290b616e3208b0994cd275b270043b8c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 52

XML : Data Driving Business? Dr. Vasudev Kamath Persistent Systems Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

Outline of Talk • Talk in 2 parts • Part 1 will focus on the following – a brief introduction to XML and the motivation for using it in business applications – Problems with Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) and the use of XML for business integration – Various XML-based standards relating to business integration – Issues relating to Indian context • Part 2 will cover some technical issues in XML 2 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk
EDI: a method for business integration • • Need felt for evolving standardized means of electronic information exchange EDI definition by EAN (standards body) – • • "the transfer of structured data, by agreed message standards, from one computer application to another by electronic means and with a minimum of human intervention. " Early EDI implementations used proprietary formats Many transaction standards for EDI have been developed over the last few years – – X 12 (ANSI) EANCOM (EAN) UN/EDIFACT OBI Dec 16, 2000 3 COMAD Talk
What does EDI contain? • EDI consists of – Trading Partners • Business organizations who agree to exchange business documents via EDI – Translation Software • software that converts files to or from an EDI format – Communications • transmission and reception of electronic data between trading partners using compatible hardware and software, or a Value Added Network (VAN). • Data may be transmitted directly between partners, or through the use of one or more VANs. 4 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk
EDI Transmission constituents • • • Communications Transport Protocol Interchange Control Header Functional Group Header Transaction Set Header Detail Segment Transaction Set Trailer Functional Group Trailer Interchange Control Trailer Communications Transport Protocol 5 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk
What does EDI implementation entail? • Costs of Communication software • Costs of Translation software – integration with existing applications • Cost for VAN • Setup costs for message transmission • Performance 6 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

Issues with EDI • Needs specialized software and hardware • Startup costs are high • Useful mainly for large companies, not smaller ones • Very rigid message standards: require padding of messages to specific lengths • Messages themselves are not viewer-friendly • EDI syntax has no mechanism formal validation 7 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

What is XML? • e. Xtensible Markup Language • Derivative of Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML) – international standard meta-language for representing text and associated information about it in electronic form • An XML document thus contains – Markup – Text 8 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

XML document structure • Markup – Elements – Tags • Elements – The content of an XML document – Delimited by start and end tags – Can have nested tag pairs • Tags – Start tag delimited by “< tagname >” – End tag delimited by “</ tagname >” 9 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk
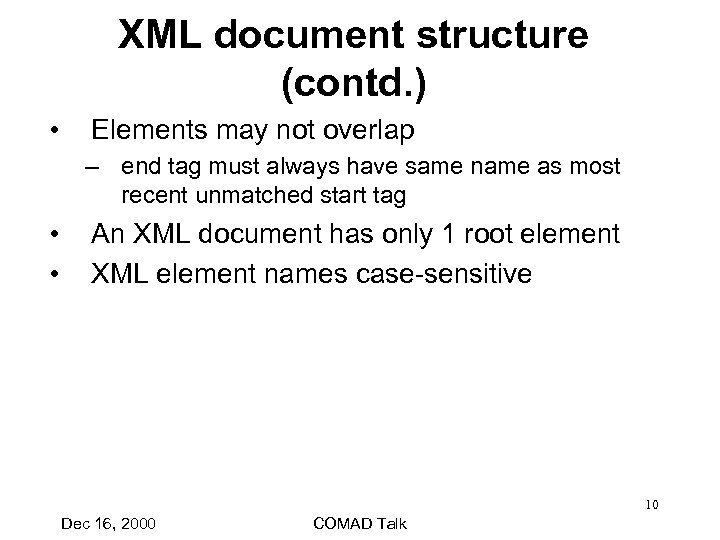
XML document structure (contd. ) • Elements may not overlap – end tag must always have same name as most recent unmatched start tag • • An XML document has only 1 root element XML element names case-sensitive 10 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk
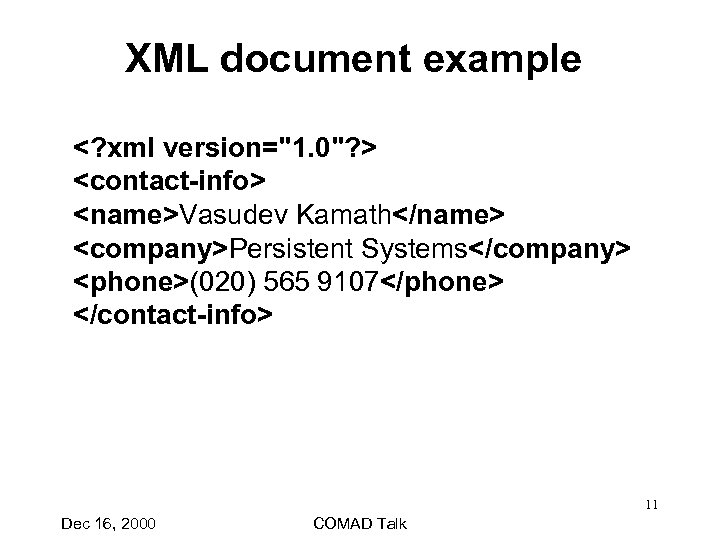
XML document example <? xml version="1. 0"? > <contact-info> <name>Vasudev Kamath</name> <company>Persistent Systems</company> <phone>(020) 565 9107</phone> </contact-info> 11 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk
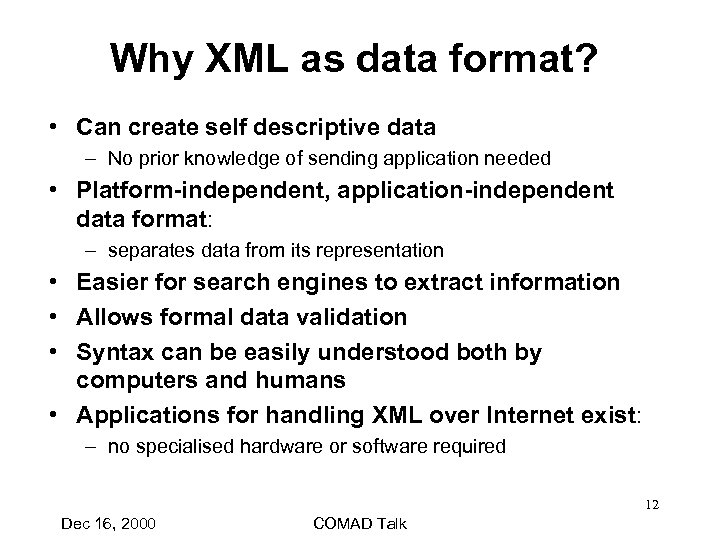
Why XML as data format? • Can create self descriptive data – No prior knowledge of sending application needed • Platform-independent, application-independent data format: – separates data from its representation • Easier for search engines to extract information • Allows formal data validation • Syntax can be easily understood both by computers and humans • Applications for handling XML over Internet exist: – no specialised hardware or software required 12 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk
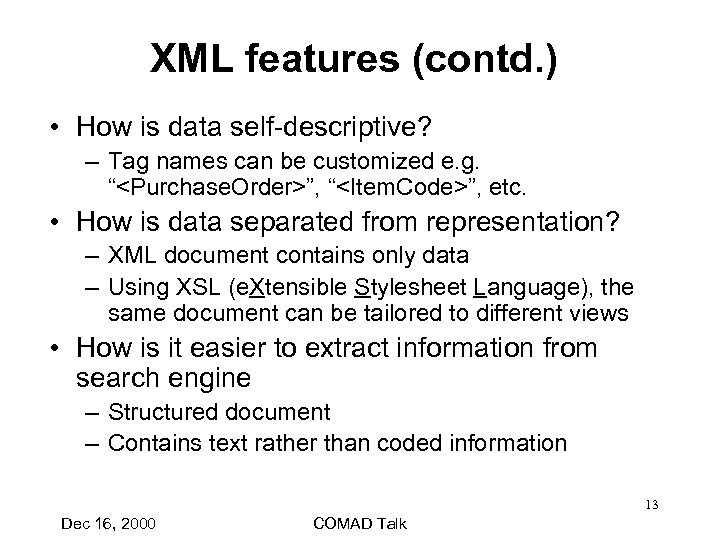
XML features (contd. ) • How is data self-descriptive? – Tag names can be customized e. g. “<Purchase. Order>”, “<Item. Code>”, etc. • How is data separated from representation? – XML document contains only data – Using XSL (e. Xtensible Stylesheet Language), the same document can be tailored to different views • How is it easier to extract information from search engine – Structured document – Contains text rather than coded information 13 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk
XML features (contd. ) • How is formal data validation done? – Through DTD (Document Type Definition) – Through Schemas • Applications for handling XML – Parsers – Database interfaces 14 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

XML DTD example <!-- Example of DTD for above XML document --> <!ELEMENT contact-info (name, company, phone? ) > <!ELEMENT name ( #PCDATA ) > <!ELEMENT company (#PCDATA ) > <!ELEMENT phone ( #PCDATA ) > 15 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

Motivation for XML in business • Most web pages today are HTML: this integrates presentation and data • Single XML document can be “viewed” in different ways – through a browser- with different colours, layout – On a mobile phone display – On the telephone, using voice • Data transformation through gateway applications is eased • Formal representation of business processes helps ease impact of any change in them – Defines sequence of events relating to document exchange – Defines content of the documents • Investment in legacy systems not necessarily wasted Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk 16
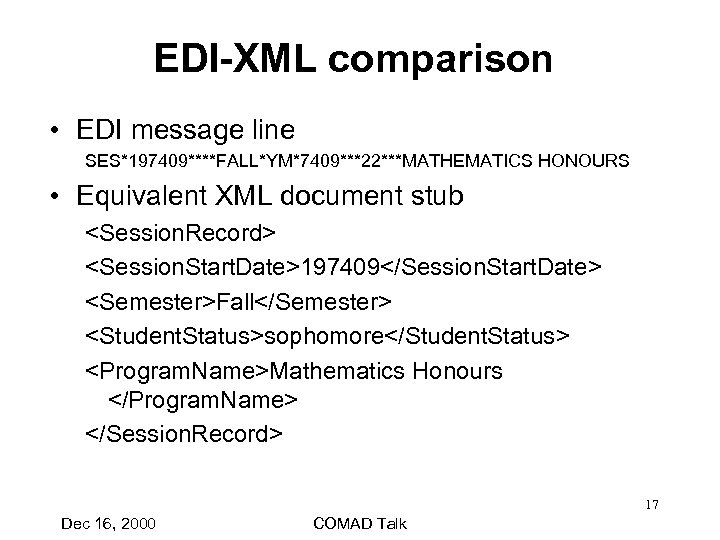
EDI-XML comparison • EDI message line SES*197409****FALL*YM*7409***22***MATHEMATICS HONOURS • Equivalent XML document stub <Session. Record> <Session. Start. Date>197409</Session. Start. Date> <Semester>Fall</Semester> <Student. Status>sophomore</Student. Status> <Program. Name>Mathematics Honours </Program. Name> </Session. Record> 17 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

A typical B 2 B scenario • Distributor requests quotation for list of products from supplier • Supplier sends quotation to distributor • Distributor places purchase order on supplier • Supplier invoices the distributor • Supplier sends goods forwarding note to transporter • Transporter sends consignment note to supplier • Supplier sends shipment along with delivery challan • Distributor sends delivery confirmation to supplier • Distributor sends payment instruction to bank 18 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

XML for business documents • Each underline in previous slide represents a business document • This would be represented in XML using an agreed framework between business partners • There would be underlying applications to convert data contained in internal systems of businesses to XML and vice versa • These applications would encapsulate the business process of the organizations • While processes may be different, the data exchanged must be same (mutually agreed) 19 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

XML-based business integration Stock Yard Represents data transformation 3 rd Party Logistics Vendor Message routing logic, service discovery, etc. Manufacturer Bank Distributor Dec 16, 2000 Represents XML document flow 20 COMAD Talk
How XML is used at various layers in business process • • At business process layer At data exchange layer At messaging, routing layer At service registration and discovery layer 21 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

XML at business process layer <!ENTITY % common-attributes "id CDATA IMPLIED" > <!ELEMENT Pip 2 A 1 Product. Information. Notification ( Product. Notice+ , from. Role , to. Role , this. Document. Generation. Date. Time , this. Document. Identifier , Global. Document. Function. Code ) > <!ELEMENT Product. Notice ( the. Notice , Global. Product. Identifier ) > <!ATTLIST Free. Form. Text xml: lang CDATA IMPLIED > <!ELEMENT Global. Product. Identifier #PCDATA ) > <!ELEMENT from. Role ( Partner. Role. Description ) > <!ELEMENT Partner. Role. Description ( Global. Partner. Role. Classification. Code , Partner. Description , Contact. Information? ) > <!ELEMENT Global. Partner. Role. Classification. Code ( #PCDATA ) > <!ELEMENT Partner. Description ( Global. Partner. Classification. Code , Business. Description ) > <!ELEMENT Global. Partner. Classification. Code( #PCDATA ) > <!ELEMENT Business. Description ( Global. Business. Identifier , Global. Supply. Chain. Code ) > <!ELEMENT Global. Business. Identifier ( #PCDATA ) > <!ELEMENT Global. Supply. Chain. Code ( #PCDATA ) > <!ELEMENT to. Role ( Partner. Role. Description ) > <!ELEMENT this. Document. Generation. Date. Time ( Date. Time. Stamp ) > <!ELEMENT Date. Time. Stamp ( #PCDATA ) > <!ELEMENT this. Document. Identifier ( Proprietary. Document. Identifier ) > <!ELEMENT Proprietary. Document. Identifier ( #PCDATA ) > <!ELEMENT Global. Document. Function. Code ( #PCDATA ) > Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk 22

XML at business document exchange layer <? xml version="1. 0" ? > <Pe. BS operation="Transport. Request"> <Transport. Request><Transport. Request. Header> <Transport. Request. Number/> <Transport. Request. Date>date</Transport. Request. Date> </Transport. Request. Header> <Transporter. Address> <Name. Address/> <Transporter. Contact/> </Transporter. Address> <!-- Name and address of the manufacturer, stockyard, delivery etc. --> <!-- List of items to be delivered --> <List. Of. Transport. Item> <Product. Code /> <Item. Description /> <Quantity/> <Required. Delivery. Date>20000810 T 10: 00</Required. Delivery. Date> </Transport. Item> </List. Of. Transport. Item> <Transporter. Response. Required. Date>20000808 T 09: 00</Transporter. Response. Required. Date> <Special. Request>Any special request</Special. Request> </Transport. Request> 23 </Pe. BS> Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

XML at routing layer <SOAP-ENV: Envelope xmlns: SOAP-ENV=“URL" xmlns: xsi=“URL"> <SOAP-ENV: Header> <dlv: delivery SOAP-ENV: must. Understand="1" xmlns: dlv=“URL" xmlns: agr=“URL"> <dlv: to> <dlv: address xsi: type="agr: department">Book Order Department</dlv: address></dlv: to> <dlv: from><dlv: address xsi: type="agr: organization">Booklovers. Anonymous</dlv: address></dlv: from> </dlv: delivery> <prop: properties SOAP-ENV: must. Understand="1" xmlns: prop=“URL"> <prop: identity>uuid: 74 b 9 f 5 d 0 -33 fb-4 a 81 -b 02 b-5 b 760641 c 1 d 6</prop: identity> <prop: sent. At>2000 -05 -14 T 03: 00+08: 00</prop: sent. At> <prop: expires. At>2000 -05 -15 T 04: 00+08: 00</prop: expires. At> <prop: topic>topic-name</prop: topic> </prop: properties> </SOAP-ENV: Header> <SOAP-ENV: Body> <po: Purchase. Order xmlns: po=“URL"> <po: Title>Essential Biz. Talk</po: Title> </po: Purchase. Order> </SOAP-ENV: Body> </SOAP-ENV: Envelope> 24 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

XML for service description <? xml version="1. 0"? > <Espeak version="Espeak 1. 0 beta" operation="Create. Vocab" xmlns="http: //localhost/e: /Esxml/Schemas/espeak. xsd"> <resource xmlns=""> <!-- Begin: Specify the vocabulary description --> <resource. Des xmlns=""> <pattern> <Name>Manufacturer. Vocabulary</Name> <Type>ESVocabulary</Type> </pattern> </resource. Des> <!-- End: Specify the vocabulary description --> <resource. Data xmlns=""> <!-- Begin: Specify attribute property set --> <attr. Group name="Manufacturer. Vocabulary" xmlns=""> <attr. Decl xmlns="" name="Entity. Name"> <datatype. Ref name="string"/> </attr. Decl> <!-- Other attr. Decl on Entity. Id, Service. Name, Company. Name, Product. Category, Address, etc. --> </attr. Group> </resource. Data> <!-- End: Specify attribute property set --> </resource> </Espeak> Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk 25

Why XML standards? • Businesses have different internal business systems • Need to agree on a common method of exchanging information in human-readable form in documents, forms and messages • Must overcome the deficiencies of EDI 26 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

What standardization do these standards do? • Formal specification of business process • Standardization of data exchanged between business applications • Standardization of other items relating to the interaction such as messaging, security • Formal mechanisms for representation of meta-information about interacting applications and data • Note: not all standards achieve all of the above! 27 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

XML standards for business • End users, solution providers and other players in the global e-commerce scene have proposed multiple XML-based standards for e -commerce • Some of the standards are: – – – – Rosetta. Net Commerce. Net eb. XML Commerce. One Biz. Talk Commerce. XML Pe. BS 28 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

Rosetta. Net • Independent, self-funded consortium of global members of IT Supply Chain, – HP, Compaq, Fedex, GE Information Services, Oracle, SAP AG, Toshiba Information Systems, Cisco, etc • Defines B 2 B process standards as well as B 2 B data standards • Rosetta. Net standards – Rosetta. Net Partner Interface Processes – Rosetta. Net Implementation Framework – Rosetta. Net Business and Technical Dictionaries 29 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk
Rosetta. Net (Contd. ) • Rosetta. Net Partner Interface Process – XML specification designed to provide common business/data models and documents enabling system developers to implement Rosetta. Net e. Business interfaces • Rosetta. Net Implementation Framework – Open, common network-application integration framework for easy adoption of processes • Application message formats • Message exchange sequences • Rosetta. Net Business Dictionaries – Definitions of Business Properties and Business Data Entities Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk 30

Business messages • XML DTDs arranged in clusters relating to – Partner, Product and Service Review • information collection, maintenance and distribution for the development of trading-partner profiles and productinformation subscriptions – Product Introduction • distribution and update of basic and extended product information, product change notices, etc. – Order Management • order catalog products, create custom solutions, manage distribution and deliveries, and support product returns and financial transactions 31 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

Business messages (contd. ) – Marketing Information Management • Communication of marketing information, including campaign plans, lead information and design registration – Inventory Management • Inventory management, including collaboration, replenishment, price protection, reporting and allocation – Service and Support • post-sales technical support, service warranty and asset management capabilities 32 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

Commerce. Net • Open, internet-based infrastructure for e- commerce, whose members include leading banks, telcos, ISPs, software services companies, major end-users worldwide • Aims to function as a market maker, generating communities of buyers & sellers • Defines a conceptual framework for interoperability between different entities in supply chain 33 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk
Commerce. Net Architecture • Architecture expected to provide common basis for two parties to negotiate understanding of how they will do business • 7 -layer architecture – – – – NETWORKS contain MARKETS where BUSINESSES provide and use SERVICES which conduct INTERACTIONS which exchange DOCUMENTS containing INFORMATION ITEMS 34 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk
Commerce. Net Architecture (Contd. ) • Layered model representing e-commerce environment • Each layer relates to next layer in defined way • Metadata of each layer described through various “Type Registries” (built on XML-based data elements) • Layer and its Registries enable an interested party – to obtain information to potentially use offered services, – or to join the marketplace and • provide new services or • interoperate as a trading partner with other businesses in that marketplace. 35 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

eb. XML • Initiative of the UN CEFACT (UN Centre for Trade Facilitation and Electronic Business) and OASIS (Organization for the Advancement of Structured Information Standards) • A framework where consistent, robust and interoperable e-business services and components can be created • will provide technical infrastructure for Global Commerce Internet Protocol – (set of recommendations governing management of data for Internet communication and other B 2 B interactions) 36 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk
eb. XML Functionality • Mechanisms to provide support for businesses to specify information such as – Support for business processes – Service interface that is implemented – Required information for each instance of a message – Mechanism to allow dynamic discovery of semantic meaning of that business information • Implemented using XML representation 37 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

eb. XML Architectural Components • Mechanism for the following related to a business process: – Description – Registration – Storage • Mechanism for the following related to a participant: – Discovery • • Business processes Business service interfaces Business messages Technical configuration for supporting transport, security and encoding protocols – Registration – Trading partner agreement description 38 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

eb. XML Architectural Components (contd. ) • Messaging services – Configuration to implement business process in accordance with constraints described in trading partner agreements – Interoperability, security, reliability of messaging 39 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

Commerce. One • Leader in e-commerce solutions • Commerce One Common Business Library (x. CBL) 2. 0 – provides transition path from EDI to XML-based commerce capability – More than just a XML wrapper for EDI messages: a set of XML building blocks itself – a document framework that allows the creation of robust, reusable, XML documents for electronic commerce 40 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

Commerce. One x. CBL • Provides XML-based standardization at business document exchange layer • Defines standards for documents such as – – Purchase order Invoice Price Catalog Availability Check Request • Endorsed by other standards bodies – – Microsoft Biz. Talk OASIS UN/CEFACT Commerce. Net 41 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

XCBL 2. 0 business documents • • • Purchase. Order. Response Order. Status. Request Order. Status. Result Invoice Availability. Check. Request Availability. Check. Result Price. Check. Request Price. Check. Result Price. Catalog Pricing. Data Product. Catalog 42 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

Biz. Talk • Promoted by Microsoft • Goal of driving rapid, consistent adoption of XML to enable e-commerce and application integration • Biz. Talk Framework: – Specs for design and development of XML-based messaging solutions for communication between applications – Builds upon standards such as HTTP, MIME, XML and SOAP • Note: Biz. Talk does not address many aspects of B 2 B e-commerce! 43 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

Use of XML in Biz. Talk • Representation of business documents • Schemas for business documents • Biz. Tags: used to specify handling of Biz. Talk messages • Biz. Talk document header entries (SOAP) – Routing and delivery – Document identification and properties – Document catalog • Information about business document and any attachments – Process management • information about the business process providing processing context for Biz. Talk Document. Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk 44

Commerce. XML (c. XML) • Developed by Ariba, and other players • Supports business documents such as – Catalogs – “Punchouts” - Dynamic catalogs – Purchase orders • Has mechanisms for – Getting supplier details – Entering into contracts – Configuring punchout sites 45 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk
Use of XML at different layers in standards • 4 “layers” in standards • Not all standards use XML at all layers – Biz. Talk is just a messaging framework, does not define content of business documents – Commerce. One defines the business data elements, but does not provide messaging, routing capability or process definitions – Pe. BS uses XML to define business documents as well as for messaging; service registration and discovery 46 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

Indian e-business issues • B 2 B e-commerce in India stresses on exchanges and marketplaces • Typical interaction is still browser-web server where one entity is a human, and not application to application • Inter-business integration of the type of “Oracle in company A talking to SAP in company B” is minimal • Scope for business integration still vast 47 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

Indian XML standards for Indian business documents • Need to replicate “brick-and-mortar” processes and documents even if business moves on-line, due to users’ expectations • XML-based standards for global businesses do not capture the documents of Indian business processes relating to interaction of businesses with government and other public entities. • 2 examples of the above: – Uttar Pradesh requires a road permit for each shipment that crosses the state borders – Information on octroi, sales taxes, excise, etc. may need to be incorporated into business documents such as invoices • Hence the need for evolving Indian standards, suited for e-commerce between Indian entities 48 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

Pe. BS • Solution uses XML-based business documents • At present focusing on business data exchange layer, taking into account Indian business practices • Working to evolve these into Indian standards for business documents, as well as process standards 49 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

Standard Pe. BS documents • • • delivery-challan delivery-confirmation dispatch-intimationconfirmation dispute-document distr-to-manuf-productenquiry invoice loading-confirmation-report loading-instructions-sheet product-catalog-request product-enquiry-response • • • production-request purchase-order-confirmation quotation-request stock-enquiry stock-status-report transport-receipt-request transport-requestconfirmation 50 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

To conclude… • Usage of XML-based documents in B 2 B interaction is catching on - more in US than in India • Businesses are using XML at various levels in supply chain, not just at the business data exchange layer • XML-based documents expected to work well in heterogeneous environments of multiple businesses who want to integrate operations • Need to popularize XML in user community in India, not just among CS fraternity 51 Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk

For further information…. • Rosetta. Net – http: //www. oasis-open. org/cover/rosetta. Net. html • Commerce. Net – http: //eco. commerce. net/what/index. cfm • eb. XML – http: //www. ebxml. org • Commerce. One – http: //www. commerceone. com • Biz. Talk – http: //www. biztalk. org • Commerce. XML – http: //www. cxml. org • Pe. BS – http: //www. e 2 econnect. net Dec 16, 2000 COMAD Talk 52
290b616e3208b0994cd275b270043b8c.ppt