14fdd887d11317f1fdfe9fb0f2ddbff0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 63
 X 4 L SDi. T - Survey Data in Teaching A resource for students and teachers Module 1 UK Data Archive 2003
X 4 L SDi. T - Survey Data in Teaching A resource for students and teachers Module 1 UK Data Archive 2003
 Module 1 Has Crime gone up? Police Recorded Crime Figures: Trends and Reasons for Change UK Data Archive 2003
Module 1 Has Crime gone up? Police Recorded Crime Figures: Trends and Reasons for Change UK Data Archive 2003
 In this module • • You find out how crime is measured You find out what has been happening to crime rates You examine the effectiveness of different governments on crime You try to figure out what you would do UK Data Archive 2003
In this module • • You find out how crime is measured You find out what has been happening to crime rates You examine the effectiveness of different governments on crime You try to figure out what you would do UK Data Archive 2003
 Section A: Police Recorded Crime Figures • In this module we look at how Police Recorded Crime Figures can be used to describe the extent of crime (or, to put a more positive slant, the extent of ‘lawfulness’) in England Wales UK Data Archive 2003
Section A: Police Recorded Crime Figures • In this module we look at how Police Recorded Crime Figures can be used to describe the extent of crime (or, to put a more positive slant, the extent of ‘lawfulness’) in England Wales UK Data Archive 2003
 Section A: Police Recorded Crime Figures • But what constitutes a ‘crime’ and how are they defined and counted? Police Recorded Crime Figures depend on the police being aware that an act that the Home Office considers a crime occurred. Box 1. 1 sets out how crime is defined by the police UK Data Archive 2003
Section A: Police Recorded Crime Figures • But what constitutes a ‘crime’ and how are they defined and counted? Police Recorded Crime Figures depend on the police being aware that an act that the Home Office considers a crime occurred. Box 1. 1 sets out how crime is defined by the police UK Data Archive 2003
 Box 1. 1 Factors Influencing Police Recording of Crime Factors influencing police recording of crime The number of crimes that are recorded by the police are dependent on two factors. Firstly, whether the victim or a representative of the victim brings that crime to the attention of the police or on the crime coming to the attention of the police through some other means (such as the police officer being present at the time). Secondly, whether that incident is determined as being a recordable offence within the categories laid down by the Home Office in the official counting rules. The Home Office Counting Rules were amended in 1998, adding a large number of crimes to the total recorded by the police, particularly in the categories of less serious violent crimes, frauds and drug offences. UK Data Archive 2003
Box 1. 1 Factors Influencing Police Recording of Crime Factors influencing police recording of crime The number of crimes that are recorded by the police are dependent on two factors. Firstly, whether the victim or a representative of the victim brings that crime to the attention of the police or on the crime coming to the attention of the police through some other means (such as the police officer being present at the time). Secondly, whether that incident is determined as being a recordable offence within the categories laid down by the Home Office in the official counting rules. The Home Office Counting Rules were amended in 1998, adding a large number of crimes to the total recorded by the police, particularly in the categories of less serious violent crimes, frauds and drug offences. UK Data Archive 2003
 Box 1. 1 Factors Influencing Police Recording of Crime Factors influencing police recording of crime The Home Office Counting Rules were revised again last year in order to incorporate the new National Crime Recording Standard (NCRS), which aims to introduce a greater degree of consistency to the ways in which crime is recorded in different police forces and to ensure that there is a comprehensive record of all crimes that are reported to the police by victims. These changes were fully introduced across all police forces from April 2002, and so have had an impact on the recorded crime statistics reported on here. There has also been a more general impetus over recent years, both from the Association of Chief Police Officers (ACPO) and from the Home Office, to increase the recording of crimes reported to the police which will also have impacted on the recorded crime figures. Simmons and Dodd, Home Office Statistical Bulletin, 2003, p. 14 UK Data Archive 2003
Box 1. 1 Factors Influencing Police Recording of Crime Factors influencing police recording of crime The Home Office Counting Rules were revised again last year in order to incorporate the new National Crime Recording Standard (NCRS), which aims to introduce a greater degree of consistency to the ways in which crime is recorded in different police forces and to ensure that there is a comprehensive record of all crimes that are reported to the police by victims. These changes were fully introduced across all police forces from April 2002, and so have had an impact on the recorded crime statistics reported on here. There has also been a more general impetus over recent years, both from the Association of Chief Police Officers (ACPO) and from the Home Office, to increase the recording of crimes reported to the police which will also have impacted on the recorded crime figures. Simmons and Dodd, Home Office Statistical Bulletin, 2003, p. 14 UK Data Archive 2003
 So the extent of criminal activity that is recorded from year to year reflects three factors: 1. The number of people reporting to the police that they (or someone they represent) were a victim 2. The number of reported incidents that the police accept met the definition of a crime. 3. Any change to the definition of what constitutes a crime. UK Data Archive 2003
So the extent of criminal activity that is recorded from year to year reflects three factors: 1. The number of people reporting to the police that they (or someone they represent) were a victim 2. The number of reported incidents that the police accept met the definition of a crime. 3. Any change to the definition of what constitutes a crime. UK Data Archive 2003
 • Over the years, the government has changed several times the way the police’s ‘official’ figures are calculated. Thus comparisons across years of changing rates of crime becomes difficult. • While the actual number of Crimes recorded by police during the period 1981 -2003 can be set out in a table, a better way to view these figures as a trend is shown in Figure 1. 1. Here we present exactly the same information as a line graph. UK Data Archive 2003
• Over the years, the government has changed several times the way the police’s ‘official’ figures are calculated. Thus comparisons across years of changing rates of crime becomes difficult. • While the actual number of Crimes recorded by police during the period 1981 -2003 can be set out in a table, a better way to view these figures as a trend is shown in Figure 1. 1. Here we present exactly the same information as a line graph. UK Data Archive 2003
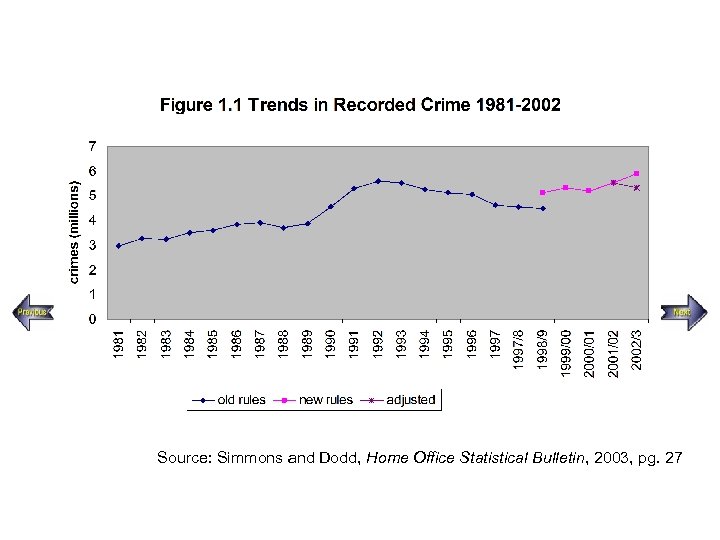 Source: Simmons and Dodd, Home Office Statistical Bulletin, 2003, pg. 27 UK Data Archive 2003
Source: Simmons and Dodd, Home Office Statistical Bulletin, 2003, pg. 27 UK Data Archive 2003
 From 1998 onwards the government began to count a greater range of crimes than it had done previously, which increased the count by approximately 15%. There were two reasons for the change: – More minor drug offences, types of fraud and less ‘serious’ violent incidents were added – There was an attempt to make the definitions consistent among all police forces (remember the definitions set out earlier in in Box 1. 1? ). UK Data Archive 2003
From 1998 onwards the government began to count a greater range of crimes than it had done previously, which increased the count by approximately 15%. There were two reasons for the change: – More minor drug offences, types of fraud and less ‘serious’ violent incidents were added – There was an attempt to make the definitions consistent among all police forces (remember the definitions set out earlier in in Box 1. 1? ). UK Data Archive 2003
 • Furthermore, the introduction of the National Crime Recording Standard (NCRS) in 2002 -03 has led to a further rise of approximately 10%. However, after adjusting for the latter changes, estimates suggest that recorded crime actually fell by 3% between 2001 -02 and 2002 -03 – and did not increase by 7% as suggested by the previous graphs. UK Data Archive 2003
• Furthermore, the introduction of the National Crime Recording Standard (NCRS) in 2002 -03 has led to a further rise of approximately 10%. However, after adjusting for the latter changes, estimates suggest that recorded crime actually fell by 3% between 2001 -02 and 2002 -03 – and did not increase by 7% as suggested by the previous graphs. UK Data Archive 2003
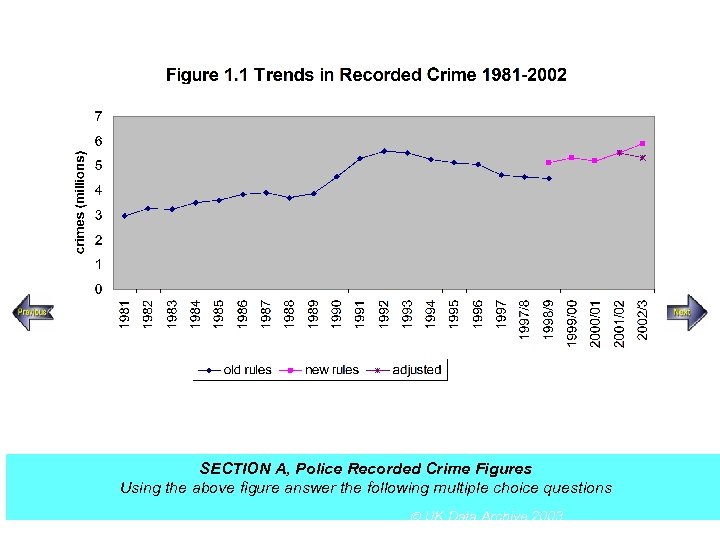 SECTION A, Police Recorded Crime Figures Using the above figure answer the following multiple choice questions UK Data Archive 2003
SECTION A, Police Recorded Crime Figures Using the above figure answer the following multiple choice questions UK Data Archive 2003
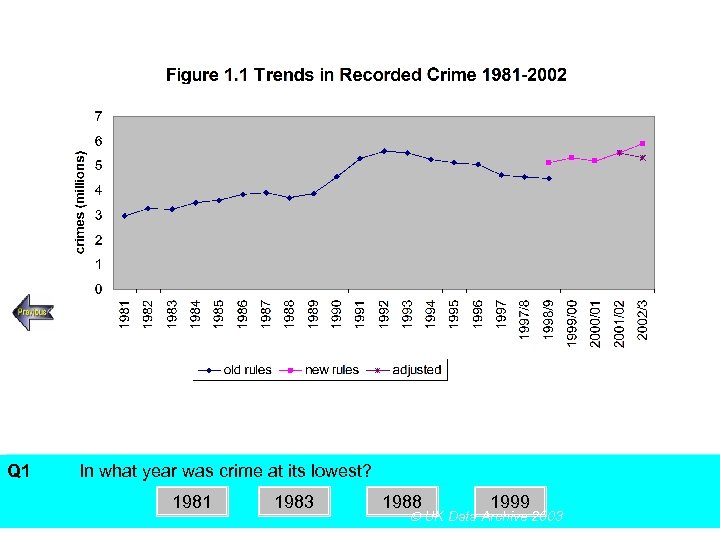 Q 1 SECTION A, Police Recorded Crime Figures In what year was crime at its lowest? Using the above figureanswer the following multiple choice questions 1981 1983 1988 1999 UK Data Archive 2003
Q 1 SECTION A, Police Recorded Crime Figures In what year was crime at its lowest? Using the above figureanswer the following multiple choice questions 1981 1983 1988 1999 UK Data Archive 2003
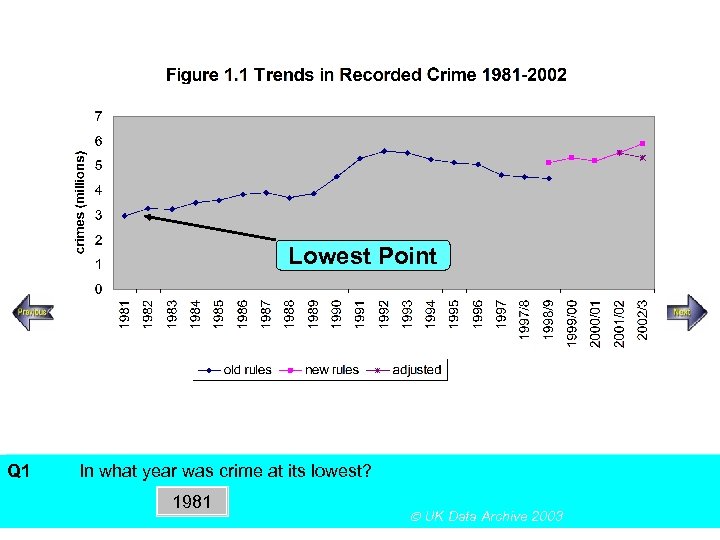 Lowest Point Q 1 SECTION A, Police Recorded Crime Figures In what year was crime at its lowest? Using the above figureanswer the following multiple choice questions 1981 UK Data Archive 2003
Lowest Point Q 1 SECTION A, Police Recorded Crime Figures In what year was crime at its lowest? Using the above figureanswer the following multiple choice questions 1981 UK Data Archive 2003
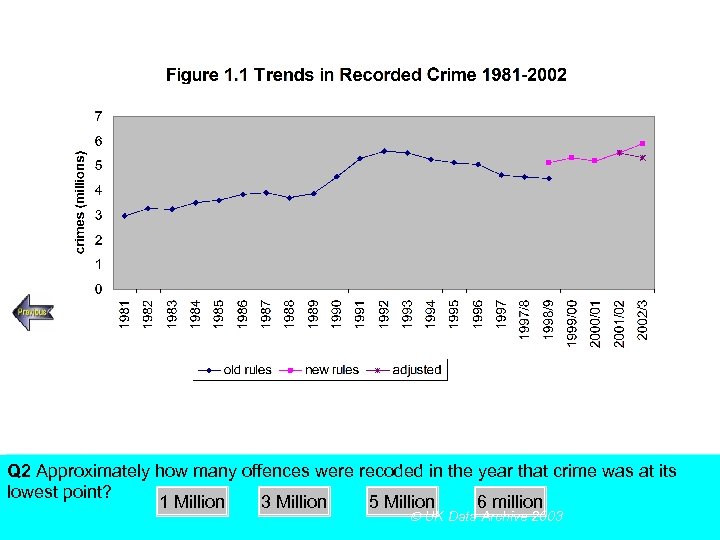 SECTION A, Police Recorded Crime Figures Q 2 Approximately how many offences were recoded in the year that crime was at its lowest point? Using the above figureanswer the following multiple choice questions 1 Million 3 Million 5 Million 6 million UK Data Archive 2003
SECTION A, Police Recorded Crime Figures Q 2 Approximately how many offences were recoded in the year that crime was at its lowest point? Using the above figureanswer the following multiple choice questions 1 Million 3 Million 5 Million 6 million UK Data Archive 2003
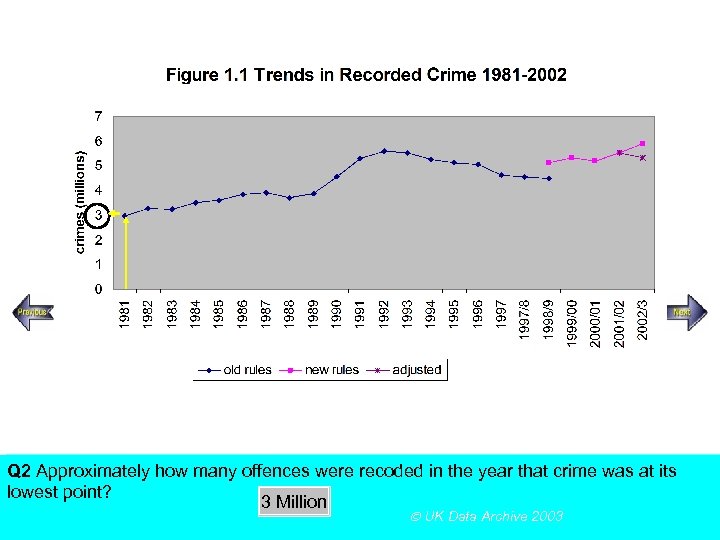 SECTION A, Police Recorded Crime Figures Q 2 Approximately how many offences were recoded in the year that crime was at its lowest point? Using the above figureanswer the following multiple choice questions 3 Million UK Data Archive 2003
SECTION A, Police Recorded Crime Figures Q 2 Approximately how many offences were recoded in the year that crime was at its lowest point? Using the above figureanswer the following multiple choice questions 3 Million UK Data Archive 2003
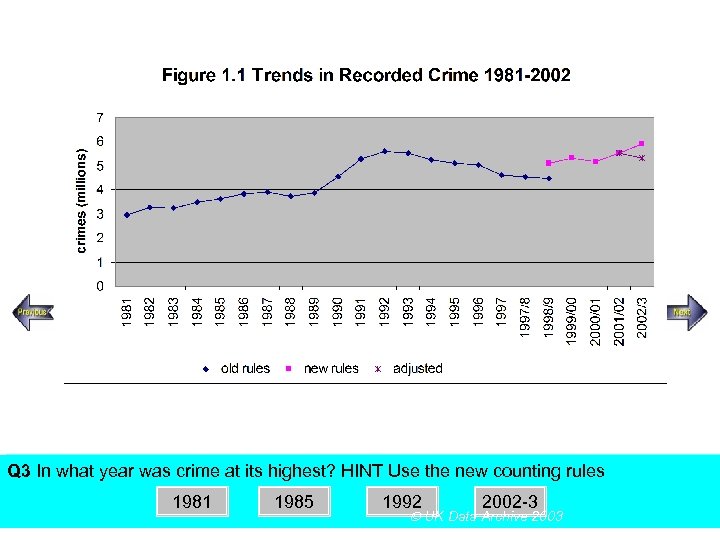 SECTION A, Police Recorded Crime Figures Q 3 In what year was crime at its highest? HINT Use the new counting rules Using the above figureanswer the following multiple choice questions 1981 1985 1992 2002 -3 UK Data Archive 2003
SECTION A, Police Recorded Crime Figures Q 3 In what year was crime at its highest? HINT Use the new counting rules Using the above figureanswer the following multiple choice questions 1981 1985 1992 2002 -3 UK Data Archive 2003
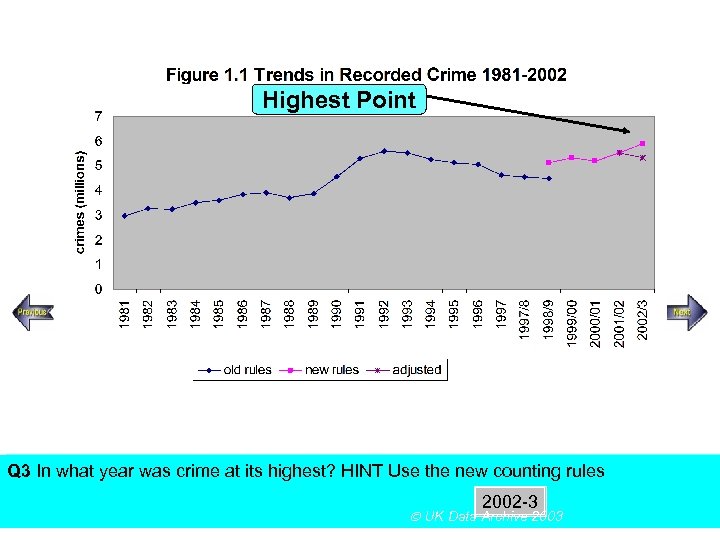 Highest Point SECTION A, Police Recorded Crime Figures Q 3 In what year was crime at its highest? HINT Use the new counting rules Using the above figureanswer the following multiple choice questions 2002 -3 UK Data Archive 2003
Highest Point SECTION A, Police Recorded Crime Figures Q 3 In what year was crime at its highest? HINT Use the new counting rules Using the above figureanswer the following multiple choice questions 2002 -3 UK Data Archive 2003
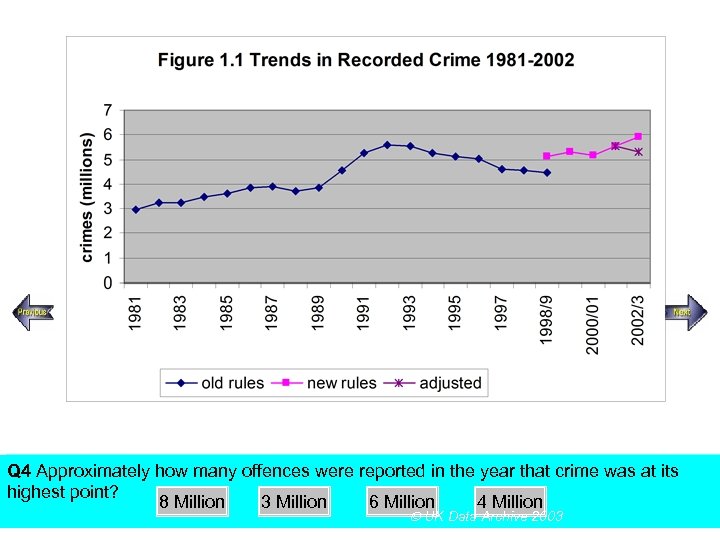 SECTION A, Police Recorded Crime Figures Q 4 Approximately how many offences were reported in the year that crime was at its highest point? Using the above figureanswer the following multiple choice questions 8 Million 3 Million 6 Million 4 Million UK Data Archive 2003
SECTION A, Police Recorded Crime Figures Q 4 Approximately how many offences were reported in the year that crime was at its highest point? Using the above figureanswer the following multiple choice questions 8 Million 3 Million 6 Million 4 Million UK Data Archive 2003
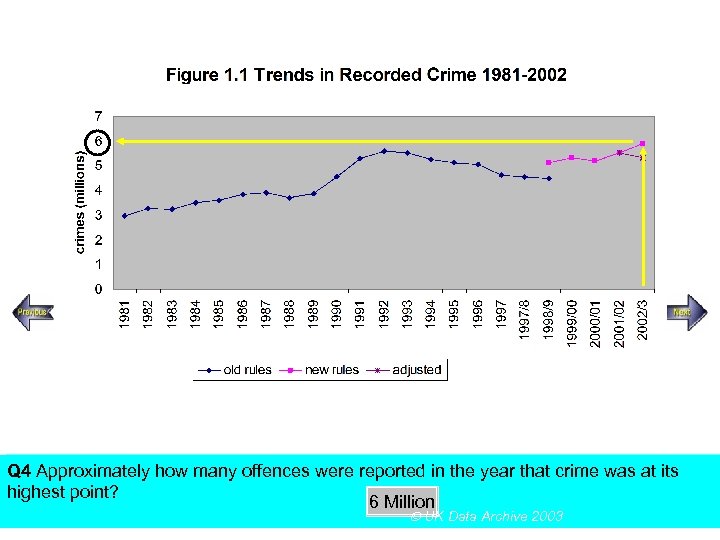 SECTION A, Police Recorded Crime Figures Q 4 Approximately how many offences were reported in the year that crime was at its highest point? Using the above figureanswer the following multiple choice questions 6 Million UK Data Archive 2003
SECTION A, Police Recorded Crime Figures Q 4 Approximately how many offences were reported in the year that crime was at its highest point? Using the above figureanswer the following multiple choice questions 6 Million UK Data Archive 2003
 Q 5 Identify in which years Margaret Thatcher was Prime Minister Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. HINT: check the web site Prime Ministers in history http: //www. number 10. gov. uk/output/page 123. asp UK Data Archive 2003
Q 5 Identify in which years Margaret Thatcher was Prime Minister Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. HINT: check the web site Prime Ministers in history http: //www. number 10. gov. uk/output/page 123. asp UK Data Archive 2003
 Q 5 Identify in which years Margaret Thatcher was Prime Minister (1979 -90) Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. HINT: check the web site Prime Ministers in history http: //www. number 10. gov. uk/output/page 123. asp UK Data Archive 2003
Q 5 Identify in which years Margaret Thatcher was Prime Minister (1979 -90) Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. HINT: check the web site Prime Ministers in history http: //www. number 10. gov. uk/output/page 123. asp UK Data Archive 2003
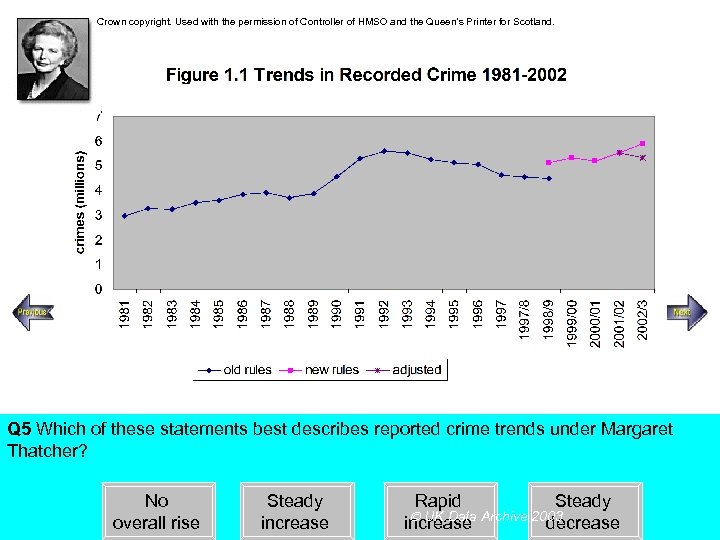 Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. Steady increase Rapid increase Q 5 Which of these statements best describes reported crime trends under Margaret Thatcher? No overall rise Steady increase Rapid Steady UK Data Archive 2003 increase decrease
Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. Steady increase Rapid increase Q 5 Which of these statements best describes reported crime trends under Margaret Thatcher? No overall rise Steady increase Rapid Steady UK Data Archive 2003 increase decrease
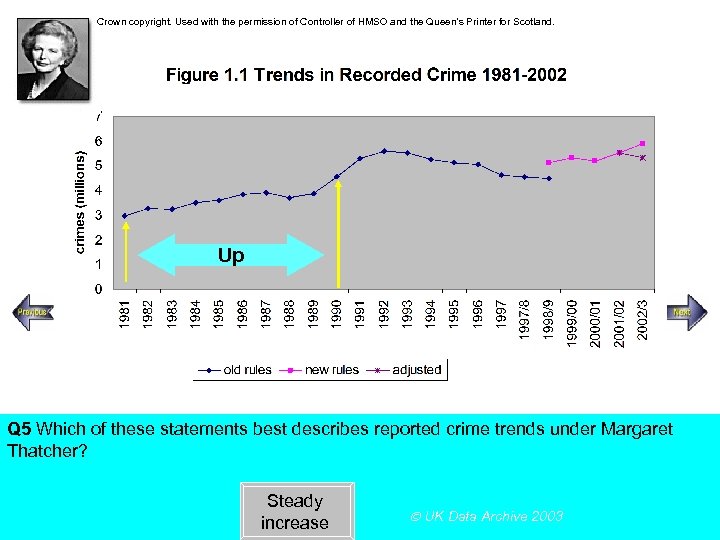 Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. Steady increase Rapid increase Up Q 5 Which of these statements best describes reported crime trends under Margaret Thatcher? Steady increase UK Data Archive 2003
Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. Steady increase Rapid increase Up Q 5 Which of these statements best describes reported crime trends under Margaret Thatcher? Steady increase UK Data Archive 2003
 What do you think? • Using only the data presented above, can we say with certainty whether Margaret Thatcher’s law and order policies were a success or not? • If you cannot be certain, what other information/data would you want? UK Data Archive 2003
What do you think? • Using only the data presented above, can we say with certainty whether Margaret Thatcher’s law and order policies were a success or not? • If you cannot be certain, what other information/data would you want? UK Data Archive 2003
 Q 6 Identify in which years John Major was Prime Minister Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. UK Data Archive 2003
Q 6 Identify in which years John Major was Prime Minister Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. UK Data Archive 2003
 Q 6 Identify in which years John Major was Prime Minister (1990 -97) Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. UK Data Archive 2003
Q 6 Identify in which years John Major was Prime Minister (1990 -97) Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. UK Data Archive 2003
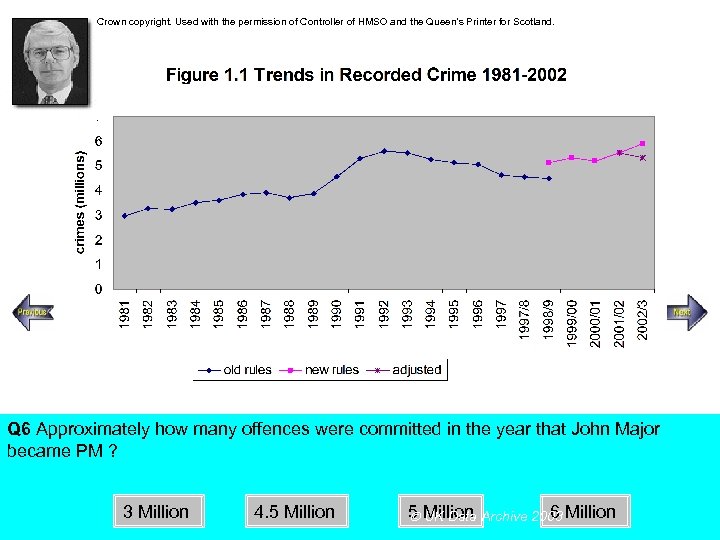 Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. Steady increase Rapid increase Q 6 Approximately how many offences were committed in the year that John Major became PM ? 3 Million 4. 5 Million 6 Million UK Data Archive 2003
Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. Steady increase Rapid increase Q 6 Approximately how many offences were committed in the year that John Major became PM ? 3 Million 4. 5 Million 6 Million UK Data Archive 2003
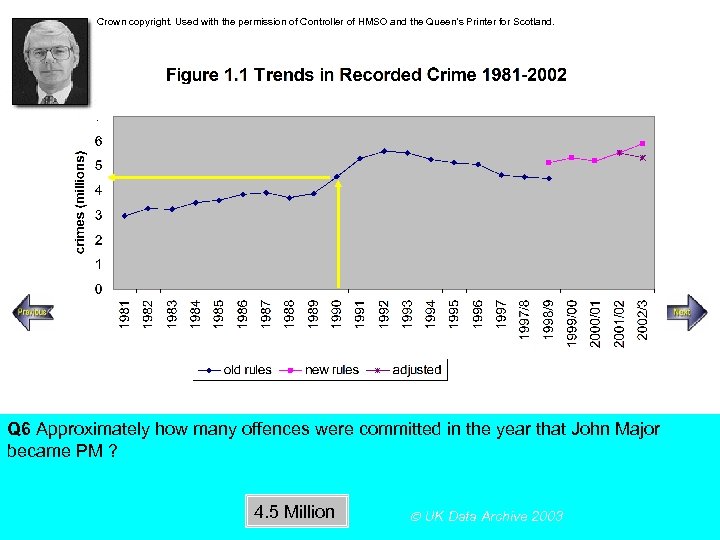 Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. Steady increase Rapid increase Q 6 Approximately how many offences were committed in the year that John Major became PM ? 4. 5 Million UK Data Archive 2003
Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. Steady increase Rapid increase Q 6 Approximately how many offences were committed in the year that John Major became PM ? 4. 5 Million UK Data Archive 2003
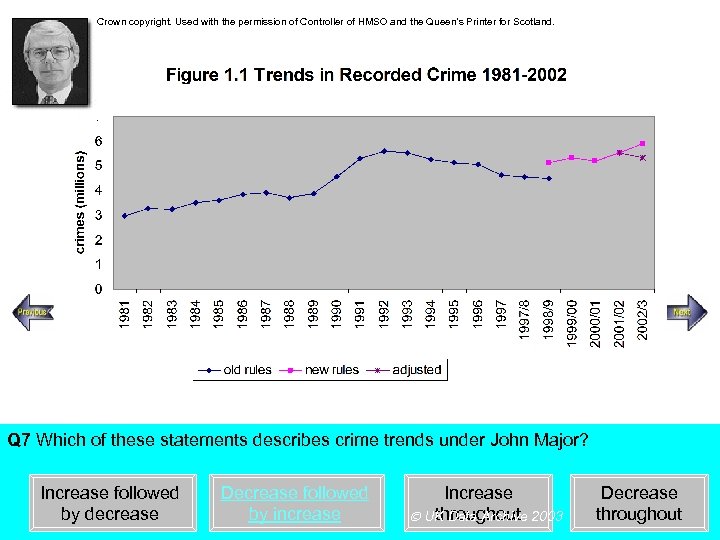 Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. Steady increase Rapid increase Q 7 Which of these statements describes crime trends under John Major? Increase followed by decrease Decrease followed by increase Increase throughout UK Data Archive 2003 Decrease throughout
Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. Steady increase Rapid increase Q 7 Which of these statements describes crime trends under John Major? Increase followed by decrease Decrease followed by increase Increase throughout UK Data Archive 2003 Decrease throughout
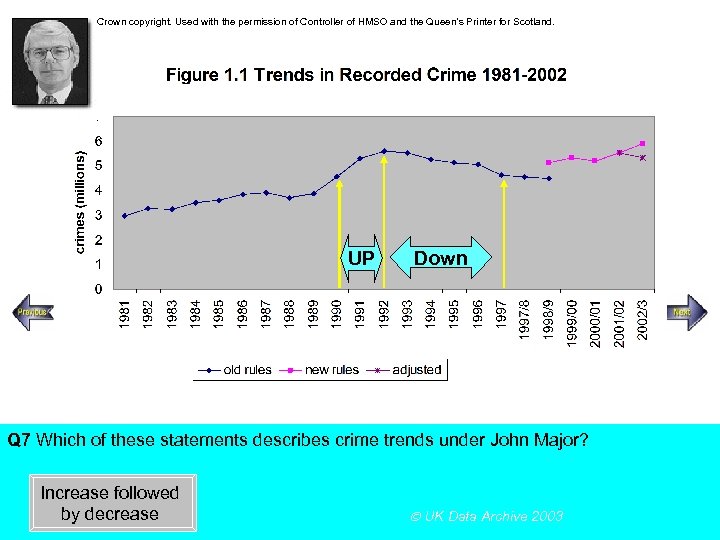 Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. Steady increase Rapid increase UP Down Q 7 Which of these statements describes crime trends under John Major? Increase followed by decrease UK Data Archive 2003
Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. Steady increase Rapid increase UP Down Q 7 Which of these statements describes crime trends under John Major? Increase followed by decrease UK Data Archive 2003
 What do you think? · From what you know about the UK’s economic history, is there any possible relationship between unemployment and crime rates? UK Data Archive 2003
What do you think? · From what you know about the UK’s economic history, is there any possible relationship between unemployment and crime rates? UK Data Archive 2003
 Q 8 Identify on the graph the years Tony Blair has been PM? Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. UK Data Archive 2003
Q 8 Identify on the graph the years Tony Blair has been PM? Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. UK Data Archive 2003
 Q 8 Identify on the graph the years Tony Blair has been PM? (1997 -) Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. UK Data Archive 2003
Q 8 Identify on the graph the years Tony Blair has been PM? (1997 -) Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. UK Data Archive 2003
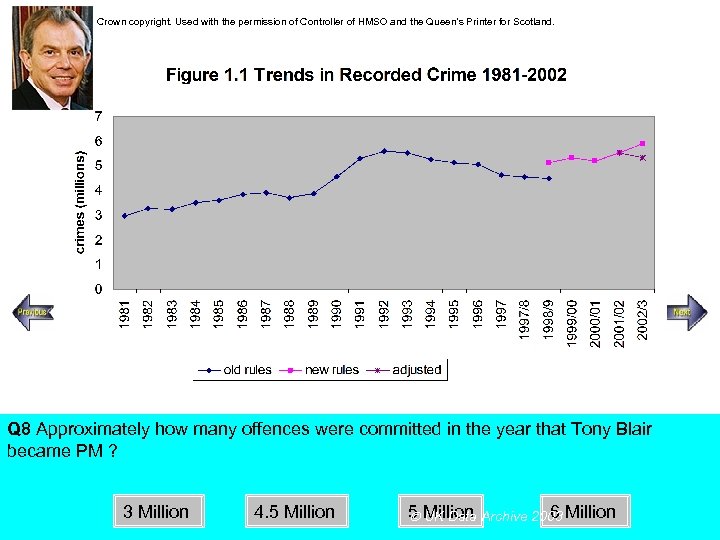 Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. Steady increase Rapid increase Q 8 Approximately how many offences were committed in the year that Tony Blair became PM ? 3 Million 4. 5 Million 6 Million UK Data Archive 2003
Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. Steady increase Rapid increase Q 8 Approximately how many offences were committed in the year that Tony Blair became PM ? 3 Million 4. 5 Million 6 Million UK Data Archive 2003
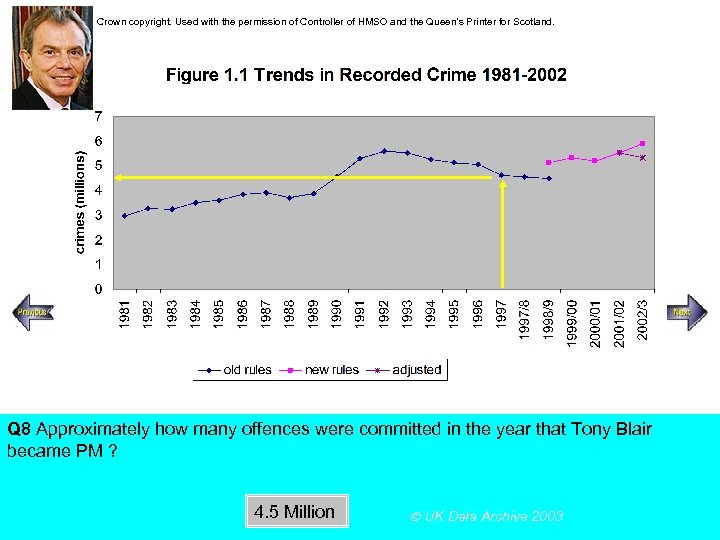 Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. Steady increase Rapid increase Q 8 Approximately how many offences were committed in the year that Tony Blair became PM ? 4. 5 Million UK Data Archive 2003
Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. Steady increase Rapid increase Q 8 Approximately how many offences were committed in the year that Tony Blair became PM ? 4. 5 Million UK Data Archive 2003
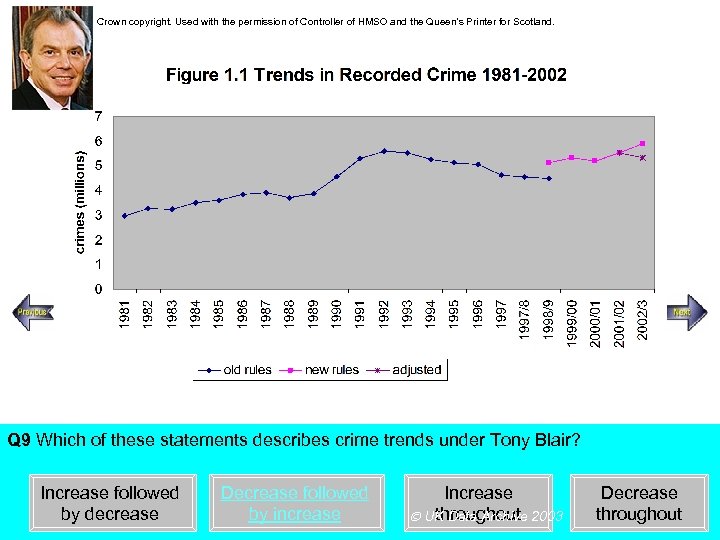 Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. Steady increase Rapid increase Q 9 Which of these statements describes crime trends under Tony Blair? Increase followed by decrease Decrease followed by increase Increase throughout UK Data Archive 2003 Decrease throughout
Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. Steady increase Rapid increase Q 9 Which of these statements describes crime trends under Tony Blair? Increase followed by decrease Decrease followed by increase Increase throughout UK Data Archive 2003 Decrease throughout
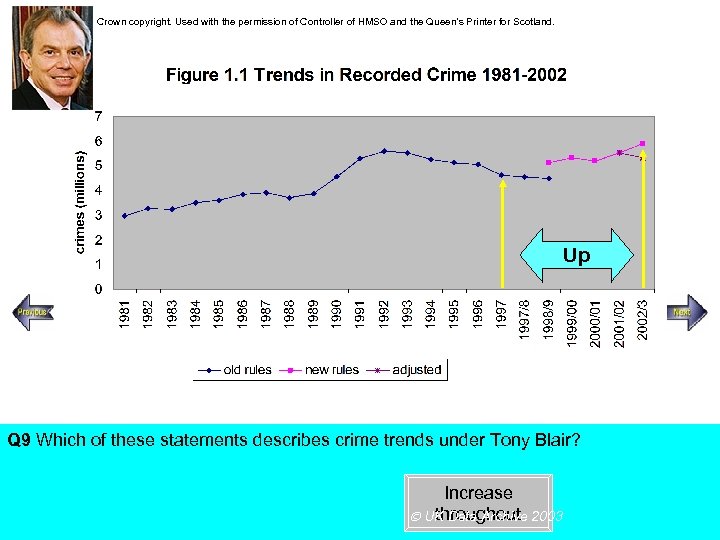 Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. Up Steady increase Rapid increase Q 9 Which of these statements describes crime trends under Tony Blair? Increase throughout UK Data Archive 2003
Crown copyright. Used with the permission of Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland. Up Steady increase Rapid increase Q 9 Which of these statements describes crime trends under Tony Blair? Increase throughout UK Data Archive 2003
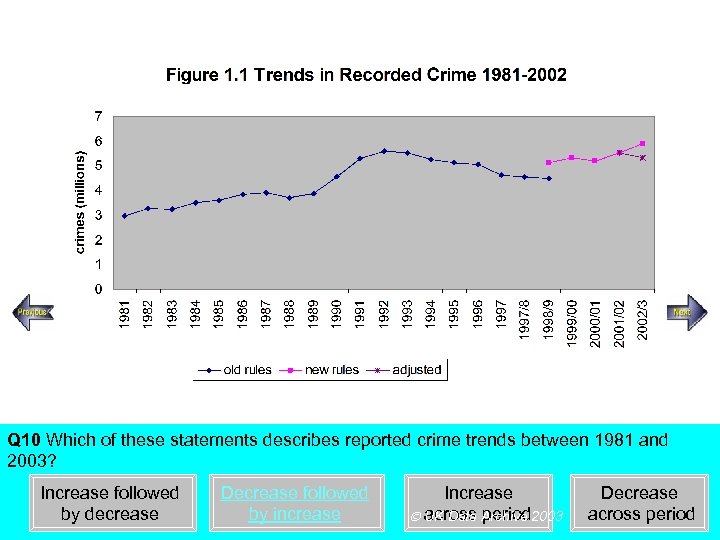 Steady increase Rapid increase Q 10 Which of these statements describes reported crime trends between 1981 and 2003? Increase followed by decrease Decrease followed by increase Increase across period UK Data Archive 2003 Decrease across period
Steady increase Rapid increase Q 10 Which of these statements describes reported crime trends between 1981 and 2003? Increase followed by decrease Decrease followed by increase Increase across period UK Data Archive 2003 Decrease across period
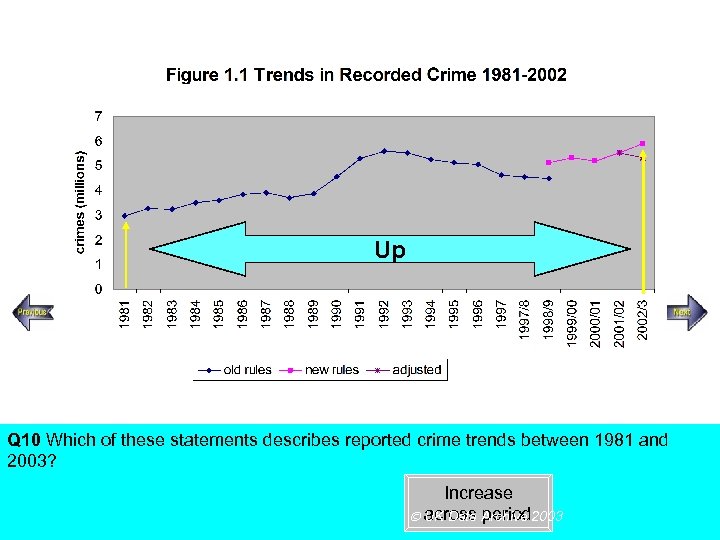 Up Steady increase Rapid increase Q 10 Which of these statements describes reported crime trends between 1981 and 2003? Increase across period UK Data Archive 2003
Up Steady increase Rapid increase Q 10 Which of these statements describes reported crime trends between 1981 and 2003? Increase across period UK Data Archive 2003
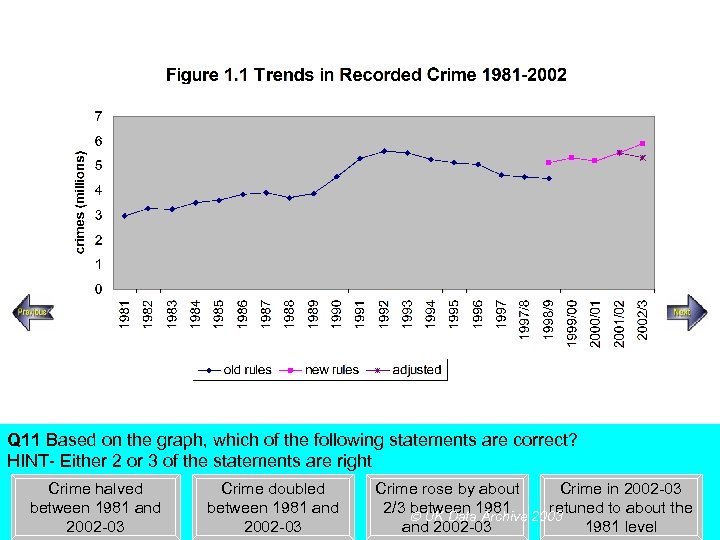 Steady increase Rapid increase Q 11 Based on the graph, which of the following statements are correct? HINT- Either 2 or 3 of the statements are right Crime halved between 1981 and 2002 -03 Crime doubled between 1981 and 2002 -03 Crime rose by about Crime in 2002 -03 2/3 between 1981 retuned to about the UK Data Archive 2003 and 2002 -03 1981 level
Steady increase Rapid increase Q 11 Based on the graph, which of the following statements are correct? HINT- Either 2 or 3 of the statements are right Crime halved between 1981 and 2002 -03 Crime doubled between 1981 and 2002 -03 Crime rose by about Crime in 2002 -03 2/3 between 1981 retuned to about the UK Data Archive 2003 and 2002 -03 1981 level
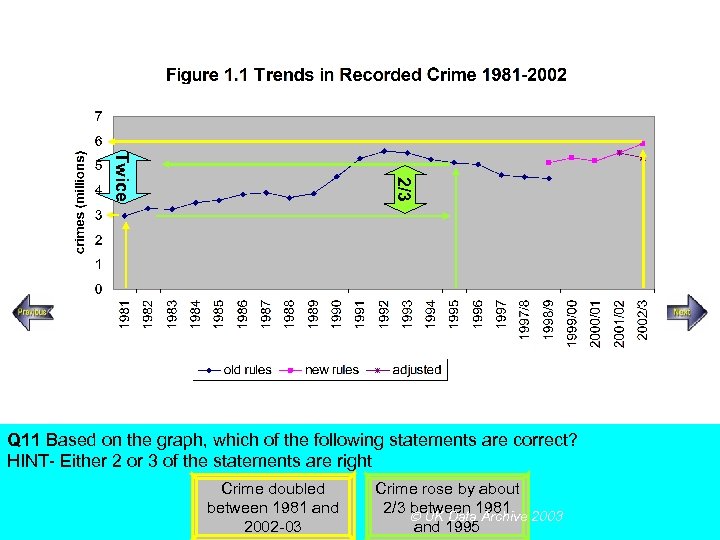 2/3 Twice Steady increase Rapid increase Q 11 Based on the graph, which of the following statements are correct? HINT- Either 2 or 3 of the statements are right Crime doubled between 1981 and 2002 -03 Crime rose by about 2/3 between 1981 UK Data Archive 2003 and 1995
2/3 Twice Steady increase Rapid increase Q 11 Based on the graph, which of the following statements are correct? HINT- Either 2 or 3 of the statements are right Crime doubled between 1981 and 2002 -03 Crime rose by about 2/3 between 1981 UK Data Archive 2003 and 1995
 Q 12 Using your knowledge gained from answering the above questions, write two simple sentences outlining trends in Police Recoded Crime from 1981 to 2003. HINT: Remember to make reference to the counting rules we learned about! {Need Model answer? } UK Data Archive 2003
Q 12 Using your knowledge gained from answering the above questions, write two simple sentences outlining trends in Police Recoded Crime from 1981 to 2003. HINT: Remember to make reference to the counting rules we learned about! {Need Model answer? } UK Data Archive 2003
 Q 13 Consider the following factors – rank them in the order in which you think has the MOST influence on the amount of crime recorded by the police? HINT: Choose the most influential first • the number of crimes committed • people’s willingness/unwillingness to report an offence • people’s willingness to report an offence but ‘they just did not get around to it’ • peoples’ fear of repercussion {NEED MODEL ANSWERS} UK Data Archive 2003
Q 13 Consider the following factors – rank them in the order in which you think has the MOST influence on the amount of crime recorded by the police? HINT: Choose the most influential first • the number of crimes committed • people’s willingness/unwillingness to report an offence • people’s willingness to report an offence but ‘they just did not get around to it’ • peoples’ fear of repercussion {NEED MODEL ANSWERS} UK Data Archive 2003
 Section B Explaining Trends in Crime GROUP WORK EXERCISE Part 1 UK Data Archive 2003
Section B Explaining Trends in Crime GROUP WORK EXERCISE Part 1 UK Data Archive 2003
 Politicians and social commentators have proposed several different arguments for crime increasing over time. Given the following types of explanations that they might give, for each think of a reason as to why crime may go up. UK Data Archive 2003
Politicians and social commentators have proposed several different arguments for crime increasing over time. Given the following types of explanations that they might give, for each think of a reason as to why crime may go up. UK Data Archive 2003
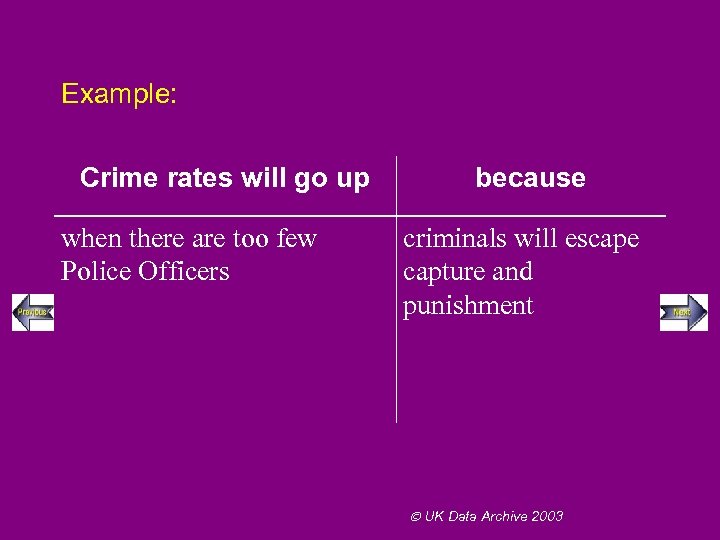 Example: Crime rates will go up when there are too few Police Officers because criminals will escape capture and punishment UK Data Archive 2003
Example: Crime rates will go up when there are too few Police Officers because criminals will escape capture and punishment UK Data Archive 2003
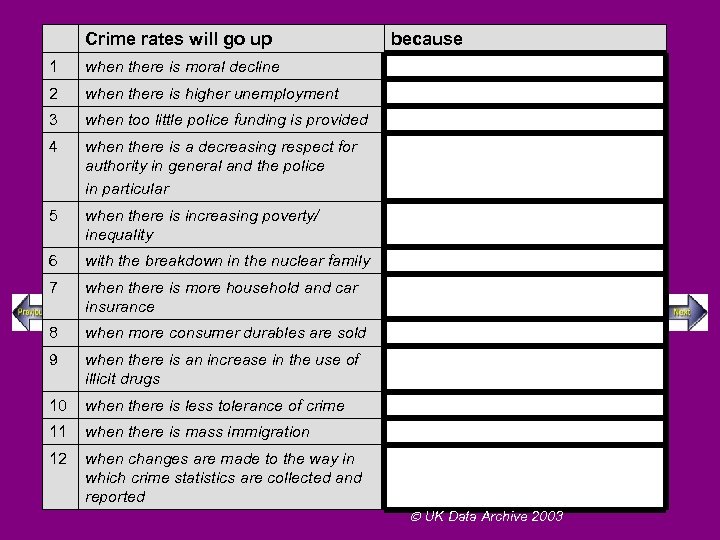 Crime rates will go up 1 when there is moral decline 2 when there is higher unemployment 3 when too little police funding is provided 4 when there is a decreasing respect for authority in general and the police in particular 5 when there is increasing poverty/ inequality 6 with the breakdown in the nuclear family 7 when there is more household and car insurance 8 when more consumer durables are sold 9 when there is an increase in the use of illicit drugs 10 when there is less tolerance of crime 11 when there is mass immigration 12 because when changes are made to the way in which crime statistics are collected and reported UK Data Archive 2003
Crime rates will go up 1 when there is moral decline 2 when there is higher unemployment 3 when too little police funding is provided 4 when there is a decreasing respect for authority in general and the police in particular 5 when there is increasing poverty/ inequality 6 with the breakdown in the nuclear family 7 when there is more household and car insurance 8 when more consumer durables are sold 9 when there is an increase in the use of illicit drugs 10 when there is less tolerance of crime 11 when there is mass immigration 12 because when changes are made to the way in which crime statistics are collected and reported UK Data Archive 2003
 What do you think? Which factors do you think are the 5 main reasons for the increase in crime in England Wales over the long term? UK Data Archive 2003
What do you think? Which factors do you think are the 5 main reasons for the increase in crime in England Wales over the long term? UK Data Archive 2003
 GROUP WORK EXERCISE Part 2 UK Data Archive 2003
GROUP WORK EXERCISE Part 2 UK Data Archive 2003
 Assume for a moment that you are the Home Secretary. From the 12 explanations for rising crime outlined above, chose the 5 that you think are most persuasive and list them in the spaces below. For each explanation, write one or two sentences describing how you as Home Secretary would address each. In other words, what would be your solution? Example: Problem suggested: Too few Police Officers Solution: Recruit more police officers UK Data Archive 2003
Assume for a moment that you are the Home Secretary. From the 12 explanations for rising crime outlined above, chose the 5 that you think are most persuasive and list them in the spaces below. For each explanation, write one or two sentences describing how you as Home Secretary would address each. In other words, what would be your solution? Example: Problem suggested: Too few Police Officers Solution: Recruit more police officers UK Data Archive 2003
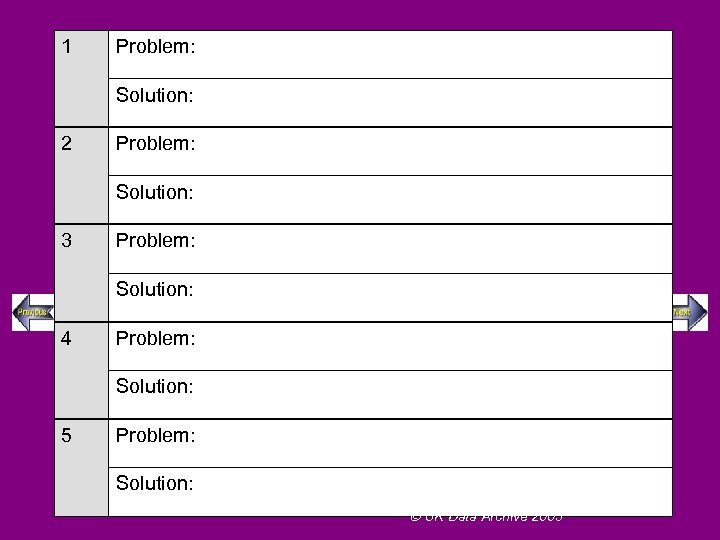 1 Problem: Solution: 2 Problem: Solution: 3 Problem: Solution: 4 Problem: Solution: 5 Problem: Solution: UK Data Archive 2003
1 Problem: Solution: 2 Problem: Solution: 3 Problem: Solution: 4 Problem: Solution: 5 Problem: Solution: UK Data Archive 2003
 GROUP WORK EXERCISE Part 3 UK Data Archive 2003
GROUP WORK EXERCISE Part 3 UK Data Archive 2003
 All solutions bring their own problems. What difficulties are you as Home Secretary, other politicians, bureaucrats and police officers likely to encounter when implementing each of your 5 above solutions? Example: Solution suggested Recruit more police officers Difficulties: Cost/public spending implications; diverting expenditure from the other key public services (e. g. health, education); an increase in police numbers is not necessarily associated with a reduction in crime figures UK Data Archive 2003
All solutions bring their own problems. What difficulties are you as Home Secretary, other politicians, bureaucrats and police officers likely to encounter when implementing each of your 5 above solutions? Example: Solution suggested Recruit more police officers Difficulties: Cost/public spending implications; diverting expenditure from the other key public services (e. g. health, education); an increase in police numbers is not necessarily associated with a reduction in crime figures UK Data Archive 2003
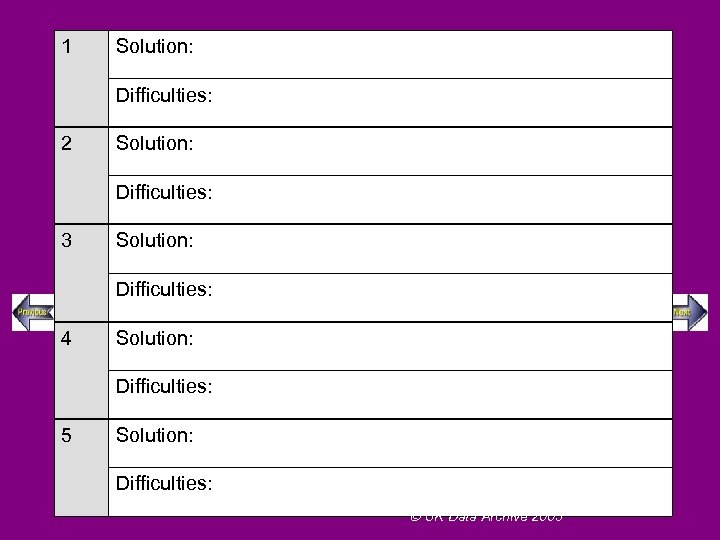 1 Solution: Difficulties: 2 Solution: Difficulties: 3 Solution: Difficulties: 4 Solution: Difficulties: 5 Solution: Difficulties: UK Data Archive 2003
1 Solution: Difficulties: 2 Solution: Difficulties: 3 Solution: Difficulties: 4 Solution: Difficulties: 5 Solution: Difficulties: UK Data Archive 2003
 What do you think? What have you learned about government’s ability to reduce crime? UK Data Archive 2003
What do you think? What have you learned about government’s ability to reduce crime? UK Data Archive 2003
 GROUP WORK EXERCISE Part 4 UK Data Archive 2003
GROUP WORK EXERCISE Part 4 UK Data Archive 2003
 The above 3 questions concentrated on increasing crime rates. However figures suggest overall crime is down in recent years. Commentators have offered several explanations for falling crime rates, which are listed below. For each explanation, try and identify the logic of the argument. UK Data Archive 2003
The above 3 questions concentrated on increasing crime rates. However figures suggest overall crime is down in recent years. Commentators have offered several explanations for falling crime rates, which are listed below. For each explanation, try and identify the logic of the argument. UK Data Archive 2003
 Example: Crime rates will go down when there is better home and car security measures because it is harder for people to break into, and steal from, property and vehicles UK Data Archive 2003
Example: Crime rates will go down when there is better home and car security measures because it is harder for people to break into, and steal from, property and vehicles UK Data Archive 2003
 Crime rates will go down 1 if there are higher unemployment rates 2 if there were increased equality 3 if there is better policing 4 if more criminals are locked up 5 if there was zero tolerance policing 6 if there were fewer adolescent males 7 if the government introduced policies to reduce social exclusion through strategies such as reducing school truancy and exclusion 8 if there were effective social measures 9 if there were longer prison sentences 10 with the Sure. Start scheme (Hint: helps deprived children 11 because if there were better education UK Data Archive 2003
Crime rates will go down 1 if there are higher unemployment rates 2 if there were increased equality 3 if there is better policing 4 if more criminals are locked up 5 if there was zero tolerance policing 6 if there were fewer adolescent males 7 if the government introduced policies to reduce social exclusion through strategies such as reducing school truancy and exclusion 8 if there were effective social measures 9 if there were longer prison sentences 10 with the Sure. Start scheme (Hint: helps deprived children 11 because if there were better education UK Data Archive 2003
 Summary • You should have some knowledge about trends in crime, as detailed in the Police Recorded Crime Figures • You should have improved your graph and table reading skills • In particular, you have explored the reasons why crime rose prior to the mid-1990 s and has since fallen • You have investigated why crime is a difficult policy problem to ‘crack’ UK Data Archive 2003
Summary • You should have some knowledge about trends in crime, as detailed in the Police Recorded Crime Figures • You should have improved your graph and table reading skills • In particular, you have explored the reasons why crime rose prior to the mid-1990 s and has since fallen • You have investigated why crime is a difficult policy problem to ‘crack’ UK Data Archive 2003
 NEXT UP…. You have explored official figures on crime rates as they are collected by the Police. But is the whole story? Not all crimes are reported to the police. Perhaps then these figures understate the ‘real’ amount of crime in England Wales. The next module explores an alternative source of data to look at crime rate. Stop UK Data Archive 2003
NEXT UP…. You have explored official figures on crime rates as they are collected by the Police. But is the whole story? Not all crimes are reported to the police. Perhaps then these figures understate the ‘real’ amount of crime in England Wales. The next module explores an alternative source of data to look at crime rate. Stop UK Data Archive 2003


