8d88be1ea080a3c88dfa4169340e173d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 World Trends in Telecommunications Eric Tyson Director Commercial Services Inter. Connect Communications
World Trends in Telecommunications Eric Tyson Director Commercial Services Inter. Connect Communications
 Eric Tyson 11 Years with BT, in Regulatory Affairs, Overseas Sales and International Relations 9 years with Inter. Connect Communications, currently Director of Commercial Services Recent work has focused on Interconnection, cost allocation and business planning Developed RIOs and RUOs for operators and interconnection regimes for regulators Developed cost allocation models for Regulators, Incumbent Operators and New Entrant Operators Undertaken costing for both fixed and mobile networks
Eric Tyson 11 Years with BT, in Regulatory Affairs, Overseas Sales and International Relations 9 years with Inter. Connect Communications, currently Director of Commercial Services Recent work has focused on Interconnection, cost allocation and business planning Developed RIOs and RUOs for operators and interconnection regimes for regulators Developed cost allocation models for Regulators, Incumbent Operators and New Entrant Operators Undertaken costing for both fixed and mobile networks
 Inter. Connect Communications Established in 1984 Focused on providing professional services to telecommunications operators, equipment suppliers and regulators Worked in Europe, CEEC, Middle East, Africa and Asia Multi disciplined staff based in the UK drawn from operational positions within operators, regulators, lawyers and suppliers Acquired by the Business Optimisation Services (BOS) of Telcordia Technologies in March 2001
Inter. Connect Communications Established in 1984 Focused on providing professional services to telecommunications operators, equipment suppliers and regulators Worked in Europe, CEEC, Middle East, Africa and Asia Multi disciplined staff based in the UK drawn from operational positions within operators, regulators, lawyers and suppliers Acquired by the Business Optimisation Services (BOS) of Telcordia Technologies in March 2001
 Agenda Economic background Policy Privatisation Regulation Summary
Agenda Economic background Policy Privatisation Regulation Summary
 Economic background Telecommunications is an enabler for economic development Long term investments in network infrastructure have been by the incumbent operators Customer expectations are for more services at lower prices Fixed network infrastructure provision no longer seen as attractive Mobile service tariff regulation is not carried out in the same way as in fixed networks Is the balance correct between the incentives offered to new entrants and to the existing incumbents?
Economic background Telecommunications is an enabler for economic development Long term investments in network infrastructure have been by the incumbent operators Customer expectations are for more services at lower prices Fixed network infrastructure provision no longer seen as attractive Mobile service tariff regulation is not carried out in the same way as in fixed networks Is the balance correct between the incentives offered to new entrants and to the existing incumbents?
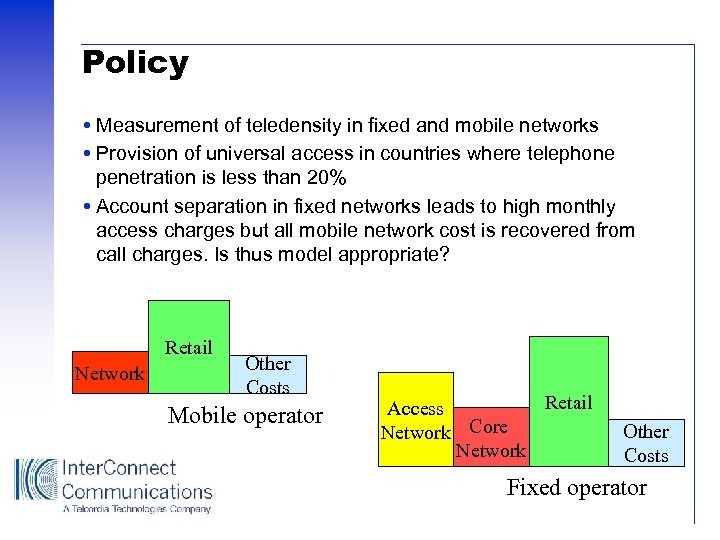 Policy Measurement of teledensity in fixed and mobile networks Provision of universal access in countries where telephone penetration is less than 20% Account separation in fixed networks leads to high monthly access charges but all mobile network cost is recovered from call charges. Is thus model appropriate? Retail Network Other Costs Mobile operator Retail Access Network Core Network Other Costs Fixed operator
Policy Measurement of teledensity in fixed and mobile networks Provision of universal access in countries where telephone penetration is less than 20% Account separation in fixed networks leads to high monthly access charges but all mobile network cost is recovered from call charges. Is thus model appropriate? Retail Network Other Costs Mobile operator Retail Access Network Core Network Other Costs Fixed operator
 Policy Competition in all services, including broadband, seen as the way of maximising customer choice and value What USO obligation is appropriate, who should provide it and who should pay or it? Mobile networks seen as the main providers of voice services and are largely unregulated Fixed networks potentially seen as providing data services but are heavily regulated (especially their voice and ULL services) Mobile services, particularly 3 G, and IP seen as the future way to spread ICT Is this balance right and does offer an appropriate long term approach?
Policy Competition in all services, including broadband, seen as the way of maximising customer choice and value What USO obligation is appropriate, who should provide it and who should pay or it? Mobile networks seen as the main providers of voice services and are largely unregulated Fixed networks potentially seen as providing data services but are heavily regulated (especially their voice and ULL services) Mobile services, particularly 3 G, and IP seen as the future way to spread ICT Is this balance right and does offer an appropriate long term approach?
 Privatisation Private sector involvement has brought significant investment into the telecommunications sector in recent years Telecoms seen by Governments as a “cash cow”: – 3 G licence fees – fee expectations from further GSM licenses in some countries (e. g. Lebanon, Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, Oman, Cyprus etc) Telecommunications is still highly political and incumbent fixed line operators still at very different stages to face competition A new entrant in a country is usually the incumbent in another country
Privatisation Private sector involvement has brought significant investment into the telecommunications sector in recent years Telecoms seen by Governments as a “cash cow”: – 3 G licence fees – fee expectations from further GSM licenses in some countries (e. g. Lebanon, Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, Oman, Cyprus etc) Telecommunications is still highly political and incumbent fixed line operators still at very different stages to face competition A new entrant in a country is usually the incumbent in another country
 Regulation Separate regulation of infrastructure and services Regulation still not technology neutral – fixed vs mobile, 2 G vs 3 G, cable modem vs ADSL Focus on voice telephony but not on voice over IP Regulation being adopted by Benchmark or political pressure rather than suitability to local circumstances EU expansion countries required to adopt EU Directives rapidly Development of sector wide “Super Regulators” e. g. Ofcom – sign of convergence Other sectors (primarily Broadcasting and content) more central to their activities
Regulation Separate regulation of infrastructure and services Regulation still not technology neutral – fixed vs mobile, 2 G vs 3 G, cable modem vs ADSL Focus on voice telephony but not on voice over IP Regulation being adopted by Benchmark or political pressure rather than suitability to local circumstances EU expansion countries required to adopt EU Directives rapidly Development of sector wide “Super Regulators” e. g. Ofcom – sign of convergence Other sectors (primarily Broadcasting and content) more central to their activities
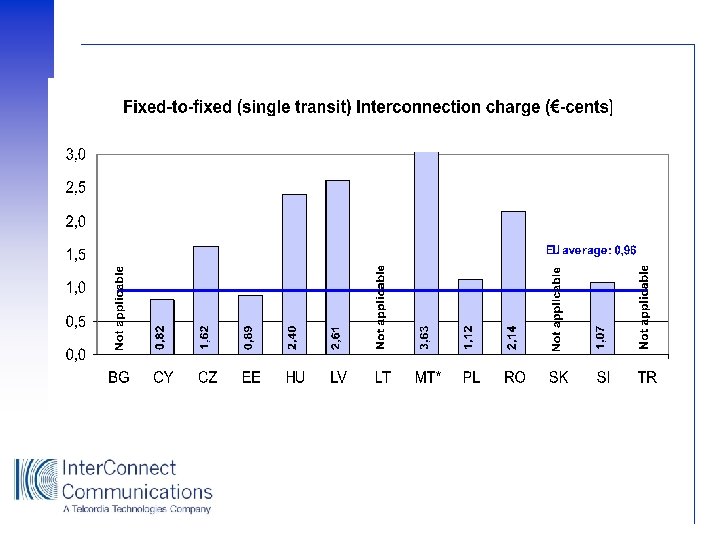
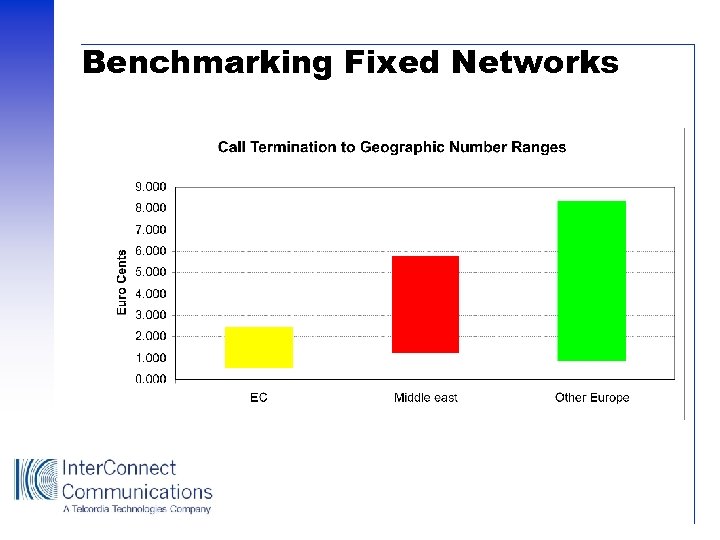 Benchmarking Fixed Networks
Benchmarking Fixed Networks
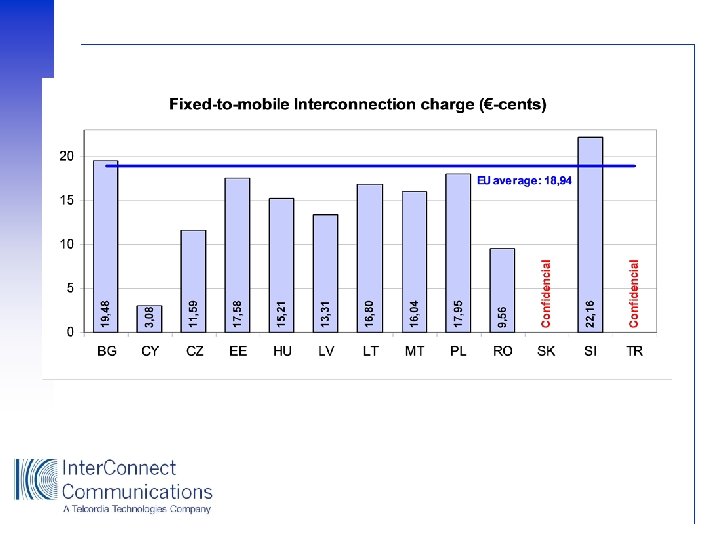
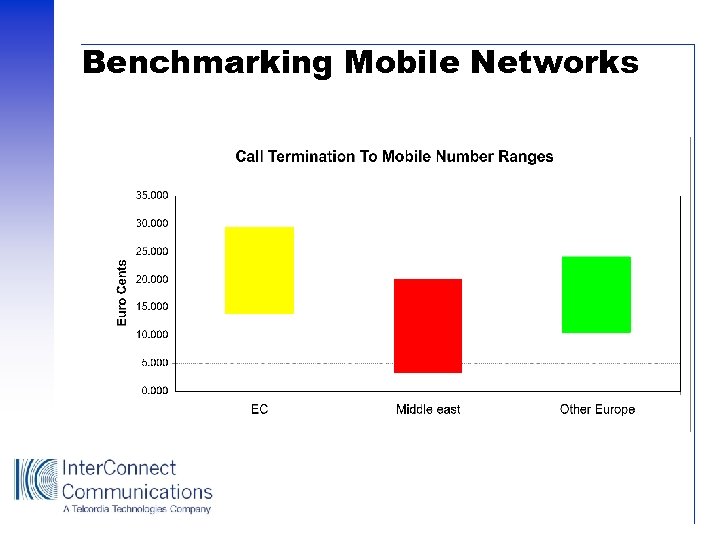 Benchmarking Mobile Networks
Benchmarking Mobile Networks
 Summary Is the regulatory balance right? How appropriate is Western European Regulation in non European countries? e. g. –LRIC costing for interconnection –Local Loop Unbundling –How to achieve tariff rebalancing in low GDP countries –Ensure balance between fixed and mobile operators
Summary Is the regulatory balance right? How appropriate is Western European Regulation in non European countries? e. g. –LRIC costing for interconnection –Local Loop Unbundling –How to achieve tariff rebalancing in low GDP countries –Ensure balance between fixed and mobile operators
 Inter. Connect Communications Ltd Merlin House Station Road Chepstow NP 16 5 PB United Kingdom Telephone: +44 (0) 1291 638400 Fax: +44 (0) 1291 638401 Email: erictyson@icc-uk. com Website: www. icc-uk. com
Inter. Connect Communications Ltd Merlin House Station Road Chepstow NP 16 5 PB United Kingdom Telephone: +44 (0) 1291 638400 Fax: +44 (0) 1291 638401 Email: erictyson@icc-uk. com Website: www. icc-uk. com


