896cbdb6d6ae1d960f10460f4373b07e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 62
 World Wars and Conflicts WWII Cold War
World Wars and Conflicts WWII Cold War
 Warm Up: n Americans want to “make the world safe for democracy. ” Who do you think says this? n What do they mean exactly? n
Warm Up: n Americans want to “make the world safe for democracy. ” Who do you think says this? n What do they mean exactly? n
 World War I n War began in Europe in 1914 Germany & Austria-Hungary VS. Britain, France, & Russia. The Great War
World War I n War began in Europe in 1914 Germany & Austria-Hungary VS. Britain, France, & Russia. The Great War
 U. S. involvement in World War I For three years, America remained neutral, and there was strong sentiment not to get involved in a European war. n The decision to enter the war was the result of continuing German submarine warfare (freedom of the seas) and American ties to Great Britain. n
U. S. involvement in World War I For three years, America remained neutral, and there was strong sentiment not to get involved in a European war. n The decision to enter the war was the result of continuing German submarine warfare (freedom of the seas) and American ties to Great Britain. n
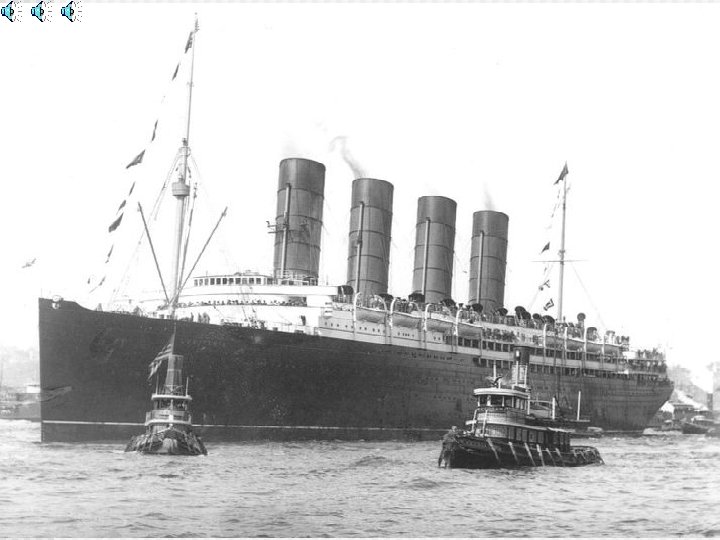

 USA Helps Win WWI n Americans wanted to “make the world safe for democracy. ” (Wilson) n America’s military resources of soldiers and war materials tipped the balance of the war and led to Germany’s defeat.
USA Helps Win WWI n Americans wanted to “make the world safe for democracy. ” (Wilson) n America’s military resources of soldiers and war materials tipped the balance of the war and led to Germany’s defeat.
 Wilson’s 14 Points Plan to eliminate the causes of war – Self-determination – Freedom of the sea – League of Nations – Mandate system
Wilson’s 14 Points Plan to eliminate the causes of war – Self-determination – Freedom of the sea – League of Nations – Mandate system
 Activity Phase 1 n n n On a sheet of paper, list some goals that YOU feel need to be achieved in the world today. Your ultimate goal is to avoid war These can be anything! • • • World Peace Animal Rights Recycling Fossil Fuels AIDS
Activity Phase 1 n n n On a sheet of paper, list some goals that YOU feel need to be achieved in the world today. Your ultimate goal is to avoid war These can be anything! • • • World Peace Animal Rights Recycling Fossil Fuels AIDS
 Activity Phase 2 n In 4 -person groups, decide which issues are important enough to bring to the attention of the world. n Narrow down your choices to your 3 most important topics. n Choose a speaker for your group.
Activity Phase 2 n In 4 -person groups, decide which issues are important enough to bring to the attention of the world. n Narrow down your choices to your 3 most important topics. n Choose a speaker for your group.
 Activity Phase 3 n As a class, let’s discuss and vote on which issues are the most important.
Activity Phase 3 n As a class, let’s discuss and vote on which issues are the most important.
 Activity Phase 4 n n Does anyone feel left out of the debates? Are there issues that still need to be resolved? Does anyone feel that other people are making their decisions without asking? What are you going to do if people don’t listen to the decisions being made?
Activity Phase 4 n n Does anyone feel left out of the debates? Are there issues that still need to be resolved? Does anyone feel that other people are making their decisions without asking? What are you going to do if people don’t listen to the decisions being made?
 Treaty of Versailles n The French and English insisted on punishment of Germany. n A League of Nations was created. n National boundaries were redrawn, creating many new nations.
Treaty of Versailles n The French and English insisted on punishment of Germany. n A League of Nations was created. n National boundaries were redrawn, creating many new nations.
 League debate in United States n Objections to U. S. foreign policy decisions made by an international organization, not by U. S. leaders n Senate’s failure to approve Treaty of Versailles
League debate in United States n Objections to U. S. foreign policy decisions made by an international organization, not by U. S. leaders n Senate’s failure to approve Treaty of Versailles
 Warm Up: n What were the causes of the Great Depression? n How did the depression affect the lives of Americans?
Warm Up: n What were the causes of the Great Depression? n How did the depression affect the lives of Americans?
 1929 Stock Market Crash & Great Depression n Business was booming, but investments were made with borrowed money (overspeculation) n Excessive expansion of credit n Business failures led to bankruptcies n Bank deposits were invested in the market n When the market collapsed, the banks had no money
1929 Stock Market Crash & Great Depression n Business was booming, but investments were made with borrowed money (overspeculation) n Excessive expansion of credit n Business failures led to bankruptcies n Bank deposits were invested in the market n When the market collapsed, the banks had no money
 SMC & GD Clients panicked, went to withdraw their money from the banks, but there was nothing to give them. n High protective tariffs that produced retaliatory tariffs in other countries, strangling world trade (Tariff Act of 1930, popularly called the Hawley-Smoot Act) n
SMC & GD Clients panicked, went to withdraw their money from the banks, but there was nothing to give them. n High protective tariffs that produced retaliatory tariffs in other countries, strangling world trade (Tariff Act of 1930, popularly called the Hawley-Smoot Act) n
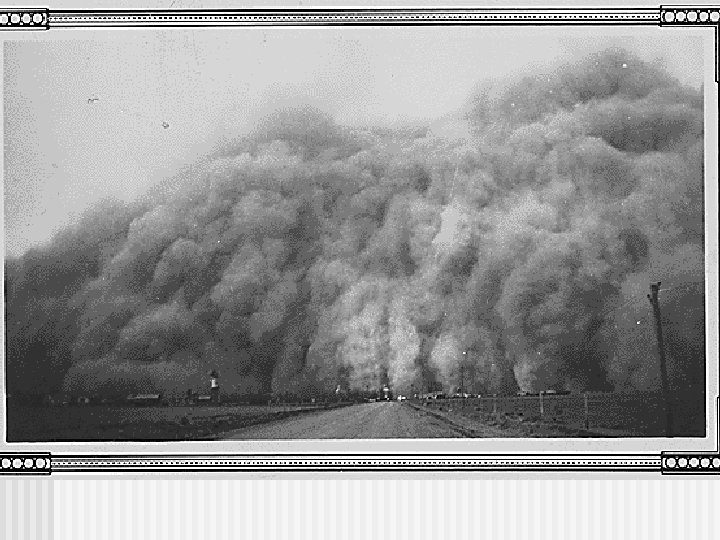
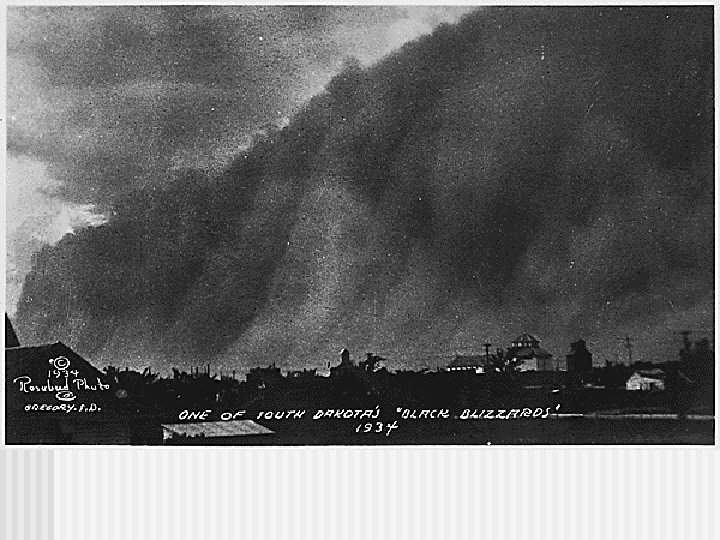
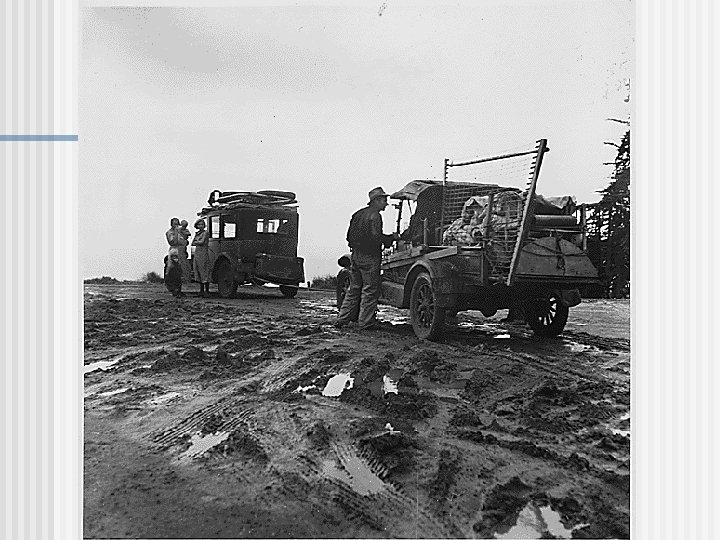
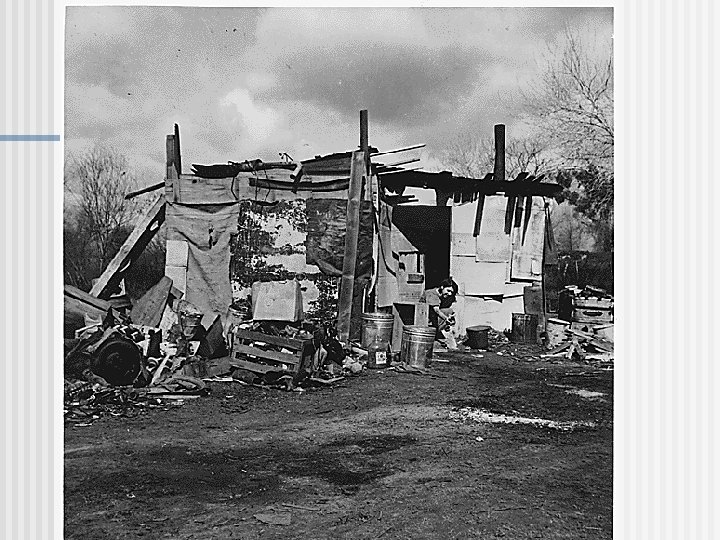
 Effects of Great Depression n Unemployment and homelessness n Bank closings n Demand for goods declined n Political unrest n Farm foreclosures and migration
Effects of Great Depression n Unemployment and homelessness n Bank closings n Demand for goods declined n Political unrest n Farm foreclosures and migration
 FDR’s NEW DEAL The New Deal influenced the public’s belief in the responsibility of government to deliver public services and intervene in the economy. n Examples: n • • Works Progress Administration - WPA Agricultural Adjustment Administration - AAA Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation – FDIC Social Security
FDR’s NEW DEAL The New Deal influenced the public’s belief in the responsibility of government to deliver public services and intervene in the economy. n Examples: n • • Works Progress Administration - WPA Agricultural Adjustment Administration - AAA Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation – FDIC Social Security










 The Interwar Period n The mood of the USA between WWI and WWII was isolationist and desperate. n WHY?
The Interwar Period n The mood of the USA between WWI and WWII was isolationist and desperate. n WHY?
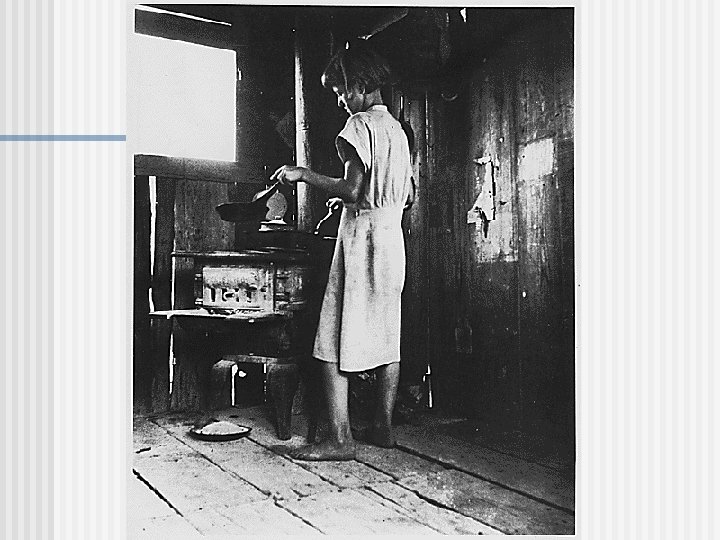
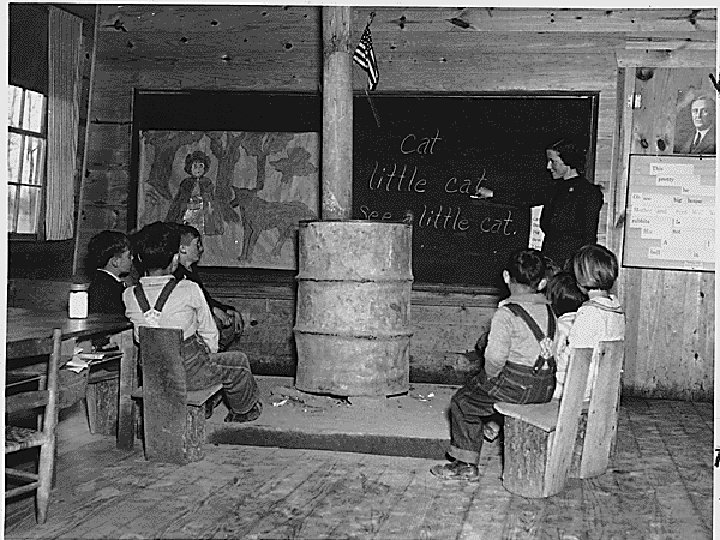
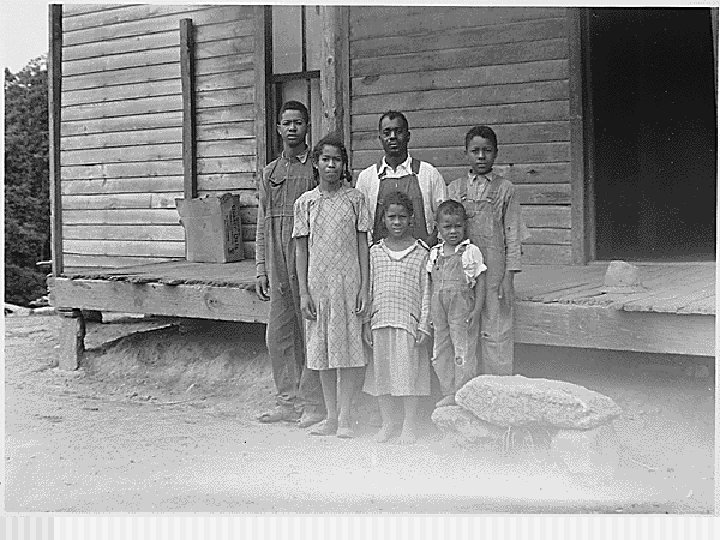
 Interwar Period Problems n Versailles Treaty was not ratified by the USA because Congress did not support it. n Over 500, 000 African Americans moved to northern and western cities, creating race riots n Low Income, High Unemployment, Stock Market Crash, Great Depression n 1930’s Neutrality Acts
Interwar Period Problems n Versailles Treaty was not ratified by the USA because Congress did not support it. n Over 500, 000 African Americans moved to northern and western cities, creating race riots n Low Income, High Unemployment, Stock Market Crash, Great Depression n 1930’s Neutrality Acts
 Europe Before and After WWI Germany blamed for war, forced to pay reparations n Break-up of Austria-Hungary n Creation of new nations from German/Russian territory n Fascism in Spain and Italy, Nazism in Germany n
Europe Before and After WWI Germany blamed for war, forced to pay reparations n Break-up of Austria-Hungary n Creation of new nations from German/Russian territory n Fascism in Spain and Italy, Nazism in Germany n
 World War II (in Europe) n Germany invades Poland, 1939 n The USA stays neutral as Germany overruns France and bombs England n Hitler turned on and invaded the Soviet Union, 1941
World War II (in Europe) n Germany invades Poland, 1939 n The USA stays neutral as Germany overruns France and bombs England n Hitler turned on and invaded the Soviet Union, 1941
 WWII in Europe United States gave Britain supplies in return for military bases. n Lend-Lease Act gave the President authority to sell or lend equipment to defend against the Axis powers. n FDR compared it to “lending a garden hose to a next-door neighbor whose house is on fire. ” n
WWII in Europe United States gave Britain supplies in return for military bases. n Lend-Lease Act gave the President authority to sell or lend equipment to defend against the Axis powers. n FDR compared it to “lending a garden hose to a next-door neighbor whose house is on fire. ” n
 WWII in Asia Japan invades Manchuria and China. n USA refuses to recognize Japanese control of Asia and imposes an embargo on exports of oil and steel to Japan. n Japan carries out an air attack on the USA naval base at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, on December 7, 1941. The attack destroys much of the USA’s Pacific fleet and kills thousands of Americans. FDR calls it “a date that will live in infamy” and asks Congress to declare war on Japan n
WWII in Asia Japan invades Manchuria and China. n USA refuses to recognize Japanese control of Asia and imposes an embargo on exports of oil and steel to Japan. n Japan carries out an air attack on the USA naval base at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, on December 7, 1941. The attack destroys much of the USA’s Pacific fleet and kills thousands of Americans. FDR calls it “a date that will live in infamy” and asks Congress to declare war on Japan n
 After Pearl Harbor n Hitler honored a pact with Japan and declared war on the United States.
After Pearl Harbor n Hitler honored a pact with Japan and declared war on the United States.
 Review n n n When Germany invaded Poland, the United States remained neutral, but deals were unofficially worked out to aid allies. Congress passed the Lend-Lease Act. In 1941, Germany invaded the Soviet Union In the 1930 s, Japan invaded China. In 1940, Japan signed an alliance with Germany and Italy (the Axis). The USA imposed an embargo on the sale of scrap metal and oil While Japanese representatives were in Washington for negotiations, Japan attacked Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, on Dec. 7, 1941. The USA lost 2, 400 people, 19 ships, and 200 planes.
Review n n n When Germany invaded Poland, the United States remained neutral, but deals were unofficially worked out to aid allies. Congress passed the Lend-Lease Act. In 1941, Germany invaded the Soviet Union In the 1930 s, Japan invaded China. In 1940, Japan signed an alliance with Germany and Italy (the Axis). The USA imposed an embargo on the sale of scrap metal and oil While Japanese representatives were in Washington for negotiations, Japan attacked Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, on Dec. 7, 1941. The USA lost 2, 400 people, 19 ships, and 200 planes.
 WW 2 Allied Strategy n America and its allies (Britain & USSR), followed a “Defeat Hitler First” strategy. n In the Pacific, American military strategy called for an “island hopping” campaign: closer and closer to Japan n use them as bases for air attacks on Japan n cut off Japanese supplies through submarine warfare against Japanese shipping. n
WW 2 Allied Strategy n America and its allies (Britain & USSR), followed a “Defeat Hitler First” strategy. n In the Pacific, American military strategy called for an “island hopping” campaign: closer and closer to Japan n use them as bases for air attacks on Japan n cut off Japanese supplies through submarine warfare against Japanese shipping. n
 WW 2 Axis Strategy Germany hoped to defeat the Soviet Union quickly, gain control of Soviet oil fields, and force Britain out of the war through a bombing campaign and submarine warfare before America’s industrial and military strength could turn the tide. n After Pearl Harbor, Japan invaded the Philippines and Indonesia and planned to invade Australia and Hawaii. n
WW 2 Axis Strategy Germany hoped to defeat the Soviet Union quickly, gain control of Soviet oil fields, and force Britain out of the war through a bombing campaign and submarine warfare before America’s industrial and military strength could turn the tide. n After Pearl Harbor, Japan invaded the Philippines and Indonesia and planned to invade Australia and Hawaii. n
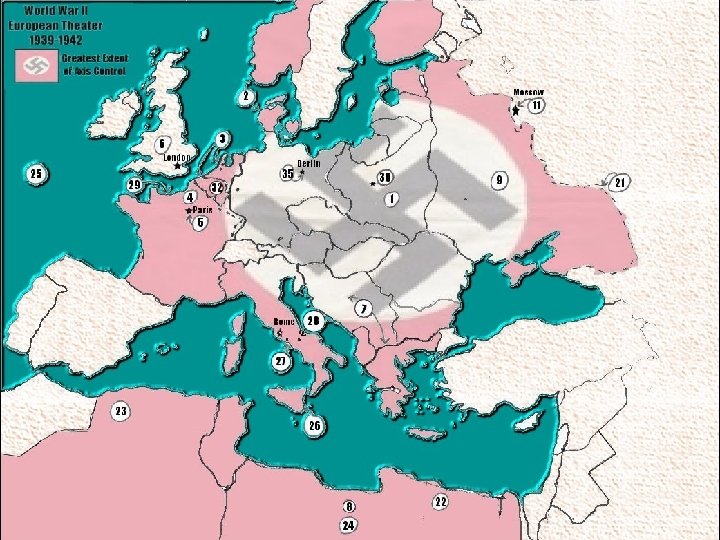
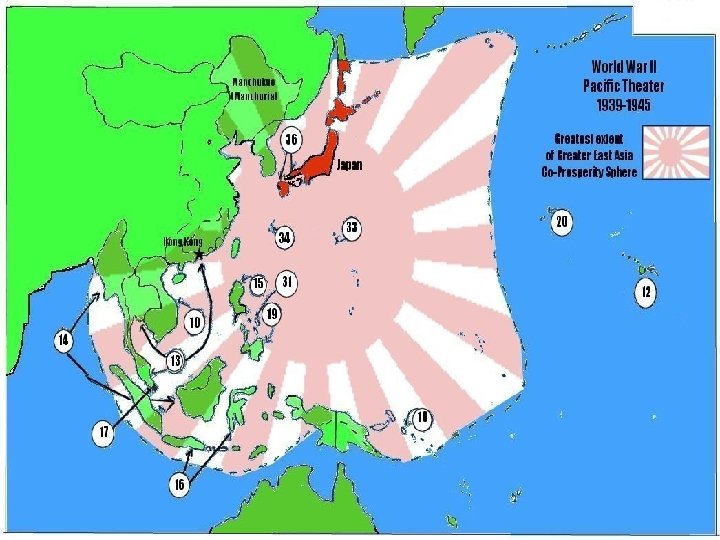
 Major Battles North Africa n El Alamein— WHO: Germans (Gen. Rommel) vs. British WHY: Germany wanted Suez Canal RESULT: British Win prevented Hitler from gaining Middle Eastern oil supplies and attacking the Soviet Union from the south.
Major Battles North Africa n El Alamein— WHO: Germans (Gen. Rommel) vs. British WHY: Germany wanted Suez Canal RESULT: British Win prevented Hitler from gaining Middle Eastern oil supplies and attacking the Soviet Union from the south.
 Major Battles Europe n Stalingrad – WHO: Germany vs. Soviet Union WHY: Germany was invading Russia RESULT: Hundreds of thousands of German soldiers were killed or captured. This defeat prevented Germany from seizing the Soviet oil fields and turned the tide against Germany in the east.
Major Battles Europe n Stalingrad – WHO: Germany vs. Soviet Union WHY: Germany was invading Russia RESULT: Hundreds of thousands of German soldiers were killed or captured. This defeat prevented Germany from seizing the Soviet oil fields and turned the tide against Germany in the east.
 Major Battles Europe Normandy (D-Day) – WHO: Allied Forces vs. Germany WHY: To reclaim France RESULT: The landings succeeded and the liberation of western Europe from Hitler had begun. n
Major Battles Europe Normandy (D-Day) – WHO: Allied Forces vs. Germany WHY: To reclaim France RESULT: The landings succeeded and the liberation of western Europe from Hitler had begun. n
 Major Battles Pacific n Midway – WHO: USA vs. Japan WHY: To prevent Japan from getting close to Hawaii RESULT: American naval forces defeated a much larger Japanese force as it prepared to seize Midway Island. The American victory ended the Japanese threat to Hawaii.
Major Battles Pacific n Midway – WHO: USA vs. Japan WHY: To prevent Japan from getting close to Hawaii RESULT: American naval forces defeated a much larger Japanese force as it prepared to seize Midway Island. The American victory ended the Japanese threat to Hawaii.
 Major Battles Pacific, Continued Iwo Jima and Okinawa – n WHO: USA vs. Japan WHY: Island Hopping closer to Japan RESULT: USA wins, but at a very high cost in lives
Major Battles Pacific, Continued Iwo Jima and Okinawa – n WHO: USA vs. Japan WHY: Island Hopping closer to Japan RESULT: USA wins, but at a very high cost in lives
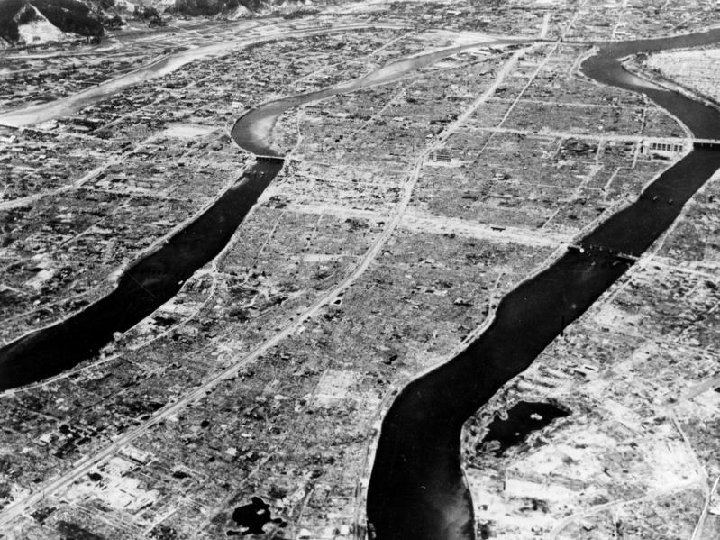
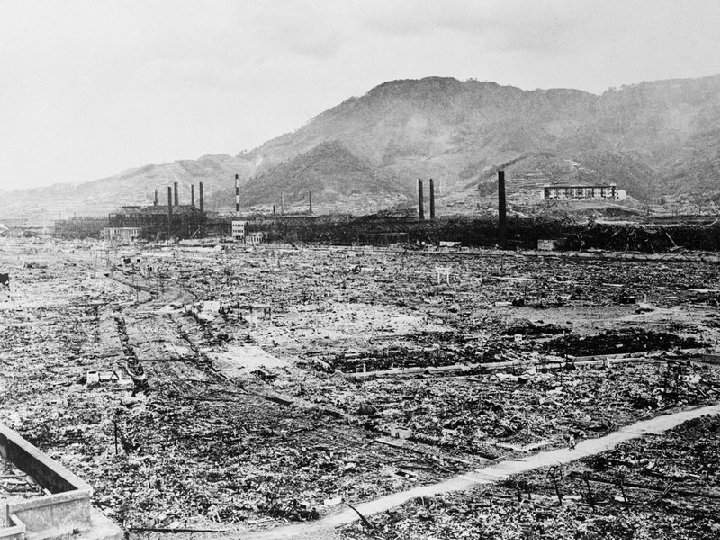
 Atomic Bomb n President Harry Truman ordered the use of atomic bombs on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki to force the Japanese to surrender. After the bombs were used, Japan surrendered, avoiding the need for American forces to invade Japan.
Atomic Bomb n President Harry Truman ordered the use of atomic bombs on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki to force the Japanese to surrender. After the bombs were used, Japan surrendered, avoiding the need for American forces to invade Japan.
 Little Boy Hiroshima Fat Man Nagasaki
Little Boy Hiroshima Fat Man Nagasaki


 Warm Up: Now that we know about the effects of nuclear weapons… n How would you explain Pres. Truman’s choice to use atomic bombs in Japan? n How could you justify the use of atomic warfare in today’s world? n
Warm Up: Now that we know about the effects of nuclear weapons… n How would you explain Pres. Truman’s choice to use atomic bombs in Japan? n How could you justify the use of atomic warfare in today’s world? n
 Minority Participation in WWII n African Americans generally served in segregated military units. n They were assigned to non-combat roles. n They demanded the right to serve in combat.
Minority Participation in WWII n African Americans generally served in segregated military units. n They were assigned to non-combat roles. n They demanded the right to serve in combat.
 All-Minority Military Units n Tuskegee Airmen (African American) served in Europe.
All-Minority Military Units n Tuskegee Airmen (African American) served in Europe.
 All-Minority Military Units n Nisei regiments (Asian American) earned a high number of decorations.
All-Minority Military Units n Nisei regiments (Asian American) earned a high number of decorations.
 Additional Contributions of Minorities n n n Communication codes of the Navajo were used. Mexican Americans (not segregated) Minority units suffered high casualties and won many medals for bravery.
Additional Contributions of Minorities n n n Communication codes of the Navajo were used. Mexican Americans (not segregated) Minority units suffered high casualties and won many medals for bravery.
 The Geneva Convention n The Geneva Convention tried to guarantee the humane treatment of prisoners of war by establishing rules to be followed by all nations.
The Geneva Convention n The Geneva Convention tried to guarantee the humane treatment of prisoners of war by establishing rules to be followed by all nations.
 Treatment of POWs n In the Bataan Death March, American POWs suffered brutal treatment by Japanese after surrender of the Philippines. n Japanese soldiers often committed suicide rather than surrender. n Europe more closely followed the ideas of the Geneva Convention
Treatment of POWs n In the Bataan Death March, American POWs suffered brutal treatment by Japanese after surrender of the Philippines. n Japanese soldiers often committed suicide rather than surrender. n Europe more closely followed the ideas of the Geneva Convention
 Concentration Camps n Genocide: The destruction of a people n Final solution: Germany’s decision to all Jews n Also affected: Gypsies, Slavs, Poles, “Undesirables”
Concentration Camps n Genocide: The destruction of a people n Final solution: Germany’s decision to all Jews n Also affected: Gypsies, Slavs, Poles, “Undesirables”
 Nuremberg Trials n Nazi leaders were convicted of war crimes. n Individuals were responsible for actions during war, not just following orders. n Led to demand for a Jewish homeland.
Nuremberg Trials n Nazi leaders were convicted of war crimes. n Individuals were responsible for actions during war, not just following orders. n Led to demand for a Jewish homeland.
 How the US Won WW 2 Rationing n War bonds n Income tax n Business changed from peacetime to wartime production n Women & minorities entered the labor force n Draft/selective service n Ad Campaigns and Mass Media n
How the US Won WW 2 Rationing n War bonds n Income tax n Business changed from peacetime to wartime production n Women & minorities entered the labor force n Draft/selective service n Ad Campaigns and Mass Media n
 After WW 2 Soviet Unions controlled most of Eastern Europe n Germany split into 4 zones n Japan occupied by US n USA helped Europe rebuild and fight off communism n United Nations formed to replace League of Nations n
After WW 2 Soviet Unions controlled most of Eastern Europe n Germany split into 4 zones n Japan occupied by US n USA helped Europe rebuild and fight off communism n United Nations formed to replace League of Nations n
 The Cold War
The Cold War


