6918e2cc0ffc60208c8fc27220685b6e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
WP D Integrating Mobility Management and Land Use Planning What is site-based Mobility Management? (D 1) slide 1

What is site based Mobility Management (MM)? • Objective: Making travel to and from the site more rational and sustainable by implementing Mobility Management measures – a choice of ways to get there • Sites: companies, hospitals, schools, concert halls, sports arenas, housing areas, universities, etc. • Main actors: developers, land-owners, tenants in cooperation with local authorities and others slide 2

Some benefits of site-based MM • Cut costs (parking, travel budgets, car fleets, etc. ) • Better accessibility of the site with all modes for all types of site-users • Motivated, satisfied and healthy site users • Fulfilling requirements of public authorities (e. g. parking requirements linked to the building permission) • Improving socially-responsibleimage as a modern company • Use land under car parks more productively slide 3
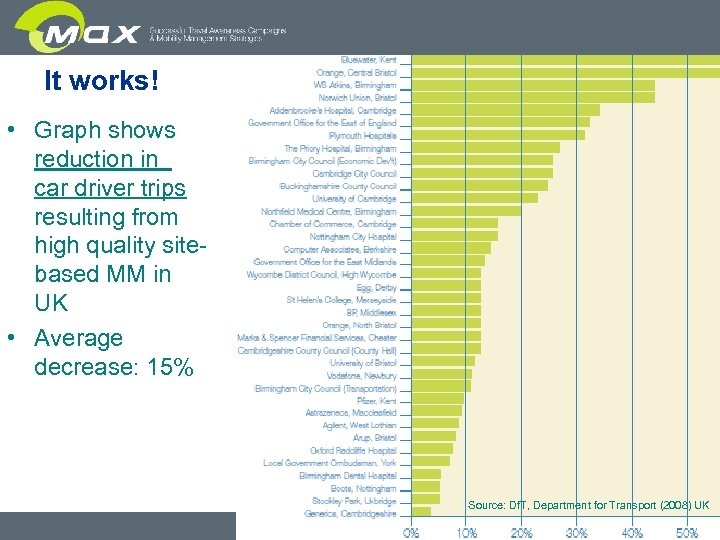
It works! • Graph shows reduction in car driver trips resulting from high quality sitebased MM in UK • Average decrease: 15% Source: Df. T, Department for Transport (2008) UK slide 4

Is site based MM expensive? • Average cost 3 -10€ per staff member per year (UK) • Most measures are cheap: – Promotional materials, bike parking, car-pool software • Parking charging generates income: – 0. 50€ a day with 1000 staff is 100. 000€ per year to spend on MM • Major cost savings from: – Savings on parking maintenance – Reduced business travel – Time saved not travelling to meetings (teleconferencing) • More costly measures: – – Daily incentive payments for not driving to work Paying for discounts on public transport Shuttle buses Infrastructure e. g. new bike paths slide 5
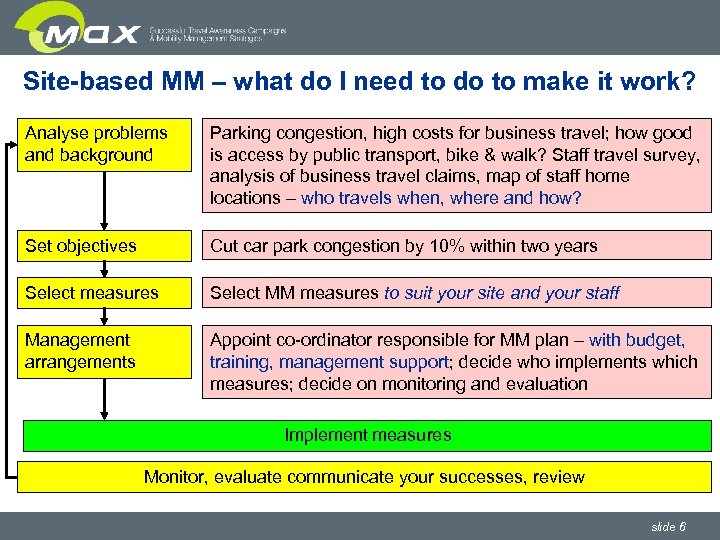
Site-based MM – what do I need to do to make it work? Analyse problems and background Parking congestion, high costs for business travel; how good is access by public transport, bike & walk? Staff travel survey, analysis of business travel claims, map of staff home locations – who travels when, where and how? Set objectives Cut car park congestion by 10% within two years Select measures Select MM measures to suit your site and your staff Management arrangements Appoint co-ordinator responsible for MM plan – with budget, training, management support; decide who implements which measures; decide on monitoring and evaluation Implement measures Monitor, evaluate communicate your successes, review slide 6

Promotion, awareness raising, information • Selling, promoting MM to staff, visitors, customers • Advertising services provided • One-off or regular events e. g. Bike to Work week • Regular promotion of new and existing measures • Prize draws, newsletters, “celebrations” of successes • Information on sustainable site access for all users • Low cost (sponsorship from local businesses) slide 7

Car-pooling – databases, reserved parking spaces • Set up online car-pooling database so staff can find others to share driving with • Best car parking spaces closest to building for car-poolers • Prize draws, vouchers for carpoolers • Works best where staff travel relatively long distances, and working hours are regular • Low cost slide 8

Improved walking and cycling facilities • On site: – Easy safe direct routes across site – Changing rooms with showers, lockers, hairdryers, ironing boards – Secure weather-protected cycle parking – Toolkit, pump, occasional visit from bike mechanic – Incentives to walk and cycle e. g. 10 min shorter working day • Off-site, work with municipality for safe routes • Costs – low • Benefits – reduced absenteeism from better employee health slide 9

Cheaper and better public transport • New/modified bus services e. g. extended to run into site • Shuttle buses to link site with town centres, railway stations, park and rides • Discounted tickets • Often highly effective measures, but more costly slide 10

Flexible and tele-working and on-site facilities • Flexible working e. g. 10 days’ work in 9 days cuts commute trips • Tele-working cuts commute and business trips • On-site facilities no need to travel off-site to go e. g. to bank • Measures often save company money - reduced time spent travelling, reduced business travel costs • Popular with staff, effective slide 11

Car park management/charging • Best introduced where there is parking problem • Controversial before introduced; normally accepted thereafter • Needs to be well-communicated – especially how money is used • Does not work well if free onstreet parking available nearby • Highly effective measure • Can raise money to pay for other MM measures slide 12
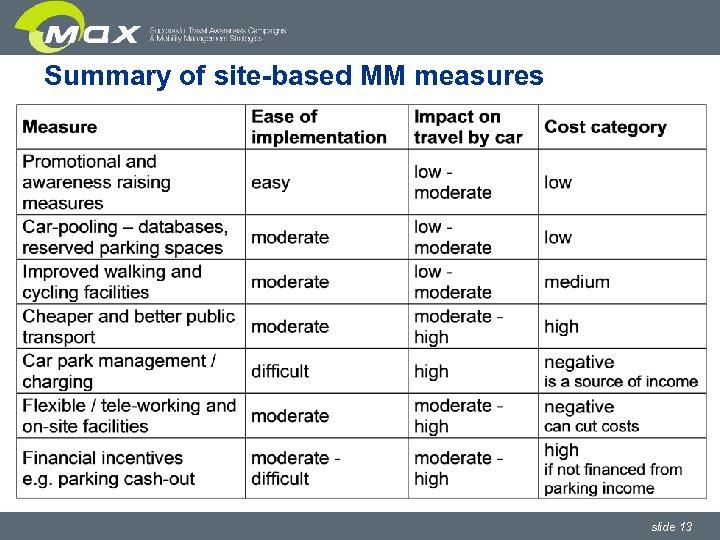
Summary of site-based MM measures slide 13

Key factors for successful sited-based MM • Enthusiastic capable MM coordinator • Management support and some budget • Select measures that suit your site’s circumstances. . but also… • Try to include some highly effective measures like shuttle bus • Follow steps of the process see slide 6: what do I need to do to make it work? slide 14

Further information • MAX project: – Compendium of Site-based Mobility Management (D 5)– tells you more about measures you can choose – Max. Explorer online guide – helps you to choose MM measures suited to your site – Max. Sumo – helps to plan, evaluate & monitor MM measures at your site – www. max-success. eu • OPTIMUM 2 project cookbook – a guide to choosing MM measures – www. optimum 2. org/cookbook slide 15

WP D Contact details Germany - ILS, Dortmund Spain - ETT, Madrid janina. welsch@ils-forschung. de cmattsson@ett. es Lithuania - VGTU, Vilnius kris@ap. vtu. lt Sweden - Trivector, Lund christer. ljungberg@trivector. se Poland - CUT, Cracow ola@transys. wil. pk. edu. pl Switzerland - synergo, Zürich detommasi@synergo. ch Slovenia - UNI, Maribor aljaz. plevnik@uirs. si United Kingdom - ENU, Edinburgh t. rye@napier. ac. uk slide 16
6918e2cc0ffc60208c8fc27220685b6e.ppt