3502111088ba90a061d07c0a361121c6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 World War II and the Cold War Dictators and War Mobilizing for War Roots of the Cold War The Cold War Expands
World War II and the Cold War Dictators and War Mobilizing for War Roots of the Cold War The Cold War Expands
 20 th Century Dictators
20 th Century Dictators
 Dictators and Wars n Treaty of Versailles from WWI caused anger/resentment among nations n Three dictators use totalitarian gov’ts to rise to power n Joseph Stalin: Russia n Communist State n 5 year plan-collectives n Est. complete control of citizens lives- totalitarian gov’t n Benito Mussolini: Italy n Created Fascist Party- Extreme Nationalism
Dictators and Wars n Treaty of Versailles from WWI caused anger/resentment among nations n Three dictators use totalitarian gov’ts to rise to power n Joseph Stalin: Russia n Communist State n 5 year plan-collectives n Est. complete control of citizens lives- totalitarian gov’t n Benito Mussolini: Italy n Created Fascist Party- Extreme Nationalism
 Dictators and War Adolf Hitler: Germany n n n Joined NAZI party when young Mein Kampf- Nazism Purity Race- Aryans anti-semitic Unite German speaking people Third Reich- political regime Japanese militarists control gov’t
Dictators and War Adolf Hitler: Germany n n n Joined NAZI party when young Mein Kampf- Nazism Purity Race- Aryans anti-semitic Unite German speaking people Third Reich- political regime Japanese militarists control gov’t
 Dictators and War in Europe n Hitler acquires Austria and Czech into the Reich Anschluss n GB uses appeasement with Hitler- let him get his way to avoid war n Stalin signs non-agression pact with Hitler as Germany launches blitzkrieg in Poland ridding Poland of Jews n France falls to Axis Powers when the Maginot Line is broken n Allies finally join Battle of Britain: G. bombs GB day/night for 2 mo.
Dictators and War in Europe n Hitler acquires Austria and Czech into the Reich Anschluss n GB uses appeasement with Hitler- let him get his way to avoid war n Stalin signs non-agression pact with Hitler as Germany launches blitzkrieg in Poland ridding Poland of Jews n France falls to Axis Powers when the Maginot Line is broken n Allies finally join Battle of Britain: G. bombs GB day/night for 2 mo.

 Dictators and War America and War n At first US adopts and isolationist policy FDR signs the Neutrality Act- allowing trade between US and Europe n Quarantine Speech: Peaceful states urge aggressive states to isolate themselves n FDR uses “cash and carry”- allowed warring nations to buy US materials if they used cash and carried them on their own ships
Dictators and War America and War n At first US adopts and isolationist policy FDR signs the Neutrality Act- allowing trade between US and Europe n Quarantine Speech: Peaceful states urge aggressive states to isolate themselves n FDR uses “cash and carry”- allowed warring nations to buy US materials if they used cash and carried them on their own ships

 Dictators and War America in the War Continued… n Congress passes “peacetime draft”, boosts defense spending n “Great Arsenal of Democracy”- FDR convinces nations that we must help Allied powers against the Axis powers n Lend Lease Act- GB, SU give any kind of aid to Allies n Churchill (GB) and FDR secretly meet to plan war. Atlantic Charter
Dictators and War America in the War Continued… n Congress passes “peacetime draft”, boosts defense spending n “Great Arsenal of Democracy”- FDR convinces nations that we must help Allied powers against the Axis powers n Lend Lease Act- GB, SU give any kind of aid to Allies n Churchill (GB) and FDR secretly meet to plan war. Atlantic Charter

 Dictators and War Japan Attacks n Japan invades China and wants to acquire as much land as possible n December 7, 1941 Pearl Harbor n FDR knew Japan was planning an attacktwo front war
Dictators and War Japan Attacks n Japan invades China and wants to acquire as much land as possible n December 7, 1941 Pearl Harbor n FDR knew Japan was planning an attacktwo front war

 Mobilizing for War Mobilizing n Women serve in noncombat roles WAC (Women Army Corps) n Lend-Lease Act begins, War Production Board manages peacetime to wartime industry start rationing n Office of Price Administrations: freeze prices on goods to fight inflation
Mobilizing for War Mobilizing n Women serve in noncombat roles WAC (Women Army Corps) n Lend-Lease Act begins, War Production Board manages peacetime to wartime industry start rationing n Office of Price Administrations: freeze prices on goods to fight inflation
 Mobilizing for War in the Pacific n Japanese on defense after Pearl Harbor Gen. Douglas Mc. Arthur in command of Pacific theater n At first, J. forces advance against US in Philippines and Southeast Asia n 1941 - US turns the tide Doolittle’s Raid, Battle of Coral Sea n Battle of Midway- turning point in Pacific War- Island Hopping n Japanese launch first kamikaze strikes to break Allied lines n Iwo Jima: Crucial Island for US base- heavy losses
Mobilizing for War in the Pacific n Japanese on defense after Pearl Harbor Gen. Douglas Mc. Arthur in command of Pacific theater n At first, J. forces advance against US in Philippines and Southeast Asia n 1941 - US turns the tide Doolittle’s Raid, Battle of Coral Sea n Battle of Midway- turning point in Pacific War- Island Hopping n Japanese launch first kamikaze strikes to break Allied lines n Iwo Jima: Crucial Island for US base- heavy losses


 Mobilizing for War The War for Europe and North Africa n FDR, Churchill, Stalin agree Pacific war is second to European fight against Hitler n Germany uses U-Boats to sink all ships in Atlantic Convoy system n 1943 - Germany slowly presses in on Stalingrad (SU) n SU army wins- major turning point in fighting on land n Allies invade Italy and N. Africa in an attempt to spread Hitler’s army thin
Mobilizing for War The War for Europe and North Africa n FDR, Churchill, Stalin agree Pacific war is second to European fight against Hitler n Germany uses U-Boats to sink all ships in Atlantic Convoy system n 1943 - Germany slowly presses in on Stalingrad (SU) n SU army wins- major turning point in fighting on land n Allies invade Italy and N. Africa in an attempt to spread Hitler’s army thin

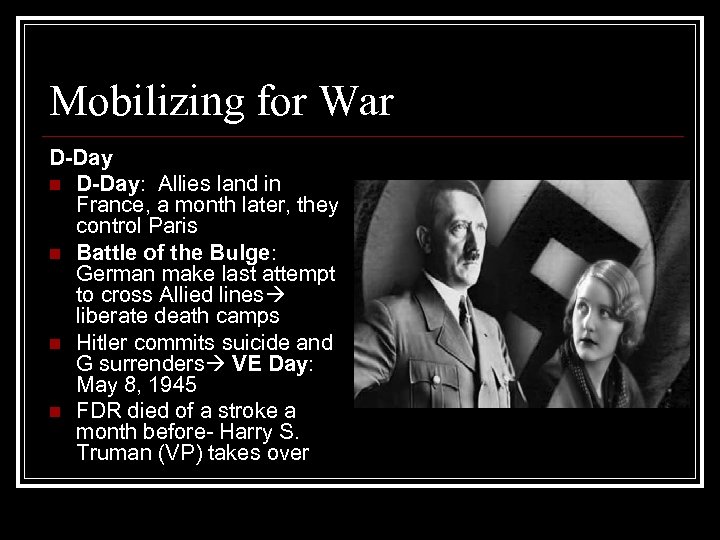 Mobilizing for War D-Day n D-Day: Allies land in France, a month later, they control Paris n Battle of the Bulge: German make last attempt to cross Allied lines liberate death camps n Hitler commits suicide and G surrenders VE Day: May 8, 1945 n FDR died of a stroke a month before- Harry S. Truman (VP) takes over
Mobilizing for War D-Day n D-Day: Allies land in France, a month later, they control Paris n Battle of the Bulge: German make last attempt to cross Allied lines liberate death camps n Hitler commits suicide and G surrenders VE Day: May 8, 1945 n FDR died of a stroke a month before- Harry S. Truman (VP) takes over
 Mobilizing for War The Atomic Bomb- Manhattan Project n US considered invading Japan, like on D-Day- too risky n US warns Japan prior to dropping bomb n Hiroshima/Nagasaki: August 6 & 9, 1945 - Japan surrenders
Mobilizing for War The Atomic Bomb- Manhattan Project n US considered invading Japan, like on D-Day- too risky n US warns Japan prior to dropping bomb n Hiroshima/Nagasaki: August 6 & 9, 1945 - Japan surrenders

 Mobilizing for War Effects of the War n The Holocaust n Yalta Conference: Feb. 1945: FDR, Churchill, Stalin meet n Discuss post war plans. Stalin favors harshness towards G; FDR, C. disagree n Poland, Bulgaria, Romania would have free elections (Stalin reneged)
Mobilizing for War Effects of the War n The Holocaust n Yalta Conference: Feb. 1945: FDR, Churchill, Stalin meet n Discuss post war plans. Stalin favors harshness towards G; FDR, C. disagree n Poland, Bulgaria, Romania would have free elections (Stalin reneged)
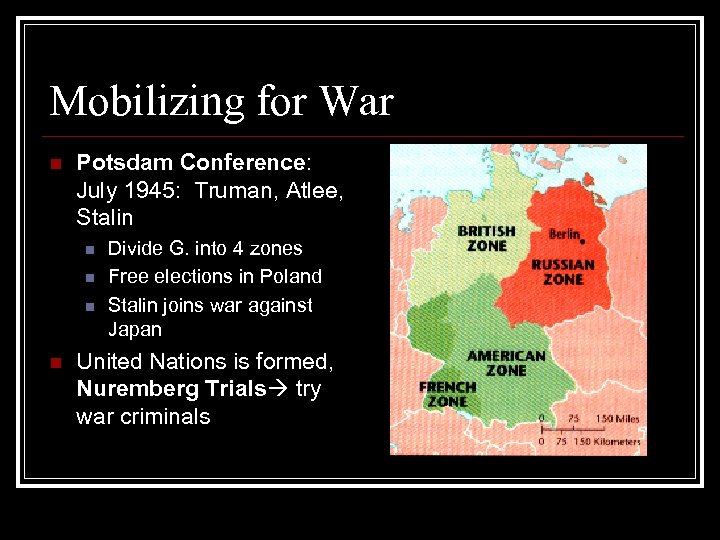 Mobilizing for War n Potsdam Conference: July 1945: Truman, Atlee, Stalin n n Divide G. into 4 zones Free elections in Poland Stalin joins war against Japan United Nations is formed, Nuremberg Trials try war criminals
Mobilizing for War n Potsdam Conference: July 1945: Truman, Atlee, Stalin n n Divide G. into 4 zones Free elections in Poland Stalin joins war against Japan United Nations is formed, Nuremberg Trials try war criminals
 Roots of the Cold War n Soviet Union vs. US (Communism vs. Democracy) n Stalin had made promises at Yalta and Potsdam to allow democratic, free elections in Poland, Bulgaria, etc n Stalin backed out of promises-created satellite states of these nations n Stalin disagrees w/ dem. , while Truman does not believe in commie n Democratic Western Europe vs. Communist East Europe n Churchill calls the division the “iron curtain” n Stand-off lasts 46 years, but never became a “hot” war militarily
Roots of the Cold War n Soviet Union vs. US (Communism vs. Democracy) n Stalin had made promises at Yalta and Potsdam to allow democratic, free elections in Poland, Bulgaria, etc n Stalin backed out of promises-created satellite states of these nations n Stalin disagrees w/ dem. , while Truman does not believe in commie n Democratic Western Europe vs. Communist East Europe n Churchill calls the division the “iron curtain” n Stand-off lasts 46 years, but never became a “hot” war militarily

 Roots of the Cold War The Cold War Begins n US starts aiding Greece and Turkey (SU influence there) n Truman Doctrine: stop aid nations struggling against communist movement n US policy is to “contain” Soviet communist expansion
Roots of the Cold War The Cold War Begins n US starts aiding Greece and Turkey (SU influence there) n Truman Doctrine: stop aid nations struggling against communist movement n US policy is to “contain” Soviet communist expansion
 Roots of the Cold War The Cold War Continues… n US provides support to any Western European nation that needed it- Marshall Plan n GB, Fr. US unify their zones in G. ; but Berlin is surrounded by SU zone n SU cuts off rail/road travel to West Berlin (Berlin Blockade)US starts Berlin Airlift n W. Europe and US join together against Communism- NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization n NATO members pledge military support to each other Warsaw Pact is SU rival organization
Roots of the Cold War The Cold War Continues… n US provides support to any Western European nation that needed it- Marshall Plan n GB, Fr. US unify their zones in G. ; but Berlin is surrounded by SU zone n SU cuts off rail/road travel to West Berlin (Berlin Blockade)US starts Berlin Airlift n W. Europe and US join together against Communism- NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization n NATO members pledge military support to each other Warsaw Pact is SU rival organization

 Roots of the Cold War The Cold War heats Up n Civil war in China Chiang Kai-Shek (nationalist leader) vs. Mao Zedong (communist) n Chiang gov’t corrupt and ineffective, Mao takes over China commie
Roots of the Cold War The Cold War heats Up n Civil war in China Chiang Kai-Shek (nationalist leader) vs. Mao Zedong (communist) n Chiang gov’t corrupt and ineffective, Mao takes over China commie
 Roots of the Cold War The Korean War n Korea divided NK- Commie vs. SK- Dem (38 th parallel) n 1950 - NK attacks SK- Soviet Union backs NK n NK troops seem unstoppable, Gen. Mac. Arthur launches counterattack n China feels threatened by US- China attacks US/UN forces n Mac. Arthur suggests attacking China- Truman says no n Truman fires Mac. Arthur for insubordination n Stalemate 1951 -1953 n 1953 - ceasefire at 38 th parallel; demilitarized zones b/t sides
Roots of the Cold War The Korean War n Korea divided NK- Commie vs. SK- Dem (38 th parallel) n 1950 - NK attacks SK- Soviet Union backs NK n NK troops seem unstoppable, Gen. Mac. Arthur launches counterattack n China feels threatened by US- China attacks US/UN forces n Mac. Arthur suggests attacking China- Truman says no n Truman fires Mac. Arthur for insubordination n Stalemate 1951 -1953 n 1953 - ceasefire at 38 th parallel; demilitarized zones b/t sides

 The Cold War Expands n 1949: SU detonates atomic bomb, China falls to commie shocks US n 1952: US tests first HBomb US/SU race to out build arms n Dwight D. Eisenhower elected in 1952 - favors strengthening nuke arms n John Foster Dulles- Sec. of State believes in brinkmanship: go to edge of war
The Cold War Expands n 1949: SU detonates atomic bomb, China falls to commie shocks US n 1952: US tests first HBomb US/SU race to out build arms n Dwight D. Eisenhower elected in 1952 - favors strengthening nuke arms n John Foster Dulles- Sec. of State believes in brinkmanship: go to edge of war
 The Cold War Expands n n n Stalin dies 1953 - Nikita Khrushchev takes over- believes Commie can work and happen peacefully Anti- commie rebellions in Czech. and Hungary rock surrounding nations US starts covert actions (CIA) to stop spread of Communism
The Cold War Expands n n n Stalin dies 1953 - Nikita Khrushchev takes over- believes Commie can work and happen peacefully Anti- commie rebellions in Czech. and Hungary rock surrounding nations US starts covert actions (CIA) to stop spread of Communism
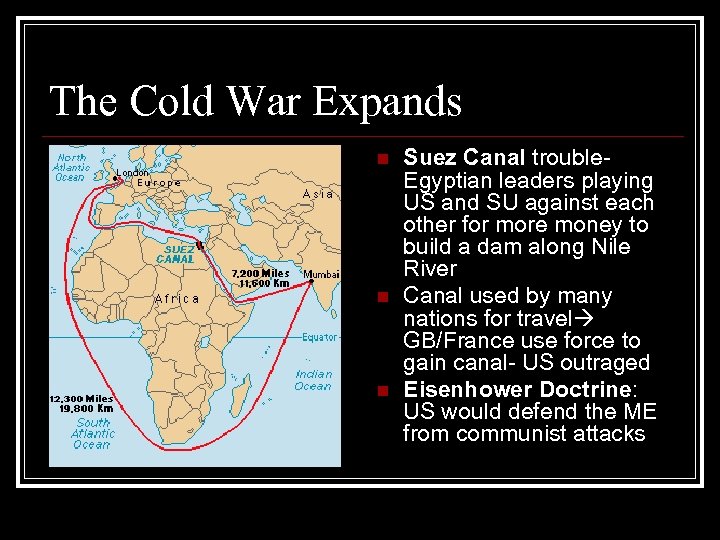 The Cold War Expands n n n Suez Canal trouble. Egyptian leaders playing US and SU against each other for more money to build a dam along Nile River Canal used by many nations for travel GB/France use force to gain canal- US outraged Eisenhower Doctrine: US would defend the ME from communist attacks
The Cold War Expands n n n Suez Canal trouble. Egyptian leaders playing US and SU against each other for more money to build a dam along Nile River Canal used by many nations for travel GB/France use force to gain canal- US outraged Eisenhower Doctrine: US would defend the ME from communist attacks
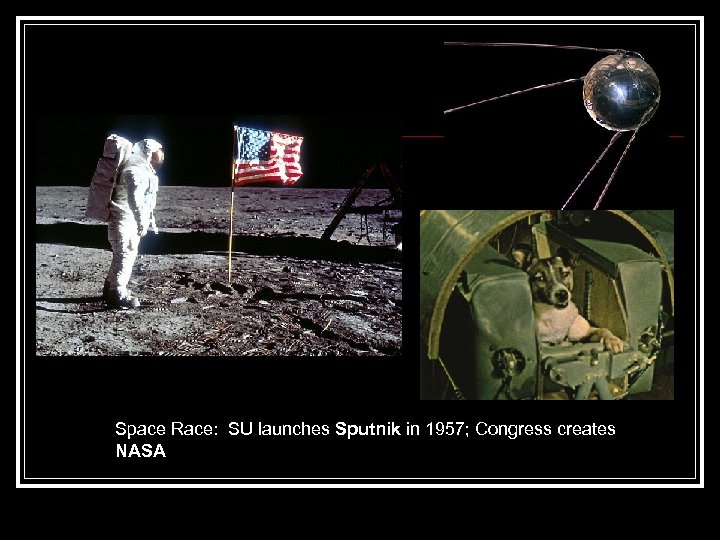 Space Race: SU launches Sputnik in 1957; Congress creates NASA
Space Race: SU launches Sputnik in 1957; Congress creates NASA
 The Cold War Expands The Cold War At Home n Cold War creates “us vs. them” attitude Red Scare re-emerges n Red Scare deeper than in 20 s gov’t creates Loyalty Review Bd: kick out gov’t workers who were “soft” on commies n House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC): investigated communist activities in and out of white house n Attack movie industry- Hollywood Ten: ten witnesses called to trial who plead the fifth
The Cold War Expands The Cold War At Home n Cold War creates “us vs. them” attitude Red Scare re-emerges n Red Scare deeper than in 20 s gov’t creates Loyalty Review Bd: kick out gov’t workers who were “soft” on commies n House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC): investigated communist activities in and out of white house n Attack movie industry- Hollywood Ten: ten witnesses called to trial who plead the fifth

 The Cold War Expands Spys in the US n Alger Hiss: spying for SU- never prosecuted, later found to be true n The Rosenbergs: helped leak A-Bomb secrets to SU sentenced to death
The Cold War Expands Spys in the US n Alger Hiss: spying for SU- never prosecuted, later found to be true n The Rosenbergs: helped leak A-Bomb secrets to SU sentenced to death
 The Cold War Expands Mc. Carthyism n Sen. Joe Mc. Carthy (Wisconsin) accused US state dept. of being infested with commies n Made constant threats to suspected communistsnever produced a single name n Made slanderous comments about US army downfall
The Cold War Expands Mc. Carthyism n Sen. Joe Mc. Carthy (Wisconsin) accused US state dept. of being infested with commies n Made constant threats to suspected communistsnever produced a single name n Made slanderous comments about US army downfall


