8c86c83f11fbf42b2b5a9a00463beca8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 52
 World War I The “Great War” 1914 to 1918 and the results
World War I The “Great War” 1914 to 1918 and the results
 MAIN Causes of WWI Militarism n Alliances n Imperialism n Nationalism n
MAIN Causes of WWI Militarism n Alliances n Imperialism n Nationalism n
 Cause: Militarism n All major nations wanted a large army in response to nationalism, imperialism and the perceived threats from other armies
Cause: Militarism n All major nations wanted a large army in response to nationalism, imperialism and the perceived threats from other armies
 Cause: Alliances n Caused many countries to join fighting once war had begun n Before the war: Triple Alliance and Triple Entente n Later: Central Powers and Allied Powers
Cause: Alliances n Caused many countries to join fighting once war had begun n Before the war: Triple Alliance and Triple Entente n Later: Central Powers and Allied Powers
 Cause: Imperialism n Desire for increased territory and wealth led to competition over colonies
Cause: Imperialism n Desire for increased territory and wealth led to competition over colonies
 Cause: Nationalism n Desire to prove national greatness led to rivalries between great powers n Highly nationalistic ethnic groups were calling for independence (e. g. , Serbians, part of Slavic ethnic group)
Cause: Nationalism n Desire to prove national greatness led to rivalries between great powers n Highly nationalistic ethnic groups were calling for independence (e. g. , Serbians, part of Slavic ethnic group)
 What is a catalyst?
What is a catalyst?
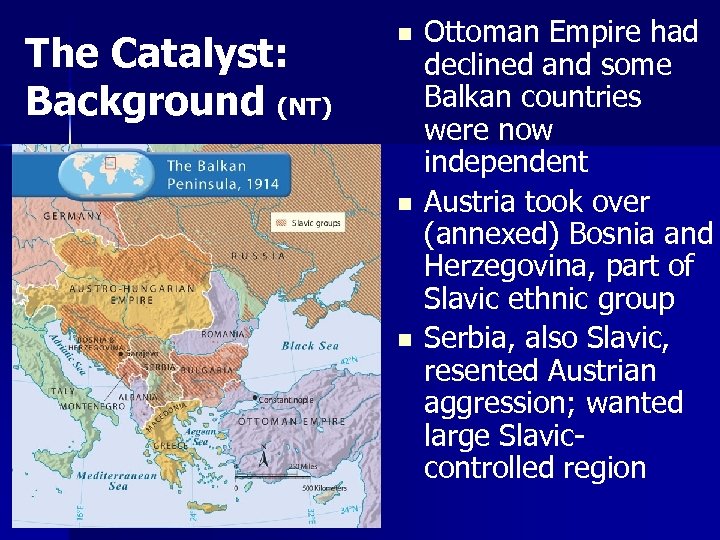 The Catalyst: Background (NT) n n n Ottoman Empire had declined and some Balkan countries were now independent Austria took over (annexed) Bosnia and Herzegovina, part of Slavic ethnic group Serbia, also Slavic, resented Austrian aggression; wanted large Slaviccontrolled region
The Catalyst: Background (NT) n n n Ottoman Empire had declined and some Balkan countries were now independent Austria took over (annexed) Bosnia and Herzegovina, part of Slavic ethnic group Serbia, also Slavic, resented Austrian aggression; wanted large Slaviccontrolled region
 The Catalyst n Assassination of Archduke Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary – Serbian nationalist group, Black Hand, wanted Bosnia freed from Austria – 19 -year-old Gavrilo Princip of the Black Hand killed the Archduke on June 28, 1914
The Catalyst n Assassination of Archduke Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary – Serbian nationalist group, Black Hand, wanted Bosnia freed from Austria – 19 -year-old Gavrilo Princip of the Black Hand killed the Archduke on June 28, 1914
 The Catalyst Leads to War – Austria wanted to punish Serbia and set demands; most agreed to, but not enough – Austria declares war against Serbia on July 28, 1914
The Catalyst Leads to War – Austria wanted to punish Serbia and set demands; most agreed to, but not enough – Austria declares war against Serbia on July 28, 1914
 War Spreads n July 28—Russia (also Slavic) mobilized troops to the Austrian border n Aug 1—Austria’s ally Germany saw this as a threat and declared war on Russia
War Spreads n July 28—Russia (also Slavic) mobilized troops to the Austrian border n Aug 1—Austria’s ally Germany saw this as a threat and declared war on Russia
 War Continues to Spread n Aug 3—Germany declared war on France, Russia’s ally n Aug 4—after Germany attacked neutral Belgium, to get to France, Britain declared war on Germany
War Continues to Spread n Aug 3—Germany declared war on France, Russia’s ally n Aug 4—after Germany attacked neutral Belgium, to get to France, Britain declared war on Germany
 Alliances Before the War Triple Alliance: – Germany, Austria-Hungary, Italy n Triple Entente: – France, Russia, Britain n
Alliances Before the War Triple Alliance: – Germany, Austria-Hungary, Italy n Triple Entente: – France, Russia, Britain n
 Alliances Shift After War Starts n Central Powers –Germany, Austria-Hungary –later, Bulgaria and Ottoman Empire (wanting to regain lost territories)
Alliances Shift After War Starts n Central Powers –Germany, Austria-Hungary –later, Bulgaria and Ottoman Empire (wanting to regain lost territories)
 n Allied Powers (the Allies) –Great Britain, France, Russia –soon Japan, and later Italy –also Serbia, Greece, Romania, etc. –much later, the U. S. (1917)
n Allied Powers (the Allies) –Great Britain, France, Russia –soon Japan, and later Italy –also Serbia, Greece, Romania, etc. –much later, the U. S. (1917)
 Europe in 1914
Europe in 1914
 “Short” war goes long n German plan worked well to start: in Paris by Sept 3 n Battle of the Marne— began on Sept 5, after 8 days of battle, German offensive was stopped n Russians soon attacking Germany in the east – the Schlieffen Plan has failed
“Short” war goes long n German plan worked well to start: in Paris by Sept 3 n Battle of the Marne— began on Sept 5, after 8 days of battle, German offensive was stopped n Russians soon attacking Germany in the east – the Schlieffen Plan has failed
 n Stuck in the trenches n Example of trench warfare – Battle of Verdun in Feb 1916—each side lost more than 300, 000 men
n Stuck in the trenches n Example of trench warfare – Battle of Verdun in Feb 1916—each side lost more than 300, 000 men
 Trenches on the Western Front
Trenches on the Western Front
 New technology of war Machine guns n Poison gas n Grenades n Armored tanks n Larger artillery: canons n Submarines n Airplanes armed with machine guns n
New technology of war Machine guns n Poison gas n Grenades n Armored tanks n Larger artillery: canons n Submarines n Airplanes armed with machine guns n
 Western Front Mostly in France, near German border n 500 miles of trenches dug in France n Trench warfare n No Man’s Land—the uninhabited land between the rows of trenches n STALEMATE—”stuck”, nobody makes any real progress n
Western Front Mostly in France, near German border n 500 miles of trenches dug in France n Trench warfare n No Man’s Land—the uninhabited land between the rows of trenches n STALEMATE—”stuck”, nobody makes any real progress n
 Eastern Front n Along Russia’s borders with Germany and Austria-Hungary n Fewer trenches, more mobile and more brutal than western front n Russians always short of supplies
Eastern Front n Along Russia’s borders with Germany and Austria-Hungary n Fewer trenches, more mobile and more brutal than western front n Russians always short of supplies
 Russia’s Role n Russia’s huge population provided plenty of soldiers to send to the front n Russia kept Germany from winning the war by occupying them in the east, dividing forces
Russia’s Role n Russia’s huge population provided plenty of soldiers to send to the front n Russia kept Germany from winning the war by occupying them in the east, dividing forces
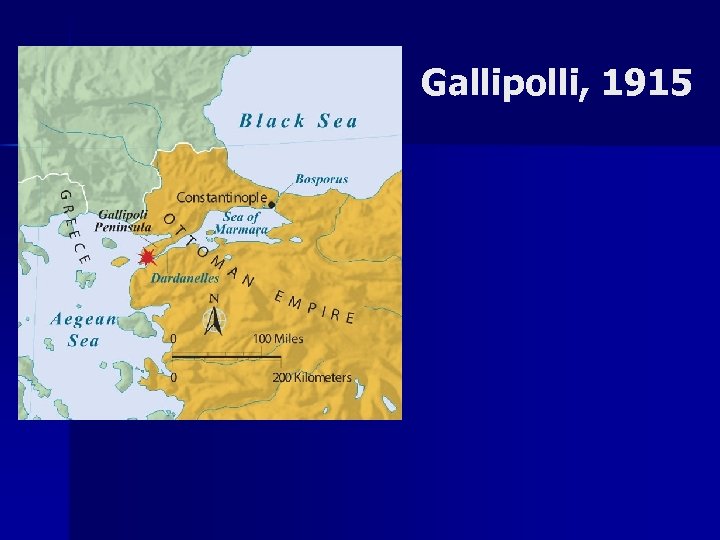 Gallipolli, 1915
Gallipolli, 1915
 “Global” war n Every continent throughout the GLOBE n Fighting over colonies n Also colonial subjects served their European masters
“Global” war n Every continent throughout the GLOBE n Fighting over colonies n Also colonial subjects served their European masters
 Who’s Fighting? Middle East (Arab nationalists helped Britain) n Asia (Japan took German colonies; India fought for Britain) n Africa (English & French wanted German land) n Americas: Brazil, Canada and later, U. S. n Australia (fighting for British) n
Who’s Fighting? Middle East (Arab nationalists helped Britain) n Asia (Japan took German colonies; India fought for Britain) n Africa (English & French wanted German land) n Americas: Brazil, Canada and later, U. S. n Australia (fighting for British) n
 “Total” War n Every country involved devoted its TOTAL resources to the war effort n Governments took over factories, etc.
“Total” War n Every country involved devoted its TOTAL resources to the war effort n Governments took over factories, etc.
 Life on the Home Front n Rationing in Europe and USA – Limiting the amount of daily supplies that people could buy (gasoline, sugar, etc. ) – On a volunteer basis in U. S. n Propaganda – Persuading the population to support the war
Life on the Home Front n Rationing in Europe and USA – Limiting the amount of daily supplies that people could buy (gasoline, sugar, etc. ) – On a volunteer basis in U. S. n Propaganda – Persuading the population to support the war




 Women worked in factories & on farms replacing men who had gone to fight
Women worked in factories & on farms replacing men who had gone to fight
 U. S. Enters the War n U. S. policy of isolationism had kept it out of the war, though they helped Allies n Unrestricted submarine warfare by Germans sank British and U. S. ships, including passenger ships (Lusitania)
U. S. Enters the War n U. S. policy of isolationism had kept it out of the war, though they helped Allies n Unrestricted submarine warfare by Germans sank British and U. S. ships, including passenger ships (Lusitania)
 U. S. Enters the War cont. n Zimmerman Note—US learned of German telegram offering Mexico US territory if it joined Germany n US entered war on April 2, 1917 n Took a year to get 2 million US soldiers over
U. S. Enters the War cont. n Zimmerman Note—US learned of German telegram offering Mexico US territory if it joined Germany n US entered war on April 2, 1917 n Took a year to get 2 million US soldiers over
 Russia Leaves the War n Bolshevik Revolution of Nov, 1917 led to Communist takeover of Russia n Bolshevik leader Lenin signed peace treaty with Germany in November, 1917 – Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
Russia Leaves the War n Bolshevik Revolution of Nov, 1917 led to Communist takeover of Russia n Bolshevik leader Lenin signed peace treaty with Germany in November, 1917 – Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
 The Russian Revolution n Russian Revolution of March, 1917 led to fall of Czar Nicholas II n 1922 Russia was renamed the USSR and became communist, a Command economy n V. I. Lenin became Soviet dictator
The Russian Revolution n Russian Revolution of March, 1917 led to fall of Czar Nicholas II n 1922 Russia was renamed the USSR and became communist, a Command economy n V. I. Lenin became Soviet dictator
 The Final Act n With Russia out, Germany could focus on Western Front n BUT…arrival of US troops and exhaustion of German army and supplies led to defeat of Germany
The Final Act n With Russia out, Germany could focus on Western Front n BUT…arrival of US troops and exhaustion of German army and supplies led to defeat of Germany
 Fighting Ends n Central Powers signed the Armistice (end to fighting)—at 11 AM Nov 11, 1918 now know as Veterans Days.
Fighting Ends n Central Powers signed the Armistice (end to fighting)—at 11 AM Nov 11, 1918 now know as Veterans Days.
 Treaty of Versailles n Allied Powers met to create a post -war treaty at the Palace of Versailles n Started on Jan 18, 1919 & signed on June 28, 1919 (5 years after assassination) n Big 4: US, France, Britain, Italy (Japan virtually shut out)
Treaty of Versailles n Allied Powers met to create a post -war treaty at the Palace of Versailles n Started on Jan 18, 1919 & signed on June 28, 1919 (5 years after assassination) n Big 4: US, France, Britain, Italy (Japan virtually shut out)
 The Fourteen-Point Plan Woodrow Wilson’s proposal for world peace – End to secret treaties – Freedom of seas – Reduce national armies and navies – Self-determination for colonial peoples – “just” peace (no harsh punishment) – League of Nations 14 th Point
The Fourteen-Point Plan Woodrow Wilson’s proposal for world peace – End to secret treaties – Freedom of seas – Reduce national armies and navies – Self-determination for colonial peoples – “just” peace (no harsh punishment) – League of Nations 14 th Point
 In the End… n Britain & France agreed to League of Nations but not the rest of Wilson’s plan
In the End… n Britain & France agreed to League of Nations but not the rest of Wilson’s plan
 n Germany was punished: –“War guilt” clause –Germany to pay $33 billion over 30 years to Allies –Lost lots of territory –Restrictions on German military
n Germany was punished: –“War guilt” clause –Germany to pay $33 billion over 30 years to Allies –Lost lots of territory –Restrictions on German military
 The Result n 4 Empires Ended: Russian, German, Ottoman, Austrian. Hungarian n Ex-colonies administered by League; colonies angry at treatment by Europe
The Result n 4 Empires Ended: Russian, German, Ottoman, Austrian. Hungarian n Ex-colonies administered by League; colonies angry at treatment by Europe
 More Results n Japan and Italy angry—gained little n Germany left virtually destroyed, broke, in debt, embittered…ready for Hitler 20 years later
More Results n Japan and Italy angry—gained little n Germany left virtually destroyed, broke, in debt, embittered…ready for Hitler 20 years later
 Total Costs n 8. 5 million soldiers died n 21 million soldiers wounded n 1918 flu epidemic killed as many as 50 million – Made worse by wartime conditions
Total Costs n 8. 5 million soldiers died n 21 million soldiers wounded n 1918 flu epidemic killed as many as 50 million – Made worse by wartime conditions
 Total Costs cont. n. A generation “lost” n Farmland, homes, & villages destroyed n Total cost in 1918 dollars: $338 billion (about $4 trillion in today’s money)
Total Costs cont. n. A generation “lost” n Farmland, homes, & villages destroyed n Total cost in 1918 dollars: $338 billion (about $4 trillion in today’s money)
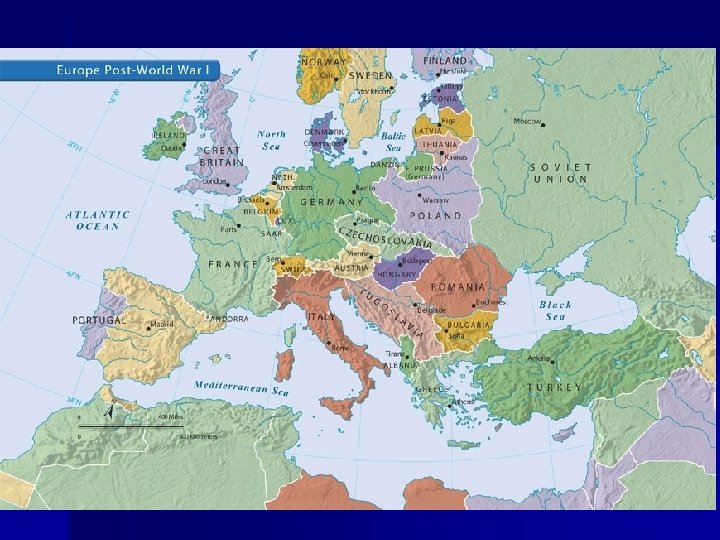
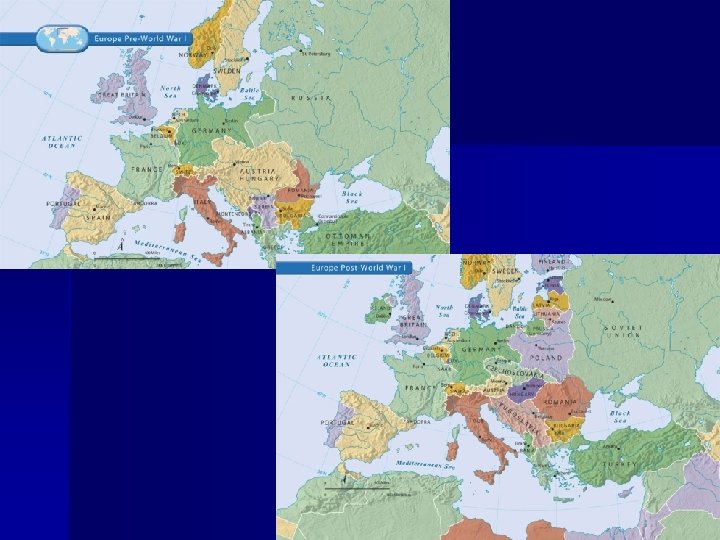
 Changes in the US after WW 1 n n n Due to the war industry in the USA grew, The women’s movement progressed, The government adopted new diplomatic policies known as Isolationism. The Great War affected all areas of life in America, Continued to have its effect for many years to come.
Changes in the US after WW 1 n n n Due to the war industry in the USA grew, The women’s movement progressed, The government adopted new diplomatic policies known as Isolationism. The Great War affected all areas of life in America, Continued to have its effect for many years to come.
 Result of the USA joining the war in 1916 n n new technologies were developed more employment opportunities opened for women and African. Americans Women embarked on campaigning for universal suffrage industry boomed, so did the economy
Result of the USA joining the war in 1916 n n new technologies were developed more employment opportunities opened for women and African. Americans Women embarked on campaigning for universal suffrage industry boomed, so did the economy
 After the end of WW 1 soldiers started to return home n industry production began to slow n less need for workers in factories n Many women stopped working n not enough jobs for the men returning n Roots of the Great Depression n
After the end of WW 1 soldiers started to return home n industry production began to slow n less need for workers in factories n Many women stopped working n not enough jobs for the men returning n Roots of the Great Depression n


