aa53b5b93cd488b9a75dc1f5611b32a9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 76
 World War ii 1939 -1945 “I hate war as only a soldier who has lived it can, only as one who has seen its brutality, its futility, its stupidity. ” - General Dwight D. Eisenhower
World War ii 1939 -1945 “I hate war as only a soldier who has lived it can, only as one who has seen its brutality, its futility, its stupidity. ” - General Dwight D. Eisenhower
 Causes of WWII 1. The Treaty of Versailles “A peace built on quicksand”
Causes of WWII 1. The Treaty of Versailles “A peace built on quicksand”
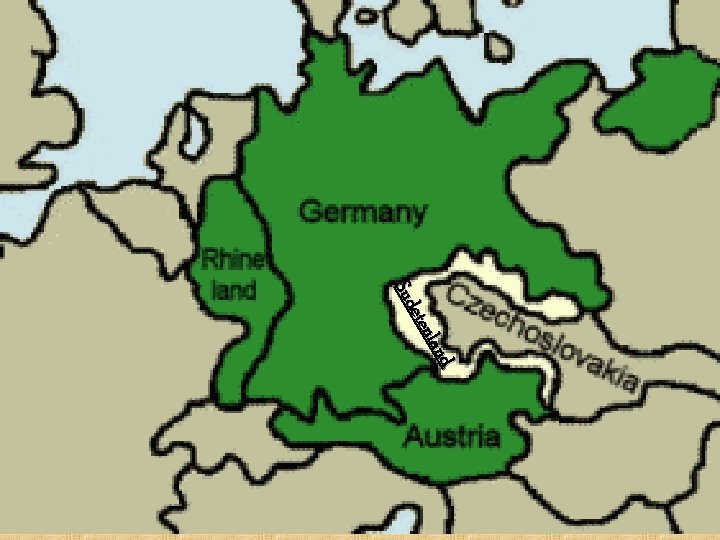
 Causes of WWII 2. Appeasement – Giving in to the demands of an aggressor in hopes of preserving peace Example: Munich Conference (1938) Western democracies agree that Germany could take control of Sudetenland from Czechoslovakia
Causes of WWII 2. Appeasement – Giving in to the demands of an aggressor in hopes of preserving peace Example: Munich Conference (1938) Western democracies agree that Germany could take control of Sudetenland from Czechoslovakia
 nd nd na nlla ete Sud
nd nd na nlla ete Sud
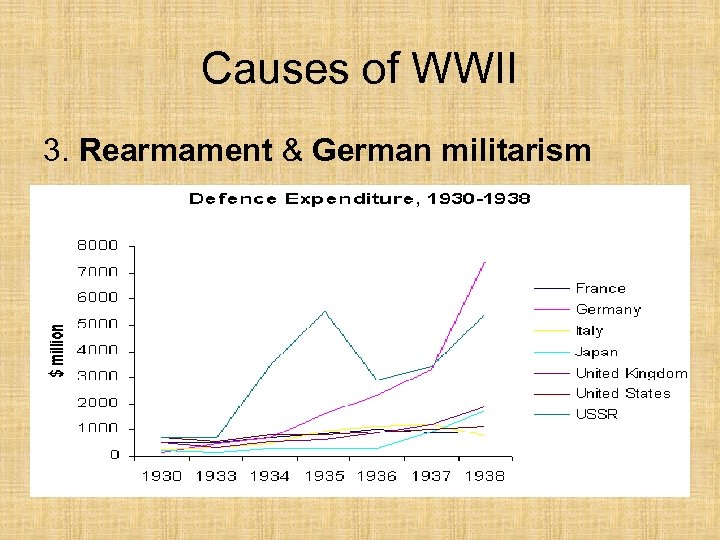 Causes of WWII 3. Rearmament & German militarism
Causes of WWII 3. Rearmament & German militarism
 Causes of WWII 4. Acts of aggression & imperialism germany, italy, & japan - adolf hitler, imperialistic germany “living space” (Lebensraum) - imperialistic japan need for natural resources desire to spread japanese influence - mussolini (n. africa)
Causes of WWII 4. Acts of aggression & imperialism germany, italy, & japan - adolf hitler, imperialistic germany “living space” (Lebensraum) - imperialistic japan need for natural resources desire to spread japanese influence - mussolini (n. africa)
 Causes of WWII 5. The ineffectiveness of the League of Nations - Never joined by U. S. - No standing army, no power to enforce - 4 permanent members: Great Britain, France, Italy, Japan - Lack of strong leadership
Causes of WWII 5. The ineffectiveness of the League of Nations - Never joined by U. S. - No standing army, no power to enforce - 4 permanent members: Great Britain, France, Italy, Japan - Lack of strong leadership

 New Alliances Rome-Berlin-Tokyo Axis “The Axis Powers” Italy, Germany & Japan United by Fascism - Agree to fight Soviet Communism - Agree to allow each other to expand
New Alliances Rome-Berlin-Tokyo Axis “The Axis Powers” Italy, Germany & Japan United by Fascism - Agree to fight Soviet Communism - Agree to allow each other to expand
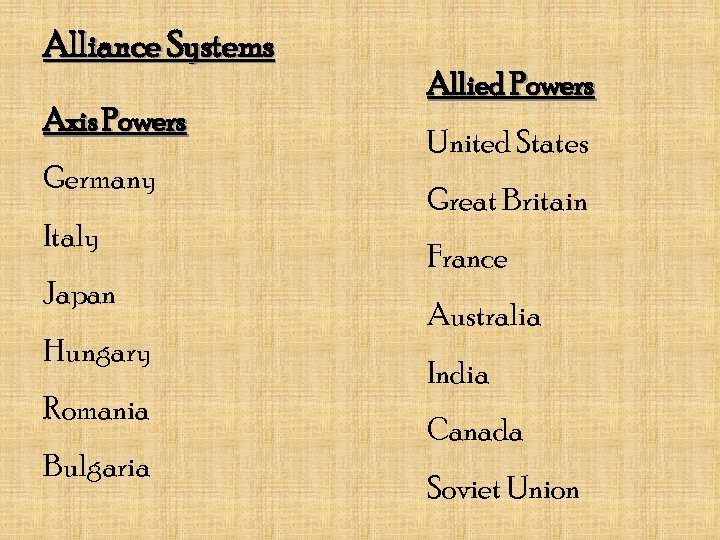 Alliance Systems Axis Powers Germany Italy Japan Hungary Romania Bulgaria Allied Powers United States Great Britain France Australia India Canada Soviet Union
Alliance Systems Axis Powers Germany Italy Japan Hungary Romania Bulgaria Allied Powers United States Great Britain France Australia India Canada Soviet Union
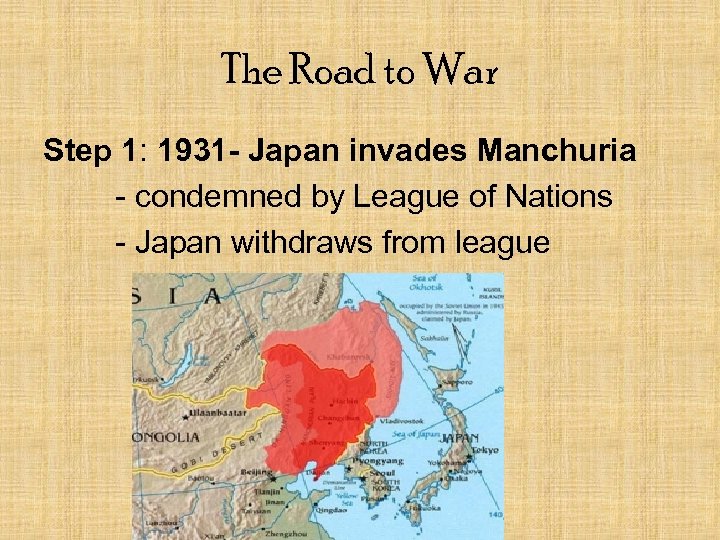 The Road to War Step 1: 1931 - Japan invades Manchuria - condemned by League of Nations - Japan withdraws from league
The Road to War Step 1: 1931 - Japan invades Manchuria - condemned by League of Nations - Japan withdraws from league
 Japan Invades Manchuria, 1931 First direct challenge of the League of Nations Japan wanted RAW MATERIALS
Japan Invades Manchuria, 1931 First direct challenge of the League of Nations Japan wanted RAW MATERIALS
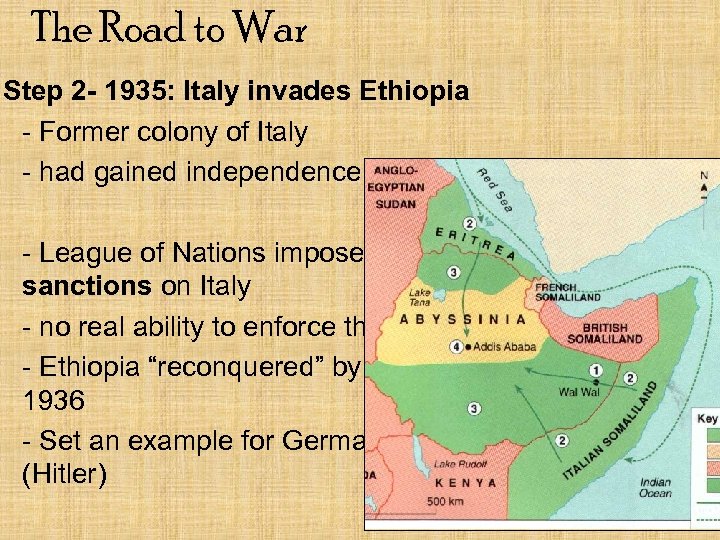 The Road to War Step 2 - 1935: Italy invades Ethiopia - Former colony of Italy - had gained independence in 1898 - League of Nations imposes sanctions on Italy - no real ability to enforce them - Ethiopia “reconquered” by Italy in 1936 - Set an example for Germany (Hitler)
The Road to War Step 2 - 1935: Italy invades Ethiopia - Former colony of Italy - had gained independence in 1898 - League of Nations imposes sanctions on Italy - no real ability to enforce them - Ethiopia “reconquered” by Italy in 1936 - Set an example for Germany (Hitler)
 The Spanish Civil War: 1936 - 1939 A Dress Rehearsal for WW II?
The Spanish Civil War: 1936 - 1939 A Dress Rehearsal for WW II?
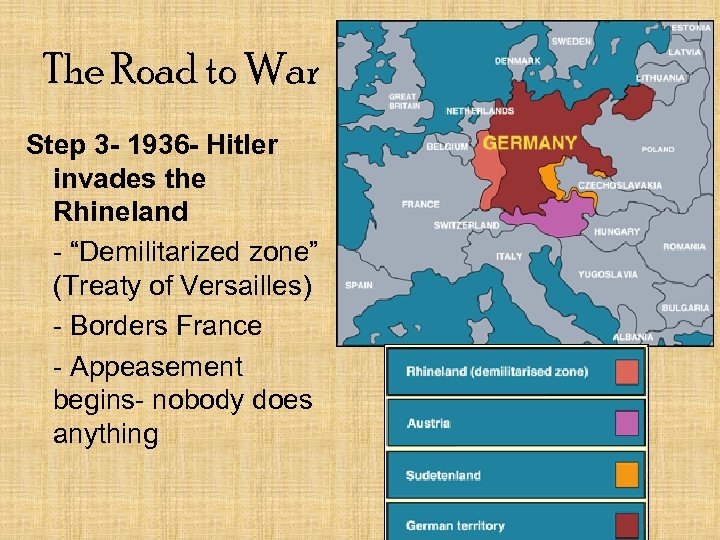 The Road to War Step 3 - 1936 - Hitler invades the Rhineland - “Demilitarized zone” (Treaty of Versailles) - Borders France - Appeasement begins- nobody does anything
The Road to War Step 3 - 1936 - Hitler invades the Rhineland - “Demilitarized zone” (Treaty of Versailles) - Borders France - Appeasement begins- nobody does anything
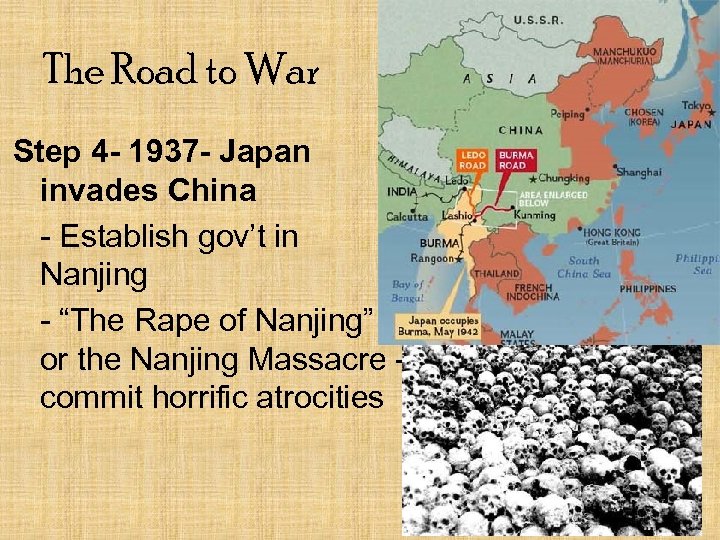 The Road to War Step 4 - 1937 - Japan invades China - Establish gov’t in Nanjing - “The Rape of Nanjing” or the Nanjing Massacre commit horrific atrocities
The Road to War Step 4 - 1937 - Japan invades China - Establish gov’t in Nanjing - “The Rape of Nanjing” or the Nanjing Massacre commit horrific atrocities
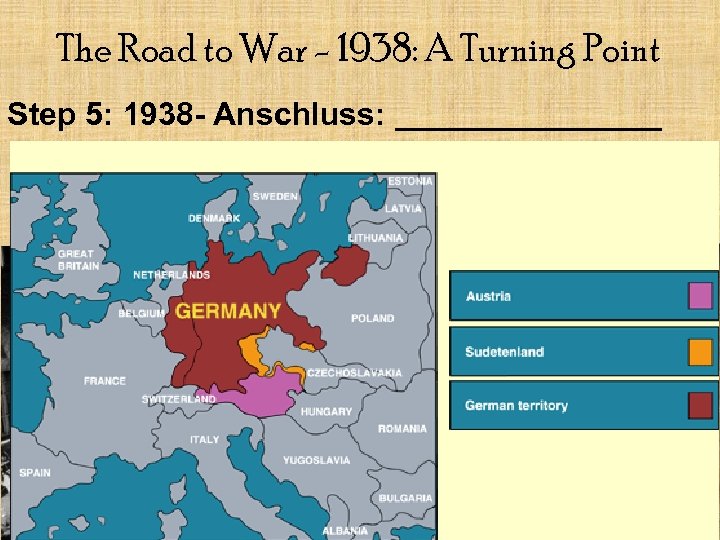 The Road to War - 1938: A Turning Point Step 5: 1938 - Anschluss: ________ Germany invades Austria becomes part of Germany
The Road to War - 1938: A Turning Point Step 5: 1938 - Anschluss: ________ Germany invades Austria becomes part of Germany
 The Evian Conference, 1938 International meeting to address the refugee crisis. Nearly no one accepted more immigrants above their quotas.
The Evian Conference, 1938 International meeting to address the refugee crisis. Nearly no one accepted more immigrants above their quotas.
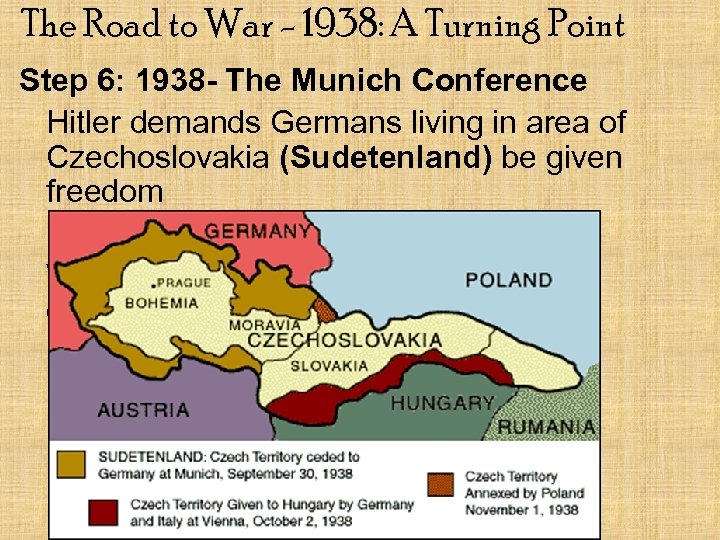 The Road to War - 1938: A Turning Point Step 6: 1938 - The Munich Conference Hitler demands Germans living in area of Czechoslovakia (Sudetenland) be given freedom Western democracies give into Hitler’s demands Appeasement
The Road to War - 1938: A Turning Point Step 6: 1938 - The Munich Conference Hitler demands Germans living in area of Czechoslovakia (Sudetenland) be given freedom Western democracies give into Hitler’s demands Appeasement
 the munich conference (1938) Neville Chamberlain, PM of Great Britain “We have preserved peace in our time. ” I promise, I won’t want any more land
the munich conference (1938) Neville Chamberlain, PM of Great Britain “We have preserved peace in our time. ” I promise, I won’t want any more land

 The Road to War Step 7: A surprising alliance Nazi-Soviet Nonaggression Pact Hitler and Stalin sign agreement not to go to war with one another. Agree to divide up Poland Hitler & Stalin– best “Frenemies”
The Road to War Step 7: A surprising alliance Nazi-Soviet Nonaggression Pact Hitler and Stalin sign agreement not to go to war with one another. Agree to divide up Poland Hitler & Stalin– best “Frenemies”

 The Road to War Step 8 - September 1, 1939: Germany invades Poland (spark of WWII) Great Britain and France have pledged to protect Poland Officially declare war on Germany September 3, 1939
The Road to War Step 8 - September 1, 1939: Germany invades Poland (spark of WWII) Great Britain and France have pledged to protect Poland Officially declare war on Germany September 3, 1939
 Invasion of Poland Start of WWII You. Tube - Little Hitler German strategy-blitzkrieg - massive bombing of cities, towns, factories, civilians - followed by fast-moving tanks and troops http: //www. 5 min. com/Video/The-Invasion-of-Poland-119993940 http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=k. Mt 2 -o 8 Mrbw
Invasion of Poland Start of WWII You. Tube - Little Hitler German strategy-blitzkrieg - massive bombing of cities, towns, factories, civilians - followed by fast-moving tanks and troops http: //www. 5 min. com/Video/The-Invasion-of-Poland-119993940 http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=k. Mt 2 -o 8 Mrbw
 Start of WWII
Start of WWII
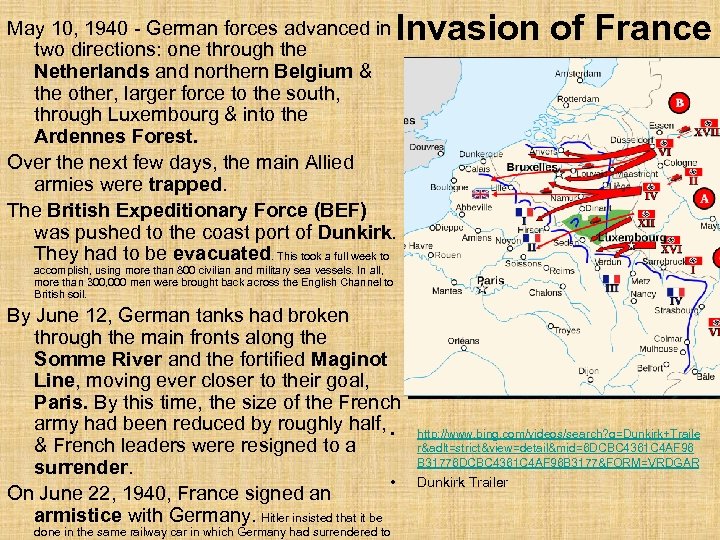 Invasion of France May 10, 1940 - German forces advanced in two directions: one through the Netherlands and northern Belgium & the other, larger force to the south, through Luxembourg & into the Ardennes Forest. Over the next few days, the main Allied armies were trapped. The British Expeditionary Force (BEF) was pushed to the coast port of Dunkirk. They had to be evacuated. This took a full week to accomplish, using more than 800 civilian and military sea vessels. In all, more than 300, 000 men were brought back across the English Channel to British soil. By June 12, German tanks had broken through the main fronts along the Somme River and the fortified Maginot Line, moving ever closer to their goal, Paris. By this time, the size of the French army had been reduced by roughly half, • & French leaders were resigned to a surrender. • On June 22, 1940, France signed an armistice with Germany. Hitler insisted that it be done in the same railway car in which Germany had surrendered to http: //www. bing. com/videos/search? q=Dunkirk+Traile r&adlt=strict&view=detail&mid=6 DCBC 4361 C 4 AF 96 B 31776 DCBC 4361 C 4 AF 96 B 3177&FORM=VRDGAR Dunkirk Trailer
Invasion of France May 10, 1940 - German forces advanced in two directions: one through the Netherlands and northern Belgium & the other, larger force to the south, through Luxembourg & into the Ardennes Forest. Over the next few days, the main Allied armies were trapped. The British Expeditionary Force (BEF) was pushed to the coast port of Dunkirk. They had to be evacuated. This took a full week to accomplish, using more than 800 civilian and military sea vessels. In all, more than 300, 000 men were brought back across the English Channel to British soil. By June 12, German tanks had broken through the main fronts along the Somme River and the fortified Maginot Line, moving ever closer to their goal, Paris. By this time, the size of the French army had been reduced by roughly half, • & French leaders were resigned to a surrender. • On June 22, 1940, France signed an armistice with Germany. Hitler insisted that it be done in the same railway car in which Germany had surrendered to http: //www. bing. com/videos/search? q=Dunkirk+Traile r&adlt=strict&view=detail&mid=6 DCBC 4361 C 4 AF 96 B 31776 DCBC 4361 C 4 AF 96 B 3177&FORM=VRDGAR Dunkirk Trailer
 Vichy France (1940 -1944) Northern France under direct German control until 1944 Establishes government in south Vichy, France which collaborates with Nazi Germany. On June 23, Hitler flew to Paris for a brief sightseeing tour of the occupied city, during which a widely published photo was taken of Hitler standing against the backdrop of the Eiffel Tower.
Vichy France (1940 -1944) Northern France under direct German control until 1944 Establishes government in south Vichy, France which collaborates with Nazi Germany. On June 23, Hitler flew to Paris for a brief sightseeing tour of the occupied city, during which a widely published photo was taken of Hitler standing against the backdrop of the Eiffel Tower.
 Hitler visiting Napoleon’s tomb
Hitler visiting Napoleon’s tomb
 major turning points of WWii The Battle of Britain • The London Blitz • Began September 1940 • Daily bombardment of London by German Luftwaffe (air force) • Lasted 57 nights • 15, 000 people died • City of London destroyed, BUT, unsuccessful in destroying Britain's morale
major turning points of WWii The Battle of Britain • The London Blitz • Began September 1940 • Daily bombardment of London by German Luftwaffe (air force) • Lasted 57 nights • 15, 000 people died • City of London destroyed, BUT, unsuccessful in destroying Britain's morale
 The London tube (subway) became air raid shelter during blitz
The London tube (subway) became air raid shelter during blitz
 British Prime Minister Winston Churchill • Raised people’s morale through speeches • Largest and longest air strike in history • Allied victory- major turning point Slogan based on Britain’s concerned about a German land invasion
British Prime Minister Winston Churchill • Raised people’s morale through speeches • Largest and longest air strike in history • Allied victory- major turning point Slogan based on Britain’s concerned about a German land invasion
 • Operation Barbarossa: Barbarossa Invasion of Soviet Union (June 1941) • Hitler’s Biggest Mistake • Violated Nazi-Soviet Pact • Successful until Russian winter began
• Operation Barbarossa: Barbarossa Invasion of Soviet Union (June 1941) • Hitler’s Biggest Mistake • Violated Nazi-Soviet Pact • Successful until Russian winter began
 The Battle of Stalingrad (1942 -43) • Huge defeat for Hitler • 300, 000 German troops killed or wounded • Stopped the German advance and marked the turning of the tide of war in favor of the Allies.
The Battle of Stalingrad (1942 -43) • Huge defeat for Hitler • 300, 000 German troops killed or wounded • Stopped the German advance and marked the turning of the tide of war in favor of the Allies.
 Turning points cont’d US Entry
Turning points cont’d US Entry
 The Atlantic Charter • Signed by FDR and Churchill in Aug. 1941 • Pledged to help each other support democracy and “end Nazi tyranny”
The Atlantic Charter • Signed by FDR and Churchill in Aug. 1941 • Pledged to help each other support democracy and “end Nazi tyranny”
 December 7, 1941 “A Date That Will Live In Infamy” Japanese bombed Pearl Harbor • Why? ? – Japan trying to conquer China – Japan began advancing into European-held colonies in SE Asia to gain raw materials – US banned sale of war materials to Japan – Japanese angry (felt this was an act of war) – Plus the US had a navy that could attack Japan and stop its expansion in the Pacific.
December 7, 1941 “A Date That Will Live In Infamy” Japanese bombed Pearl Harbor • Why? ? – Japan trying to conquer China – Japan began advancing into European-held colonies in SE Asia to gain raw materials – US banned sale of war materials to Japan – Japanese angry (felt this was an act of war) – Plus the US had a navy that could attack Japan and stop its expansion in the Pacific.
 “A Date That Will Live In Infamy” • Hideki Tojo planned surprise attack on American fleet stationed in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. • 2, 400 people killed • Ships and airplanes destroyed- USS Arizona • December 8, 1941 - US declares war on Japan • December 11, 1941 – Germany & Italy declare war on US (allies of Japan) Pearl Harbor Attack Scene
“A Date That Will Live In Infamy” • Hideki Tojo planned surprise attack on American fleet stationed in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. • 2, 400 people killed • Ships and airplanes destroyed- USS Arizona • December 8, 1941 - US declares war on Japan • December 11, 1941 – Germany & Italy declare war on US (allies of Japan) Pearl Harbor Attack Scene
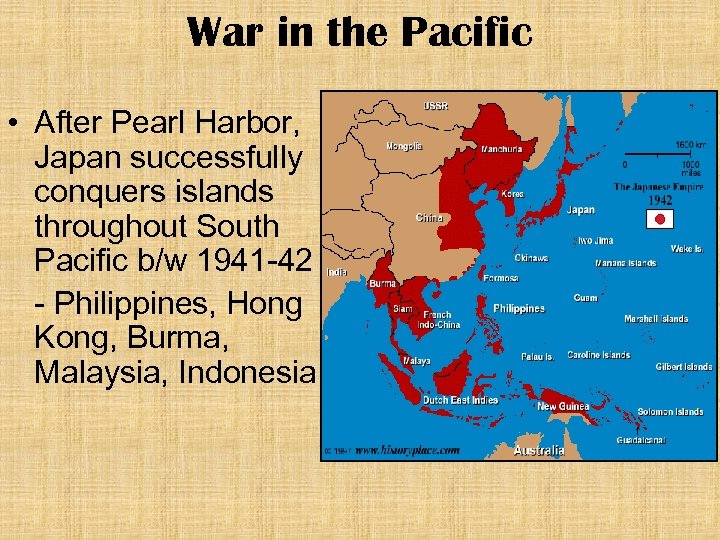 War in the Pacific • After Pearl Harbor, Japan successfully conquers islands throughout South Pacific b/w 1941 -42 - Philippines, Hong Kong, Burma, Malaysia, Indonesia
War in the Pacific • After Pearl Harbor, Japan successfully conquers islands throughout South Pacific b/w 1941 -42 - Philippines, Hong Kong, Burma, Malaysia, Indonesia
 War in the Pacific: Island Hopping: Allied strategy for taking back Japanese held territory. Battle of Midway, June 1942 - Turning Point in the Pacific – Allies win battle, start winning war in Pacific General Douglas Mac. Arthur
War in the Pacific: Island Hopping: Allied strategy for taking back Japanese held territory. Battle of Midway, June 1942 - Turning Point in the Pacific – Allies win battle, start winning war in Pacific General Douglas Mac. Arthur
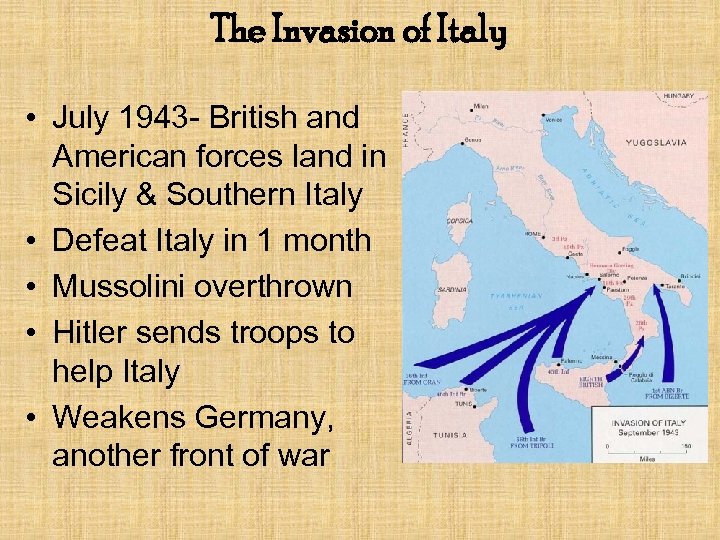 The Invasion of Italy • July 1943 - British and American forces land in Sicily & Southern Italy • Defeat Italy in 1 month • Mussolini overthrown • Hitler sends troops to help Italy • Weakens Germany, another front of war
The Invasion of Italy • July 1943 - British and American forces land in Sicily & Southern Italy • Defeat Italy in 1 month • Mussolini overthrown • Hitler sends troops to help Italy • Weakens Germany, another front of war
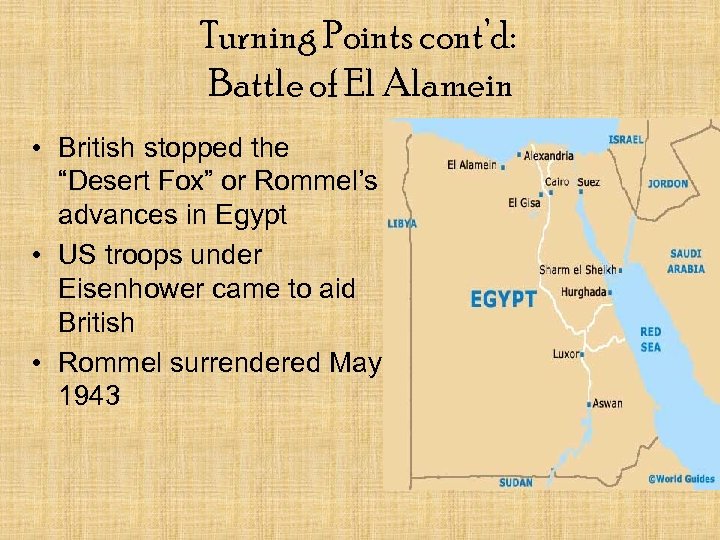 Turning Points cont’d: Battle of El Alamein • British stopped the “Desert Fox” or Rommel’s advances in Egypt • US troops under Eisenhower came to aid British • Rommel surrendered May 1943
Turning Points cont’d: Battle of El Alamein • British stopped the “Desert Fox” or Rommel’s advances in Egypt • US troops under Eisenhower came to aid British • Rommel surrendered May 1943
 Turning Points cont’d: “D-Day” June 6, 1944 Allied invasion of Normandy, France Allied troops crossed English Channel Greatest single Allied attack in history of war
Turning Points cont’d: “D-Day” June 6, 1944 Allied invasion of Normandy, France Allied troops crossed English Channel Greatest single Allied attack in history of war
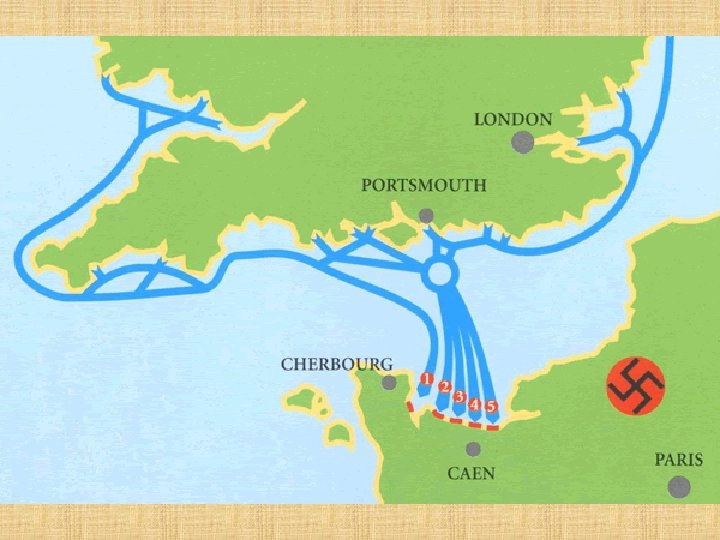
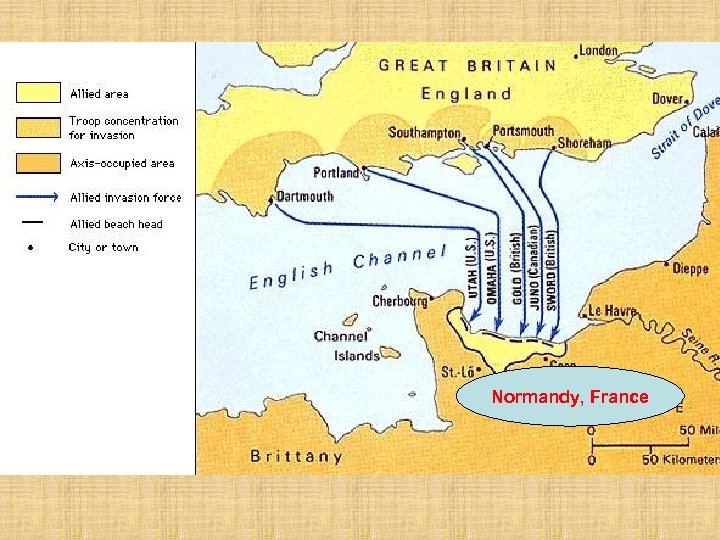 Normandy, France
Normandy, France
 http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=kx 7 d. Fp 0 Wh. N 4
http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=kx 7 d. Fp 0 Wh. N 4
 The Liberation of Paris • August 25, 1944 • Allied troops free France from German control
The Liberation of Paris • August 25, 1944 • Allied troops free France from German control
 The Allies Advance • Allies advance on Germany • Battle of the Bulge- one month battle b/w Allies & Germany • Soviet troops advanced on Germany from east (surrounded)
The Allies Advance • Allies advance on Germany • Battle of the Bulge- one month battle b/w Allies & Germany • Soviet troops advanced on Germany from east (surrounded)
 The Death of the Axis Powers • Mussolini executed by guerillas in Italy • Body dragged through streets and strung up
The Death of the Axis Powers • Mussolini executed by guerillas in Italy • Body dragged through streets and strung up
 “V-E Day” Victory in Europe Day May 8, 1945
“V-E Day” Victory in Europe Day May 8, 1945
 The Yalta Conference • Stalin, Churchill, Roosevelt“The Big Three” • Unconditional surrender by Germany • $20 billion in reparations • Germany divided and will be run by allied powers • Established United Nations • Establish right to self-determination
The Yalta Conference • Stalin, Churchill, Roosevelt“The Big Three” • Unconditional surrender by Germany • $20 billion in reparations • Germany divided and will be run by allied powers • Established United Nations • Establish right to self-determination
 War in the Pacific • Allied invasion of Japan? • Some American officials estimated 1 million casualties if allies invaded • Japanese fight to the death, don’t surrender (tradition) • Kamikaze pilots- suicide pilots
War in the Pacific • Allied invasion of Japan? • Some American officials estimated 1 million casualties if allies invaded • Japanese fight to the death, don’t surrender (tradition) • Kamikaze pilots- suicide pilots
 World’s 1 st use of Atomic Weapons • President Harry Truman makes decision to use 2 atomic bombs against Japan to end war • Hiroshima bombed August 6 th 1945 • Nagasaki bombed August 9 th, 1945 • Potsdam Declaration- Warning issued to Japan – “Surrender or face utter and complete destruction” – http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=NF 4 LQa. WJRDg https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=j. Y 9 Vw. CE_Dsg#t=794. 3515277
World’s 1 st use of Atomic Weapons • President Harry Truman makes decision to use 2 atomic bombs against Japan to end war • Hiroshima bombed August 6 th 1945 • Nagasaki bombed August 9 th, 1945 • Potsdam Declaration- Warning issued to Japan – “Surrender or face utter and complete destruction” – http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=NF 4 LQa. WJRDg https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=j. Y 9 Vw. CE_Dsg#t=794. 3515277
 Hiroshima On August 6, 1945 as the Enola Gay approached the Japanese city of Hiroshima, I fervently hoped for success in the first use of a nuclear weapon. To me it meant putting an end to World War II. I viewed my mission as one to save lives. • August 6, 1945 - bomb dropped on Hiroshima - Paul W. Tibbets, pilot of the Enola Gay
Hiroshima On August 6, 1945 as the Enola Gay approached the Japanese city of Hiroshima, I fervently hoped for success in the first use of a nuclear weapon. To me it meant putting an end to World War II. I viewed my mission as one to save lives. • August 6, 1945 - bomb dropped on Hiroshima - Paul W. Tibbets, pilot of the Enola Gay
 Effects • • 70, 000 people killed instantly Many die later from radiation Flattened 4 square miles Still no surrender
Effects • • 70, 000 people killed instantly Many die later from radiation Flattened 4 square miles Still no surrender
 Nagasaki August 9. 1945 40, 000 people killed August 14, 1945 - Japan surrenders
Nagasaki August 9. 1945 40, 000 people killed August 14, 1945 - Japan surrenders
 V-J Day “Victory in Japan day” August 14, 1945 September 2, 1945 formally sign surrender documents
V-J Day “Victory in Japan day” August 14, 1945 September 2, 1945 formally sign surrender documents
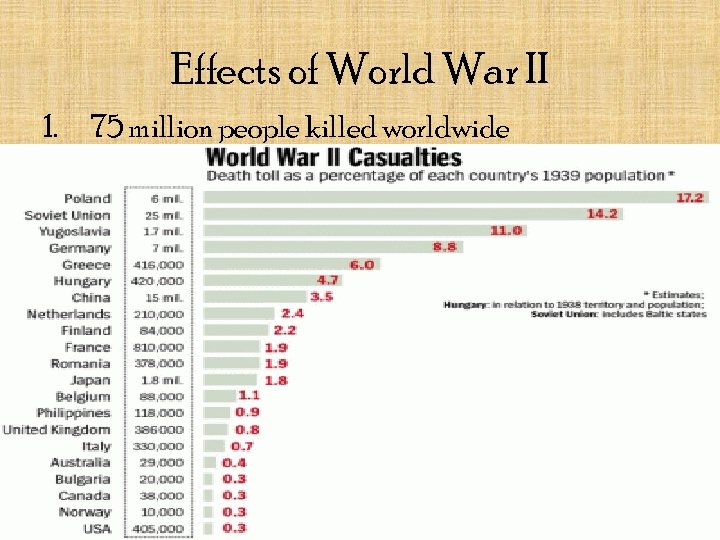 Effects of World War II 1. 75 million people killed worldwide
Effects of World War II 1. 75 million people killed worldwide
 Effects of World War II 2. The Holocaust
Effects of World War II 2. The Holocaust
 Effects of World War II 3. The Nuremburg Trials (1945 -1949) Nazi officials tried for crimes against humanity & convicted 22 sentenced to death by hanging 1 suicide (Goering- night before hanging) “I was just following orders. ”- The Nazi defense: fails Sets a precedent & guidelines for international law
Effects of World War II 3. The Nuremburg Trials (1945 -1949) Nazi officials tried for crimes against humanity & convicted 22 sentenced to death by hanging 1 suicide (Goering- night before hanging) “I was just following orders. ”- The Nazi defense: fails Sets a precedent & guidelines for international law
 “Never do anything against conscience even if the state demands it. ” - Albert Einstein
“Never do anything against conscience even if the state demands it. ” - Albert Einstein
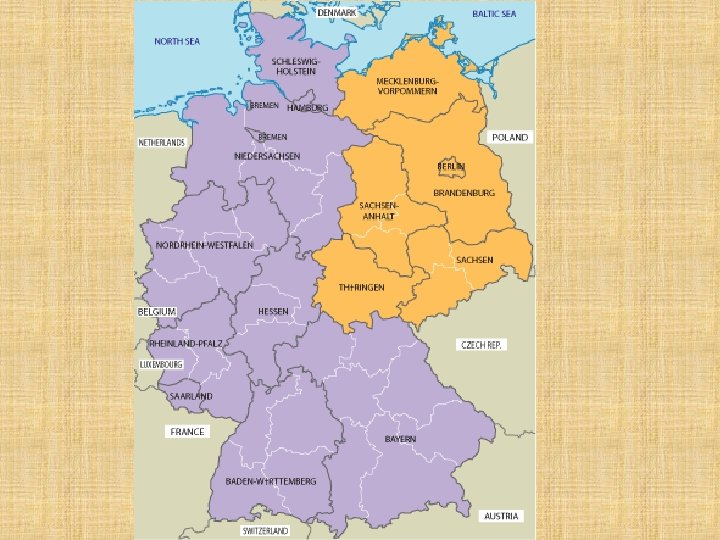
 Effects of World War II 4. Germany divided Separated into 4 allied occupied zones - Britian - France - US - Soviet Union
Effects of World War II 4. Germany divided Separated into 4 allied occupied zones - Britian - France - US - Soviet Union
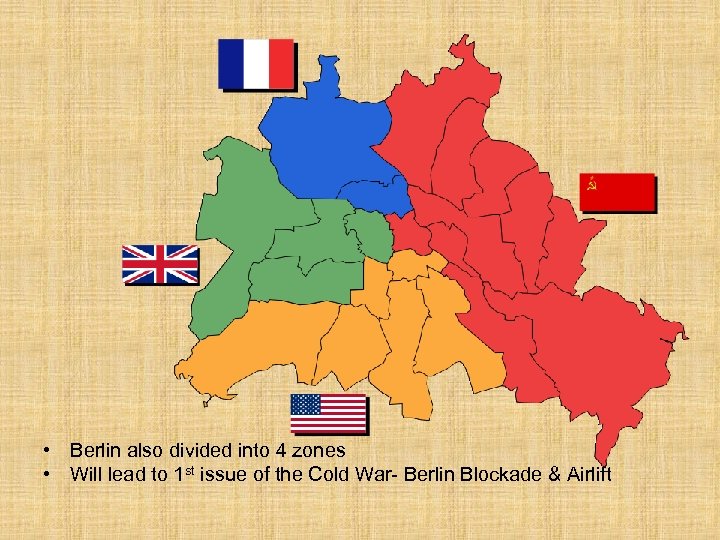 • Berlin also divided into 4 zones • Will lead to 1 st issue of the Cold War- Berlin Blockade & Airlift
• Berlin also divided into 4 zones • Will lead to 1 st issue of the Cold War- Berlin Blockade & Airlift
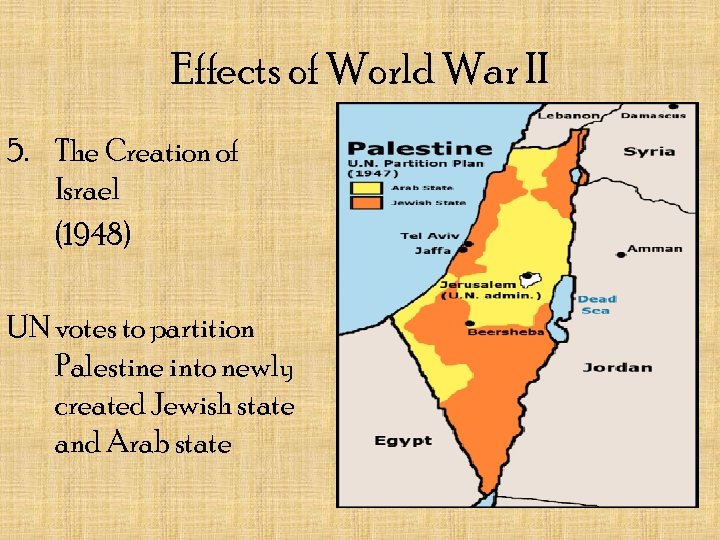 Effects of World War II 5. The Creation of Israel (1948) UN votes to partition Palestine into newly created Jewish state and Arab state
Effects of World War II 5. The Creation of Israel (1948) UN votes to partition Palestine into newly created Jewish state and Arab state
 Effects of World War II 6. Establishment of the United Nations (1945) -Replaced the League of Nations • International Peacekeeping organization • To deal with matters of international security • Standing Army • Currently 192 Member Nations
Effects of World War II 6. Establishment of the United Nations (1945) -Replaced the League of Nations • International Peacekeeping organization • To deal with matters of international security • Standing Army • Currently 192 Member Nations
 The United Nations 1. 2. 3. 4. International Peace Keeping organization United States & Russia are a part of this organization Created the Declaration of Human Rights Much stronger than the League of Nations, but still restricted.
The United Nations 1. 2. 3. 4. International Peace Keeping organization United States & Russia are a part of this organization Created the Declaration of Human Rights Much stronger than the League of Nations, but still restricted.

 Universal Declaration of Human Rights • Adopted in 1948 by UN • Guarantees rights that all people are entitled to, regardless of nationality, race, gender, ethnicity – Life, freedom, right to practice religion, work – Governments that deprive citizens of these rights are committing “Human Rights Violations”
Universal Declaration of Human Rights • Adopted in 1948 by UN • Guarantees rights that all people are entitled to, regardless of nationality, race, gender, ethnicity – Life, freedom, right to practice religion, work – Governments that deprive citizens of these rights are committing “Human Rights Violations”
 Effects of World War II 7. The Collapse of Colonial Empires • Colonies in Africa & Asia began to gain independence • India (1947) • Colonies in Africa (1950 s &60 s)
Effects of World War II 7. The Collapse of Colonial Empires • Colonies in Africa & Asia began to gain independence • India (1947) • Colonies in Africa (1950 s &60 s)
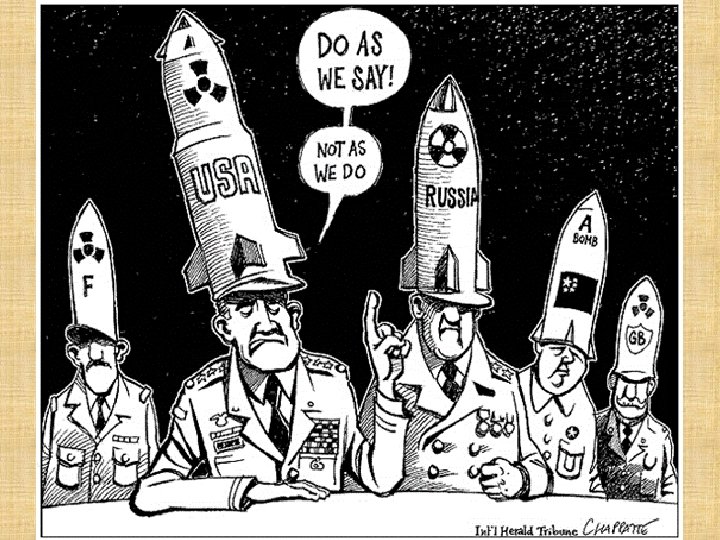
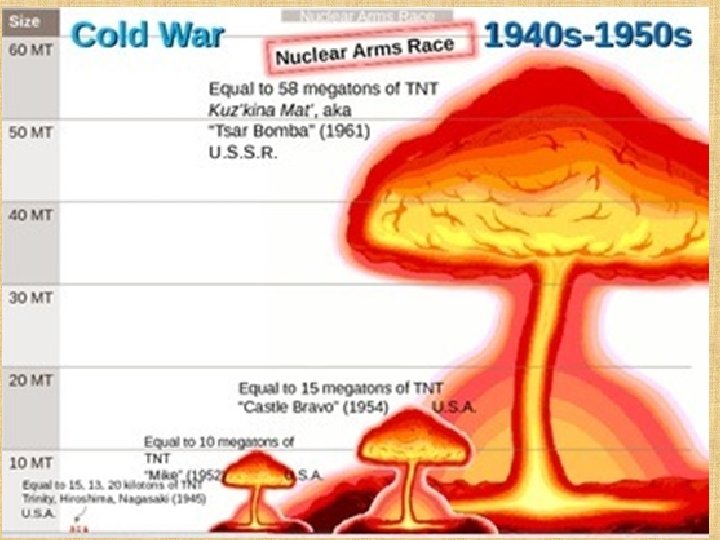
 Effects of World War II 8. The beginning of the Nuclear Age Use of atomic bomb scares the Soviet Union Beginning of arms race “I know not with what weapons World War III will be fought, but World War IV will be fought with sticks and stones. ” - Albert Einstein
Effects of World War II 8. The beginning of the Nuclear Age Use of atomic bomb scares the Soviet Union Beginning of arms race “I know not with what weapons World War III will be fought, but World War IV will be fought with sticks and stones. ” - Albert Einstein
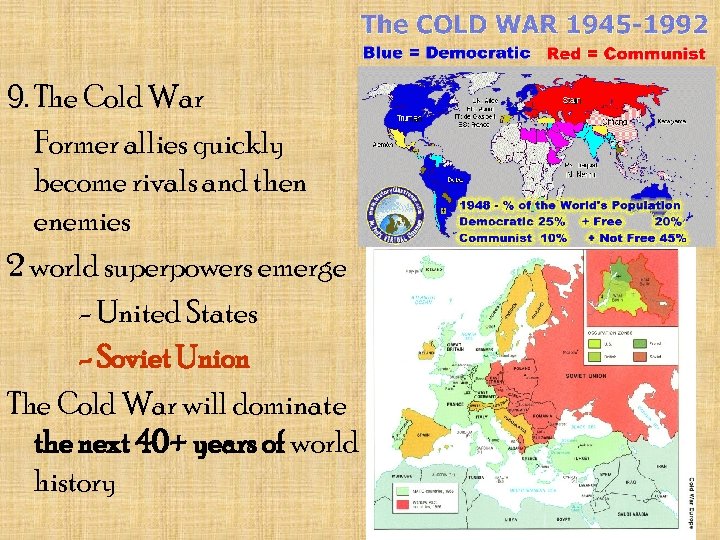 9. The Cold War Former allies quickly become rivals and then enemies 2 world superpowers emerge - United States - Soviet Union The Cold War will dominate the next 40+ years of world history
9. The Cold War Former allies quickly become rivals and then enemies 2 world superpowers emerge - United States - Soviet Union The Cold War will dominate the next 40+ years of world history