2015-09-27 WTO Law - basics.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 29

WTO Law Fernando Piérola Presentation Basic Aspects 27 October 2015

Outline Presentation of the course Definition of International Trade Law and International Economic Law WTO Law and Regional Trade Agreements

International Trade Law W O T u r s le

Course Structure Basic notions of international trade law WTO legal framework Trade in Goods Basic rules Exceptions Special Agreements Intellectual Property Trade in Services Basic rules Exceptions General Principles IPs covered Enforcement 27 -29 October 2015 Dispute Settlement Structure Requirements

Outline Presentation of the course Definition of International Trade Law and International Economic Law WTO Law and Regional Trade Agreements
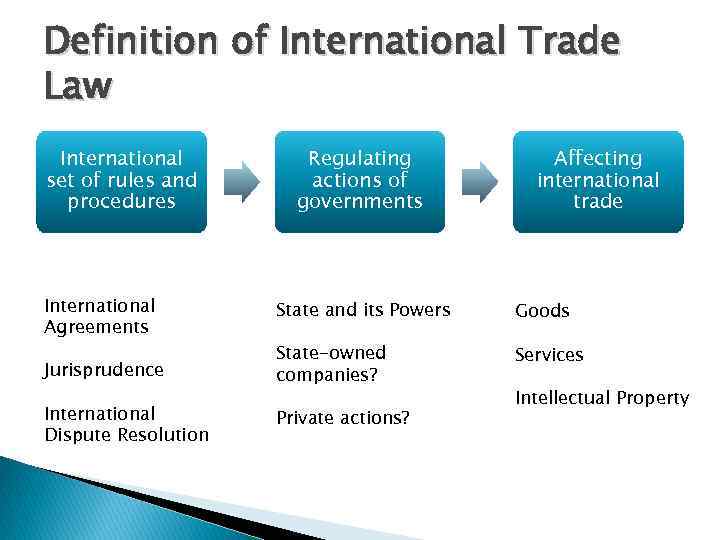
Definition of International Trade Law International set of rules and procedures International Agreements Regulating actions of governments Affecting international trade State and its Powers Goods Jurisprudence State-owned companies? Services International Dispute Resolution Private actions? Intellectual Property

Outline Presentation of the course Definition of International Trade Law and International Economic Law WTO Law and Regional Trade Agreements

International Trade Law and International Economic Law International Strategy International Trade Law International Competition Law Int’l IP Law Delivery Exporting Country Payment International Business Law Importing Country International Tax Law

Outline Presentation of the course Definition of International Trade Law and International Economic Law WTO Law and Regional Trade Agreements
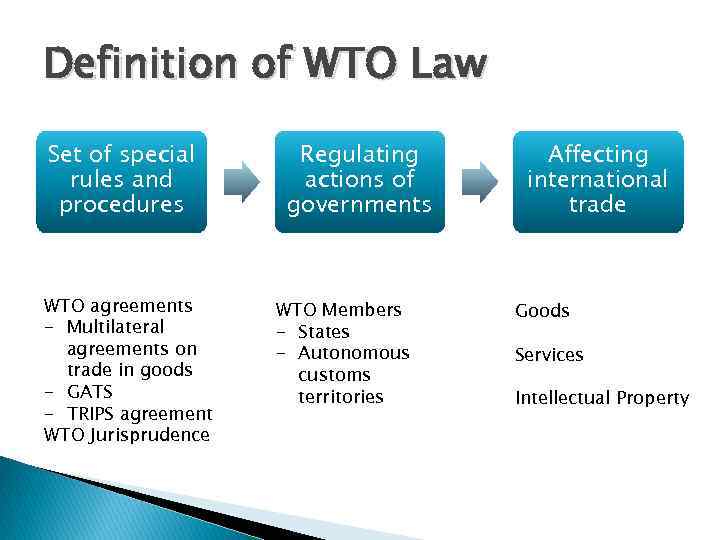
Definition of WTO Law Set of special rules and procedures WTO agreements - Multilateral agreements on trade in goods - GATS - TRIPS agreement WTO Jurisprudence Regulating actions of governments WTO Members - States - Autonomous customs territories Affecting international trade Goods Services Intellectual Property
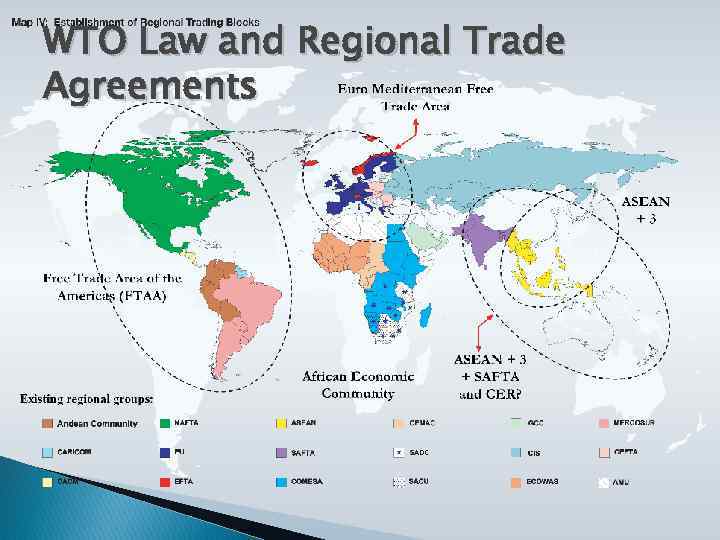
WTO Law and Regional Trade Agreements
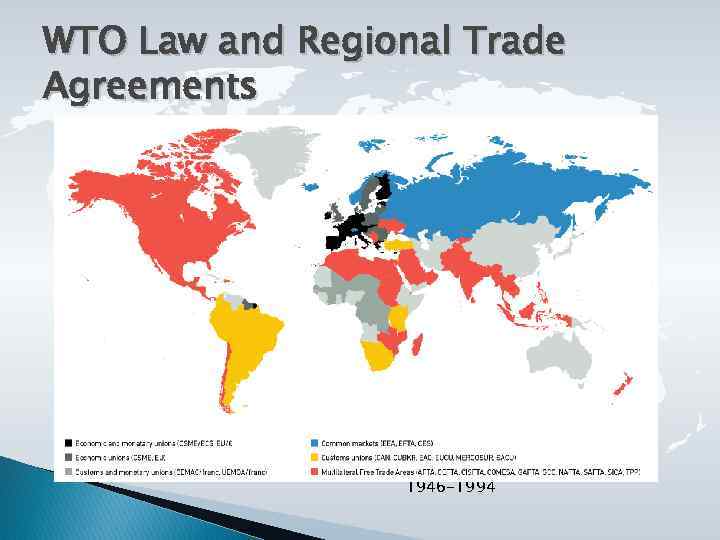
WTO Law and Regional Trade Agreements 1946 -1994

Exercises The deficient delivery of oil in a contract A payment default for a product The imposition of an excessive import duty The existence of a price cartel Misleading publicity affecting consumers A discriminatory tax on imported cigarettes The establishment of licenses to import in A An export tax applicable to oil and gas A state-owned company buying computers

BREAK!!!

Outline Overview of the basic rules in trade in goods History of the system The WTO institutional framework The Dispute Settlement Process
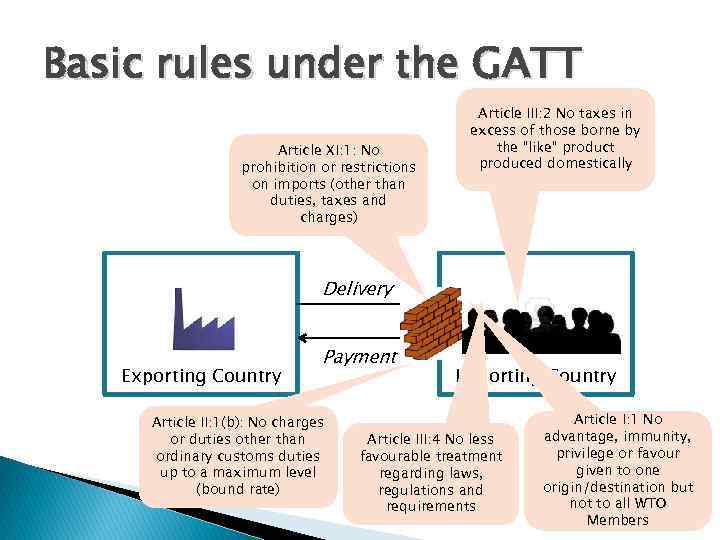
Basic rules under the GATT Article XI: 1: No prohibition or restrictions on imports (other than duties, taxes and charges) Article III: 2 No taxes in excess of those borne by the “like” product produced domestically Delivery Exporting Country Payment Article II: 1(b): No charges or duties other than ordinary customs duties up to a maximum level (bound rate) Importing Country Article III: 4 No less favourable treatment regarding laws, regulations and requirements Article I: 1 No advantage, immunity, privilege or favour given to one origin/destination but not to all WTO Members

Outline Overview of the basic rules in trade in goods History of the system The WTO institutional framework The Dispute Settlement Process

History International Conference Trade 1946 -1947 Atlantic Conference 1941 1946 -1994

Origins of the System -Post WWII regime -Theory of comparative advantages -Elimination of protectionism -Mitigation of colonial preferences -In the light of Bretton Woods agreements -Based on Havanna Charter (International Trade Organization) -23 signatories -Based on tariff reductions and concessions -Other rules protecting tariff concessions -Initially, broad coverage, incl. employment and competition -Lack of institutional framework -Decision-making by consensus -Unclear dispute settlement process 1947 1994

The objectives of the GATT
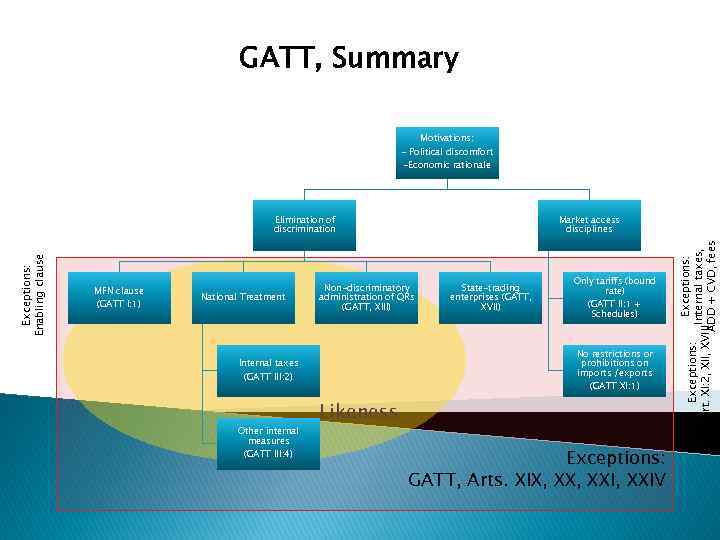
GATT, Summary Motivations: - Political discomfort -Economic rationale MFN clause (GATT I: 1) National Treatment Non-discriminatory administration of QRs (GATT, XIII) (GATT III: 4) State-trading enterprises (GATT, XVII) Only tariffs (bound rate) (GATT II: 1 + Schedules) No restrictions or prohibitions on imports /exports Internal taxes (GATT III: 2) Other internal measures Market access disciplines (GATT XI: 1) Likeness Exceptions: GATT, Arts. XIX, XXI, XXIV Exceptions: Internal taxes, Art. XI: 2, XII, XVIII ADD + CVD, fees Exceptions: Enabling clause Elimination of discrimination

Outline Overview of the basic rules in trade in goods History of the system The WTO institutional framework The Dispute Settlement Process

WTO System -Post cold war regime -Based on Uruguay Round Negotiations -160 Members - Tariff concessions but also other areas, such as services and intellectual property - Regulatory developments in trade in goods: new agreements -Formal institutional framework: WTO Goods Services IP DSU 1995 -Decision-making by consensus -Sophisticated dispute settlement process: Dispute Settlement Understanding present
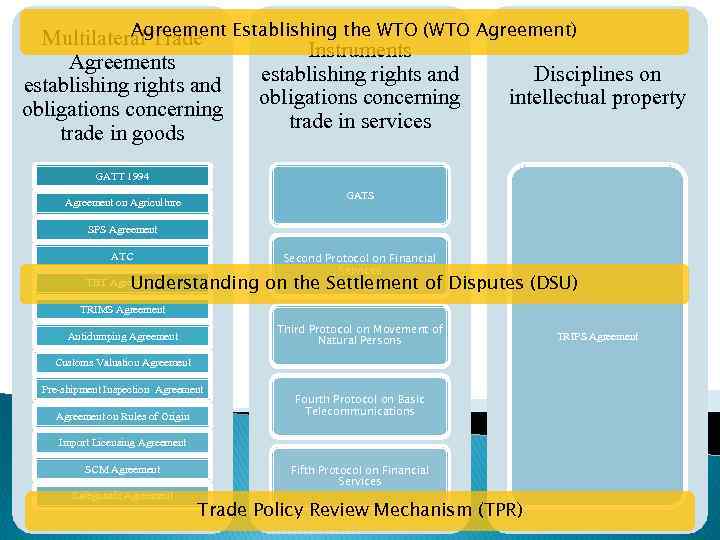
Agreement Multilateral Trade Establishing the WTO (WTO Agreement) Instruments Agreements establishing rights and Disciplines on establishing rights and obligations concerning intellectual property obligations concerning trade in services trade in goods GATT 1994 GATS Agreement on Agriculture SPS Agreement ATC Second Protocol on Financial Services Understanding on the Settlement of Disputes (DSU) TBT Agreement TRIMS Agreement Third Protocol on Movement of Natural Persons Antidumping Agreement Customs Valuation Agreement Pre-shipment Inspection Agreement on Rules of Origin Fourth Protocol on Basic Telecommunications Import Licensing Agreement SCM Agreement Safeguards Agreement Fifth Protocol on Financial Services Trade Policy Review Mechanism (TPR) TRIPS Agreement

Functions of the WTO
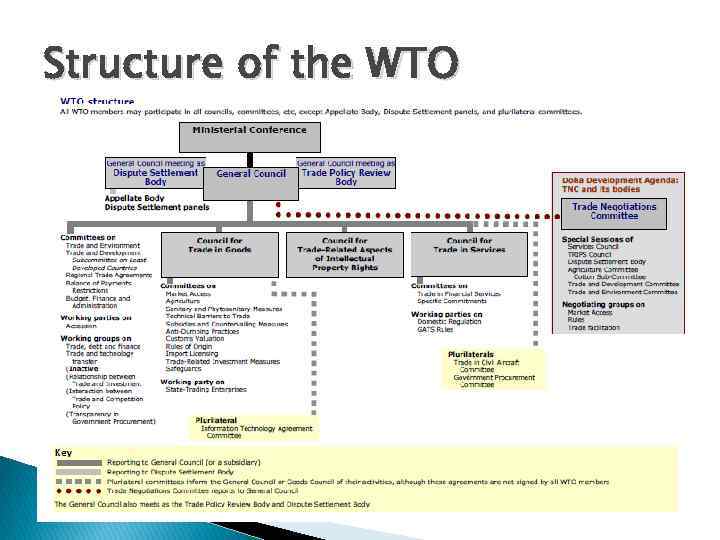
Structure of the WTO

Outline Overview of the basic rules in trade in goods History of the system The WTO institutional framework The Dispute Settlement Process
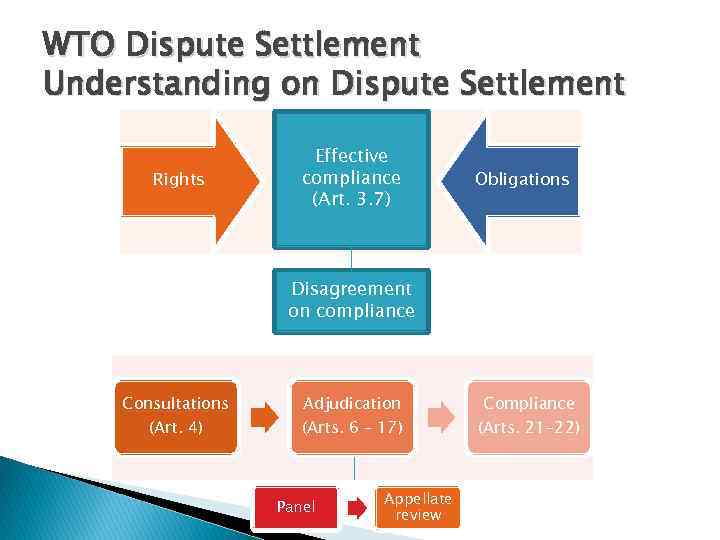
WTO Dispute Settlement Understanding on Dispute Settlement Rights Effective compliance (Art. 3. 7) Obligations Disagreement on compliance Consultations (Art. 4) Adjudication (Arts. 6 – 17) Panel Appellate review Compliance (Arts. 21 -22)

Debate What is the difference between the obligation of most-favoured nation and the obligation of national treatment? How could market access concessions be eroded by discrimination? How could intellectual property protection could preserve market access conditions? Is it simple for the WTO to create new agreements?
2015-09-27 WTO Law - basics.pptx