43d0d95fb3daa93282cefc746d906ec9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 55
 Write down three causes and three results of the Great Reforms
Write down three causes and three results of the Great Reforms
 Chapter 27 • I. Russia modernizes • A. Byzantine Empire: copied its culture & technology • B. 1700 s: Peter the Great modernized military based on West ideas
Chapter 27 • I. Russia modernizes • A. Byzantine Empire: copied its culture & technology • B. 1700 s: Peter the Great modernized military based on West ideas
 Nov 1815: Holy Alliance (conservatism, repression) Fr, Aust, Pruss, & Russ agree to suppress liberal ideas in Europe
Nov 1815: Holy Alliance (conservatism, repression) Fr, Aust, Pruss, & Russ agree to suppress liberal ideas in Europe
 The Decembrist Revolt • Dec 1825, officers & • Alex I died in 1825 soldiers proclaimed • Army officers had Constantine tsar become aware of new ideas about govt while • The rebellion was in Europe quickly put down, 5 officers were hanged • Alex had 2 brothers, & the others sent to a Nicholas & Constantine labor camp • Constantine had more liberal ideas, but had • Result: autocracy in renounced the throne in Russia beginning favor of his brother w/Nicholas I
The Decembrist Revolt • Dec 1825, officers & • Alex I died in 1825 soldiers proclaimed • Army officers had Constantine tsar become aware of new ideas about govt while • The rebellion was in Europe quickly put down, 5 officers were hanged • Alex had 2 brothers, & the others sent to a Nicholas & Constantine labor camp • Constantine had more liberal ideas, but had • Result: autocracy in renounced the throne in Russia beginning favor of his brother w/Nicholas I
 C. The Decembrist Revolt • 1. Dec 1825: officers & soldiers proclaimed Constantine tsar • 2. Nick CRUSHED rebellion • 3. Russ- more autocratic
C. The Decembrist Revolt • 1. Dec 1825: officers & soldiers proclaimed Constantine tsar • 2. Nick CRUSHED rebellion • 3. Russ- more autocratic
 The Decembrist Uprising - 1825 Tsar Alex I died, next brother Constantine married a commoner from Poland. Officers wanted a liberal constitutional monarchy. 3, 000 troops mutiny when told to swear allegiance to new tsar.
The Decembrist Uprising - 1825 Tsar Alex I died, next brother Constantine married a commoner from Poland. Officers wanted a liberal constitutional monarchy. 3, 000 troops mutiny when told to swear allegiance to new tsar.
 Random & Useless Constantine • Younger brother of Alexander, second in line to the throne. • Named by his grandmother Catherine after Emperor Constantine (R. Empire) • Catherine arranged his marriage to a German princess Juliane of Sax. Coberg when he was 16 and she was 14. • She left him 3 year later & went home. They had no children. • His brother Alex put him in charge of Congress Poland in 1815. • In 1820, his marriage to Juliane was annulled after 20 yrs of separation & he married a Polish countess, & renounced his claim to the throne. • During the Polish uprising, he remained neutral hoping the Poles could settle it themselves. • He died of cholera in 1831.
Random & Useless Constantine • Younger brother of Alexander, second in line to the throne. • Named by his grandmother Catherine after Emperor Constantine (R. Empire) • Catherine arranged his marriage to a German princess Juliane of Sax. Coberg when he was 16 and she was 14. • She left him 3 year later & went home. They had no children. • His brother Alex put him in charge of Congress Poland in 1815. • In 1820, his marriage to Juliane was annulled after 20 yrs of separation & he married a Polish countess, & renounced his claim to the throne. • During the Polish uprising, he remained neutral hoping the Poles could settle it themselves. • He died of cholera in 1831.
 Alex I died in 1825, Army officers had become aware of new ideas about govt while in Europe. Alex had 2 bros, Nicholas (left) & Constantine (right)
Alex I died in 1825, Army officers had become aware of new ideas about govt while in Europe. Alex had 2 bros, Nicholas (left) & Constantine (right)
 D. The Crimean War • 1. Russ occupies Danubian provinces (Ott territory) • 2. Brit & Fr suppt Ott Emp & send industrialized military • 3. Russian milit disaster social change & modernization
D. The Crimean War • 1. Russ occupies Danubian provinces (Ott territory) • 2. Brit & Fr suppt Ott Emp & send industrialized military • 3. Russian milit disaster social change & modernization
 Random & Useless Crimean War • Started over a dispute about which country (Fr or Russia) should protect Christian shrines in the Holy Land • Fr sent fleet & forced Otts to accept new treaty • Russia sent army to Danube & tried to negotiate with Otts & annexed Wallachia & Moldavia (principalities under Ott protection) • Otts declare war on Russia • Brit & Fr declare war when Russia refuses to leave Wallachia & Moldavia • Sardinia sent 15 K troops to win Fr allies, pt of a long term plan to unite Italy under the Sardinian king • 1856 peace agreement said neither Otts or Russians could have a navy in the Black Sea
Random & Useless Crimean War • Started over a dispute about which country (Fr or Russia) should protect Christian shrines in the Holy Land • Fr sent fleet & forced Otts to accept new treaty • Russia sent army to Danube & tried to negotiate with Otts & annexed Wallachia & Moldavia (principalities under Ott protection) • Otts declare war on Russia • Brit & Fr declare war when Russia refuses to leave Wallachia & Moldavia • Sardinia sent 15 K troops to win Fr allies, pt of a long term plan to unite Italy under the Sardinian king • 1856 peace agreement said neither Otts or Russians could have a navy in the Black Sea
 Random & Useless Crimean War • It was the first “published • The treaty was war” with frequent reports enforced until 1871 in newspapers & the first when Fr allied with “photographed war. ” Russia & refused to • Brit army came under enforce treaty attack for its sale of • During the war commissions after the railroads & telegraphs Battle of Balaclava & were widely used for “charge of the light the first time brigade. ” • Florence Nightingale • In Russia the war led to the organized nurses to abolition of serfdom & new care for the wounded emphasis on technology
Random & Useless Crimean War • It was the first “published • The treaty was war” with frequent reports enforced until 1871 in newspapers & the first when Fr allied with “photographed war. ” Russia & refused to • Brit army came under enforce treaty attack for its sale of • During the war commissions after the railroads & telegraphs Battle of Balaclava & were widely used for “charge of the light the first time brigade. ” • Florence Nightingale • In Russia the war led to the organized nurses to abolition of serfdom & new care for the wounded emphasis on technology
 Tsar Alexander II, freed the serfs amid fears of rebellion after Russia’s loss in the Crimean War He was assassinated in 1881
Tsar Alexander II, freed the serfs amid fears of rebellion after Russia’s loss in the Crimean War He was assassinated in 1881
 E. 1892 -1903: Count Sergei Witte (minister of finance) : • 1. Before 1900: Russ exported grain & imported luxury goods • 2. state sponsored industrialization; created a railway system • 3. promoted foreign investment & indust devel • 4. incr in steel prod, petroleum & textiles • 5. After 1900 • a. ½ of Russ industry owned by foreign industrialists (Euros) • b. ranked 4 th in steel production & 2 nd in petroleum production
E. 1892 -1903: Count Sergei Witte (minister of finance) : • 1. Before 1900: Russ exported grain & imported luxury goods • 2. state sponsored industrialization; created a railway system • 3. promoted foreign investment & indust devel • 4. incr in steel prod, petroleum & textiles • 5. After 1900 • a. ½ of Russ industry owned by foreign industrialists (Euros) • b. ranked 4 th in steel production & 2 nd in petroleum production
 F. 1905 Revolution • 1. Defeat in the Russo. Japanese war- protests & strikes • 2. Tsar Nick II agrees to create a Duma (parliament)
F. 1905 Revolution • 1. Defeat in the Russo. Japanese war- protests & strikes • 2. Tsar Nick II agrees to create a Duma (parliament)
 • 3. Stolypin reforms • a. Finance min Peter Stolypin reduces restrictions on peas • b. peasants could buy & sell land freely more land ownership among peas • c. kulaks: landowning peas (very capitalist) • 4. Russian intelligentsia grows • a. wanted polit & social reform • b. promoted preservation of Russ cult
• 3. Stolypin reforms • a. Finance min Peter Stolypin reduces restrictions on peas • b. peasants could buy & sell land freely more land ownership among peas • c. kulaks: landowning peas (very capitalist) • 4. Russian intelligentsia grows • a. wanted polit & social reform • b. promoted preservation of Russ cult
 Count Sergei Witte (above) & Peter Stolypin (right)
Count Sergei Witte (above) & Peter Stolypin (right)
 Vladimir Lenin Middle class family, educated in law Brother executed by govt Studied Marxism, lived in exile
Vladimir Lenin Middle class family, educated in law Brother executed by govt Studied Marxism, lived in exile
 G. Vladimir Lenin • 1. Social revol possible in bkward Russia, do not need a bourgeoise (middle class) • 2. Led Bolsheviks (“majority” in Russian)
G. Vladimir Lenin • 1. Social revol possible in bkward Russia, do not need a bourgeoise (middle class) • 2. Led Bolsheviks (“majority” in Russian)

 Lenin as orator, 1920 The Bolsheviks were a small but tightly disciplined group of radicals obedient to the will of their leader, Vladimir Lenin (1870 -1924). Here he is addressing Red Army soldiers in Sverdlov Square, Moscow, in 1920. At the time, the Bolsheviks were mopping up the last of the anti. Bolshevik forces and were fully engaged in a war with Poland. The fate of the Revolution depended on the fighting spirit of the Red Army soldiers and on their loyalty to Lenin. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Lenin as orator, 1920 The Bolsheviks were a small but tightly disciplined group of radicals obedient to the will of their leader, Vladimir Lenin (1870 -1924). Here he is addressing Red Army soldiers in Sverdlov Square, Moscow, in 1920. At the time, the Bolsheviks were mopping up the last of the anti. Bolshevik forces and were fully engaged in a war with Poland. The fate of the Revolution depended on the fighting spirit of the Red Army soldiers and on their loyalty to Lenin. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
 This Russian said that a Marxist revolution did not have to pass through a middle class or bourgeoisie phase Vladimir Lenin
This Russian said that a Marxist revolution did not have to pass through a middle class or bourgeoisie phase Vladimir Lenin
 Better communication & technology led to the Western powers’ victory against Russia in this war The Crimean War
Better communication & technology led to the Western powers’ victory against Russia in this war The Crimean War
 After the Great Reforms of 1861, this group was granted freedom & the opportunity to buy land from nobles Serfs
After the Great Reforms of 1861, this group was granted freedom & the opportunity to buy land from nobles Serfs
 In addition to social & political reform, this group wanted to preserve Russian culture The Russian intelligentsia
In addition to social & political reform, this group wanted to preserve Russian culture The Russian intelligentsia
 By 1900, Russia was a world leader in the production of steel and this Petroleum
By 1900, Russia was a world leader in the production of steel and this Petroleum
 After this event, the political oppression that followed, Russia would not experience revolution in 1830 & 1848 The Decembrist Revolt
After this event, the political oppression that followed, Russia would not experience revolution in 1830 & 1848 The Decembrist Revolt
 Russia imitated this empire’s culture & technology Byzantine
Russia imitated this empire’s culture & technology Byzantine
 By 1900, ½ of this was owned by Euro industrialists Russian industry
By 1900, ½ of this was owned by Euro industrialists Russian industry
 Russia began industrializing by creating this A railway system
Russia began industrializing by creating this A railway system
 II. Japan • A. Imitated Chinese culture & tech beginning in the 7 th cent • B. Tokugawa Shogunate • 1. Centralized bureaucracy, semifeudal state (shogun allied w/daimyo & samurai to keep power) • 2. crop failure- famine & starvation
II. Japan • A. Imitated Chinese culture & tech beginning in the 7 th cent • B. Tokugawa Shogunate • 1. Centralized bureaucracy, semifeudal state (shogun allied w/daimyo & samurai to keep power) • 2. crop failure- famine & starvation
 Commodore Matthew Perry demanded Js open a port to trade w/Ams more opposition to Tokugawa rule 1866: civil war rebels demand shogun resign. Emp. Mutsuhito takes power 1856: treaty opened 2 ports, etc 1860 s: Samurais attacked foreigners
Commodore Matthew Perry demanded Js open a port to trade w/Ams more opposition to Tokugawa rule 1866: civil war rebels demand shogun resign. Emp. Mutsuhito takes power 1856: treaty opened 2 ports, etc 1860 s: Samurais attacked foreigners
 C. 1868: Meiji Restoration “gift to ppl” • 1. upper (nobles) & lower (elected) houses • 2. “sacred” emp controls army, appts prime min & cabinet (emp had previously been a figurehead & did not rule) • 3. gave power to rich business ppl (unlike Russia)
C. 1868: Meiji Restoration “gift to ppl” • 1. upper (nobles) & lower (elected) houses • 2. “sacred” emp controls army, appts prime min & cabinet (emp had previously been a figurehead & did not rule) • 3. gave power to rich business ppl (unlike Russia)
 Random & Useless Meiji Changes • 1871: Abolished the hereditary privileges of the samurai • Meiji Constitution: a “gift to the ppl”: ppl have individual rights except for when they conflict with national interests • 5% of males could vote • no unions (illegal) • 1894 -1914: women represented 60% of J wkforce • govt funded railrds, telegraphs, steamships, & new agric methods • Land reforms created more indiv farm ownership • more educ: stressed science, patriotism
Random & Useless Meiji Changes • 1871: Abolished the hereditary privileges of the samurai • Meiji Constitution: a “gift to the ppl”: ppl have individual rights except for when they conflict with national interests • 5% of males could vote • no unions (illegal) • 1894 -1914: women represented 60% of J wkforce • govt funded railrds, telegraphs, steamships, & new agric methods • Land reforms created more indiv farm ownership • more educ: stressed science, patriotism
 D. Economic Change: • 1. J elite was willing to sponsor reform • 2. 1872: 1 st railrd financed by GB, all rest financed by J govt • 3. govt started new banks to fund trade, ended internal tariffs • 4. Sought Western expertise & equipment • 5. 1880 s: govt sold businesses to investors
D. Economic Change: • 1. J elite was willing to sponsor reform • 2. 1872: 1 st railrd financed by GB, all rest financed by J govt • 3. govt started new banks to fund trade, ended internal tariffs • 4. Sought Western expertise & equipment • 5. 1880 s: govt sold businesses to investors
 6. Urban labor • a. Js needed exports to pay for machinery, incr silk production for West • b. silkweavers: women, poorly pd, wkd in homes or sweatshops • c. $ earned by J women was essential to development of milit & industry • d. increased literacy (highest outside of West Eur)
6. Urban labor • a. Js needed exports to pay for machinery, incr silk production for West • b. silkweavers: women, poorly pd, wkd in homes or sweatshops • c. $ earned by J women was essential to development of milit & industry • d. increased literacy (highest outside of West Eur)
 Japanese Factory
Japanese Factory
 The Russo-Japanese War: 1904 -1905 Russians told Js to get out of Liaotung peninsula & J refused Battle of Tsushima (Js won)
The Russo-Japanese War: 1904 -1905 Russians told Js to get out of Liaotung peninsula & J refused Battle of Tsushima (Js won)
![Russo-Japanese War [19041905] The “Yellow Peril” Russo-Japanese War [19041905] The “Yellow Peril”](https://present5.com/presentation/43d0d95fb3daa93282cefc746d906ec9/image-41.jpg) Russo-Japanese War [19041905] The “Yellow Peril”
Russo-Japanese War [19041905] The “Yellow Peril”
 President Teddy Roosevelt Mediates the Peace The Treaty of Portsmouth, NH ended the Russo-Japanese War.
President Teddy Roosevelt Mediates the Peace The Treaty of Portsmouth, NH ended the Russo-Japanese War.
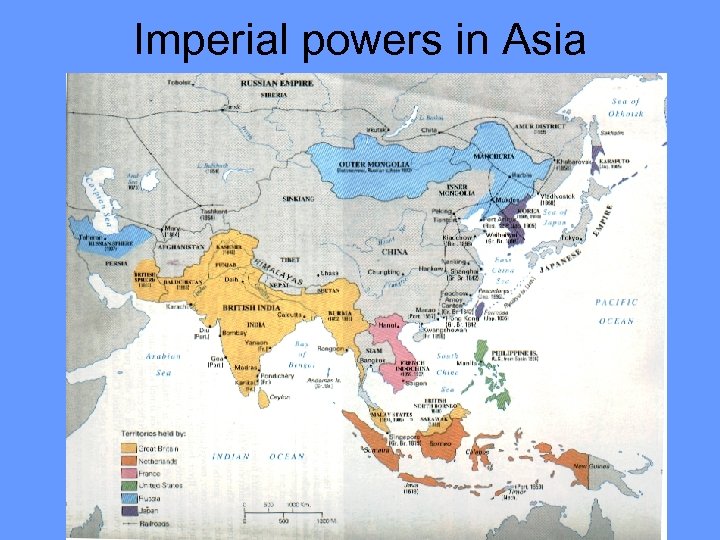 Imperial powers in Asia
Imperial powers in Asia
 Japan Annexes Korea
Japan Annexes Korea
 E. Western influence on J society • 1. adopted western dress, calendar, baseball, hairstyles • 2. Christianity did not become popular (Shintoism was popular; more natlism patriotism) • 3. Js remained patriarchal
E. Western influence on J society • 1. adopted western dress, calendar, baseball, hairstyles • 2. Christianity did not become popular (Shintoism was popular; more natlism patriotism) • 3. Js remained patriarchal
 The Japanese Became Obsessed with Western Styles Civilization and Enlightenment!
The Japanese Became Obsessed with Western Styles Civilization and Enlightenment!
 Japan copied this country’s culture & technology in the 700 s China
Japan copied this country’s culture & technology in the 700 s China
 Russia & this country defied the pattern of Western domination in th century the 19 Japan
Russia & this country defied the pattern of Western domination in th century the 19 Japan
 This religion never became popular in Japan Christianity
This religion never became popular in Japan Christianity
 Unlike Japan, this country started borrowing from the West in the 1700 s Russia
Unlike Japan, this country started borrowing from the West in the 1700 s Russia
 The leaders of this govt came to power without violence, instituted an aristocratic Diet (Parliament) & a Constitution Meiji
The leaders of this govt came to power without violence, instituted an aristocratic Diet (Parliament) & a Constitution Meiji
 By 1900, a higher % of ppl in Japan could do this than anywhere else in the world outside of Europe Read
By 1900, a higher % of ppl in Japan could do this than anywhere else in the world outside of Europe Read
 This govt combined a central bureaucracy w/feudal alliances w/daimyo & samurai The Tokugawa Shogunate
This govt combined a central bureaucracy w/feudal alliances w/daimyo & samurai The Tokugawa Shogunate
 The Japanese needed to export products to pay for these Machinery & natural resources
The Japanese needed to export products to pay for these Machinery & natural resources
 Compare and contrast China, Japan and Russia’s response to western intervention
Compare and contrast China, Japan and Russia’s response to western intervention


