f8b513dae1aa734fe22c9a11be41e0da.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 XLink: Open Linking Standard n XML / XSL separate ¨ data semantics ¨ presentation semantics n Need to also separate out ¨ navigation n semantics Single unique feature of the Web ¨ hypertext link
XLink: Open Linking Standard n XML / XSL separate ¨ data semantics ¨ presentation semantics n Need to also separate out ¨ navigation n semantics Single unique feature of the Web ¨ hypertext link
 XML: Linking By Explicit ID n XML & SGML provide simple linking ¨ ID / IDREF combination Buy me a
XML: Linking By Explicit ID n XML & SGML provide simple linking ¨ ID / IDREF combination Buy me a
a" src="https://present5.com/presentation/f8b513dae1aa734fe22c9a11be41e0da/image-3.jpg" alt="HTML: Cross-Document Linking n HTML adds cross-document named element linking Buy me a" />
HTML: Cross-Document Linking n HTML adds cross-document named element linking Buy me a present
 Linking: Pointing and Clicking A link embodies a relationship n A link must specify n ¨ the items taking place in the relationship ¨ the meaning of the relationship ¨ the user interface for the link n Need standards for each of these
Linking: Pointing and Clicking A link embodies a relationship n A link must specify n ¨ the items taking place in the relationship ¨ the meaning of the relationship ¨ the user interface for the link n Need standards for each of these
 XPointer Addressing n XLink adds location language XPointer ¨ simple id-based addressing ¨ XPath addressing ¨ stepwise addressing Dear Father Christmas, Here is what I want
XPointer Addressing n XLink adds location language XPointer ¨ simple id-based addressing ¨ XPath addressing ¨ stepwise addressing Dear Father Christmas, Here is what I want
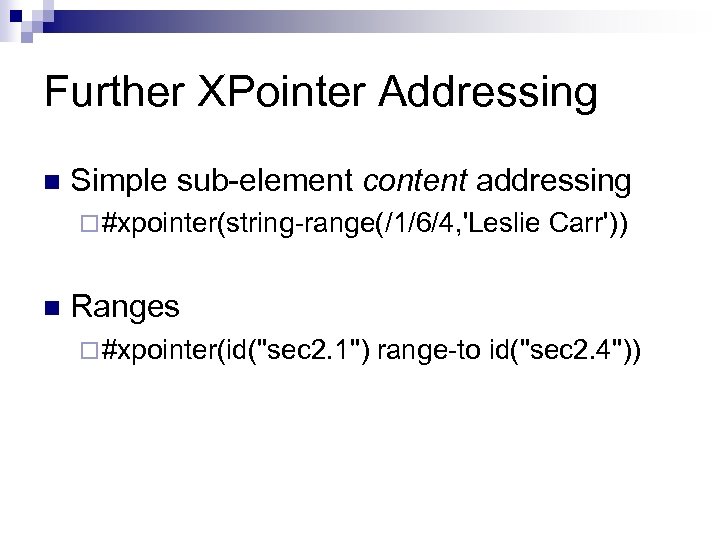 Further XPointer Addressing n Simple sub-element content addressing ¨ #xpointer(string-range(/1/6/4, 'Leslie n Carr')) Ranges ¨ #xpointer(id("sec 2. 1") range-to id("sec 2. 4"))
Further XPointer Addressing n Simple sub-element content addressing ¨ #xpointer(string-range(/1/6/4, 'Leslie n Carr')) Ranges ¨ #xpointer(id("sec 2. 1") range-to id("sec 2. 4"))
 XLink Structures n Links have ¨ locators – identify the resources ¨ arcs – specify the connections between resources ¨ title – description of a link / arc for a human ¨ role – description of a link / arc for a computer
XLink Structures n Links have ¨ locators – identify the resources ¨ arcs – specify the connections between resources ¨ title – description of a link / arc for a human ¨ role – description of a link / arc for a computer
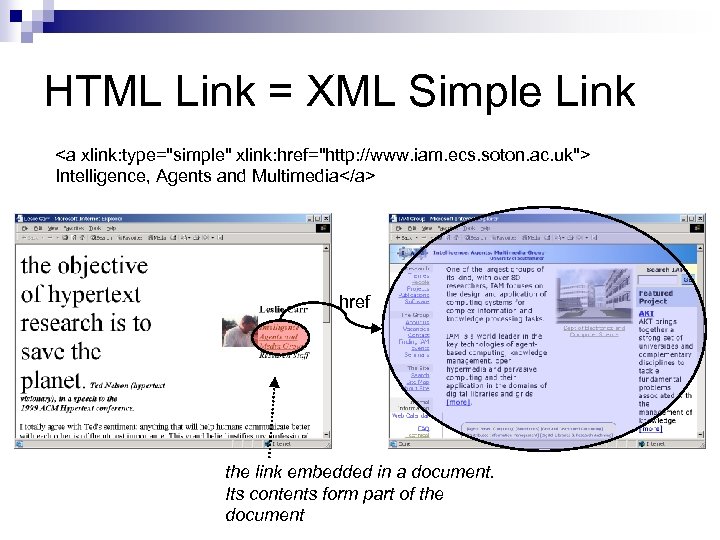 HTML Link = XML Simple Link Intelligence, Agents and Multimedia href the link embedded in a document. Its contents form part of the document
HTML Link = XML Simple Link Intelligence, Agents and Multimedia href the link embedded in a document. Its contents form part of the document
 XLink Behaviour n Links can be triggered (actuate attribute) ¨ by user clicks ¨ by the application n user auto Links can be displayed (show attribute) ¨ in another window new ¨ in the current window replace ¨ instead of the current element embed
XLink Behaviour n Links can be triggered (actuate attribute) ¨ by user clicks ¨ by the application n user auto Links can be displayed (show attribute) ¨ in another window new ¨ in the current window replace ¨ instead of the current element embed
 XLink Recap n Simple links involve the current resource and one other (like …) n Extended links may involve many resources ¨ no longer source and destination ¨ each link end has a title and role n Links may appear out of line, even in a linkbase
XLink Recap n Simple links involve the current resource and one other (like …) n Extended links may involve many resources ¨ no longer source and destination ¨ each link end has a title and role n Links may appear out of line, even in a linkbase
 Using Linkbases n Linkbases ¨ are collections of links ¨ can be swapped, allowing different links on same resources Amazon linkbase IMDB linkbase
Using Linkbases n Linkbases ¨ are collections of links ¨ can be swapped, allowing different links on same resources Amazon linkbase IMDB linkbase
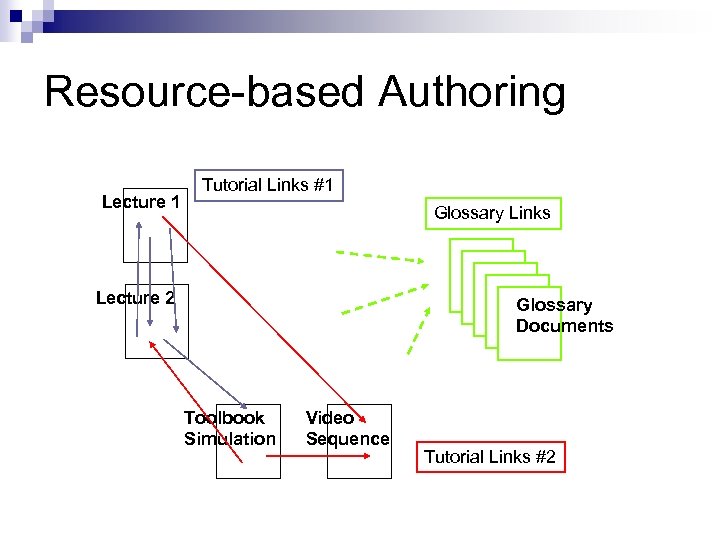
 Generic Links n Generic links are not limited in scope to a single document ¨ usually expressed as a content-based query keyword n citation n aka smart tag n ¨ used for glossary purposes
Generic Links n Generic links are not limited in scope to a single document ¨ usually expressed as a content-based query keyword n citation n aka smart tag n ¨ used for glossary purposes
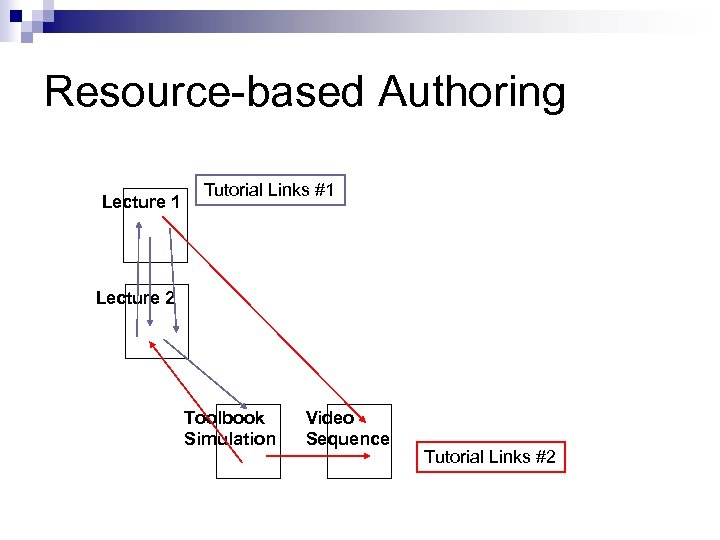
 Resource-based Authoring Linkbases + generic links improve flexibility n Resource-based authoring is the natural authoring paradigm of an open hypermedia* system n ¨ create a set of independent resources ¨ integrate them using sets of link databases * See later lectures
Resource-based Authoring Linkbases + generic links improve flexibility n Resource-based authoring is the natural authoring paradigm of an open hypermedia* system n ¨ create a set of independent resources ¨ integrate them using sets of link databases * See later lectures
 Resource-based Authoring Lecture 1 Lecture 2
Resource-based Authoring Lecture 1 Lecture 2
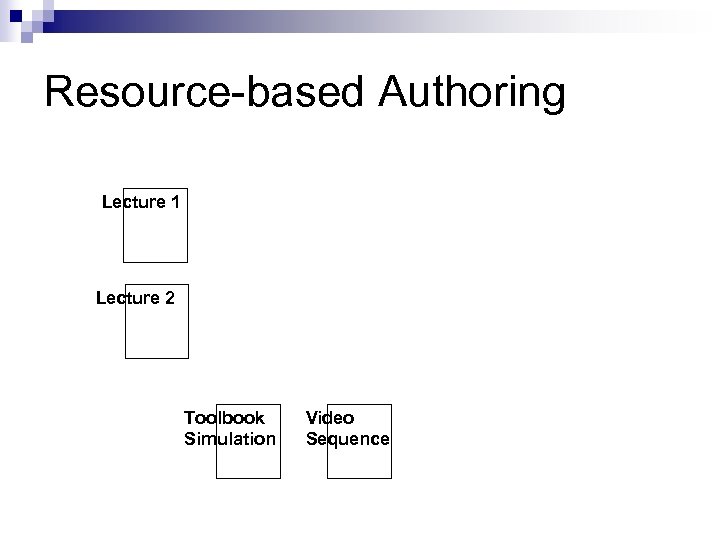 Resource-based Authoring Lecture 1 Lecture 2 Toolbook Simulation Video Sequence
Resource-based Authoring Lecture 1 Lecture 2 Toolbook Simulation Video Sequence
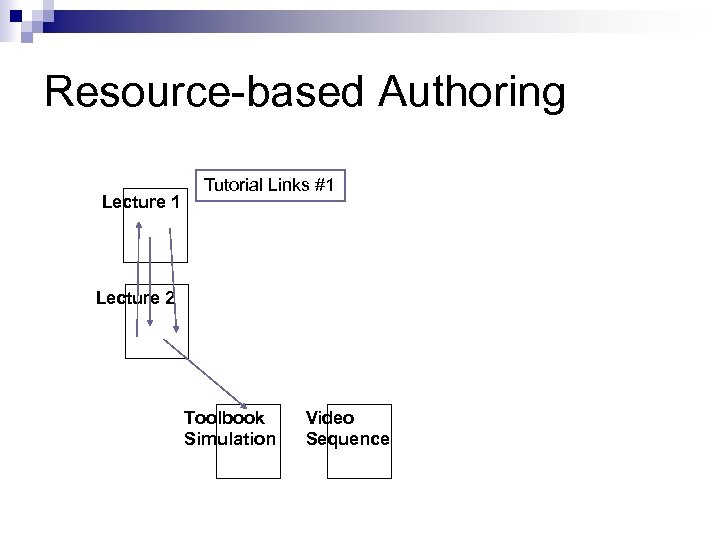 Resource-based Authoring Lecture 1 Tutorial Links #1 Lecture 2 Toolbook Simulation Video Sequence
Resource-based Authoring Lecture 1 Tutorial Links #1 Lecture 2 Toolbook Simulation Video Sequence
 Resource-based Authoring Lecture 1 Tutorial Links #1 Lecture 2 Toolbook Simulation Video Sequence Tutorial Links #2
Resource-based Authoring Lecture 1 Tutorial Links #1 Lecture 2 Toolbook Simulation Video Sequence Tutorial Links #2
 Resource-based Authoring Lecture 1 Tutorial Links #1 Glossary Links Lecture 2 Glossary Documents Toolbook Simulation Video Sequence Tutorial Links #2
Resource-based Authoring Lecture 1 Tutorial Links #1 Glossary Links Lecture 2 Glossary Documents Toolbook Simulation Video Sequence Tutorial Links #2
 Resource-based Authoring n Note that the creation of the content (web pages, videos, simulations etc) is INDEPENDENT n of the creation and deployment of the links THANKS TO n the use of a separate linking process
Resource-based Authoring n Note that the creation of the content (web pages, videos, simulations etc) is INDEPENDENT n of the creation and deployment of the links THANKS TO n the use of a separate linking process
 Resource-based Authoring n Adapt the integrated information resource for different audiences by ¨ Using different linkbases ¨ Chosen according to user profile n e. g. ¨ simple explanatory links for first year undergraduates ¨ vs links to in depth reading and further challenges for Ph. D students
Resource-based Authoring n Adapt the integrated information resource for different audiences by ¨ Using different linkbases ¨ Chosen according to user profile n e. g. ¨ simple explanatory links for first year undergraduates ¨ vs links to in depth reading and further challenges for Ph. D students
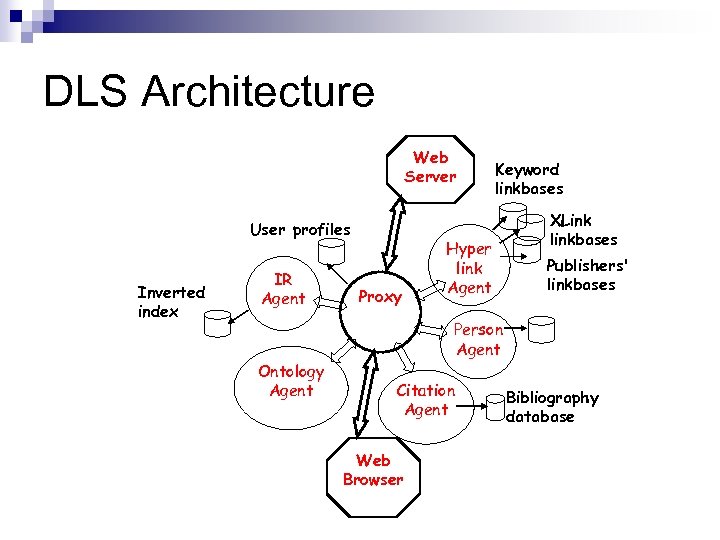
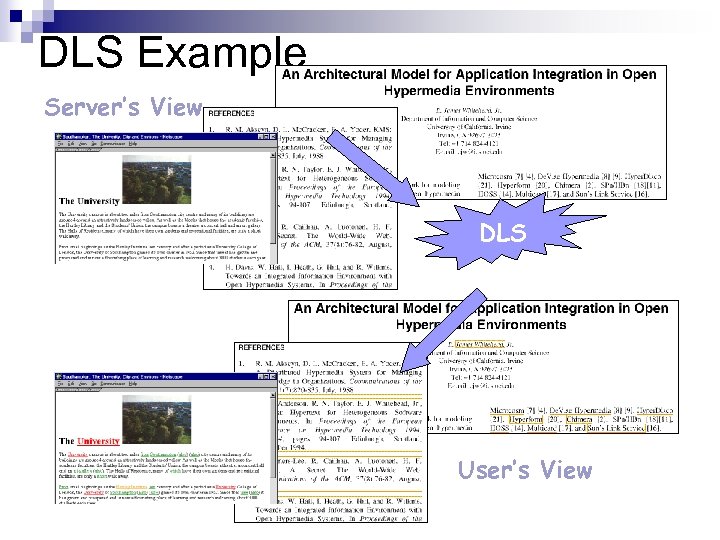
 DLS: A Linking Service n Distributed Link Service ¨ developed in IAM group (predates XLink) ¨ independent service providing linking ¨ maintains separate databases of links ¨ merges them with documents on the fly n Uses two linking forms ¨ explicit (positional) addressing ¨ implicit (content-based) linking
DLS: A Linking Service n Distributed Link Service ¨ developed in IAM group (predates XLink) ¨ independent service providing linking ¨ maintains separate databases of links ¨ merges them with documents on the fly n Uses two linking forms ¨ explicit (positional) addressing ¨ implicit (content-based) linking
 DLS Architecture Web Server User profiles Inverted index IR Agent Ontology Agent Proxy Keyword linkbases Hyper link Agent XLink linkbases Publishers' linkbases Person Agent Citation Agent Web Browser Bibliography database
DLS Architecture Web Server User profiles Inverted index IR Agent Ontology Agent Proxy Keyword linkbases Hyper link Agent XLink linkbases Publishers' linkbases Person Agent Citation Agent Web Browser Bibliography database
 DLS Example Server’s View DLS User’s View
DLS Example Server’s View DLS User’s View
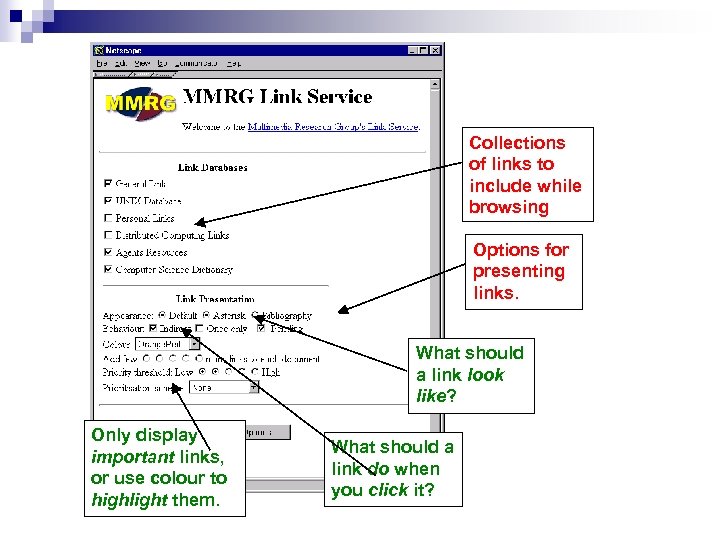 Collections of links to include while browsing Options for presenting links. What should a link look like? Only display important links, or use colour to highlight them. What should a link do when you click it?
Collections of links to include while browsing Options for presenting links. What should a link look like? Only display important links, or use colour to highlight them. What should a link do when you click it?
 DLS Styles Pristine original document Document + plain link style Bibliographic link style Link priorities distinguished b colour scheme
DLS Styles Pristine original document Document + plain link style Bibliographic link style Link priorities distinguished b colour scheme
 DLS Behaviours Pending Links Click here and choose from lots of different destinations here Clicking on links adds them to a link notepad so that you can finish reading this page before you go to another one!
DLS Behaviours Pending Links Click here and choose from lots of different destinations here Clicking on links adds them to a link notepad so that you can finish reading this page before you go to another one!
 DLS and XLink n DLS ‘knows about’ ¨ citations, people etc ¨ formatting and behaviour semantics n XLink has no knowledge ¨ meaning of contents ¨ meaning of presentation semantics
DLS and XLink n DLS ‘knows about’ ¨ citations, people etc ¨ formatting and behaviour semantics n XLink has no knowledge ¨ meaning of contents ¨ meaning of presentation semantics
 XLink Future Not yet implemented widely n Needs to be tied in with XML processing model n ¨ Provide extra info to XSL about things that are link anchors (XML Link Info. Set? ) ¨ Define position in processing After entities are resolved n Before stylesheet is invoked n If some text is transcluded, what is its URL? n
XLink Future Not yet implemented widely n Needs to be tied in with XML processing model n ¨ Provide extra info to XSL about things that are link anchors (XML Link Info. Set? ) ¨ Define position in processing After entities are resolved n Before stylesheet is invoked n If some text is transcluded, what is its URL? n


