1ba103784e1be92f3651e08ea81ddb97.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 XCON data modeling – NETCONF, RDF and others draft-schulzrinne-sipping-emergency-req-01 draft-sipping-sos Henning Schulzrinne Dept. of Computer Science Columbia University XCON - IETF 62 (March 2005) Minneapolis 1
XCON data modeling – NETCONF, RDF and others draft-schulzrinne-sipping-emergency-req-01 draft-sipping-sos Henning Schulzrinne Dept. of Computer Science Columbia University XCON - IETF 62 (March 2005) Minneapolis 1
 Executive summary • XCON is an instance of a standard problem avoid the IETF tendency to create one-off protocols – excusable a decade ago, recipe for delay now • Provide both “semantic” (tightly constrained) and user interface-oriented interface • Use XForms where user interface is needed • Consider NETCONF for object content manipulation and state retrieval XCON - IETF 62 (March 2005) Minneapolis 2
Executive summary • XCON is an instance of a standard problem avoid the IETF tendency to create one-off protocols – excusable a decade ago, recipe for delay now • Provide both “semantic” (tightly constrained) and user interface-oriented interface • Use XForms where user interface is needed • Consider NETCONF for object content manipulation and state retrieval XCON - IETF 62 (March 2005) Minneapolis 2
 Data representation models • Document model – structured document • RPC model – set/get variables • Data models – RDF – NETCONF – user-interface oriented XCON - IETF 62 (March 2005) Minneapolis 3
Data representation models • Document model – structured document • RPC model – set/get variables • Data models – RDF – NETCONF – user-interface oriented XCON - IETF 62 (March 2005) Minneapolis 3
 “Semantic” description • Tightly described set of properties • No expectation that user interface would directly correspond to each element • No I 18 N issue application maps description elements to UI elements in appropriate language – translation into other languages done by client – and may derive some parts through local policy, rather than user input • Well-defined extension policy XCON - IETF 62 (March 2005) Minneapolis 4
“Semantic” description • Tightly described set of properties • No expectation that user interface would directly correspond to each element • No I 18 N issue application maps description elements to UI elements in appropriate language – translation into other languages done by client – and may derive some parts through local policy, rather than user input • Well-defined extension policy XCON - IETF 62 (March 2005) Minneapolis 4
 RDF • “Resource Description Framework (RDF) is a language for representing information about resources in the World Wide Web. ” • describing resources in terms of simple properties and property values XCON - IETF 62 (March 2005) Minneapolis 5
RDF • “Resource Description Framework (RDF) is a language for representing information about resources in the World Wide Web. ” • describing resources in terms of simple properties and property values XCON - IETF 62 (March 2005) Minneapolis 5
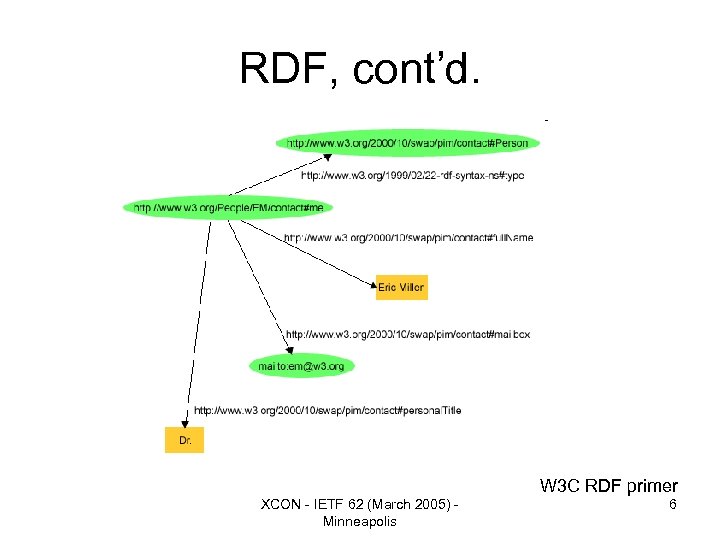 RDF, cont’d. W 3 C RDF primer XCON - IETF 62 (March 2005) Minneapolis 6
RDF, cont’d. W 3 C RDF primer XCON - IETF 62 (March 2005) Minneapolis 6
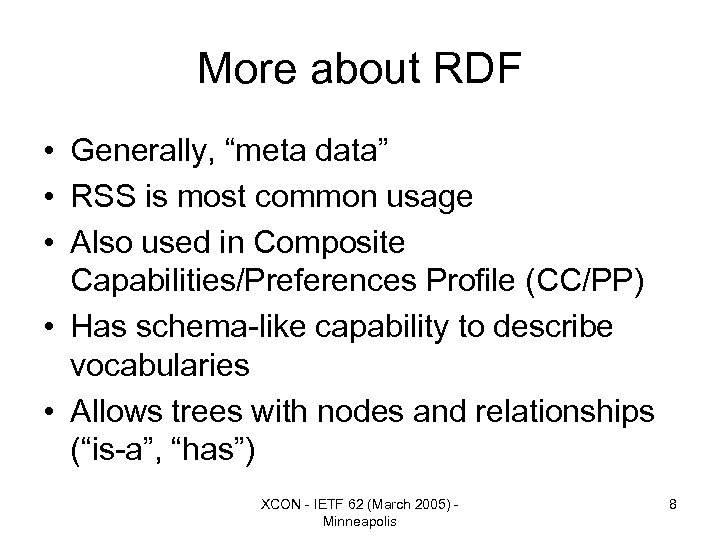 More about RDF • Generally, “meta data” • RSS is most common usage • Also used in Composite Capabilities/Preferences Profile (CC/PP) • Has schema-like capability to describe vocabularies • Allows trees with nodes and relationships (“is-a”, “has”) XCON - IETF 62 (March 2005) Minneapolis 8
More about RDF • Generally, “meta data” • RSS is most common usage • Also used in Composite Capabilities/Preferences Profile (CC/PP) • Has schema-like capability to describe vocabularies • Allows trees with nodes and relationships (“is-a”, “has”) XCON - IETF 62 (March 2005) Minneapolis 8
 RDF: evaluation • Good – limited parameter-value expressiveness – type definition – tools available • Bad: – static document, does not define protocol to get/set elements – would need XCAP, XPath or similar XCON - IETF 62 (March 2005) Minneapolis 9
RDF: evaluation • Good – limited parameter-value expressiveness – type definition – tools available • Bad: – static document, does not define protocol to get/set elements – would need XCAP, XPath or similar XCON - IETF 62 (March 2005) Minneapolis 9
 NETCONF • “The NETCONF protocol defines a simple mechanism through which a network device can be managed, configuration data information can be retrieved, and new configuration data can be uploaded and manipulated. The protocol allows the device to expose a full, formal, application programming interface (API). ” • http: //www. ietf. org/internet-drafts/draft-ietfnetconf-prot-05. txt • Defined to run over HTTP, BEEP, UDP, … XCON - IETF 62 (March 2005) Minneapolis 10
NETCONF • “The NETCONF protocol defines a simple mechanism through which a network device can be managed, configuration data information can be retrieved, and new configuration data can be uploaded and manipulated. The protocol allows the device to expose a full, formal, application programming interface (API). ” • http: //www. ietf. org/internet-drafts/draft-ietfnetconf-prot-05. txt • Defined to run over HTTP, BEEP, UDP, … XCON - IETF 62 (March 2005) Minneapolis 10
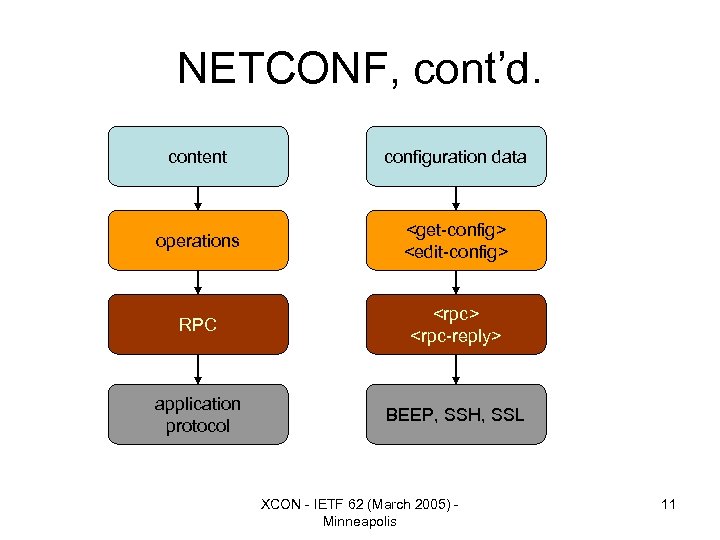 NETCONF, cont’d. content configuration data operations
NETCONF, cont’d. content configuration data operations
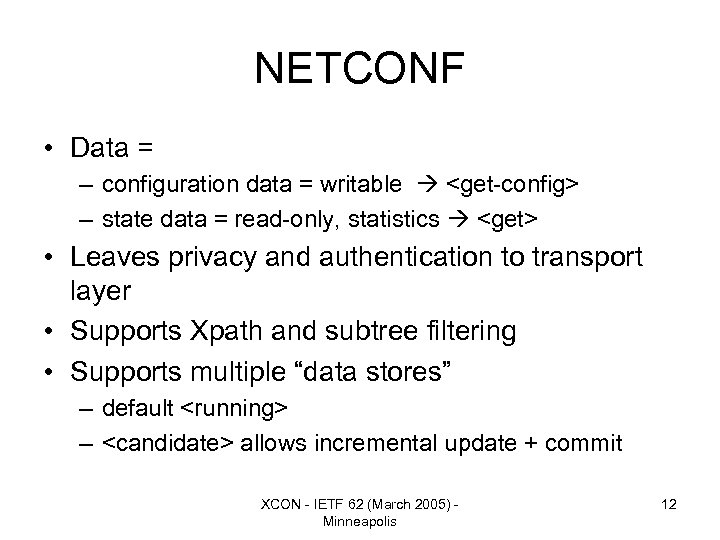 NETCONF • Data = – configuration data = writable
NETCONF • Data = – configuration data = writable
 NETCONF – subtree filtering
NETCONF – subtree filtering
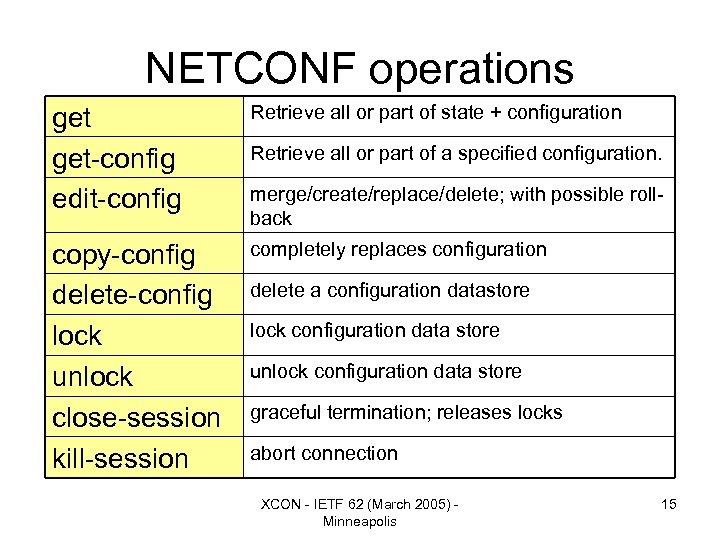 NETCONF operations get-config edit-config Retrieve all or part of state + configuration copy-config delete-config lock unlock close-session kill-session completely replaces configuration Retrieve all or part of a specified configuration. merge/create/replace/delete; with possible rollback delete a configuration datastore lock configuration data store unlock configuration data store graceful termination; releases locks abort connection XCON - IETF 62 (March 2005) Minneapolis 15
NETCONF operations get-config edit-config Retrieve all or part of state + configuration copy-config delete-config lock unlock close-session kill-session completely replaces configuration Retrieve all or part of a specified configuration. merge/create/replace/delete; with possible rollback delete a configuration datastore lock configuration data store unlock configuration data store graceful termination; releases locks abort connection XCON - IETF 62 (March 2005) Minneapolis 15
 User-interface oriented • Describe suggested rendering on controlling client without client knowing meaning of controls – element names are just labels – e. g. , can’t gateway to other systems based on equivalence • user interface can change at any time • Element names are text strings, not XML elements – no schema verification possible XCON - IETF 62 (March 2005) Minneapolis 17
User-interface oriented • Describe suggested rendering on controlling client without client knowing meaning of controls – element names are just labels – e. g. , can’t gateway to other systems based on equivalence • user interface can change at any time • Element names are text strings, not XML elements – no schema verification possible XCON - IETF 62 (March 2005) Minneapolis 17
 User-interface oriented • Client software does not need to understand meaning of terms – just variables and prompts – includes necessary prompts and structure – needs to be translated into different languages by server • Existing work: XForms – http: //www. w 3. org/Mark. Up/Forms/2003/xforms-for-html-authors • Allows use of CSS to render on variety of devices • Allows use of Java. Script for client-side verification • Specifies type of control (“selection”), not rendering (“radio button”, “select list”) • Suggestion: allow as alternate representation XCON - IETF 62 (March 2005) Minneapolis 18
User-interface oriented • Client software does not need to understand meaning of terms – just variables and prompts – includes necessary prompts and structure – needs to be translated into different languages by server • Existing work: XForms – http: //www. w 3. org/Mark. Up/Forms/2003/xforms-for-html-authors • Allows use of CSS to render on variety of devices • Allows use of Java. Script for client-side verification • Specifies type of control (“selection”), not rendering (“radio button”, “select list”) • Suggestion: allow as alternate representation XCON - IETF 62 (March 2005) Minneapolis 18
 XForms example
XForms example
 Conclusion • If desired, XForms provides rich user interaction environment • NETCONF provides flexible configuration retrieval mechanism, with extensibility – incremental configuration + commit – stored configurations (startup, running, candidate) – XPath and subtree selection – no constraints on configuration content XCON - IETF 62 (March 2005) Minneapolis 20
Conclusion • If desired, XForms provides rich user interaction environment • NETCONF provides flexible configuration retrieval mechanism, with extensibility – incremental configuration + commit – stored configurations (startup, running, candidate) – XPath and subtree selection – no constraints on configuration content XCON - IETF 62 (March 2005) Minneapolis 20


