22729748c62ae9de13ae41176fa4af02.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 122
 WORLD WAR II 1939 -1945
WORLD WAR II 1939 -1945
 Axis Powers and Leaders
Axis Powers and Leaders
 Germany • Adolph Hitler • Leader of Nazi political party • Blamed Jews for all of Germany’s economic problems
Germany • Adolph Hitler • Leader of Nazi political party • Blamed Jews for all of Germany’s economic problems
 Italy • Benito Mussolini • Promised a new Roman Empire
Italy • Benito Mussolini • Promised a new Roman Empire
 Japan • Emperor Hirohito • Wanted full political and economic control of Pacific • Believed in militarism and military run society
Japan • Emperor Hirohito • Wanted full political and economic control of Pacific • Believed in militarism and military run society
 Japan • Prime Minister Hideki Tojo –Responsible for all military operations during the war
Japan • Prime Minister Hideki Tojo –Responsible for all military operations during the war
 Allied Leaders
Allied Leaders
 Great Britain • Winston Churchill • Great orator and leader who kept British citizens from giving up
Great Britain • Winston Churchill • Great orator and leader who kept British citizens from giving up
 France • Charles De Gaulle • Led opposition against Germany after they took over France
France • Charles De Gaulle • Led opposition against Germany after they took over France
 Soviet Union (Russia) • Joseph Stalin • Great Purge – killed all people who opposed his rule or spoke against Soviet Union
Soviet Union (Russia) • Joseph Stalin • Great Purge – killed all people who opposed his rule or spoke against Soviet Union
 Soviet Union (Russia) • Did not join allies until Hitler double crossed him
Soviet Union (Russia) • Did not join allies until Hitler double crossed him
 CAUSES OF WWII
CAUSES OF WWII
 Axis Aggression • Axis Powers wanted to gain economic and political control of the World • Japan invaded Manchuria and China to force US to recognize their dominance
Axis Aggression • Axis Powers wanted to gain economic and political control of the World • Japan invaded Manchuria and China to force US to recognize their dominance
 Axis Aggression • US refused to recognize Japan and placed embargos of oil and steel • Germany wanted to gain all lands lost after the WWI in the treaty of Versailles
Axis Aggression • US refused to recognize Japan and placed embargos of oil and steel • Germany wanted to gain all lands lost after the WWI in the treaty of Versailles
 Axis Aggression • Italy invaded Ethiopia in 1935 to show its dominance
Axis Aggression • Italy invaded Ethiopia in 1935 to show its dominance
 Appeasement • Policy of giving into political pressure to avoid war • Allowed Germany to recapture some lands & rebuild their military
Appeasement • Policy of giving into political pressure to avoid war • Allowed Germany to recapture some lands & rebuild their military
 War Breaks out in Europe
War Breaks out in Europe
 Munich Pact • Hitler and Stalin sign a nonaggression pact agreeing not to attack each other
Munich Pact • Hitler and Stalin sign a nonaggression pact agreeing not to attack each other
 September 1, 1939 • Germany and Soviet Union invade Poland after being warned not to invade by France and Great Britain • Official start of World War II
September 1, 1939 • Germany and Soviet Union invade Poland after being warned not to invade by France and Great Britain • Official start of World War II
 US Isolationism • US did not want to be involved in another European War • US was still going through the Great Depression
US Isolationism • US did not want to be involved in another European War • US was still going through the Great Depression
 Lend-Lease Act • US gave military supplies to Great Britain in exchange for islands in the Caribbean • FDR compared it to “lending a garden hose to a next-door neighbor whose house is on fire”.
Lend-Lease Act • US gave military supplies to Great Britain in exchange for islands in the Caribbean • FDR compared it to “lending a garden hose to a next-door neighbor whose house is on fire”.
 Lend-Lease Act • US used the war to end the Great Depression
Lend-Lease Act • US used the war to end the Great Depression
 World War II Battles and Strategies
World War II Battles and Strategies
 Axis War Strategy
Axis War Strategy
 Strategies - Europe • Blitzkrieg – fast, lightning attacks on your enemy before they can recover • Invade and conquer France • Use German Air Force to bomb Great Britain until they surrender
Strategies - Europe • Blitzkrieg – fast, lightning attacks on your enemy before they can recover • Invade and conquer France • Use German Air Force to bomb Great Britain until they surrender
 Strategies - Europe • Destroy Munich Pact and quickly defeat Soviet Union • Take complete control of Europe before US got involved in the war
Strategies - Europe • Destroy Munich Pact and quickly defeat Soviet Union • Take complete control of Europe before US got involved in the war
 Strategies - Pacific • Japan wanted full military and economic control of Pacific • Felt US needed to recognize their power in Pacific
Strategies - Pacific • Japan wanted full military and economic control of Pacific • Felt US needed to recognize their power in Pacific
 Strategies - Pacific • Attack US Pacific Ocean military base and then invade Australia and Hawaii • They thought US would rather respect them than fight a long, costly war
Strategies - Pacific • Attack US Pacific Ocean military base and then invade Australia and Hawaii • They thought US would rather respect them than fight a long, costly war
 Pearl Harbor • Dec 7, 1941 Japan attacked the US military base in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii • Destroyed US Pacific fleet of warships
Pearl Harbor • Dec 7, 1941 Japan attacked the US military base in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii • Destroyed US Pacific fleet of warships
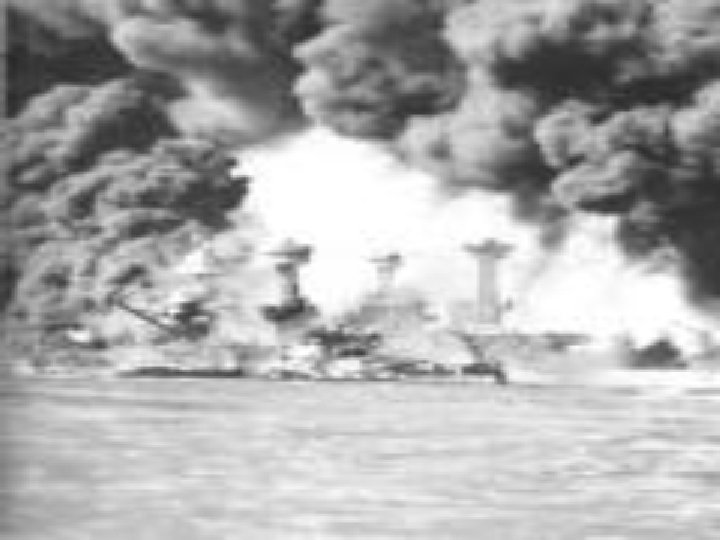
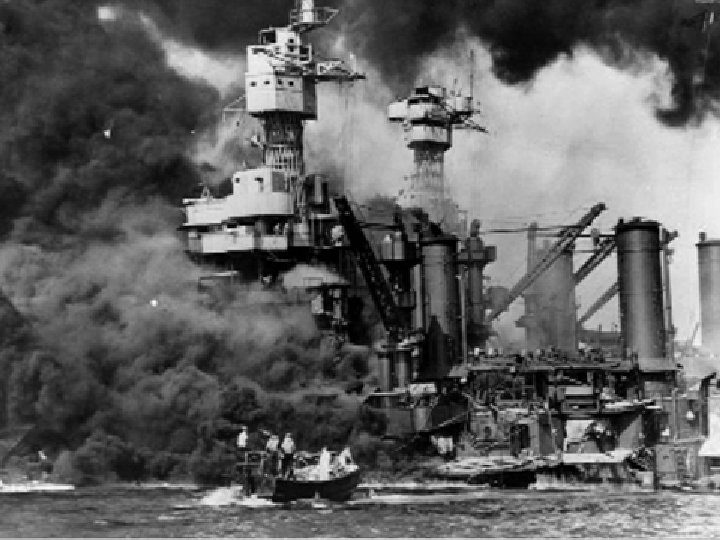
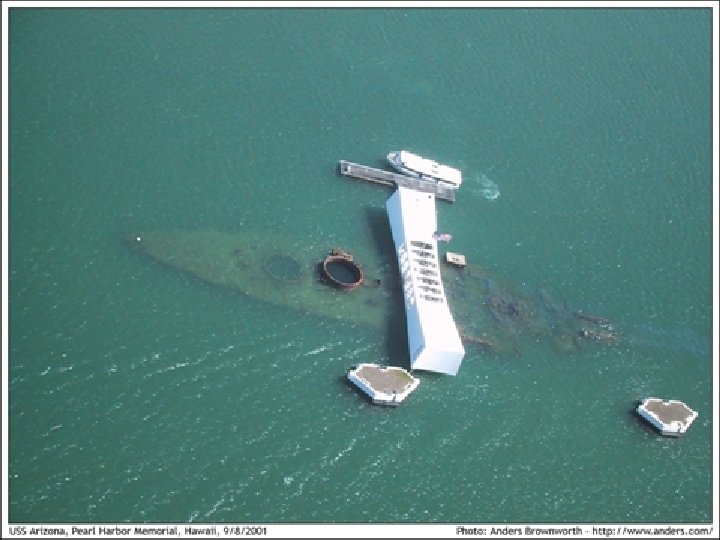





 Pearl Harbor • Dec 8 – US declared war on Japan • Dec 10 – Germany and Italy declared war on US • US now fully involved in World War II
Pearl Harbor • Dec 8 – US declared war on Japan • Dec 10 – Germany and Italy declared war on US • US now fully involved in World War II
 Allied Strategy
Allied Strategy
 Strategy - Europe • Defeat Hitler first • Most US resources were sent to Europe and Africa to fight Germany and Italy • Attack Hitler from all directions and push back toward Germany
Strategy - Europe • Defeat Hitler first • Most US resources were sent to Europe and Africa to fight Germany and Italy • Attack Hitler from all directions and push back toward Germany
 Battles – Europe and Africa
Battles – Europe and Africa
 Battle of Britain (Aug 1940) • British cities were relentlessly bombed by German Air force • Churchill refused to allow British citizens to give up
Battle of Britain (Aug 1940) • British cities were relentlessly bombed by German Air force • Churchill refused to allow British citizens to give up
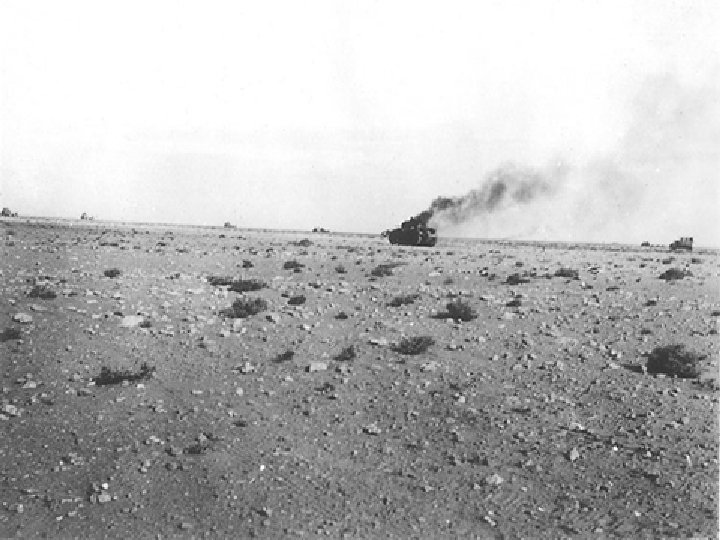
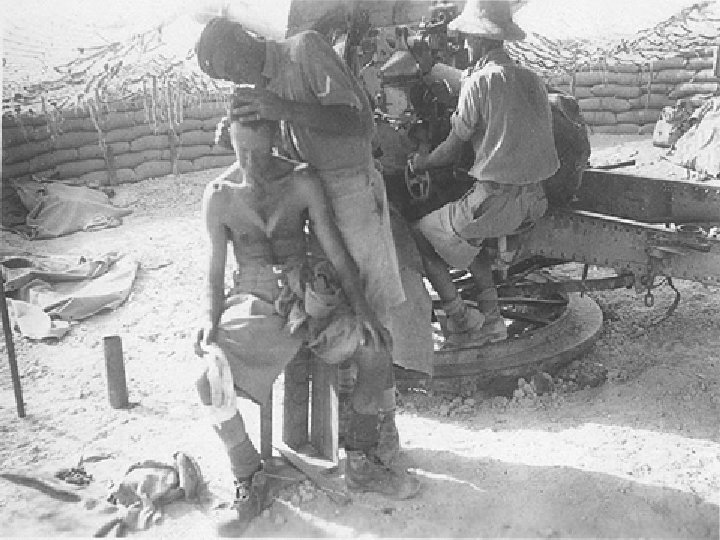
 El Alamein (Nov 1942) • German forces threatening to seize Egypt and the Suez Canal were defeated by the British. • Importance – Prevented Hitler from gaining access to Middle Eastern oil and attacking the Soviet Union from the south. – Allies got access to Germany from the South
El Alamein (Nov 1942) • German forces threatening to seize Egypt and the Suez Canal were defeated by the British. • Importance – Prevented Hitler from gaining access to Middle Eastern oil and attacking the Soviet Union from the south. – Allies got access to Germany from the South
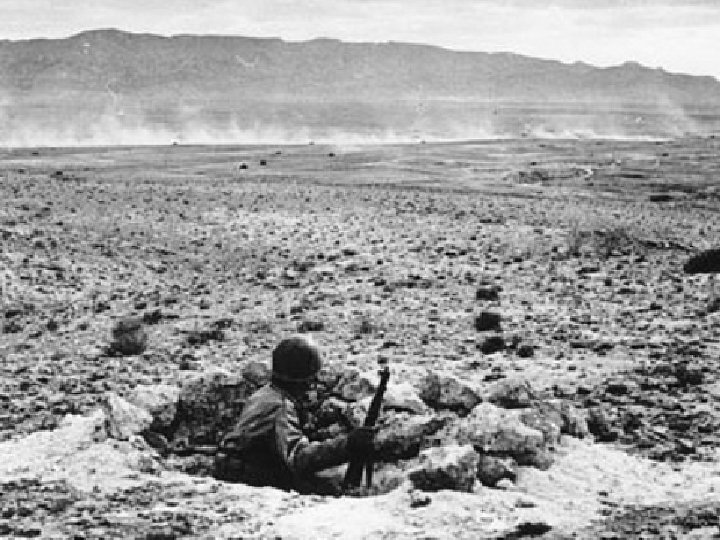



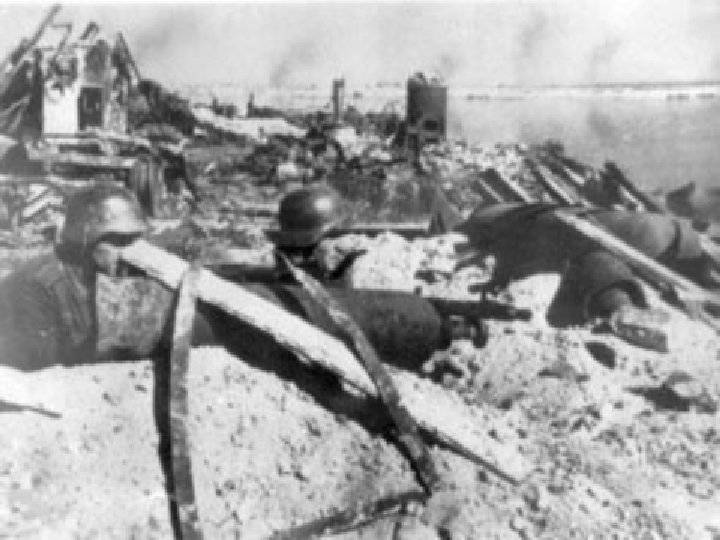
 Stalingrad (Sept 1942) • Hundreds of thousands of German soldiers were killed or captured in the Russian city of Stalingrad. • Importance – This defeat prevented Germany from seizing the Soviet oil fields – Allies got access to Germany from East
Stalingrad (Sept 1942) • Hundreds of thousands of German soldiers were killed or captured in the Russian city of Stalingrad. • Importance – This defeat prevented Germany from seizing the Soviet oil fields – Allies got access to Germany from East
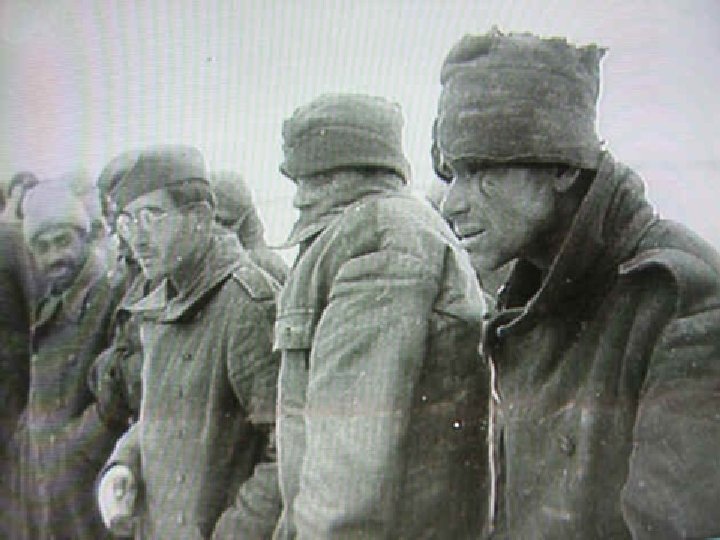




 Normandy (D-Day) June 6, 1944 • Allied troops under Gen. Dwight Eisenhower landed in German-occupied France • Importance – Despite intense German opposition and heavy American casualties, the Americans were able to liberate France. – Allies were able to attack Germany from the west
Normandy (D-Day) June 6, 1944 • Allied troops under Gen. Dwight Eisenhower landed in German-occupied France • Importance – Despite intense German opposition and heavy American casualties, the Americans were able to liberate France. – Allies were able to attack Germany from the west
 V-E Day (May 8, 1945) • US and Russian forces closed in on Germany from all sides • Adolph Hitler killed himself before he could be captured • German forces surrendered, ending the war in Europe
V-E Day (May 8, 1945) • US and Russian forces closed in on Germany from all sides • Adolph Hitler killed himself before he could be captured • German forces surrendered, ending the war in Europe
 World War II Battles and Strategies Pt 2
World War II Battles and Strategies Pt 2
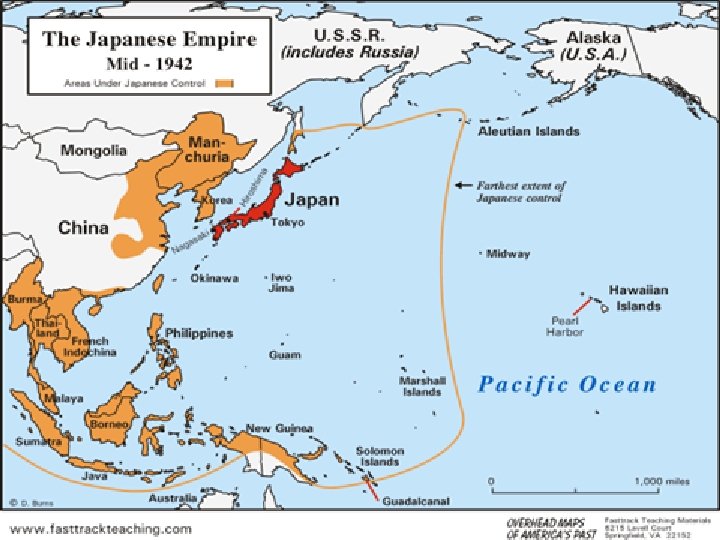
 Strategy - Pacific • Island Hopping – seizing islands closer and closer to Japan and using them as bases for air attacks on Japan – cutting off Japanese supplies through submarine warfare against Japanese shipping
Strategy - Pacific • Island Hopping – seizing islands closer and closer to Japan and using them as bases for air attacks on Japan – cutting off Japanese supplies through submarine warfare against Japanese shipping
 Battles – Pacific Ocean
Battles – Pacific Ocean
 “Miracle of Midway” • American naval forces defeated a much larger Japanese force as it prepared to seize Midway Island • Importance – The American victory ended the Japanese threat to invade Hawaii.
“Miracle of Midway” • American naval forces defeated a much larger Japanese force as it prepared to seize Midway Island • Importance – The American victory ended the Japanese threat to invade Hawaii.
 Iwo Jima and Okinawa • Islands were within a couple hundred miles of Japan • Both invasions cost thousands of American lives and even more Japanese lives • Heavy fighting by Japanese soldiers to protect these islands
Iwo Jima and Okinawa • Islands were within a couple hundred miles of Japan • Both invasions cost thousands of American lives and even more Japanese lives • Heavy fighting by Japanese soldiers to protect these islands
 Kamikaze Fighters • Japanese soldiers who would commit suicide rather than surrender
Kamikaze Fighters • Japanese soldiers who would commit suicide rather than surrender
 Iwo Jima and Okinawa • Importance –US could set up military air fields to easier bomb Japan –Made an invasion of Japan possible
Iwo Jima and Okinawa • Importance –US could set up military air fields to easier bomb Japan –Made an invasion of Japan possible
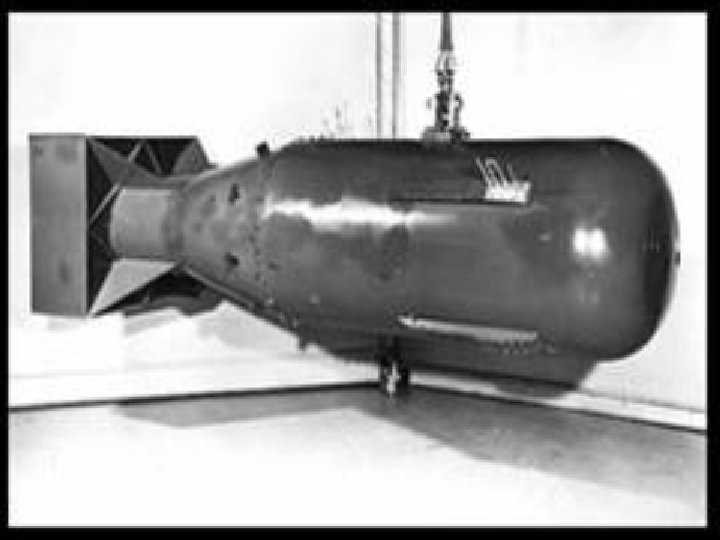
 Use of the atomic bomb • US did not want to invade Japan because they did not want heavy casualties • President Truman ordered the use of a new weapon called an atomic bomb
Use of the atomic bomb • US did not want to invade Japan because they did not want heavy casualties • President Truman ordered the use of a new weapon called an atomic bomb
 August 6, 1945 • America dropped the atomic bomb on Japanese city, Hiroshima
August 6, 1945 • America dropped the atomic bomb on Japanese city, Hiroshima
 August 9, 1945 • America dropped atomic bomb on Nagasaki • Over 250, 000 people instantly killed in both cities • Thousands more died from radiation
August 9, 1945 • America dropped atomic bomb on Nagasaki • Over 250, 000 people instantly killed in both cities • Thousands more died from radiation
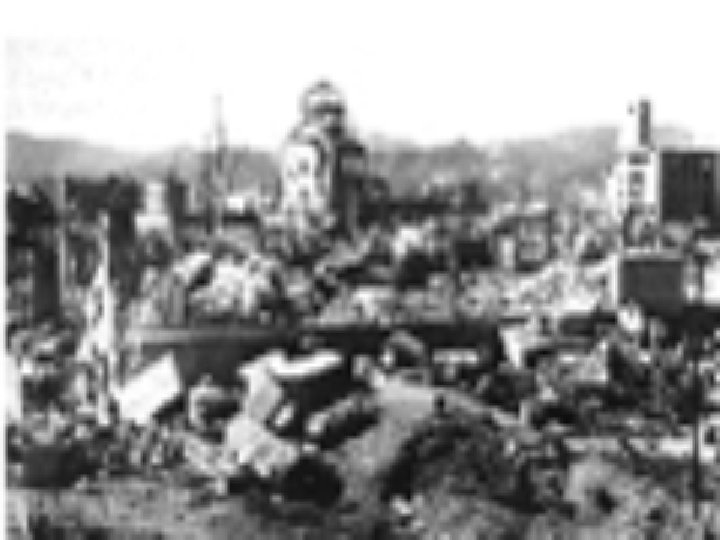

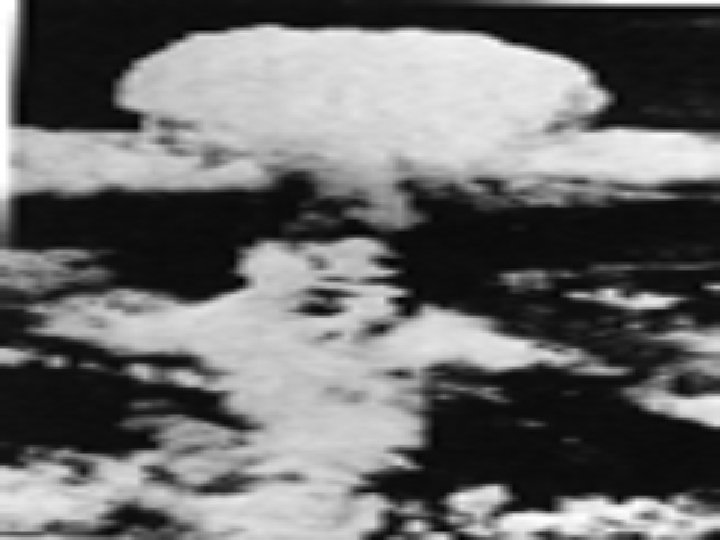


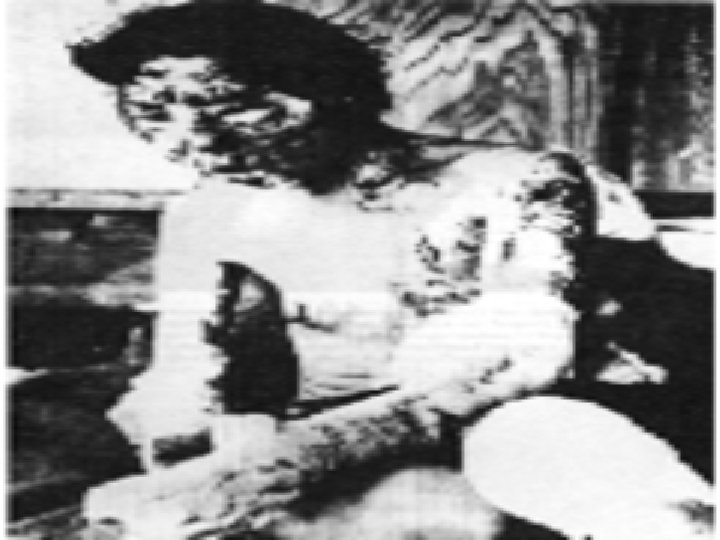
 V-J Day • September 2, 1945 • Japan formally surrendered to the United States
V-J Day • September 2, 1945 • Japan formally surrendered to the United States
 Contributions of Minorities to Allies Minority units suffered high casualties and won numerous medals for bravery in action.
Contributions of Minorities to Allies Minority units suffered high casualties and won numerous medals for bravery in action.
 Tuskegee Airmen • Squad of black air fighter pilots who served with distinction in Europe • No pilots were shot down during war
Tuskegee Airmen • Squad of black air fighter pilots who served with distinction in Europe • No pilots were shot down during war
 Nisei Regiments • Asian American groups who worked as spies and soldiers for United States
Nisei Regiments • Asian American groups who worked as spies and soldiers for United States
 Codetalkers • Navajo Indians who used their language to code US messages in Pacific • Japanese could not decode intercepted US messages
Codetalkers • Navajo Indians who used their language to code US messages in Pacific • Japanese could not decode intercepted US messages
 Mexican Americans • Fought for US in non-segregated military units • Other minorities were segregated from white units
Mexican Americans • Fought for US in non-segregated military units • Other minorities were segregated from white units
 WWII – War Crimes
WWII – War Crimes
 War Crimes • During WWII, brutal crimes were committed against the innocent by all countries involved in war • Millions of innocent people were killed by random bombing, genocide, and discrimination
War Crimes • During WWII, brutal crimes were committed against the innocent by all countries involved in war • Millions of innocent people were killed by random bombing, genocide, and discrimination
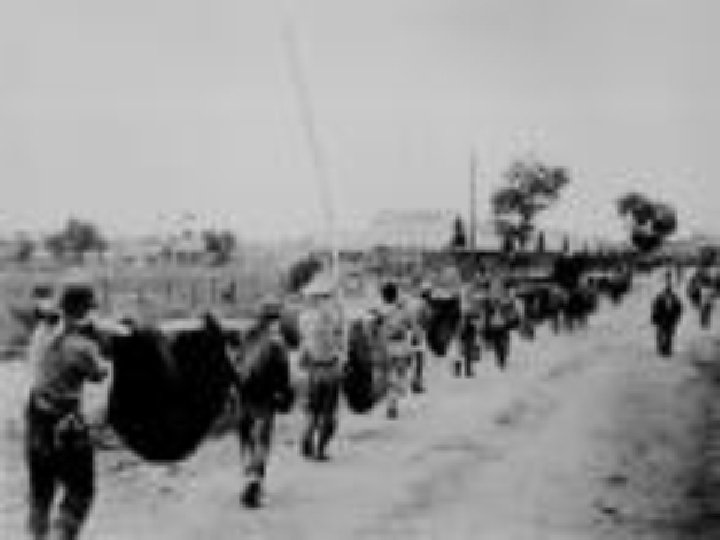
 Bataan Death March • American POWs suffered brutal treatment by the Japanese after the surrender of the Philippines in 1942. • Forced to march through jungle without food or water • The treatment of POW’s in the Pacific war reflected the savagery of the fighting
Bataan Death March • American POWs suffered brutal treatment by the Japanese after the surrender of the Philippines in 1942. • Forced to march through jungle without food or water • The treatment of POW’s in the Pacific war reflected the savagery of the fighting


 Holocaust
Holocaust
 Holocaust • Genocide: The systematic and purposeful destruction of a racial, political, religious, or cultural group • Final solution: Hitler’s decision to exterminate all Jews • Jews were rounded up and sent to concentration camps to be killed
Holocaust • Genocide: The systematic and purposeful destruction of a racial, political, religious, or cultural group • Final solution: Hitler’s decision to exterminate all Jews • Jews were rounded up and sent to concentration camps to be killed
 Holocaust • Holocaust victims: 11 million total – Jews (6 million) – Poles – Slavs – Gypsies – “Undesirables” (homosexuals, mentally ill, political dissidents)
Holocaust • Holocaust victims: 11 million total – Jews (6 million) – Poles – Slavs – Gypsies – “Undesirables” (homosexuals, mentally ill, political dissidents)
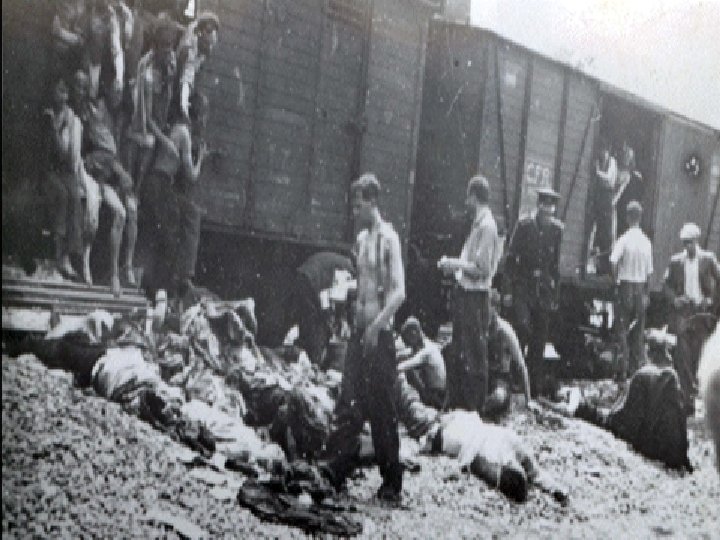
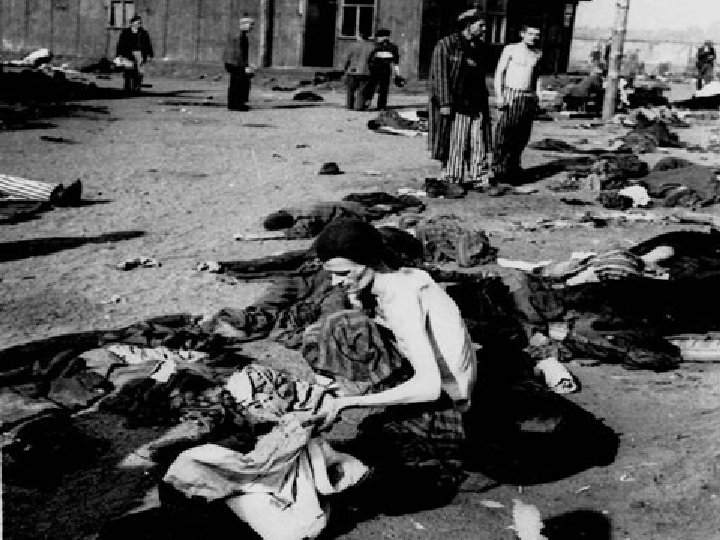
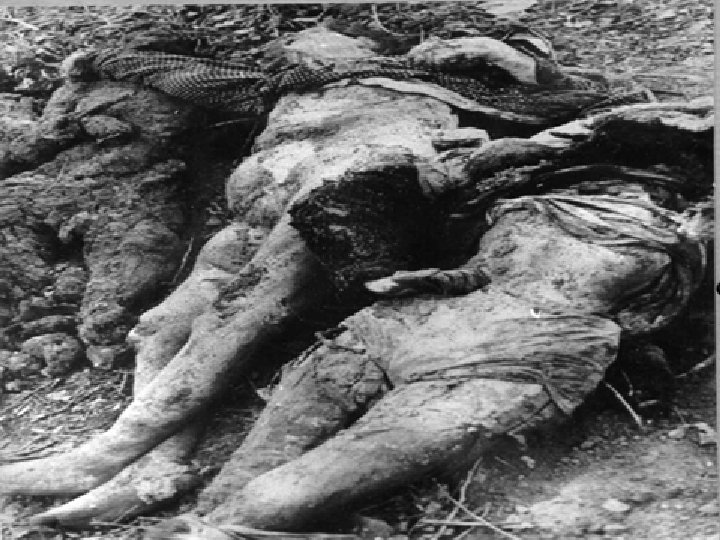




 Nuremburg Trials • Nazi leaders and others were convicted of war crimes • Emphasized individual responsibility for actions during a war, regardless of orders received • Led to increased demand for a Jewish homeland
Nuremburg Trials • Nazi leaders and others were convicted of war crimes • Emphasized individual responsibility for actions during a war, regardless of orders received • Led to increased demand for a Jewish homeland
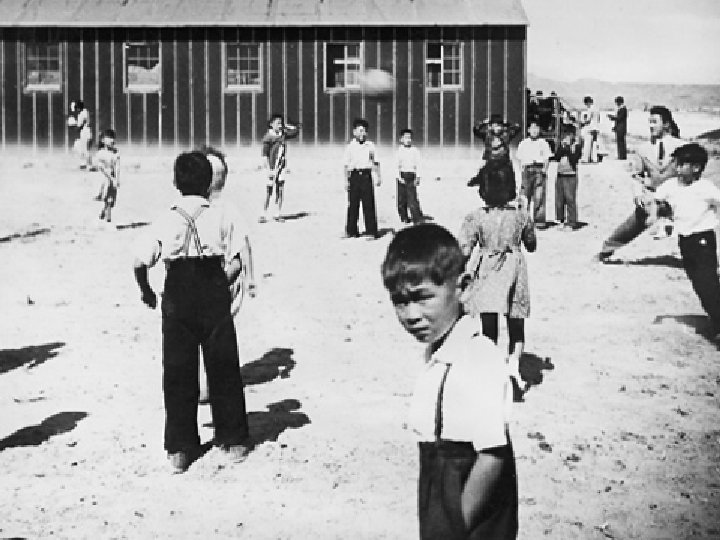
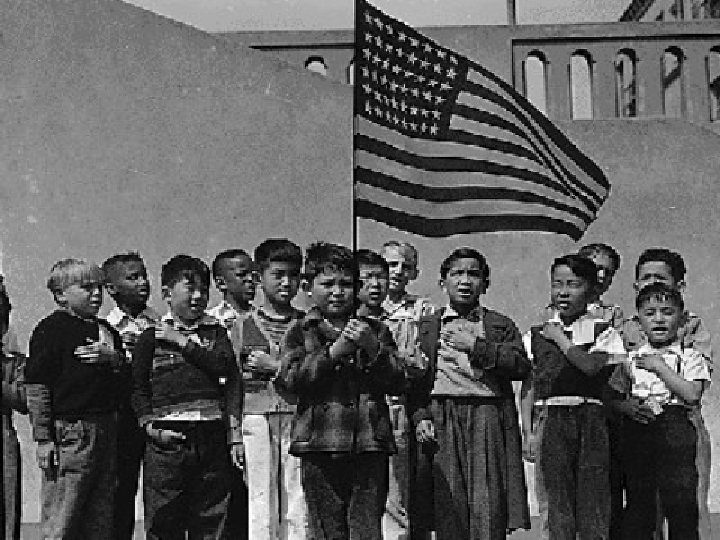
 Japanese Internment Japanese Americans were sent to camps (prison) during the war
Japanese Internment Japanese Americans were sent to camps (prison) during the war
 Reasons for Internment • Strong anti-Japanese prejudice on the West Coast • False belief that Japanese Americans were aiding the enemy
Reasons for Internment • Strong anti-Japanese prejudice on the West Coast • False belief that Japanese Americans were aiding the enemy
 Internment • Japanese sued gov’t for violating their civil rights • Supreme Court Case of Korematsu vs United States ruled US did not violate Japanese civil rights
Internment • Japanese sued gov’t for violating their civil rights • Supreme Court Case of Korematsu vs United States ruled US did not violate Japanese civil rights
 Internment • A public apology was eventually issued by the U. S. government in 1980’s. • Financial restitution was made to survivors
Internment • A public apology was eventually issued by the U. S. government in 1980’s. • Financial restitution was made to survivors
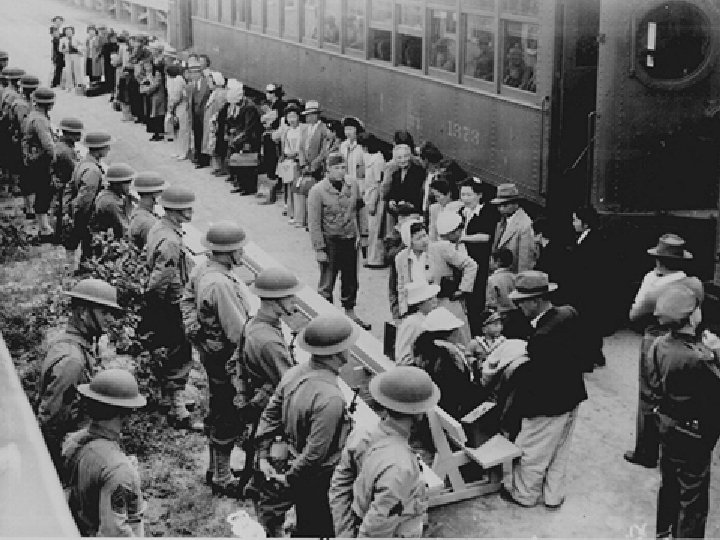



 Geneva Convention • Meeting in Switzerland to ensure the humane treatment of prisoners of war by establishing rules to be followed by all nations • “The conduct of war often reflects social and moral codes of a nation “ • Set up the rules of war for future wars
Geneva Convention • Meeting in Switzerland to ensure the humane treatment of prisoners of war by establishing rules to be followed by all nations • “The conduct of war often reflects social and moral codes of a nation “ • Set up the rules of war for future wars
 World War II On the Homefront
World War II On the Homefront
 On the Homefront • United States success in World War II required the total commitment of the nation’s resources. • Public education and the mass media promoted nationalism
On the Homefront • United States success in World War II required the total commitment of the nation’s resources. • Public education and the mass media promoted nationalism
 United States Resources
United States Resources
 US Resources • U. S. government and industry worked together to distribute resources • Office of War Mobilization created to control resources
US Resources • U. S. government and industry worked together to distribute resources • Office of War Mobilization created to control resources
 Economic Resources
Economic Resources
 Economic Resources • Rationing maintained a steady supply of materials for war • War bonds and income tax were used for financing the war
Economic Resources • Rationing maintained a steady supply of materials for war • War bonds and income tax were used for financing the war
 Economic Resources • Business was retooled from peacetime to wartime production
Economic Resources • Business was retooled from peacetime to wartime production
 Human Resources
Human Resources
 Human Resources • More women and minorities entered the labor force • Citizens volunteered in support of the war effort
Human Resources • More women and minorities entered the labor force • Citizens volunteered in support of the war effort
 Women • Replaced men who went to serve in the military (e. g. , Rosie the Riveter). • They participated in non-combat military roles
Women • Replaced men who went to serve in the military (e. g. , Rosie the Riveter). • They participated in non-combat military roles



 African-Americans • Double V Campaign – Victory in war and victory in equality at home – Demanded an end to segregation in military
African-Americans • Double V Campaign – Victory in war and victory in equality at home – Demanded an end to segregation in military

 Military Resources • The draft/selective service was used to provide personnel for the military
Military Resources • The draft/selective service was used to provide personnel for the military
 Role of Media and Mass Communications
Role of Media and Mass Communications
 Role of the Media • Media and communications assisted the gov’t in supporting the war • U. S. government maintained strict censorship of reporting of the war –Censorship: blocking certain materials from being published
Role of the Media • Media and communications assisted the gov’t in supporting the war • U. S. government maintained strict censorship of reporting of the war –Censorship: blocking certain materials from being published
 Role of the Media • Hollywood produced movies, plays, and shows that boosted morale and patriotism • Portrayed the enemy in stereotypical ways
Role of the Media • Hollywood produced movies, plays, and shows that boosted morale and patriotism • Portrayed the enemy in stereotypical ways





 Political, economic and social consequences of the war
Political, economic and social consequences of the war
 Legacy Of WWII 1. Massive destruction and death 2. End of Allied cooperation and beginning of “Cold War” – political tensions
Legacy Of WWII 1. Massive destruction and death 2. End of Allied cooperation and beginning of “Cold War” – political tensions
 Legacy Of WWII 3. US and Soviet Unions are only superpower countries 4. Atomic fallout – all countries rushed to get atomic bomb
Legacy Of WWII 3. US and Soviet Unions are only superpower countries 4. Atomic fallout – all countries rushed to get atomic bomb
 Legacy Of WWII 5. US troops permanently stationed around the world 6. US will maintain a standing army in peacetime
Legacy Of WWII 5. US troops permanently stationed around the world 6. US will maintain a standing army in peacetime
 Legacy Of WWII 7. Germany (and Berlin) divided into 4 military zones • each zone controlled by one of the 4 major Allied powers
Legacy Of WWII 7. Germany (and Berlin) divided into 4 military zones • each zone controlled by one of the 4 major Allied powers


