c95c1185b3caeb677edcd64486430dbd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 World War I • Causes? • Sides – Triple Entente – Central Powers • Fronts – – Western Front East Asia and the Pacific Sub-saharan Africa
World War I • Causes? • Sides – Triple Entente – Central Powers • Fronts – – Western Front East Asia and the Pacific Sub-saharan Africa
 Secret Agreements – Booking-in. Advance – Constantinople Agreement (1915) – Sykes-Picot Agreement (1916) – Balfour Declaration (1917) - Sheik Huseyin-Mc. Mahon Correspondence (1915) • Russian Revolution (1917) – Brest-Litovsk Agreement (1918) • US Intervention and the Collapse of Central Powers
Secret Agreements – Booking-in. Advance – Constantinople Agreement (1915) – Sykes-Picot Agreement (1916) – Balfour Declaration (1917) - Sheik Huseyin-Mc. Mahon Correspondence (1915) • Russian Revolution (1917) – Brest-Litovsk Agreement (1918) • US Intervention and the Collapse of Central Powers
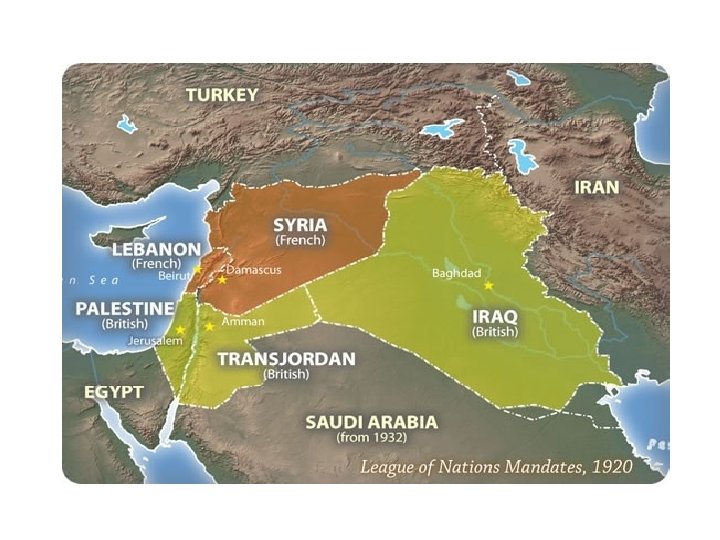
 Post-war Settlement • The Paris Settlement • The Peace Treaties – Treaty of Versailles (1919) (Germany) – Treaty of Saint-German (Austria-Hungary) – Treaty of Sevres (The Ottoman Empire) • The League of Nations • Self-Determination and Mandate System
Post-war Settlement • The Paris Settlement • The Peace Treaties – Treaty of Versailles (1919) (Germany) – Treaty of Saint-German (Austria-Hungary) – Treaty of Sevres (The Ottoman Empire) • The League of Nations • Self-Determination and Mandate System
 Post-War Economic Disasters • • The Costs of the War The Debt Problem Germany: Reparations and Inflation The Great Depression of 1929
Post-War Economic Disasters • • The Costs of the War The Debt Problem Germany: Reparations and Inflation The Great Depression of 1929
 Russia after the Revolution • • • The Birth of Soviet Union (USSR) Civil War and the N. E. P. Collectivization of Agriculture The Five-Year Plans The Great Purges
Russia after the Revolution • • • The Birth of Soviet Union (USSR) Civil War and the N. E. P. Collectivization of Agriculture The Five-Year Plans The Great Purges
 The Rise of Fascism • Mussolini in Italy • Hitler in Germany • Japanese Aggression – The Sino-Japanese War (1937 -1945)
The Rise of Fascism • Mussolini in Italy • Hitler in Germany • Japanese Aggression – The Sino-Japanese War (1937 -1945)
 World War II The Global Origins of WW II • Japan’s War in Asia and Pacific – China Under Japanese Occupation 1937 -1945 • European Aggression – Italian Invasion of Ethiopia 1935 – German Anschluss 1838 – Appeasement Politics and the Munich Conference of 1938
World War II The Global Origins of WW II • Japan’s War in Asia and Pacific – China Under Japanese Occupation 1937 -1945 • European Aggression – Italian Invasion of Ethiopia 1935 – German Anschluss 1838 – Appeasement Politics and the Munich Conference of 1938
 Total War: The World Under Fire • • Blitzkrieg: Germany Conquers Europe The Decisive Entry of USSR and US Battles in the Pacific The Holocaust and the “Final Solution”
Total War: The World Under Fire • • Blitzkrieg: Germany Conquers Europe The Decisive Entry of USSR and US Battles in the Pacific The Holocaust and the “Final Solution”
 Cold War and Decolonization • The Age of American Hegemony – Bretton Woods Agreement 1944 – IMF – World Bank • Rebuilding Europe and Marshall Plan • Beginning of Cold War: Nuclear Age
Cold War and Decolonization • The Age of American Hegemony – Bretton Woods Agreement 1944 – IMF – World Bank • Rebuilding Europe and Marshall Plan • Beginning of Cold War: Nuclear Age
 Decolonization • Three Patterns of Decolonization – Civil War (e. g. China) – Negotiated Independence (e. g. South Asia, Africa) – Incomplete Decolonization (e. g. Algeria, South Africa)
Decolonization • Three Patterns of Decolonization – Civil War (e. g. China) – Negotiated Independence (e. g. South Asia, Africa) – Incomplete Decolonization (e. g. Algeria, South Africa)
 Three Worlds • The Capitalist First World – Europe, US, Japan • The Communist Second World – USSR, Eastern Europe • The Third World – Limits to Autonomy – Third World Revolutionaries and Radicals
Three Worlds • The Capitalist First World – Europe, US, Japan • The Communist Second World – USSR, Eastern Europe • The Third World – Limits to Autonomy – Third World Revolutionaries and Radicals
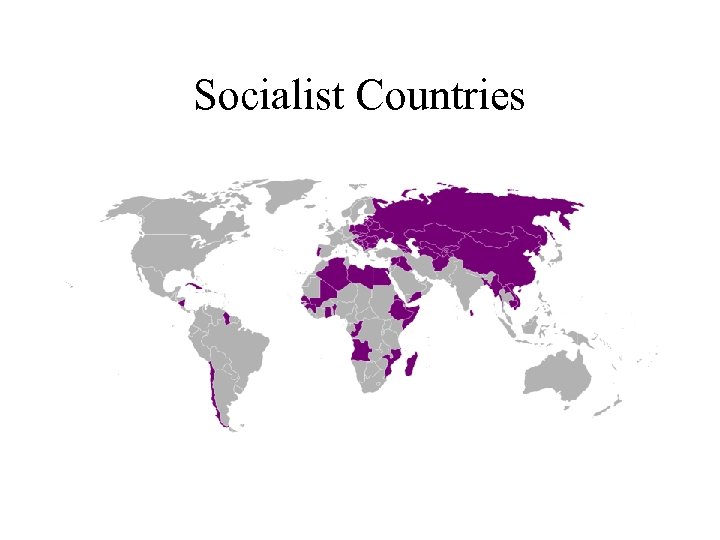 Socialist Countries
Socialist Countries
 The Middle East in the Age of Nasser • Egypt: a British colony • The Free Officers - Military Coup of 1952 • Nasser Reforms – Land reform – Elimination of Opposition • Suez Crisis of 1956 – Nationalization of Suez Canal – Egypt between US and USSR
The Middle East in the Age of Nasser • Egypt: a British colony • The Free Officers - Military Coup of 1952 • Nasser Reforms – Land reform – Elimination of Opposition • Suez Crisis of 1956 – Nationalization of Suez Canal – Egypt between US and USSR
 • Britain, France, Israel Invade Egypt (1956) • Nasser’s Influence in the ME – United Arab Republic – Yemeni Civil War • The Rise of Arab Radicalism
• Britain, France, Israel Invade Egypt (1956) • Nasser’s Influence in the ME – United Arab Republic – Yemeni Civil War • The Rise of Arab Radicalism
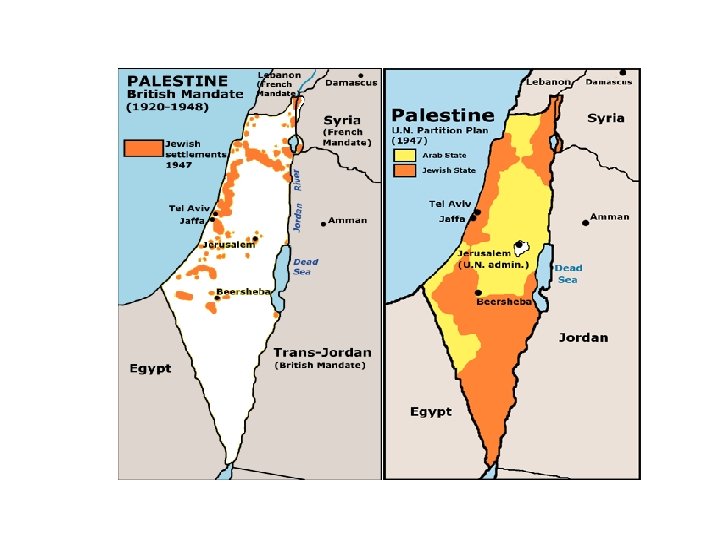
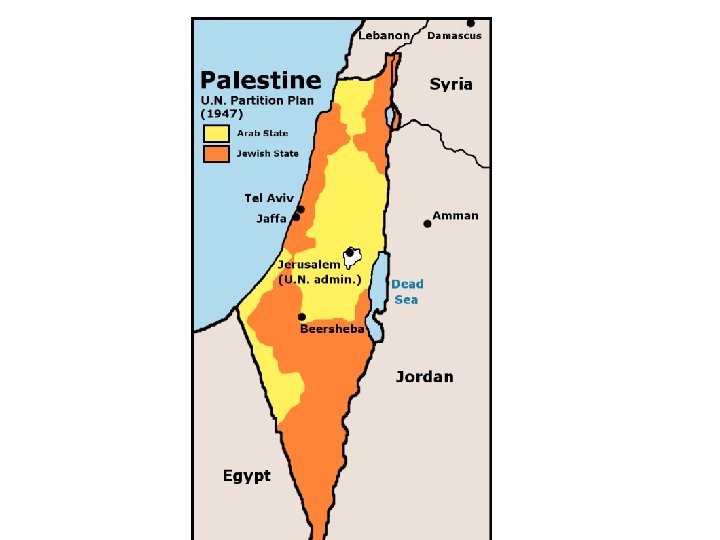
 Palestine Until 1948 • • • Theodor Herzl and Zionism Balfour Declaration of 1917 Immigration and Land Conflicts and Revolts Establishment of the State of Israel – 1948 The First Arab-Israeli War
Palestine Until 1948 • • • Theodor Herzl and Zionism Balfour Declaration of 1917 Immigration and Land Conflicts and Revolts Establishment of the State of Israel – 1948 The First Arab-Israeli War
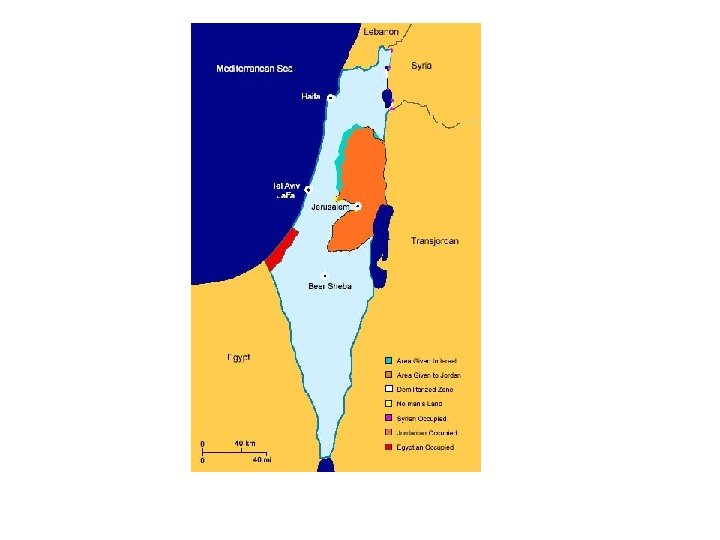
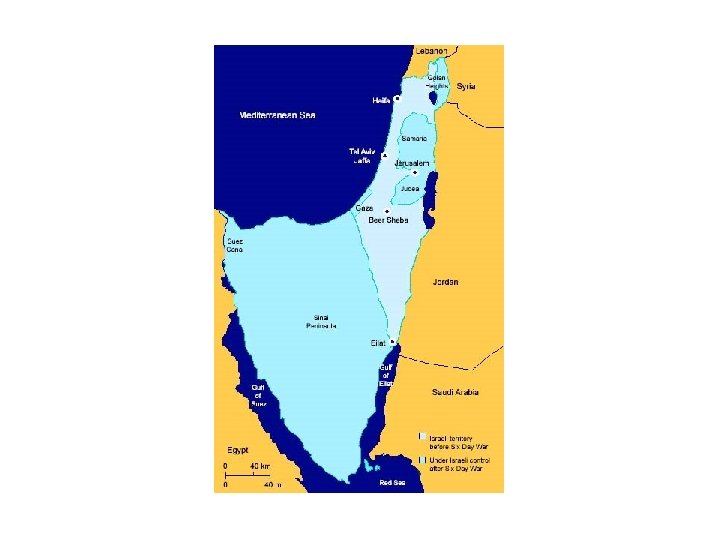
 Israel-Palestine After 1948 • The June War (1967) – Occupied Territories: • Sinai • West Bank • Golan Heights – UN Resolution 242 • PLO and Yasir Arafat • Black September of 1970
Israel-Palestine After 1948 • The June War (1967) – Occupied Territories: • Sinai • West Bank • Golan Heights – UN Resolution 242 • PLO and Yasir Arafat • Black September of 1970
 • • • Palestinians as Refugees Israeli Invasion of Lebanon – 1982 Settlement in Occupied Territories Intifada 1987 -1991 Peace?
• • • Palestinians as Refugees Israeli Invasion of Lebanon – 1982 Settlement in Occupied Territories Intifada 1987 -1991 Peace?
 Keynesian Economy • a. large state • b. involved in the economy through fiscal policies • c. involved in the economy through public investments and provides public goods.
Keynesian Economy • a. large state • b. involved in the economy through fiscal policies • c. involved in the economy through public investments and provides public goods.
 – i. public transportation – ii. public utilities like electricity, water etc • iii. roads, dams, railways, airports, seaports. • d. provides extra money through social wages – i. Social security – ii. health care iii. public education • e. wage agreement and rights to workers.
– i. public transportation – ii. public utilities like electricity, water etc • iii. roads, dams, railways, airports, seaports. • d. provides extra money through social wages – i. Social security – ii. health care iii. public education • e. wage agreement and rights to workers.
 Production (Fordism) • a. capital – i. fixed investments – ii. large stocks – iii. standardized goods – iv. cheap costs – v. rationalization
Production (Fordism) • a. capital – i. fixed investments – ii. large stocks – iii. standardized goods – iv. cheap costs – v. rationalization
 • • b. Labor i. high wages ii. routine iii. de-skilling
• • b. Labor i. high wages ii. routine iii. de-skilling
 Consumption • • New understanding of leisure and new management of time and space work day getting shorter 1920 s. 60 hours 1929 48 hours. Weekends. Saturday half day off tehn the weekend off now we have the long weekends the roads are already there and the cars but new spaces of leisure. Country suddenly became accessible. Vacation homes, tourist cabins, motels. eating out macdonalds
Consumption • • New understanding of leisure and new management of time and space work day getting shorter 1920 s. 60 hours 1929 48 hours. Weekends. Saturday half day off tehn the weekend off now we have the long weekends the roads are already there and the cars but new spaces of leisure. Country suddenly became accessible. Vacation homes, tourist cabins, motels. eating out macdonalds
 • • – a new aethetics and set of values re-definition of the home (suburbanization) change of domestic space. No more separate rooms for sewing, laundry, library, drawing, servant. Tvs central; tv in the room at the center. Advertisements re-definition of feminity nuclear family. Men breadwinner, and women orginizer of consumption. Home-economics – new household appliances – fordism at home Ready food you become what you consume not what you do
• • – a new aethetics and set of values re-definition of the home (suburbanization) change of domestic space. No more separate rooms for sewing, laundry, library, drawing, servant. Tvs central; tv in the room at the center. Advertisements re-definition of feminity nuclear family. Men breadwinner, and women orginizer of consumption. Home-economics – new household appliances – fordism at home Ready food you become what you consume not what you do
 Globalization • Why should we know it? • Commodity Chains • Colonial vs. New International Division of Labor • Third World, IMF, World Bank • Transnational Corporations • Social Responses to Globalization
Globalization • Why should we know it? • Commodity Chains • Colonial vs. New International Division of Labor • Third World, IMF, World Bank • Transnational Corporations • Social Responses to Globalization
 Elements of Globalization • Market based rather than state managed development strategies, • Centralized Management of Global Rules by G 7 • Implementation of these rules by IMF-World Bank • Concentration of market power in the hands of TNCs • Subordination of former Second world and Third world states to these global institutional forces
Elements of Globalization • Market based rather than state managed development strategies, • Centralized Management of Global Rules by G 7 • Implementation of these rules by IMF-World Bank • Concentration of market power in the hands of TNCs • Subordination of former Second world and Third world states to these global institutional forces
 Effects of Globalization • • Separation of Power from Politics Migrations Widening gap between rich and poor Multiculturalism and the Rise of Identity Politics • Gettoization and Segregation
Effects of Globalization • • Separation of Power from Politics Migrations Widening gap between rich and poor Multiculturalism and the Rise of Identity Politics • Gettoization and Segregation


