2f4ff48d35258f38dfb6bdccc753815b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 78
 World History Overview 1500 -Present Mc. Eachern High School GHGST Saturday Tutoring
World History Overview 1500 -Present Mc. Eachern High School GHGST Saturday Tutoring
 SSWH 9 abcdefg • The student will analyze change and continuity in the Renaissance and Reformation. – Explain the social, economic, and political changes that contributed to the rise of Florence and the ideas of Machiavelli. – Identify artistic and scientific achievements of Leonardo da Vinci, the “Renaissance Man, ” and Michelangelo. – Analyze the impact of the Protestant Reformation; include the ideas of Martin Luther and John Calvin. – Describe the Counter Reformation at the Council of Trent and the role of Jesuits. – Describe the English Reformation and the role of Henry VIII and Elizabeth I. – Explain the importance of Gutenberg and the invention of the printing press.
SSWH 9 abcdefg • The student will analyze change and continuity in the Renaissance and Reformation. – Explain the social, economic, and political changes that contributed to the rise of Florence and the ideas of Machiavelli. – Identify artistic and scientific achievements of Leonardo da Vinci, the “Renaissance Man, ” and Michelangelo. – Analyze the impact of the Protestant Reformation; include the ideas of Martin Luther and John Calvin. – Describe the Counter Reformation at the Council of Trent and the role of Jesuits. – Describe the English Reformation and the role of Henry VIII and Elizabeth I. – Explain the importance of Gutenberg and the invention of the printing press.
 Explain the social, economic, and political changes that contributed to the rise of Florence and the ideas of Machiavelli. • The Italian city-states had three advantages that made it the birthplace of the Renaissance: – Thriving cities – A wealthy merchant class – The classical heritage of Greece and Rome • Machiavelli-wrote The Prince – was concerned with how a ruler gains power and how to keep it.
Explain the social, economic, and political changes that contributed to the rise of Florence and the ideas of Machiavelli. • The Italian city-states had three advantages that made it the birthplace of the Renaissance: – Thriving cities – A wealthy merchant class – The classical heritage of Greece and Rome • Machiavelli-wrote The Prince – was concerned with how a ruler gains power and how to keep it.
 Practice 1. Which statement explains why the Renaissance began in Italy? a. Italy was not influenced by a classical heritage. b. The Italian city-states were wealthy centers of trade and manufacturing. c. Italy was politically unified by a strong central government. d. The Catholic Church did not have any influence in Italy.
Practice 1. Which statement explains why the Renaissance began in Italy? a. Italy was not influenced by a classical heritage. b. The Italian city-states were wealthy centers of trade and manufacturing. c. Italy was politically unified by a strong central government. d. The Catholic Church did not have any influence in Italy.
 Identify artistic and scientific achievements of Leonardo da Vinci, the “Renaissance Man, ” and Michelangelo. • Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo both helped to shape Western art – Use of perspective-three dimension in painting – Studied anatomy to make sculptures more life-like – Frescoes-water based paint on wet plaster • Leonardo da Vinci was considered a “Renaissance Man” because he was a painter, sculptor, inventor, and scientist
Identify artistic and scientific achievements of Leonardo da Vinci, the “Renaissance Man, ” and Michelangelo. • Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo both helped to shape Western art – Use of perspective-three dimension in painting – Studied anatomy to make sculptures more life-like – Frescoes-water based paint on wet plaster • Leonardo da Vinci was considered a “Renaissance Man” because he was a painter, sculptor, inventor, and scientist
 Practice 1. In what way did Leonardo da Vinci represent the Renaissance Man? a. He was a painter, sculptor, inventor, and scientist. b. He painted the Mona Lisa while holding scientific discussions. c. He lived in Italy during the 1500’s. d. He used perspective in all his drawings and paintings. 2. Which was NOT a technique used by Italian Renaissance artists? a. Perspective b. Realistic human forms c. Frescoes d. Oil painting
Practice 1. In what way did Leonardo da Vinci represent the Renaissance Man? a. He was a painter, sculptor, inventor, and scientist. b. He painted the Mona Lisa while holding scientific discussions. c. He lived in Italy during the 1500’s. d. He used perspective in all his drawings and paintings. 2. Which was NOT a technique used by Italian Renaissance artists? a. Perspective b. Realistic human forms c. Frescoes d. Oil painting
 Analyze the impact of the Protestant Reformation; include the ideas of Martin Luther and John Calvin. • Began 1517 when Luther published his 95 Thesis (list of complaints against the Catholic Church). – – Criticized the selling of Indulgences. Bible only source of religious authority. Salvation came through faith alone in God. All people of faith were equal. • Peace of Augsburg-German princes were granted the power to decide the religion in their states. • Peace of Westphalia • Other reform movements: – Calvinism (John Calvin)-believed in predestination. – Anabaptism-
Analyze the impact of the Protestant Reformation; include the ideas of Martin Luther and John Calvin. • Began 1517 when Luther published his 95 Thesis (list of complaints against the Catholic Church). – – Criticized the selling of Indulgences. Bible only source of religious authority. Salvation came through faith alone in God. All people of faith were equal. • Peace of Augsburg-German princes were granted the power to decide the religion in their states. • Peace of Westphalia • Other reform movements: – Calvinism (John Calvin)-believed in predestination. – Anabaptism-
 Practice 1. All of the following ideas were part of martin Luther’s teachings EXCEPT a. The Bible was the only source of religious authority. b. Salvation came only through faith. c. Salvation was predestined by God. d. All people of faith were equal. 1. German princes were granted the power to decide the religion of their states in the a. Peace of Augsburg b. Edict of Worms c. Council of Trent d. Act of Supremacy
Practice 1. All of the following ideas were part of martin Luther’s teachings EXCEPT a. The Bible was the only source of religious authority. b. Salvation came only through faith. c. Salvation was predestined by God. d. All people of faith were equal. 1. German princes were granted the power to decide the religion of their states in the a. Peace of Augsburg b. Edict of Worms c. Council of Trent d. Act of Supremacy
 Describe the Counter Reformation at the Council of Trent and the role of Jesuits. • Counter Reformation-reaction of the Catholic Church to the Protestant Reformation. • Catholic Church officials meet at the Council of Trent: – The churches interpretation of the Bible was final. – Ended the sale of indulgences. – Salvation though faith AND good works. • Jesuits-evangelical male Catholic order. Goal was to spread Catholicism.
Describe the Counter Reformation at the Council of Trent and the role of Jesuits. • Counter Reformation-reaction of the Catholic Church to the Protestant Reformation. • Catholic Church officials meet at the Council of Trent: – The churches interpretation of the Bible was final. – Ended the sale of indulgences. – Salvation though faith AND good works. • Jesuits-evangelical male Catholic order. Goal was to spread Catholicism.
 Practice 1. a. b. c. d. The Council of Trent agreed that Christians need only faith for salvation. The Church’s interpretation of the Bible is final. Priests cannot pardon sinners for committing sins. The Bible is the ONLY authority or guiding Christian life. 2. A a. b. c. d. major goal of the Counter-Reformation was to reinstate the power of the Roman Catholic Church. reduce the authority of absolute monarchs. encourage new ideas in science and philosophy throughout Europe. compromise with European Protestants.
Practice 1. a. b. c. d. The Council of Trent agreed that Christians need only faith for salvation. The Church’s interpretation of the Bible is final. Priests cannot pardon sinners for committing sins. The Bible is the ONLY authority or guiding Christian life. 2. A a. b. c. d. major goal of the Counter-Reformation was to reinstate the power of the Roman Catholic Church. reduce the authority of absolute monarchs. encourage new ideas in science and philosophy throughout Europe. compromise with European Protestants.
 Describe the English Reformation and the role of Henry VIII and Elizabeth I. • Ties between the Catholic Church and England were broken for political and personal reasons. • Henry VIII wanted a son. – Asked the Pope for a divorce and was refused. – Called for Parliament to end the pope’s authority in England make the king the head of the church.
Describe the English Reformation and the role of Henry VIII and Elizabeth I. • Ties between the Catholic Church and England were broken for political and personal reasons. • Henry VIII wanted a son. – Asked the Pope for a divorce and was refused. – Called for Parliament to end the pope’s authority in England make the king the head of the church.
 Practice 1. Ties between the Catholic Church and England were broken by a. Henry VIII’s decision to execute Anne Boleyn. b. Queen Mary’s decision to bring Protestant doctrine into the English Church. c. Henry VIII’s decision to divorce Catherine of Aragon. d. The death of young Edward VI. 2. One major criticism of Elizabeth I’s reign as Queen of England was a. her failure to prepare England for future wars. b. her inability to deal with rebellions from Scotland. c. her constant entanglements with France which bankrupted the treasury. d. her failure to produce a successor.
Practice 1. Ties between the Catholic Church and England were broken by a. Henry VIII’s decision to execute Anne Boleyn. b. Queen Mary’s decision to bring Protestant doctrine into the English Church. c. Henry VIII’s decision to divorce Catherine of Aragon. d. The death of young Edward VI. 2. One major criticism of Elizabeth I’s reign as Queen of England was a. her failure to prepare England for future wars. b. her inability to deal with rebellions from Scotland. c. her constant entanglements with France which bankrupted the treasury. d. her failure to produce a successor.
 Explain the importance of Gutenberg and the invention of the printing press. • Johann Gutenberg invented the printing press in – Books became less expensive and more widely available – Expanded literacy – Spread scientific discoveries and Renaissance ideas to wider audiences.
Explain the importance of Gutenberg and the invention of the printing press. • Johann Gutenberg invented the printing press in – Books became less expensive and more widely available – Expanded literacy – Spread scientific discoveries and Renaissance ideas to wider audiences.
 Practice 1. In Western Europe, a long-term effect of the invention of Gutenberg’s printing press was that the a. monarchies were restored to absolute power. b. feudal system declined. c. literacy rate increased. d. development of new ideas was discouraged. 2. Gutenberg facilitated the spread of Renaissance ideas by a. developing a revolutionary printing method. b. opening a school in Venice for northern Europeans. c. opening a school in Florence for sculptors. d. bringing Leonardo da Vinci and other scholars to Paris.
Practice 1. In Western Europe, a long-term effect of the invention of Gutenberg’s printing press was that the a. monarchies were restored to absolute power. b. feudal system declined. c. literacy rate increased. d. development of new ideas was discouraged. 2. Gutenberg facilitated the spread of Renaissance ideas by a. developing a revolutionary printing method. b. opening a school in Venice for northern Europeans. c. opening a school in Florence for sculptors. d. bringing Leonardo da Vinci and other scholars to Paris.
 SSWH 10 abc • The student will analyze the impact of the age of discovery and expansion into the Americas, Africa, and Asia. – Explain the roles of explorers and conquistadors; include Zheng He, Vasco de Gama, Christopher Columbus, Ferdinand Magellan, James Cook, and Samuel de Champlain. – Define the Columbian Exchange and its global economic and cultural impact. – Explain the role of improved technology in European exploration; include the astrolabe.
SSWH 10 abc • The student will analyze the impact of the age of discovery and expansion into the Americas, Africa, and Asia. – Explain the roles of explorers and conquistadors; include Zheng He, Vasco de Gama, Christopher Columbus, Ferdinand Magellan, James Cook, and Samuel de Champlain. – Define the Columbian Exchange and its global economic and cultural impact. – Explain the role of improved technology in European exploration; include the astrolabe.
 Explain the roles of explorers and conquistadors; include Zheng He, Vasco de Gama, Christopher Columbus, Ferdinand Magellan, James Cook, and Samuel de Champlain. • Zheng He-China-1405 -1433 -Explored coast of South East Asia and East Africa • Vasco de Gama-Portugal-1497 -First to sail around the Cape of Good Hope to India • Christopher Columbus-Spain-1492 -Landed in the Caribbean while searching for new trade routes to Asia • Ferdinand Magellan-Italy-1519 -First to sail around the world • James Cook-England-1770 -Claimed New Zealand Australia for England • Samuel de Champlain-France-1608 -Established the Quebec colony for France
Explain the roles of explorers and conquistadors; include Zheng He, Vasco de Gama, Christopher Columbus, Ferdinand Magellan, James Cook, and Samuel de Champlain. • Zheng He-China-1405 -1433 -Explored coast of South East Asia and East Africa • Vasco de Gama-Portugal-1497 -First to sail around the Cape of Good Hope to India • Christopher Columbus-Spain-1492 -Landed in the Caribbean while searching for new trade routes to Asia • Ferdinand Magellan-Italy-1519 -First to sail around the world • James Cook-England-1770 -Claimed New Zealand Australia for England • Samuel de Champlain-France-1608 -Established the Quebec colony for France
 Practice 1. Who captained the first European ship to sail around the tip of Africa, now known as the Cape of Good Hope? a. Prince Henry b. Vasco de Gama c. Bartolomeu Dias d. Christopher Columbus 2. The main motive for European exploration in the 1400’s was a. New navigational tools. b. The invention of the caravel. c. To find new sources of wealth. d. To spread Christianity.
Practice 1. Who captained the first European ship to sail around the tip of Africa, now known as the Cape of Good Hope? a. Prince Henry b. Vasco de Gama c. Bartolomeu Dias d. Christopher Columbus 2. The main motive for European exploration in the 1400’s was a. New navigational tools. b. The invention of the caravel. c. To find new sources of wealth. d. To spread Christianity.
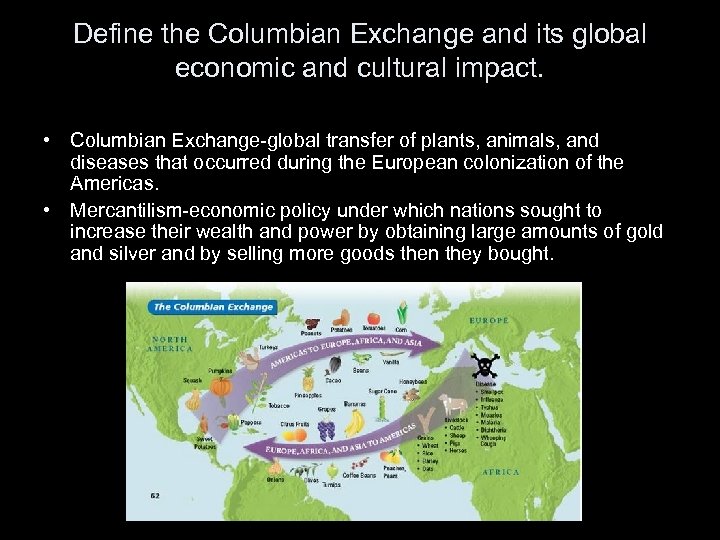 Define the Columbian Exchange and its global economic and cultural impact. • Columbian Exchange-global transfer of plants, animals, and diseases that occurred during the European colonization of the Americas. • Mercantilism-economic policy under which nations sought to increase their wealth and power by obtaining large amounts of gold and silver and by selling more goods then they bought.
Define the Columbian Exchange and its global economic and cultural impact. • Columbian Exchange-global transfer of plants, animals, and diseases that occurred during the European colonization of the Americas. • Mercantilism-economic policy under which nations sought to increase their wealth and power by obtaining large amounts of gold and silver and by selling more goods then they bought.
 Practice 1. a. b. c. d. According to the politics of mercantilism, how could a nation increase its wealth? It should center its wealth and power in its government. It should spread its wealth and power among private individuals. It should sell more goods then it buys from other countries. It should buy more goods than it sells to other countries. 2. The spread of corn and potatoes beyond the Americas a. Helped boost the world’s population. b. Preceded the Columbian Exchange. c. Caused the outbreak of disease. d. Created a favorable balance of trade.
Practice 1. a. b. c. d. According to the politics of mercantilism, how could a nation increase its wealth? It should center its wealth and power in its government. It should spread its wealth and power among private individuals. It should sell more goods then it buys from other countries. It should buy more goods than it sells to other countries. 2. The spread of corn and potatoes beyond the Americas a. Helped boost the world’s population. b. Preceded the Columbian Exchange. c. Caused the outbreak of disease. d. Created a favorable balance of trade.
 Explain the role of improved technology in European exploration; include the astrolabe. • New technology allowed explorers to travel longer distances and beyond the sight of land. – Astrolabe-used the position of stars, moon, sun and planet to determine location. – Sextant-replaced the astrolabe, measured height of stars against the horizon to determine latitude and longitude. – Caravel-triangular sails, large cargo area, could sail in shallow water.
Explain the role of improved technology in European exploration; include the astrolabe. • New technology allowed explorers to travel longer distances and beyond the sight of land. – Astrolabe-used the position of stars, moon, sun and planet to determine location. – Sextant-replaced the astrolabe, measured height of stars against the horizon to determine latitude and longitude. – Caravel-triangular sails, large cargo area, could sail in shallow water.
 Practice 1. The astrolabe and improvements in cartography helped Europeans to a. launch the Crusades. b. defeat the Mongols. c. expel the Moors. d. explore the Western Hemisphere. 2. The journeys of Vasco da Gama, Bartholomeu Dias, and Christopher Columbus becamepossible in the late 1400 s because of the a. support of exploration by the English government. b. trade connections established by Ibn Battuta. c. effects of the Atlantic slave trade. d. development of new navigational instruments and technology.
Practice 1. The astrolabe and improvements in cartography helped Europeans to a. launch the Crusades. b. defeat the Mongols. c. expel the Moors. d. explore the Western Hemisphere. 2. The journeys of Vasco da Gama, Bartholomeu Dias, and Christopher Columbus becamepossible in the late 1400 s because of the a. support of exploration by the English government. b. trade connections established by Ibn Battuta. c. effects of the Atlantic slave trade. d. development of new navigational instruments and technology.
 SSWH 13 ab • The student will examine the intellectual, political, social, and economic factors that changed the world view of Europeans. – Explain the scientific contributions of Copernicus, Galileo, Kepler, and Newton and how these ideas changed the European world view. – Identify the major ideas of the Enlightenment from the writings of Locke, Voltaire, and Rousseau and their relationship to politics and society.
SSWH 13 ab • The student will examine the intellectual, political, social, and economic factors that changed the world view of Europeans. – Explain the scientific contributions of Copernicus, Galileo, Kepler, and Newton and how these ideas changed the European world view. – Identify the major ideas of the Enlightenment from the writings of Locke, Voltaire, and Rousseau and their relationship to politics and society.
 Explain the scientific contributions of Copernicus, Galileo, Kepler, and Newton and how these ideas changed the European world view. • Scientific Revolution-change in European thought, natural world was characterized by observation and questioning. Advancements in science, medicine, and astronomy. – Challenged accepted knowledge. – Developed scientific method-only believed something if it could be tested and proven. • Copernicus-heliocentric theory • Galileo-built telescope, findings supported Copernicus, forced to recant by the Catholic Church and live under house arrest. • Kepler-Laws of planetary motion • Newton- laws of gravity and motion
Explain the scientific contributions of Copernicus, Galileo, Kepler, and Newton and how these ideas changed the European world view. • Scientific Revolution-change in European thought, natural world was characterized by observation and questioning. Advancements in science, medicine, and astronomy. – Challenged accepted knowledge. – Developed scientific method-only believed something if it could be tested and proven. • Copernicus-heliocentric theory • Galileo-built telescope, findings supported Copernicus, forced to recant by the Catholic Church and live under house arrest. • Kepler-Laws of planetary motion • Newton- laws of gravity and motion
 Practice 1. During the Scientific Revolution, scientists did all the following, except… a. challenge accepted knowledge. b. believed something only if it could be tested and proven. c. accepted tradition and traditional knowledge. d. ran experiments to test accepted knowledge. 2.
Practice 1. During the Scientific Revolution, scientists did all the following, except… a. challenge accepted knowledge. b. believed something only if it could be tested and proven. c. accepted tradition and traditional knowledge. d. ran experiments to test accepted knowledge. 2.
 Identify the major ideas of the Enlightenment from the writings of Locke, Voltaire, and Rousseau and their relationship to politics and society. • Locke- “All men have certain natural rights: the right to life, liberty, and property. The purpose of government is to protect these rights. If it fails to do so the people may set up a new government. ” • Voltaire- “it is to him who masters our minds by force of truth, not to those who enslave men by violence that we our reverence. Popular government in itself is less [unjust], less [hated] than despotic power. • Rousseau- “Man is born free, yet everywhere he is chains. The government is created by a contract among the people and receives its just powers from them. The government exists to serve the people and when it no longer does so the people may change it. ”
Identify the major ideas of the Enlightenment from the writings of Locke, Voltaire, and Rousseau and their relationship to politics and society. • Locke- “All men have certain natural rights: the right to life, liberty, and property. The purpose of government is to protect these rights. If it fails to do so the people may set up a new government. ” • Voltaire- “it is to him who masters our minds by force of truth, not to those who enslave men by violence that we our reverence. Popular government in itself is less [unjust], less [hated] than despotic power. • Rousseau- “Man is born free, yet everywhere he is chains. The government is created by a contract among the people and receives its just powers from them. The government exists to serve the people and when it no longer does so the people may change it. ”
 Practice 1. John Locke and Jean Jacques Rousseau would be most likely to support a. a return to feudalism in Europe. b. a government ruled by a divine right monarchy. c. a society ruled by the Catholic Church. d. the right of citizens to decide the best form of government. 2. One of the most results of the Enlightenment was the a. the French monarchy was strengthened. b. the status quo was reaffirmed. c. the discoveries of the Scientific Revolution was disproved. d. democratic ideals were spread.
Practice 1. John Locke and Jean Jacques Rousseau would be most likely to support a. a return to feudalism in Europe. b. a government ruled by a divine right monarchy. c. a society ruled by the Catholic Church. d. the right of citizens to decide the best form of government. 2. One of the most results of the Enlightenment was the a. the French monarchy was strengthened. b. the status quo was reaffirmed. c. the discoveries of the Scientific Revolution was disproved. d. democratic ideals were spread.
 SSWH 14 bc • The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions. – Identify the causes and results of the revolutions in England (1689), United States (1776), France (1789), Haiti (1791), Latin America (1808 -1825). – Explain Napoleon’s rise to power, and his defeat; and explain the consequences for Europe.
SSWH 14 bc • The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions. – Identify the causes and results of the revolutions in England (1689), United States (1776), France (1789), Haiti (1791), Latin America (1808 -1825). – Explain Napoleon’s rise to power, and his defeat; and explain the consequences for Europe.
 Identify the causes and results of the revolutions in England (1689), United States (1776). • Glorious Revolution – Parliament removed Charles II from power because he violated the Petition of Rights (established in – Invited William and Mary or Orange to take throne as long as the singed the English Bill of Rights – Created a constitutional monarchy in England • American Revolution – Influenced by ideas of the Enlightenment. – Colonists enforced a social contract. • Ended rule by a king • Established first large scale democracy – Declaration of Independence-written by Thomas Jefferson • Demonstrated that enlightened ideals could be used to govern country. • “Life, Liberty, and the Pursuit of Happiness. ”
Identify the causes and results of the revolutions in England (1689), United States (1776). • Glorious Revolution – Parliament removed Charles II from power because he violated the Petition of Rights (established in – Invited William and Mary or Orange to take throne as long as the singed the English Bill of Rights – Created a constitutional monarchy in England • American Revolution – Influenced by ideas of the Enlightenment. – Colonists enforced a social contract. • Ended rule by a king • Established first large scale democracy – Declaration of Independence-written by Thomas Jefferson • Demonstrated that enlightened ideals could be used to govern country. • “Life, Liberty, and the Pursuit of Happiness. ”
 Practice 1. The Glorious Revolution in England resulted in a. strengthening of divine right rule. b. formation of a limited monarchy. c. weakening of the parliament’s power over the purse. d. end of civil liberties guaranteed by the Petition of Rights. 2. How did the Declaration of Independence embody Enlightenment ideals? a. It stated that all titles of nobility should be abolished. b. It protected the rights of the accused and prohibited cruel punishment. c. It set up a system of checks and balances for the U. S. government. d. It said that people have rights of life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness.
Practice 1. The Glorious Revolution in England resulted in a. strengthening of divine right rule. b. formation of a limited monarchy. c. weakening of the parliament’s power over the purse. d. end of civil liberties guaranteed by the Petition of Rights. 2. How did the Declaration of Independence embody Enlightenment ideals? a. It stated that all titles of nobility should be abolished. b. It protected the rights of the accused and prohibited cruel punishment. c. It set up a system of checks and balances for the U. S. government. d. It said that people have rights of life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness.
 Identify the causes and results of the revolutions in France (1789). • Long term causes: – Inequality among the estates. • First Estate-Clergy (approx 1% of pop) • Second Estate-Nobility (approx 2% of pop) • Third Estate-Everyone else • Short term causes– Bankruptcy of the government – Bad harvests=food prices rise – Calling of the Estates General • Tennis Court Oath-Third Estate creates new constitution. – King forces other estates to accept. • Storming of the Bastille – First violent event of the FR • Declaration of Rights of Man and Citizen • Reign of Terror
Identify the causes and results of the revolutions in France (1789). • Long term causes: – Inequality among the estates. • First Estate-Clergy (approx 1% of pop) • Second Estate-Nobility (approx 2% of pop) • Third Estate-Everyone else • Short term causes– Bankruptcy of the government – Bad harvests=food prices rise – Calling of the Estates General • Tennis Court Oath-Third Estate creates new constitution. – King forces other estates to accept. • Storming of the Bastille – First violent event of the FR • Declaration of Rights of Man and Citizen • Reign of Terror
 Practice 1. The principles of the American Revolution and French Revolution are similar in many ways. Which of the following best summarizes their similarities? a. Both favored representative governments. b. Both limited voting rights to an economic elite. c. Both retained certain hereditary rights for aristocrats. d. Both supported equal rights for women.
Practice 1. The principles of the American Revolution and French Revolution are similar in many ways. Which of the following best summarizes their similarities? a. Both favored representative governments. b. Both limited voting rights to an economic elite. c. Both retained certain hereditary rights for aristocrats. d. Both supported equal rights for women.
 Identify the causes and results of the revolutions in Haiti (1791), Latin America (1808 -1825). • Haiti was one of France’s richest colonies-based on harsh slave labor. • Slaves used the turmoil of the French Revolution to revolt. – Led by Toussaint L’Overture – Freed all slaves on the island – France sent troops to take back the island reinstate slavery, but they were defeated by Yellow Fever and Haitian rebel fighters. • Inspired by revolutions in America, France, and Haiti Creoles (Europeans born in LA) wanted independence too. • Simon Bolivar-know as the “Liberator” for helping many nations in Latin America gain their independence. • Jose de san Martin-
Identify the causes and results of the revolutions in Haiti (1791), Latin America (1808 -1825). • Haiti was one of France’s richest colonies-based on harsh slave labor. • Slaves used the turmoil of the French Revolution to revolt. – Led by Toussaint L’Overture – Freed all slaves on the island – France sent troops to take back the island reinstate slavery, but they were defeated by Yellow Fever and Haitian rebel fighters. • Inspired by revolutions in America, France, and Haiti Creoles (Europeans born in LA) wanted independence too. • Simon Bolivar-know as the “Liberator” for helping many nations in Latin America gain their independence. • Jose de san Martin-
 Practice 1. Throughout Latin America, the fight for independence was led by a. Mestizos b. Peninsulares c. Creoles d. Indians 2. Simón Bolívar, José de San Martin, and Toussaint l’Ouverture are best known as a. scientists who supported the heliocentric theory. b. leaders of Latin American independence movements. c. early Spanish explorers of the New World. d. communist leaders of the 19 th century.
Practice 1. Throughout Latin America, the fight for independence was led by a. Mestizos b. Peninsulares c. Creoles d. Indians 2. Simón Bolívar, José de San Martin, and Toussaint l’Ouverture are best known as a. scientists who supported the heliocentric theory. b. leaders of Latin American independence movements. c. early Spanish explorers of the New World. d. communist leaders of the 19 th century.
 Explain Napoleon’s rise to power, and his defeat; and explain the consequences for Europe. • Napoleon was a popular military leader, came to power by popular consent, and declared himself emperor. – Napoleonic Code-basis for legal system in Europe for many years – Abolished estates, all MEN equal – Improved education – Restored ties between France and the Catholic Church • Napoleon’s downfall began when he invaded Russia for violating the Continental System. – 600, 000 troops lost • Final defeat came at the Battle of Waterloo – Napoleon id finally exiled to the island of St. Helena
Explain Napoleon’s rise to power, and his defeat; and explain the consequences for Europe. • Napoleon was a popular military leader, came to power by popular consent, and declared himself emperor. – Napoleonic Code-basis for legal system in Europe for many years – Abolished estates, all MEN equal – Improved education – Restored ties between France and the Catholic Church • Napoleon’s downfall began when he invaded Russia for violating the Continental System. – 600, 000 troops lost • Final defeat came at the Battle of Waterloo – Napoleon id finally exiled to the island of St. Helena
 Practice 1. Pope Pius VII’s coronation of Napoleon as emperor was the culmination of a. French military supremacy on the continent. b. the Continental system. c. restored relations between the Catholic Church and France. d. the implementation of the Napoleonic Code. 2. Napoleon’s code of laws extended the ideals of the French Revolution by a. limiting freedom of speech and of the press. b. abolishing the three estates and granting equal rights. c. permitting slavery in the French colonies. d. expanding the rights of women.
Practice 1. Pope Pius VII’s coronation of Napoleon as emperor was the culmination of a. French military supremacy on the continent. b. the Continental system. c. restored relations between the Catholic Church and France. d. the implementation of the Napoleonic Code. 2. Napoleon’s code of laws extended the ideals of the French Revolution by a. limiting freedom of speech and of the press. b. abolishing the three estates and granting equal rights. c. permitting slavery in the French colonies. d. expanding the rights of women.
 SSWH 16 abcd • The student will demonstrate an understanding of long-term causes of World War I and its global impact. – Identify the causes of the war; include Balkan nationalism, entangling alliances, and militarism. – Describe conditions on the war front for soldiers; include the Battle of Verdun. – Explain the major decisions made in the treaty of Versailles; include German reparations and the mandate system that replaced Ottoman control. – Analyze the destabilization of Europe in the collapse of the great empires; include the Romanov and Hapsburg dynasties.
SSWH 16 abcd • The student will demonstrate an understanding of long-term causes of World War I and its global impact. – Identify the causes of the war; include Balkan nationalism, entangling alliances, and militarism. – Describe conditions on the war front for soldiers; include the Battle of Verdun. – Explain the major decisions made in the treaty of Versailles; include German reparations and the mandate system that replaced Ottoman control. – Analyze the destabilization of Europe in the collapse of the great empires; include the Romanov and Hapsburg dynasties.
 Identify the causes of the war; include Balkan nationalism, entangling alliances, and militarism. • M-Militarism-policy of glorifying military power and keeping a standing army ready for war. • A-Alliances– Triple Entente-Russia, France, Great Britain – Triple Alliance-Germany, Austria-Hungary, Italy • I-Imperialism-European nations sought to dominate weaker countries socially, economically, and politically. • N-Nationalism-belief that people should be loyal to their nation of people. – “Powder Keg”-Balkan region of Europe was a hotbed of slav nationalism. • Archduke Franz Ferdinand was shot-Austria blames Serbia, Germany declares war on Russia
Identify the causes of the war; include Balkan nationalism, entangling alliances, and militarism. • M-Militarism-policy of glorifying military power and keeping a standing army ready for war. • A-Alliances– Triple Entente-Russia, France, Great Britain – Triple Alliance-Germany, Austria-Hungary, Italy • I-Imperialism-European nations sought to dominate weaker countries socially, economically, and politically. • N-Nationalism-belief that people should be loyal to their nation of people. – “Powder Keg”-Balkan region of Europe was a hotbed of slav nationalism. • Archduke Franz Ferdinand was shot-Austria blames Serbia, Germany declares war on Russia
 Practice 1. a. b. c. d. All of the following forces set the stage for WWI EXCEPT Nationalism Military alliances Ottoman decline 2. Why was the Balkan region referred to as the “Powder Keg of Europe” prior to WWI? a. The aggression of the Ottoman Empire was disrupting the balance of power. b. Yugoslavia was invading its neighboring countries. c. Nationalistic and imperialistic rivalries were competing. d. The area was the leading supplier of military equipment to the rest of the world.
Practice 1. a. b. c. d. All of the following forces set the stage for WWI EXCEPT Nationalism Military alliances Ottoman decline 2. Why was the Balkan region referred to as the “Powder Keg of Europe” prior to WWI? a. The aggression of the Ottoman Empire was disrupting the balance of power. b. Yugoslavia was invading its neighboring countries. c. Nationalistic and imperialistic rivalries were competing. d. The area was the leading supplier of military equipment to the rest of the world.
 Describe conditions on the war front for soldiers; include the Battle of Verdun. • Western Front-Germany v France and GB – Quickly became a stalemate – Trench warfare – War of attrition – New weapons-machine gun, zepplin, poison gas – Battle of Verdun-5 months, over 1 million men dead • Eastern Front-Germany and Austria-Hungary v Russia
Describe conditions on the war front for soldiers; include the Battle of Verdun. • Western Front-Germany v France and GB – Quickly became a stalemate – Trench warfare – War of attrition – New weapons-machine gun, zepplin, poison gas – Battle of Verdun-5 months, over 1 million men dead • Eastern Front-Germany and Austria-Hungary v Russia
 Practice 1. a. b. c. d. What was trench warfare intended to accomplish? To protect soldiers from enemy gun fire on the front line. To trap enemy soldiers in mud pits on the front lines. To force enemy soldiers to pass through a “no man’s land. ” All of the above. 2. The MOST important reason a. b. c. d. the Allies had for wanting to keep the Russians in the war was (SSWH 16. b) the superior training and equipment of the Russians had such a large population that they could send extra troops to the western front. the need for food from the Ukraine, the “bread basket” of central Europe. to keep the Germans and Austrians fighting on two fronts at the same time.
Practice 1. a. b. c. d. What was trench warfare intended to accomplish? To protect soldiers from enemy gun fire on the front line. To trap enemy soldiers in mud pits on the front lines. To force enemy soldiers to pass through a “no man’s land. ” All of the above. 2. The MOST important reason a. b. c. d. the Allies had for wanting to keep the Russians in the war was (SSWH 16. b) the superior training and equipment of the Russians had such a large population that they could send extra troops to the western front. the need for food from the Ukraine, the “bread basket” of central Europe. to keep the Germans and Austrians fighting on two fronts at the same time.
 Explain the major decisions made in the treaty of Versailles; include German reparations and the mandate system that replaced Ottoman control. • Paris Peace Conference attended by US (Wilson), GB (Lloyd George), France (Clemenceau), Italy (Orlando) • Wilson’s Fourteen Points. US plan for Europe after WWI – Self-determination – League of Nations-to keep peace • GB and France wanted to punish Germany • Provisions of the Treaty of Versailles – League of Nations – Article #231 -War Guilt Clause-blamed Germany – Reparations-Germany pays France and GB approx $33 billion dollars. – Germany forced to reduce army to 100, 000, dismantle navy and all airplanes – Mandate System-gave France and GB control over Ottoman territories of Syria, Palestine, Jordan, and Lebannon
Explain the major decisions made in the treaty of Versailles; include German reparations and the mandate system that replaced Ottoman control. • Paris Peace Conference attended by US (Wilson), GB (Lloyd George), France (Clemenceau), Italy (Orlando) • Wilson’s Fourteen Points. US plan for Europe after WWI – Self-determination – League of Nations-to keep peace • GB and France wanted to punish Germany • Provisions of the Treaty of Versailles – League of Nations – Article #231 -War Guilt Clause-blamed Germany – Reparations-Germany pays France and GB approx $33 billion dollars. – Germany forced to reduce army to 100, 000, dismantle navy and all airplanes – Mandate System-gave France and GB control over Ottoman territories of Syria, Palestine, Jordan, and Lebannon
 Practice 1. The major objective in the Treaty of Versailles was a. To further the principle of self-determination b. To implement Wilson’s Fourteen Points c. To punish Germany d. To institute a lasting world peace 2. The Mandate System that replaced Ottoman control (SSWH 16. c) a. gave Great Britain control over Palestine, Iraq, and Jordan. b. resulted in the creation of Finland. c. allowed the Ottoman Empire to retain control of the Balkans. d. made Germany a part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire.
Practice 1. The major objective in the Treaty of Versailles was a. To further the principle of self-determination b. To implement Wilson’s Fourteen Points c. To punish Germany d. To institute a lasting world peace 2. The Mandate System that replaced Ottoman control (SSWH 16. c) a. gave Great Britain control over Palestine, Iraq, and Jordan. b. resulted in the creation of Finland. c. allowed the Ottoman Empire to retain control of the Balkans. d. made Germany a part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire.
 Analyze the destabilization of Europe in the collapse of the great empires; include the Romanov and Hapsburg dynasties.
Analyze the destabilization of Europe in the collapse of the great empires; include the Romanov and Hapsburg dynasties.
 Practice
Practice
 SSWH 17 bcef • The student will be able to identify the major political and economic factors that shaped world societies between WWI and WWII. – Determine the causes and results of the Russian Revolution from the rise of the Bolsheviks under Lenin to Stalin’s first Five Year Plan. – Describe the rise of fascism in Europe and Asia by comparing policies of Benito Mussolini in Italy, Adolf Hitler in Germany, and Hirohito in Japan. – Describe the nature of totalitarianism and the police state that existed in Russia, Germany, and Italy and how they differ from other authoritarian governments. – Explain the aggression and conflict leading to WWII in Europe and Asia; include the Italian invasion of Ethiopia, the Spanish Civil War, the rape of Nanjing in China, and the German annexation of the Sudentenland.
SSWH 17 bcef • The student will be able to identify the major political and economic factors that shaped world societies between WWI and WWII. – Determine the causes and results of the Russian Revolution from the rise of the Bolsheviks under Lenin to Stalin’s first Five Year Plan. – Describe the rise of fascism in Europe and Asia by comparing policies of Benito Mussolini in Italy, Adolf Hitler in Germany, and Hirohito in Japan. – Describe the nature of totalitarianism and the police state that existed in Russia, Germany, and Italy and how they differ from other authoritarian governments. – Explain the aggression and conflict leading to WWII in Europe and Asia; include the Italian invasion of Ethiopia, the Spanish Civil War, the rape of Nanjing in China, and the German annexation of the Sudentenland.
 Determine the causes and results of the Russian Revolution from the rise of the Bolsheviks under Lenin to Stalin’s first Five Year Plan. • WWI was devastating for Russia – Heavy casualties – Economic troubles • Revolts in March of 1917 resulted in the Tsar ordering troops to fire on the protestors. – Rioting spread – Tsar is forced to abdicate • Led by Lenin and promising “Land, bread, and peace” the Bolsheviks took control of Russia – Russia withdrew from WWI – Renamed the Union of Soviet Socialist Republic – Banned all other political parties – Set up a secret police • Josef Stalin took over – Five Years Plans-aimed to make USSR an industrial nation
Determine the causes and results of the Russian Revolution from the rise of the Bolsheviks under Lenin to Stalin’s first Five Year Plan. • WWI was devastating for Russia – Heavy casualties – Economic troubles • Revolts in March of 1917 resulted in the Tsar ordering troops to fire on the protestors. – Rioting spread – Tsar is forced to abdicate • Led by Lenin and promising “Land, bread, and peace” the Bolsheviks took control of Russia – Russia withdrew from WWI – Renamed the Union of Soviet Socialist Republic – Banned all other political parties – Set up a secret police • Josef Stalin took over – Five Years Plans-aimed to make USSR an industrial nation
 Practice 1. Who were the Bolsheviks? a. Soldiers in the White Army. b. Radical Russian Marxists revolutionaries. c. Members of the Duma, Russia’s parliament. d. Followers of Rasputin. 2. Heavy military losses in World War I, food and fuel shortages, and opposition to the czar led to the a. French Revolution b. Russian Revolution c. Chinese Revolution d. Cuban Revolution
Practice 1. Who were the Bolsheviks? a. Soldiers in the White Army. b. Radical Russian Marxists revolutionaries. c. Members of the Duma, Russia’s parliament. d. Followers of Rasputin. 2. Heavy military losses in World War I, food and fuel shortages, and opposition to the czar led to the a. French Revolution b. Russian Revolution c. Chinese Revolution d. Cuban Revolution
 Describe the rise of fascism in Europe and Asia by comparing policies of Benito Mussolini in Italy, Adolf Hitler in Germany, and Hirohito in Japan. • Fascism-a political movement that promotes an extreme form of nationalism, a denial of individual rights, and a dictatorial one-party rule. • Germany-Adolf Hitler told the humiliated Germans to take back their empire, improved economy, ended German democracy, banned all other political parties, secret police • Italy-Benito Mussolini improved the economy, made himself dictator, took over news media, and set up a secret police • Japan-
Describe the rise of fascism in Europe and Asia by comparing policies of Benito Mussolini in Italy, Adolf Hitler in Germany, and Hirohito in Japan. • Fascism-a political movement that promotes an extreme form of nationalism, a denial of individual rights, and a dictatorial one-party rule. • Germany-Adolf Hitler told the humiliated Germans to take back their empire, improved economy, ended German democracy, banned all other political parties, secret police • Italy-Benito Mussolini improved the economy, made himself dictator, took over news media, and set up a secret police • Japan-
 Practice 1. One of the main causes of the rise of fascism during the 1930’s was a. A fear of communism. b. Anti-Semitism. c. Foreign invasions. d. Worldwide economic crisis. 2. a. b. c. d. Fascism in Europe during the 1920 s and 1930 s may be best described as a Demonstration of laissez-faire capitalism that promoted free enterprise. Form of totalitarianism that glorified the nation above the individual. Type of economic system that stressed a classless society. Set of humanist ideals that emphasized an individual’s worth and dignity.
Practice 1. One of the main causes of the rise of fascism during the 1930’s was a. A fear of communism. b. Anti-Semitism. c. Foreign invasions. d. Worldwide economic crisis. 2. a. b. c. d. Fascism in Europe during the 1920 s and 1930 s may be best described as a Demonstration of laissez-faire capitalism that promoted free enterprise. Form of totalitarianism that glorified the nation above the individual. Type of economic system that stressed a classless society. Set of humanist ideals that emphasized an individual’s worth and dignity.
 Describe the nature of totalitarianism and the police state that existed in Russia, Germany, and Italy and how they differ from other authoritarian governments. • Totalitarianism-government control over every aspect of public and private life. – God-like dictators – Sacrifice of individuality – Elimination of dissent – Gave up personal freedoms • Authoritarian states are similar, but the term implies somewhat less control by the government.
Describe the nature of totalitarianism and the police state that existed in Russia, Germany, and Italy and how they differ from other authoritarian governments. • Totalitarianism-government control over every aspect of public and private life. – God-like dictators – Sacrifice of individuality – Elimination of dissent – Gave up personal freedoms • Authoritarian states are similar, but the term implies somewhat less control by the government.
 Practice 1. One similarity between Fascism and Communism, as practiced in the 1930 s, was that both systems generally a. Provided hereditary rulers. b. Promoted ethnic diversity. c. Supported democratic elections. d. Suppressed opposition views. 2. Which factor contributed most to the rise of totalitarian governments in Europe before WWII? a. Improved educational systems. b. Expanding democratic reforms. c. Increasing political stability. d. Worsening economic conditions.
Practice 1. One similarity between Fascism and Communism, as practiced in the 1930 s, was that both systems generally a. Provided hereditary rulers. b. Promoted ethnic diversity. c. Supported democratic elections. d. Suppressed opposition views. 2. Which factor contributed most to the rise of totalitarian governments in Europe before WWII? a. Improved educational systems. b. Expanding democratic reforms. c. Increasing political stability. d. Worsening economic conditions.
 Explain the aggression and conflict leading to WWII in Europe and Asia; include the Italian invasion of Ethiopia, the Spanish Civil War, the rape of Nanjing in China, and the German annexation of the Sudentenland. • Italian invasion of Ethiopia-in retaliation for their defeat in the 1800’s • Spanish Civil War-fascist take over of Spain supported by Mussolini and Hitler – Hitler tried out his new Luftwaffe (airforce) by civilian bombing raids – After three years, fascists • Rape of Nanjing in China-Japanese took the Chinese capital of Nanjing – Massacred 100, 000 -300, 000 Chinese – Brutally raped 20, 000 Chinese women and left them to die • German annexation of the Sudentenland-took over the German speaking part of Czechoslovakia – Promised he would stop, later took over the rest of the country
Explain the aggression and conflict leading to WWII in Europe and Asia; include the Italian invasion of Ethiopia, the Spanish Civil War, the rape of Nanjing in China, and the German annexation of the Sudentenland. • Italian invasion of Ethiopia-in retaliation for their defeat in the 1800’s • Spanish Civil War-fascist take over of Spain supported by Mussolini and Hitler – Hitler tried out his new Luftwaffe (airforce) by civilian bombing raids – After three years, fascists • Rape of Nanjing in China-Japanese took the Chinese capital of Nanjing – Massacred 100, 000 -300, 000 Chinese – Brutally raped 20, 000 Chinese women and left them to die • German annexation of the Sudentenland-took over the German speaking part of Czechoslovakia – Promised he would stop, later took over the rest of the country
 Practice 1. Japan’s invasion of Manchuria, Italy’s attack on Ethiopia, and Germany’s blitzkrieg in Poland are examples of a. military aggression. b. containment. c. appeasement. d. the domino theory.
Practice 1. Japan’s invasion of Manchuria, Italy’s attack on Ethiopia, and Germany’s blitzkrieg in Poland are examples of a. military aggression. b. containment. c. appeasement. d. the domino theory.
 SSWH 18 abcd • The student will demonstrate an understanding of the global political, economic, and social impact of WWII. – Describe the major conflicts and outcomes; include Pearl Harbor, El-Alamein, Stalingrad, D-Day, Guadacanal, the Philippines, and the end of the war in Europe and Asia. – Identify Nazi ideology, policies, and consequences that led to the Holocaust. – Explain the military and diplomatic negotiations between the leaders of Great Britain (Churchill), the Soviet Union (Stalin), and the United States (Roosevelt/Truman) from Tehran to Yalta and Potsdam and the impact on the nations of Eastern Europe.
SSWH 18 abcd • The student will demonstrate an understanding of the global political, economic, and social impact of WWII. – Describe the major conflicts and outcomes; include Pearl Harbor, El-Alamein, Stalingrad, D-Day, Guadacanal, the Philippines, and the end of the war in Europe and Asia. – Identify Nazi ideology, policies, and consequences that led to the Holocaust. – Explain the military and diplomatic negotiations between the leaders of Great Britain (Churchill), the Soviet Union (Stalin), and the United States (Roosevelt/Truman) from Tehran to Yalta and Potsdam and the impact on the nations of Eastern Europe.
 Describe the major conflicts and outcomes; include Pearl Harbor, El-Alamein, Stalingrad, D-Day, Guadacanal, the Philippines, and the end of the war in Europe and Asia.
Describe the major conflicts and outcomes; include Pearl Harbor, El-Alamein, Stalingrad, D-Day, Guadacanal, the Philippines, and the end of the war in Europe and Asia.
 Practice 1. Why did President Truman agree to use the atomic bomb? a. to punish Japan for Pearl Harbor b. to revenge those who died in the Bataan death March c. to destroy weapon plants in Japan d. to bring the war to the quickest possible end 2. What did the Allies’ strategy of “island hopping” in the Pacific involve? a. attacks on all Japaneseheld islands b. attack on all island within 500 miles of Japan c. attack only on islands that were not well defended d. attack only on islands that were Japanese strongholds
Practice 1. Why did President Truman agree to use the atomic bomb? a. to punish Japan for Pearl Harbor b. to revenge those who died in the Bataan death March c. to destroy weapon plants in Japan d. to bring the war to the quickest possible end 2. What did the Allies’ strategy of “island hopping” in the Pacific involve? a. attacks on all Japaneseheld islands b. attack on all island within 500 miles of Japan c. attack only on islands that were not well defended d. attack only on islands that were Japanese strongholds
 Identify Nazi ideology, policies, and consequences that led to the Holocaust. • Hitler created an empire that stretched from Scandinavia to North Africa. – People in the conquered lands were expected to serve the German “master” race – “Inferior” people were to be enslaved or eliminated • Hitler’s plan for the Jews was called the “Final Solution” – It included sending Jews to concentration camps were they would either work or be systematically killed – Approx 6 million Jews were killed during the Holocaust • Genocide-the intentional and systematic destruction of an entire race or culture group
Identify Nazi ideology, policies, and consequences that led to the Holocaust. • Hitler created an empire that stretched from Scandinavia to North Africa. – People in the conquered lands were expected to serve the German “master” race – “Inferior” people were to be enslaved or eliminated • Hitler’s plan for the Jews was called the “Final Solution” – It included sending Jews to concentration camps were they would either work or be systematically killed – Approx 6 million Jews were killed during the Holocaust • Genocide-the intentional and systematic destruction of an entire race or culture group
 Practice 1. The deliberate attempt to kill an entire people is known as a. anti-Semitism. b. underground. c. genocide d. blitzkrieg. 2. What was the goal of Hitler’s “Final Solution”? a. It was a process to divide up his territories among his generals. b. It was the system of winning the war before the Americans entered. c. It was a way to invade the Soviet Union. d. It was genocide of people the Nazis considered inferior.
Practice 1. The deliberate attempt to kill an entire people is known as a. anti-Semitism. b. underground. c. genocide d. blitzkrieg. 2. What was the goal of Hitler’s “Final Solution”? a. It was a process to divide up his territories among his generals. b. It was the system of winning the war before the Americans entered. c. It was a way to invade the Soviet Union. d. It was genocide of people the Nazis considered inferior.
 Explain the military and diplomatic negotiations between the leaders of Great Britain (Churchill), the Soviet Union (Stalin), and the United States (Roosevelt/Truman) from Tehran to Yalta and Potsdam and the impact on the nations of Eastern Europe.
Explain the military and diplomatic negotiations between the leaders of Great Britain (Churchill), the Soviet Union (Stalin), and the United States (Roosevelt/Truman) from Tehran to Yalta and Potsdam and the impact on the nations of Eastern Europe.
 Practice 1. Which newspaper headline illustrates a policy of appeasement? a. “Dien Bien Phu Falls; French to Leave Vietnam” b. “Chamberlain Agrees to German Demands: Sudetenland to Germany” c. “Marshall Plan Proposes Economic Aid Program for Europe” d. “Soviet Troops and Tanks Crush Hungarian Revolt”
Practice 1. Which newspaper headline illustrates a policy of appeasement? a. “Dien Bien Phu Falls; French to Leave Vietnam” b. “Chamberlain Agrees to German Demands: Sudetenland to Germany” c. “Marshall Plan Proposes Economic Aid Program for Europe” d. “Soviet Troops and Tanks Crush Hungarian Revolt”
 SSWH 19 abc • The student will demonstrate an understanding of the global social, economic, and political impact of the Cold War and decolonization from 1945 to 1989. – Analyze the revolutionary movements in India (Gandhi, Nehru), China (Mao Zedong), and Ghana. – Describe the formation of the state of Israel. – Explain the arms race; include the development of the hydrogen bomb (1954) and SALT.
SSWH 19 abc • The student will demonstrate an understanding of the global social, economic, and political impact of the Cold War and decolonization from 1945 to 1989. – Analyze the revolutionary movements in India (Gandhi, Nehru), China (Mao Zedong), and Ghana. – Describe the formation of the state of Israel. – Explain the arms race; include the development of the hydrogen bomb (1954) and SALT.
 Analyze the revolutionary movements in India (Gandhi, Nehru), China (Mao Zedong), and Ghana. • India-first major country to gain independence after WWII, led by Mohandas Gandhi, non-violent resistance, protest of “salt-tax”, boycott British goods, India divided into India and Pakistan to prevent Muslim-Hindu violence. • Ghana-led by Kwame Nkrumah, used Gandhi’s non-violent methods, Gold Coast won independence in 1957, changed name to Ghana.
Analyze the revolutionary movements in India (Gandhi, Nehru), China (Mao Zedong), and Ghana. • India-first major country to gain independence after WWII, led by Mohandas Gandhi, non-violent resistance, protest of “salt-tax”, boycott British goods, India divided into India and Pakistan to prevent Muslim-Hindu violence. • Ghana-led by Kwame Nkrumah, used Gandhi’s non-violent methods, Gold Coast won independence in 1957, changed name to Ghana.
 Practice 1. Mohandas Gandhi used his philosophy of nonviolent noncooperation in an effort to a. form a Marxist government in India. b. convince his fellow Indians to support the Allies in WWII. c. persuade Pakistanis to separate from India. d. achieve India’s independence from Great Britain. • In 1947, the Indian subcontinent became independent and was divided into India and Pakistan. The division recognized the a. Hostility between religious groups. b. Strength of Fascism. c. Natural geographic boundaries. d. Existing tribal divisions.
Practice 1. Mohandas Gandhi used his philosophy of nonviolent noncooperation in an effort to a. form a Marxist government in India. b. convince his fellow Indians to support the Allies in WWII. c. persuade Pakistanis to separate from India. d. achieve India’s independence from Great Britain. • In 1947, the Indian subcontinent became independent and was divided into India and Pakistan. The division recognized the a. Hostility between religious groups. b. Strength of Fascism. c. Natural geographic boundaries. d. Existing tribal divisions.
 Describe the formation of the state of Israel. • Zionism-movement calling for Jews around the world to emigrate to Palestine-increased after the Holocaust. • The U. N. voted to create the country of Israel as a Jewish homeland. • Arab nations refused to recognize the new state. • Israel was attacked but victorious in 1956, 1967, and 1973 (added territory of Gaza Strip, Sinai Peninsula, West Bank, and Golan Heights).
Describe the formation of the state of Israel. • Zionism-movement calling for Jews around the world to emigrate to Palestine-increased after the Holocaust. • The U. N. voted to create the country of Israel as a Jewish homeland. • Arab nations refused to recognize the new state. • Israel was attacked but victorious in 1956, 1967, and 1973 (added territory of Gaza Strip, Sinai Peninsula, West Bank, and Golan Heights).
 Describe the formation of the state of Israel. • Camp David Accords-Egypt president (Anwar Sadat), Israeli prime minister (Menachim Begin), and US president (Jimmy Carter) agreed that Israel would return lands in exchange for peace. • PLO (Palestinian Liberation Organization) is formed. – Vowed to win back their homeland. – Used terrorism as political weapon.
Describe the formation of the state of Israel. • Camp David Accords-Egypt president (Anwar Sadat), Israeli prime minister (Menachim Begin), and US president (Jimmy Carter) agreed that Israel would return lands in exchange for peace. • PLO (Palestinian Liberation Organization) is formed. – Vowed to win back their homeland. – Used terrorism as political weapon.
 Practice
Practice
 Explain the arms race; include the development of the hydrogen bomb (1954) and SALT. • US was the only country to create and use the atomic bomb during WWII, Soviets soon developed their own. – Cold War competition turned into a race to see who could build the most deadly weapons. • Hydrogen bomb-1000 x the power of atom bomb • ICBM-could carry nuclear warheads across the world • Cuban Missile Crisis of 1962 -Russia had nuclear bombs in Cuba, US had them in Turkey. – Both sides agreed to remove the weapons – Very narrowly escaped nuclear war • SALT-series of meetings in the 1970’s were both sides agreed to limit the nuclear stocks
Explain the arms race; include the development of the hydrogen bomb (1954) and SALT. • US was the only country to create and use the atomic bomb during WWII, Soviets soon developed their own. – Cold War competition turned into a race to see who could build the most deadly weapons. • Hydrogen bomb-1000 x the power of atom bomb • ICBM-could carry nuclear warheads across the world • Cuban Missile Crisis of 1962 -Russia had nuclear bombs in Cuba, US had them in Turkey. – Both sides agreed to remove the weapons – Very narrowly escaped nuclear war • SALT-series of meetings in the 1970’s were both sides agreed to limit the nuclear stocks
 Practice
Practice
 SSWH 20 ac • The student will examine change and continuity in the world since the 1960’s. – Identify ethnic conflicts and new nationalisms; include pan-Africanism, pan-Arabism, and the conflicts in Bosnia-Herzegovina and Rwanda. – Analyze terrorism as a form of warfare in the 20 th century; include Shining Path, Red Brigade, Hamas, and Al Qaeda; and analyze the impact of terrorism on daily life; include travel, world energy supplies, and financial markets.
SSWH 20 ac • The student will examine change and continuity in the world since the 1960’s. – Identify ethnic conflicts and new nationalisms; include pan-Africanism, pan-Arabism, and the conflicts in Bosnia-Herzegovina and Rwanda. – Analyze terrorism as a form of warfare in the 20 th century; include Shining Path, Red Brigade, Hamas, and Al Qaeda; and analyze the impact of terrorism on daily life; include travel, world energy supplies, and financial markets.
 Identify ethnic conflicts and new nationalisms; include pan. Africanism, pan-Arabism, and the conflicts in Bosnia. Herzegovina and Rwanda. • Yugoslavia-
Identify ethnic conflicts and new nationalisms; include pan. Africanism, pan-Arabism, and the conflicts in Bosnia. Herzegovina and Rwanda. • Yugoslavia-
 Practice 1. Which statement about the Balkan Peninsula since 1995 is most accurate? a. Bosnia-Herzegovina and Croatia are now both controlled by Yugoslavia. b. Ethnic tensions and conflict continue to be a problem in much of the region. c. Slobodan Milosevic of Serbia became the first democratically elected leader of the region. d. The Balkan Peninsula has become one of the most prosperous regions in Europe. 2. The genocide in Rwanda and the atrocities in Yugoslavia demonstrate a. Inability of a command economy to satisfy the needs of people. b. Fact that most conflict are caused by economic interests. c. Isolation of these countries from international influences. d. Inability of some societies to resolve religious and ethnic differences.
Practice 1. Which statement about the Balkan Peninsula since 1995 is most accurate? a. Bosnia-Herzegovina and Croatia are now both controlled by Yugoslavia. b. Ethnic tensions and conflict continue to be a problem in much of the region. c. Slobodan Milosevic of Serbia became the first democratically elected leader of the region. d. The Balkan Peninsula has become one of the most prosperous regions in Europe. 2. The genocide in Rwanda and the atrocities in Yugoslavia demonstrate a. Inability of a command economy to satisfy the needs of people. b. Fact that most conflict are caused by economic interests. c. Isolation of these countries from international influences. d. Inability of some societies to resolve religious and ethnic differences.
 Analyze terrorism as a form of warfare in the 20 th century; include Shining Path, Red Brigade, Hamas, and Al Qaeda; and analyze the impact of terrorism on daily life; include travel, world energy supplies, and financial markets. • Fundamentalists believe that people should adopt basic religious values and that religion should influence government policies. • Terror usually refers to an attack on civilians that is not directed by a government. • Examples: – 2001 bombing of the World Trade Center in NYC-3, 000 people lost their lives – 1995 Oklahoma City Bombing-168 people died
Analyze terrorism as a form of warfare in the 20 th century; include Shining Path, Red Brigade, Hamas, and Al Qaeda; and analyze the impact of terrorism on daily life; include travel, world energy supplies, and financial markets. • Fundamentalists believe that people should adopt basic religious values and that religion should influence government policies. • Terror usually refers to an attack on civilians that is not directed by a government. • Examples: – 2001 bombing of the World Trade Center in NYC-3, 000 people lost their lives – 1995 Oklahoma City Bombing-168 people died
 Practice
Practice
 SSWH 21 ab • The student will analyze globalization in the contemporary world. – Describe the cultural and intellectual integration of countries into the world economy through the development of television, satellites, and computers. – Analyze the global economic and political connections; include multinational corporations, the United Nations, OPEC, and the World Trade Organization.
SSWH 21 ab • The student will analyze globalization in the contemporary world. – Describe the cultural and intellectual integration of countries into the world economy through the development of television, satellites, and computers. – Analyze the global economic and political connections; include multinational corporations, the United Nations, OPEC, and the World Trade Organization.
 Describe the cultural and intellectual integration of countries into the world economy through the development of television, satellites, and computers. • Globalization– Major industries do trade in a world market – Labor market is being “outsourced” to lower paid foreign workers • Pros of globalization: – More countries communicate with each other, the less likely they are to go to war. • Cons of globalization: – Countries will loose their distinct characteristics – Industrial nations are controlling world resources and causing pollution
Describe the cultural and intellectual integration of countries into the world economy through the development of television, satellites, and computers. • Globalization– Major industries do trade in a world market – Labor market is being “outsourced” to lower paid foreign workers • Pros of globalization: – More countries communicate with each other, the less likely they are to go to war. • Cons of globalization: – Countries will loose their distinct characteristics – Industrial nations are controlling world resources and causing pollution
 Practice 1. Technological changes in developing countries have most often resulted in a. Migrations from rural to urban areas. b. Fewer education opportunities. c. A weakening of traditional values. d. a decreased use of natural resources. 2. A valid statement about technology in the 20 th century is that it has a. Eliminated famine and disease throughout the world. b. Delayed economic progress. c. Reduced the destructiveness of war. d. Accelerated the pace of cultural diffusion.
Practice 1. Technological changes in developing countries have most often resulted in a. Migrations from rural to urban areas. b. Fewer education opportunities. c. A weakening of traditional values. d. a decreased use of natural resources. 2. A valid statement about technology in the 20 th century is that it has a. Eliminated famine and disease throughout the world. b. Delayed economic progress. c. Reduced the destructiveness of war. d. Accelerated the pace of cultural diffusion.
 Analyze the global economic and political connections; include multinational corporations, the United Nations, OPEC, and the World Trade Organization.
Analyze the global economic and political connections; include multinational corporations, the United Nations, OPEC, and the World Trade Organization.
 Practice 1. Which group of countries earns much of their revenue from the sale of oil? a. China, Korea, Jordan b. Turkey, Brazil, Lebanon c. Argentina, Malaysia, Chile d. Saudi Arabia, Nigeria, Venezuela
Practice 1. Which group of countries earns much of their revenue from the sale of oil? a. China, Korea, Jordan b. Turkey, Brazil, Lebanon c. Argentina, Malaysia, Chile d. Saudi Arabia, Nigeria, Venezuela


