a05c47702809de7101d8170b80b26a63.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 WSEAS European Computing Conference (ECC’ 08) Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications M. J. Morón*, J. R. Luque*, E. J. Cuberos*, A. A. Botella*, E. Gallardo*, E. Casilari*, A. Díaz Estrella*, J. A. Gázquez** *UNIVERSITY OF MÁLAGA, **UNIVERSITY OF ALMERÍA, SPAIN Malta, September 11 th, 2008 Departamento de Tecnología Electrónica. University of Málaga ETSI de Telecomunicación, Campus de Teatinos, 29071 – Málaga- Spain E-mail: mjmoron@uma. es, ecasilari@uma. es 1 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications
WSEAS European Computing Conference (ECC’ 08) Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications M. J. Morón*, J. R. Luque*, E. J. Cuberos*, A. A. Botella*, E. Gallardo*, E. Casilari*, A. Díaz Estrella*, J. A. Gázquez** *UNIVERSITY OF MÁLAGA, **UNIVERSITY OF ALMERÍA, SPAIN Malta, September 11 th, 2008 Departamento de Tecnología Electrónica. University of Málaga ETSI de Telecomunicación, Campus de Teatinos, 29071 – Málaga- Spain E-mail: mjmoron@uma. es, ecasilari@uma. es 1 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications
 Index 1. Introduction: Brief state of the art 2. Goals 3. System description 4. Testbed Results and present state of the prototype 2 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications
Index 1. Introduction: Brief state of the art 2. Goals 3. System description 4. Testbed Results and present state of the prototype 2 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications
 INTRODUCTION Certain illnesses/sectors of population Continuous Monitoring Traditional wired sensors 1) 2) Quality of life Mobility Ø NEED of Wireless Telemedicine Ø SOLUTION: M-health Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications 3
INTRODUCTION Certain illnesses/sectors of population Continuous Monitoring Traditional wired sensors 1) 2) Quality of life Mobility Ø NEED of Wireless Telemedicine Ø SOLUTION: M-health Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications 3
 Experiences on M-health: Medical Wireless BAN ØMobile Health (M-Health): integration of technologies of mobile computing and medical sensors with wireless communications in a system of sanitary assistance ØStrong international efforts and research on this issue… ØCode. Blue, a wireless architecture designed in Harvard University for emergency medical care. The project integrates low-power, wireless vital sign sensors, PDAs, and PC-class systems ØAMON [Dec. 2004]: A wearable multi-parameter sensor. Continuous collection of multiple vital signs in wrist-worn enclosure with cellular communications USE of short-range communication Standards ØLow-power standards (Bluetooth, Zigbee, ) in telemedicine reduces cost and eases the deployment of systems ØMany commercial wearable BT sensors have appeared in recent years (ECG, glucometers, tensiometers, pulse-oximeters, stehoscopes, …) ØCommercial GPRS gateways for BT medical sensors ØBody/Personal Area Networks: piconet of sensors. Many examples in the literature [Lee 2006] [Yao 2005] [Krco 2005] [Dong 2004] 4 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications
Experiences on M-health: Medical Wireless BAN ØMobile Health (M-Health): integration of technologies of mobile computing and medical sensors with wireless communications in a system of sanitary assistance ØStrong international efforts and research on this issue… ØCode. Blue, a wireless architecture designed in Harvard University for emergency medical care. The project integrates low-power, wireless vital sign sensors, PDAs, and PC-class systems ØAMON [Dec. 2004]: A wearable multi-parameter sensor. Continuous collection of multiple vital signs in wrist-worn enclosure with cellular communications USE of short-range communication Standards ØLow-power standards (Bluetooth, Zigbee, ) in telemedicine reduces cost and eases the deployment of systems ØMany commercial wearable BT sensors have appeared in recent years (ECG, glucometers, tensiometers, pulse-oximeters, stehoscopes, …) ØCommercial GPRS gateways for BT medical sensors ØBody/Personal Area Networks: piconet of sensors. Many examples in the literature [Lee 2006] [Yao 2005] [Krco 2005] [Dong 2004] 4 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications
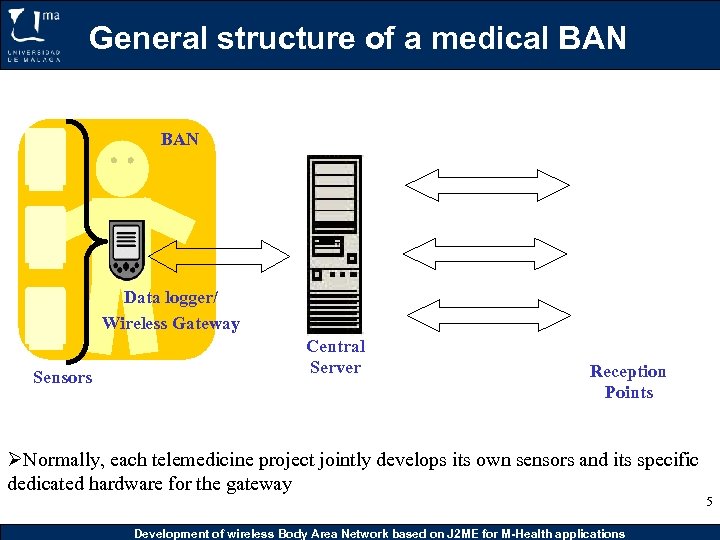 General structure of a medical BAN Data logger/ Wireless Gateway Sensors Central Server Reception Points ØNormally, each telemedicine project jointly develops its own sensors and its specific dedicated hardware for the gateway Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications 5
General structure of a medical BAN Data logger/ Wireless Gateway Sensors Central Server Reception Points ØNormally, each telemedicine project jointly develops its own sensors and its specific dedicated hardware for the gateway Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications 5
 OBJECTIVES Ø Definition of a wearable medical Personal Area Networks Ø Goals: ü Use/evaluation of commercial smart phones as the master of the sensor piconet ü Integration of commercial BT biosensors: use of Serial Server Profile (SSP) ü Adoption of Java (J 2 ME) to ease software portability • J 2 ME: Java Technology for the development of software applications in mobile devices. üHybrid transmissions (Always Best Connected Paradigm): free mobility of the users üTo enable mobility in the medical monitor üDetection/Priority of medical alarms: emission of SMS/MMS 6 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications
OBJECTIVES Ø Definition of a wearable medical Personal Area Networks Ø Goals: ü Use/evaluation of commercial smart phones as the master of the sensor piconet ü Integration of commercial BT biosensors: use of Serial Server Profile (SSP) ü Adoption of Java (J 2 ME) to ease software portability • J 2 ME: Java Technology for the development of software applications in mobile devices. üHybrid transmissions (Always Best Connected Paradigm): free mobility of the users üTo enable mobility in the medical monitor üDetection/Priority of medical alarms: emission of SMS/MMS 6 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications
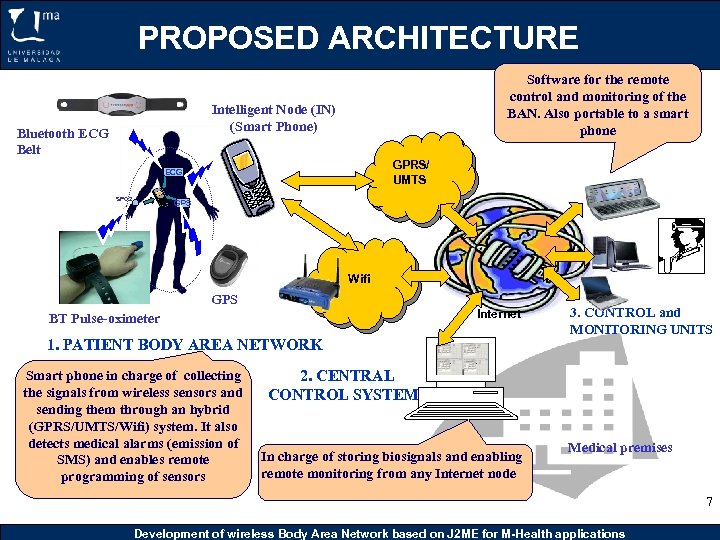 PROPOSED ARCHITECTURE Software for the remote control and monitoring of the BAN. Also portable to a smart phone Intelligent Node (IN) (Smart Phone) Bluetooth ECG Belt GPRS/ UMTS ECG SPO 2 GPS Wifi Internet GPS Internet BT Pulse-oximeter 1. PATIENT BODY AREA NETWORK Smart phone in charge of collecting the signals from wireless sensors and sending them through an hybrid (GPRS/UMTS/Wifi) system. It also detects medical alarms (emission of SMS) and enables remote programming of sensors 3. CONTROL and MONITORING UNITS 2. CENTRAL CONTROL SYSTEM In charge of storing biosignals and enabling remote monitoring from any Internet node Medical premises 7 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications
PROPOSED ARCHITECTURE Software for the remote control and monitoring of the BAN. Also portable to a smart phone Intelligent Node (IN) (Smart Phone) Bluetooth ECG Belt GPRS/ UMTS ECG SPO 2 GPS Wifi Internet GPS Internet BT Pulse-oximeter 1. PATIENT BODY AREA NETWORK Smart phone in charge of collecting the signals from wireless sensors and sending them through an hybrid (GPRS/UMTS/Wifi) system. It also detects medical alarms (emission of SMS) and enables remote programming of sensors 3. CONTROL and MONITORING UNITS 2. CENTRAL CONTROL SYSTEM In charge of storing biosignals and enabling remote monitoring from any Internet node Medical premises 7 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications
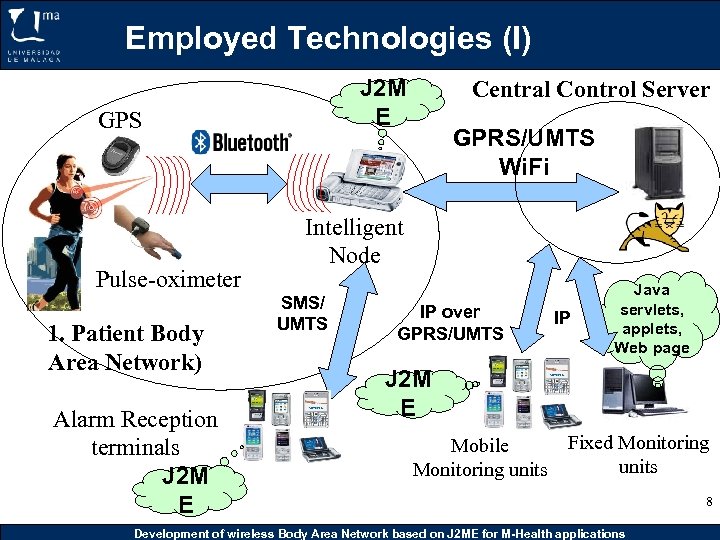 Employed Technologies (I) J 2 M E GPS Pulse-oximeter 1. Patient Body Area Network) Alarm Reception terminals J 2 M E Central Control Server GPRS/UMTS Wi. Fi Intelligent Node SMS/ UMTS IP over GPRS/UMTS IP Java servlets, applets, Web page J 2 M E Fixed Monitoring Mobile units Monitoring units Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications 8
Employed Technologies (I) J 2 M E GPS Pulse-oximeter 1. Patient Body Area Network) Alarm Reception terminals J 2 M E Central Control Server GPRS/UMTS Wi. Fi Intelligent Node SMS/ UMTS IP over GPRS/UMTS IP Java servlets, applets, Web page J 2 M E Fixed Monitoring Mobile units Monitoring units Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications 8
 Employed Technologies (II) Ø Smart Phones: Nokia 9500, E 61, N 93, N 95 (Symbian OS) ØIntelligent Node: J 2 ME (Java) program, Bluetooth API (JSR-82) for managing BT connections and Wireless Messaging API (JSR-120 & JSR-205) for sending SMSs/MMSs, Security and Trust Services API (JSR-177) to manage encryption. ØBiosignals are encrypted by means of a symmetric algorithm DES with a prefixed key ØProtocols used for transmissions: HTTP commands or TCP or UDP/ IP sockets (configurable) ØCentral Control Server: Apache Server. Servlets ØMonitoring reception software : ü Web interface (with a a Java Applet) available for any browser with RMI support. ü J 2 ME midlet in the Mobile monitoring unit ØBandwidth: üGPRS: up to 64 -144 Kbps üUMTS: up to 384 -3600 Kbps üWifi: up to 11 Mbps (802. 11 b), up to 54 Mbps (802. 11 g) Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications 9
Employed Technologies (II) Ø Smart Phones: Nokia 9500, E 61, N 93, N 95 (Symbian OS) ØIntelligent Node: J 2 ME (Java) program, Bluetooth API (JSR-82) for managing BT connections and Wireless Messaging API (JSR-120 & JSR-205) for sending SMSs/MMSs, Security and Trust Services API (JSR-177) to manage encryption. ØBiosignals are encrypted by means of a symmetric algorithm DES with a prefixed key ØProtocols used for transmissions: HTTP commands or TCP or UDP/ IP sockets (configurable) ØCentral Control Server: Apache Server. Servlets ØMonitoring reception software : ü Web interface (with a a Java Applet) available for any browser with RMI support. ü J 2 ME midlet in the Mobile monitoring unit ØBandwidth: üGPRS: up to 64 -144 Kbps üUMTS: up to 384 -3600 Kbps üWifi: up to 11 Mbps (802. 11 b), up to 54 Mbps (802. 11 g) Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications 9
 Employed BT devices (I) Bluetooth Basics §Frequency Band (ISM) at 2. 4 GHz. No licence required §Transmission Range: 10 -100 m §Robustness to interferences due to Frecuency hopping §Binary rate: up to 1 Mbps (v 1. 1), 2 -3 Mbps (v 2. 0): far enough for most biosignals §Low consume (acceptable for most external biosensors) §Extremely popular technology: in many models of PDA and cell phones §GPS Leadtek 9553 X §Chipset Si. RF Star. III §Bluetooth v 1. 2(slave mode, Serial Port Profile) § 5 V rechargeable Battery ± 5%V DC §NMEA-0183 Protocol 10 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications
Employed BT devices (I) Bluetooth Basics §Frequency Band (ISM) at 2. 4 GHz. No licence required §Transmission Range: 10 -100 m §Robustness to interferences due to Frecuency hopping §Binary rate: up to 1 Mbps (v 1. 1), 2 -3 Mbps (v 2. 0): far enough for most biosignals §Low consume (acceptable for most external biosensors) §Extremely popular technology: in many models of PDA and cell phones §GPS Leadtek 9553 X §Chipset Si. RF Star. III §Bluetooth v 1. 2(slave mode, Serial Port Profile) § 5 V rechargeable Battery ± 5%V DC §NMEA-0183 Protocol 10 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications
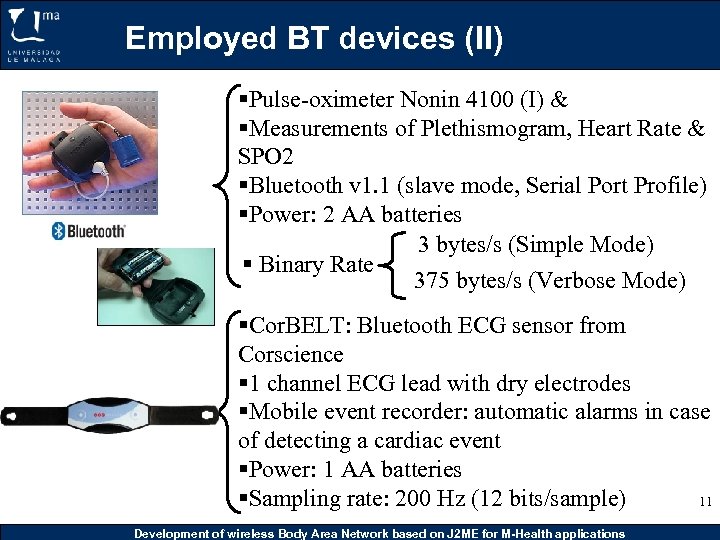 Employed BT devices (II) §Pulse-oximeter Nonin 4100 (I) & §Measurements of Plethismogram, Heart Rate & SPO 2 §Bluetooth v 1. 1 (slave mode, Serial Port Profile) §Power: 2 AA batteries 3 bytes/s (Simple Mode) § Binary Rate 375 bytes/s (Verbose Mode) §Cor. BELT: Bluetooth ECG sensor from Corscience § 1 channel ECG lead with dry electrodes §Mobile event recorder: automatic alarms in case of detecting a cardiac event §Power: 1 AA batteries §Sampling rate: 200 Hz (12 bits/sample) 11 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications
Employed BT devices (II) §Pulse-oximeter Nonin 4100 (I) & §Measurements of Plethismogram, Heart Rate & SPO 2 §Bluetooth v 1. 1 (slave mode, Serial Port Profile) §Power: 2 AA batteries 3 bytes/s (Simple Mode) § Binary Rate 375 bytes/s (Verbose Mode) §Cor. BELT: Bluetooth ECG sensor from Corscience § 1 channel ECG lead with dry electrodes §Mobile event recorder: automatic alarms in case of detecting a cardiac event §Power: 1 AA batteries §Sampling rate: 200 Hz (12 bits/sample) 11 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications
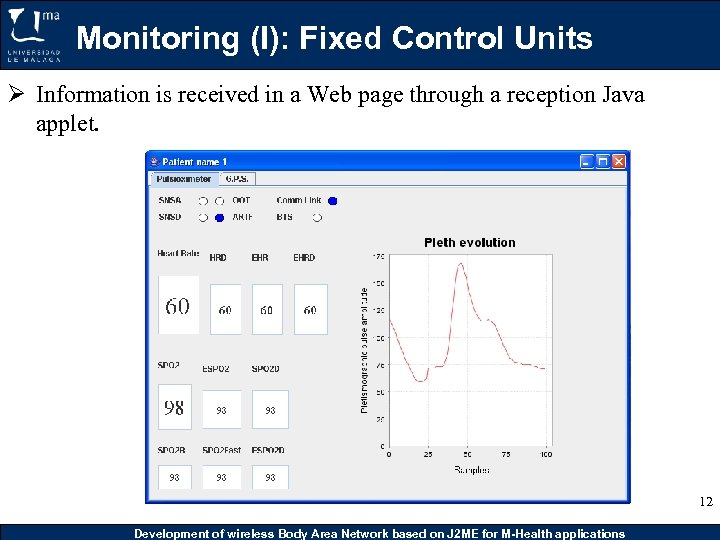 Monitoring (I): Fixed Control Units Ø Information is received in a Web page through a reception Java applet. 12 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications
Monitoring (I): Fixed Control Units Ø Information is received in a Web page through a reception Java applet. 12 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications
 Monitoring (II): Mobile Control Units Ø Screenshots of Mobile Control Monitoring Units Ø A reception J 2 ME midlet processes and present the encrypted biosignals 13 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications
Monitoring (II): Mobile Control Units Ø Screenshots of Mobile Control Monitoring Units Ø A reception J 2 ME midlet processes and present the encrypted biosignals 13 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications
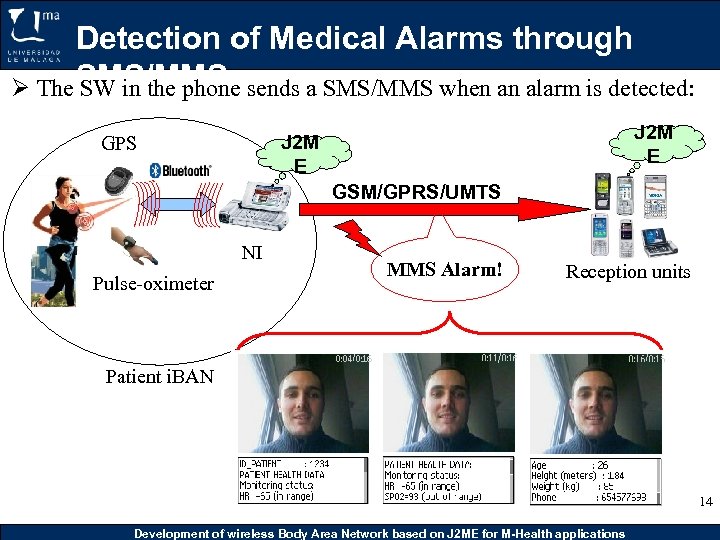 Detection of Medical Alarms through Ø The SMS/MMS sends a SMS/MMS when an alarm is detected: SW in the phone J 2 M E GPS GSM/GPRS/UMTS NI Pulse-oximeter MMS Alarm! Reception units Patient i. BAN 14 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications
Detection of Medical Alarms through Ø The SMS/MMS sends a SMS/MMS when an alarm is detected: SW in the phone J 2 M E GPS GSM/GPRS/UMTS NI Pulse-oximeter MMS Alarm! Reception units Patient i. BAN 14 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications
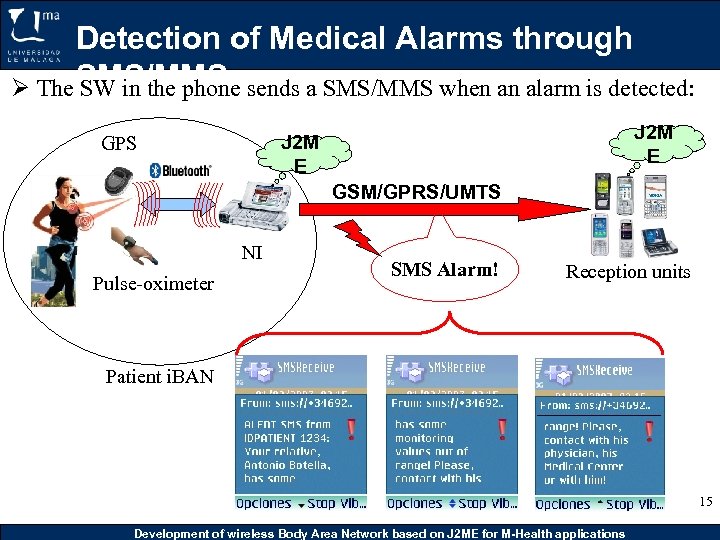 Detection of Medical Alarms through Ø The SMS/MMS sends a SMS/MMS when an alarm is detected: SW in the phone J 2 M E GPS GSM/GPRS/UMTS NI Pulse-oximeter SMS Alarm! Reception units Patient i. BAN 15 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications
Detection of Medical Alarms through Ø The SMS/MMS sends a SMS/MMS when an alarm is detected: SW in the phone J 2 M E GPS GSM/GPRS/UMTS NI Pulse-oximeter SMS Alarm! Reception units Patient i. BAN 15 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications
 Wireless biosignal emulator (I) ØTwo main research topics about medical WPANs/WBANs: ØScalability: how many sensors can be properly integrated in the BAN? ØCoexistence: different wireless technology (BT, Zigbee, Wifi) may coexist in the same ISM band ØThe evaluation of practical application environments for BANs may require utilization in parallel of dozens of biosensors (still far from being economical) ØSolution: to implement a generic software biosignal emulator: any BT biosensor can be emulated with a device having BT connectivity (e. g. : a laptop with one ore more BT dongles). ØPresently, the software emulates electrocardiogram (ECG) signals. ØSignals can be downloaded from an Internet Physio. Bank Data Base) ØVast archive of formatted digital recordings of biomedical signals from both healthy and pathological subjects: http: //www. physionet. org/physiobank/ 16 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications
Wireless biosignal emulator (I) ØTwo main research topics about medical WPANs/WBANs: ØScalability: how many sensors can be properly integrated in the BAN? ØCoexistence: different wireless technology (BT, Zigbee, Wifi) may coexist in the same ISM band ØThe evaluation of practical application environments for BANs may require utilization in parallel of dozens of biosensors (still far from being economical) ØSolution: to implement a generic software biosignal emulator: any BT biosensor can be emulated with a device having BT connectivity (e. g. : a laptop with one ore more BT dongles). ØPresently, the software emulates electrocardiogram (ECG) signals. ØSignals can be downloaded from an Internet Physio. Bank Data Base) ØVast archive of formatted digital recordings of biomedical signals from both healthy and pathological subjects: http: //www. physionet. org/physiobank/ 16 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications
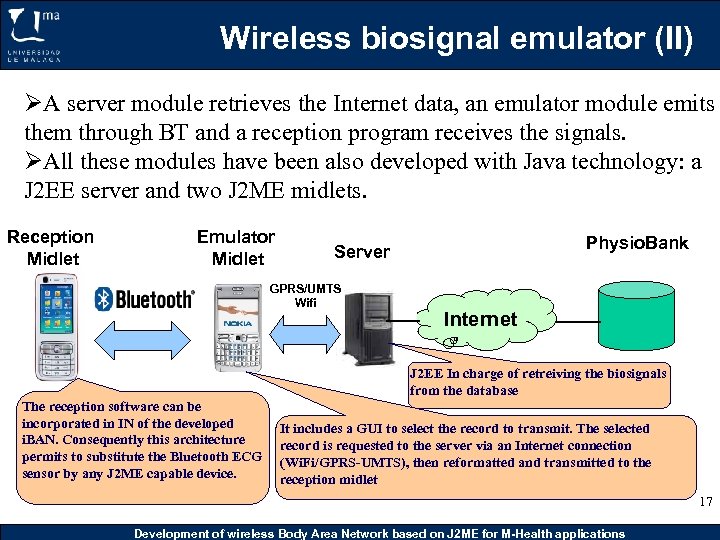 Wireless biosignal emulator (II) ØA server module retrieves the Internet data, an emulator module emits them through BT and a reception program receives the signals. ØAll these modules have been also developed with Java technology: a J 2 EE server and two J 2 ME midlets. Reception Midlet Emulator Midlet Physio. Bank Server GPRS/UMTS Wifi Internet J 2 EE In charge of retreiving the biosignals from the database The reception software can be incorporated in IN of the developed i. BAN. Consequently this architecture permits to substitute the Bluetooth ECG sensor by any J 2 ME capable device. It includes a GUI to select the record to transmit. The selected record is requested to the server via an Internet connection (Wi. Fi/GPRS-UMTS), then reformatted and transmitted to the reception midlet 17 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications
Wireless biosignal emulator (II) ØA server module retrieves the Internet data, an emulator module emits them through BT and a reception program receives the signals. ØAll these modules have been also developed with Java technology: a J 2 EE server and two J 2 ME midlets. Reception Midlet Emulator Midlet Physio. Bank Server GPRS/UMTS Wifi Internet J 2 EE In charge of retreiving the biosignals from the database The reception software can be incorporated in IN of the developed i. BAN. Consequently this architecture permits to substitute the Bluetooth ECG sensor by any J 2 ME capable device. It includes a GUI to select the record to transmit. The selected record is requested to the server via an Internet connection (Wi. Fi/GPRS-UMTS), then reformatted and transmitted to the reception midlet 17 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications
 Conclusions (I) ØThe system was systematically tested (not with real patients) ØSmart phone: good candidate for the role of central node in medical BANs ØAdvantages üDecrease of cost (not specific hardware is required) üHybrid communications are natively supported in present smart phones üFamiliarity of the patient with this type of devices ØUse of Java (J 2 ME) üSoftware is easily developed (Easy sinstaxis) üPortability Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications 18
Conclusions (I) ØThe system was systematically tested (not with real patients) ØSmart phone: good candidate for the role of central node in medical BANs ØAdvantages üDecrease of cost (not specific hardware is required) üHybrid communications are natively supported in present smart phones üFamiliarity of the patient with this type of devices ØUse of Java (J 2 ME) üSoftware is easily developed (Easy sinstaxis) üPortability Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications 18
 Conclusions (II) ØDisadvantages ØUsability problems: need of some user interaction ØMonitoring applications carry out tasks considered by operating system as risky for security. Therefore acknowledgement is requested to user before continuing certain actions Ø This drawback could be avoided by means of a validated certificate ØINSTABILITIES of OS (Symbian) in certain phone models (portability is not perfect!) ØHAND OFF between technologies and reconnection to BT sensors is slow and still present problems ØNo all the (low-level) functionalities in the smart-phone are accessible through J 2 ME ØDifficulty of debugging errors en complex J 2 ME applications Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications 19
Conclusions (II) ØDisadvantages ØUsability problems: need of some user interaction ØMonitoring applications carry out tasks considered by operating system as risky for security. Therefore acknowledgement is requested to user before continuing certain actions Ø This drawback could be avoided by means of a validated certificate ØINSTABILITIES of OS (Symbian) in certain phone models (portability is not perfect!) ØHAND OFF between technologies and reconnection to BT sensors is slow and still present problems ØNo all the (low-level) functionalities in the smart-phone are accessible through J 2 ME ØDifficulty of debugging errors en complex J 2 ME applications Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications 19
 29 th IEEE EMBS Annual International Conference J 2 ME and Smart Phones as Platform for a Bluetooth Body Area Network for Patient. Telemonitoring M. J. Morón, J. R. Luque, E. J. Cuberos, A. A. Botella, E. Casilari, A. Díaz Estrella UNIVERSITY OF MÁLAGA, SPAIN Lyon (France), 24 th August 2007 Departamento de Tecnología Electrónica. University of Málaga ETSI de Telecomunicación, Campus de Teatinos, 29071 – Málaga- Spain E-mail: mjmoron@uma. es, ecasilari@uma. es 20 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications
29 th IEEE EMBS Annual International Conference J 2 ME and Smart Phones as Platform for a Bluetooth Body Area Network for Patient. Telemonitoring M. J. Morón, J. R. Luque, E. J. Cuberos, A. A. Botella, E. Casilari, A. Díaz Estrella UNIVERSITY OF MÁLAGA, SPAIN Lyon (France), 24 th August 2007 Departamento de Tecnología Electrónica. University of Málaga ETSI de Telecomunicación, Campus de Teatinos, 29071 – Málaga- Spain E-mail: mjmoron@uma. es, ecasilari@uma. es 20 Development of wireless Body Area Network based on J 2 ME for M-Health applications


