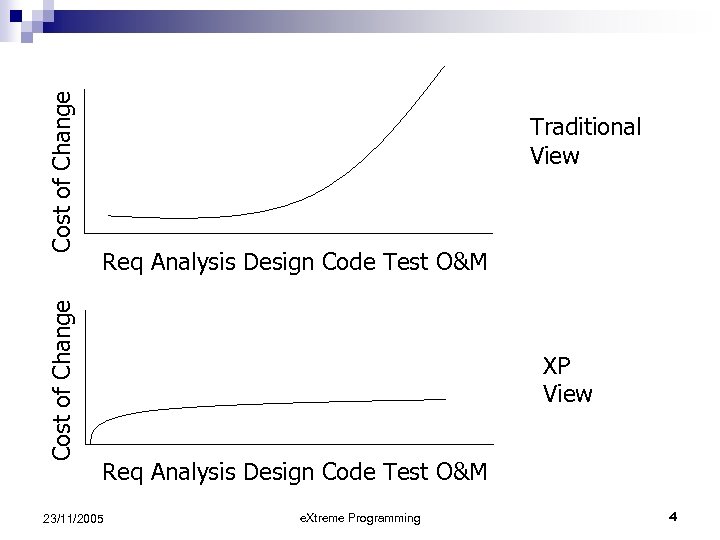 Cost of Change Traditional View Req Analysis Design Code Test O&M XP View Req Analysis Design Code Test O&M 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 4
Cost of Change Traditional View Req Analysis Design Code Test O&M XP View Req Analysis Design Code Test O&M 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 4
 4 Values of XP n Simplicity ¨ n Communication ¨ n KISS Implement the simplest that works Use all means that enable better communication Feedback at various levels minutes unit tests, days functional tests, weeks early production ¨ User stories determine the scope ¨ n Courage ¨ ¨ Refactor when needed Throw away code when no longer needed 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 5
4 Values of XP n Simplicity ¨ n Communication ¨ n KISS Implement the simplest that works Use all means that enable better communication Feedback at various levels minutes unit tests, days functional tests, weeks early production ¨ User stories determine the scope ¨ n Courage ¨ ¨ Refactor when needed Throw away code when no longer needed 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 5
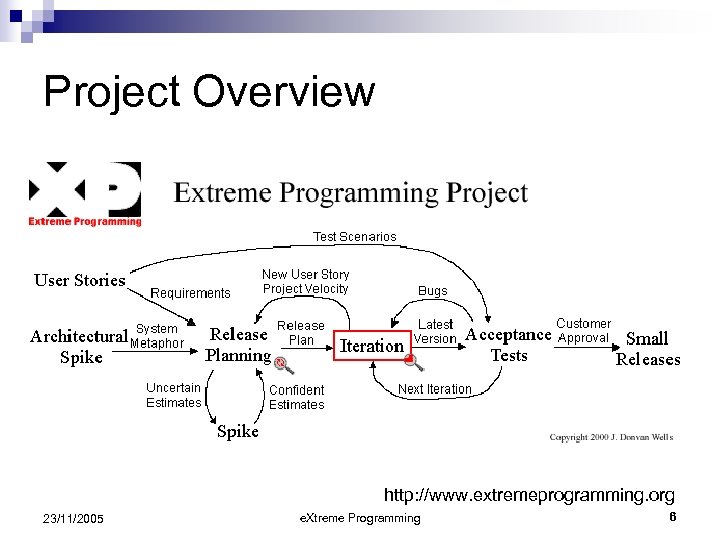 Project Overview http: //www. extremeprogramming. org 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 6
Project Overview http: //www. extremeprogramming. org 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 6
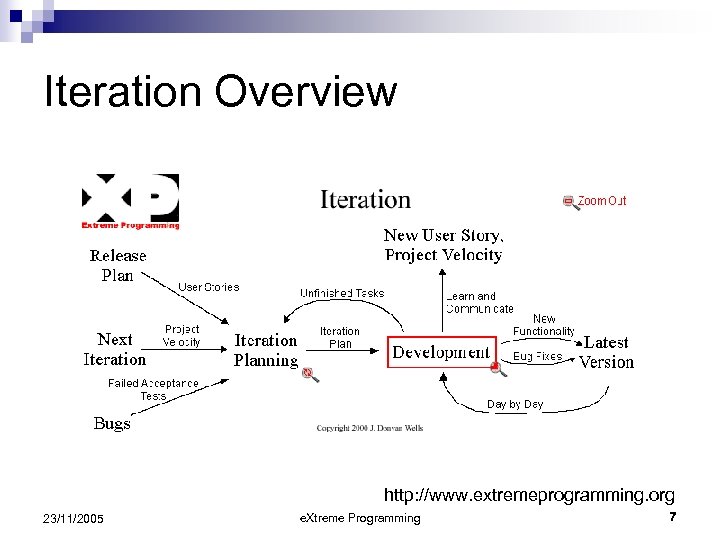 Iteration Overview http: //www. extremeprogramming. org 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 7
Iteration Overview http: //www. extremeprogramming. org 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 7
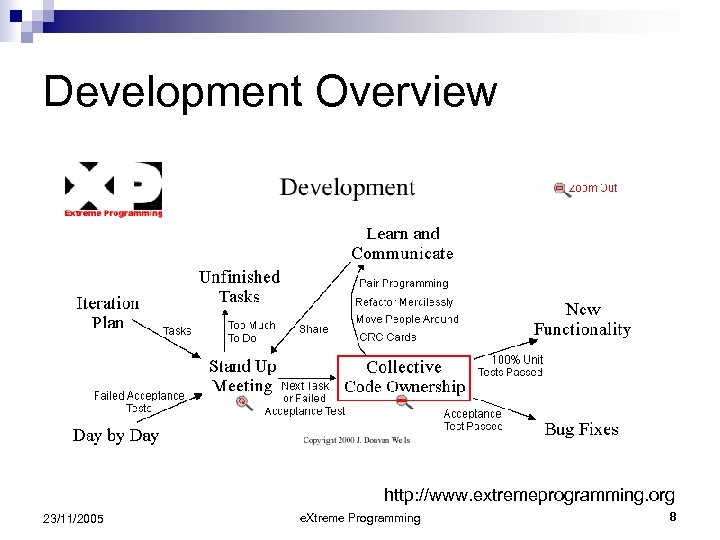 Development Overview http: //www. extremeprogramming. org 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 8
Development Overview http: //www. extremeprogramming. org 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 8
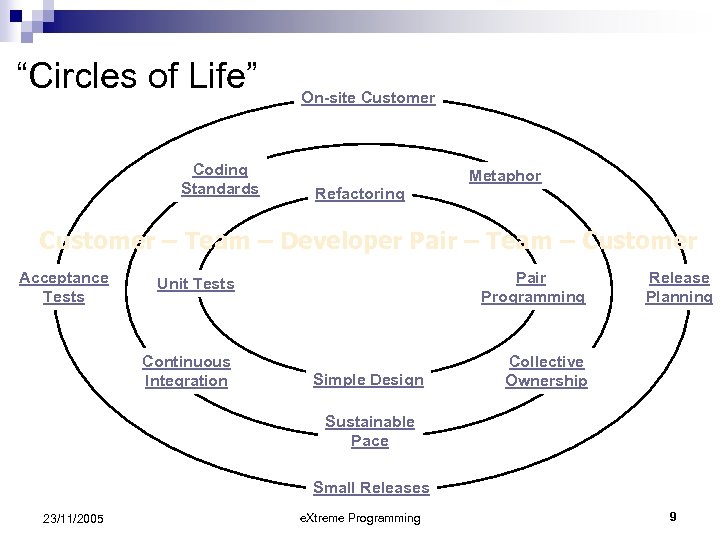 “Circles of Life” Coding Standards On-site Customer Metaphor Refactoring Customer – Team – Developer Pair – Team – Customer Acceptance Tests Unit Tests Pair Programming Continuous Integration Collective Ownership Simple Design Release Planning Sustainable Pace Small Releases 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 9
“Circles of Life” Coding Standards On-site Customer Metaphor Refactoring Customer – Team – Developer Pair – Team – Customer Acceptance Tests Unit Tests Pair Programming Continuous Integration Collective Ownership Simple Design Release Planning Sustainable Pace Small Releases 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 9
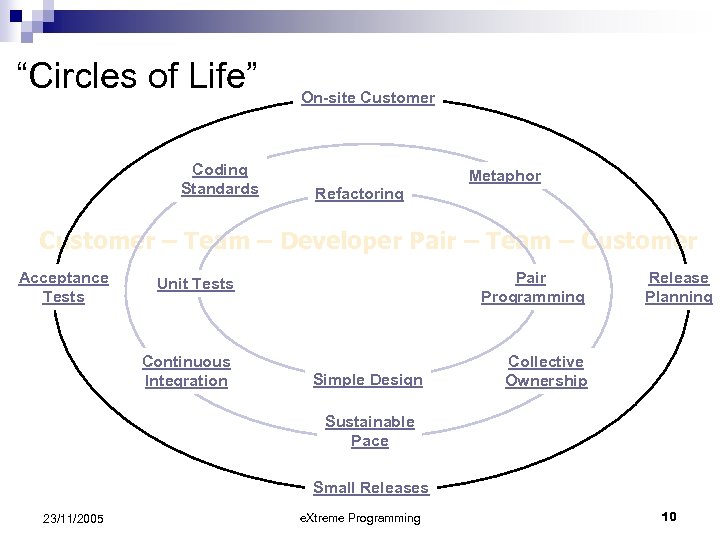 “Circles of Life” Coding Standards On-site Customer Metaphor Refactoring Customer – Team – Developer Pair – Team – Customer Acceptance Tests Unit Tests Pair Programming Continuous Integration Collective Ownership Simple Design Release Planning Sustainable Pace Small Releases 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 10
“Circles of Life” Coding Standards On-site Customer Metaphor Refactoring Customer – Team – Developer Pair – Team – Customer Acceptance Tests Unit Tests Pair Programming Continuous Integration Collective Ownership Simple Design Release Planning Sustainable Pace Small Releases 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 10
 On-Site Customer(s) n Empowered to determine requirements, define functionality, set priorities, and answer questions for the programmers n Daily, face-to-face customer interaction should… ¨ reduce the amount of hard-copy documentation ¨ and the high cost associated with its creation and maintenance 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 11
On-Site Customer(s) n Empowered to determine requirements, define functionality, set priorities, and answer questions for the programmers n Daily, face-to-face customer interaction should… ¨ reduce the amount of hard-copy documentation ¨ and the high cost associated with its creation and maintenance 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 11
 Release Planning n a. k. a. “Planning Game” n Requires the XP "customer" to define the business value of desired features ¨ User Stories n Programmers (not just PM) provide cost estimates for those features n Using this information, customer and developers perform a cost/benefit analysis of each feature ¨ 23/11/2005 enables them to make intelligent decisions about which features to implement and which to defer e. Xtreme Programming 12
Release Planning n a. k. a. “Planning Game” n Requires the XP "customer" to define the business value of desired features ¨ User Stories n Programmers (not just PM) provide cost estimates for those features n Using this information, customer and developers perform a cost/benefit analysis of each feature ¨ 23/11/2005 enables them to make intelligent decisions about which features to implement and which to defer e. Xtreme Programming 12
 User Story #1 Story 1 A person registers with the agency by providing personal information, about the kind of person they are seeking, an alias to conceal Their true identity, and confidential contact details. 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 13
User Story #1 Story 1 A person registers with the agency by providing personal information, about the kind of person they are seeking, an alias to conceal Their true identity, and confidential contact details. 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 13
 User Story #2 Story 2 A selection of matching clients is displayed, and an email may be sent to any one of them. A charge will be made for this service. 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 14
User Story #2 Story 2 A selection of matching clients is displayed, and an email may be sent to any one of them. A charge will be made for this service. 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 14
 Small Releases n Put a simple system into production quickly, then release new versions on a very short cycle n For example ¨ ¨ n Release might be 2 -3 months Each release might have multiple 2 -4 week iterations Helps establish a “rhythm” ¨ n Customer and team knows when feedback will occur Allows the real business value of the product to be evaluated in a real-world environment 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 15
Small Releases n Put a simple system into production quickly, then release new versions on a very short cycle n For example ¨ ¨ n Release might be 2 -3 months Each release might have multiple 2 -4 week iterations Helps establish a “rhythm” ¨ n Customer and team knows when feedback will occur Allows the real business value of the product to be evaluated in a real-world environment 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 15
 Test-Driven Development n a. k. a. “Test First”, “Test Infected” ¨ ACCEPTANCE TESTS: Customers are asked to provide acceptance tests in advance of the development of the system. (automated? ) ¨ UNIT TESTS: Programmers write tests first based on user stories (requirements) and then create software that fulfills the requirements reflected in the tests. n ¨ 23/11/2005 AUTOMATE, AUTOMATE (JUnit, XUnit) By coding to meet test requirements, we ensure that mandatory features are provided e. Xtreme Programming 16
Test-Driven Development n a. k. a. “Test First”, “Test Infected” ¨ ACCEPTANCE TESTS: Customers are asked to provide acceptance tests in advance of the development of the system. (automated? ) ¨ UNIT TESTS: Programmers write tests first based on user stories (requirements) and then create software that fulfills the requirements reflected in the tests. n ¨ 23/11/2005 AUTOMATE, AUTOMATE (JUnit, XUnit) By coding to meet test requirements, we ensure that mandatory features are provided e. Xtreme Programming 16
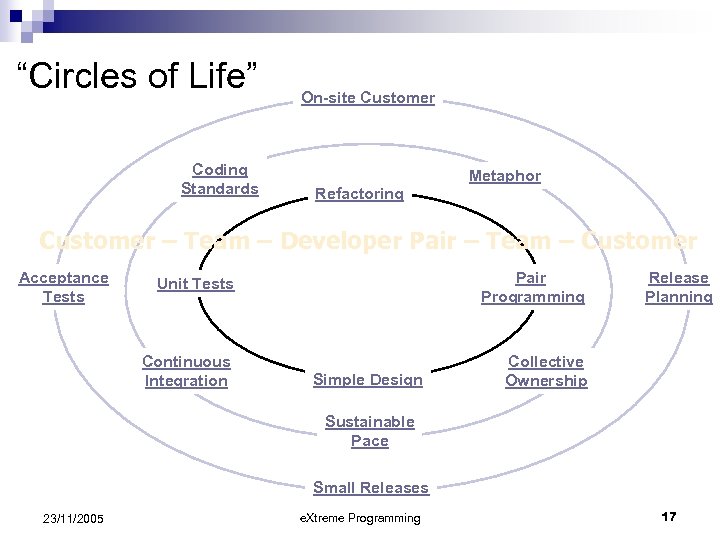 “Circles of Life” Coding Standards On-site Customer Metaphor Refactoring Customer – Team – Developer Pair – Team – Customer Acceptance Tests Unit Tests Pair Programming Continuous Integration Collective Ownership Simple Design Release Planning Sustainable Pace Small Releases 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 17
“Circles of Life” Coding Standards On-site Customer Metaphor Refactoring Customer – Team – Developer Pair – Team – Customer Acceptance Tests Unit Tests Pair Programming Continuous Integration Collective Ownership Simple Design Release Planning Sustainable Pace Small Releases 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 17
 Refactoring n Programmers restructure system without changing its behavior to remove duplication, improve communication, simplify, or add flexibility n Small steps n Code, test, refactor, test, code, test, refactor ¨ n Beck suggests short cycle (10 minutes) Typical goal of refactoring is to move toward a design pattern 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 18
Refactoring n Programmers restructure system without changing its behavior to remove duplication, improve communication, simplify, or add flexibility n Small steps n Code, test, refactor, test, code, test, refactor ¨ n Beck suggests short cycle (10 minutes) Typical goal of refactoring is to move toward a design pattern 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 18
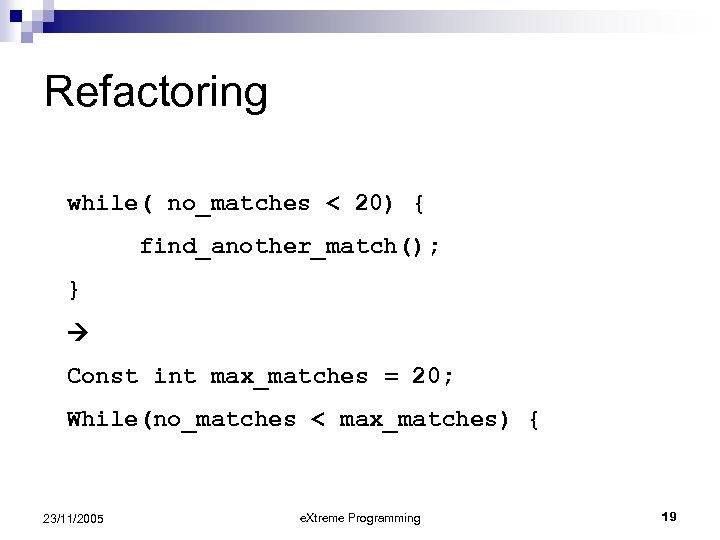 Refactoring while( no_matches < 20) { find_another_match(); } Const int max_matches = 20; While(no_matches < max_matches) { 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 19
Refactoring while( no_matches < 20) { find_another_match(); } Const int max_matches = 20; While(no_matches < max_matches) { 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 19
 Pair Programming n All production code written with 2 programmers at 1 machine ¨ n One tactical, one strategic Pairing should be dynamic ¨ ¨ n Members in pair switch roles every 30 -60 minutes Change pairs each task Experiments showing effectivenes 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 20
Pair Programming n All production code written with 2 programmers at 1 machine ¨ n One tactical, one strategic Pairing should be dynamic ¨ ¨ n Members in pair switch roles every 30 -60 minutes Change pairs each task Experiments showing effectivenes 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 20
 Pair Programming n What does it buy you? Continuous Code Review ¨ Continuous requirements & domain knowledge reinforcement ¨ Continuous skills training (Java, Design Patterns, Refactoring, CM or IDE tools, etc. ) ¨ n Developers have more trouble with this concept than managers Need to try it a few times to see if it works ¨ Takes time to get acclimated ¨ More intense development experience ¨ 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 21
Pair Programming n What does it buy you? Continuous Code Review ¨ Continuous requirements & domain knowledge reinforcement ¨ Continuous skills training (Java, Design Patterns, Refactoring, CM or IDE tools, etc. ) ¨ n Developers have more trouble with this concept than managers Need to try it a few times to see if it works ¨ Takes time to get acclimated ¨ More intense development experience ¨ 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 21
 Simple Design n Based on philosophy that highest business value is derived from the simplest program that will meet current requirements. n Don’t over-engineer a solution! n While many preach K. I. S. S. , this concept is one of the hardest to apply! n 2 common philosophies of XP teams: ¨ DTSTTCPW - Do The Simplest Thing That Could Possibly Work ¨ YAGNI - You Aren't Gonna Need It 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 22
Simple Design n Based on philosophy that highest business value is derived from the simplest program that will meet current requirements. n Don’t over-engineer a solution! n While many preach K. I. S. S. , this concept is one of the hardest to apply! n 2 common philosophies of XP teams: ¨ DTSTTCPW - Do The Simplest Thing That Could Possibly Work ¨ YAGNI - You Aren't Gonna Need It 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 22
 Unit Tests Test a little, code a little… ¨ “Test-first programming” Tests become the specification n Tests give confidence in the system n Tests give courage to change the system n 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 23
Unit Tests Test a little, code a little… ¨ “Test-first programming” Tests become the specification n Tests give confidence in the system n Tests give courage to change the system n 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 23
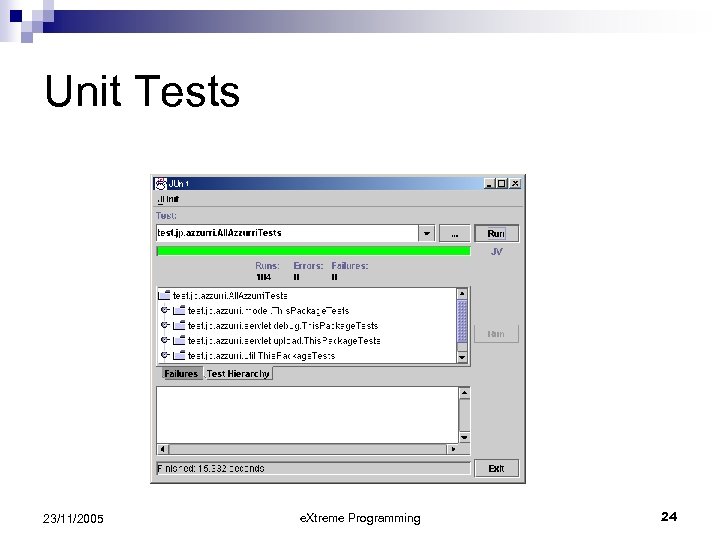 Unit Tests 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 24
Unit Tests 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 24
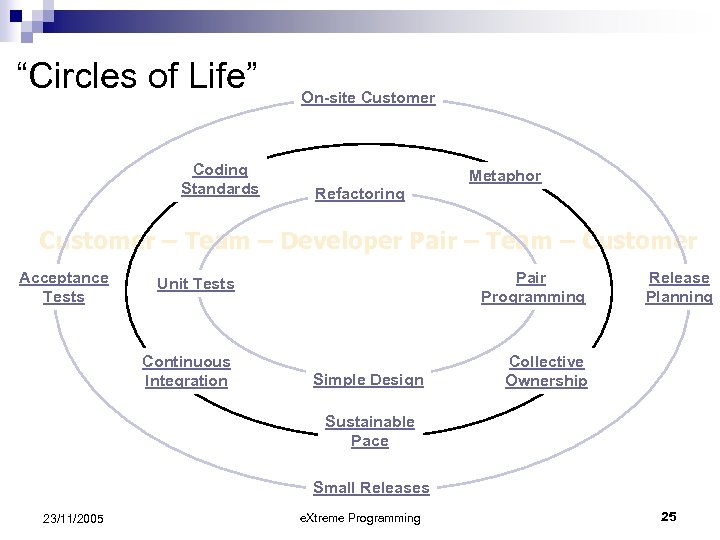 “Circles of Life” Coding Standards On-site Customer Metaphor Refactoring Customer – Team – Developer Pair – Team – Customer Acceptance Tests Unit Tests Pair Programming Continuous Integration Collective Ownership Simple Design Release Planning Sustainable Pace Small Releases 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 25
“Circles of Life” Coding Standards On-site Customer Metaphor Refactoring Customer – Team – Developer Pair – Team – Customer Acceptance Tests Unit Tests Pair Programming Continuous Integration Collective Ownership Simple Design Release Planning Sustainable Pace Small Releases 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 25
 Coding Standards n Programmers write all code in accordance with rules emphasizing communication throughout the code n Goal: Self-documenting code n Because the “common language” is the code n More than Javadoc; good Javadocs with clear inline comments 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 26
Coding Standards n Programmers write all code in accordance with rules emphasizing communication throughout the code n Goal: Self-documenting code n Because the “common language” is the code n More than Javadoc; good Javadocs with clear inline comments 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 26
 Metaphor n The XP concept of “architecture” n Guide all development with a single shared story of how the whole system works n Defines a "system of names" and guides the team's development and communication 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 27
Metaphor n The XP concept of “architecture” n Guide all development with a single shared story of how the whole system works n Defines a "system of names" and guides the team's development and communication 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 27
 Continuous Integration n Integrate & build the system several times a day n Integrate every time a task is completed n Let’s you know every day the status of the system 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 28
Continuous Integration n Integrate & build the system several times a day n Integrate every time a task is completed n Let’s you know every day the status of the system 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 28
 Collective Ownership n Any programmer can change any code anywhere in the system at any time n This works best if using Coding Standards, Test. Driven Development and Pair Programming (Synergy) n Gives the team more flexibility for vacation, sick leave, turn over ¨ Progress doesn’t stop on a component because one of the team members is not present 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 29
Collective Ownership n Any programmer can change any code anywhere in the system at any time n This works best if using Coding Standards, Test. Driven Development and Pair Programming (Synergy) n Gives the team more flexibility for vacation, sick leave, turn over ¨ Progress doesn’t stop on a component because one of the team members is not present 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 29
 Sustainable Pace n Tired programmers often write lower-quality code n Minimizing overtime and keeping programmers fresh will produce higher-quality code in less time n Set 40 -45 hours as a rule ¨ n Based on team preference Corollary: Never work overtime a second week in a row ¨ 23/11/2005 Avoid burnout e. Xtreme Programming 30
Sustainable Pace n Tired programmers often write lower-quality code n Minimizing overtime and keeping programmers fresh will produce higher-quality code in less time n Set 40 -45 hours as a rule ¨ n Based on team preference Corollary: Never work overtime a second week in a row ¨ 23/11/2005 Avoid burnout e. Xtreme Programming 30
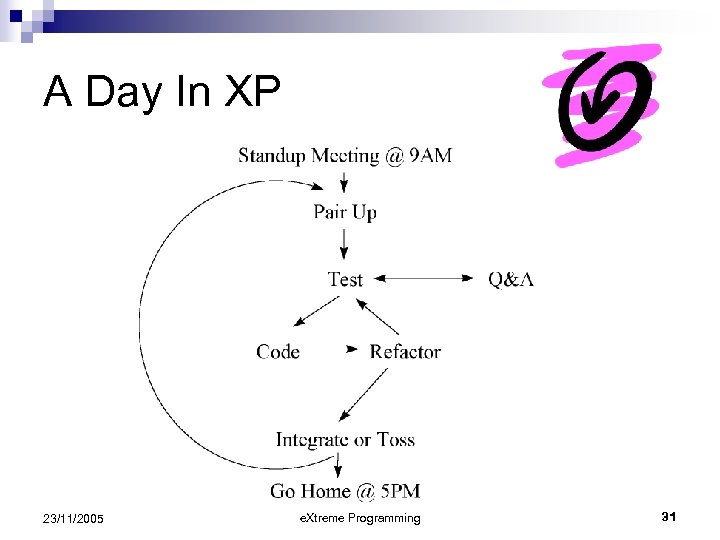 A Day In XP 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 31
A Day In XP 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 31
 References n n n n http: //www. extremeprogramming. org http: //www. xprogramming. com http: //www. junit. org http: //www. refactoring. com http: //www. pairprogramming. com Extreme Programming Explained – Kent Beck Refactoring – Martin Fowler Planning Extreme Programming – Kent Beck et al Extreme Programming Installed – Ron Jeffries et al Extreme Programming Examined – Giancarlo Succi et al Extreme Programming in Practice – Robert C. Martin et al Extreme Programming Explored – William C. Wake Extreme Programming Applied – Ken Auer et al The Costs and Benefits of Pair Programming – Alistair Cockburn et al 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 32
References n n n n http: //www. extremeprogramming. org http: //www. xprogramming. com http: //www. junit. org http: //www. refactoring. com http: //www. pairprogramming. com Extreme Programming Explained – Kent Beck Refactoring – Martin Fowler Planning Extreme Programming – Kent Beck et al Extreme Programming Installed – Ron Jeffries et al Extreme Programming Examined – Giancarlo Succi et al Extreme Programming in Practice – Robert C. Martin et al Extreme Programming Explored – William C. Wake Extreme Programming Applied – Ken Auer et al The Costs and Benefits of Pair Programming – Alistair Cockburn et al 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 32
 Discussion n n Is pair programming a good idea? Under what conditions can it be or vice versa? Do you really believe XP can solve dynamic requirements problem? Do you think involving the customer into the development area is a good idea? What are the (possible) pros and cons of XP? If you were a project manager what would you consider before adopting XP? 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 33
Discussion n n Is pair programming a good idea? Under what conditions can it be or vice versa? Do you really believe XP can solve dynamic requirements problem? Do you think involving the customer into the development area is a good idea? What are the (possible) pros and cons of XP? If you were a project manager what would you consider before adopting XP? 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming 33
 Thank you… Any questions? 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming
Thank you… Any questions? 23/11/2005 e. Xtreme Programming


