62c33000ccc56d00e523590e6cbe4e17.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24

www. oasis-open. org “Panel on Embedding Communications into IT Applications: Oracle Perspective” OASIS SOA for Telecom workshop Stéphane H. Maes CTO & Chief Architect Mobility, Voice and Communications stephane. maes@oracle. com

Agenda n n n Today’s industry situatioon Positioning SOA in SP domain l SDP l OMA OSE l TMF SDF l AIA SOA and new services/strategies in Telcos Technology challenges with SOA Conclusions

Agenda Ø n n Today’s industry situatioon Positioning SOA in SP domain l SDP l OMA OSE l TMF SDF l AIA SOA and new services/strategies in Telcos Technology challenges with SOA Conclusions

Today’s Silos of Web & Telecom Domains Web lacks Telecom, and Telecom lacks Web 2. 0, SOA Web Telecom Search Telephony Shopping Broadband IM Vo. IP i. Tunes 2. 5 G / 3 G / LTE Web 2. 0 Wi. Fi / Wi. Max News / Info IPTV

Agenda n Ø n n n Today’s industry situatioon Positioning SOA in SP domain l SDP l OMA OSE l TMF SDF l AIA SOA and new services/strategies in Telcos Technology challenges with SOA Conclusions
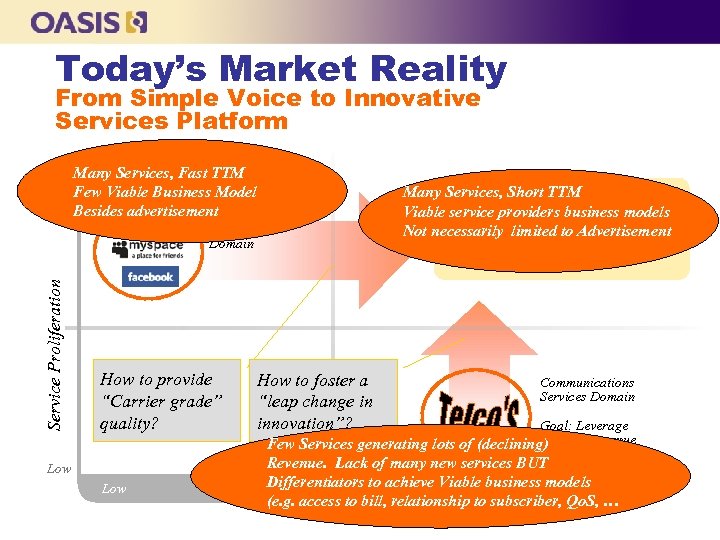
Today’s Market Reality From Simple Voice to Innovative Services Platform Many Services, Fast TTM Few Viable Business Model High Besides advertisement Internet Many Services, Short TTM Goal for Everybody Viable service providers business models – Customer Care and service quality Not necessarily limited to Advertisement – Rapid, efficient customer-centric services Service Proliferation Services Domain How to provide “Carrier grade” quality? Low – – How to foster a “leap change in innovation”? Value curve understood to maximize revenue Lean operation with Business Agility Communications Services Domain Goal: Leverage Existing Revenue Few Services generating lots of (declining) Relationship Revenue. Lack of many new services BUT Differentiators to achieve Viable business models High Service Revenues (e. g. access to bill, relationship to subscriber, Qo. S, …
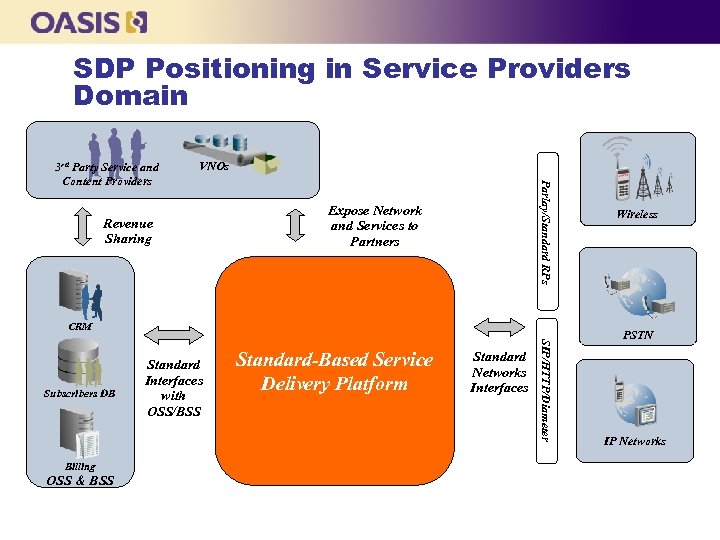
SDP Positioning in Service Providers Domain VNOs Revenue Sharing Parlay/Standard RPs 3 rd Party Service and Content Providers Expose Network and Services to Partners CRM Billing OSS & BSS Standard-Based Service Delivery Platform Standard Networks Interfaces SIP/HTTP/Diameter Subscribers DB Standard Interfaces with OSS/BSS Wireless PSTN IP Networks
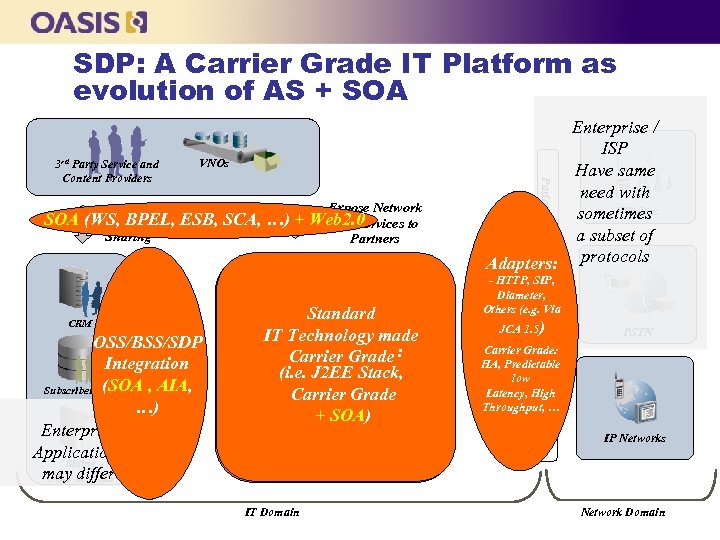
SDP: A Carrier Grade IT Platform as evolution of AS + SOA VNOs Revenue SOA (WS, BPEL, ESB, SCA, …) + Sharing CRM Standard IT Technology made Carrier Grade : Standard-Based Service (i. e. J 2 EE Stack, Delivery Platform Carrier Grade + SOA) IT Domain - HTTP, SIP, Diameter, Others (e. g. Via JCA 1. 5) SIP/HTTP/Diameter OSS/BSS/SDP Standard Integration (SOA Interfaces , AIA, Subscribers DB with …) OSS/BSS Enterprise Applications Billing may & BSS OSS differ Expose Network Web 2. 0 and Services to Partners Parlay/Standard RPs 3 rd Party Service and Content Providers Enterprise / ISP Have same need with Wireless sometimes a subset of Adapters: protocols PSTN Carrier Standard. Grade: HA, Predictable Networks low Interfaces Latency, High Throughput, … IP Networks Network Domain
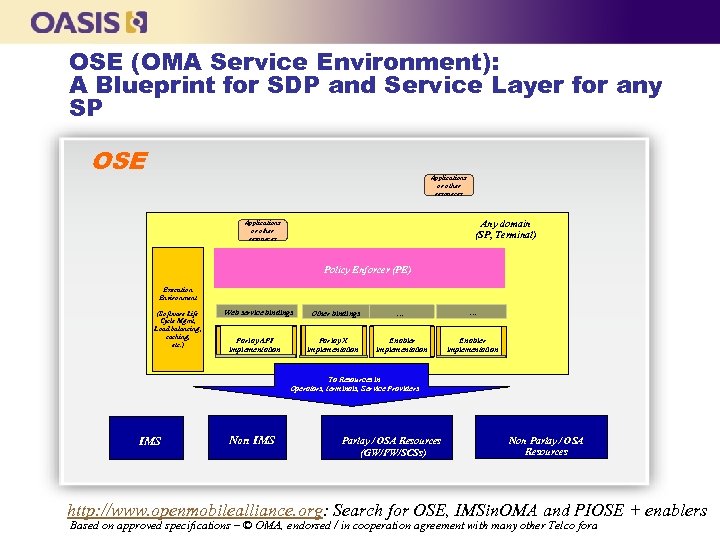
OSE (OMA Service Environment): A Blueprint for SDP and Service Layer for any SP OSE Applications or other resources Any domain (SP, Terminal) Applications or other resources Policy Enforcer (PE) Execution Environment (Software Life Cycle Mgmt, Load balancing, caching, etc. ) Web service bindings Parlay API implementation Other bindings Parlay X implementation … … Enabler implementation To Resources in Operators, terminals, Service Providers IMS Non IMS Parlay / OSA Resources (GW/FW/SCSs) Non Parlay / OSA Resources http: //www. openmobilealliance. org: Search for OSE, IMSin. OMA and PIOSE + enablers Based on approved specifications – © OMA, endorsed / in cooperation agreement with many other Telco fora
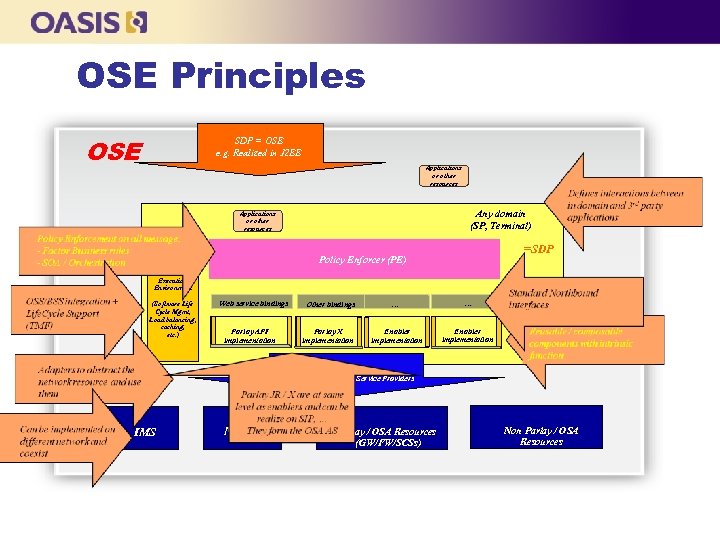
OSE Principles OSE SDP = OSE e. g. Realized in J 2 EE Applications or other resources Any domain (SP, Terminal) Applications or other resources =SDP Policy Enforcer (PE) Execution Environment (Software Life Cycle Mgmt, Load balancing, caching, etc. ) Web service bindings Parlay API implementation Other bindings Parlay X implementation … … Enabler implementation To Resources in Operators, terminals, Service Providers IMS Non IMS Parlay / OSA Resources (GW/FW/SCSs) Non Parlay / OSA Resources
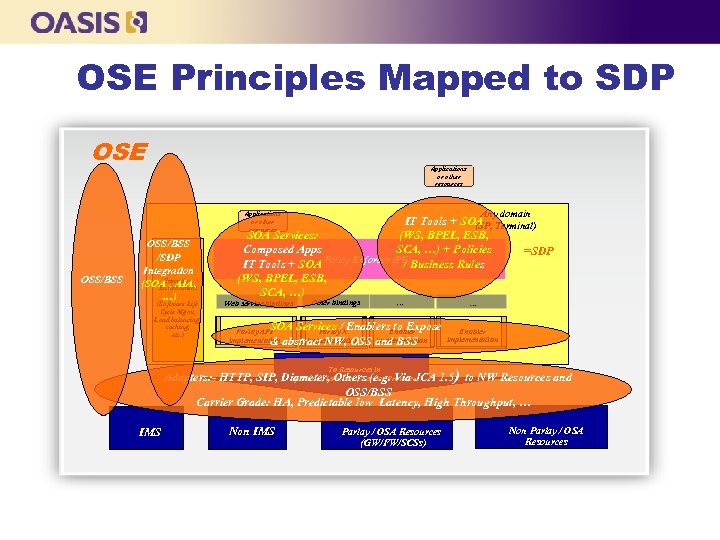
OSE Principles Mapped to SDP OSE Applications or other resources Any domain Applications or other resources OSS/BSS /SDP Integration Execution (SOA , AIA, Environment …) (Software Life Cycle Mgmt, Load balancing, caching, etc. ) IT Tools + SOA Terminal) (SP, SOA Services: (WS, BPEL, ESB, Composed Apps SCA, …) + Policies =SDP IT Tools + SOA Policy Enforcer (PE)Business Rules / (WS, BPEL, ESB, SCA, …) Web service bindings Other bindings … … SOA Services /XEnablers. Enabler to Expose Enabler Parlay API implementation abstract NW, OSS and BSS implementation & Adapters: - HTTP, SIP, Diameter, Others (e. g. Via JCA 1. 5 ) to NW Resources and Operators, terminals, Service Providers OSS/BSS Carrier Grade: HA, Predictable low Latency, High Throughput, … To Resources in IMS Non IMS Parlay / OSA Resources (GW/FW/SCSs) Non Parlay / OSA Resources
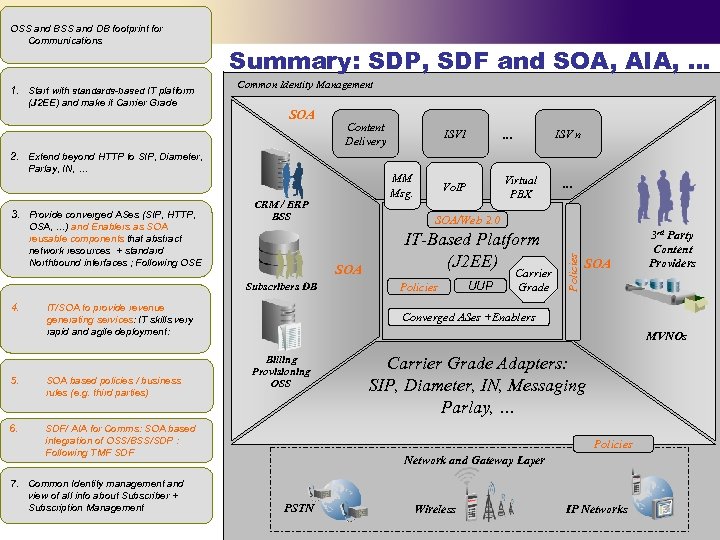
1. Start with standards-based IT platform (J 2 EE) and make it Carrier Grade Summary: SDP, SDF and SOA, AIA, … Common Identity Management SOA Content Delivery 2. Extend beyond HTTP to SIP, Diameter, Parlay, IN, … 3. Provide converged ASes (SIP, HTTP, OSA, …) and Enablers as SOA reusable components that abstract network resources + standard Northbound interfaces ; Following OSE 4. 5. SOA based policies / business rules (e. g. third parties) 6. … IT-Based Platform (J 2 EE) Policies UUP Carrier Grade SOA 3 rd Party Content Providers Converged ASes +Enablers MVNOs Billing Provisioning OSS SDF/ AIA for Comms: SOA based integration of OSS/BSS/SDP : Following TMF SDF 7. Common Identity management and view of all info about Subscriber + Subscription Management Virtual PBX ISV n SOA/Web 2. 0 SOA IT/SOA to provide revenue generating services: IT skills very rapid and agile deployment: … Vo. IP MM Msg. CRM / ERP BSS Subscribers DB ISV 1 Policies OSS and BSS and DB footprint for Communications Carrier Grade Adapters: SIP, Diameter, IN, Messaging Parlay, … Policies Network and Gateway Layer PSTN Wireless IP Networks
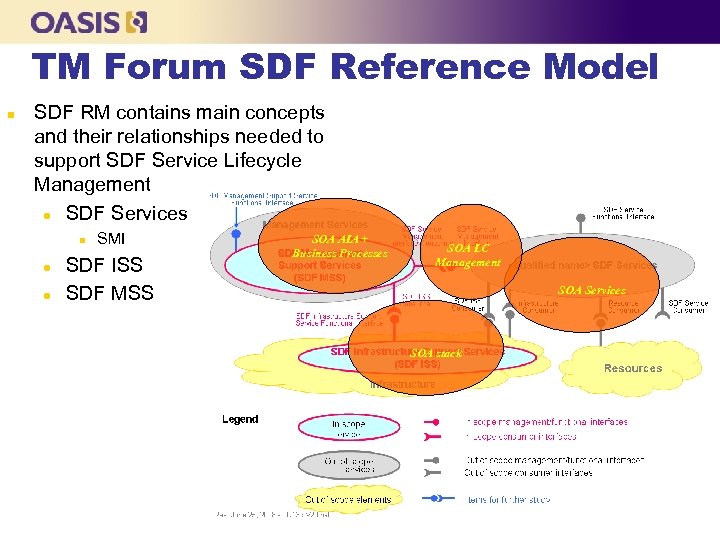
TM Forum SDF Reference Model n SDF RM contains main concepts and their relationships needed to support SDF Service Lifecycle Management l SDF Services n l l SMI SDF ISS SDF MSS SOA AIA + Business Processes SOA LC Management SOA Services SOA stack
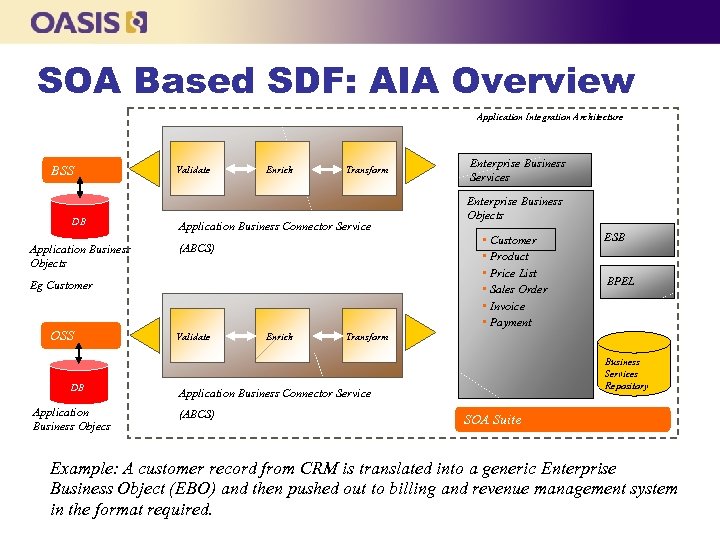
SOA Based SDF: AIA Overview Application Integration Architecture BSS DB DB Application Business Objects Validate Enrich Transform Application Business Connector Service (ABCS) Eg Customer OSS DB DB Application Business Objecs Validate Enrich Enterprise Business Services Enterprise Business Objects • Customer • Product • Price List • Sales Order • Invoice • Payment BPEL Transform Business Services Repository Application Business Connector Service (ABCS) ESB SOA Suite Example: A customer record from CRM is translated into a generic Enterprise Business Object (EBO) and then pushed out to billing and revenue management system in the format required.
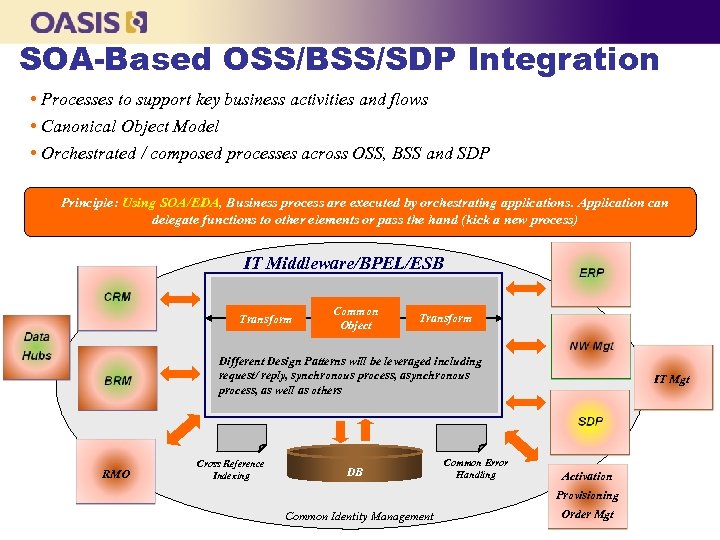
SOA-Based OSS/BSS/SDP Integration • Processes to support key business activities and flows • Canonical Object Model • Orchestrated / composed processes across OSS, BSS and SDP Principle: Using SOA/EDA, Business process are executed by orchestrating applications. Application can delegate functions to other elements or pass the hand (kick a new process) IT Middleware/BPEL/ESB Transform Common Object Transform Different Design Patterns will be leveraged including request/ reply, synchronous process, as well as others RMO Cross Reference Indexing DB Common Error Handling IT Mgt Activation Provisioning Common Identity Management Order Mgt

Agenda n n Ø n n Today’s industry situatioon Positioning SOA in SP domain l SDP l OMA OSE l TMF SDF l AIA SOA and new services/strategies in Telcos Technology challenges with SOA Conclusions
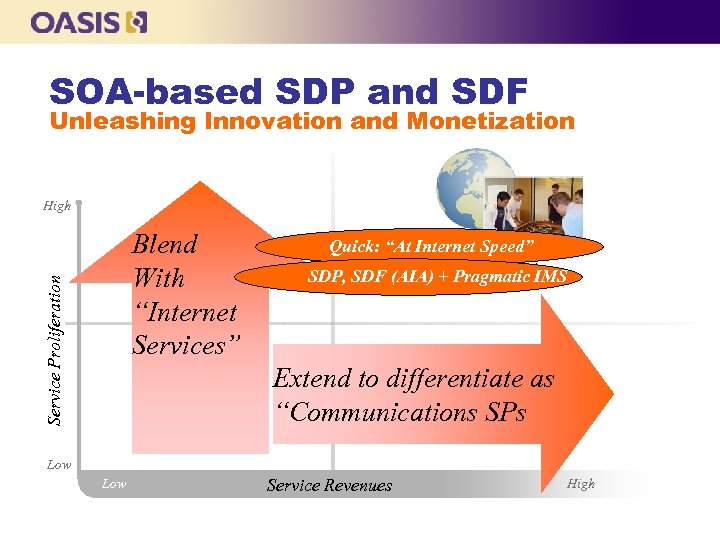
SOA-based SDP and SDF Unleashing Innovation and Monetization High Service Proliferation Blend With “Internet Services” Quick: “At Internet Speed” SDP, SDF (AIA) + Need for Speed. IMS Pragmatic Extend to differentiate as “Communications SPs Low Service Revenues High
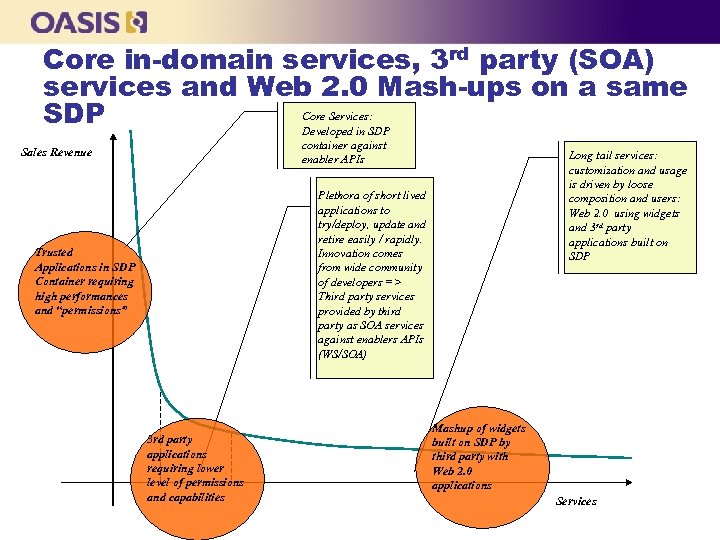
Core in-domain services, 3 rd party (SOA) services and Web 2. 0 Mash-ups on a same Core Services: SDP Developed in SDP container against enabler APIs Sales Revenue Long tail services: customization and usage is driven by loose composition and users: Web 2. 0 using widgets and 3 rd party applications built on SDP Plethora of short lived applications to try/deploy, update and retire easily / rapidly. Innovation comes from wide community of developers => Third party services provided by third party as SOA services against enablers APIs (WS/SOA) Trusted Applications in SDP Container requiring high performances and “permissions” 3 rd party applications requiring lower level of permissions and capabilities Mashup of widgets built on SDP by third party with Web 2. 0 applications Services

New services and SOA n n Any “internet service” is a Telco service possible specialized / robustized (carrier grade) for network or simply expose on network Services can be SOA-based or web 2. 0 based l n n Includes customization / built by subscribers Service are provided by internet service providers or IT developers, less and less by Telco service providers or Telco specialized vendors Service can be built / customized / integrated by users (e. g. web 2. 0 mash-ups) Advertisement based services (a la internet) + adapted to communications (e. g. ad subsidized communications) Services specialized for users

Requirements l Need to be able to target many services offered by widest community (e. g. Internet): n IT / Internet friendly, open and standard mainstream approaches and technology: • Capture economies of scales • Tap the widest pool of developers and entrepreneurs as developers or Partners l Need to efficiently and rapidly develop , deploy services, validate, extract revenue and update or retire them: n n l l Rely on common service (i. e. software) development practices Automate with open, standard and customizable ways all business processes within the service providers an d with partners Need to Provide services in future proof manner over as many network technologies as possible Need to be Carrier grade!

Agenda n n n Ø n Today’s industry situatioon Positioning SOA in SP domain l SDP l OMA OSE l TMF SDF l AIA SOA and new services/strategies in Telcos Technology challenges with SOA Conclusions

Technology challenges with SOA n n If we defined Carrier Grade (CG) as: l High Availability l Predictable low latencies l Efficient (e. g. throughput per CPU) / Economically viable l Scalable l Hot upgradable MW containers can be carrier grade today SOA CG has some challenges. E. g. (non exhaustive): l Delays, predictable latencies, time to instantiate l Throughput l Qo. S, SLA enforcement l LC Management like manageability of composed services and web 2. 0 mash-ups (see TMF SDF) n Dependencies modeling l Distributed SOA and impact on instance selection, catalogs etc… Adoption / endorsement by Telco SP and NEMs

Agenda n n Ø Today’s industry situatioon Positioning SOA in SP domain l SDP l OMA OSE l TMF SDF l AIA SOA and new services/strategies in Telcos Technology challenges with SOA Conclusions

Conclusions: Technology trends n n n n Commoditization of core MW CG SOA and web 2. 0 CG SOA based Policies consolidated across whole service provider domain (including network) Service level SCIM and SOA for complex orchestration of services while simple orchestration may be lower in network Automated business processes CG SOA can implement core Telco services (e. g. even call control functions) CG SOA may be achievable as SOA + distributed caching / grid computing Product based services - end to end l “Telco in box except NW” with OSS/BSS/SDP/services SOA integration and SOA business processes extended to market places and web 2. 0
62c33000ccc56d00e523590e6cbe4e17.ppt