0e372801e21a56c72530aaf3c87866dc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 World War II
World War II
 54. America’s 1920’s Foreign Policy A. League of Nations – America never joined which made the organization weak and ineffective B. Washington Disarmament Conference several powerful nations agreed to limit the number of new battleships they produced and to retire older ones quicker C. Kellogg-Briand Pact- agreement proposed by the USA and France, agreed to by Germany, Great Britain , and Soviet Union, renounced the use of war and called for the peaceful settlement of disputes.
54. America’s 1920’s Foreign Policy A. League of Nations – America never joined which made the organization weak and ineffective B. Washington Disarmament Conference several powerful nations agreed to limit the number of new battleships they produced and to retire older ones quicker C. Kellogg-Briand Pact- agreement proposed by the USA and France, agreed to by Germany, Great Britain , and Soviet Union, renounced the use of war and called for the peaceful settlement of disputes.
 Totalitarianism Government that exerts total control over the nation and citizen's lives Two types 1. Fascism- emphasizes importance of the nation (or one ethnic group) and the supreme authority of a single leader over that of the individual 2. Communism- government owns all land property, one political party, and needs of the country take priority over the individual
Totalitarianism Government that exerts total control over the nation and citizen's lives Two types 1. Fascism- emphasizes importance of the nation (or one ethnic group) and the supreme authority of a single leader over that of the individual 2. Communism- government owns all land property, one political party, and needs of the country take priority over the individual
 56 A. Adolf Hitler Blamed Jews and Socialists for Germany’s defeat Formed the National Socialist German Workers Party (Nazi) Used the economic depression in Germany to gain power by promising a return to the pre-WWI glory days Saw Germans as a master race (Aryans)
56 A. Adolf Hitler Blamed Jews and Socialists for Germany’s defeat Formed the National Socialist German Workers Party (Nazi) Used the economic depression in Germany to gain power by promising a return to the pre-WWI glory days Saw Germans as a master race (Aryans)
 56 B. Benito Mussolini The father of fascism Became Prime Minster of Italy in 1922 Invaded Ethiopia in 1936
56 B. Benito Mussolini The father of fascism Became Prime Minster of Italy in 1922 Invaded Ethiopia in 1936
 56 C. Joseph Stalin Communist leader of the Soviet Union Sent more than 2 million opponents to Siberian labor camps Signed a nonaggression pact with Germany before the start of WWII
56 C. Joseph Stalin Communist leader of the Soviet Union Sent more than 2 million opponents to Siberian labor camps Signed a nonaggression pact with Germany before the start of WWII
 WWII Begins Germany annexed Austria and parts of Czechoslovakia in 1938 England France hoping to avoid war told Hitler he could do this if he promised not to cause any more trouble (appeasement) Germany, however, invaded Poland in 1939 starting WWII France and England came to the aide of Poland but it was too late
WWII Begins Germany annexed Austria and parts of Czechoslovakia in 1938 England France hoping to avoid war told Hitler he could do this if he promised not to cause any more trouble (appeasement) Germany, however, invaded Poland in 1939 starting WWII France and England came to the aide of Poland but it was too late
 Dark Days for Europe France falls to Germany in 1940 leaving England only country left to fight Italy and Germany in 1941 breaks its nonaggression pact and invades the Soviet Union Germany’s blitzkrieg (lighting war) made it to the suburbs of Moscow before Russian troops and the Russian winter stopped their advance
Dark Days for Europe France falls to Germany in 1940 leaving England only country left to fight Italy and Germany in 1941 breaks its nonaggression pact and invades the Soviet Union Germany’s blitzkrieg (lighting war) made it to the suburbs of Moscow before Russian troops and the Russian winter stopped their advance
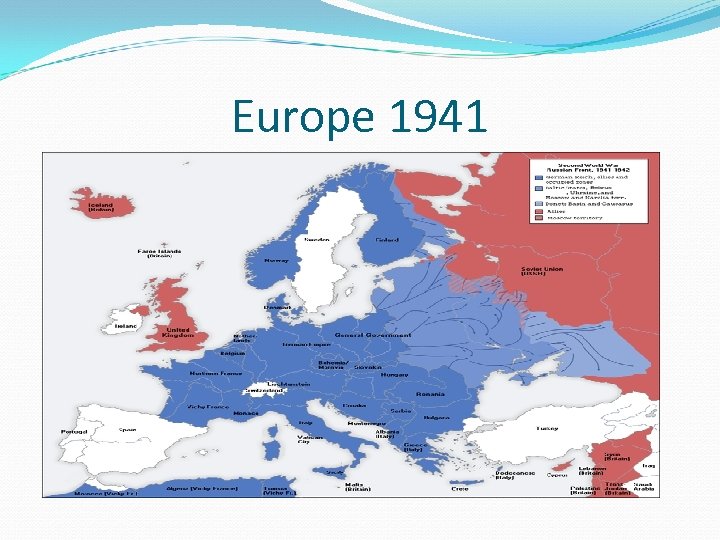 Europe 1941
Europe 1941
 55. America’s 1930’s Foreign Policy A. Hoover- Stimson Note- stated that the USA would not recognize territorial changes between nations brought about by the use of force (China/Japan) B. The Johnson Debt Default Act- prohibited future loans to nations that have defaulted on repayment of previous loans to the U. S C. The Neutrality Acts of 1935, 1937, and 1939 - put an embargo on arms sales to nations at war, forbade American ships from entering war zones
55. America’s 1930’s Foreign Policy A. Hoover- Stimson Note- stated that the USA would not recognize territorial changes between nations brought about by the use of force (China/Japan) B. The Johnson Debt Default Act- prohibited future loans to nations that have defaulted on repayment of previous loans to the U. S C. The Neutrality Acts of 1935, 1937, and 1939 - put an embargo on arms sales to nations at war, forbade American ships from entering war zones
 57. America and WWII A. The Quarantine Speech - given by FDR, called for an international "quarantine of the aggressor nations”, first attempt to alter American neutrality and nonintervention policies B. The Four Freedoms Speech- FDR speech about the four fundamental freedoms that people "everywhere in the world" ought to enjoy: 1. Freedom of speech 2. Freedom of worship 3. Freedom from want 4. Freedom from fear
57. America and WWII A. The Quarantine Speech - given by FDR, called for an international "quarantine of the aggressor nations”, first attempt to alter American neutrality and nonintervention policies B. The Four Freedoms Speech- FDR speech about the four fundamental freedoms that people "everywhere in the world" ought to enjoy: 1. Freedom of speech 2. Freedom of worship 3. Freedom from want 4. Freedom from fear
 57. America and WWII C. The Atlantic Charter- issued by the USA and Great Britain, defined goals for the post-war world: 1. self-determination and self-government 2. reduction of trade restrictions 3. the disarmament of aggressor nations D. Lend-Lease- program where the USA supplied the allies with food and war materials in return for leases to use army and naval bases in Allied territory
57. America and WWII C. The Atlantic Charter- issued by the USA and Great Britain, defined goals for the post-war world: 1. self-determination and self-government 2. reduction of trade restrictions 3. the disarmament of aggressor nations D. Lend-Lease- program where the USA supplied the allies with food and war materials in return for leases to use army and naval bases in Allied territory
 58. Pearl Harbor December 7, 1941 “ A day that will live in infamy” Japan launched a surprise attack on the US pacific fleet in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii United States declares war on Japan Germany declares war on the USA
58. Pearl Harbor December 7, 1941 “ A day that will live in infamy” Japan launched a surprise attack on the US pacific fleet in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii United States declares war on Japan Germany declares war on the USA
 59. The Allies vs. The Axis The Allies 1. USA (FDR) 2. Soviet Union (Joseph Stalin) 3. Great Britain (Winston Churchill) The Axis 1. Germany (Adolf Hitler) 2. Japan (Hideki Tojo) 3. Italy (Benito Mussolini)
59. The Allies vs. The Axis The Allies 1. USA (FDR) 2. Soviet Union (Joseph Stalin) 3. Great Britain (Winston Churchill) The Axis 1. Germany (Adolf Hitler) 2. Japan (Hideki Tojo) 3. Italy (Benito Mussolini)

 Rosie the Riveter
Rosie the Riveter
 66. The Home Front A. Rationing- helped conserve resources for war effort B. Bond Drives- programs that encouraged citizens to buy war bonds to help pay for the war effort C. Urbanization- people moved to cities to work in factories D. Bracero Program- Series of laws and diplomatic agreements between USA and Mexico to increase the number of Mexican contract laborers in the United States during WWII
66. The Home Front A. Rationing- helped conserve resources for war effort B. Bond Drives- programs that encouraged citizens to buy war bonds to help pay for the war effort C. Urbanization- people moved to cities to work in factories D. Bracero Program- Series of laws and diplomatic agreements between USA and Mexico to increase the number of Mexican contract laborers in the United States during WWII
 64. Women and WWII Went to work in defense factories AVCO- aviation factory in Nashville, TN that produced the Vultee A-31 Vengeance dive bomber and the P-38 Lightning fighters, 1/3 of employees during WWII were female Many women volunteered for the war effort (nurses and office jobs) Cornelia Fort - the first US pilot to encounter the Japanese air fleet during the Attack on Pearl Harbor while conducting a civilian training flight, joined Women Air Force Service Pilots, first female pilot in American history to die on active duty.
64. Women and WWII Went to work in defense factories AVCO- aviation factory in Nashville, TN that produced the Vultee A-31 Vengeance dive bomber and the P-38 Lightning fighters, 1/3 of employees during WWII were female Many women volunteered for the war effort (nurses and office jobs) Cornelia Fort - the first US pilot to encounter the Japanese air fleet during the Attack on Pearl Harbor while conducting a civilian training flight, joined Women Air Force Service Pilots, first female pilot in American history to die on active duty.
 65. Minorities and WWII A. Fair Employment Practices Committee- banned racial discrimination in any defense industry receiving federal contracts B. The service of African Americans in the armed forces and the work force- many worked in factories or served in segregated military units C. Integration of the armed forces- After WWII President Truman issued an executive order to fully integrate the US armed forces
65. Minorities and WWII A. Fair Employment Practices Committee- banned racial discrimination in any defense industry receiving federal contracts B. The service of African Americans in the armed forces and the work force- many worked in factories or served in segregated military units C. Integration of the armed forces- After WWII President Truman issued an executive order to fully integrate the US armed forces
 63. Japanese Internment American citizens of Japanese descent were placed in concentration camps out of fear that many were spies or traitors A. Fred Korematsu v. United States of America – supreme court case that found internment constitutional because the need to protect the nation against espionage outweighed Korematsu's individual rights, and the rights of Americans of Japanese descent.
63. Japanese Internment American citizens of Japanese descent were placed in concentration camps out of fear that many were spies or traitors A. Fred Korematsu v. United States of America – supreme court case that found internment constitutional because the need to protect the nation against espionage outweighed Korematsu's individual rights, and the rights of Americans of Japanese descent.
 Office of War Information Controlled the release of all information concerning the war effort Propaganda machine for the US war effort Job was to keep moral high, keep nation united, and encourage all citizens to do their part in the war effort 1. Newspapers 2. Radio 3. Movies 4. Cartoons 5. Comics
Office of War Information Controlled the release of all information concerning the war effort Propaganda machine for the US war effort Job was to keep moral high, keep nation united, and encourage all citizens to do their part in the war effort 1. Newspapers 2. Radio 3. Movies 4. Cartoons 5. Comics
 Assignment Pick one of the WWII propaganda cartoons and answer the following questions 1. What were symbols used in the cartoon and what did they represent 2. What historical figures and countries were represented in the cartoon? 3. What was the message of the cartoon? 4. Do you believe that the cartoon successfully promoted its message? Why or Why Not? (answer in a paragraph)
Assignment Pick one of the WWII propaganda cartoons and answer the following questions 1. What were symbols used in the cartoon and what did they represent 2. What historical figures and countries were represented in the cartoon? 3. What was the message of the cartoon? 4. Do you believe that the cartoon successfully promoted its message? Why or Why Not? (answer in a paragraph)
 Assignment Use page 304 of text to label the following on the WWII in Europe Map 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Countries United Kingdom Germany Soviet Union Italy France Poland 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Battles Stalingrad Kasserine Pass Sicily Anzio D-Day Battle of the Bulge
Assignment Use page 304 of text to label the following on the WWII in Europe Map 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Countries United Kingdom Germany Soviet Union Italy France Poland 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Battles Stalingrad Kasserine Pass Sicily Anzio D-Day Battle of the Bulge
 60. Key Battles in Europe F. North Africa- first area of Allied attack against Nazi Germany, not as well defended as other areas Invasion of Italy- attempt by Allies to cut off Italy from Nazi Germany became a stalemate G. D-day- Allied amphibious invasion of Normandy, France, beginning of the end for Hitler H. Battle of the Budge- Hitler's final desperate attempt to defeat the allies in Western Europe, caused a budge in the Allies’ lines but ultimately failed
60. Key Battles in Europe F. North Africa- first area of Allied attack against Nazi Germany, not as well defended as other areas Invasion of Italy- attempt by Allies to cut off Italy from Nazi Germany became a stalemate G. D-day- Allied amphibious invasion of Normandy, France, beginning of the end for Hitler H. Battle of the Budge- Hitler's final desperate attempt to defeat the allies in Western Europe, caused a budge in the Allies’ lines but ultimately failed
 Assignment Use page 298 of text to label the following on the WWII in Pacific Map 1. 2. 3. Countries Japan China Philippines Cities Tokyo Hiroshima Nagasaki 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Battles Coral Sea Midway Guadalcanal Saipan Iwo Jima Okinawa
Assignment Use page 298 of text to label the following on the WWII in Pacific Map 1. 2. 3. Countries Japan China Philippines Cities Tokyo Hiroshima Nagasaki 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Battles Coral Sea Midway Guadalcanal Saipan Iwo Jima Okinawa
 60 Key Battles of the Pacific A. Bataan Death March- forced 60 mile march of American POWs in the Philippines by the Japanese B. Midway- Battle over a island/airfield half way between Tokyo and Honolulu, first major victory by America over Japan, large part of Japanese Navy destroyed C. Island Hopping- Allied war strategy in Pacific to bypass heavily fortified Japanese positions and focus on strategically important islands that were not well defended but capable of supporting the drive to the main islands of Japan. D. Iwo Jima and Okinawa- Invasion of two small islands near Japan, Heavy US casualties as Japanese soldiers fought to the death, many civilians also committed suicide rather than surrendering to American Forces
60 Key Battles of the Pacific A. Bataan Death March- forced 60 mile march of American POWs in the Philippines by the Japanese B. Midway- Battle over a island/airfield half way between Tokyo and Honolulu, first major victory by America over Japan, large part of Japanese Navy destroyed C. Island Hopping- Allied war strategy in Pacific to bypass heavily fortified Japanese positions and focus on strategically important islands that were not well defended but capable of supporting the drive to the main islands of Japan. D. Iwo Jima and Okinawa- Invasion of two small islands near Japan, Heavy US casualties as Japanese soldiers fought to the death, many civilians also committed suicide rather than surrendering to American Forces
 61. Unique American Fighting Forces Tuskegee Airmen- the popular name of a group of African-American military pilots in World War II. Formally, they formed the 332 nd Fighter Group and the 477 th Bombardment Group 2. 442 nd Regimental Combat Team- fighting unit composed almost entirely of American soldiers of Japanese ancestry, fought mostly in Europe 3. 101 st Airborne- Army paratrooper unit, famous for its role in D-Day (Band of Brothers) 4. Navajo Code Talkers- bilingual Navajo speakers specially recruited during World War II by the Marines to serve in their standard communications units in the Pacific Theater. 1.
61. Unique American Fighting Forces Tuskegee Airmen- the popular name of a group of African-American military pilots in World War II. Formally, they formed the 332 nd Fighter Group and the 477 th Bombardment Group 2. 442 nd Regimental Combat Team- fighting unit composed almost entirely of American soldiers of Japanese ancestry, fought mostly in Europe 3. 101 st Airborne- Army paratrooper unit, famous for its role in D-Day (Band of Brothers) 4. Navajo Code Talkers- bilingual Navajo speakers specially recruited during World War II by the Marines to serve in their standard communications units in the Pacific Theater. 1.
 Use Chapters 11 & 12 to match the following individuals to their role in WWII 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Franklin Roosevelt Winston Churchill Joseph Stalin Harry Truman Adolph Hitler Benito Mussolini Hideki Togo Dwight Eisenhower George Marshall Douglas Mac. Arthur A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. President of USA at end of WWII United States Army Chief of Staff Prime minster of Japan Supreme commander of Allied forces in Europe Prime minster of Italy Prime minster of Great Britain President of USA at start of WWII Commander of U. S. Army Forces in the Far East Leader of the Soviet Union Chancellor of Germany
Use Chapters 11 & 12 to match the following individuals to their role in WWII 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Franklin Roosevelt Winston Churchill Joseph Stalin Harry Truman Adolph Hitler Benito Mussolini Hideki Togo Dwight Eisenhower George Marshall Douglas Mac. Arthur A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. President of USA at end of WWII United States Army Chief of Staff Prime minster of Japan Supreme commander of Allied forces in Europe Prime minster of Italy Prime minster of Great Britain President of USA at start of WWII Commander of U. S. Army Forces in the Far East Leader of the Soviet Union Chancellor of Germany
 Write down everything you know about the dropping of the atomic bomb at the end of WWII
Write down everything you know about the dropping of the atomic bomb at the end of WWII
 68 B. Manhattan Project Research and development of the atomic bomb Most of the research done in Oak Ridge, TN Oak Ridge chosen because of its isolated location (fear of espionage) Provided the uranium for “Little Boy”
68 B. Manhattan Project Research and development of the atomic bomb Most of the research done in Oak Ridge, TN Oak Ridge chosen because of its isolated location (fear of espionage) Provided the uranium for “Little Boy”
 69. The Atomic Bomb First weapon of mass destruction First bomb (Little Boy) dropped on Hiroshima Second bomb (Fat Man) dropped on Nagasaki Led to Japan’s unconditional surrender a few days later Supporters argue that it ended the war quickly and saved American lives Opponents argue that it was not necessary because Japan was already defeated
69. The Atomic Bomb First weapon of mass destruction First bomb (Little Boy) dropped on Hiroshima Second bomb (Fat Man) dropped on Nagasaki Led to Japan’s unconditional surrender a few days later Supporters argue that it ended the war quickly and saved American lives Opponents argue that it was not necessary because Japan was already defeated
 Assignment Answer the following question in a ½ page response Was America justified in using atomic weapons on the Japanese? What were the arguments for and against their use? Do you believe they should have been used? Why or Why Not?
Assignment Answer the following question in a ½ page response Was America justified in using atomic weapons on the Japanese? What were the arguments for and against their use? Do you believe they should have been used? Why or Why Not?
 68. Tennessee and WWII C. TVA- powered Oak Ridge D. Alcoa- Manufactured aluminum for Manhattan Project A. Fort Campbell, KY- near Clarksville TN, training facility for WWII soldiers, home of the 101 st Airborne today E. Camp Forest- Tullahoma TN, Army training camp for WWII, later a POW camp for German soldiers Chattanooga War Production Plants- Produced army ammunition (TNT) during WWII (site of current VW plant)
68. Tennessee and WWII C. TVA- powered Oak Ridge D. Alcoa- Manufactured aluminum for Manhattan Project A. Fort Campbell, KY- near Clarksville TN, training facility for WWII soldiers, home of the 101 st Airborne today E. Camp Forest- Tullahoma TN, Army training camp for WWII, later a POW camp for German soldiers Chattanooga War Production Plants- Produced army ammunition (TNT) during WWII (site of current VW plant)
 70. Holocaust Hitler’s “final solution” to the “Jewish problem” Millions of Jews and other minority groups were killed in gas chambers (elimination chambers) America heard reports of this before and during the war but doubted their creditability because it was to horrible to comprehend German officials' put on trial in Nuremberg, Germany by the allies for crimes against humanity (genocide)
70. Holocaust Hitler’s “final solution” to the “Jewish problem” Millions of Jews and other minority groups were killed in gas chambers (elimination chambers) America heard reports of this before and during the war but doubted their creditability because it was to horrible to comprehend German officials' put on trial in Nuremberg, Germany by the allies for crimes against humanity (genocide)
 71. Yalta and Potsdam Yalta Potsdam Allies agreed to the demand of unconditional surrender Agreed to dived Germany and Berlin among the Allies while it was demilitarized Soviet Union promised to allow free election in Eastern Europe Nazi war criminals would be punished Called for the unconditional surrender of Japan Soviet Union argued it need to keep a presence in Eastern Europe for its own protection
71. Yalta and Potsdam Yalta Potsdam Allies agreed to the demand of unconditional surrender Agreed to dived Germany and Berlin among the Allies while it was demilitarized Soviet Union promised to allow free election in Eastern Europe Nazi war criminals would be punished Called for the unconditional surrender of Japan Soviet Union argued it need to keep a presence in Eastern Europe for its own protection
 72. United Nations Cordell Hull- from TN, Secretary of State under FDR, Held position longer than anyone in history, “Father of the United Nations” United Nations- A replacement for the ineffective League of Nations, the organization was established after World War II in order to prevent another such conflict, USA, Soviet Union, France, UK, and China given veto power over the use of force
72. United Nations Cordell Hull- from TN, Secretary of State under FDR, Held position longer than anyone in history, “Father of the United Nations” United Nations- A replacement for the ineffective League of Nations, the organization was established after World War II in order to prevent another such conflict, USA, Soviet Union, France, UK, and China given veto power over the use of force


