e3f869783b07a0703c1a3e2779cd7988.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 World War II 1939 -1945
World War II 1939 -1945
 Appeasement § Policy begun by Britain and France § Instituted to prevent war and possibly right the wrongs done by the Treaty of Versailles § Included no reaction to rearmament, conscription (1935) reoccupation of the Rhineland (1936), anschluss with Austria (1938), taking of the Sudetenland (1938), and taking of Czechoslovakia § Many believed that Hitler could stop the progress of Communis and act as a defense against it’s influence
Appeasement § Policy begun by Britain and France § Instituted to prevent war and possibly right the wrongs done by the Treaty of Versailles § Included no reaction to rearmament, conscription (1935) reoccupation of the Rhineland (1936), anschluss with Austria (1938), taking of the Sudetenland (1938), and taking of Czechoslovakia § Many believed that Hitler could stop the progress of Communis and act as a defense against it’s influence
 Hitler’s Germany § Hitler’s Goals • Lebensraum • Uniting all Germans • Abolish the Treaty of Versailles § Rearmament • 1933 – begins training of “road crew” • 1935 • • • Introduced conscription Increased spending on arms Huge rearmament rally. Naval agreement with Britain allowed German navy of 35% of British navy. Increased airforce to 8, 250 by 1939. § Steps to War • • • Rhineland Anschluss Sudetenland Czechoslovakia Poland
Hitler’s Germany § Hitler’s Goals • Lebensraum • Uniting all Germans • Abolish the Treaty of Versailles § Rearmament • 1933 – begins training of “road crew” • 1935 • • • Introduced conscription Increased spending on arms Huge rearmament rally. Naval agreement with Britain allowed German navy of 35% of British navy. Increased airforce to 8, 250 by 1939. § Steps to War • • • Rhineland Anschluss Sudetenland Czechoslovakia Poland
 Europe 1939 -1940 § § § § § Nazi-Soviet Pact, August 23, 1939 Hitler invades Poland September 1, 1939 Blitzkrieg September 3, 1939 Britain, France, Australia, and New Zealand declare war on Germany The Phoney War April 9, 1940 Germany invades Denmark and Norway Churchill becomes Prime Minister May 10, 1940 Germany invades France, Belgium, Netherlands, and Luxembourg Germans attack France through the Ardennes
Europe 1939 -1940 § § § § § Nazi-Soviet Pact, August 23, 1939 Hitler invades Poland September 1, 1939 Blitzkrieg September 3, 1939 Britain, France, Australia, and New Zealand declare war on Germany The Phoney War April 9, 1940 Germany invades Denmark and Norway Churchill becomes Prime Minister May 10, 1940 Germany invades France, Belgium, Netherlands, and Luxembourg Germans attack France through the Ardennes
 Europe 1940 § May 26, 1940 Allied troops evacuate from Dunkirk § June 12, 1940 Italy declares war on France § June 14, 1940 Germans take Paris § June 22, 1940 France signs armistice with Hitler (Petain becomes the new premier of Vichy France) § France divided into occupied and un-occupied territory – Vichy France is un-occupied territory but under control of Hitler
Europe 1940 § May 26, 1940 Allied troops evacuate from Dunkirk § June 12, 1940 Italy declares war on France § June 14, 1940 Germans take Paris § June 22, 1940 France signs armistice with Hitler (Petain becomes the new premier of Vichy France) § France divided into occupied and un-occupied territory – Vichy France is un-occupied territory but under control of Hitler
 North Africa and the Mediterranean 1940 - 1943 § Mediterranean • Important for trade, military, and oil supplies • British wanted it for trade and to protect the Suez Canal • Mussolini wanted it “Italian Lake” • Hitler wanted it to get control of Britain’s oil supplies in Iraq and Persia (Iran) • Balkans - Germans and Italians occupy Greece, Yugoslavia § North Africa • Italians invade Egypt, Sept. 1940 • British begin offensive against Italians in North Africa, Dec. 1940 • Battle of Tobruk, January 1941 Italians defeated by O’Connor – also Sidi Barrani, Bardia, Benghazi, and El Alghelia • Hitler sends Rommel (“Desert Fox”) and the Afrika Korps fight back – takes Libya back • British on the defensive, pushed back to El Alamein
North Africa and the Mediterranean 1940 - 1943 § Mediterranean • Important for trade, military, and oil supplies • British wanted it for trade and to protect the Suez Canal • Mussolini wanted it “Italian Lake” • Hitler wanted it to get control of Britain’s oil supplies in Iraq and Persia (Iran) • Balkans - Germans and Italians occupy Greece, Yugoslavia § North Africa • Italians invade Egypt, Sept. 1940 • British begin offensive against Italians in North Africa, Dec. 1940 • Battle of Tobruk, January 1941 Italians defeated by O’Connor – also Sidi Barrani, Bardia, Benghazi, and El Alghelia • Hitler sends Rommel (“Desert Fox”) and the Afrika Korps fight back – takes Libya back • British on the defensive, pushed back to El Alamein
 North Africa and the Mediterranean 1940 – 1943 (Con’t) • Battle of El Alamein • Montgomery defeats Rommel, pushes him back to Libya • Beginning in late 1942 Montgomery begins defeating Rommel, then Patton lands in Morocco • Operation Torch • American and British led by Patton land in Morocco and Algeria • German troops land in Tunisia to help Rommel
North Africa and the Mediterranean 1940 – 1943 (Con’t) • Battle of El Alamein • Montgomery defeats Rommel, pushes him back to Libya • Beginning in late 1942 Montgomery begins defeating Rommel, then Patton lands in Morocco • Operation Torch • American and British led by Patton land in Morocco and Algeria • German troops land in Tunisia to help Rommel
 Europe 1941 § Operation Sealion – Invasion of Britain after the defeat of the RAF § The Battle of Britain– Luftwaffe v. RAF (July. Sept. 1941) § The Blitz – September 7, 1941 – May 1942 § The Battle of the Atlantic (1939 -1944) • Battle for control of the North Atlantic Ocean
Europe 1941 § Operation Sealion – Invasion of Britain after the defeat of the RAF § The Battle of Britain– Luftwaffe v. RAF (July. Sept. 1941) § The Blitz – September 7, 1941 – May 1942 § The Battle of the Atlantic (1939 -1944) • Battle for control of the North Atlantic Ocean
 The War becomes a World War § Attack on Russia, begins Eastern Front – June 1941 § Attack on America, begins war in the Pacific - December 7, 1941
The War becomes a World War § Attack on Russia, begins Eastern Front – June 1941 § Attack on America, begins war in the Pacific - December 7, 1941
 Eastern Front 1941 -1943 § Operation Barbarossa – June 1941 • Blitzkrieg – very successful against Russia • Scorched Earth Policy and guerilla units used by Russia • 3 groups of Germans invade – 1 to Leningrad (North), 1 to Moscow (Center), 1 to the Ukraine (South) • January 1942 Russians pushing them out from Moscow • Hitler orders Paulus to take Stalingrad “whatever the cost” § Battle of Stalingrad – Sept. 1942 -January 1943 • Germans surrounded in Stalingrad • Cut off from supplies by Soviet planes • Paulus surrenders Jan. 31 +300, 000 soldiers § Battle of Leningrad – Sept. 8, 1941 - January 18, 1944 • 670, 000 Russians estimated (up to 1. 2 million) died from starvation • Operation Spark ends the seige
Eastern Front 1941 -1943 § Operation Barbarossa – June 1941 • Blitzkrieg – very successful against Russia • Scorched Earth Policy and guerilla units used by Russia • 3 groups of Germans invade – 1 to Leningrad (North), 1 to Moscow (Center), 1 to the Ukraine (South) • January 1942 Russians pushing them out from Moscow • Hitler orders Paulus to take Stalingrad “whatever the cost” § Battle of Stalingrad – Sept. 1942 -January 1943 • Germans surrounded in Stalingrad • Cut off from supplies by Soviet planes • Paulus surrenders Jan. 31 +300, 000 soldiers § Battle of Leningrad – Sept. 8, 1941 - January 18, 1944 • 670, 000 Russians estimated (up to 1. 2 million) died from starvation • Operation Spark ends the seige
 War in the Pacific 1941 -1942 § Pearl Harbor attacked Dec. 7, 1941 § United Nations declaration signed, January 1, 1942 § Japanese take over Manila (Americans in the Bataan Peninsula) Nimitz in charge of Pacific • Then Take KL, Borneo, Mali, Sumatra, Timor, Singapore, Burma, Java, Corregidor – Battle of Java Sea, Battle of Coral Sea § Bataan Death March – 75, 000 down to 54, 000 (April) § Doolittle Raid – April § Battle of Midway – 4 Japanese carriers lost! – Turning Point for the Allies (enigma machine captured) § Guadalcanal, another limited victory
War in the Pacific 1941 -1942 § Pearl Harbor attacked Dec. 7, 1941 § United Nations declaration signed, January 1, 1942 § Japanese take over Manila (Americans in the Bataan Peninsula) Nimitz in charge of Pacific • Then Take KL, Borneo, Mali, Sumatra, Timor, Singapore, Burma, Java, Corregidor – Battle of Java Sea, Battle of Coral Sea § Bataan Death March – 75, 000 down to 54, 000 (April) § Doolittle Raid – April § Battle of Midway – 4 Japanese carriers lost! – Turning Point for the Allies (enigma machine captured) § Guadalcanal, another limited victory

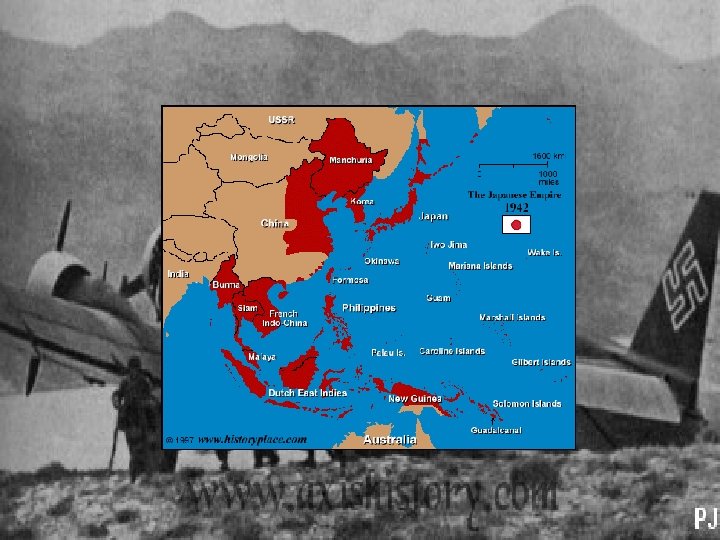
 War in Europe (with American soldiers) 1942 § § § January – UN Declaration signed January - Germans meet , decide Final Solution March - first Jews arrive at Auschwitz July – Treblinka extermination camp opens December – a British diplomat informs the House of Commons of mass executions of Jews by the Nazis § December - Battle of Barents Sea • Between British and Germans • All 14 British merchant ships reached their destination • Hitler ends battleship program and concentrates on subs
War in Europe (with American soldiers) 1942 § § § January – UN Declaration signed January - Germans meet , decide Final Solution March - first Jews arrive at Auschwitz July – Treblinka extermination camp opens December – a British diplomat informs the House of Commons of mass executions of Jews by the Nazis § December - Battle of Barents Sea • Between British and Germans • All 14 British merchant ships reached their destination • Hitler ends battleship program and concentrates on subs
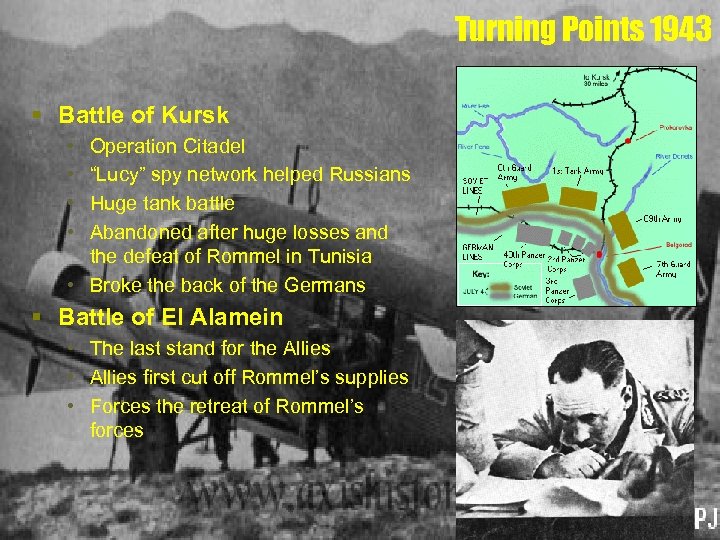 Turning Points 1943 § Battle of Kursk • • Operation Citadel “Lucy” spy network helped Russians Huge tank battle Abandoned after huge losses and the defeat of Rommel in Tunisia • Broke the back of the Germans § Battle of El Alamein • The last stand for the Allies • Allies first cut off Rommel’s supplies • Forces the retreat of Rommel’s forces
Turning Points 1943 § Battle of Kursk • • Operation Citadel “Lucy” spy network helped Russians Huge tank battle Abandoned after huge losses and the defeat of Rommel in Tunisia • Broke the back of the Germans § Battle of El Alamein • The last stand for the Allies • Allies first cut off Rommel’s supplies • Forces the retreat of Rommel’s forces
 War in Europe and Africa 1943 § January - Casablanca Conference • Churchill and Roosevelt § § § January - Montgomery takes Tripoli February - German’s surrender at Stalingrad February - Soviets take back Kursk March – Germans retreat from Tunisia March - Battle of Atlantic at its height • 27 Merchant ships sunk by U-boats § April – Warsaw ghetto uprising § June – Himmler orders elimination of all Jewish ghettos in Poland § July – Allies land in Sicily § July – Mussolini arrested, Italians surrender, Germans rescue him in Sept.
War in Europe and Africa 1943 § January - Casablanca Conference • Churchill and Roosevelt § § § January - Montgomery takes Tripoli February - German’s surrender at Stalingrad February - Soviets take back Kursk March – Germans retreat from Tunisia March - Battle of Atlantic at its height • 27 Merchant ships sunk by U-boats § April – Warsaw ghetto uprising § June – Himmler orders elimination of all Jewish ghettos in Poland § July – Allies land in Sicily § July – Mussolini arrested, Italians surrender, Germans rescue him in Sept.
 Europe and Africa 1943 § October – Italy declares war on Germany § November - Russians recapture Kiev § November – Cairo Conference • Roosevelt , Churchill, Chiang-Kai Shek § November – Tehran Conference • Roosevelt, Churchill, and Stalin
Europe and Africa 1943 § October – Italy declares war on Germany § November - Russians recapture Kiev § November – Cairo Conference • Roosevelt , Churchill, Chiang-Kai Shek § November – Tehran Conference • Roosevelt, Churchill, and Stalin
 Europe 1944 § § § January – Allies land at Anzio January – Battle of Leningrad ends March – Soviets begin pushing Germans back June – Allies enter Rome June 6 – D-Day (Operation Overlord) • British, Canadian, and U. S. troops (planned by Eisenhower) – invasion of Fortress Europe • Omaha, Utah, Gold, Juno, and Sword • Allies misled Germans – calling up Patton to head up the invasion with a phantom army opposite Calais • 1 st Airborne troops dropped, capture key bridges • 2 nd followed up with landings at all 5 beaches, Omaha worst hit of all – 2, 000 casualties
Europe 1944 § § § January – Allies land at Anzio January – Battle of Leningrad ends March – Soviets begin pushing Germans back June – Allies enter Rome June 6 – D-Day (Operation Overlord) • British, Canadian, and U. S. troops (planned by Eisenhower) – invasion of Fortress Europe • Omaha, Utah, Gold, Juno, and Sword • Allies misled Germans – calling up Patton to head up the invasion with a phantom army opposite Calais • 1 st Airborne troops dropped, capture key bridges • 2 nd followed up with landings at all 5 beaches, Omaha worst hit of all – 2, 000 casualties
 Europe 1944 § § § June – 1 st German V-1 Rocket used July – Soviets capture Minsk July 20 – Assassination attempt on Hitler fails August – Allies take Paris, Soviets take Bucharest September - Allies take back most of Belgium, most of France § October – Allies take Athens, Erwin Rommel commits suicide § October – last use of gas chambers in Auschwitz § December (- January) – Battle of the Bulge • Over 1 million fought – casualties – 100, 000 German - 80, 000 American – 1400 Brits • Hitler thought he could take Antwerp and create disagreements amongst the Allies • Hitler is unstable, making questionable decisions § December – Soviets take Budapest
Europe 1944 § § § June – 1 st German V-1 Rocket used July – Soviets capture Minsk July 20 – Assassination attempt on Hitler fails August – Allies take Paris, Soviets take Bucharest September - Allies take back most of Belgium, most of France § October – Allies take Athens, Erwin Rommel commits suicide § October – last use of gas chambers in Auschwitz § December (- January) – Battle of the Bulge • Over 1 million fought – casualties – 100, 000 German - 80, 000 American – 1400 Brits • Hitler thought he could take Antwerp and create disagreements amongst the Allies • Hitler is unstable, making questionable decisions § December – Soviets take Budapest
 Europe 1945 § January – Soviets take Warsaw, liberate Auschwitz § February – Yalta Conference • Stalin, Churchill, FDR § § § § § February – Dresden destroyed March - Allies take Danzig April – Buchenwald liberated, FDR dies April – Soviets reach Berlin, Americans in Nuremberg April – Mussolini is hanged April – Americans liberate Dachau April 30 – Hitler commits suicide May 7 – Unconditional surrender of German troops May 8 – V-E Day May 23 – Himmler commits suicide
Europe 1945 § January – Soviets take Warsaw, liberate Auschwitz § February – Yalta Conference • Stalin, Churchill, FDR § § § § § February – Dresden destroyed March - Allies take Danzig April – Buchenwald liberated, FDR dies April – Soviets reach Berlin, Americans in Nuremberg April – Mussolini is hanged April – Americans liberate Dachau April 30 – Hitler commits suicide May 7 – Unconditional surrender of German troops May 8 – V-E Day May 23 – Himmler commits suicide
 Europe and Pacific 1945 § § § June 5 – Allies divide Germany and Berlin June 26 – UN Charter is signed July – Potsdam Conference July – Atlee becomes Prime Minister August 6 – Bomb dropped on Hiroshima August 8 – Soviets declare war on Japan August 9 – Bomb dropped on Nagasaki August 14 – Japanese surrender August 15 – V-J (V-P) Day October 24 – UN officially begins November 20 – Nuremberg Trials begin
Europe and Pacific 1945 § § § June 5 – Allies divide Germany and Berlin June 26 – UN Charter is signed July – Potsdam Conference July – Atlee becomes Prime Minister August 6 – Bomb dropped on Hiroshima August 8 – Soviets declare war on Japan August 9 – Bomb dropped on Nagasaki August 14 – Japanese surrender August 15 – V-J (V-P) Day October 24 – UN officially begins November 20 – Nuremberg Trials begin
 Main War Conferences § Casablanca (Jan 14 -24, 1943) • Churchill, Roosevelt • Plans to invade Sicily and Italy • Decision to invade France in 1944 • “unconditional surrender” § Cairo (Nov. 23 -26, 1943) § Bretton Woods (July 1 -15, 1944) • Established the IMF § Yalta (Feb 4 -11, 1945) • • • Churchill, Roosevelt, Stalin in a strong position Division of Germany decided The beginning of the Cold War? Gave USSR much of Eastern Europe • Churchill, Roosevelt, Chiang Kai. Shek § United Nations Conference (April • Return Manchuria to China, free 25 – June 26, 1945) Korea – • Reps from 50 countries • strip Japan of all overseas • October 24 is UN Day territory § Tehran (Nov. 28 – Dec 1, 1943) • Churchill, Roosevelt, Stalin • Plans for two-front war + postwar cooperation • Russia to enter war vs. Japan § Potsdam (July 17 – Aug 2, 1945) • Truman, Stalin, Churchill (Atlee) • Demand Japanese surrender • Agree on postwar Germany issues – 4 power Allied Control Council • To Japan - Unconditional surrender or total destruction
Main War Conferences § Casablanca (Jan 14 -24, 1943) • Churchill, Roosevelt • Plans to invade Sicily and Italy • Decision to invade France in 1944 • “unconditional surrender” § Cairo (Nov. 23 -26, 1943) § Bretton Woods (July 1 -15, 1944) • Established the IMF § Yalta (Feb 4 -11, 1945) • • • Churchill, Roosevelt, Stalin in a strong position Division of Germany decided The beginning of the Cold War? Gave USSR much of Eastern Europe • Churchill, Roosevelt, Chiang Kai. Shek § United Nations Conference (April • Return Manchuria to China, free 25 – June 26, 1945) Korea – • Reps from 50 countries • strip Japan of all overseas • October 24 is UN Day territory § Tehran (Nov. 28 – Dec 1, 1943) • Churchill, Roosevelt, Stalin • Plans for two-front war + postwar cooperation • Russia to enter war vs. Japan § Potsdam (July 17 – Aug 2, 1945) • Truman, Stalin, Churchill (Atlee) • Demand Japanese surrender • Agree on postwar Germany issues – 4 power Allied Control Council • To Japan - Unconditional surrender or total destruction
 Churchill, Roosevelt, Stalin at Yalta
Churchill, Roosevelt, Stalin at Yalta


