1f56d31164b73209a80c5477c31cc9d5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 99

World War II (1 st Global War – 1939 -1945) Ch 16 USH

World War II (1 st Global War – 1939 -1945) • *fighting takes place on four continents, over four oceans • *100 million fought (40 -50 million died – many civilians) • *Key Allies – Great Britain, Soviet Union (Russia), USA, • France (colonies), China • *Axis Powers – Germany, Japan, Italy



How did it start • Treaty of Versailles – end of WWI left Europe uneasy • Germany – destroyed, embarrassed • Defeat – Ger. Forced to take full blame for WWI • Reparations – Ger. Forced to pay France $ • *importance – Ger. Does not have $ to rebuild • European Depression – all of Europe hurt economically • (Ger. Becomes poorest country in Europe) » *importance – Germans are hurt, mad, and looking for hope (breeding ground for a new leader)


Rise of Fascism • duty to the state is more important than individual freedom. Strong leader limits personal freedom to insure countries success – *states that if the people of a country work together, they can improve their situation • • • Attraction Nationalism – pride in county (shows that you are better than others) *promise to create a new Empire

Rise of Fascism • Leadership – a strong leader who will raise the country and create a better economy and way of life • *people want leadership and new ideas during bad times • Anti-Communist – control of the country by countrymen, not Russia • *fascism state that the problem is not economic (rich VS. poor) but between countries (Fr. and Ger. )


How did it start • Three Axis/Fascist Nations (Italy, Germany, Japan) • Italy – Benito Mussolini – 1 st fascist leader in 1926 • Italians felt they deserved more from Treaty of Versailles and were hurt economically by European depression • *Mussolini promises Italy to create a new Roman Empire. • Ethiopia – only free country in Africa, 1935 invaded by Italy • Haile Salassie – leader of Ethiopia, spoke at League of Nations for help (denied) • Germany – National Socialist Workers Party (NAZIs)


Adolf Hitler • – born in Austria, failed artist (hate of Jews), fought in WWI (bad soldier) – *took advantage of Post WWI Ger. Economy to take over Germany using lies, hate, and brilliant speaking skills. – Beer Hall Putsch – 1923 – Hitler and NAZI’s first attempt to take over Germany • * failed and Hitler was sentenced to prison (served less than 1 year)


Adolf Hitler – Mein Kampf (My Struggle) book written by Hitler outlining his beliefs and political goals for Germany – Stated German’s were the supreme race (gave hope to downtrodden) • Aryans-blond, blue eyed – Jews – claimed they were racially inferior and responsible for nations problems • *book became a best seller


Adolf Hitler • Jan 1933 Hitler is ELECTED leader of Germany with 35% of vote – 1935 pulls out of Treaty of Versailles and begins rebuilding German military



Japan “Rising Sun” • Russo-Japanese war (1904) 1 st defeat of European power (Russia) by an Eastern nation • *Japan is a modern, industrial nation and emerging world power


Japan “Rising Sun” • 1920’s – right wing leaders feel only way Japan could earn it’s rightful place in the world was through force. • *example – US bans all Japanese immigration to US in 1924 • Manchuria (part of China) invaded in 1931 for fuel, timber, and food. • •



Japan “Rising Sun” • Japan wants to expand take over colonies in Asia • *threatens U. S. trade with China and Philippines colony of U. S.


. US enters the War • • Isolationism – US avoids fighting for the first two years (but sides with England) • Lend Lease Act – Allows US to provide Eng. With $ to buy and borrow US supplies (weapons, boats, planes, etc. ) • A total of $50. 1 billion (equivalent to $759 billion at 2008 prices) worth of supplies were shipped

Lend Lease Act • signed into law on March 11, 1941, a year and a half after the outbreak of the European war in September 1939, but six months before the U. S. entrance into the war in December 1941, this act ended the pretense of US neutrality.

Tripartite Pact • – Ger. , Japan, and Italy sign an alliance to fight together if a new country enters the war • *designed to keep the US out (US would have to fight two wars – Europe and Pacific)


US enters the War • Atlantic Charter – US and Eng meet to spell out reasons WWII is to be fought for (554) • 1)No new territorial gain • 2)Self determination of free nations • 3) Freedom from fear and want (peace) • *became the basis of the United Nations


Planning for war • – by 1940 US knew it would be dragged into the war to help allies (Eng. ) • Selective Service Act (1940) draft is started before US goes to war (1 million drafted – 16 mi. Registered ) • Military Spending - US had a weak military due to isolationism ($s are spent, helps end depression) • FDR re-elected – seeks a 3 rd term as President due to WWII • Only pres. To serve more than 2 terms

Pearl Harbor • – US naval base in Hawaii • Attack on PH pulls US into WWII • Japan – want an Empire in the Pacific • Jap. Navy (Nov 25, 1941 SET OUT FOR HA. • *Idea – Japan wants a surprise attack and take out the US navy while in harbor • • • Dec. 7. 1941 (Sunday, 7: 55 am) Japanese planes attack PH and kill 2, 400 sailors *1 st attack on US soil since Civil War *9/11 worst attack on US soil since PH (3500 died) US declares war – Dec. 8, 1941 Ger. and Italy declare war on US Dec. 9, 1941.

the beginning of the attack. The explosion in the center is a torpedo strike on the USS Oklahoma

Jap. - Americans • Internment camps – 110, 000 more (Barbed wire, crowded barracks, community mess hall and restrooms) • 442 combat until – Hawaii – Most decorated unit in WWII • Koreamatsu VS US (1944) set up Jap to spying and sabotage duress wartime (pp. 595 -597)



US and WWII • Gov. and Industry – ended depression (demand for labor due to war effort) • War bonds – asked America to put aside 10% of income to purchase (Am. Bought $175 million) helped pay for war • Factories – 1941 – 19, 000 planes are produced • *war time agencies staffed by businessmen, not politicians • Rubber – lack due to Jap. Control of far east.


US and WWII Am. Workforce • – Am. Workers eager for employment after depression • Women - 6 million women (due to lack of men) made 65% (no child care) but glad to do their part. •

US and WWII Am. Workforce • Blacks – migration from South to industrial cities like LA, Detroit • – more than 5 million

US and WWII • Armed forces – 15 million served in war • Peacetime draft – (1940) 1. 8 million in uniforms before war • Blacks – 1 million served, segregation • The Tuskegee Airmen were the first African American military aviators in the United States armed forces. During World War II
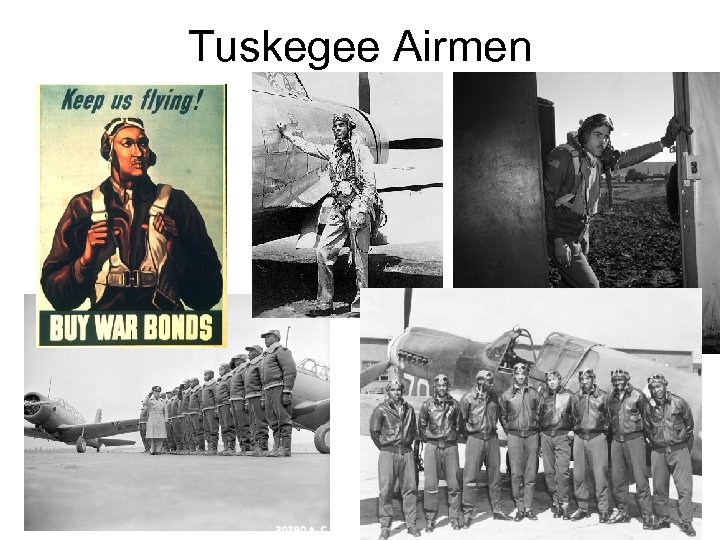

Tuskegee Airmen

US and WWII Effect of civilian life • – US economy and geography meant Am. experienced fewer hardships compared to Europe severe shortage • Family – separation - increase in marriages and birth rates (Baby Boomers)

The War in Europe • *Defeating Germany was the 1 st priority • Soviet Union – invaded by Gr. (June 1941), • Hitler wants Russian resources (oil) • *Violates Nazi-Soviet Non- Aggression Pact Battles – Russia suffers high casualties, but Stalin forbids Russians to quit. • Moscow – surrounded by Nov. • *Winter pushes Ger. back • Leningrad – attacked for 900 days, • 500, 000 Russians starve to death • *City is never captured by Nazi’s • Stalingrad – (Spr. 42) Hitler wants control of Russian oil fields, sends 300, 000 troops » (5 month battle) • • Ger. Lost and is turning point in Russian (/Russia pushes Ger. back) *Eng. And US do not aid Russia with troops; Stalin mistrusts allies for rest of war

Operation Barbarossa

The War in Europe • Africa (USA and GB) – invade North Africa first • (Operation Torch Nov. 42) • (Seen as less risky than Russia) • General Patton – USA top general, turn US into an effective fighting force • *Allies take AF. by May 1943

Operation Torch Allied troops hit the beaches near Algiers, behind a large American flag (left).

The War in Europe • Italy – invaded after N. Af. Captured (Summer 1943) • Mussolini ousted by Italians (July 1943) • *Sept. 43 Italy captured


The War in Europe • Invasion of Europe – Allies need to free France and push Ger. back • D-Day (June 6, 1944) largest air-sea-land battle in History • *Normandy, France – 160. 000 troops land on 60 mile stretch of beach (4, 400 landing craft, 600 war ships, 11, 000 planes) • *5 beaches (US land at Omaha and Utah) Eng. , Canadian and FR. Troops and at Gold, Juno and Sword • *Allies suffer severe casualties but capture the beaches •
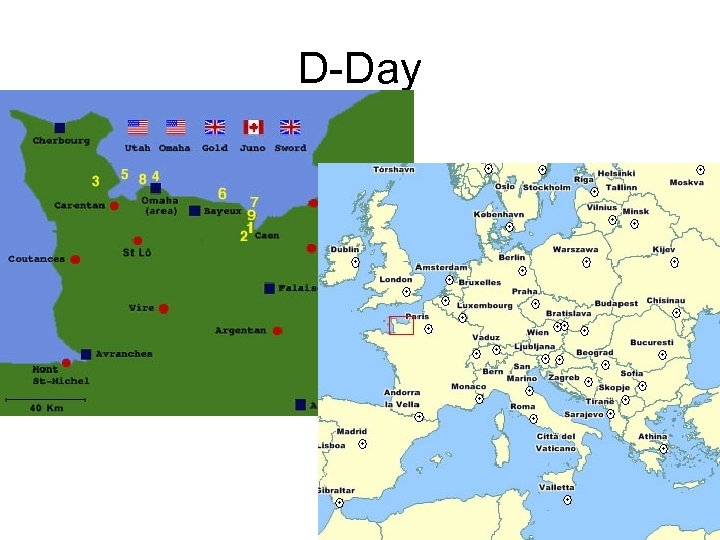
D-Day

D-Day



The War in Europe Beginning of the End – German starts losing by ‘ 44 • 1) Air Superiority – Allies control the skies and can support ground troops • 2)France liberated – Aug. 25, 1944 • 3)Sea Power – allies control sea and can ship supplies from US • *Sonar and Radar are invented by allies (can detect Ger. Subs and planes )
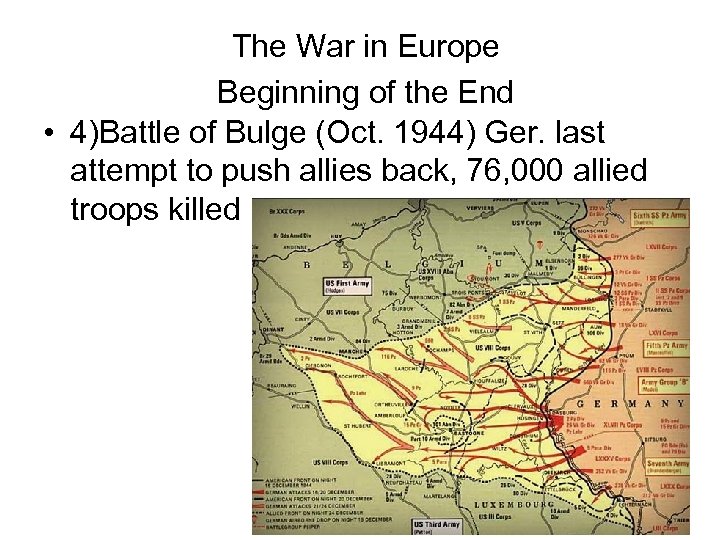
The War in Europe Beginning of the End • 4)Battle of Bulge (Oct. 1944) Ger. last attempt to push allies back, 76, 000 allied troops killed


The War in Europe Beginning of the End • 5)Race for Berlin – Russia and US/GB want to be first to capture Berlin


The War in Europe Beginning of the End • 6)Concentration Camps liberated – Nazis tried to hide evidence by exterminating as many Jews as possible and digging mass graves • *Shows allies what they are fighting for



The War in Europe Beginning of the End • 7) VE DAY May 8, 1945 war in Europe is over • • *Japan is still fighting and troops are supposed to now fight in Asia

END of WWII • I. Battle of the Bulge-Ger. Last counterattack (Allies suffered 60, 000 casualties, Ger 120, 000 casualties) » » – • *Ger. Never recovered and retreated the rest of the war * Apr. 29, 1945 - Russians capture Berlin and Hitler shoots himself A. VE Day –May 8, 1945 - Germany surrenders * War not over, Japan still fighting

END of WWII • II. Japan- not surrendering yet – Hiroshima and Nagasaki- Atomic bomb dropped on both cities • *Sep. 2, 1945 - (VJ Day) Japan surrenders to Douglass Mac. Arthur

END of WWII • III. Yalta Conference – FDR (US), Churchill (GB), Stalin (Russia) meet to discuss future after WWII – A. United Nations- is established to keep international peace • 1. General Assembly- all countries meet • 2. Security Council- controlled UN military power to prevent future atrocities – a. 5 permanent members on SC- US, Russia, GB, France, China » *each has power to veto any UN actions (reason UN is ineffective)

United Nations General Assembly hall •

United Nations Security Council
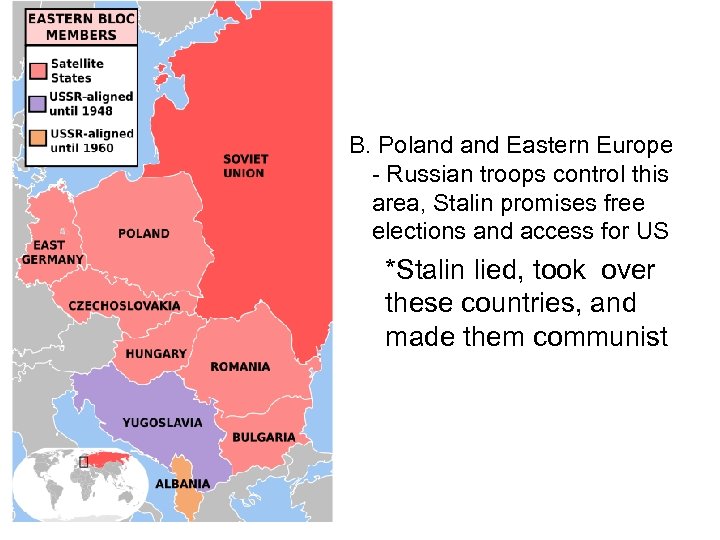
B. Poland Eastern Europe - Russian troops control this area, Stalin promises free elections and access for US • *Stalin lied, took over these countries, and made them communist

END of WWII • IV. Nuremberg War Trials- Nazi are tried for war crimes (many sentence to death or life in prison) • *1 st time nations leaders held responsible for countries actions

War in the Pacific (Japan VS. US) • Jap. Offensive – after Pearl Harbor, Japan takes more land in Pacific • Philippines – (Dec – Apr 42) US colony, US holds out for 5 months, US vows to return • *Bataan Death March – 85 mile forced march to Prison camp for US, Eng. , and Aus. POWs, 140, 000 soldiers died • *Why? Japanese believe in death before surrender, those who do surrender are cowards and deserve to die. – *March 42 – Japan controls much of Asia and Pacific


War in the Pacific (Japan VS. US) – Battle of Midway – (June 42) Japan tries to attack weak US navy after PH and capture Island of Midway – *Turning point of the war – US wins in a major air battle and puts Japan on defensive rest of the war. – Campaign against Japan – with US victory at Midway, US focus’ on pushing Jap. Back to Japan



War in the Pacific (Japan VS. US) – Battle of Guadalcanal (Aug 42 -Feb. 43) – Japan building an airstrip to bomb Aus. In Solomon Islands. – *US wins major land battle against Jap.


War in the Pacific (Japan VS. US) – Battle of Leyte Gulf – US takes back the Phil. • generally considered to be the largest naval battle of World War II – *Jap. Navy almost completely destroyed, Jap. Showing no sign of giving up.

General Douglas Mac. Arthur

The U. S. had over 3, 500 killed in action during the Battle of Leyte, and the Australian • forces had 30 killed in action.

War in the Pacific (Japan VS. US) – Iwo Jima (Feb 1945) island would allow US planes to bomb Japan (Japan expected attack and poured troops to Island) – *US marines suffered 20, 000 casualties but took the island after 1 month – *US starts firebombing Tokyo (75, 000 die in June raids)

• mission of capturing the three airfields on Iwo Jima, resulted in some of the fiercest fighting in the Pacific. • Japanese Army were heavily fortified, with a vast network of bunkers, hidden artillery, and 18 km (11 mi) of underground tunnels. • . Of the more than 18, 000 Japanese soldiers present at the beginning of the battle, only 216 were taken prisoner.

War in the Pacific (Japan VS. US) – Okinawa (Apr. – June 45) – final island needed to invade Japan – *Kamikaze – Japan suicide planes, sank 30 US ships and damaged hundreds more – *US suffered 55, 000 casualties, Japan 100, 000 (10, 000 Jap. Soldiers jumped off cliffs rather than surrender) – Japan showing no sign of surrender.
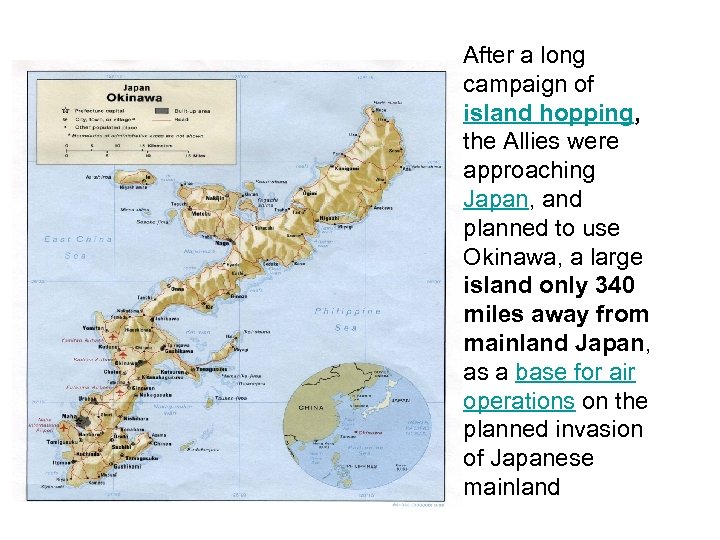
After a long campaign of island hopping, the Allies were approaching Japan, and planned to use Okinawa, a large island only 340 miles away from mainland Japan, as a base for air operations on the planned invasion of Japanese mainland

Atomic Bomb ends WWII • Atomic Bomb – largest weapon ever invented (recreates power of the sun) • Temp – 7000 degrees F • 980 wind speed • 1 mt=20, 000 tons of TNT • Albert Einstein – told FDR the Germans were trying to build an A-Bomb • *US in race with Ger. to build A-Bomb first

War in the Pacific (Japan VS. US) • Manhattan Project – produced the A-Bomb for US • July 16, 1945 - : US tests 1 st A-bomb in Los Alamos, NM • *FDR dies Apr. 1945, VP Harry Truman has to decide to use the bomb

• Nuclear War – Truman decides to drop the bomb • Hiroshima – (Aug. 6, 1945) 1 st city bombed, 78, 000 died instantly (140, 000 died by end of 1945) 200, 000 died total • Nagasaki – (Aug. 9, 1945)2 nd city bombed, 90, 000 died • *No one knew effects of radiation (slow death), thought A-bomb only produced a huge explosion • *Japan surrenders Aug. 14, 1945




• Decision to use the bomb – not easy for Truman • In Favor • End the war/save American lives-people felt an invasion of Japan would have cost 1 mil. Am. lives and millions of Japanese lives • *Japan believes in death before surrender • Stop spread of Communism – show Stalin / Soviet Union that US has the biggest weapon on earth and are willing to use it • Naivety – no one knew about the after effects of radiation

• Against – Moral Crime – using A-Bomb against civilian • *US is the only country in the world to have used A-Bomb (TWICE) – Japan surrender – many people felt Japan would have eventually surrendered, they just needed more time

Cold War • (1945 -1991) diplomatic confrontation, without battles, between… • US/Democracy VS. Soviet Union/Communism • Why? • US mistrusts communism (claims it will eventually take over the world – Workers/poor will kill the owners/rich • Communists use fear to gain power Comm. Don’t believe in freedom, private property, and religion Stalin killed his own people who spoke out against his gov. (gulag)

Soviet Union mistrust US because • US was expanding it’s influence worldwide • Economically (world buying US products…) • Politically (US influences gov. around the world) • Militarily (: US has the A-Bomb) • Socially (world wanting to act like Americans) • Soviets never want to be invaded again (20 mil. Russians died in WWII)

End of WWII • – 35 million died and Europe is completely destroyed, needs to be rebuilt • US – came out of WWII as the strongest country in the world and untouched by bombing • Soviets – need to rebuild and want to be a world power like the US – End of Allied Unity- US and Soviets fought together in WWII • *alliance was based on defending Hitler, not friendship

Stalin • – has troops in Eastern Europe and keeps those countries under Soviet control after WWII (does not set them free) • Iron Curtain – Eastern European countries that Stalin forces to become Communist

• Buffer Zone – Stalin wanted a safety area to prevent another invasion of Soviet Union • Communist Countries in Europe – Poland, Czechoslovakia, Romania, Bulgaria, Hungary, East Germany

1f56d31164b73209a80c5477c31cc9d5.ppt