a69e0d1cabb08a8db679c9baff87c6be.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 World War II – Important Facts 1939 - 1945
World War II – Important Facts 1939 - 1945
 Causes of World War II • Worldwide economic depression in the 1930’s added frustration and fear with anger. • Massive unemployment and high inflation fueled the anger of the people seeking change. • Germany was also plagued by high war debt. • Treaty of Versailles • Japan, an island nation believed that by expanding their power in East Asia, they would solve their need for resources.
Causes of World War II • Worldwide economic depression in the 1930’s added frustration and fear with anger. • Massive unemployment and high inflation fueled the anger of the people seeking change. • Germany was also plagued by high war debt. • Treaty of Versailles • Japan, an island nation believed that by expanding their power in East Asia, they would solve their need for resources.
 The allied leaders of the Munich Conference (1938) agreed to allow Germany to occupy the Sudetenland (part of Czechoslovakia) if Hitler would not expand his territory any further. This was appeasement. The invasion of Poland in 1939 was the deciding factor for most nations to enter WWII. Hitler’s blitzkrieg, or “Lightning War” in Poland lasted only a few days.
The allied leaders of the Munich Conference (1938) agreed to allow Germany to occupy the Sudetenland (part of Czechoslovakia) if Hitler would not expand his territory any further. This was appeasement. The invasion of Poland in 1939 was the deciding factor for most nations to enter WWII. Hitler’s blitzkrieg, or “Lightning War” in Poland lasted only a few days.
 WORLD WAR II • What is a dictator? • What is fascism? ~ a ruler who rules ~ a political system, with total authority, headed by a often in a cruel and dictator, that calls brutal manner. for extreme nationalism and racism and no tolerance of opposition.
WORLD WAR II • What is a dictator? • What is fascism? ~ a ruler who rules ~ a political system, with total authority, headed by a often in a cruel and dictator, that calls brutal manner. for extreme nationalism and racism and no tolerance of opposition.
 World dictators in the 1920’s and 1930’s • Hideki Tojo ~ Japan • Benito Mussolini~ Italy • Adolf Hitler~ Germany
World dictators in the 1920’s and 1930’s • Hideki Tojo ~ Japan • Benito Mussolini~ Italy • Adolf Hitler~ Germany
 Major Countries Involved in World War II Axis Powers Allied Powers Germany United States Italy France Japan Great Britain Soviet Union Canada
Major Countries Involved in World War II Axis Powers Allied Powers Germany United States Italy France Japan Great Britain Soviet Union Canada
 Opposition to the entry of the United States into World War II • Isolationists believed that the United States should keep its nose out of the European theater. They banded together to form the America First Committee ~ members included Charles Lindbergh and Henry Ford. Jeanette Rankin was the first woman elected to the U. S. Congress and the only Congress person to vote against going to war with Japan.
Opposition to the entry of the United States into World War II • Isolationists believed that the United States should keep its nose out of the European theater. They banded together to form the America First Committee ~ members included Charles Lindbergh and Henry Ford. Jeanette Rankin was the first woman elected to the U. S. Congress and the only Congress person to vote against going to war with Japan.
 American response to WWII between 1939 -1941 • A national policy of avoiding involvement in world affairs is called isolationism. • The position of not taking sides on an issue is called neutrality.
American response to WWII between 1939 -1941 • A national policy of avoiding involvement in world affairs is called isolationism. • The position of not taking sides on an issue is called neutrality.
 • The Lend-lease act of 1941 allowed the U. S. to sell, lend, or lease arms or other war supplies to nations considered “vital to the defense” of the United States. • Between 1935 -1937 congress agreed to allow the U. S to sell weapons on a “cash and carry basis”.
• The Lend-lease act of 1941 allowed the U. S. to sell, lend, or lease arms or other war supplies to nations considered “vital to the defense” of the United States. • Between 1935 -1937 congress agreed to allow the U. S to sell weapons on a “cash and carry basis”.
 • Japanese aggression in East Asia was a result of their need for oil and rubber. • The Japanese sneak attack on Pearl Harbor inflicted over 2, 400 deaths and devastated the U. S Pacifice Naval fleet. 8 battleships and 3 cruisers were among the losses. • December 7, 1941 –”a date which will live in infamy”. • Today, the U. S. S. Arizona stands as a memorial.
• Japanese aggression in East Asia was a result of their need for oil and rubber. • The Japanese sneak attack on Pearl Harbor inflicted over 2, 400 deaths and devastated the U. S Pacifice Naval fleet. 8 battleships and 3 cruisers were among the losses. • December 7, 1941 –”a date which will live in infamy”. • Today, the U. S. S. Arizona stands as a memorial.
 Key Individuals of WWII • Franklin D. Roosevelt. President of U. S from 19331945. Polio victim who died in office. Adored president whose New Deal programs gave people jobs. • Dwight D. Eisenhower- he was the first 5 star general to become president. During WWII, Ike was the Supreme Allied commander.
Key Individuals of WWII • Franklin D. Roosevelt. President of U. S from 19331945. Polio victim who died in office. Adored president whose New Deal programs gave people jobs. • Dwight D. Eisenhower- he was the first 5 star general to become president. During WWII, Ike was the Supreme Allied commander.
 • Harry S. Truman- he was the first president to take office during war time and also the first and only president to use the atomic bomb on another country. Known for his feisty persona, Truman kept a sign on his desk that said, “the Buck Stops Here. ”
• Harry S. Truman- he was the first president to take office during war time and also the first and only president to use the atomic bomb on another country. Known for his feisty persona, Truman kept a sign on his desk that said, “the Buck Stops Here. ”
 • Douglas Mac. Arthurgeneral in command of American forces in the Pacific. He was a controversial figure. Quoted as saying, “I shall return” upon leaving the Philippines when the Japanese invaded. He did!
• Douglas Mac. Arthurgeneral in command of American forces in the Pacific. He was a controversial figure. Quoted as saying, “I shall return” upon leaving the Philippines when the Japanese invaded. He did!
 • Neville Chamberlain-Prime Minister of England before 1940. He supported a policy of appeasement, allowing Hitler to take Czechoslovakia, to avoid war. Died in 1940. • Winston Churchill- Prime Minister of England after 1940. He was a brilliant statesman. He is considered to be the architect for victory during WWII.
• Neville Chamberlain-Prime Minister of England before 1940. He supported a policy of appeasement, allowing Hitler to take Czechoslovakia, to avoid war. Died in 1940. • Winston Churchill- Prime Minister of England after 1940. He was a brilliant statesman. He is considered to be the architect for victory during WWII.
 • Josef Stalin- communist dictator of the Soviet Union. He industrialized Russia in order to compete with the rest of the world. He built gulags where Russians who did not meet his goals or who disagreed with his ideology were then imprisoned. Millions died or were executed during his reign of power.
• Josef Stalin- communist dictator of the Soviet Union. He industrialized Russia in order to compete with the rest of the world. He built gulags where Russians who did not meet his goals or who disagreed with his ideology were then imprisoned. Millions died or were executed during his reign of power.
 • Dr. Charles Drew - developed the first large-scale blood bank early during World War II, saving thousands Allied soldiers. J. Robert Oppenheimer – physicists and scientific director of the Manhattan Project, the World War II effort to develop the first nuclear weapons. "The Father of the Atomic Bomb”
• Dr. Charles Drew - developed the first large-scale blood bank early during World War II, saving thousands Allied soldiers. J. Robert Oppenheimer – physicists and scientific director of the Manhattan Project, the World War II effort to develop the first nuclear weapons. "The Father of the Atomic Bomb”
 The Effects of WWII on Women and Minorities within the U. S. • The term: Rosie the Riviter was a catch phrase that influenced many women to take on factory jobs. • For many women this was their first job outside of the home. "Richmond Welders" Courtesy of the Family of Margaret Fong
The Effects of WWII on Women and Minorities within the U. S. • The term: Rosie the Riviter was a catch phrase that influenced many women to take on factory jobs. • For many women this was their first job outside of the home. "Richmond Welders" Courtesy of the Family of Margaret Fong
 Women’s Place in War
Women’s Place in War
 • After Pearl Harbor, many Americans resented Japanese. Americans (Nisei). This was a question of loyalty. Nisei were sent to internment camps that were very crowded and harsh.
• After Pearl Harbor, many Americans resented Japanese. Americans (Nisei). This was a question of loyalty. Nisei were sent to internment camps that were very crowded and harsh.
 • Despite discrimination Japanese-Americans did serve in the military. After almost two years of fighting, the 100 th/442 nd, an all Japanese fighting squadron, emerged from the war the most highly decorated unit in U. S. military history.
• Despite discrimination Japanese-Americans did serve in the military. After almost two years of fighting, the 100 th/442 nd, an all Japanese fighting squadron, emerged from the war the most highly decorated unit in U. S. military history.
 • African-Americans still faced continued discrimination. • Many African-American civilians began moving North/West out of the south to find jobs.
• African-Americans still faced continued discrimination. • Many African-American civilians began moving North/West out of the south to find jobs.
 • Nearly 700, 000 men served in the armed forces with segregated units in low-level jobs.
• Nearly 700, 000 men served in the armed forces with segregated units in low-level jobs.
 In 1942 the army allowed white/black soldiers to train together. An African. American fighter group known as the Tuskegee Airmen shot down more than 200 enemy planes. A class of twin-engine pilots in front in flight caps and single engine pilots in rear in helmets and goggles, Dec. 1943.
In 1942 the army allowed white/black soldiers to train together. An African. American fighter group known as the Tuskegee Airmen shot down more than 200 enemy planes. A class of twin-engine pilots in front in flight caps and single engine pilots in rear in helmets and goggles, Dec. 1943.
 Navajo Code Talkers – young Navajo men who created an unbreakable code based on their ancient language. It saved countless lives and helped to end the war. The Code - the Navajo word for tortoise, "chay-da-gahi, " meant tank, and a dive-bomber, "gini, " was a "chicken hawk, " (a bird which dives on its prey). The selection of a given term was based on the first letter of the English meaning of the Navajo word. For instance, "Wo-La-Chee" means "ant, " and would represent the letter "A".
Navajo Code Talkers – young Navajo men who created an unbreakable code based on their ancient language. It saved countless lives and helped to end the war. The Code - the Navajo word for tortoise, "chay-da-gahi, " meant tank, and a dive-bomber, "gini, " was a "chicken hawk, " (a bird which dives on its prey). The selection of a given term was based on the first letter of the English meaning of the Navajo word. For instance, "Wo-La-Chee" means "ant, " and would represent the letter "A".
 Efforts to Support the War Effort at Home • Many Americans at home did their part by conserving resources and goods needed for the war effort. • Americans rationed items such as shoes, gasoline, tires, sugar and meat, and for the most part accepted these inconveniences as part of the war effort. Americans were allowed 16 points per month to spend on rationed foods.
Efforts to Support the War Effort at Home • Many Americans at home did their part by conserving resources and goods needed for the war effort. • Americans rationed items such as shoes, gasoline, tires, sugar and meat, and for the most part accepted these inconveniences as part of the war effort. Americans were allowed 16 points per month to spend on rationed foods.
 • Due to the short supply of vegetables, many planted “victory gardens” • American coastal cities enforced blackouts so enemy pilots could not use lights as beacons. • The conversion of American industries to the production of war goods such as trucks, tanks, and airplanes, led to the end of America’s Great Depression.
• Due to the short supply of vegetables, many planted “victory gardens” • American coastal cities enforced blackouts so enemy pilots could not use lights as beacons. • The conversion of American industries to the production of war goods such as trucks, tanks, and airplanes, led to the end of America’s Great Depression.
 • A concentration camp is a prison camp for civilians where prisoners were forced to do hard labor. • The deliberate destruction of a racial, political or cultural group is known as genocide. • death camps were established in 1941 in Poland designed for mass murder. The Holocaust
• A concentration camp is a prison camp for civilians where prisoners were forced to do hard labor. • The deliberate destruction of a racial, political or cultural group is known as genocide. • death camps were established in 1941 in Poland designed for mass murder. The Holocaust
 • Germany blamed the Jewish people for the destruction of Europe after WWI and this immense hatred led to the Nazi development known as “the final solution”. • The Nazis exterminated almost 2 million Jews in Auschwitz- a concentration camp in Poland.
• Germany blamed the Jewish people for the destruction of Europe after WWI and this immense hatred led to the Nazi development known as “the final solution”. • The Nazis exterminated almost 2 million Jews in Auschwitz- a concentration camp in Poland.
 • As many as 6 million Jews lost their lives during the holocaust and another 4 million gypsies, soviet prisoners, and the disabled fell victim to these horrible atrocities. • 2 out of 3 European Jews were killed.
• As many as 6 million Jews lost their lives during the holocaust and another 4 million gypsies, soviet prisoners, and the disabled fell victim to these horrible atrocities. • 2 out of 3 European Jews were killed.
 • Hitler’s final solution began with a boycott of Jewish stores followed by their segregation from the rest of the German people. • Jews were forced to wear armbands, known as the “Star of David”, that alienated them from others.
• Hitler’s final solution began with a boycott of Jewish stores followed by their segregation from the rest of the German people. • Jews were forced to wear armbands, known as the “Star of David”, that alienated them from others.
 • The allied forces saw firsthand the horrors that the Jewish people felt as they liberated the concentration camps while they advanced through Germany.
• The allied forces saw firsthand the horrors that the Jewish people felt as they liberated the concentration camps while they advanced through Germany.
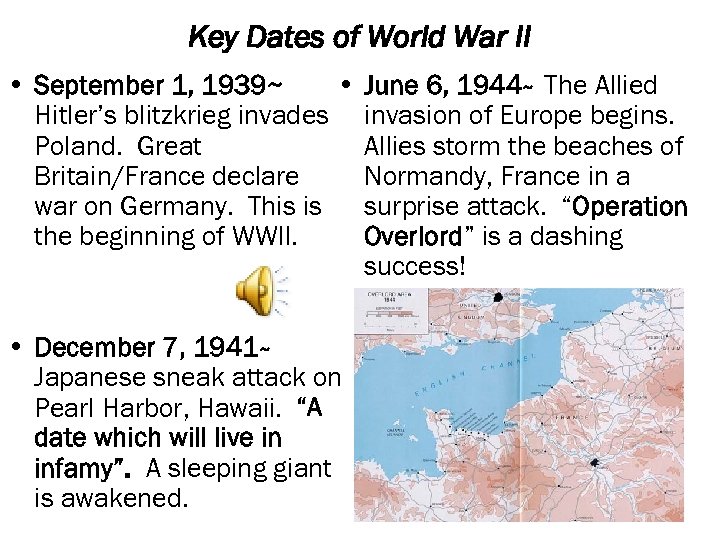 Key Dates of World War II • September 1, 1939~ • June 6, 1944~ The Allied Hitler’s blitzkrieg invades invasion of Europe begins. Poland. Great Allies storm the beaches of Britain/France declare Normandy, France in a war on Germany. This is surprise attack. “Operation the beginning of WWII. Overlord” is a dashing success! • December 7, 1941~ Japanese sneak attack on Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. “A date which will live in infamy”. A sleeping giant is awakened.
Key Dates of World War II • September 1, 1939~ • June 6, 1944~ The Allied Hitler’s blitzkrieg invades invasion of Europe begins. Poland. Great Allies storm the beaches of Britain/France declare Normandy, France in a war on Germany. This is surprise attack. “Operation the beginning of WWII. Overlord” is a dashing success! • December 7, 1941~ Japanese sneak attack on Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. “A date which will live in infamy”. A sleeping giant is awakened.
 1945 ~ End of WWII is achieved after V-E Day (Victory in Europe – May 8) when Germany and Italy surrender. Japan will surrender on August 15 after the dropping of two atomic bombs over Hiroshima and Nagasaki. V-J Day (victory in Japan).
1945 ~ End of WWII is achieved after V-E Day (Victory in Europe – May 8) when Germany and Italy surrender. Japan will surrender on August 15 after the dropping of two atomic bombs over Hiroshima and Nagasaki. V-J Day (victory in Japan).
 Major reasons for victory in World War II • American industrial production ~The U. S. went from having one of the world’s smaller armies to one of the largest. • The atomic bomb (Manhattan Project) caused unimaginable damage to Japan that forced them to realize they were defeated. • The surprise attack on D-Day in Normandy paved the way for the Allies to liberate Europe.
Major reasons for victory in World War II • American industrial production ~The U. S. went from having one of the world’s smaller armies to one of the largest. • The atomic bomb (Manhattan Project) caused unimaginable damage to Japan that forced them to realize they were defeated. • The surprise attack on D-Day in Normandy paved the way for the Allies to liberate Europe.
 Significance of the Atomic Bomb • The Japanese are a very proud people that did not know when they were defeated. In fact the word “surrender” does not have a Japanese translation. • August 6, 1945 the American bomber Enola Gay dropped the first atomic bomb over Hiroshima, Japan. Three days later, another bomb was dropped on Nagasaki.
Significance of the Atomic Bomb • The Japanese are a very proud people that did not know when they were defeated. In fact the word “surrender” does not have a Japanese translation. • August 6, 1945 the American bomber Enola Gay dropped the first atomic bomb over Hiroshima, Japan. Three days later, another bomb was dropped on Nagasaki.
 • The two atomic bombs collectively killed over 100, 000 Japanese citizens. Many more died after the blast due to radiation poisoning. • The atomic bomb proved to be too much for the Japanese who agreed to surrender. • Japan signed the formal unconditional surrender on September 2, 1945, on the battleship U. S. S Missouri.
• The two atomic bombs collectively killed over 100, 000 Japanese citizens. Many more died after the blast due to radiation poisoning. • The atomic bomb proved to be too much for the Japanese who agreed to surrender. • Japan signed the formal unconditional surrender on September 2, 1945, on the battleship U. S. S Missouri.
 International Effects of World War II • In the years following the war, Nazi and Japanese leaders were put on trial. These “war criminals” were to be tried for crimes against humanity in Nuremberg, Germany. • The Nuremberg trials eventually convicted and executed 24 Nazi and 7 Japanese for their crimes and hundreds more were imprisoned. Defendant Julius Streicher, Editor-in-Chief of the venomous antisemitic paper, Der Stürmer, on the stand during the Nuremberg Trials. Streicher was sentenced to death by hanging.
International Effects of World War II • In the years following the war, Nazi and Japanese leaders were put on trial. These “war criminals” were to be tried for crimes against humanity in Nuremberg, Germany. • The Nuremberg trials eventually convicted and executed 24 Nazi and 7 Japanese for their crimes and hundreds more were imprisoned. Defendant Julius Streicher, Editor-in-Chief of the venomous antisemitic paper, Der Stürmer, on the stand during the Nuremberg Trials. Streicher was sentenced to death by hanging.
 • After WWII, many states broke free of colonial rule and tried to establish their independence. In the Middle East, Jews and Arabs both lay claim to the region of Palestine. • In 1947 the United Nations divided Palestine into independent Jewish and Arab states. This led to the formation of Israel. The displaced Jews accepted the plan, but the Arabs did not. Six wars have since followed.
• After WWII, many states broke free of colonial rule and tried to establish their independence. In the Middle East, Jews and Arabs both lay claim to the region of Palestine. • In 1947 the United Nations divided Palestine into independent Jewish and Arab states. This led to the formation of Israel. The displaced Jews accepted the plan, but the Arabs did not. Six wars have since followed.
 • With the end of World War II, the Soviet Union promised to allow free elections in Soviet controlled Eastern Europe. • Instead of these “free elections”, Stalin set up Communist governments and Soviet forces stayed in the region creating Soviet “satellites” influencing Eastern Europe for more than 40 years. • The Soviet Union and Western nations never had a very good relationship due to ideological differences.
• With the end of World War II, the Soviet Union promised to allow free elections in Soviet controlled Eastern Europe. • Instead of these “free elections”, Stalin set up Communist governments and Soviet forces stayed in the region creating Soviet “satellites” influencing Eastern Europe for more than 40 years. • The Soviet Union and Western nations never had a very good relationship due to ideological differences.


