X-Rays Radiation Application in Medicine IONIZING RADIATION





- Размер: 9.4 Mегабайта
- Количество слайдов: 17
Описание презентации X-Rays Radiation Application in Medicine IONIZING RADIATION по слайдам
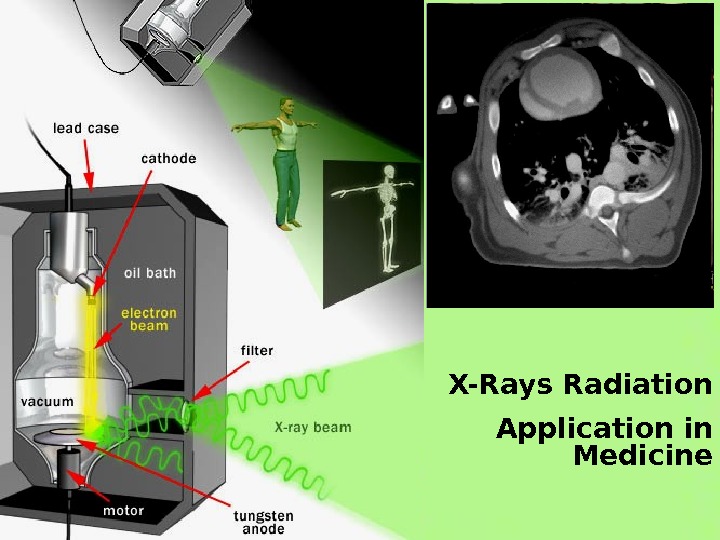
 X-Rays Radiation Application in Medicine
X-Rays Radiation Application in Medicine
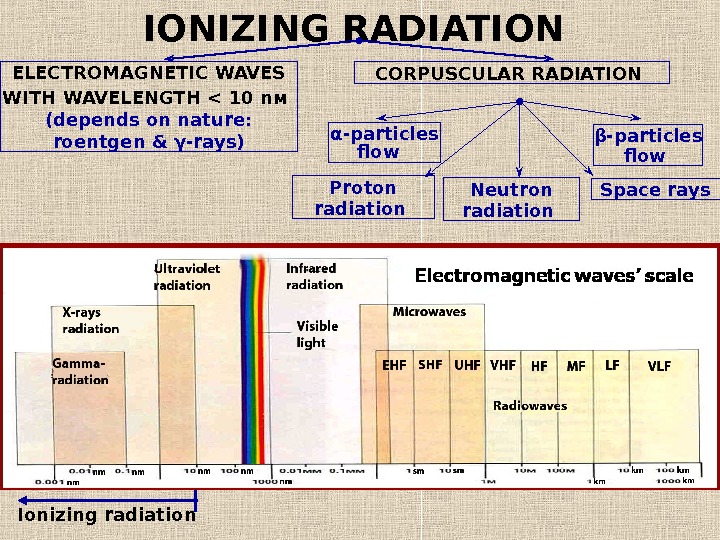
 IONIZING RADIATION ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES WITH WAVELENGTH < 10 n м ( depends on nature : roentgen & γ- rays ) CORPUSCULAR RADIATION α — particles flow Proton radiation Space raysβ — particles flow Neutron radiation Ionizing radiat іо n Electromagnetic waves’ scale
IONIZING RADIATION ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES WITH WAVELENGTH < 10 n м ( depends on nature : roentgen & γ- rays ) CORPUSCULAR RADIATION α — particles flow Proton radiation Space raysβ — particles flow Neutron radiation Ionizing radiat іо n Electromagnetic waves’ scale
 W. Roentgen – is an author of fundamental works in different fields of experimental physics. 1895 he discovered new kind of rays & called them X-Rays. These rays are known now as Roentgen Rays. He made the first roentgen pictures – pictures of his & his wife’s arms. ROENTGEN RADIATION is electromagnetic waves with wavelength 10 е V. hc h. E Wilhelm Roentgen (1845 -1923), germany physicist – experimentalist, Nobel prize laureate (1901) HYSTORY OF X-RAYS DISCOVERY
W. Roentgen – is an author of fundamental works in different fields of experimental physics. 1895 he discovered new kind of rays & called them X-Rays. These rays are known now as Roentgen Rays. He made the first roentgen pictures – pictures of his & his wife’s arms. ROENTGEN RADIATION is electromagnetic waves with wavelength 10 е V. hc h. E Wilhelm Roentgen (1845 -1923), germany physicist – experimentalist, Nobel prize laureate (1901) HYSTORY OF X-RAYS DISCOVERY
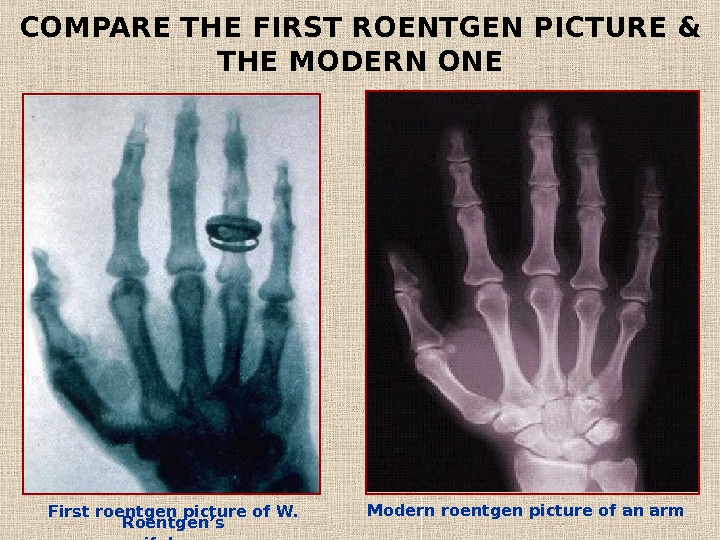
 First roentgen picture of W. Roentgen’s wife’s arm. COMPARE THE FIRST ROENTGEN PICTURE & THE MODERN ONE Modern roentgen picture of an arm
First roentgen picture of W. Roentgen’s wife’s arm. COMPARE THE FIRST ROENTGEN PICTURE & THE MODERN ONE Modern roentgen picture of an arm
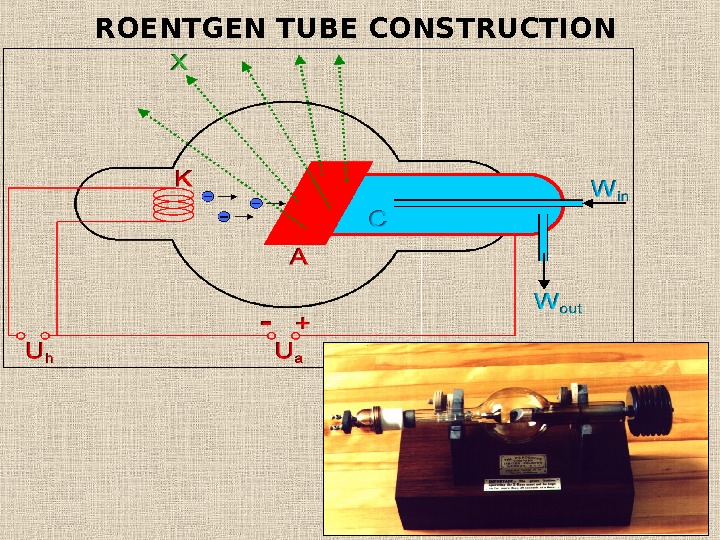
 ROENTGEN TUBE CONSTRUCTION
ROENTGEN TUBE CONSTRUCTION
 ROENTGEN RADIATION Braking (Bremsstrahlung) characteristic Braking (Bremsstrahlung) radiation U 1 < U 2 < U 3 Ф 123 λUe=hν Bremsstrahlung(from Germanbremsen(to brake) and. Strahlung(radiation)) is X ray radiation (green) emitted by charged particles, such as electrons (yellow), which are braking around other charged particles, such as an atom nucleus (blue)
ROENTGEN RADIATION Braking (Bremsstrahlung) characteristic Braking (Bremsstrahlung) radiation U 1 < U 2 < U 3 Ф 123 λUe=hν Bremsstrahlung(from Germanbremsen(to brake) and. Strahlung(radiation)) is X ray radiation (green) emitted by charged particles, such as electrons (yellow), which are braking around other charged particles, such as an atom nucleus (blue)
 , BZA А, В= const , Z – element number. CHARACTERISTIC RADIATION When a sample is bombarded by an electron beam, some electrons are knocked out of their shells in a process called inner-shell ionization. About 0. 1% of the electrons produce K-shell vacancies; most produce heat. Outer-shell electrons fall in to fill a vacancy in a process of self-neutralization. The energy required to produce inner-shell ionization is termed the excitation potential or critical ionization potential (E c ). MOZLY LAW
, BZA А, В= const , Z – element number. CHARACTERISTIC RADIATION When a sample is bombarded by an electron beam, some electrons are knocked out of their shells in a process called inner-shell ionization. About 0. 1% of the electrons produce K-shell vacancies; most produce heat. Outer-shell electrons fall in to fill a vacancy in a process of self-neutralization. The energy required to produce inner-shell ionization is termed the excitation potential or critical ionization potential (E c ). MOZLY LAW
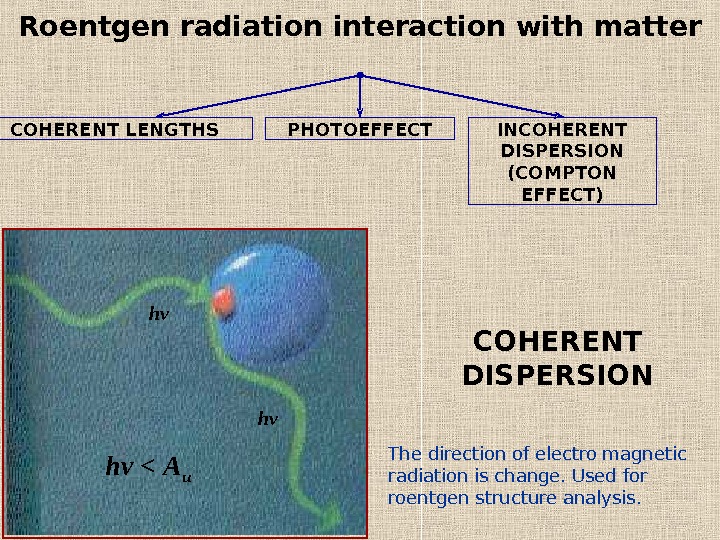
 Roentgen radiation interaction with matter COHERENT LENGTHS INCOHERENT DISPERSION (COMPTON EFFECT)PHOTOEFFECT COHERENT DISPERSIONhν hν hν < A и The direction of electro magnetic radiation is change. Used for roentgen structure analysis.
Roentgen radiation interaction with matter COHERENT LENGTHS INCOHERENT DISPERSION (COMPTON EFFECT)PHOTOEFFECT COHERENT DISPERSIONhν hν hν < A и The direction of electro magnetic radiation is change. Used for roentgen structure analysis.
 Due tothe phenomenaof diffractionandinterference of. X-rayson a crystalona photographic plate, behind the crystal, symmetricalpatternofspots (Lauegram) appears. German scientist. Maxvon. Laue(1879 -1960)was the first who predicted thepossibility of using. X-raysto determine the structureof bodies. Lauehramreading whenthe structure of crystal is unknown — a difficulttask. If thestructure of thecrystalis known, the. Lauemethodallows todeterminethe wavelengths, to make. Roentgenspectroscopy. Lauehram Letthe distancebetween the twocrystal-planewemarkedbyd. Twoparallelon-me 1 and 2 are fallingat an angleαto theseplanesanddiffractsations. A and B. diffractedrays 1 ‘and 2’interfere, and ifthe beam 2. 2’has relativelybeam 1. 1’path differenceequal tol ora wholemultipleof it, theirintensityyutsyacomplexity. Spot ona photographic plateoccursonly whenstrictlyacorner, whichis performedforconditions of Bragg: , . . . )2, 1(, sin 2 kkd. For this purposeit is better touse the methoddeveloped by father and son. Braggs. Eachcrystalcan be imagined asa set of separateparallellayersof ions oratoms, called thecrystalplanes. COHERENT LENGTHS US
Due tothe phenomenaof diffractionandinterference of. X-rayson a crystalona photographic plate, behind the crystal, symmetricalpatternofspots (Lauegram) appears. German scientist. Maxvon. Laue(1879 -1960)was the first who predicted thepossibility of using. X-raysto determine the structureof bodies. Lauehramreading whenthe structure of crystal is unknown — a difficulttask. If thestructure of thecrystalis known, the. Lauemethodallows todeterminethe wavelengths, to make. Roentgenspectroscopy. Lauehram Letthe distancebetween the twocrystal-planewemarkedbyd. Twoparallelon-me 1 and 2 are fallingat an angleαto theseplanesanddiffractsations. A and B. diffractedrays 1 ‘and 2’interfere, and ifthe beam 2. 2’has relativelybeam 1. 1’path differenceequal tol ora wholemultipleof it, theirintensityyutsyacomplexity. Spot ona photographic plateoccursonly whenstrictlyacorner, whichis performedforconditions of Bragg: , . . . )2, 1(, sin 2 kkd. For this purposeit is better touse the methoddeveloped by father and son. Braggs. Eachcrystalcan be imagined asa set of separateparallellayersof ions oratoms, called thecrystalplanes. COHERENT LENGTHS US
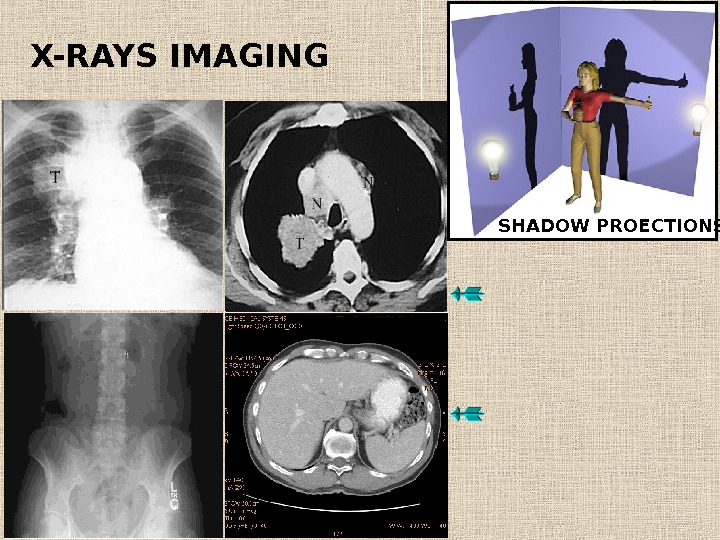
 X-RAYS IMAGING SHADOW PROECTIONS
X-RAYS IMAGING SHADOW PROECTIONS
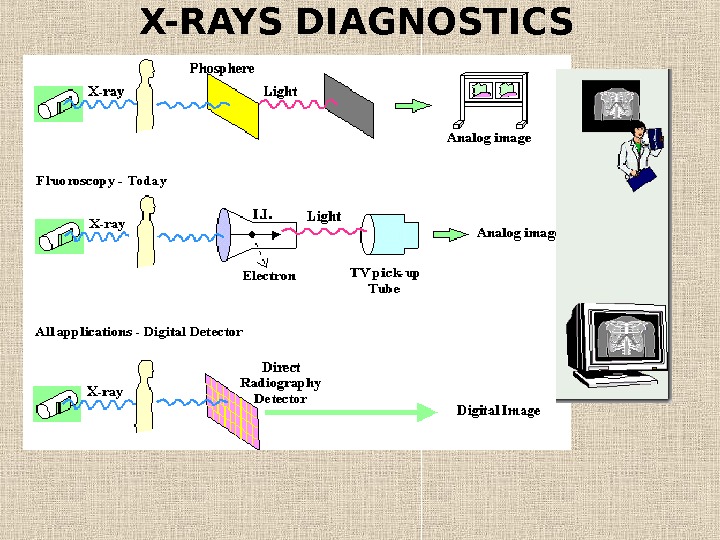
 X-RAYS DIAGNOSTICS
X-RAYS DIAGNOSTICS
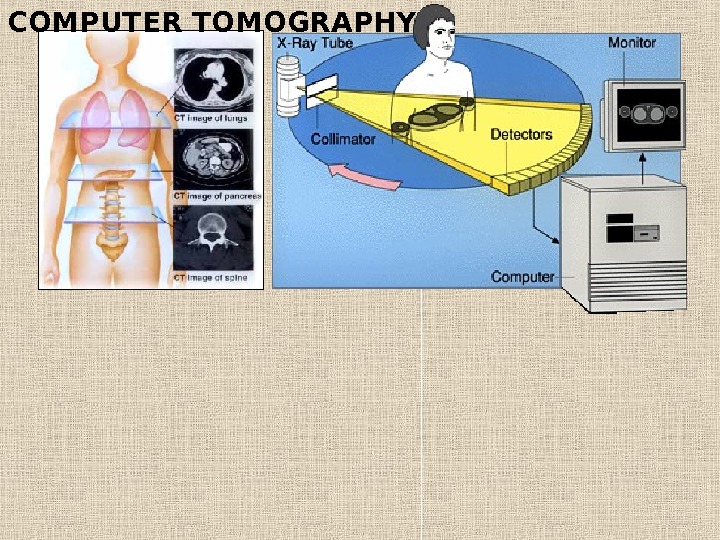
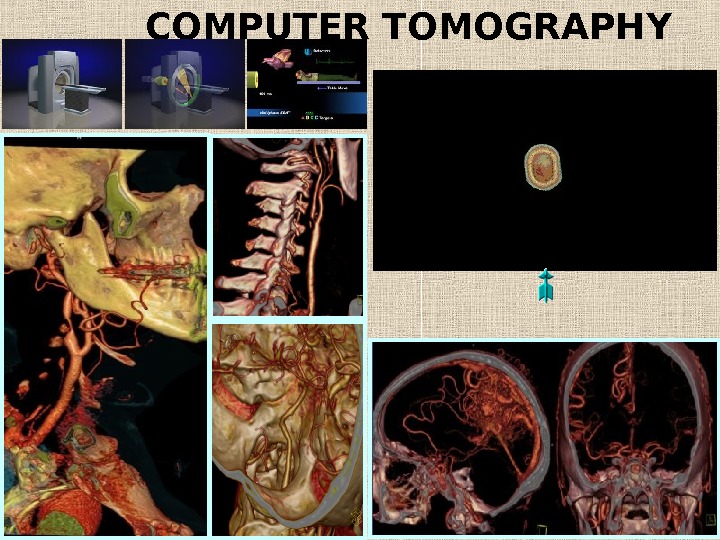
 COMPUTER TOMOGRAPHY
COMPUTER TOMOGRAPHY
 COMPUTER TOMOGRAPHY
COMPUTER TOMOGRAPHY
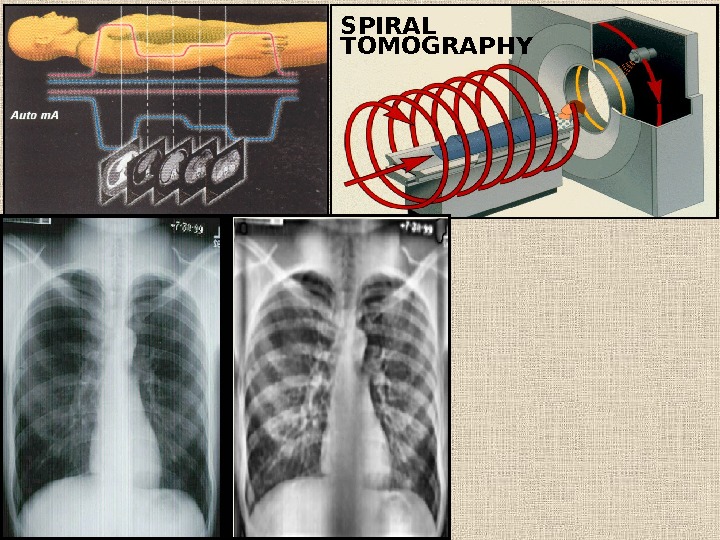
 SPIRAL TOMOGRAPHY
SPIRAL TOMOGRAPHY
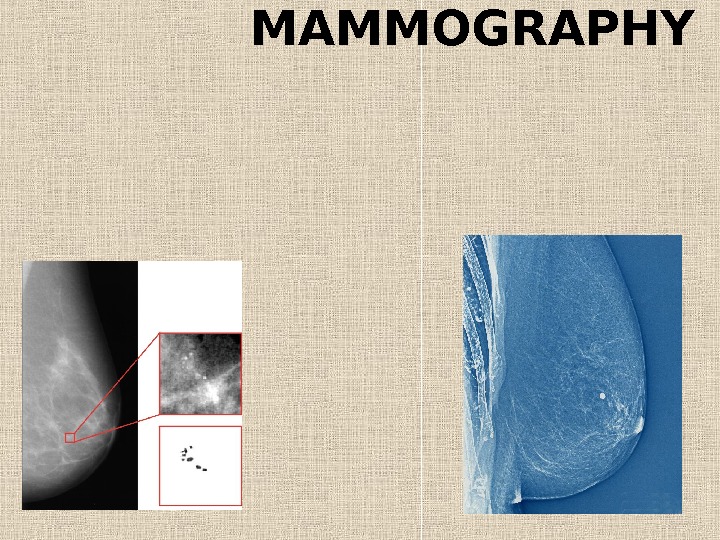
 MAMMOGRAPHY
MAMMOGRAPHY
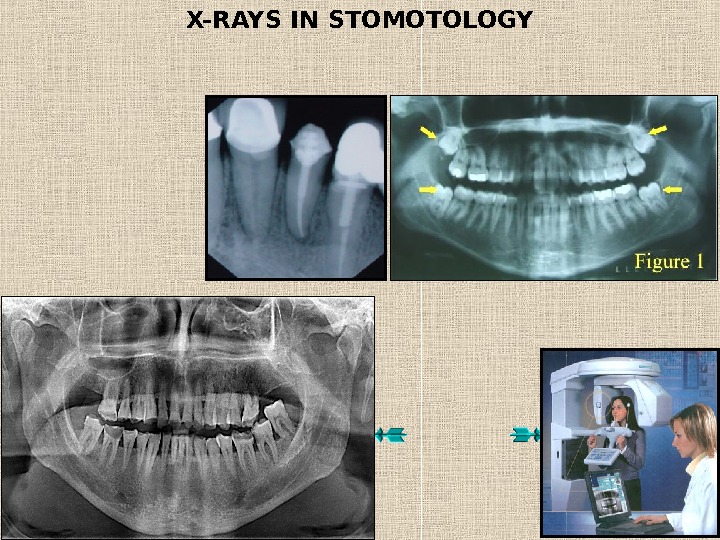
 X-RAYS IN STOMOTOLOGY
X-RAYS IN STOMOTOLOGY
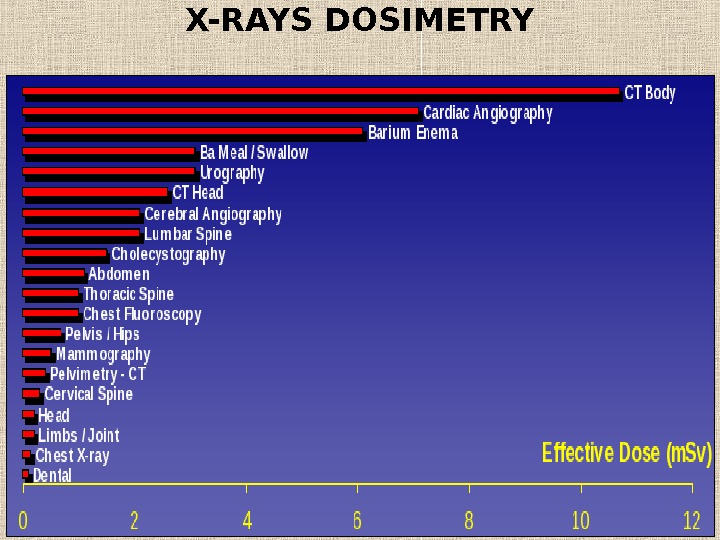
 X-RAYS DOSIMETRY
X-RAYS DOSIMETRY

