8581657bd897b5b4f2590fac5940a345.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 World Meteorological Organization Working together in weather, climate and water WMO Climate services for improved disaster risk reduction National – Regional - Global Dr Maryam Golnaraghi Chief of Disaster Risk Reduction Programme www. wmo. int
World Meteorological Organization Working together in weather, climate and water WMO Climate services for improved disaster risk reduction National – Regional - Global Dr Maryam Golnaraghi Chief of Disaster Risk Reduction Programme www. wmo. int
 WMO Disaster Risk Reduction Programme was established in 2003 to … Leverage WMO Research and Operational Capacities to Address Meteorological, Hydrological and Climate Information Challenge in supporting DRM at all levels
WMO Disaster Risk Reduction Programme was established in 2003 to … Leverage WMO Research and Operational Capacities to Address Meteorological, Hydrological and Climate Information Challenge in supporting DRM at all levels
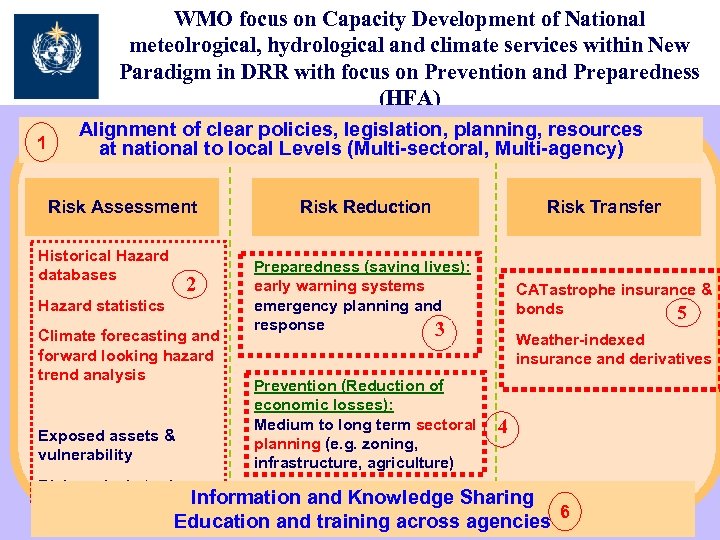 WMO focus on Capacity Development of National meteolrogical, hydrological and climate services within New Paradigm in DRR with focus on Prevention and Preparedness (HFA) 1 Alignment of clear policies, legislation, planning, resources at national to local Levels (Multi-sectoral, Multi-agency) Risk Assessment Historical Hazard databases 2 Hazard statistics Climate forecasting and forward looking hazard trend analysis Exposed assets & vulnerability Risk analysis tools Risk Reduction Risk Transfer Preparedness (saving lives): early warning systems emergency planning and response 3 Prevention (Reduction of economic losses): Medium to long term sectoral planning (e. g. zoning, infrastructure, agriculture) CATastrophe insurance & bonds 5 Weather-indexed insurance and derivatives 4 Information and Knowledge Sharing 6 Education and training across agencies
WMO focus on Capacity Development of National meteolrogical, hydrological and climate services within New Paradigm in DRR with focus on Prevention and Preparedness (HFA) 1 Alignment of clear policies, legislation, planning, resources at national to local Levels (Multi-sectoral, Multi-agency) Risk Assessment Historical Hazard databases 2 Hazard statistics Climate forecasting and forward looking hazard trend analysis Exposed assets & vulnerability Risk analysis tools Risk Reduction Risk Transfer Preparedness (saving lives): early warning systems emergency planning and response 3 Prevention (Reduction of economic losses): Medium to long term sectoral planning (e. g. zoning, infrastructure, agriculture) CATastrophe insurance & bonds 5 Weather-indexed insurance and derivatives 4 Information and Knowledge Sharing 6 Education and training across agencies
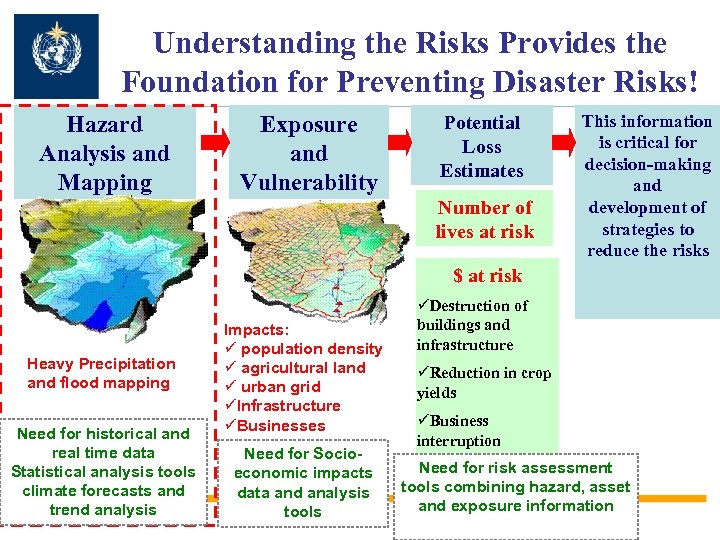 Understanding the Risks Provides the Foundation for Preventing Disaster Risks! Hazard Analysis and Mapping Exposure and Vulnerability Potential Loss Estimates Number of lives at risk This information is critical for decision-making and development of strategies to reduce the risks $ at risk Heavy Precipitation and flood mapping Need for historical and real time data Statistical analysis tools climate forecasts and trend analysis Impacts: ü population density ü agricultural land ü urban grid üInfrastructure üBusinesses Need for Socioeconomic impacts data and analysis tools üDestruction of buildings and infrastructure üReduction in crop yields üBusiness interruption Need for risk assessment tools combining hazard, asset and exposure information
Understanding the Risks Provides the Foundation for Preventing Disaster Risks! Hazard Analysis and Mapping Exposure and Vulnerability Potential Loss Estimates Number of lives at risk This information is critical for decision-making and development of strategies to reduce the risks $ at risk Heavy Precipitation and flood mapping Need for historical and real time data Statistical analysis tools climate forecasts and trend analysis Impacts: ü population density ü agricultural land ü urban grid üInfrastructure üBusinesses Need for Socioeconomic impacts data and analysis tools üDestruction of buildings and infrastructure üReduction in crop yields üBusiness interruption Need for risk assessment tools combining hazard, asset and exposure information
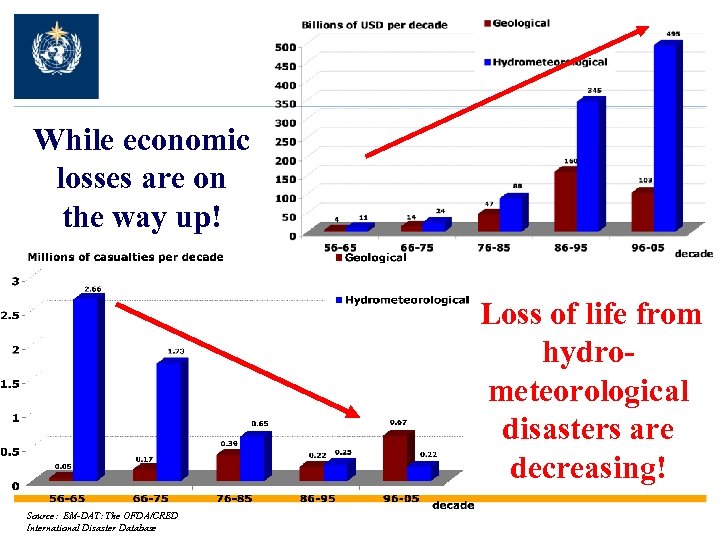 While economic losses are on the way up! Loss of life from hydrometeorological disasters are decreasing! Source: EM-DAT: The OFDA/CRED International Disaster Database
While economic losses are on the way up! Loss of life from hydrometeorological disasters are decreasing! Source: EM-DAT: The OFDA/CRED International Disaster Database
 Early Warning Systems save lives Coordination Across Many Levels and Agencies National to local disaster risk reduction plans, legislation and coordination mechanisms 1 3 2 4
Early Warning Systems save lives Coordination Across Many Levels and Agencies National to local disaster risk reduction plans, legislation and coordination mechanisms 1 3 2 4
 Recent advances in seasonal climate forecasting and trend analysis provide unprecedented opportunities…. …. to support sectoral risk assessment and management! • • Land zoning Infrastructure and Urban planning Insurance / Finance Agricultural productivity and food security Tourism Health epidemics Water resource management
Recent advances in seasonal climate forecasting and trend analysis provide unprecedented opportunities…. …. to support sectoral risk assessment and management! • • Land zoning Infrastructure and Urban planning Insurance / Finance Agricultural productivity and food security Tourism Health epidemics Water resource management
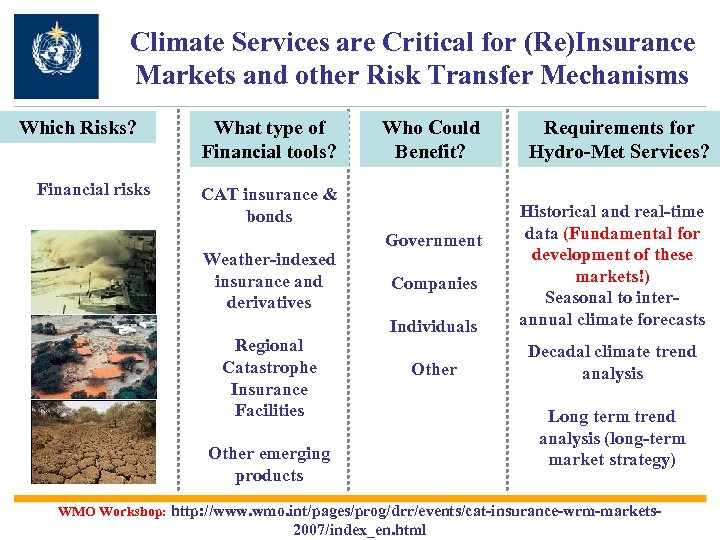 Climate Services are Critical for (Re)Insurance Markets and other Risk Transfer Mechanisms Which Risks? Financial risks What type of Financial tools? Who Could Benefit? CAT insurance & bonds Weather-indexed insurance and derivatives Regional Catastrophe Insurance Facilities Requirements for Hydro-Met Services? Individuals Historical and real-time data (Fundamental for development of these markets!) Seasonal to interannual climate forecasts Other Decadal climate trend analysis Government Companies Other emerging products Long term trend analysis (long-term market strategy) WMO Workshop: http: //www. wmo. int/pages/prog/drr/events/cat-insurance-wrm-markets- 2007/index_en. html
Climate Services are Critical for (Re)Insurance Markets and other Risk Transfer Mechanisms Which Risks? Financial risks What type of Financial tools? Who Could Benefit? CAT insurance & bonds Weather-indexed insurance and derivatives Regional Catastrophe Insurance Facilities Requirements for Hydro-Met Services? Individuals Historical and real-time data (Fundamental for development of these markets!) Seasonal to interannual climate forecasts Other Decadal climate trend analysis Government Companies Other emerging products Long term trend analysis (long-term market strategy) WMO Workshop: http: //www. wmo. int/pages/prog/drr/events/cat-insurance-wrm-markets- 2007/index_en. html
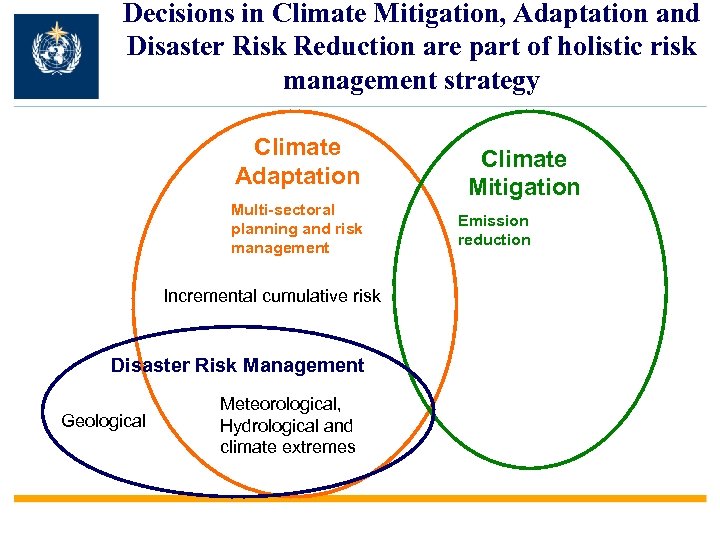 Decisions in Climate Mitigation, Adaptation and Disaster Risk Reduction are part of holistic risk management strategy Climate Adaptation Multi-sectoral planning and risk management Incremental cumulative risk Disaster Risk Management Geological Meteorological, Hydrological and climate extremes Climate Mitigation Emission reduction
Decisions in Climate Mitigation, Adaptation and Disaster Risk Reduction are part of holistic risk management strategy Climate Adaptation Multi-sectoral planning and risk management Incremental cumulative risk Disaster Risk Management Geological Meteorological, Hydrological and climate extremes Climate Mitigation Emission reduction
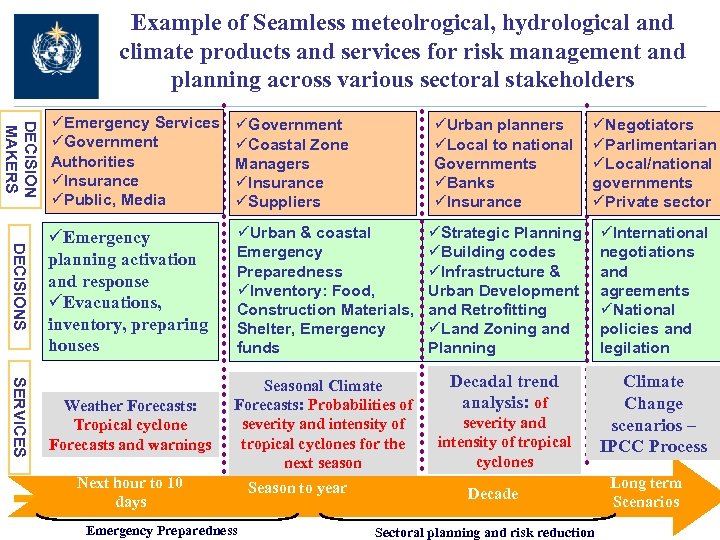 Example of Seamless meteolrogical, hydrological and climate products and services for risk management and planning across various sectoral stakeholders DECISION MAKERS DECISIONS SERVICES üEmergency Services üGovernment Authorities üInsurance üPublic, Media üGovernment üCoastal Zone Managers üInsurance üSuppliers üEmergency planning activation and response üEvacuations, inventory, preparing houses Weather Forecasts: Tropical cyclone Forecasts and warnings üUrban planners üLocal to national Governments üBanks üInsurance üNegotiators üParlimentarian üLocal/national governments üPrivate sector üUrban & coastal Emergency Preparedness üInventory: Food, Construction Materials, Shelter, Emergency funds üStrategic Planning üBuilding codes üInfrastructure & Urban Development and Retrofitting üLand Zoning and Planning üInternational negotiations and agreements üNational policies and legilation Seasonal Climate Forecasts: Probabilities of severity and intensity of tropical cyclones for the next season Decadal trend analysis: of Climate Change scenarios – IPCC Process Next hour to 10 days Emergency Preparedness Season to year severity and intensity of tropical cyclones Decade Sectoral planning and risk reduction Long term Scenarios
Example of Seamless meteolrogical, hydrological and climate products and services for risk management and planning across various sectoral stakeholders DECISION MAKERS DECISIONS SERVICES üEmergency Services üGovernment Authorities üInsurance üPublic, Media üGovernment üCoastal Zone Managers üInsurance üSuppliers üEmergency planning activation and response üEvacuations, inventory, preparing houses Weather Forecasts: Tropical cyclone Forecasts and warnings üUrban planners üLocal to national Governments üBanks üInsurance üNegotiators üParlimentarian üLocal/national governments üPrivate sector üUrban & coastal Emergency Preparedness üInventory: Food, Construction Materials, Shelter, Emergency funds üStrategic Planning üBuilding codes üInfrastructure & Urban Development and Retrofitting üLand Zoning and Planning üInternational negotiations and agreements üNational policies and legilation Seasonal Climate Forecasts: Probabilities of severity and intensity of tropical cyclones for the next season Decadal trend analysis: of Climate Change scenarios – IPCC Process Next hour to 10 days Emergency Preparedness Season to year severity and intensity of tropical cyclones Decade Sectoral planning and risk reduction Long term Scenarios
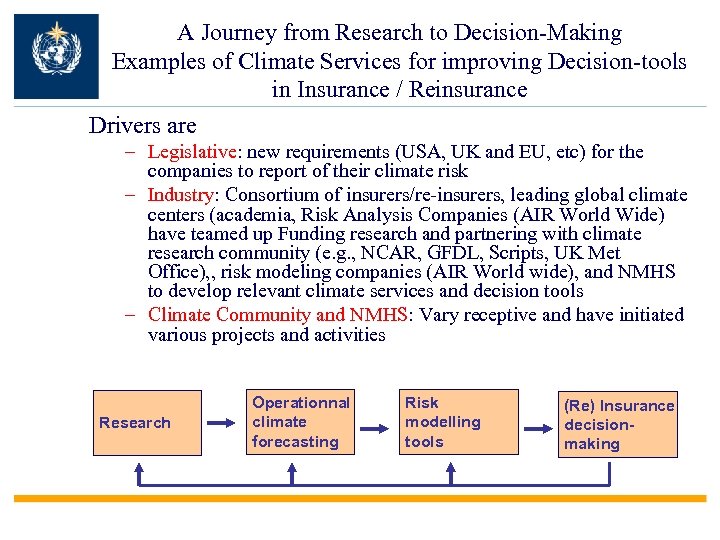 A Journey from Research to Decision-Making Examples of Climate Services for improving Decision-tools in Insurance / Reinsurance Drivers are – Legislative: new requirements (USA, UK and EU, etc) for the companies to report of their climate risk – Industry: Consortium of insurers/re-insurers, leading global climate centers (academia, Risk Analysis Companies (AIR World Wide) have teamed up Funding research and partnering with climate research community (e. g. , NCAR, GFDL, Scripts, UK Met Office), , risk modeling companies (AIR World wide), and NMHS to develop relevant climate services and decision tools – Climate Community and NMHS: Vary receptive and have initiated various projects and activities Research Operationnal climate forecasting Risk modelling tools (Re) Insurance decisionmaking
A Journey from Research to Decision-Making Examples of Climate Services for improving Decision-tools in Insurance / Reinsurance Drivers are – Legislative: new requirements (USA, UK and EU, etc) for the companies to report of their climate risk – Industry: Consortium of insurers/re-insurers, leading global climate centers (academia, Risk Analysis Companies (AIR World Wide) have teamed up Funding research and partnering with climate research community (e. g. , NCAR, GFDL, Scripts, UK Met Office), , risk modeling companies (AIR World wide), and NMHS to develop relevant climate services and decision tools – Climate Community and NMHS: Vary receptive and have initiated various projects and activities Research Operationnal climate forecasting Risk modelling tools (Re) Insurance decisionmaking
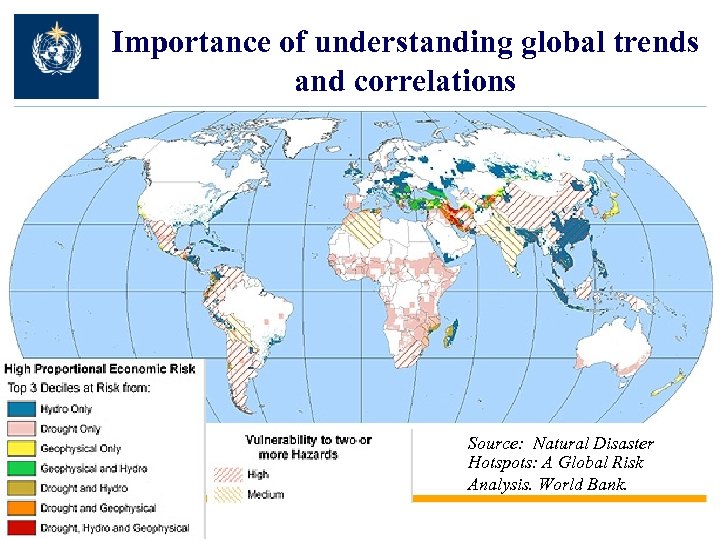 Importance of understanding global trends and correlations Source: Natural Disaster Hotspots: A Global Risk Analysis. World Bank.
Importance of understanding global trends and correlations Source: Natural Disaster Hotspots: A Global Risk Analysis. World Bank.
 Highly Diverse Users of Climate Information at different levels • Global: – International policy negotiations – International development and funding agencies – Multi-nationals and global companies (private) • Regional – – Inter-governmental economic groupings Regional development banks Private sector Multi- and bi-lateral national cooperation and planning • National to local – – Government and policy applications Strategic planning (Public and private sectors) Medium to long-term operational planning (multi-sectoral) Long term infrastructure planning and development
Highly Diverse Users of Climate Information at different levels • Global: – International policy negotiations – International development and funding agencies – Multi-nationals and global companies (private) • Regional – – Inter-governmental economic groupings Regional development banks Private sector Multi- and bi-lateral national cooperation and planning • National to local – – Government and policy applications Strategic planning (Public and private sectors) Medium to long-term operational planning (multi-sectoral) Long term infrastructure planning and development
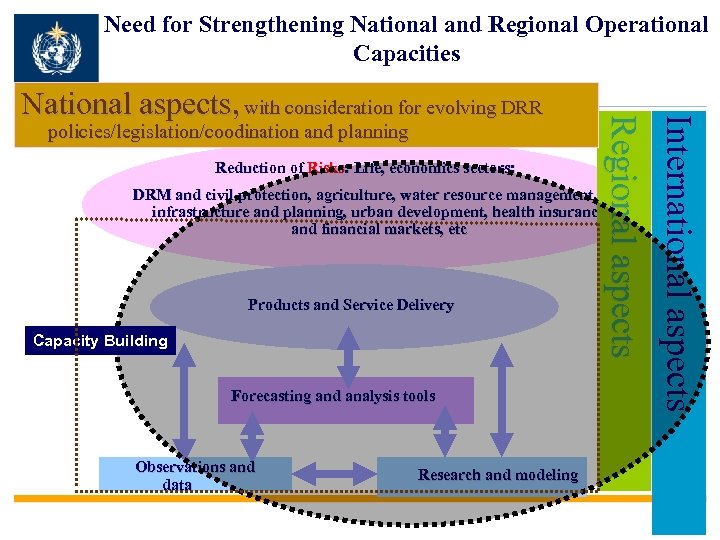 Need for Strengthening National and Regional Operational Capacities policies/legislation/coodination and planning Reduction of Risks: Life, economics sectors: International aspects Regional aspects National aspects, with consideration for evolving DRR DRM and civil protection, agriculture, water resource management, infrastructure and planning, urban development, health insurance and financial markets, etc Products and Service Delivery Capacity Building Forecasting and analysis tools Observations and data Research and modeling
Need for Strengthening National and Regional Operational Capacities policies/legislation/coodination and planning Reduction of Risks: Life, economics sectors: International aspects Regional aspects National aspects, with consideration for evolving DRR DRM and civil protection, agriculture, water resource management, infrastructure and planning, urban development, health insurance and financial markets, etc Products and Service Delivery Capacity Building Forecasting and analysis tools Observations and data Research and modeling
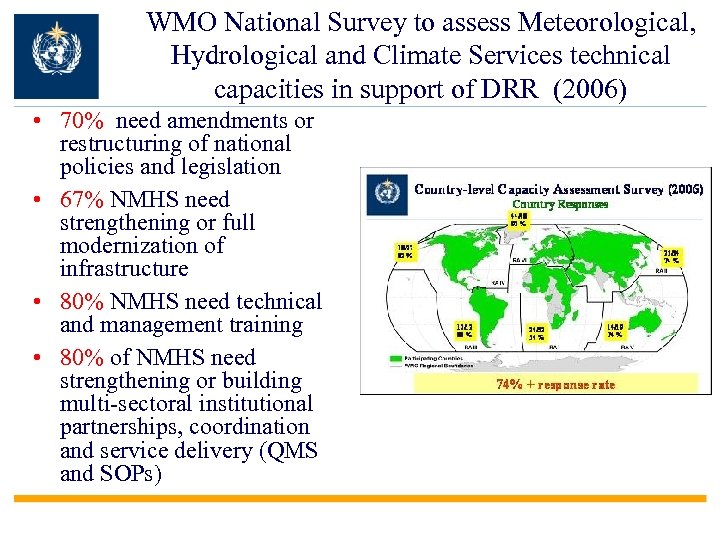 WMO National Survey to assess Meteorological, Hydrological and Climate Services technical capacities in support of DRR (2006) • 70% need amendments or restructuring of national policies and legislation • 67% NMHS need strengthening or full modernization of infrastructure • 80% NMHS need technical and management training • 80% of NMHS need strengthening or building multi-sectoral institutional partnerships, coordination and service delivery (QMS and SOPs)
WMO National Survey to assess Meteorological, Hydrological and Climate Services technical capacities in support of DRR (2006) • 70% need amendments or restructuring of national policies and legislation • 67% NMHS need strengthening or full modernization of infrastructure • 80% NMHS need technical and management training • 80% of NMHS need strengthening or building multi-sectoral institutional partnerships, coordination and service delivery (QMS and SOPs)
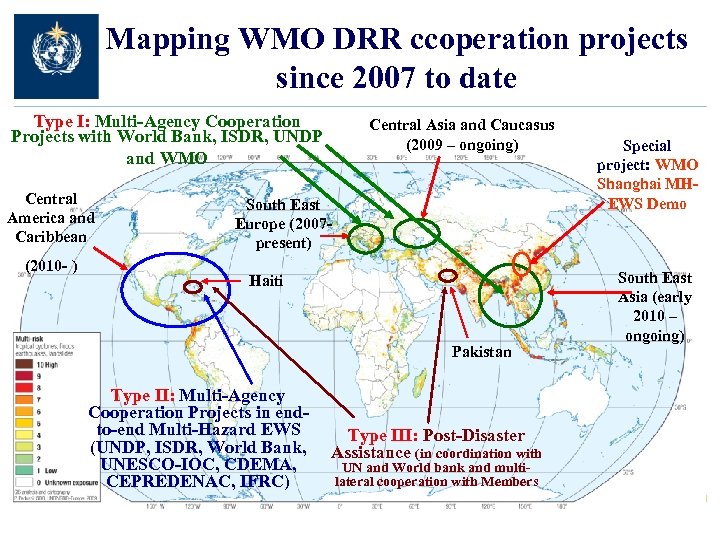 Mapping WMO DRR ccoperation projects since 2007 to date Type I: Multi-Agency Cooperation Projects with World Bank, ISDR, UNDP and WMO Central America and Caribbean (2010 - ) Central Asia and Caucasus (2009 – ongoing) South East Europe (2007 present) Haiti Pakistan Type II: Multi-Agency Cooperation Projects in endto-end Multi-Hazard EWS (UNDP, ISDR, World Bank, UNESCO-IOC, CDEMA, CEPREDENAC, IFRC) Type III: Post-Disaster Assistance (in coordination with UN and World bank and multilateral cooperation with Members Special project: WMO Shanghai MHEWS Demo South East Asia (early 2010 – ongoing)
Mapping WMO DRR ccoperation projects since 2007 to date Type I: Multi-Agency Cooperation Projects with World Bank, ISDR, UNDP and WMO Central America and Caribbean (2010 - ) Central Asia and Caucasus (2009 – ongoing) South East Europe (2007 present) Haiti Pakistan Type II: Multi-Agency Cooperation Projects in endto-end Multi-Hazard EWS (UNDP, ISDR, World Bank, UNESCO-IOC, CDEMA, CEPREDENAC, IFRC) Type III: Post-Disaster Assistance (in coordination with UN and World bank and multilateral cooperation with Members Special project: WMO Shanghai MHEWS Demo South East Asia (early 2010 – ongoing)
 Conclusions • Decisions in disaster risk reduction are interlinked with climate adaptation and mitigation • Disaster risk reduction provides new multistakeholders mechanisms (national / regional / global) for access to users and identification of their needs • Highly diverse user community at different levels (global to local) • Need for seamless products from next minute to longterm to adress risk management holistically
Conclusions • Decisions in disaster risk reduction are interlinked with climate adaptation and mitigation • Disaster risk reduction provides new multistakeholders mechanisms (national / regional / global) for access to users and identification of their needs • Highly diverse user community at different levels (global to local) • Need for seamless products from next minute to longterm to adress risk management holistically
 Thank You
Thank You


