206f279b6a24494a9c3ae0b981754c1c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 59

www. oasis-open. org Industry-Centered Business Strategies n Presented by Jo. Ann Hackos, Bob Beims, Chip Gettinger, and Scott Hudson 1

www. oasis-open. org Understanding DITA: Its Impact On A Global Business Strategy n n n Jo. Ann T Hackos, Ph. D President Comtech Services Inc. 2
www. oasis-open. org What is DITA? Pronounced Dit-Uh n Darwin: n Information Typing: n Architecture: DITA uses the principles of inheritance for specialization DITA is designed for topic based technical information based on an information architecture of concept, task, and reference DITA provides the framework for the development of an Information Model 3

www. oasis-open. org DITA at OASIS n n n OASIS DITA Technical Committee at OASIS DITA architecture (including base topic types defined in DTD and schema) contributed to OASIS in 2004 DITA 1. 0 specification formally published by OASIS in 2005 DITA 1. 1 specification now under review DITA public toolkit available through open source (Source. Forge) Domain specific communities beginning to emerge in semiconductor, telecomm, aerospace, and more 4

www. oasis-open. org Technical author maintains brand integrity By selecting the best DITA type, I can ensure consistency of content and language and enhance our information branding across information libraries. 5

www. oasis-open. org What is DITA exactly? n n n DITA is an architecture for creating topic oriented, information typed content that can be reused and single sourced in a variety of ways It is also an architecture for creating new topic types and describing new information domains based on existing types and domains DITA is not just another tool but an international standard to support structured authoring and reuse in any technical domain 6

www. oasis-open. org Core design principles of DITA n Topic orientation l n Topic granularity l n DTDs and schemas guarantee that DITA types follow identical information structures Specialization l n Self contained topics combine with other topics into information sets Strong typing l n Discrete units of information covering a specific subject with a specific intent Architecture for extending basic types to new types adapted for a particular use within an information set Common base class l Top level "generic" base type provides “fallback” for all types 7

www. oasis-open. org What are the business opportunities? n n n n n Enhanced standards at the source More opportunities for standardized, consistent content More consistent branding of content Customized, branded look and feel for OEMs and VARs More reliable use of translation memory Better schedules, less chaos at the end Reduced time and cost of production in multiple languages Automated topic interrelationships to eliminate hand coding of references and links More languages and greater customization for global audiences 8
www. oasis-open. org The DITA Model n n Standard, tested DTD A set of hierarchical DTDs (or schemas) Three basic information types based on a generic topic type A set of elements l l Information type specific elements Generic elements Map/Book specific elements Domain specific elements 9
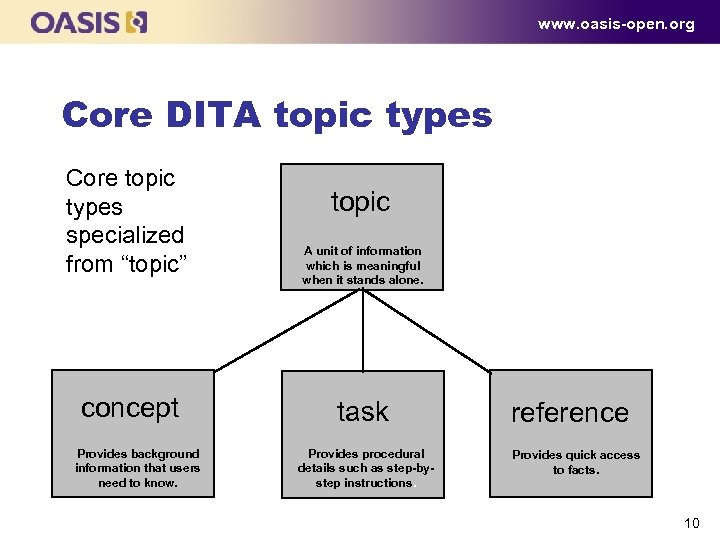
www. oasis-open. org Core DITA topic types Core topic types specialized from “topic” concept Provides background information that users need to know. topic A unit of information which is meaningful when it stands alone. task Provides procedural details such as step-bystep instructions. reference Provides quick access to facts. 10

www. oasis-open. org The DITA Model n n n The DITA Maps to assemble topics for output Relationship tables so that we can relate topics to one another Standard metadata attributes and values to select and filter content 11

www. oasis-open. org The DITA Model n n Specialization capabilities that allow us to create new information types and domain specific elements to meet unique organizational and industry needs Processes that automate the production of deliverables in PDF, HTML, Help, Eclipse and others 12
www. oasis-open. org DITA domains n n A DITA domain defines a set of elements associated with a particular subject area or authoring requirement regardless of topic type Current implemented domains l l l Programming languages Software User interfaces 13
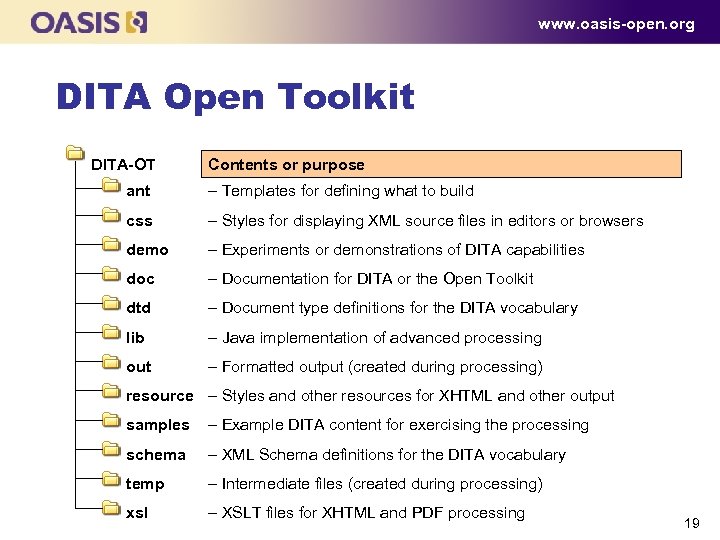
www. oasis-open. org DITA Open Toolkit DITA-OT Contents or purpose ant – Templates for defining what to build css – Styles for displaying XML source files in editors or browsers demo – Experiments or demonstrations of DITA capabilities doc – Documentation for DITA or the Open Toolkit dtd – Document type definitions for the DITA vocabulary lib – Java implementation of advanced processing out – Formatted output (created during processing) resource – Styles and other resources for XHTML and other output samples – Example DITA content for exercising the processing schema – XML Schema definitions for the DITA vocabulary temp – Intermediate files (created during processing) xsl – XSLT files for XHTML and PDF processing 19
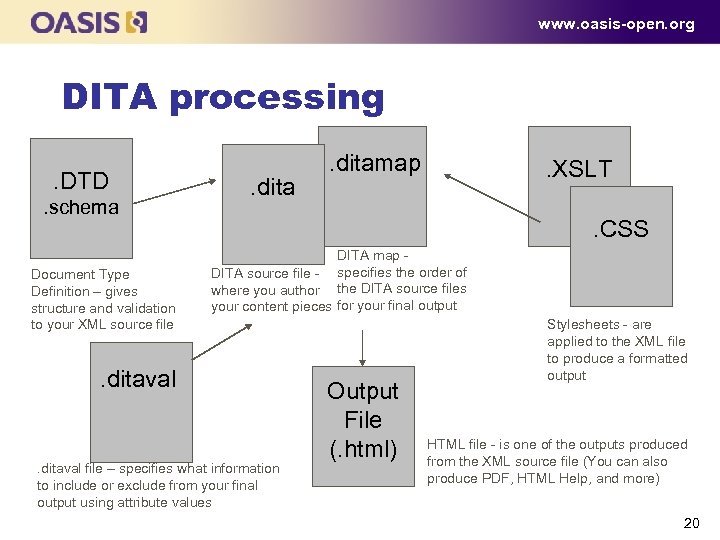
www. oasis-open. org DITA processing. DTD. schema Document Type Definition – gives structure and validation to your XML source file . ditamap . XSLT. CSS DITA map DITA source file specifies the order of where you author the DITA source files your content pieces for your final output . ditaval file – specifies what information to include or exclude from your final output using attribute values Output File (. html) Stylesheets are applied to the XML file to produce a formatted output HTML file is one of the outputs produced from the XML source file (You can also produce PDF, HTML Help, and more) 20

www. oasis-open. org DITA Specialization to Streamline Data Interchange n n The Business Case for a Semiconductor industry DITA Specialization Effort Bob Beims, Application Engineer Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 21

www. oasis-open. org Outline n n n Are Industry Standards In Place? Are Problems Solved by Exchange? Do the Data Models Match Up? How Will DITA Specializations Help? How Will We Do It? 22
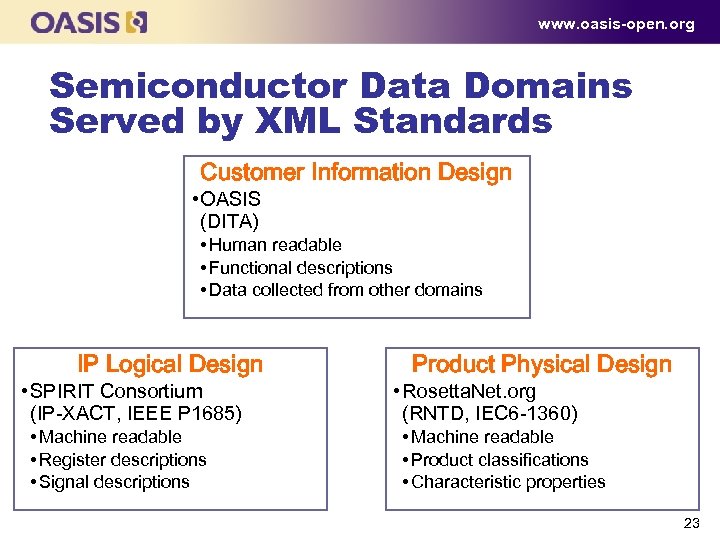
www. oasis-open. org Semiconductor Data Domains Served by XML Standards Customer Information Design • OASIS (DITA) • Human readable • Functional descriptions • Data collected from other domains IP Logical Design • SPIRIT Consortium (IP-XACT, IEEE P 1685) • Machine readable • Register descriptions • Signal descriptions Product Physical Design • Rosetta. Net. org (RNTD, IEC 6 -1360) • Machine readable • Product classifications • Characteristic properties 23

www. oasis-open. org Outline n n n Are Industry Standards In Place? Are Problems Solved by Exchange? Do the Data Models Match Up? How Will DITA Specializations Help? How Will We Do It? 24
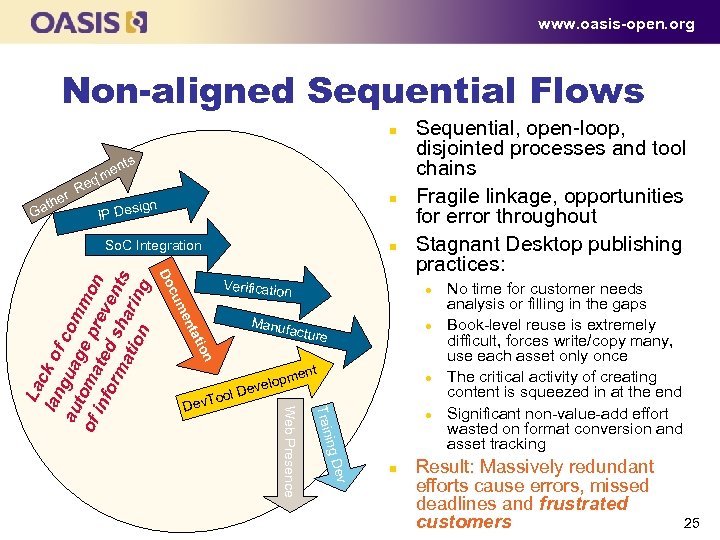
www. oasis-open. org Non-aligned Sequential Flows n ts r the Ga Re n ’me q n sign IP De n Do Verification m cu l Manu en factur l e ion tat ent oo l Train Dev. T opm evel l. D ev ing D Web Presence La l an ck o f au g u a co m g o f to m a e p r m o n inf e t o rm ed s ven a ti h a r i ts on ng So. C Integration Sequential, open loop, disjointed processes and tool chains Fragile linkage, opportunities for error throughout Stagnant Desktop publishing practices: l n No time for customer needs analysis or filling in the gaps Book level reuse is extremely difficult, forces write/copy many, use each asset only once The critical activity of creating content is squeezed in at the end Significant non value add effort wasted on format conversion and asset tracking Result: Massively redundant efforts cause errors, missed deadlines and frustrated customers 25
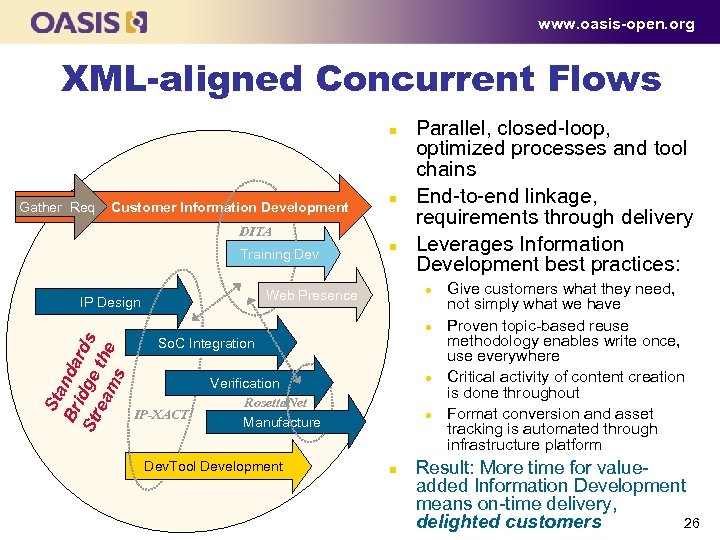
www. oasis-open. org XML-aligned Concurrent Flows n Gather Req Customer Information Development n DITA Training Dev n l Web Presence IP Design Parallel, closed loop, optimized processes and tool chains End to end linkage, requirements through delivery Leverages Information Development best practices: S ta Br n d a i S tr d g e r d s e a th e ms l So. C Integration IP-XACT l Verification Rosetta. Net Manufacture Dev. Tool Development l n Give customers what they need, not simply what we have Proven topic based reuse methodology enables write once, use everywhere Critical activity of content creation is done throughout Format conversion and asset tracking is automated through infrastructure platform Result: More time for value added Information Development means on time delivery, delighted customers 26
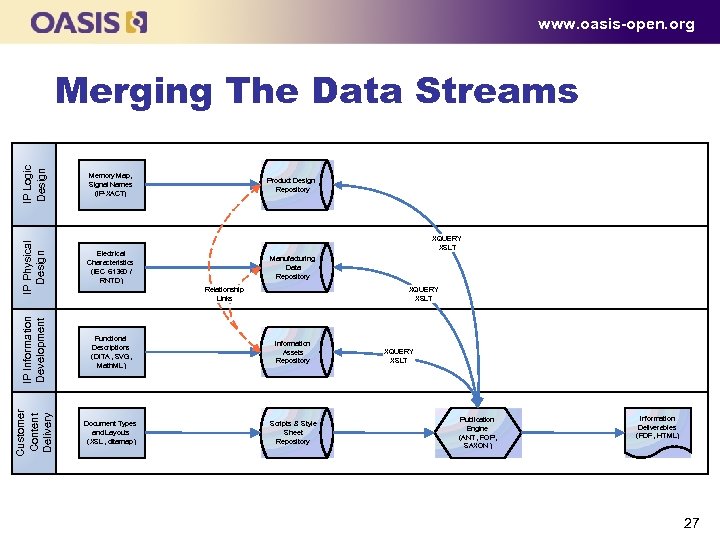
www. oasis-open. org Memory Map, Signal Names (IP XACT) Product Design Repository IP Physical Design Electrical Characteristics (IEC 61360 / RNTD ) IP Information Development XQUERY XSLT Functional Descriptions (DITA , SVG , Math. ML ) Information Assets Repository Customer Content Delivery IP Logic Design Merging The Data Streams Document Types and Layouts (XSL , ditamap ) Scripts & Style Sheet Repository Manufacturing Data Repository Relationship Links XQUERY XSLT Publication Engine (ANT , FOP , SAXON ) Information Deliverables (PDF, HTML ) 27

www. oasis-open. org Outline n n n Are Industry Standards In Place? Are Problems Solved by Exchange? Do the Data Models Match Up? How Will DITA Specializations Help? How Will We Do It? 28

www. oasis-open. org Example: IP-XACT memory. Maps <? xml version="1. 0" encoding="UTF-8"? > <spirit: component xmlns: spirit="http: //www. spiritconsortium. org/XMLSchema/SPIRIT/1. 0" xmlns: xsi="http: //www. w 3. org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi: schema. Location="http: //www. spiritconsortium. org/XMLSchema/SPIRIT/1. 0"> <spirit: vendor>Spirit</spirit: vendor> <spirit: library>Leon 2</spirit: library> <spirit: name>uart</spirit: name> <spirit: version>1. 0</spirit: version> <spirit: memory. Maps> <spirit: memory. Map> <spirit: name>amba. APB</spirit: name> <spirit: address. Block> <spirit: base. Address>0</spirit: base. Address> <spirit: bit. Offset spirit: format="long">0</spirit: bit. Offset> <spirit: range spirit: format="long">16</spirit: range> <spirit: width spirit: format="long" spirit: id="width">6</spirit: width> <spirit: register> <spirit: name>data</spirit: name> <spirit: address. Offset>0 x 0</spirit: address. Offset> <spirit: size>32</spirit: size> <spirit: access>read-write</spirit: access> <spirit: description>Data read/write register</spirit: description> </spirit: register> </spirit: address. Block> </spirit: memory. Maps> </spirit: component> 29
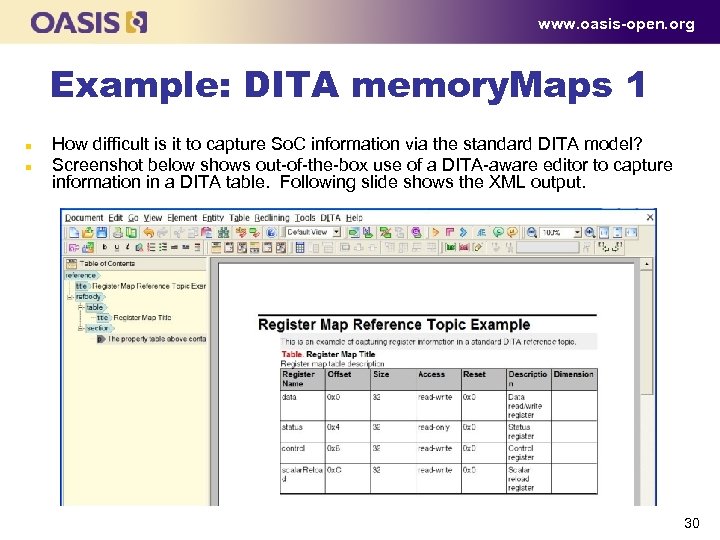
www. oasis-open. org Example: DITA memory. Maps 1 n n How difficult is it to capture So. C information via the standard DITA model? Screenshot below shows out of the box use of a DITA aware editor to capture information in a DITA table. Following slide shows the XML output. 30
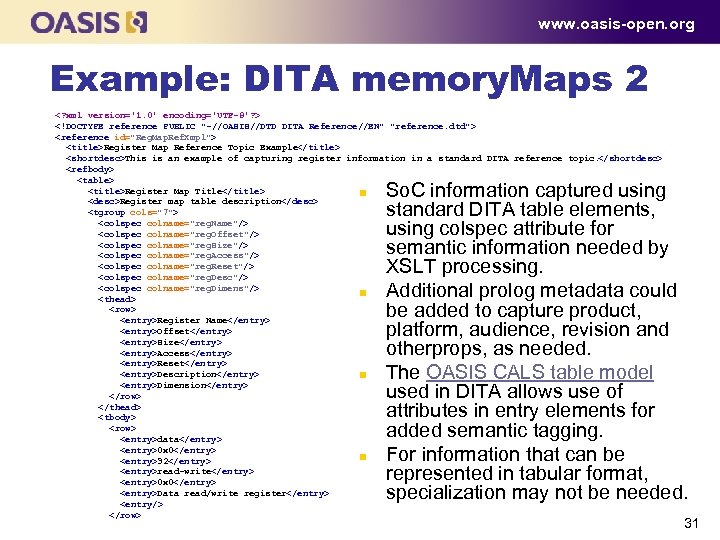
www. oasis-open. org Example: DITA memory. Maps 2 <? xml version='1. 0' encoding='UTF-8'? > <!DOCTYPE reference PUBLIC "-//OASIS//DTD DITA Reference//EN" "reference. dtd"> <reference id="Reg. Map. Ref. Xmpl"> <title>Register Map Reference Topic Example</title> <shortdesc>This is an example of capturing register information in a standard DITA reference topic. </shortdesc> <refbody> <table> <title>Register Map Title</title> n <desc>Register map table description</desc> <tgroup cols="7"> <colspec colname="reg. Name"/> <colspec colname="reg. Offset"/> <colspec colname="reg. Size"/> <colspec colname="reg. Access"/> <colspec colname="reg. Reset"/> <colspec colname="reg. Desc"/> <colspec colname="reg. Dimens"/> n <thead> <row> <entry>Register Name</entry> <entry>Offset</entry> <entry>Size</entry> <entry>Access</entry> <entry>Reset</entry> <entry>Description</entry> n <entry>Dimension</entry> </row> </thead> <tbody> <row> <entry>data</entry> <entry>0 x 0</entry> n <entry>32</entry> <entry>read-write</entry> <entry>0 x 0</entry> <entry>Data read/write register</entry> <entry/> </row> So. C information captured using standard DITA table elements, using colspec attribute for semantic information needed by XSLT processing. Additional prolog metadata could be added to capture product, platform, audience, revision and otherprops, as needed. The OASIS CALS table model used in DITA allows use of attributes in entry elements for added semantic tagging. For information that can be represented in tabular format, specialization may not be needed. 31
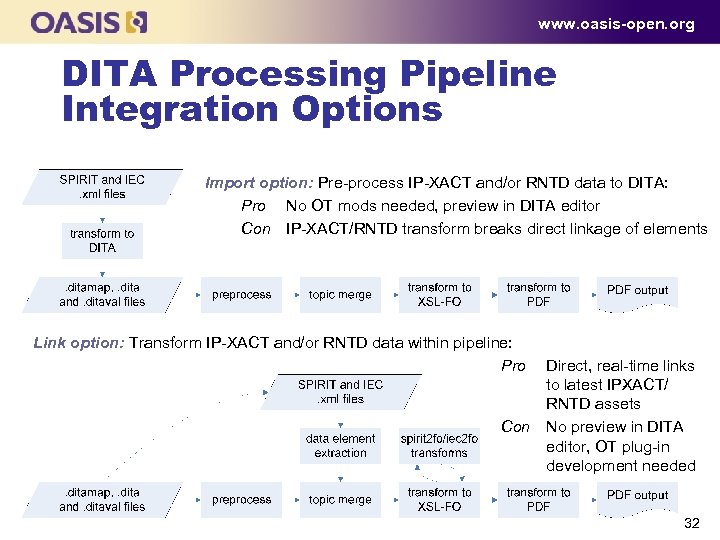
www. oasis-open. org DITA Processing Pipeline Integration Options Import option: Pre process IP XACT and/or RNTD data to DITA: Pro No OT mods needed, preview in DITA editor Con IP XACT/RNTD transform breaks direct linkage of elements Link option: Transform IP XACT and/or RNTD data within pipeline: Pro Direct, real time links to latest IP ACT/ X RNTD assets Con No preview in DITA editor, OT plug in development needed 32

www. oasis-open. org Outline n n n Are Industry Standards In Place? Are Problems Solved by Exchange? Do the Data Models Match Up? How Will DITA Specializations Help? How Will We Do It? 33

www. oasis-open. org How Will Specializations Help? n n Guide authors toward more consistent content creation Enable round trip exchange with other XML vocabularies Symantec information typing for output processing Potential semiconductor specific information types: l l l Instruction Set Architecture reference Memory Map / Register / Bit Field reference Signal Characteristics reference Electrical Characteristics reference Mechanical Specifications reference 34

www. oasis-open. org Finding the Specialization Fit n Legacy Document Analysis l l n Identify often repeated patterns Are these patterns filled / created from common data sources of other business processes? If so, is there an applicable open standard for the data source(s)? If so … single source and merge the streams! Specialization Targets l l l Structures Element Types Element Attributes 35

www. oasis-open. org Outline n n n Are Industry Standards In Place? Are Problems Solved by Exchange? Do the Data Models Match Up? How Will DITA Specializations Help? How Will We Do It? 36

www. oasis-open. org How Will We Do It? n n n Gap analysis: information type needs versus base DITA types Select closest match base DITA elements / structures Define deltas, create specialized content and processing modules 37

www. oasis-open. org Do We Need To Do It? n DITA components / attributes vs. So. C customer information set deliverables l l Are there So. C information types that get lost in ditabase? Are there So. C vocabularies that can’t be expressed in ditabase? Is DITA IP XACT / RNTD round trip impossible with ditabase? (Is it needed? ) Are specific semantic keys needed to generate the output customers have come to expect? 38

www. oasis-open. org Document Engineering Defined “The principles of document engineering seek to find a balance between technology and business, between process and information, between bottom up and top down thinking, and between concepts and implementation. Successful document engineers will do the same. ” Robert Glushko and Tim Mc. Grath Document Engineering 39

www. oasis-open. org Adoption of DITA in Medical Devices n n Chip Gettinger VP, Services and Sales Support Astoria Software cgettinger@astoriasoftware. com 40
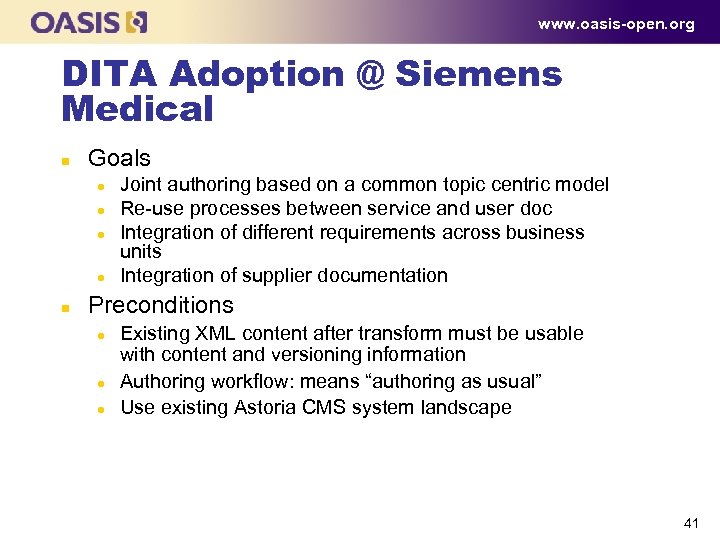
www. oasis-open. org DITA Adoption @ Siemens Medical n Goals l l n Joint authoring based on a common topic centric model Re use processes between service and user doc Integration of different requirements across business units Integration of supplier documentation Preconditions l l l Existing XML content after transform must be usable with content and versioning information Authoring workflow: means “authoring as usual” Use existing Astoria CMS system landscape 41
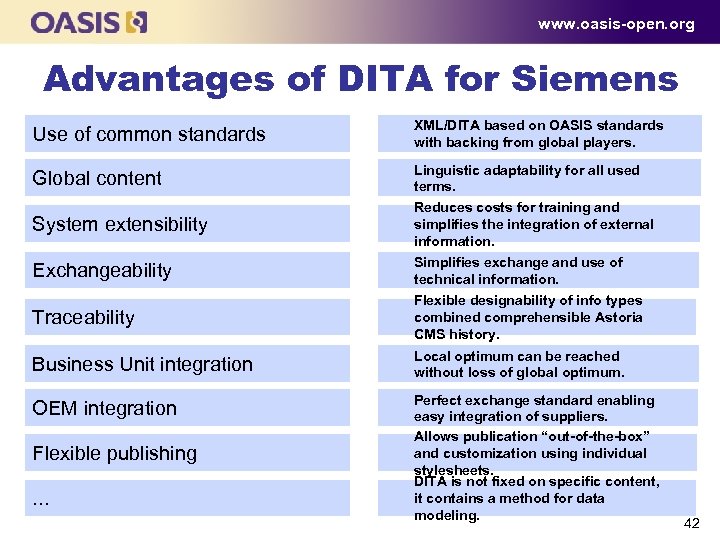
www. oasis-open. org Advantages of DITA for Siemens Use of common standards XML/DITA based on OASIS standards with backing from global players. Global content Linguistic adaptability for all used terms. Reduces costs for training and simplifies the integration of external information. System extensibility Exchangeability Simplifies exchange and use of technical information. Traceability Flexible designability of info types combined comprehensible Astoria CMS history. Business Unit integration Local optimum can be reached without loss of global optimum. OEM integration Perfect exchange standard enabling easy integration of suppliers. Allows publication “out-of-the-box” and customization using individual stylesheets. DITA is not fixed on specific content, it contains a method for data modeling. Flexible publishing. . . 42
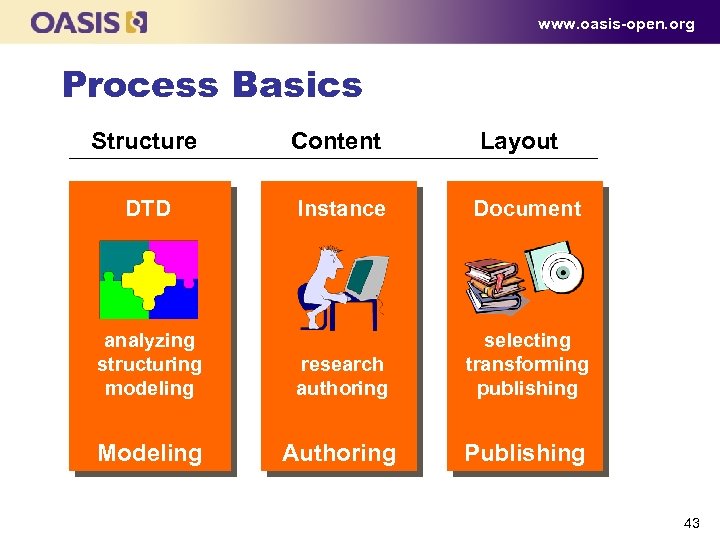
www. oasis-open. org Process Basics Structure Content Layout DTD Instance Document analyzing structuring modeling research authoring selecting transforming publishing Modeling Authoring Publishing 43

www. oasis-open. org Evolution within the last years. . . With adoption of the Astoria CMS and DITA n n n n n Innovation cycles dramatically shortened Dramatically increased volumes, e. g. content, output media, languages, doc types, authors, products, . . . Documentation creation today concurrent with development # of languages today = 23 Speeding up translation & localization cycles Focus on translation costs Global use of information according to Single Source principle Integration of OEM documentation Increasing process requirements 44
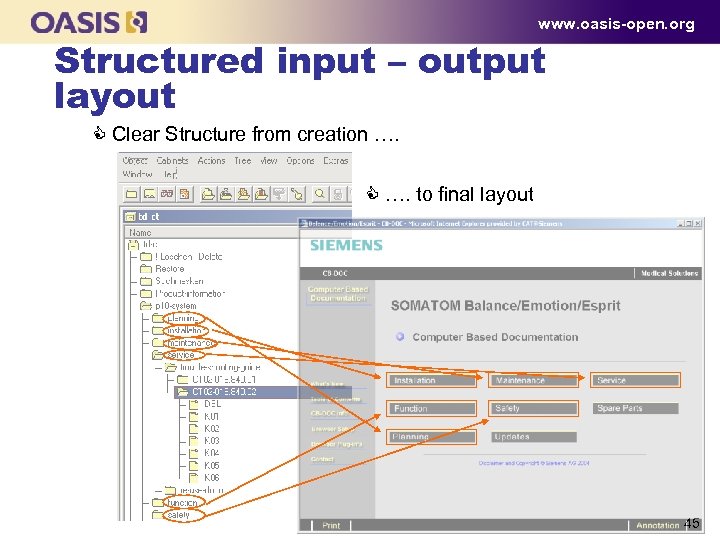
www. oasis-open. org Structured input – output layout C Clear Structure from creation …. C …. to final layout 45
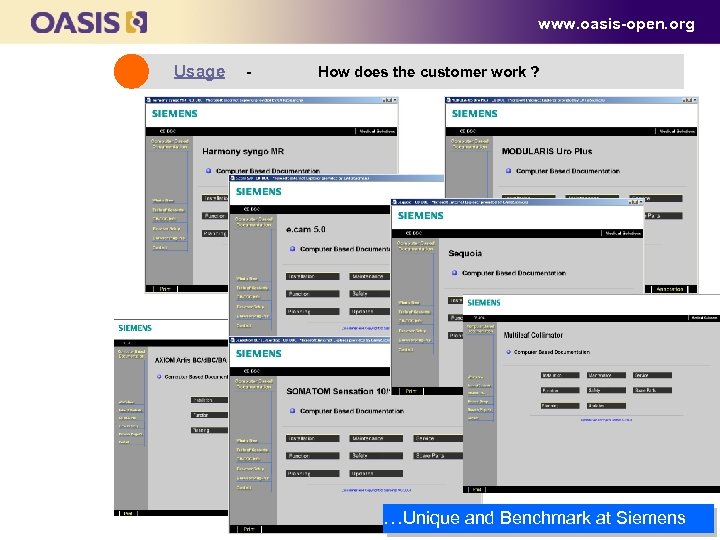
www. oasis-open. org Usage - How does the customer work ? …Unique and Benchmark at Siemens 46
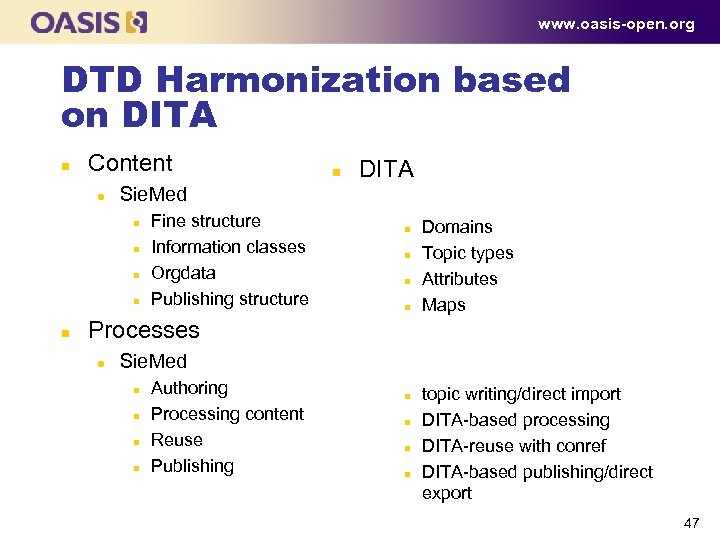
www. oasis-open. org DTD Harmonization based on DITA n Content l DITA Sie. Med n n n Fine structure Information classes Orgdata Publishing structure n n Domains Topic types Attributes Maps Processes l Sie. Med n n Authoring Processing content Reuse Publishing n n topic writing/direct import DITA based processing DITA reuse with conref DITA based publishing/direct export 47
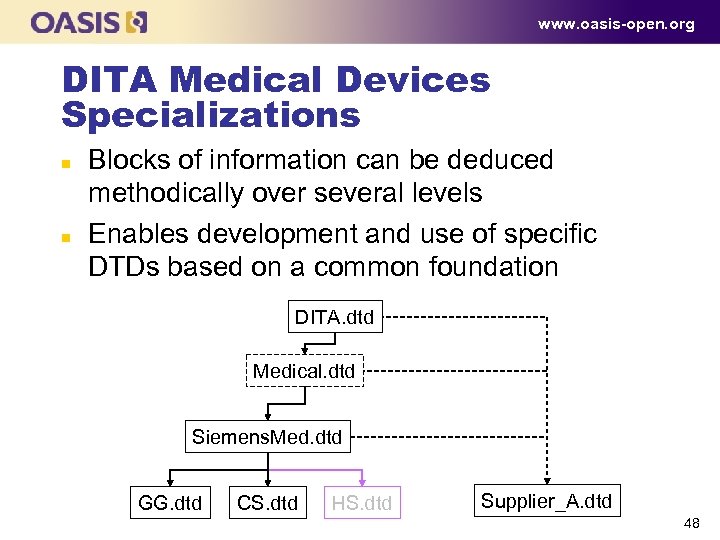
www. oasis-open. org DITA Medical Devices Specializations n n Blocks of information can be deduced methodically over several levels Enables development and use of specific DTDs based on a common foundation DITA. dtd Medical. dtd Siemens. Med. dtd GG. dtd CS. dtd HS. dtd Supplier_A. dtd 48
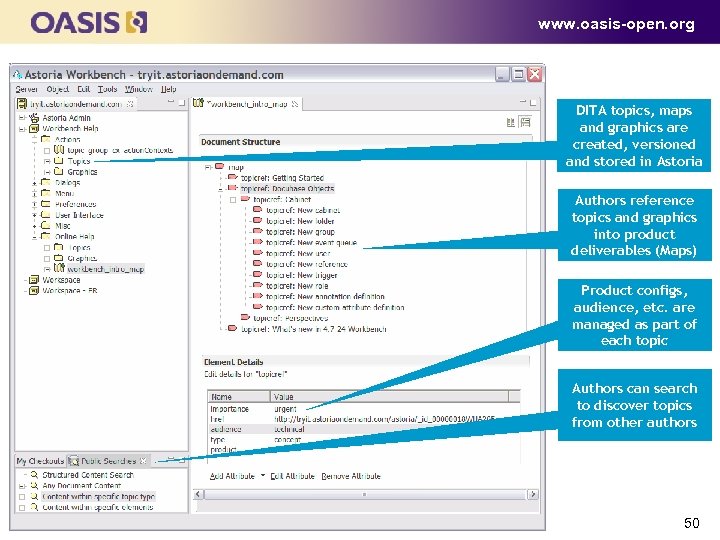
www. oasis-open. org DITA topics, maps and graphics are created, versioned and stored in Astoria Authors reference topics and graphics into product deliverables (Maps) Product configs, audience, etc. are managed as part of each topic Authors can search to discover topics from other authors 50
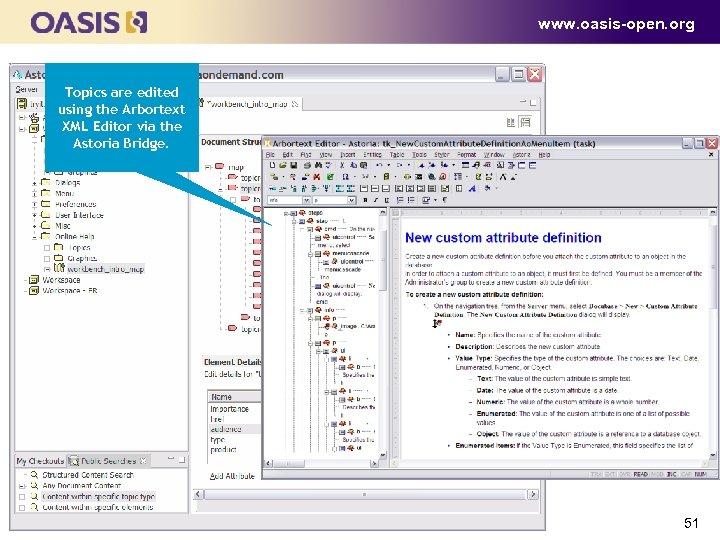
www. oasis-open. org Topics are edited using the Arbortext XML Editor via the Astoria Bridge. 51
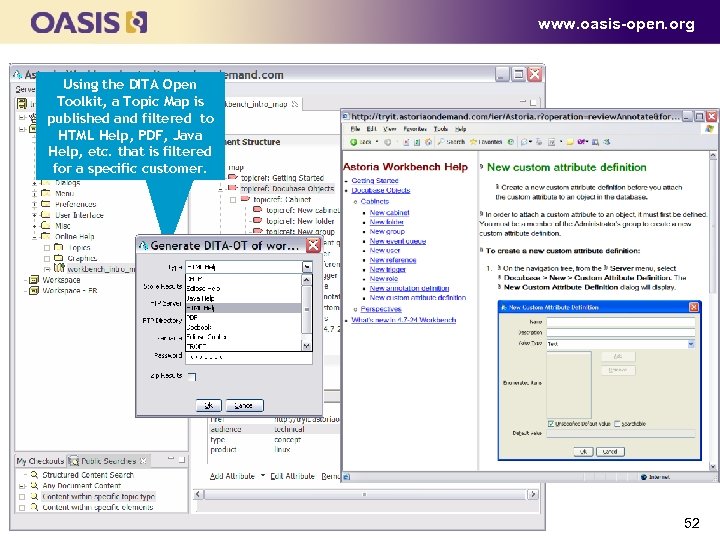
www. oasis-open. org Using the DITA Open Toolkit, a Topic Map is published and filtered to HTML Help, PDF, Java Help, etc. that is filtered for a specific customer. 52

www. oasis-open. org Medical Devices DITA Subcommittee n n n Defining goals and objectives Siemens Medical specializations to be available in public domain Faster time for adoption Adoption of industry best practices Supplier content interchange and updates 53

www. oasis-open. org Learning Content Specialization SC Goal: Develop a general top-level design for structured, intent-based authoring of learning content with good learning architecture, following DITA principles and best practices. Scott Hudson, Senior Consultant 54

www. oasis-open. org Top-level approach and assumptions n Adopt a top-level design for DITA topic-based learning content that is equally informed by the Cisco/Clark learning objects approach and by leading instructional models, and complements the Sharable Content Object Reference Model (SCORM). 55
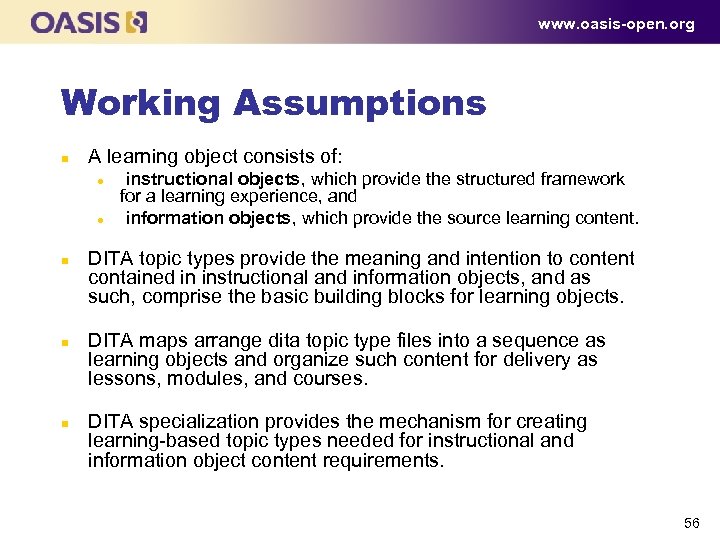
www. oasis-open. org Working Assumptions n A learning object consists of: l l n n n instructional objects, which provide the structured framework for a learning experience, and information objects, which provide the source learning content. DITA topic types provide the meaning and intention to content contained in instructional and information objects, and as such, comprise the basic building blocks for learning objects. DITA maps arrange dita topic type files into a sequence as learning objects and organize such content for delivery as lessons, modules, and courses. DITA specialization provides the mechanism for creating learning based topic types needed for instructional and information object content requirements. 56

www. oasis-open. org Instructional Objects Instructional objects are comprised of the following specialized DITA topic types: n Instructional Design topic type l n Learning Overview topic type l n Identifies the learning objectives, includes other information helpful to the learner, such prerequisites, duration, intended audience, and can include information and strategies that seeks to gain attention and stimulate recall of prior learning. Learning Summary topic type l n Describes learning needs and goals, instructional design models, task analyses, learning taxonomies, and other information necessary to the lesson planning process. Recaps and provides context for the learning objectives, provides guidance to reinforce learning and long term memory, and may pose questions to enhance encoding and verification of the learning content. Learning Assessment topic type l Presents instruments that measure progress, encourage retrieval, and stimulate reinforcement of the learning content, and can be presented before the content as a pre assessment or as a post assessment test. The interactions use a sub set of the Question Test Interoperability (QTI) specification, implemented as a DITA domain specialization. 57

www. oasis-open. org Information Objects Information objects are comprised of the following specialized DITA topic types: n Learning Content topic type l n Provides the learning content itself, and enables direct use of content from DITA task, concept, and reference topics, as well as additional content of any topic type that supports specific objectives declared in the Learning Overview topic type. A Learning Content topic comprises a set of self contained content about a single terminal learning objective supported by zero or more enabling learning objectives. Learning Enhancement topic type l Describes and presents content that supplements the primary learning content, such as practices, exercises, or simulations, and could also include scenarios that invoke role playing, games, in class homework, and group discussions. 58
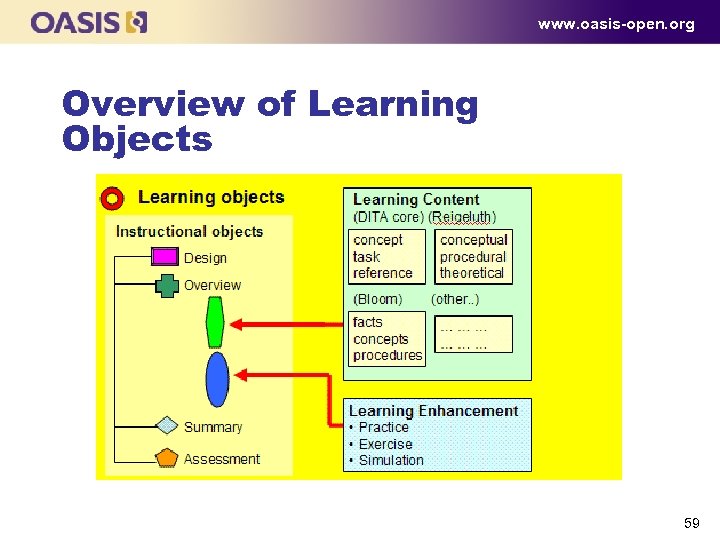
www. oasis-open. org Overview of Learning Objects 59
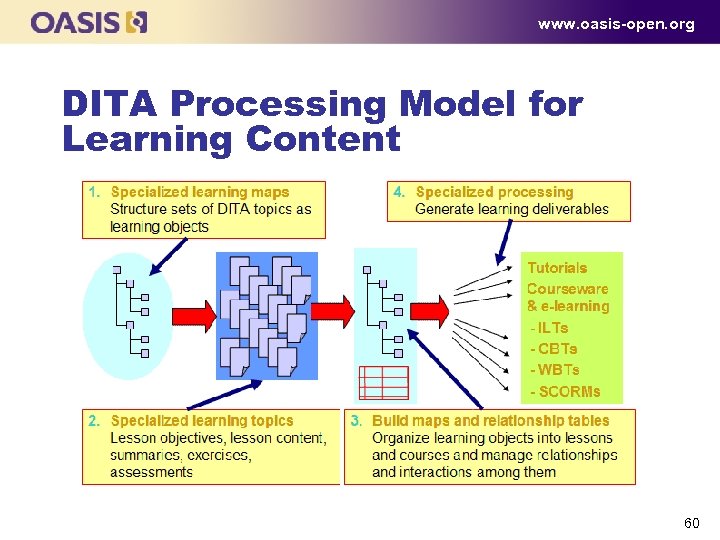
www. oasis-open. org DITA Processing Model for Learning Content 60

www. oasis-open. org S 1000 D-DITA Interoperability Forum n "One way to facilitate interoperability between S 1000 D and DITA is to use S 1000 D element names and semantics when creating DITA specializations for domains such as the machine industry. “ l l Should a full OASIS TC address the issue of Interoperability via a separate specification for Specialization? Should a DITA SC be set up to create a specialization for mapping S 1000 D data module elements to DITA? 61

www. oasis-open. org Resources online l Download the DITA toolkit n l Talk to others about DITA n l Join the dialog on the DITA forum – http: //groups. yahoo. com/group/dita users/ Research more about DITA n n n l http: //sourceforge. net/projects/dita ot/ OASIS – http: //www. oasis open. org/committees/dita Cover pages – http: //xml. coverpages. org/dita. html Knowledge base – http: //dita. xml. org Developer workshops Arbortext series n n http: //www 128. ibm. com/developerworks/xml/library/x dita 1/index. html http: //www. arbortext. com/resources/ 62

www. oasis-open. org DITA Translation Subcommittee n n n Advises the DITA Technical Committee on issues critical to localization and translation Proposes enhancements to the DITA architectural specification Develops DITA best practices for authors, businesses, and localization service providers 63

www. oasis-open. org Translation SC n Membership l l Organizations that require translation and localization of technical content Industry consultants Localization services provides Localization technology developers 64
www. oasis-open. org Contributions to date n DITA architectural specification 1. 1 l l l l n Directionality attribute Translation attribute XML lang attribute clarification Translatable block and inline elements Indexing sort order XLIFF compatibility Liaison with the W 3 C ITS Working Group Best Practices l l Indexing Translation memory Multi language documents Content references (conrefs) 65
206f279b6a24494a9c3ae0b981754c1c.ppt