5006d00582daf979a200b51c49799c31.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 XI International Academic Conference on Economic and Social Development Do Firms Move towards Target Capital Structure? Empirical Analysis of Dynamic Trade-Off Theory’s Application for BRIC Companies Irina Ivashkovskaya Maria Kokoreva www. cfcenter. ru http: //en. cfcenter. ru/ www. cfjournal. ru Basic Research Programme of the Higher School of Economics in 2009
XI International Academic Conference on Economic and Social Development Do Firms Move towards Target Capital Structure? Empirical Analysis of Dynamic Trade-Off Theory’s Application for BRIC Companies Irina Ivashkovskaya Maria Kokoreva www. cfcenter. ru http: //en. cfcenter. ru/ www. cfjournal. ru Basic Research Programme of the Higher School of Economics in 2009
 Corporate Finance Center Established in 2006 (http: //en. cfcenter. ru/) One of the first academic research centers in Corporate Finance in Russia (part of Center for Fundamental Research) Professors, Lecturers and Master Students of HSE (24 members) Research projects in the Areas: Corporate Financial Decisions Corporate Financial Architecture Corporate Governance and Performance Intellectual Capital: Valuation, Performance “Empirical Corporate Finance in emerging markets” in progress Network of Excellence “Corporate Financial Architecture and Role of Boards” Corporate Finance E-Journal (www. cfjournal. ru)
Corporate Finance Center Established in 2006 (http: //en. cfcenter. ru/) One of the first academic research centers in Corporate Finance in Russia (part of Center for Fundamental Research) Professors, Lecturers and Master Students of HSE (24 members) Research projects in the Areas: Corporate Financial Decisions Corporate Financial Architecture Corporate Governance and Performance Intellectual Capital: Valuation, Performance “Empirical Corporate Finance in emerging markets” in progress Network of Excellence “Corporate Financial Architecture and Role of Boards” Corporate Finance E-Journal (www. cfjournal. ru)
 Capital Structure Research on Emerging Markets DETERMINANTS: COUNTRY LEVEL: Hungary, India, The Czech Republic, Turkey, Taiwan, Thailand, Slovenia, China, Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Hong Kong, Israel, South Africa, South Korea, Sri Lanka, Malaysia, Mexico, Pakistan, Peru, Philippines, Poland, Russia, Singapore, Turkey, and Venezuela MULTICOUNTRY LEVEL: Booth et al. , 2001 (10 countries); Delcoure (2007); Seifert, Gonenc (2008, 23 countries, including Russia); Ivashkovskaya, Solntseva (Kokoreva) (2009, BRIC) BASIC TEORIES TESTING: Delcoure N. 2007 (Central and Eastern Europe), Zou, H. , Xiao, J. Z. , 2006 (China) , Berk A. , 2007 (Slovenia), Chakraborty, I. , 2010 (India) DYNAMIC CAPITAL STRUCTURE: Nivorozhkin E. , 2005 (Central and Eastern Europe, former Soviet Union), Karadeniz, E. et. al, 2009 (Turkey), Bhaduri, S. N. , 2002 (India)
Capital Structure Research on Emerging Markets DETERMINANTS: COUNTRY LEVEL: Hungary, India, The Czech Republic, Turkey, Taiwan, Thailand, Slovenia, China, Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Hong Kong, Israel, South Africa, South Korea, Sri Lanka, Malaysia, Mexico, Pakistan, Peru, Philippines, Poland, Russia, Singapore, Turkey, and Venezuela MULTICOUNTRY LEVEL: Booth et al. , 2001 (10 countries); Delcoure (2007); Seifert, Gonenc (2008, 23 countries, including Russia); Ivashkovskaya, Solntseva (Kokoreva) (2009, BRIC) BASIC TEORIES TESTING: Delcoure N. 2007 (Central and Eastern Europe), Zou, H. , Xiao, J. Z. , 2006 (China) , Berk A. , 2007 (Slovenia), Chakraborty, I. , 2010 (India) DYNAMIC CAPITAL STRUCTURE: Nivorozhkin E. , 2005 (Central and Eastern Europe, former Soviet Union), Karadeniz, E. et. al, 2009 (Turkey), Bhaduri, S. N. , 2002 (India)
 WHY BRIC? BRIC term (Brazil, Russia, India, China) appeared in 2001 (Goldman Sachs) for fast developing economies Economic reasoning (since 2006 – politics also) Cheap resources countries (agriculture, minerals, intellectual, labour) June, 16 2009 – First BRIC summit in Russia Current Goldman Sachs forecasts (taking crisis into account): Average annual growth: BRIC (2009) 4, 8% World (2009) -1, 1% BRIC (2010) 8% World (2010) 3, 3% Appear within 8 largest economies in 2027 Appear within 5 largest economies in 2050
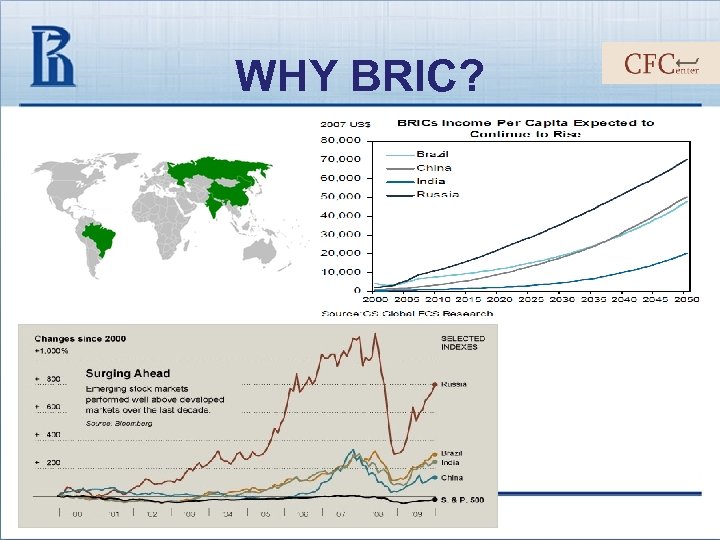
WHY BRIC? BRIC term (Brazil, Russia, India, China) appeared in 2001 (Goldman Sachs) for fast developing economies Economic reasoning (since 2006 – politics also) Cheap resources countries (agriculture, minerals, intellectual, labour) June, 16 2009 – First BRIC summit in Russia Current Goldman Sachs forecasts (taking crisis into account): Average annual growth: BRIC (2009) 4, 8% World (2009) -1, 1% BRIC (2010) 8% World (2010) 3, 3% Appear within 8 largest economies in 2027 Appear within 5 largest economies in 2050
 WHY BRIC?
WHY BRIC?
 Pecking Order Theory Testing: Results 2009 RUSSIAN SAMPLE: DO NOT REJECT Internal financing deficit explains up to 41% of the new debt Higher significance for capital structure variables based on market value of equity SUB SAMPLES: PO motives are more important for companies with foreign shareholders BRAZILIAN SAMPLE : REJECT The majority of the companies do not have internal deficit for the period of study, the coefficients are not significant Not significant for all sub samples CHINESE SAMPLE : REJECT Explanatory power of regressions is too low (Rsquared is from 0, 003 to 0, 04) Not significant for all sub samples
Pecking Order Theory Testing: Results 2009 RUSSIAN SAMPLE: DO NOT REJECT Internal financing deficit explains up to 41% of the new debt Higher significance for capital structure variables based on market value of equity SUB SAMPLES: PO motives are more important for companies with foreign shareholders BRAZILIAN SAMPLE : REJECT The majority of the companies do not have internal deficit for the period of study, the coefficients are not significant Not significant for all sub samples CHINESE SAMPLE : REJECT Explanatory power of regressions is too low (Rsquared is from 0, 003 to 0, 04) Not significant for all sub samples
 Trade-off Theory Testing: Results 2009 RUSSIAN SAMPLE: DO NOT REJECT Deviation from the target level is responsible for a significant part of new debt, but never achieve the unit level (less than 63%) The DL has higher coefficients than the DEF for Pecking Order tests almost in all specifications SUB SAMPLES: for HIGH debt level firms and firms NOT controlled by the government BRAZILIAN SAMPLE : DO NOT REJECT Low significance in all specifications (R-squared from 0, 02 to 0, 06) Could not be rejected for sub samples analysis but preference for a specific sub sample can not be revealed CHINESE SAMPLE : DO NOT REJECT Chinese large-scale companies most likely follow trade-off logic of financing (DL stands for 16 -69% of new debt) Could not be rejected for sub samples analysis but preference for a specific sub sample can not be revealed
Trade-off Theory Testing: Results 2009 RUSSIAN SAMPLE: DO NOT REJECT Deviation from the target level is responsible for a significant part of new debt, but never achieve the unit level (less than 63%) The DL has higher coefficients than the DEF for Pecking Order tests almost in all specifications SUB SAMPLES: for HIGH debt level firms and firms NOT controlled by the government BRAZILIAN SAMPLE : DO NOT REJECT Low significance in all specifications (R-squared from 0, 02 to 0, 06) Could not be rejected for sub samples analysis but preference for a specific sub sample can not be revealed CHINESE SAMPLE : DO NOT REJECT Chinese large-scale companies most likely follow trade-off logic of financing (DL stands for 16 -69% of new debt) Could not be rejected for sub samples analysis but preference for a specific sub sample can not be revealed
 Dynamic Trade-Off OPTIMAL CAPITAL STRUCTURE: ■ Modeling from determinants (fitted values for target capital structure) ■ Historical average leverage (Shyam-Sunder, Myers, 1999), (Fama, French, 2002) ADJUSTMENT COSTS: ■ Optimal and observed capital structures do not coinside (Heshmati, 2001) ■ Determinants of adjustment costs : - standard determinants plus the distance from the optimal (Bangeree et al, 2004); -Institutional factors: market and institution specific (Wanzenried) -Macroeconomic (Cook and Tang, 2008) MODELLING: Interaction of financing, investing, dividend decisions
Dynamic Trade-Off OPTIMAL CAPITAL STRUCTURE: ■ Modeling from determinants (fitted values for target capital structure) ■ Historical average leverage (Shyam-Sunder, Myers, 1999), (Fama, French, 2002) ADJUSTMENT COSTS: ■ Optimal and observed capital structures do not coinside (Heshmati, 2001) ■ Determinants of adjustment costs : - standard determinants plus the distance from the optimal (Bangeree et al, 2004); -Institutional factors: market and institution specific (Wanzenried) -Macroeconomic (Cook and Tang, 2008) MODELLING: Interaction of financing, investing, dividend decisions
 Methodology of the Research DATA : 2004 -2008 panel data 54 Russian large companies 139 Brazilian large companies 143 Indian large companies 110 Chinese large companies RESEARCH METHODOLOGY: Target ratio modeling Adjustment model Final model Checking for individual effects RESULTS, INTERPRETATION, APPLICATIONS
Methodology of the Research DATA : 2004 -2008 panel data 54 Russian large companies 139 Brazilian large companies 143 Indian large companies 110 Chinese large companies RESEARCH METHODOLOGY: Target ratio modeling Adjustment model Final model Checking for individual effects RESULTS, INTERPRETATION, APPLICATIONS
 Leverage Variables and Capital Structure Determinants Leverage ratios: Based on Book value and Market value of equity Based on interest bearing debt and liabilities Capital structure determinants: Profitability Asset structure MTB Size Growth Tax shields 2008 Dummy National Dummy Industry Dummy
Leverage Variables and Capital Structure Determinants Leverage ratios: Based on Book value and Market value of equity Based on interest bearing debt and liabilities Capital structure determinants: Profitability Asset structure MTB Size Growth Tax shields 2008 Dummy National Dummy Industry Dummy
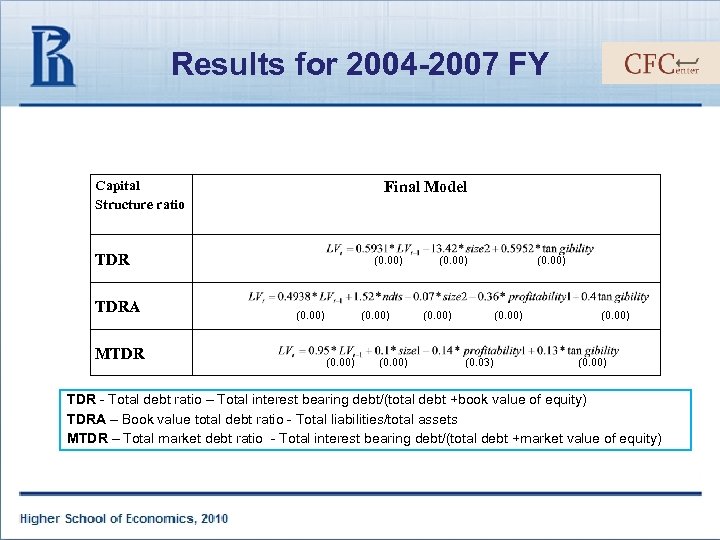 Results for 2004 -2007 FY Capital Structure ratio Final Model TDRA MTDR (0. 00) (0. 03) (0. 00) TDR - Total debt ratio – Total interest bearing debt/(total debt +book value of equity) TDRA – Book value total debt ratio - Total liabilities/total assets MTDR – Total market debt ratio - Total interest bearing debt/(total debt +market value of equity)
Results for 2004 -2007 FY Capital Structure ratio Final Model TDRA MTDR (0. 00) (0. 03) (0. 00) TDR - Total debt ratio – Total interest bearing debt/(total debt +book value of equity) TDRA – Book value total debt ratio - Total liabilities/total assets MTDR – Total market debt ratio - Total interest bearing debt/(total debt +market value of equity)
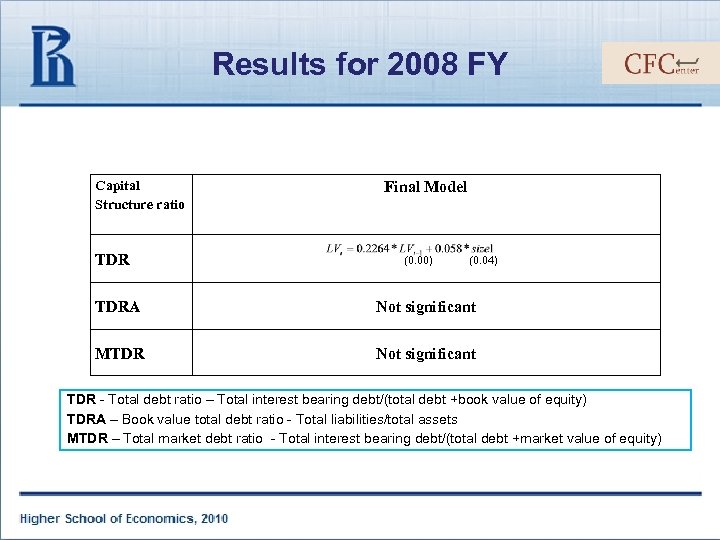 Results for 2008 FY Capital Structure ratio TDR Final Model (0. 00) (0. 04) TDRA Not significant MTDR Not significant TDR - Total debt ratio – Total interest bearing debt/(total debt +book value of equity) TDRA – Book value total debt ratio - Total liabilities/total assets MTDR – Total market debt ratio - Total interest bearing debt/(total debt +market value of equity)
Results for 2008 FY Capital Structure ratio TDR Final Model (0. 00) (0. 04) TDRA Not significant MTDR Not significant TDR - Total debt ratio – Total interest bearing debt/(total debt +book value of equity) TDRA – Book value total debt ratio - Total liabilities/total assets MTDR – Total market debt ratio - Total interest bearing debt/(total debt +market value of equity)
 Results Large BRIC companies follow similar dynamic strategy in capital structure choice Large BRIC companies move to their target capital structure ratio but face recapitalization costs The speed of adjustment is high (due to companies size mostly) – 4151% Target level of capital structure depends on: Profitability (negative relationship) Size calculated as ln(Total Assets) (positive relationship) Size calculated as ln(Sales) (negative relationship) Tangibility (positive relationship) Non debt tax shield (positive relationship) Model is not applicable for 2008 (external factors matter)
Results Large BRIC companies follow similar dynamic strategy in capital structure choice Large BRIC companies move to their target capital structure ratio but face recapitalization costs The speed of adjustment is high (due to companies size mostly) – 4151% Target level of capital structure depends on: Profitability (negative relationship) Size calculated as ln(Total Assets) (positive relationship) Size calculated as ln(Sales) (negative relationship) Tangibility (positive relationship) Non debt tax shield (positive relationship) Model is not applicable for 2008 (external factors matter)
 Thank you for your attention!
Thank you for your attention!
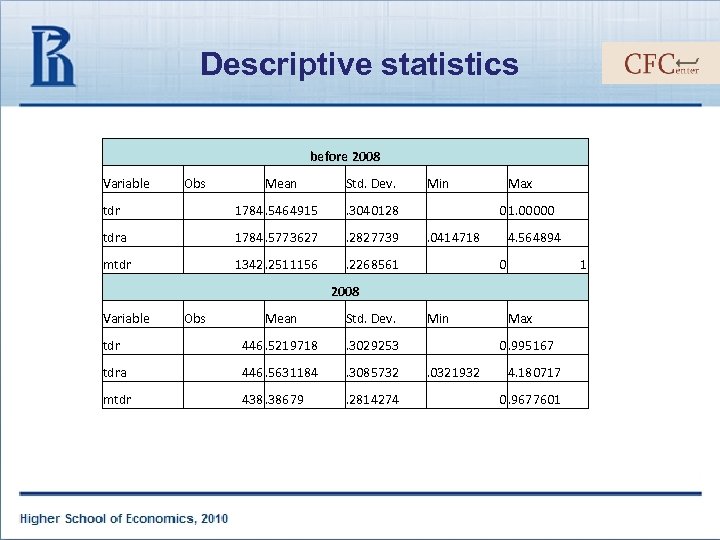 Descriptive statistics before 2008 Variable Obs Mean Std. Dev. tdr 1784. 5464915 . 3040128 tdra 1784. 5773627 . 2827739 mtdr 1342. 2511156 Min . 2268561 Max 0 1. 00000 . 0414718 4. 564894 0 1 2008 Variable Obs Mean Std. Dev. tdr 446. 5219718 . 3029253 tdra 446. 5631184 . 3085732 mtdr 438. 38679 . 2814274 Min Max 0. 995167 . 0321932 4. 180717 0. 9677601
Descriptive statistics before 2008 Variable Obs Mean Std. Dev. tdr 1784. 5464915 . 3040128 tdra 1784. 5773627 . 2827739 mtdr 1342. 2511156 Min . 2268561 Max 0 1. 00000 . 0414718 4. 564894 0 1 2008 Variable Obs Mean Std. Dev. tdr 446. 5219718 . 3029253 tdra 446. 5631184 . 3085732 mtdr 438. 38679 . 2814274 Min Max 0. 995167 . 0321932 4. 180717 0. 9677601
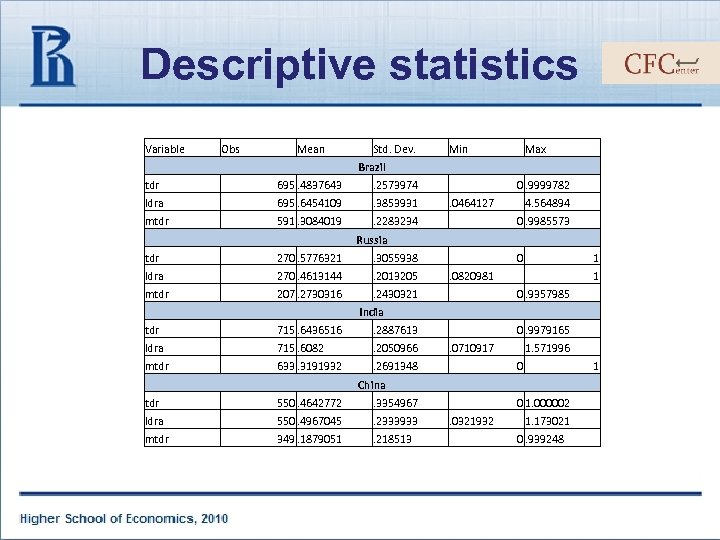 Descriptive statistics Variable Obs Mean Std. Dev. Min Max Brazil tdr 695. 4837643 . 2573974 ldra 695. 6454109 . 3853931 mtdr 591. 3084019 0. 9999782 . 2283234 . 0464127 4. 564894 0. 9985573 Russia tdr 270. 5776321 . 3055938 ldra 270. 4613144 . 2013205 mtdr 207. 2730316 0 . 2430321 1 . 0820981 1 0. 9357985 India tdr 715. 6436516 . 2887613 ldra 715. 6082 . 2050966 mtdr 633. 3191932 0. 9979165 . 2691348 . 0710917 1. 571996 0 1 China tdr 550. 4642772 . 3354967 ldra 550. 4967045 . 2333933 mtdr 349. 1879051 . 218513 0 1. 000002. 0321932 1. 173021 0. 939248
Descriptive statistics Variable Obs Mean Std. Dev. Min Max Brazil tdr 695. 4837643 . 2573974 ldra 695. 6454109 . 3853931 mtdr 591. 3084019 0. 9999782 . 2283234 . 0464127 4. 564894 0. 9985573 Russia tdr 270. 5776321 . 3055938 ldra 270. 4613144 . 2013205 mtdr 207. 2730316 0 . 2430321 1 . 0820981 1 0. 9357985 India tdr 715. 6436516 . 2887613 ldra 715. 6082 . 2050966 mtdr 633. 3191932 0. 9979165 . 2691348 . 0710917 1. 571996 0 1 China tdr 550. 4642772 . 3354967 ldra 550. 4967045 . 2333933 mtdr 349. 1879051 . 218513 0 1. 000002. 0321932 1. 173021 0. 939248
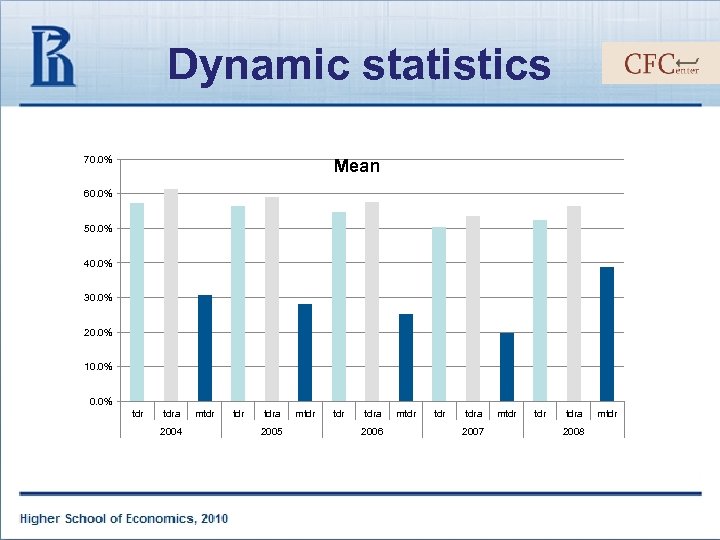 Dynamic statistics 70. 0% Mean 60. 0% 50. 0% 40. 0% 30. 0% 20. 0% 10. 0% tdr tdra 2004 mtdr tdra 2005 mtdr tdra 2006 mtdr tdra 2007 mtdr tdra 2008 mtdr
Dynamic statistics 70. 0% Mean 60. 0% 50. 0% 40. 0% 30. 0% 20. 0% 10. 0% tdr tdra 2004 mtdr tdra 2005 mtdr tdra 2006 mtdr tdra 2007 mtdr tdra 2008 mtdr


