 WW 1 The Great War The War to End all Wars
WW 1 The Great War The War to End all Wars
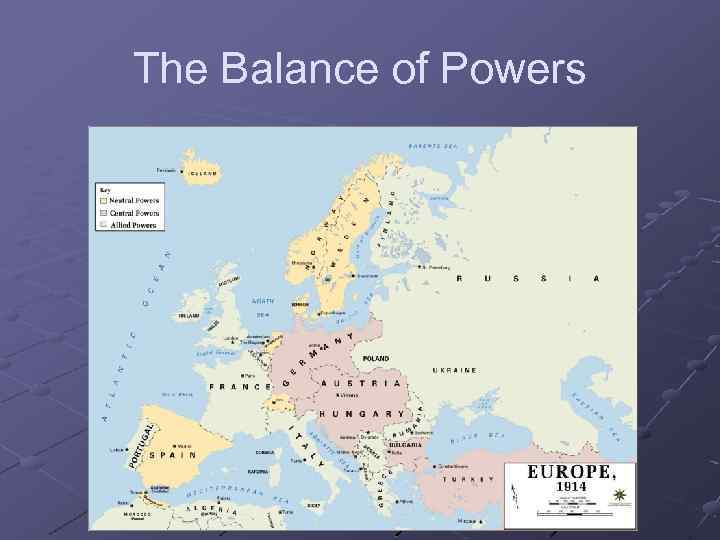 The Balance of Powers
The Balance of Powers
 UK before the War Britain, the staunch advocate of free trade, emerged in 1914 with not only the largest overseas empire thanks to her long-standing presence in India, but also the greatest gains in the "scramble for Africa", reflecting her advantageous position at its inception. Between 1885 and 1914 Britain took nearly 30% of Africa's population under her control, compared to 15 % for France, 9 % for Germany, 7 % for Belgium and 1 % for Italy: Nigeria alone contributed 15 million subjects, more than in the whole of French West Africa or the entire German colonial empire.
UK before the War Britain, the staunch advocate of free trade, emerged in 1914 with not only the largest overseas empire thanks to her long-standing presence in India, but also the greatest gains in the "scramble for Africa", reflecting her advantageous position at its inception. Between 1885 and 1914 Britain took nearly 30% of Africa's population under her control, compared to 15 % for France, 9 % for Germany, 7 % for Belgium and 1 % for Italy: Nigeria alone contributed 15 million subjects, more than in the whole of French West Africa or the entire German colonial empire.
 Tangled Alliances
Tangled Alliances
 A clash of 20 th century technology with 19 th century tactics Much of the war's combat involved trench warfare, where hundreds often died for each meter of land gained. Many of the deadliest battles in history occurred during the First World War. Such battles include Ypres, Vimy Ridge, Marne, Cambrai, Somme, Verdun, and Gallipoli.
A clash of 20 th century technology with 19 th century tactics Much of the war's combat involved trench warfare, where hundreds often died for each meter of land gained. Many of the deadliest battles in history occurred during the First World War. Such battles include Ypres, Vimy Ridge, Marne, Cambrai, Somme, Verdun, and Gallipoli.
 Advances in Military Technology
Advances in Military Technology
 First Bombers
First Bombers
 Trench War
Trench War
 The War of Attrition Throughout 1915 -17, the British Empire and France suffered many more casualties than Germany, but both sides lost millions of soldiers to injury and disease. Around 800, 000 soldiers from the British Empire were on the Western Front at any one time. 1, 000 battalions, each occupying a sector of the line from the North Sea to the Orne River, operated on a month-long four-stage rotation system, unless an offensive was underway. The front contained over 6, 000 miles of trenches. Each battalion held its sector for around a week before moving back to support lines and then further back to the reserve lines before a week out-of-line.
The War of Attrition Throughout 1915 -17, the British Empire and France suffered many more casualties than Germany, but both sides lost millions of soldiers to injury and disease. Around 800, 000 soldiers from the British Empire were on the Western Front at any one time. 1, 000 battalions, each occupying a sector of the line from the North Sea to the Orne River, operated on a month-long four-stage rotation system, unless an offensive was underway. The front contained over 6, 000 miles of trenches. Each battalion held its sector for around a week before moving back to support lines and then further back to the reserve lines before a week out-of-line.
 1918 Treaty of Versailles "The economic clauses of the treaty were malignant and silly to an extent that made them obviously futile [condemning] Germany to pay reparations on a fabulous scale" Article 231 of the treaty, the "War Guilt Clause", that held Germany responsible for the war, "imposed upon [the Allies] by the aggression of Germany and her Allies" (Article 231, Treaty of Versailles, 1919), was also widely considered to be unjust. Yet another flawed attribute of the treaty was the fact that it was devised by dissimilar people, with clashing objectives, and different interpretations of Woodrow Wilson's "Fourteen Points", upon which the treaty was supposed to have been based. It was therefore "a maze of compromises and a clash of principles".
1918 Treaty of Versailles "The economic clauses of the treaty were malignant and silly to an extent that made them obviously futile [condemning] Germany to pay reparations on a fabulous scale" Article 231 of the treaty, the "War Guilt Clause", that held Germany responsible for the war, "imposed upon [the Allies] by the aggression of Germany and her Allies" (Article 231, Treaty of Versailles, 1919), was also widely considered to be unjust. Yet another flawed attribute of the treaty was the fact that it was devised by dissimilar people, with clashing objectives, and different interpretations of Woodrow Wilson's "Fourteen Points", upon which the treaty was supposed to have been based. It was therefore "a maze of compromises and a clash of principles".
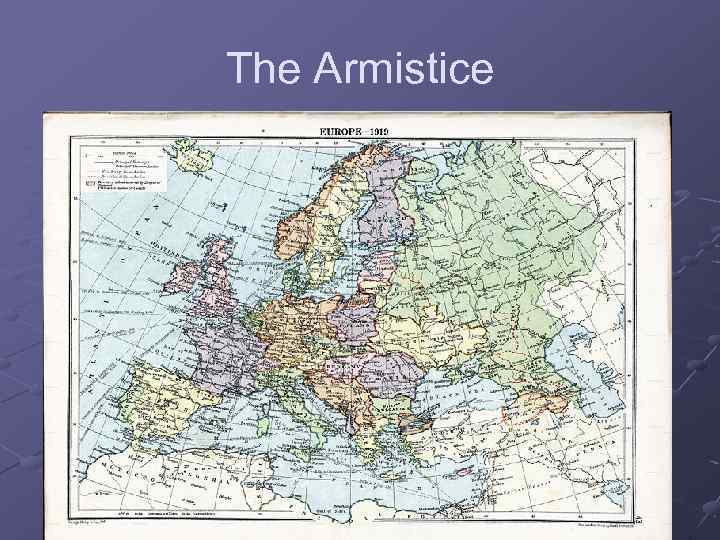 The Armistice
The Armistice
 War Consequences Major problems the country faced right after the war were: Demobilization; Inflation; A slump in the areas bought under government control during the war, i. e. coal industry; Reduction of governmental revenue; Ireland; Foreign affairs (intervention in Russia and sentiment for the ‘Reds’).
War Consequences Major problems the country faced right after the war were: Demobilization; Inflation; A slump in the areas bought under government control during the war, i. e. coal industry; Reduction of governmental revenue; Ireland; Foreign affairs (intervention in Russia and sentiment for the ‘Reds’).
 Victory? The aftermath of World War I saw the last major extension of British rule, with Britain gaining control through League of Nations Mandates in Palestine and Iraq (British League of Nations Trust Territory of Iraq) after the collapse of the Ottoman Empire in the Middle East, as well as in the former German colonies of Tanganyika, South-West Africa (now Namibia) and New Guinea (the last two actually under South African and Australian rule respectively). But although Britain emerged among the war's victors, and her rule expanded into new areas, the heavy costs of the war undermined her capacity to maintain the vast empire.
Victory? The aftermath of World War I saw the last major extension of British rule, with Britain gaining control through League of Nations Mandates in Palestine and Iraq (British League of Nations Trust Territory of Iraq) after the collapse of the Ottoman Empire in the Middle East, as well as in the former German colonies of Tanganyika, South-West Africa (now Namibia) and New Guinea (the last two actually under South African and Australian rule respectively). But although Britain emerged among the war's victors, and her rule expanded into new areas, the heavy costs of the war undermined her capacity to maintain the vast empire.
 Transformation of Dominion Status Full Dominion independence was formalized in the 1926 Balfour Declaration and the 1931 Statute of Westminster: each Dominion was henceforth to be equal in status to Britain herself, free of British legislative interference and autonomous in international relations. The Dominions section created within the Colonial Office in 1907 was upgraded in 1925 to a separate Dominions Office and given its own Secretary of State in 1930.
Transformation of Dominion Status Full Dominion independence was formalized in the 1926 Balfour Declaration and the 1931 Statute of Westminster: each Dominion was henceforth to be equal in status to Britain herself, free of British legislative interference and autonomous in international relations. The Dominions section created within the Colonial Office in 1907 was upgraded in 1925 to a separate Dominions Office and given its own Secretary of State in 1930.
 Lost Generation The horrors of the First World War led to widespread social trauma. This Disillusionment following the war manifested itself in a number of ways, sparking manifold artistic, literary, philosophical, musical, and cultural movements. In contrast to pre-war artistic movements, such as Impressionism, post-war art became bleak and cynical, changing the rules, abandoning tradition, experimenting with the unknown, and, above all, exposing the sham of western civilization
Lost Generation The horrors of the First World War led to widespread social trauma. This Disillusionment following the war manifested itself in a number of ways, sparking manifold artistic, literary, philosophical, musical, and cultural movements. In contrast to pre-war artistic movements, such as Impressionism, post-war art became bleak and cynical, changing the rules, abandoning tradition, experimenting with the unknown, and, above all, exposing the sham of western civilization
 Follow Up Name countries of the a) Triple Entente; b) Triple Alliance. Which explanations are given as to the reasons of WWI? What other reasons could be given? Find on the map and show zones of colonial hostilities. Explain what is ‘Shieffen Plan’; why did it fail? Dwell upon European warfare; what made this war different from all the previous ones? Comment upon coordination, effectiveness and staff competence. Write out places of major battles. Explain what is ‘a war of attrition’. What was the role of Ottoman Empire in the conflict? Write out dates you consider most important for the period. What happened? Name major problems GB faced after the Armistice and sum up the way they were dealt with. Sum up transformation of the Dominion Status; why was it so rapid? Which countries gained independence? Name nations that consider WWI ‘Baptism of fire’; name nations that suffered psychological trauma after the war; how did the trauma manifest itself? Speak about social reforms of the 20 -s. What is ‘depression’? Why was it so bad?
Follow Up Name countries of the a) Triple Entente; b) Triple Alliance. Which explanations are given as to the reasons of WWI? What other reasons could be given? Find on the map and show zones of colonial hostilities. Explain what is ‘Shieffen Plan’; why did it fail? Dwell upon European warfare; what made this war different from all the previous ones? Comment upon coordination, effectiveness and staff competence. Write out places of major battles. Explain what is ‘a war of attrition’. What was the role of Ottoman Empire in the conflict? Write out dates you consider most important for the period. What happened? Name major problems GB faced after the Armistice and sum up the way they were dealt with. Sum up transformation of the Dominion Status; why was it so rapid? Which countries gained independence? Name nations that consider WWI ‘Baptism of fire’; name nations that suffered psychological trauma after the war; how did the trauma manifest itself? Speak about social reforms of the 20 -s. What is ‘depression’? Why was it so bad?


