dd2d2dcdf957a106ea49834ebb9e4c81.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 101
 World War II Chapter 26
World War II Chapter 26
 Road to War Section 1
Road to War Section 1
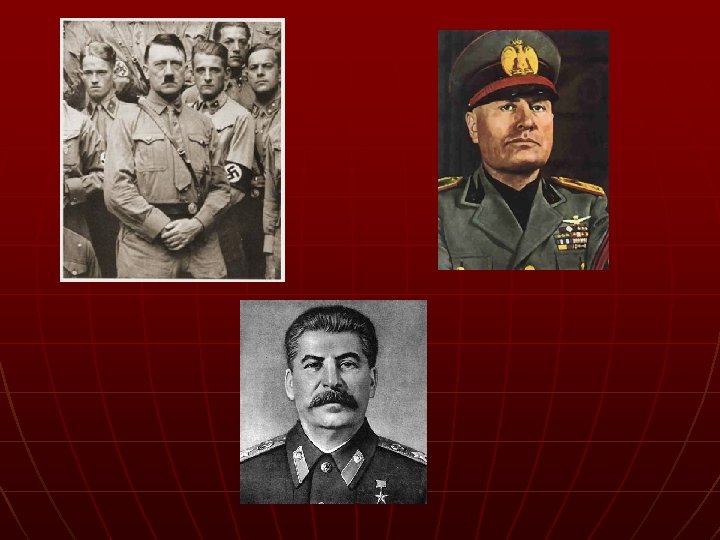
 The Rise of Dictators n Dictator – a leader who takes control by force 1. Adolf Hitler – Germany – – – Nazi Party Anti-Semitism – hatred of the Jewish race Ended democracy – totalitarian rule 2. Benito Mussolini – Italy – Fascism – extreme nationalism and racism 3. Joseph Stalin – Soviet Union (Communism) 4. Japan – military led gov’t invaded China
The Rise of Dictators n Dictator – a leader who takes control by force 1. Adolf Hitler – Germany – – – Nazi Party Anti-Semitism – hatred of the Jewish race Ended democracy – totalitarian rule 2. Benito Mussolini – Italy – Fascism – extreme nationalism and racism 3. Joseph Stalin – Soviet Union (Communism) 4. Japan – military led gov’t invaded China

 American Neutrality n n US wanted nothing to do w/ world conflict Neutrality Acts – no sale of weapons to nations at war
American Neutrality n n US wanted nothing to do w/ world conflict Neutrality Acts – no sale of weapons to nations at war
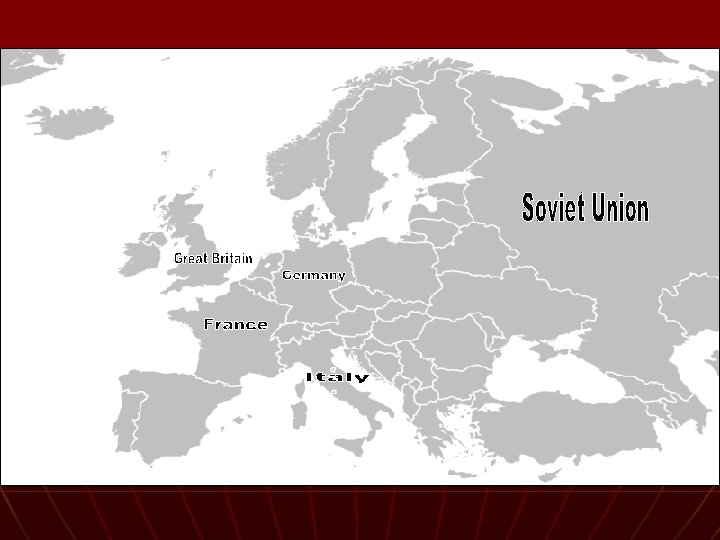
 Germany on the Move n n n Munich Conference – no more German expansion (Britain, France Germany) Soviet-German Non-Aggressive Pact Putting force near the Rhineland, Austria and Czechoslovakia
Germany on the Move n n n Munich Conference – no more German expansion (Britain, France Germany) Soviet-German Non-Aggressive Pact Putting force near the Rhineland, Austria and Czechoslovakia
 War Begins Section 2
War Begins Section 2
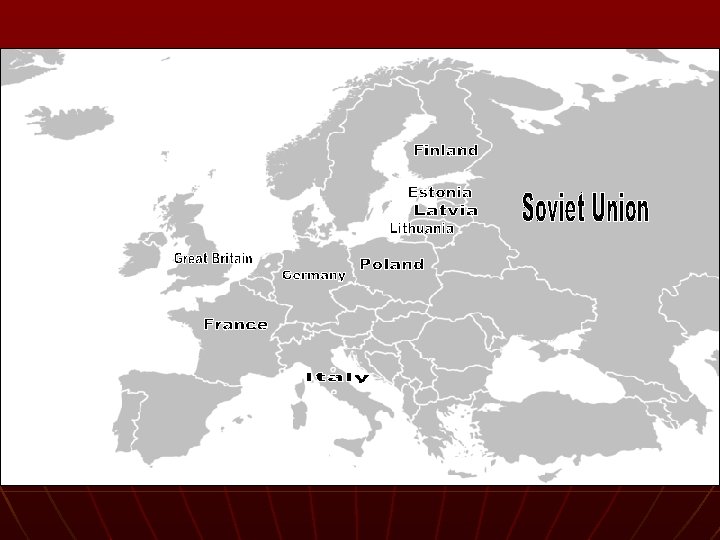
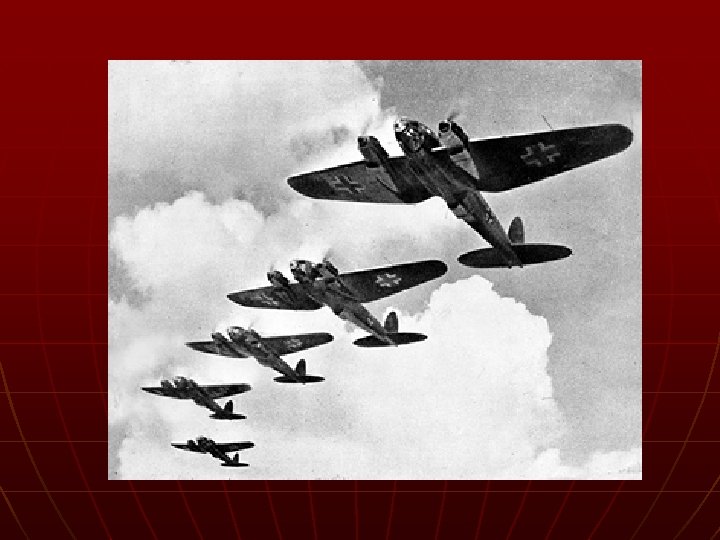
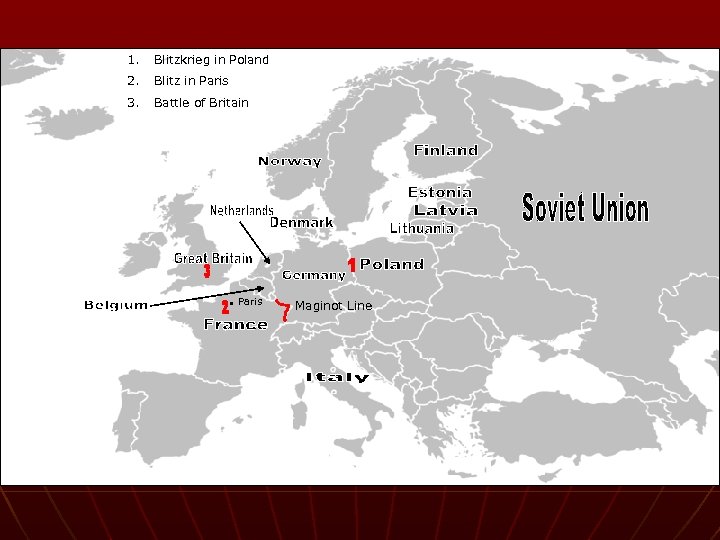
 Germany Invades: Poland n n Blitzkrieg – lightning war (quick strike) September 1, 1939 Germany & Sov. Un. split Poland 50/50 Britain and France declare war • Little they could do n Soviets attack: Latvia, Lithuania, Estonia, and Finland
Germany Invades: Poland n n Blitzkrieg – lightning war (quick strike) September 1, 1939 Germany & Sov. Un. split Poland 50/50 Britain and France declare war • Little they could do n Soviets attack: Latvia, Lithuania, Estonia, and Finland
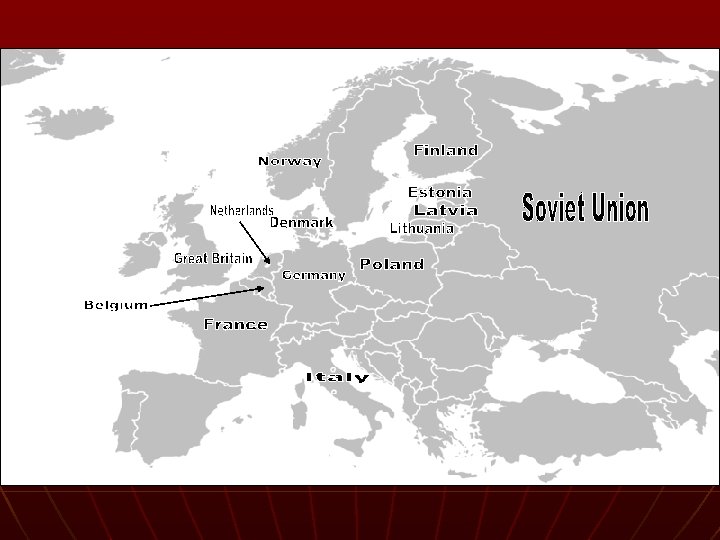
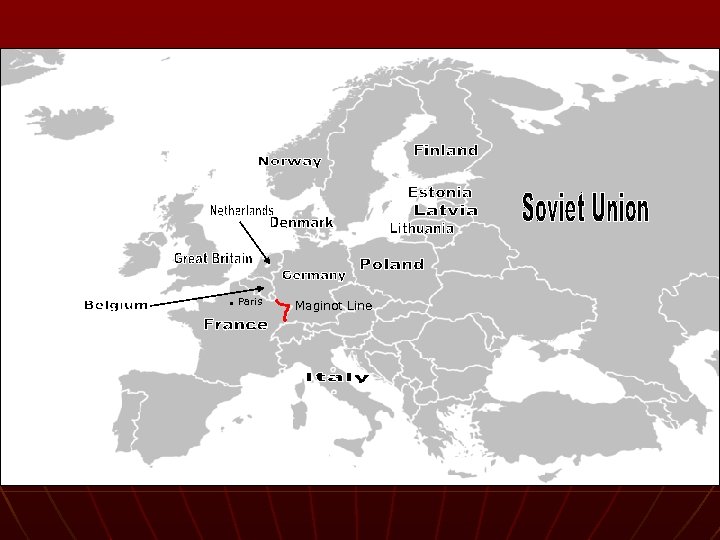
 The War Expands n Maginot Line – fortified line between Belgium and Switzerland • Major dividing line in the west n n n Hitler attacked: Denmark, Norway, Netherlands, Belgium Axis Powers formed (Germany, Italy, later on Japan June 14, 1940 – blitz and capture Paris
The War Expands n Maginot Line – fortified line between Belgium and Switzerland • Major dividing line in the west n n n Hitler attacked: Denmark, Norway, Netherlands, Belgium Axis Powers formed (Germany, Italy, later on Japan June 14, 1940 – blitz and capture Paris
 . Paris Maginot Line
. Paris Maginot Line
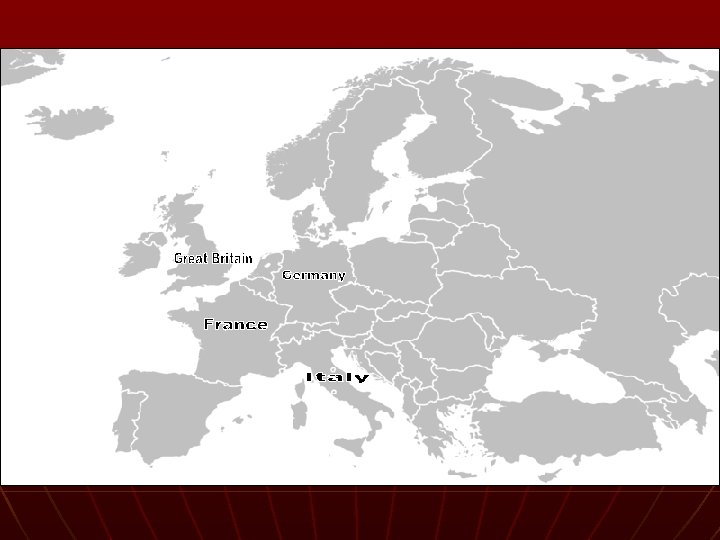
 On your MAP: n Countries • • • n Czechoslovakia Austria Switzerland Sweden Hungary Cities • • • London Warsaw Rome Moscow Berlin n Bodies of Water • • Mediterranean Sea Black Sea English Channel North Sea Baltic Sea Adriatic Sea Atlantic Ocean
On your MAP: n Countries • • • n Czechoslovakia Austria Switzerland Sweden Hungary Cities • • • London Warsaw Rome Moscow Berlin n Bodies of Water • • Mediterranean Sea Black Sea English Channel North Sea Baltic Sea Adriatic Sea Atlantic Ocean
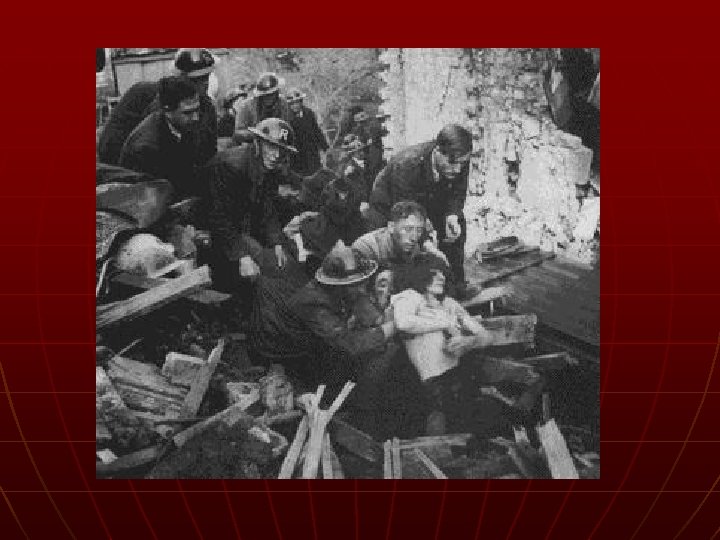
 The Battle of Britain n German Air Attacks on London • Many civilian deaths n n n Britain never gave up Nazis never gained control Germans gave up
The Battle of Britain n German Air Attacks on London • Many civilian deaths n n n Britain never gave up Nazis never gained control Germans gave up
 “We shall defend our island, whatever the cost may be. We shall fight on the beaches, we shall fight on the landing grounds, we shall fight in the fields and in the streets, we shall fight in the hills; we shall never surrender. ” - Winston Churchill Battle of Britain
“We shall defend our island, whatever the cost may be. We shall fight on the beaches, we shall fight on the landing grounds, we shall fight in the fields and in the streets, we shall fight in the hills; we shall never surrender. ” - Winston Churchill Battle of Britain



 1. Blitzkrieg in Poland 2. Blitz in Paris 3. Battle of Britain . Paris Maginot Line
1. Blitzkrieg in Poland 2. Blitz in Paris 3. Battle of Britain . Paris Maginot Line
 Germany Turns East n Frustrated by not winning Britain Hitler attacks the Soviet Union • June 1941 • This broke a non-aggressive pact that the two countries had
Germany Turns East n Frustrated by not winning Britain Hitler attacks the Soviet Union • June 1941 • This broke a non-aggressive pact that the two countries had
 Election of 1940 n FDR runs and wins a 3 rd Term • 1 st time ever n “Your boys are not going to be sent into any foreign wars. ”
Election of 1940 n FDR runs and wins a 3 rd Term • 1 st time ever n “Your boys are not going to be sent into any foreign wars. ”
 US Begins Involvement 1. 2. Lend-Lease – supplying arms to other countries Atlantic Charter n n End “Nazi Tyranny” Disarmament and freedom for the whole world
US Begins Involvement 1. 2. Lend-Lease – supplying arms to other countries Atlantic Charter n n End “Nazi Tyranny” Disarmament and freedom for the whole world
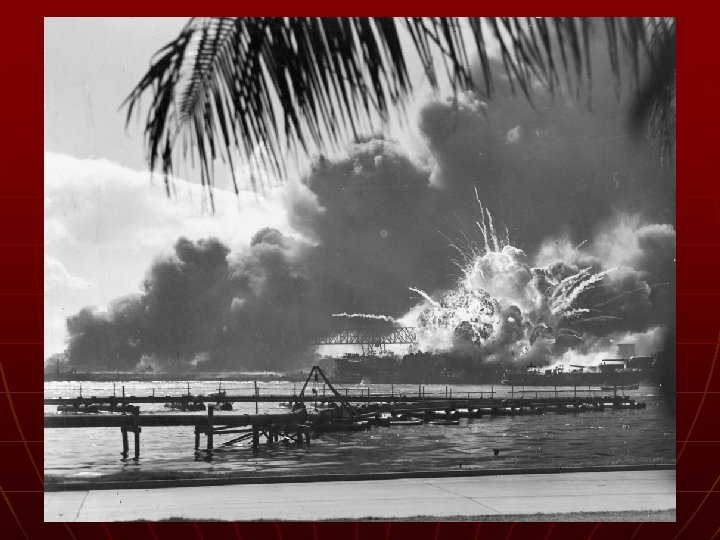
 Pearl Harbor n n Dec. 7, 1941 – 7: 55 am – Hawaii Japanese sneak attack 8 battleships, 3 cruisers, 4 other ships 2, 400 killed “… a date that will live in infamy. ” - Franklin D. Roosevelt
Pearl Harbor n n Dec. 7, 1941 – 7: 55 am – Hawaii Japanese sneak attack 8 battleships, 3 cruisers, 4 other ships 2, 400 killed “… a date that will live in infamy. ” - Franklin D. Roosevelt




 US Declares War n n n Dec. 7, 1941 US declares war on Japan 3 days later Axis Powers declare war on US Congress approves war on Axis Powers
US Declares War n n n Dec. 7, 1941 US declares war on Japan 3 days later Axis Powers declare war on US Congress approves war on Axis Powers
 On the Home Front Section 3
On the Home Front Section 3
 Raising the Army n n Selective Service Act – Draft 15, 000 joined military • 350, 000 women n Mobilization – preparations for war
Raising the Army n n Selective Service Act – Draft 15, 000 joined military • 350, 000 women n Mobilization – preparations for war
 Financing the War n n $320 billion Income Tax & war bonds
Financing the War n n $320 billion Income Tax & war bonds

 Factories n Traded consumer goods for war goods • 70, 000 ships • 100, 000 tanks and airplanes • Millions of guns n n Very efficient Prosperity returns to US
Factories n Traded consumer goods for war goods • 70, 000 ships • 100, 000 tanks and airplanes • Millions of guns n n Very efficient Prosperity returns to US
 Sacrifices n n Families separated Goods rationed: consumers can only buy a limited amount
Sacrifices n n Families separated Goods rationed: consumers can only buy a limited amount

 Women in the War Activity: what do you think the role of a women was prior to 1940? n Military n Worked in factories • Rosie the Riveter n n Lost jobs after the war Opinions changed about women
Women in the War Activity: what do you think the role of a women was prior to 1940? n Military n Worked in factories • Rosie the Riveter n n Lost jobs after the war Opinions changed about women



 African Americans n n 700, 000 served in military Tuskegee Airmen Equal Rights movement in factories Migration north – racial tensions “You say we’re fightin’ for democracy, then why don’t democracy include me? ” - Langston Hughes
African Americans n n 700, 000 served in military Tuskegee Airmen Equal Rights movement in factories Migration north – racial tensions “You say we’re fightin’ for democracy, then why don’t democracy include me? ” - Langston Hughes

 Native Americans n n Code talkers – Navajo language Ira Hayes raises flag at Iwo Jima
Native Americans n n Code talkers – Navajo language Ira Hayes raises flag at Iwo Jima

 Hispanic Americans n n 500, 000 served 17 Mexicans awarded the Congressional Medal of Honor
Hispanic Americans n n 500, 000 served 17 Mexicans awarded the Congressional Medal of Honor
 Japanese Americans n n National fear of internal attack Internment camps • 100, 000 from the west coast • 3 years
Japanese Americans n n National fear of internal attack Internment camps • 100, 000 from the west coast • 3 years
 ACTIVITY Compare how America reacted to WWII to how we are reacting to our current war. How are they the same and how are they different? Why do you think this is so?
ACTIVITY Compare how America reacted to WWII to how we are reacting to our current war. How are they the same and how are they different? Why do you think this is so?
 War in Europe and Africa Section 4
War in Europe and Africa Section 4
 Hitler Expands n n n Almost all of Europe Much of N. Africa America goes to war in Europe before Japan • Bigger threat
Hitler Expands n n n Almost all of Europe Much of N. Africa America goes to war in Europe before Japan • Bigger threat
 Allied Forces n n n n n n n United States Great Britain France Poland Australia New Zealand India Newfoundland South Africa Canada Norway Denmark Belgium Luxembourg Czechoslovakia Brazil Ethiopia Iraq Bolivia Columbia Liberia Peru Lebanon Saudi Arabia Argentina Chile n n n n n n n Greece Yugoslavia Soviet Union*** Mongolia Panama Samoa Guam Puerto Rico Dominican Republic El Salvador Haiti Honduras Nicaragua China Mexico Guatemala Cuba Italy*** Romania Bulgaria San Marino Albania Ecuador Paraguay Uruguay Venezuela Turkey
Allied Forces n n n n n n n United States Great Britain France Poland Australia New Zealand India Newfoundland South Africa Canada Norway Denmark Belgium Luxembourg Czechoslovakia Brazil Ethiopia Iraq Bolivia Columbia Liberia Peru Lebanon Saudi Arabia Argentina Chile n n n n n n n Greece Yugoslavia Soviet Union*** Mongolia Panama Samoa Guam Puerto Rico Dominican Republic El Salvador Haiti Honduras Nicaragua China Mexico Guatemala Cuba Italy*** Romania Bulgaria San Marino Albania Ecuador Paraguay Uruguay Venezuela Turkey
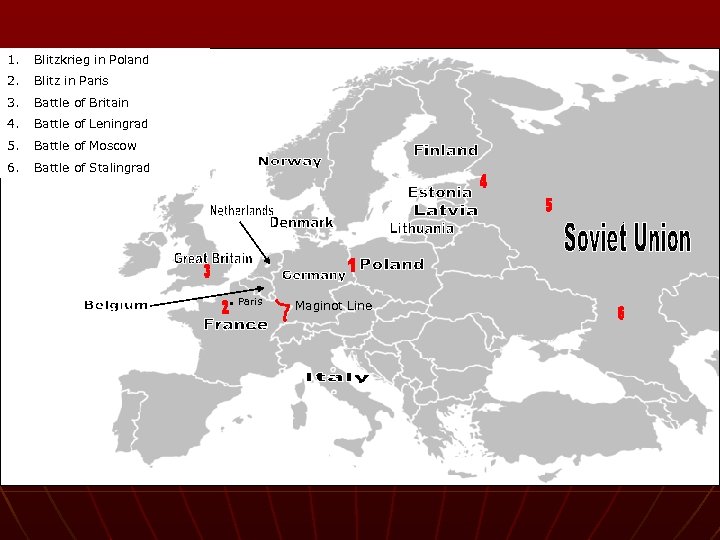
 The Eastern Front n Leningrad – 900 day siege – military blockade • Supplies ran low (cats/dogs) • Thousands Died – NEVER GAVE UP n Moscow – Soviet capital • Bad weather • Germany reaches the middle of the city but never takes control - retreat
The Eastern Front n Leningrad – 900 day siege – military blockade • Supplies ran low (cats/dogs) • Thousands Died – NEVER GAVE UP n Moscow – Soviet capital • Bad weather • Germany reaches the middle of the city but never takes control - retreat
 The Eastern Front n Stalingrad – oil rich city in the south • Street by street/house by house • Won by Germany • Soviets reclaim within a few months n Heavy losses on both sides
The Eastern Front n Stalingrad – oil rich city in the south • Street by street/house by house • Won by Germany • Soviets reclaim within a few months n Heavy losses on both sides
 1. Blitzkrieg in Poland 2. Blitz in Paris 3. Battle of Britain 4. Battle of Leningrad 5. Battle of Moscow 6. Battle of Stalingrad . Paris Maginot Line
1. Blitzkrieg in Poland 2. Blitz in Paris 3. Battle of Britain 4. Battle of Leningrad 5. Battle of Moscow 6. Battle of Stalingrad . Paris Maginot Line

 Air Attacks Over Germany n n Summer 1942 – British/USA bombings over Germany Factories/Cities • Massive destruction n Didn’t phase German military
Air Attacks Over Germany n n Summer 1942 – British/USA bombings over Germany Factories/Cities • Massive destruction n Didn’t phase German military
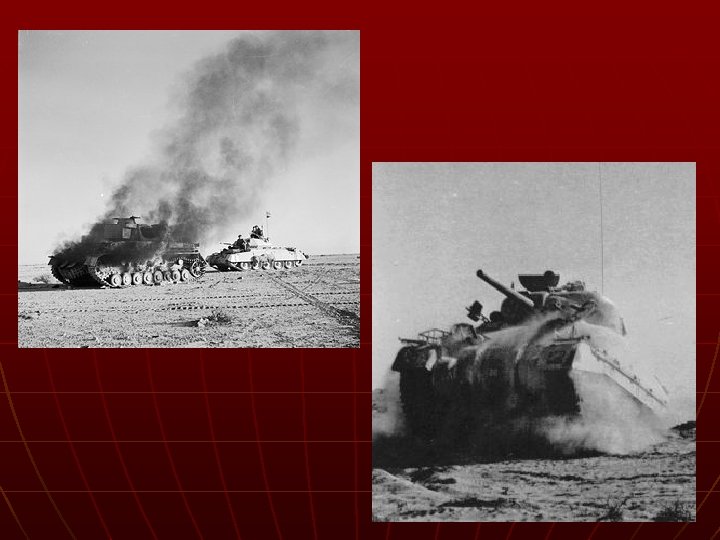
 North African Campaign n General Erwin Rommel (German) • “Desert Fox n n n Gen. Eisenhower & Gen. Patton Nov. 1942 to May 1943 Hitler driven from Africa ACTIVITY: describe the conditions of the desert. What problems would occur in fighting a war in the desert.
North African Campaign n General Erwin Rommel (German) • “Desert Fox n n n Gen. Eisenhower & Gen. Patton Nov. 1942 to May 1943 Hitler driven from Africa ACTIVITY: describe the conditions of the desert. What problems would occur in fighting a war in the desert.

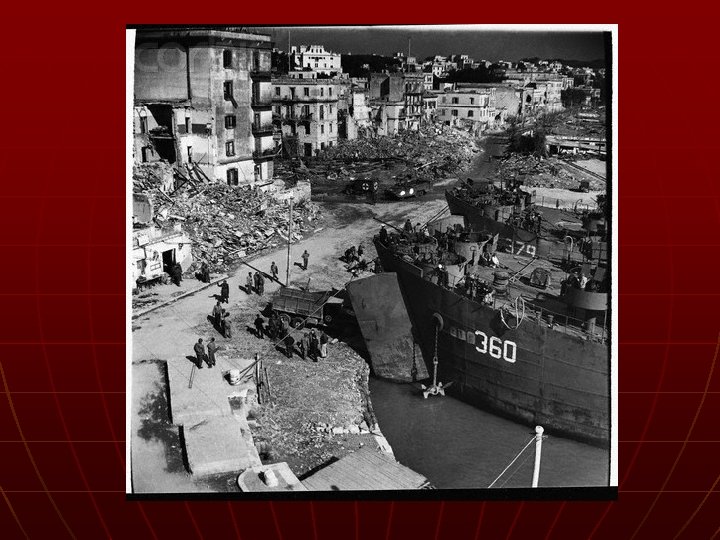
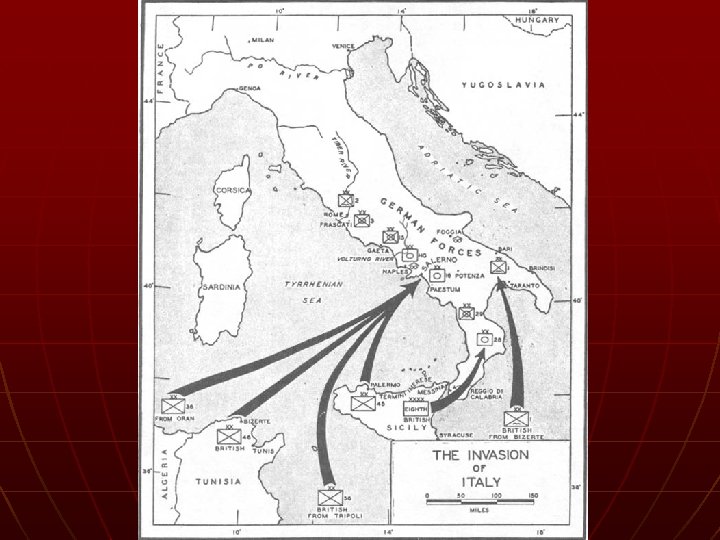
 Invasion of Italy n n Summer 1943 Italians easily beaten, Hitler continued to fight • Germany held for 4 months n Allies liberated Rome in June 1944
Invasion of Italy n n Summer 1943 Italians easily beaten, Hitler continued to fight • Germany held for 4 months n Allies liberated Rome in June 1944

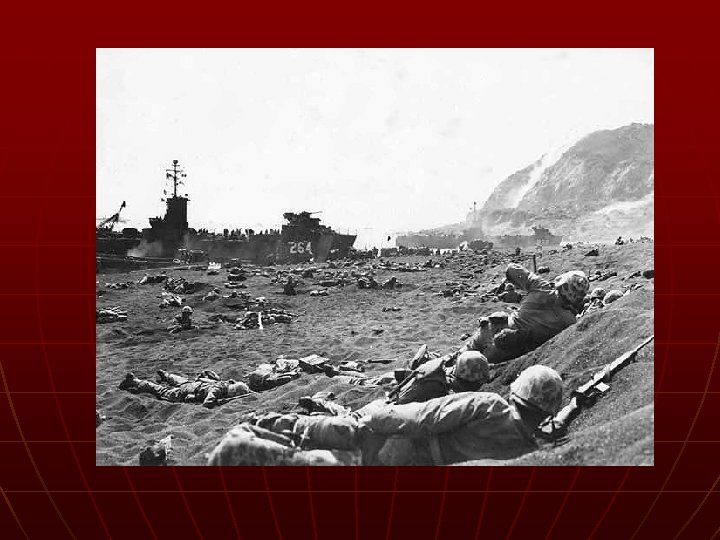
 D-Day n Operation Overload • Gen. Dwight D. Eisenhower n n n French coast of Normandy Over 1 million Allied troops After storming the beach, Allies pushed forward and liberated Paris • Aug. 15, 1944
D-Day n Operation Overload • Gen. Dwight D. Eisenhower n n n French coast of Normandy Over 1 million Allied troops After storming the beach, Allies pushed forward and liberated Paris • Aug. 15, 1944
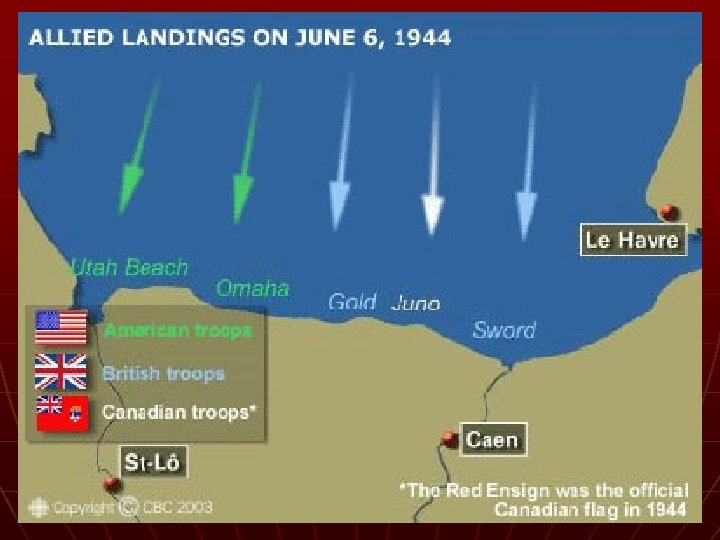




 D-Day Statistics n 150, 000 troops landed on the beach on June 6 th • Over a million followed n n n Around 10, 000 Allies dead on June 6 th 9, 000 Germans dead of June 6 th 425, 000 total dead @ Normandy 566, 648 tons of supplies 171, 532 vehicles
D-Day Statistics n 150, 000 troops landed on the beach on June 6 th • Over a million followed n n n Around 10, 000 Allies dead on June 6 th 9, 000 Germans dead of June 6 th 425, 000 total dead @ Normandy 566, 648 tons of supplies 171, 532 vehicles
 Battle of the Buldge n Stand off @ the Rhine River • COLD!!! n n Dec. 16, 1944 – surprise attack Germany drives deep into Allied lines Allies overcome force Last major German offensive • 75, 000 dead
Battle of the Buldge n Stand off @ the Rhine River • COLD!!! n n Dec. 16, 1944 – surprise attack Germany drives deep into Allied lines Allies overcome force Last major German offensive • 75, 000 dead
 Final Stages in Europe n FDR dies in Feb. 1945 • Harry Truman takes over n n Hitler’s suicide – April 30, 1945 V-E Day – Victory in Europe • May 7, 1945 • German Surrender
Final Stages in Europe n FDR dies in Feb. 1945 • Harry Truman takes over n n Hitler’s suicide – April 30, 1945 V-E Day – Victory in Europe • May 7, 1945 • German Surrender
 War in the Pacific Section 5
War in the Pacific Section 5
 The Pacific Front n On Dec. 7, 1941 (Pearl Harbor Day) Japan also bombed American air fields in: • Philippines • Wake • Guam n Gen. Douglas Mac. Arthur – retreat to Bataan Peninsula in the Philippines
The Pacific Front n On Dec. 7, 1941 (Pearl Harbor Day) Japan also bombed American air fields in: • Philippines • Wake • Guam n Gen. Douglas Mac. Arthur – retreat to Bataan Peninsula in the Philippines
 The Philippines n Allied troops @ Bataan forced to surrender • 76, 000 taken prisoner n Bataan Death March • 60 miles • Killed if they couldn’t walk • 22, 000 killed n “I shall return” – Gen. Mac. Arthur
The Philippines n Allied troops @ Bataan forced to surrender • 76, 000 taken prisoner n Bataan Death March • 60 miles • Killed if they couldn’t walk • 22, 000 killed n “I shall return” – Gen. Mac. Arthur
 Island Hopping n n Island Hopping – attacking and capturing key islands Quick Strike – James Doolittle • Tokyo – moral victory n Battle of the Coral Sea • Strategic victory – no advancement to Australia n n n Midway Guadal Canal – most vicious battle Battle of Leyte Gulf • Philippines – Mac. Arthur’s revenge
Island Hopping n n Island Hopping – attacking and capturing key islands Quick Strike – James Doolittle • Tokyo – moral victory n Battle of the Coral Sea • Strategic victory – no advancement to Australia n n n Midway Guadal Canal – most vicious battle Battle of Leyte Gulf • Philippines – Mac. Arthur’s revenge
 Advance to Japan n Iwo Jima, Okinawa Allied pounding of Japan’s mainland Kamikazes – suicide pilots • Desperation, planes full of explosives • Sunk many battle ships
Advance to Japan n Iwo Jima, Okinawa Allied pounding of Japan’s mainland Kamikazes – suicide pilots • Desperation, planes full of explosives • Sunk many battle ships



 On Your Map n Countries • • n Japan China Korea Australia Philippines New Guinea Indonesia Bodies of Water • • • Pacific Ocean Indian Ocean Coral Sea n Cities, States, or Islands • • • Hawaii Guam Midway Wake Tokyo Okinawa Beijing Hong Kong Hiroshima Nagasaki
On Your Map n Countries • • n Japan China Korea Australia Philippines New Guinea Indonesia Bodies of Water • • • Pacific Ocean Indian Ocean Coral Sea n Cities, States, or Islands • • • Hawaii Guam Midway Wake Tokyo Okinawa Beijing Hong Kong Hiroshima Nagasaki
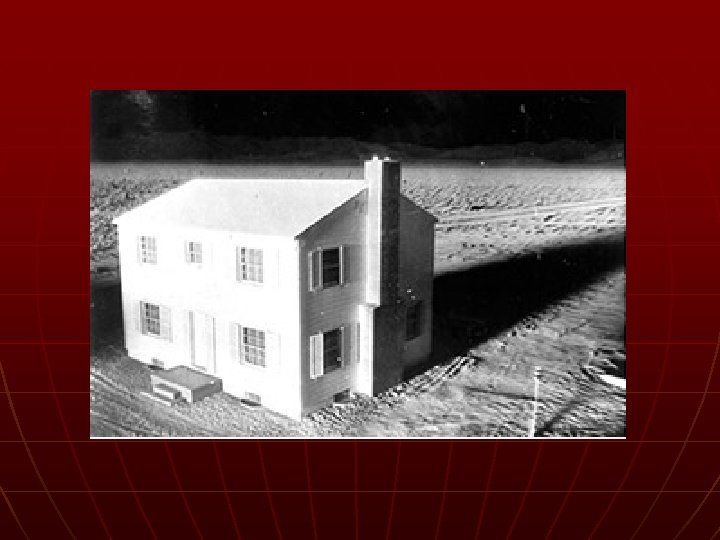
 Atomic Bomb n n n Albert Einstein Manhattan Project – a program to develop new extremely powerful weapons Potsdam Declaration • Surrender or “UTTER DESTRUCTION”
Atomic Bomb n n n Albert Einstein Manhattan Project – a program to develop new extremely powerful weapons Potsdam Declaration • Surrender or “UTTER DESTRUCTION”
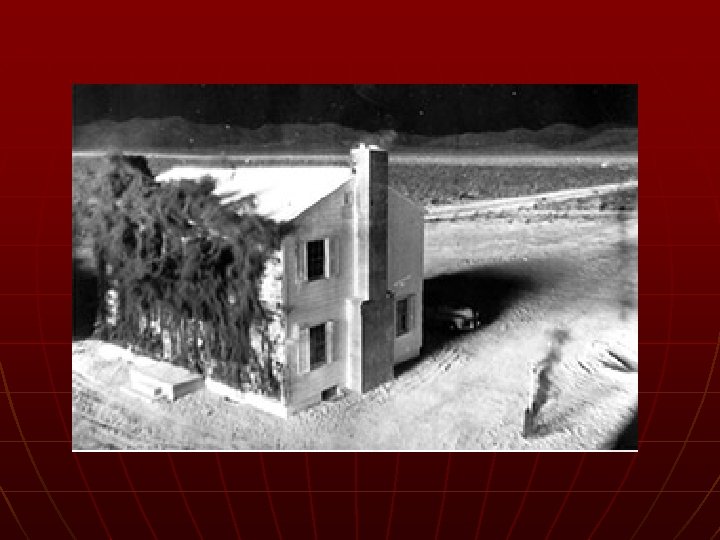
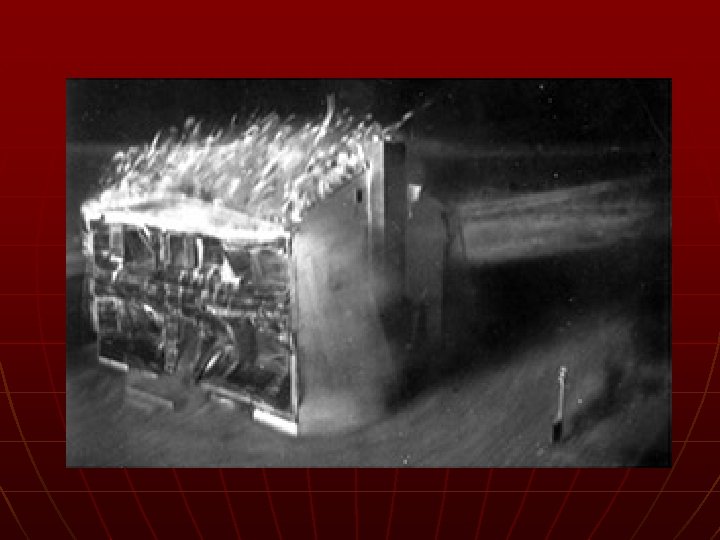
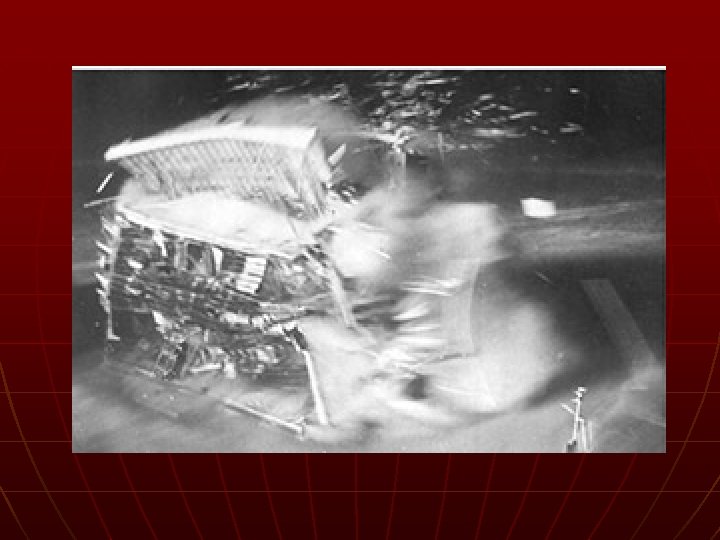






 Click on Link http: //video. google. com/videoplay? docid=2552156377245852199&hl=en
Click on Link http: //video. google. com/videoplay? docid=2552156377245852199&hl=en
 Final Stages of War n August 6, 1945 - Hiroshima • Enola Gay – Little Boy • 70, 000 dead n 3 days later – Nagasaki • Fat Man • 40, 000 dead n Thousands more would die from radiation
Final Stages of War n August 6, 1945 - Hiroshima • Enola Gay – Little Boy • 70, 000 dead n 3 days later – Nagasaki • Fat Man • 40, 000 dead n Thousands more would die from radiation
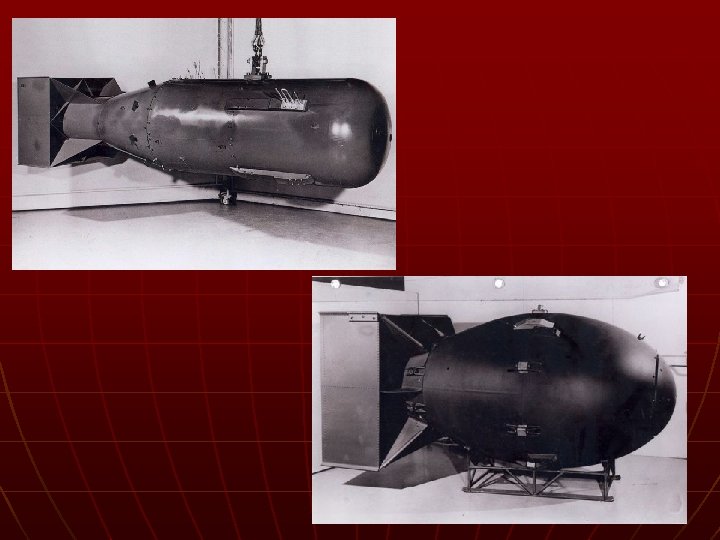



 ACTIVITY n In Pairs • Did the United States need to drop the A -bomb? Explain. • What are the pros and cons to using this kind of weapon? • What would be an alternative to dropping the A-bomb in this situation?
ACTIVITY n In Pairs • Did the United States need to drop the A -bomb? Explain. • What are the pros and cons to using this kind of weapon? • What would be an alternative to dropping the A-bomb in this situation?
 THE END n August 15, 1945 – “V-J Day” • Victory over Japan n September 2, 1945 – Japan signs a surrender
THE END n August 15, 1945 – “V-J Day” • Victory over Japan n September 2, 1945 – Japan signs a surrender

 War Trials n n Nazi/Japanese leaders on trial for crimes against humanity 31 executed, hundreds put in prison
War Trials n n Nazi/Japanese leaders on trial for crimes against humanity 31 executed, hundreds put in prison
 Cost of the War n Total Dead – over 40 million (some sources say as many as 70 million) • ½ from the Soviet Union n n 322, 000 Americans died, 800, 000 injured 11 million dead in Holocaust • Over 6 million of them were Jews n US Cost – $288, 000, 000 • Today this would be 4 trillion
Cost of the War n Total Dead – over 40 million (some sources say as many as 70 million) • ½ from the Soviet Union n n 322, 000 Americans died, 800, 000 injured 11 million dead in Holocaust • Over 6 million of them were Jews n US Cost – $288, 000, 000 • Today this would be 4 trillion


