2015-10-28 WTO Law - Goods - Special Agreements.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 23
 WTO Law Fernando Piérola Special agreements on trade in goods
WTO Law Fernando Piérola Special agreements on trade in goods
 Outline Trade remedies: Anti-dumping Agreement, Agreement on Subsidies and Countervailing Measures (SCM) and Agreement on Safeguards SCM Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Agreement on Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures (SPS)
Outline Trade remedies: Anti-dumping Agreement, Agreement on Subsidies and Countervailing Measures (SCM) and Agreement on Safeguards SCM Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Agreement on Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures (SPS)
 WHAT IS A TRADE REMEDY? World Trade & Trade Rules e. g. , discriminatory import requirements on imported products from certain origins Tariff: e. g. , 10% ad valorem CHF 5 per tonne in excess of bindings Delivery Exporting Country Payment Quantitative restriction: e. g. importation allowed until 1000 tonnes/units, etc. Importing Country e. g. , discriminatory technical requirements on imported products, etc
WHAT IS A TRADE REMEDY? World Trade & Trade Rules e. g. , discriminatory import requirements on imported products from certain origins Tariff: e. g. , 10% ad valorem CHF 5 per tonne in excess of bindings Delivery Exporting Country Payment Quantitative restriction: e. g. importation allowed until 1000 tonnes/units, etc. Importing Country e. g. , discriminatory technical requirements on imported products, etc
 WHAT IS A TRADE REMEDY? Political economy of trade rules is ho W d? te fec af Delivery Exporting Country Payment Importing Country
WHAT IS A TRADE REMEDY? Political economy of trade rules is ho W d? te fec af Delivery Exporting Country Payment Importing Country
 WHAT IS A TRADE REMEDY? Political economy of trade rules Trade policy’s decisionmaking Whose interest do I pursue? Considerations: - Economic cost and benefit analysis - Political cost and benefit analysis
WHAT IS A TRADE REMEDY? Political economy of trade rules Trade policy’s decisionmaking Whose interest do I pursue? Considerations: - Economic cost and benefit analysis - Political cost and benefit analysis
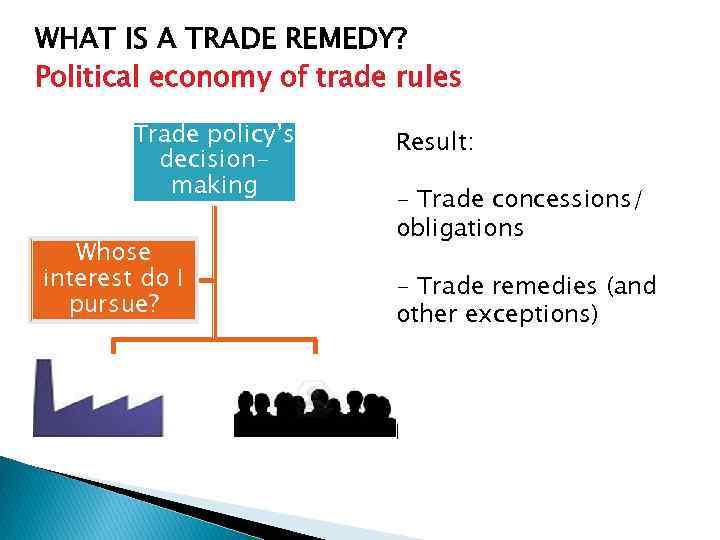 WHAT IS A TRADE REMEDY? Political economy of trade rules Trade policy’s decisionmaking Whose interest do I pursue? Result: - Trade concessions/ obligations - Trade remedies (and other exceptions)
WHAT IS A TRADE REMEDY? Political economy of trade rules Trade policy’s decisionmaking Whose interest do I pursue? Result: - Trade concessions/ obligations - Trade remedies (and other exceptions)
 WHAT IS A TRADE REMEDY? Trade remedies - explanation • • • Specific type of trade measures against imports To prevent/remedy injury to the domestic industry of specific products (and to facilitate “adjustment” in the case of safeguards) Only under specific circumstances
WHAT IS A TRADE REMEDY? Trade remedies - explanation • • • Specific type of trade measures against imports To prevent/remedy injury to the domestic industry of specific products (and to facilitate “adjustment” in the case of safeguards) Only under specific circumstances
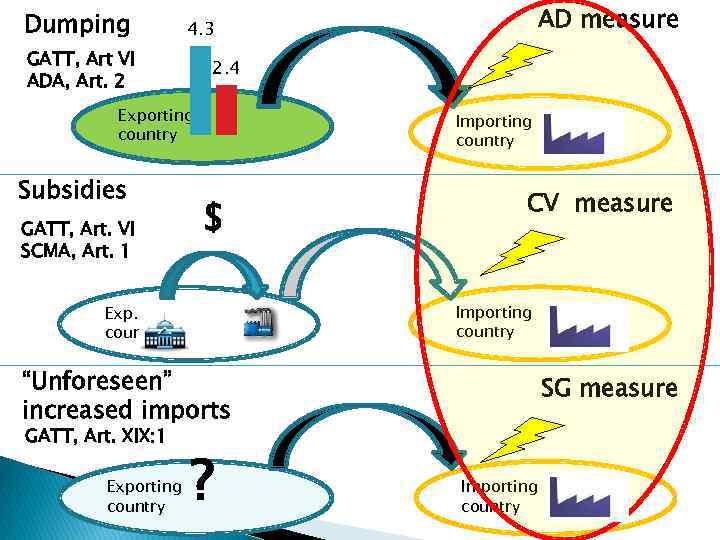 Dumping GATT, Art VI ADA, Art. 2 2. 4 Exporting country Subsidies GATT, Art. VI SCMA, Art. 1 AD measure 4. 3 Importing country $ CV measure Importing country Exp. country “Unforeseen” increased imports GATT, Art. XIX: 1 Exporting country ? SG measure Importing country
Dumping GATT, Art VI ADA, Art. 2 2. 4 Exporting country Subsidies GATT, Art. VI SCMA, Art. 1 AD measure 4. 3 Importing country $ CV measure Importing country Exp. country “Unforeseen” increased imports GATT, Art. XIX: 1 Exporting country ? SG measure Importing country
 WHAT IS A TRADE REMEDY? Trade remedies - explanation Antidumping measures (AD) • AD duties • Price undertakings Countervailing • CV duties measures • Undertakings (CVD) Safeguard measures (SG) • Tariff increases, Tariff-rate quotas • Quotas, others? ?
WHAT IS A TRADE REMEDY? Trade remedies - explanation Antidumping measures (AD) • AD duties • Price undertakings Countervailing • CV duties measures • Undertakings (CVD) Safeguard measures (SG) • Tariff increases, Tariff-rate quotas • Quotas, others? ?
 WHAT IS A TRADE REMEDY? Trade remedies - explanation 4 relevant instruments: 1. GATT 1994 (Articles II: 2(b), VI and XIX) 2. Agreement on Implementation of Article VI of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade 1994 (“Antidumping /AD Agreement”) 3. Agreement on Subsidies and Countervailing Measures (“SCM Agreement”) 4. Agreement on Safeguards (“”SG Agreement”)
WHAT IS A TRADE REMEDY? Trade remedies - explanation 4 relevant instruments: 1. GATT 1994 (Articles II: 2(b), VI and XIX) 2. Agreement on Implementation of Article VI of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade 1994 (“Antidumping /AD Agreement”) 3. Agreement on Subsidies and Countervailing Measures (“SCM Agreement”) 4. Agreement on Safeguards (“”SG Agreement”)
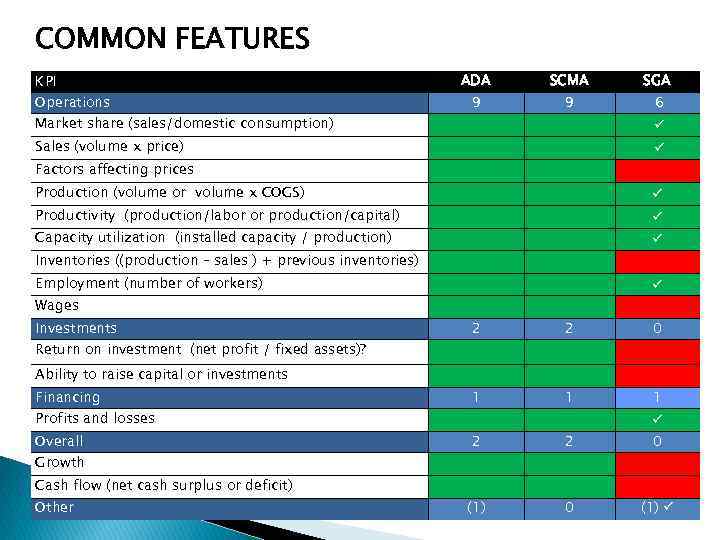 COMMON FEATURES KPI Operations Market share (sales/domestic consumption) ADA 9 SCMA 9 SGA 6 Sales (volume x price) Factors affecting prices Production (volume or volume x COGS) Productivity (production/labor or production/capital) Capacity utilization (installed capacity / production) Inventories ((production – sales ) + previous inventories) Employment (number of workers) Wages Investments Return on investment (net profit / fixed assets)? 2 2 0 1 1 1 2 2 0 (1) Ability to raise capital or investments Financing Profits and losses Overall Growth Cash flow (net cash surplus or deficit) Other
COMMON FEATURES KPI Operations Market share (sales/domestic consumption) ADA 9 SCMA 9 SGA 6 Sales (volume x price) Factors affecting prices Production (volume or volume x COGS) Productivity (production/labor or production/capital) Capacity utilization (installed capacity / production) Inventories ((production – sales ) + previous inventories) Employment (number of workers) Wages Investments Return on investment (net profit / fixed assets)? 2 2 0 1 1 1 2 2 0 (1) Ability to raise capital or investments Financing Profits and losses Overall Growth Cash flow (net cash surplus or deficit) Other
 Outline Trade remedies: Anti-dumping Agreement, Agreement on Subsidies and Countervailing Measures (SCM) and Agreement on Safeguards SCM Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Agreement on Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures (SPS)
Outline Trade remedies: Anti-dumping Agreement, Agreement on Subsidies and Countervailing Measures (SCM) and Agreement on Safeguards SCM Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Agreement on Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures (SPS)
 SCM Agreement Prohibits the use of certain subsidies. Regulates the actions Members can take when their interests are adversely affected by permitted subsidies, e. g. , countervailing measures. Expands considerably on GATT Articles VI and XVI. © ACWL
SCM Agreement Prohibits the use of certain subsidies. Regulates the actions Members can take when their interests are adversely affected by permitted subsidies, e. g. , countervailing measures. Expands considerably on GATT Articles VI and XVI. © ACWL
 SCM Agreement Direct transfer of funds Revenue foregone Financial contribution – price, income support Definition of a subsidy (Art. 1. 1) Provision of goods or services / purchase of goods Benefit Specificity (Arts. 1. 2, 2) Funding mechanism Export contingency (Art. 3. 1(a)) Prohibited subsidies (Art. 3) Import substitution (Art. 3. 1(b)) Categories of subsidies SCM Agreement Actionable subsidies Serious prejudice (Art. 6) Multilateral Remedies (through dispute settlement) Remedial tracks Special and Differential Treatment (Arts. 27. 2, 27. 4, Annex VII) Relationship with Agreement on Agriculture Violation (Art. 3) Unilateral route (through CV duties) (Introduction) (Section V)
SCM Agreement Direct transfer of funds Revenue foregone Financial contribution – price, income support Definition of a subsidy (Art. 1. 1) Provision of goods or services / purchase of goods Benefit Specificity (Arts. 1. 2, 2) Funding mechanism Export contingency (Art. 3. 1(a)) Prohibited subsidies (Art. 3) Import substitution (Art. 3. 1(b)) Categories of subsidies SCM Agreement Actionable subsidies Serious prejudice (Art. 6) Multilateral Remedies (through dispute settlement) Remedial tracks Special and Differential Treatment (Arts. 27. 2, 27. 4, Annex VII) Relationship with Agreement on Agriculture Violation (Art. 3) Unilateral route (through CV duties) (Introduction) (Section V)
 Outline Trade remedies: Anti-dumping Agreement, Agreement on Subsidies and Countervailing Measures (SCM) and Agreement on Safeguards SCM Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Agreement on Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures (SPS)
Outline Trade remedies: Anti-dumping Agreement, Agreement on Subsidies and Countervailing Measures (SCM) and Agreement on Safeguards SCM Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Agreement on Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures (SPS)
 TBT Agreement § "[W]hether a measure is a 'technical regulation' is a threshold issue because the outcome of this issue determines whether the TBT Agreement is applicable" EC-Asbestos, Appellate Body Report, para. 59 and ECSardines, Appellate Body Report, para. 175. § "Technical regulation" is defined in Annex 1. 1 as a: Document which lays down product characteristics or their related processes and production methods, including the applicable administrative provisions with which compliance is mandatory. It may also include or deal exclusively with terminology, symbols, packaging, marking or labelling requirements as they apply to a product, process or production method. © ACWL
TBT Agreement § "[W]hether a measure is a 'technical regulation' is a threshold issue because the outcome of this issue determines whether the TBT Agreement is applicable" EC-Asbestos, Appellate Body Report, para. 59 and ECSardines, Appellate Body Report, para. 175. § "Technical regulation" is defined in Annex 1. 1 as a: Document which lays down product characteristics or their related processes and production methods, including the applicable administrative provisions with which compliance is mandatory. It may also include or deal exclusively with terminology, symbols, packaging, marking or labelling requirements as they apply to a product, process or production method. © ACWL
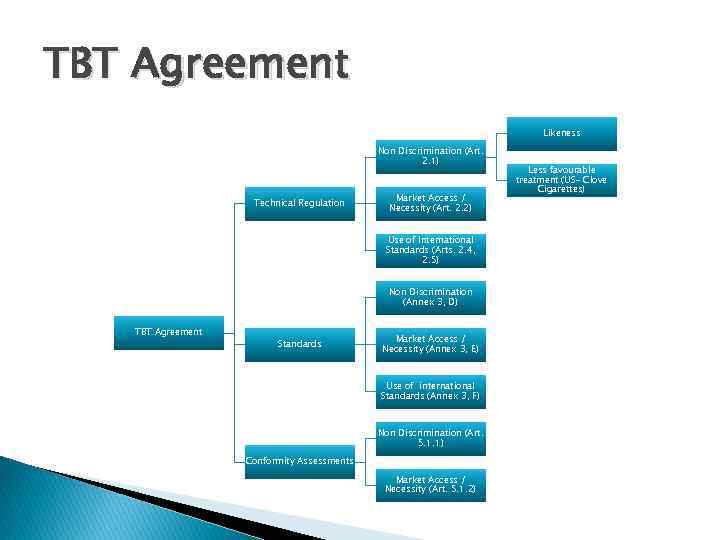 TBT Agreement Likeness Non Discrimination (Art. 2. 1) Technical Regulation Market Access / Necessity (Art. 2. 2) Use of International Standards (Arts. 2. 4, 2. 5) Non Discrimination (Annex 3, D) TBT Agreement Standards Market Access / Necessity (Annex 3, E) Use of international Standards (Annex 3, F) Non Discrimination (Art. 5. 1. 1) Conformity Assessments Market Access / Necessity (Art. 5. 1. 2) Less favourable treatment (US- Clove Cigarettes)
TBT Agreement Likeness Non Discrimination (Art. 2. 1) Technical Regulation Market Access / Necessity (Art. 2. 2) Use of International Standards (Arts. 2. 4, 2. 5) Non Discrimination (Annex 3, D) TBT Agreement Standards Market Access / Necessity (Annex 3, E) Use of international Standards (Annex 3, F) Non Discrimination (Art. 5. 1. 1) Conformity Assessments Market Access / Necessity (Art. 5. 1. 2) Less favourable treatment (US- Clove Cigarettes)
 Outline Trade remedies: Anti-dumping Agreement, Agreement on Subsidies and Countervailing Measures (SCM) and Agreement on Safeguards SCM Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Agreement on Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures (SPS)
Outline Trade remedies: Anti-dumping Agreement, Agreement on Subsidies and Countervailing Measures (SCM) and Agreement on Safeguards SCM Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Agreement on Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures (SPS)
 SPS Agreement What measures are subject to the Agreement: Article 1: All SPS measures "which may, directly or indirectly, affect international trade". Annex 1 A: Any measure applied – • To protect human or animal life within the territory of the Member from risks arising from the entry, establishment or spread of pests, disease-carrying organisms or diseasecausing organisms; • To protect human or animal life within the territory of the Member from risks arising from additives, contaminants, toxins or disease causing organisms in foods, beverages, or foodstuffs; © ACWL
SPS Agreement What measures are subject to the Agreement: Article 1: All SPS measures "which may, directly or indirectly, affect international trade". Annex 1 A: Any measure applied – • To protect human or animal life within the territory of the Member from risks arising from the entry, establishment or spread of pests, disease-carrying organisms or diseasecausing organisms; • To protect human or animal life within the territory of the Member from risks arising from additives, contaminants, toxins or disease causing organisms in foods, beverages, or foodstuffs; © ACWL
 SCOPE OF THE SPS AGREEMENT SPS Agreement What measures are subject to the Agreement (cont'd): • To protect human or animal life within the territory of the Member from risks arising from diseases carried by animals, plants or products thereof, or from the entry, establishment or spread of pests; or • To prevent or limit other damage within the territory of the Member from the entry, establishment or spread of pests. © ACWL
SCOPE OF THE SPS AGREEMENT SPS Agreement What measures are subject to the Agreement (cont'd): • To protect human or animal life within the territory of the Member from risks arising from diseases carried by animals, plants or products thereof, or from the entry, establishment or spread of pests; or • To prevent or limit other damage within the territory of the Member from the entry, establishment or spread of pests. © ACWL
 SPS Agreement Are the following measures SPS measures? § A requirement that the maximum pesticide residue level in tomatoes is X. § A prohibition on flavoured cigarettes, seeking to deter young people from taking up smoking. § A prohibition on the use of growth hormones when raising cattle (or animal husbandry in general). © ACWL
SPS Agreement Are the following measures SPS measures? § A requirement that the maximum pesticide residue level in tomatoes is X. § A prohibition on flavoured cigarettes, seeking to deter young people from taking up smoking. § A prohibition on the use of growth hormones when raising cattle (or animal husbandry in general). © ACWL
 SPS Agreement SPS Measure Confirmation of right to maintain SPS measures (Art. 2. 1) Presumption of compliance with XX(b) if compliance with SPS Agreement (Art. 2. 4) Market Access / Necessity (Art. 2. 2) SPS Agreement Risks involved (Annex 1 A) No more trade restrictive than necessary (Art. 5. 6) Non Discrimination (Art. 3. 3) Use of international Standards (Art. 3. 1) Risk assessment (Arts. 5. 1, 5. 2) Provisional measures (Art. 5. 7) Presumption of compliance with XX(b) and SPS Agreement if conformity with international standards (Art. 3. 2)
SPS Agreement SPS Measure Confirmation of right to maintain SPS measures (Art. 2. 1) Presumption of compliance with XX(b) if compliance with SPS Agreement (Art. 2. 4) Market Access / Necessity (Art. 2. 2) SPS Agreement Risks involved (Annex 1 A) No more trade restrictive than necessary (Art. 5. 6) Non Discrimination (Art. 3. 3) Use of international Standards (Art. 3. 1) Risk assessment (Arts. 5. 1, 5. 2) Provisional measures (Art. 5. 7) Presumption of compliance with XX(b) and SPS Agreement if conformity with international standards (Art. 3. 2)
 The end!
The end!


