013a48adb8753e19f81947517572a49c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 WWI WWII The Deep Roots of the Two World Wars
WWI WWII The Deep Roots of the Two World Wars
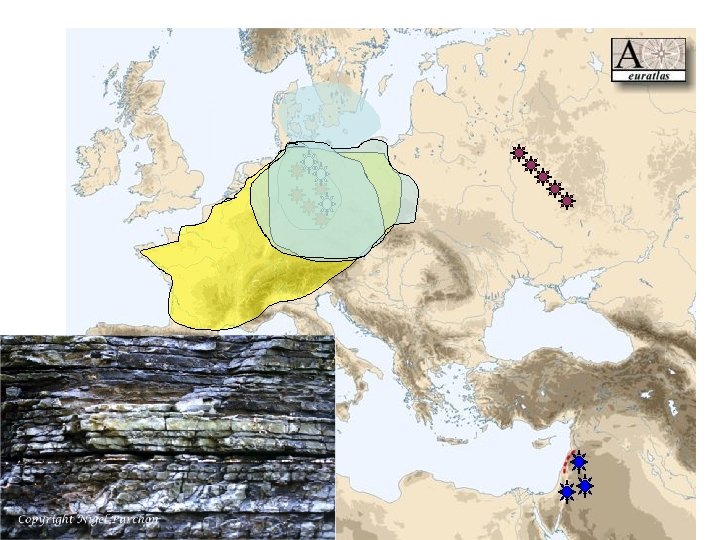
 The Mixed Ethnicities of Europe • Ethnic groups aren’t neatly organized in Europe (or anywhere else) – There have been numerous migrations of people into and around Europe at various times in history • Thus groups of people are mixed together – Examples • Balkans • Sudetenland
The Mixed Ethnicities of Europe • Ethnic groups aren’t neatly organized in Europe (or anywhere else) – There have been numerous migrations of people into and around Europe at various times in history • Thus groups of people are mixed together – Examples • Balkans • Sudetenland
 A Noteworthy Ethnic Group- the Jews of Europe • Ejected from Israel by the Romans in the 1 st century AD • Diaspora • Unwanted – pushed around Europe – Many countries accepted them, then booted them out, accepted them again – Example: Spanish ejection of the Moors and Jews in the same year Columbus sailed • Jewish ‘apartness’ – – Religious beliefs culture ‘Killers’ of Christ Model minority • Money lenders – Why? – Why did this lead to persecution? • Devotion to education – Why? – Why leads to persecution?
A Noteworthy Ethnic Group- the Jews of Europe • Ejected from Israel by the Romans in the 1 st century AD • Diaspora • Unwanted – pushed around Europe – Many countries accepted them, then booted them out, accepted them again – Example: Spanish ejection of the Moors and Jews in the same year Columbus sailed • Jewish ‘apartness’ – – Religious beliefs culture ‘Killers’ of Christ Model minority • Money lenders – Why? – Why did this lead to persecution? • Devotion to education – Why? – Why leads to persecution?
 Jews of Europe (cont. ) • (model minority, cont. ) • Devotion to education – Why? – Why leads to persecution? • A Long History of Persecution – Pogroms • Black death • Ghettoes in many places until Napoleon
Jews of Europe (cont. ) • (model minority, cont. ) • Devotion to education – Why? – Why leads to persecution? • A Long History of Persecution – Pogroms • Black death • Ghettoes in many places until Napoleon
 Kingdoms Versus Nations • Until about 300 years ago, most of Europe was divided by political ruler, not ethnicity – Subjects versus citizen – Political groups were heterogeneous ethnically – Habsburg example • Germans, Slavs (eastern Europe/Russia), and Gauls (French) were some of the largest ethnic groups • For 1000 yrs after the fall of the Roman Empire, the German ethnic group was divided into 300 weak states – The Holy Roman Empire • Central goal of many in Europe (for example, the French) was to keep Germany divided into these 300 states – Why?
Kingdoms Versus Nations • Until about 300 years ago, most of Europe was divided by political ruler, not ethnicity – Subjects versus citizen – Political groups were heterogeneous ethnically – Habsburg example • Germans, Slavs (eastern Europe/Russia), and Gauls (French) were some of the largest ethnic groups • For 1000 yrs after the fall of the Roman Empire, the German ethnic group was divided into 300 weak states – The Holy Roman Empire • Central goal of many in Europe (for example, the French) was to keep Germany divided into these 300 states – Why?
 The Rise of Nationalism • Age of Nationalism – Started in 19 th century – Political entities should be defined by ethnic group • Nationalism upset the European balance of power – Germany unified under Bismarck – Prussian Leadership • Sparta of the North • Militaristic – Germany is now the largest nation on the continent
The Rise of Nationalism • Age of Nationalism – Started in 19 th century – Political entities should be defined by ethnic group • Nationalism upset the European balance of power – Germany unified under Bismarck – Prussian Leadership • Sparta of the North • Militaristic – Germany is now the largest nation on the continent
 The German Behemoth • Germany leapt into the Industrial Revolution – Quickly became 2 nd or 3 rd ish behind Britain/U. S. – German nationalism peaked • Deutschland uber alles • Bitter legacy of manipulation from the outside – Thirty Years’ War, Napoleon, etc. • Bitterness of having missed out mostly in imperial land grab in Africa/Asia – Ironically, the Jewish situation wasn’t bad (relatively) in 19 th century Germany
The German Behemoth • Germany leapt into the Industrial Revolution – Quickly became 2 nd or 3 rd ish behind Britain/U. S. – German nationalism peaked • Deutschland uber alles • Bitter legacy of manipulation from the outside – Thirty Years’ War, Napoleon, etc. • Bitterness of having missed out mostly in imperial land grab in Africa/Asia – Ironically, the Jewish situation wasn’t bad (relatively) in 19 th century Germany
 Germany, Germany above all, Above all in the world, When, for protection and defense, it always takes a brotherly stand together. From the Meuse to the Memel, From the Adige to the Belt, Germany above everything, Above everything in the world.
Germany, Germany above all, Above all in the world, When, for protection and defense, it always takes a brotherly stand together. From the Meuse to the Memel, From the Adige to the Belt, Germany above everything, Above everything in the world.
 Social Darwinism’s Impact on Nationalism in the 19 th Century • Darwin’s ideas Do we cry for this guy? Boo! Yay! VS Survival of the Fittest among animal species
Social Darwinism’s Impact on Nationalism in the 19 th Century • Darwin’s ideas Do we cry for this guy? Boo! Yay! VS Survival of the Fittest among animal species
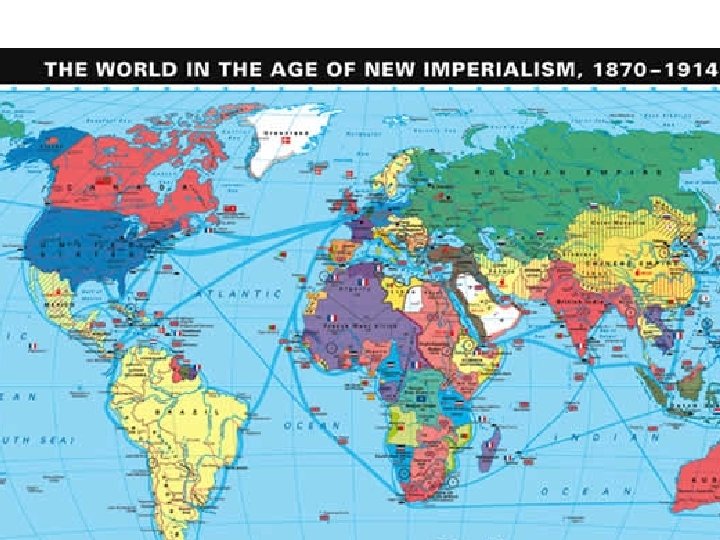
 1870 Franco-Prussian War • Germany defeated its old nemesis, France • Starvation and shelling of Paris • Humiliating treaty (for France) • Afterwards Bismarck's goal was to keep France isolated – He knew they want revenge • Bismarck fired by Wilhelm II • Wilhelm II = dunderhead – Allowed France to make alliances with Russia and Britain – Messed with British dominance • Guarantees Germans “A Place in the sun” • Naval arms race
1870 Franco-Prussian War • Germany defeated its old nemesis, France • Starvation and shelling of Paris • Humiliating treaty (for France) • Afterwards Bismarck's goal was to keep France isolated – He knew they want revenge • Bismarck fired by Wilhelm II • Wilhelm II = dunderhead – Allowed France to make alliances with Russia and Britain – Messed with British dominance • Guarantees Germans “A Place in the sun” • Naval arms race
 In 1914 WWI erupted • Result of M. A. I. N. – Militarism • Arms race of new industrial-age weapons – Alliance • Any outbreak could cascade into a giant war – Imperialism • Struggle for the best colonies – Nationalism • Intense patriotism • Social Darwinism • New kind of war – total war – stalemate • Germans attack first
In 1914 WWI erupted • Result of M. A. I. N. – Militarism • Arms race of new industrial-age weapons – Alliance • Any outbreak could cascade into a giant war – Imperialism • Struggle for the best colonies – Nationalism • Intense patriotism • Social Darwinism • New kind of war – total war – stalemate • Germans attack first
 Hansen WWII Name _______ Per ______ Lecture #2 - Deep Roots of the Two World Wars Ø The Mixed Ethnicities of Europe Ethnic groups aren’t _____________________________________ • There have been ____________ of people into and around Europe at various times in history – Thus groups of people are mixed together • Examples – ______ – Sudetenland – A Noteworthy Ethnic Group- the Jews of Europe Ejected from Israel by the _______ in the ___century AD Diaspora- ___________________ Unwanted – pushed around Europe • Many countries _______, then _______, _________ again • Example: Spanish ejection of the Moors and Jews in the same year Columbus sailed – Jewish ‘apartness’ • __________________ • Model minority – Money lenders » Why? __________________________ » Why did this lead to persecution? ___________________________ – Devotion to education » Why? __________________________ » Why leads to persecution? ________________ A Long History of Persecution • Pogroms - _____________ – Black death - _______________________________ • – Ø Note-taking Guide Ghettoes in many places until ________ Ø Kingdoms versus Nations – Until about 300 years ago, most of Europe was divided by _______________________ • Subjects versus citizen - ______________________________ • Political groups were heterogeneous ethnically • Habsburg example – _______, _____(eastern Europe/Russia), and _____(French) were some of the largest ethnic groups – For 1000 yrs after the fall of the Roman Empire, the German ethnic group was _____________ • The Holy ______ Empire – Central goal of many in Europe (for example, _____) was to keep Germany _______________ • Why? - _________________________________________ Ø The Rise of Nationalism – Age of Nationalism • Started in ________ • Political entities should be defined _______ – Nationalism upset the European ___________ • Germany unified under Bismarck • _______________ – Sparta of the North – Militaristic • Germany is now the _________on the continent – – –
Hansen WWII Name _______ Per ______ Lecture #2 - Deep Roots of the Two World Wars Ø The Mixed Ethnicities of Europe Ethnic groups aren’t _____________________________________ • There have been ____________ of people into and around Europe at various times in history – Thus groups of people are mixed together • Examples – ______ – Sudetenland – A Noteworthy Ethnic Group- the Jews of Europe Ejected from Israel by the _______ in the ___century AD Diaspora- ___________________ Unwanted – pushed around Europe • Many countries _______, then _______, _________ again • Example: Spanish ejection of the Moors and Jews in the same year Columbus sailed – Jewish ‘apartness’ • __________________ • Model minority – Money lenders » Why? __________________________ » Why did this lead to persecution? ___________________________ – Devotion to education » Why? __________________________ » Why leads to persecution? ________________ A Long History of Persecution • Pogroms - _____________ – Black death - _______________________________ • – Ø Note-taking Guide Ghettoes in many places until ________ Ø Kingdoms versus Nations – Until about 300 years ago, most of Europe was divided by _______________________ • Subjects versus citizen - ______________________________ • Political groups were heterogeneous ethnically • Habsburg example – _______, _____(eastern Europe/Russia), and _____(French) were some of the largest ethnic groups – For 1000 yrs after the fall of the Roman Empire, the German ethnic group was _____________ • The Holy ______ Empire – Central goal of many in Europe (for example, _____) was to keep Germany _______________ • Why? - _________________________________________ Ø The Rise of Nationalism – Age of Nationalism • Started in ________ • Political entities should be defined _______ – Nationalism upset the European ___________ • Germany unified under Bismarck • _______________ – Sparta of the North – Militaristic • Germany is now the _________on the continent – – –
 Ø – The Rise of Nationalism Germany leapt into the Industrial Revolution • Quickly became __________ behind ______________ • German nationalism peaked – Deutschland uber alles - ___________________ – Bitter legacy of _________ from the outside » Thirty Years’ War, Napoleon, Ø etc. – Bitterness of having missed out mostly ___________________in Africa/Asia • Ironically, the Jewish situation wasn’t bad (relatively) in 19 th century Germany Ø Social Darwinism’s Impact on Nationalism in the 19 th Century – Darwin’s ideas ___________________________________ – Impact on Nationalism and minority groups? _______________________ Ø • • 1870 Franco-Prussian War Germany defeated its old nemesis, ______ Starvation and shelling _____________________ treaty (for France) Afterwards Bismarck's goal was to keep France ____ – He knew they wanted ________ Bismarck fired by Wilhelm II = _________ – Allowed France to make alliances with _________________________ • • – Messed with British dominance • Guarantees Germans “A Place in the sun” - ___________________________________ • Naval arms race - ____________________________ In 1914 WWI Erupted – Result of M. A. I. N. • Militarism – ____________________________ • Alliance – Any outbreak could ____________________ • Imperialism – Struggle for the best ______ • Nationalism – Intense _________ – Social Darwinism – New kind of war • total war- ________________________________ • Stalemate- ________________________________ – Germans ________
Ø – The Rise of Nationalism Germany leapt into the Industrial Revolution • Quickly became __________ behind ______________ • German nationalism peaked – Deutschland uber alles - ___________________ – Bitter legacy of _________ from the outside » Thirty Years’ War, Napoleon, Ø etc. – Bitterness of having missed out mostly ___________________in Africa/Asia • Ironically, the Jewish situation wasn’t bad (relatively) in 19 th century Germany Ø Social Darwinism’s Impact on Nationalism in the 19 th Century – Darwin’s ideas ___________________________________ – Impact on Nationalism and minority groups? _______________________ Ø • • 1870 Franco-Prussian War Germany defeated its old nemesis, ______ Starvation and shelling _____________________ treaty (for France) Afterwards Bismarck's goal was to keep France ____ – He knew they wanted ________ Bismarck fired by Wilhelm II = _________ – Allowed France to make alliances with _________________________ • • – Messed with British dominance • Guarantees Germans “A Place in the sun” - ___________________________________ • Naval arms race - ____________________________ In 1914 WWI Erupted – Result of M. A. I. N. • Militarism – ____________________________ • Alliance – Any outbreak could ____________________ • Imperialism – Struggle for the best ______ • Nationalism – Intense _________ – Social Darwinism – New kind of war • total war- ________________________________ • Stalemate- ________________________________ – Germans ________


