440722a4dfdd6a05093e4296d0cbfa37.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

Writing System Implementation On-the-Fly Extensibility for the common man Sharon Correll, SIL International Copyright © 2001
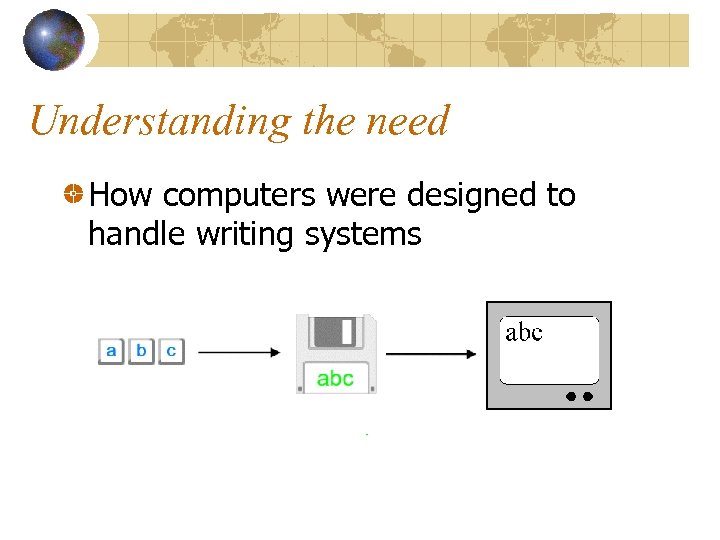
Understanding the need How computers were designed to handle writing systems

Understanding the need Problems Data input • Characters needed don’t match keyboard keys • More characters needed than available on keyboard Rendering • Contextual forms • Positioning • Stacking • Reordering • Ligatures • Split letter forms
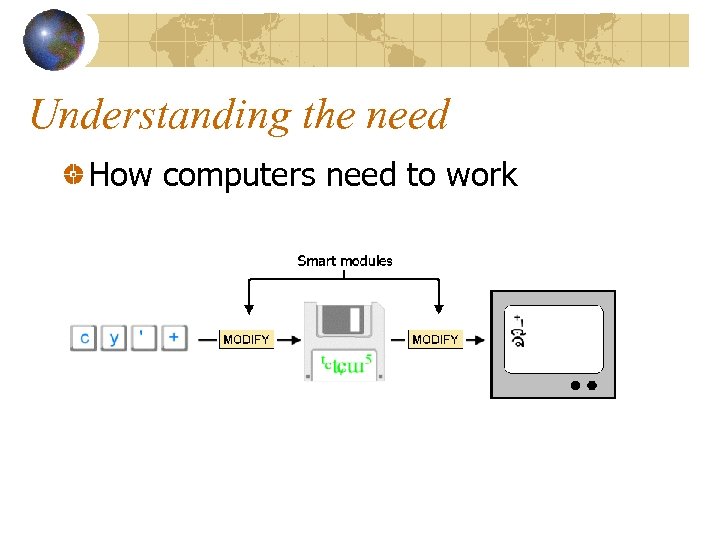
Understanding the need How computers need to work

Existing“smart module” technologies Operating system solutions Standard system keyboards Built-in rendering systems • Windows: Uniscribe • Java

Inadequacies of built-in solutions Orthographic variations of standard scripts Variant orthographies for lesser-known languages represent small market share Standardization issues Experimental orthographies

Inadequacies of built-in solutions Examples Khmer script used for Krung • Consonants with single and double tick marks Ethiopic script used for Me’en • Extra syllabic forms to handle an additional vowel Arabic script • Additional vowels • Parkari: implosive dental d, retroflexed l, voiceless h • Vowel mark in relation to consonant & shadda

Inadequacies of system solutions Need: “smart modules” that can be customized

Customizable solutions Keyboarding Keyman (Tavultesoft) Rendering Apple Macintosh: ATSUI/AAT Graphite (SIL International) • Windows platform • Rule-based programming language (Open. Type? )

Keyman (Keyboard Manager) Available from Tavultesoft: www. tavultesoft. com/keyman Current version: 5. 0 Rule-based programming language Integrated keyboard editor “ANSI” and Unicode
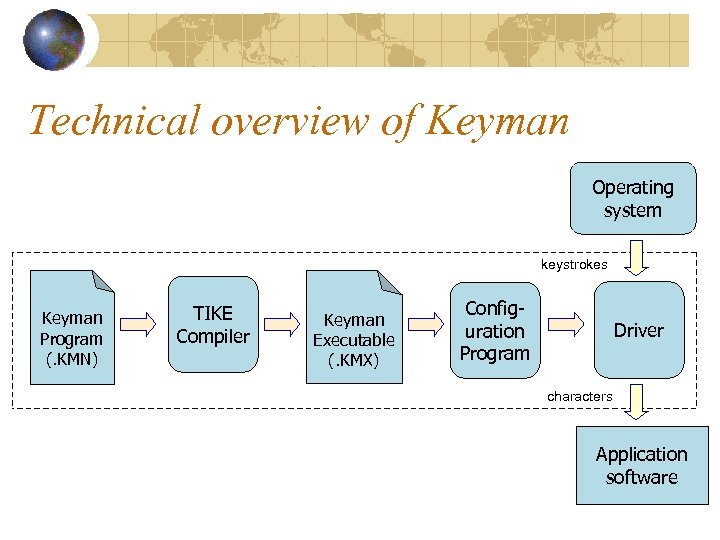
Technical overview of Keyman Operating system keystrokes Keyman Program (. KMN) TIKE Compiler Keyman Executable (. KMX) Configuration Program Driver characters Application software

Graphite Windows platform Unicode-compliant, including support for PUA Bidirectional support Contextual glyph selection Ligatures Stacking diacritics Glyph positioning and attachment Glyph reordering Cursor management, split cursors
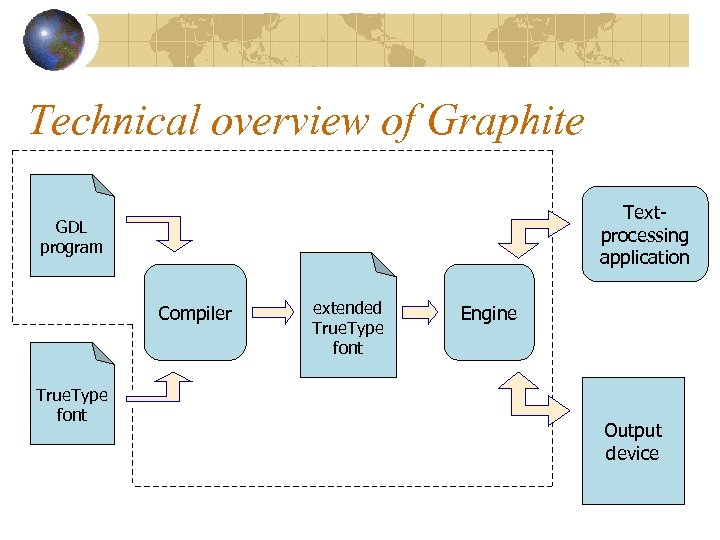
Technical overview of Graphite Textprocessing application GDL program Compiler True. Type font extended True. Type font Engine Output device

Graphite Demo

Steps in extending a writing system “on the fly” Choose the encoding Add glyphs to the font Implement keyboarding extensions Implement rendering extensions

Choosing the encoding Private Use Area? Is the character a typographical variant of a standard Unicode character? • Semantics, not glyph shape (eg. • Unicode normative properties ) Can the character be composed from standard Unicode characters? • Base character plus diacritic (eg, ≡ c + ˜) • Digraph or multigraph (eg, mb ≡ m + b) Disadvantages to the PUA

Choosing the encoding Private Use Area? Is the character a typographical variant of a standard Unicode character? • Semantics, not glyph shape (eg. • Unicode normative properties ) Can the character be composed from standard Unicode characters? • Base character plus diacritic (eg, ≡ c + ˜) • Digraph or multigraph (eg, mb ≡ m + b) Disadvantages to the PUA

Example Add a retroflex “s” to Arabic script PUA character: U+E 000 Keyboard sequence: “s~” Rendering requires four contextual forms Isolated Word-medial Word-initial Word-final

Example: font extensions Add four glyphs to the font Map U+E 000 to isolated form Add postscript names for the new glyphs

Example: keyboarding Add a rule to the Keyman program Existing rule + ‘s’ > U+0633 > U+E 000 Rule to add U+0633 + ‘~’

Example: rendering Extend GDL program Define Graphite attributes for PUA characters • breakweight • directionality Add rules Add glyphs to classes Add positioning information

Example: rendering More specifically: Add four glyph definitions to GDL program Add the four glyphs to the four contextual classes • The rules to handle contextual selection already exist Define attachment points for attaching diacritical marks

Example: rendering More specifically: Add four glyph definitions to GDL program Add the four glyphs to the four contextual classes • The rules to handle contextual selection already exist Define attachment points for attaching diacritical marks

Example: rendering More specifically: Add four glyph definitions to GDL program Add the four glyphs to the four contextual classes • The rules to handle contextual selection already exist Define attachment points for attaching diacritical marks
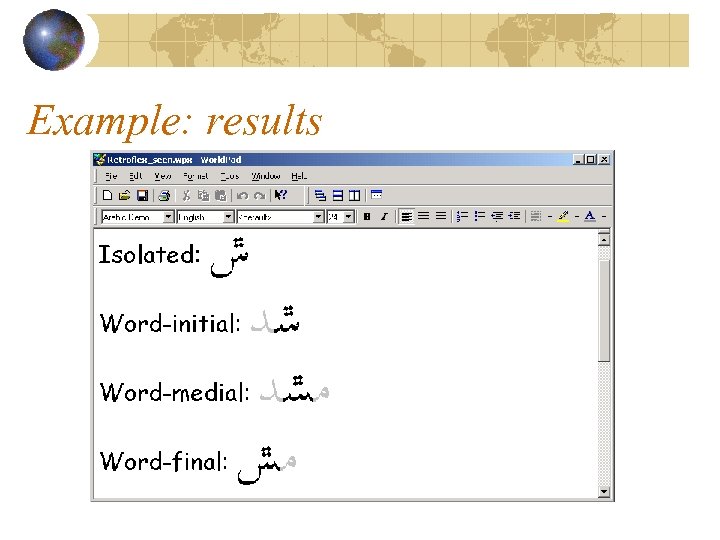
Example: results

Status of Graphite beta version 0. 8 Windows platform Text-editing application: World. Pad Not available in standard commercial applications Open-source

Future of Graphite SIL Field. Works linguistic applications Open-sourcing Web site: graphite. sil. org Linux, Java Other open-source possibilities • Integration into open-source applications – Active. X • Extensions to Graphite • Programming environment Graphite font development

Summary Graphite and Keyman allow custom writing system implementations for minority languages Modest level of effort More support needed Wider variety of platforms Application integration
Contact us Visit our web sites: www. sil. org graphite. sil. org Sign up on our mailing lists: graphite. sil. org/mailman Write: SIL Non-Roman Script Initiative 7500 W. Camp Wisdom Rd. Dallas, TX 75236 E-mail: graphite_nrsi@sil. org Phone: 972/708 -7440
440722a4dfdd6a05093e4296d0cbfa37.ppt