63b9b00d20fc826dd7d0a0e797dd5371.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 73

World Diabetes Day 2011 Presented by: Prof. Md. Nazrul Islam Siddiqui FCPS (MED), MD (EM), FACP (USA) FRCP (Glasg), FRCP (Edin), FACE (USA) Professor and Head Department of Endocrinology Mymensingh Medical College & Hospital Email: mnisendo@yahoo. com

Theme: Diabetes Education & Prevention (2009 -2013)

Objectives: 1. To highlight the World Diabetes Day, 14 November 2011 2. Scientific perspective of the day.


The Impact of Diabetes: Million lives are lost annually Millions of $ lost income and Productivity. 1 million amputation per year. Diabetes kills 1 person in every 8 seconds. Every 10 seconds, 2 people develop diabetes. -IDF Bulletin; November 2011.



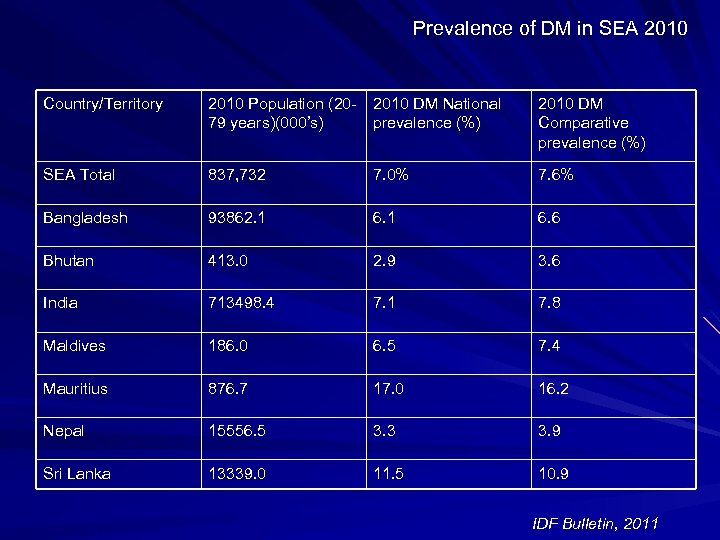
Prevalence of DM in SEA 2010 Country/Territory 2010 Population (20 - 2010 DM National 79 years)(000’s) prevalence (%) 2010 DM Comparative prevalence (%) SEA Total 837, 732 7. 0% 7. 6% Bangladesh 93862. 1 6. 6 Bhutan 413. 0 2. 9 3. 6 India 713498. 4 7. 1 7. 8 Maldives 186. 0 6. 5 7. 4 Mauritius 876. 7 17. 0 16. 2 Nepal 15556. 5 3. 3 3. 9 Sri Lanka 13339. 0 11. 5 10. 9 IDF Bulletin, 2011
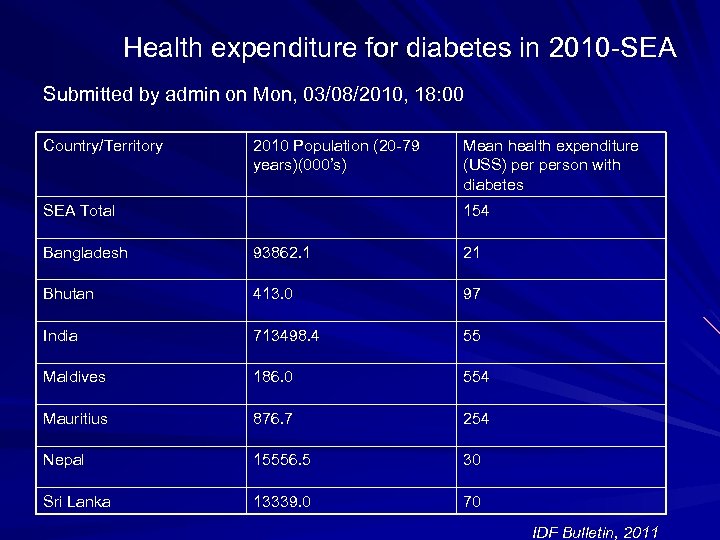
Health expenditure for diabetes in 2010 -SEA Submitted by admin on Mon, 03/08/2010, 18: 00 Country/Territory 2010 Population (20 -79 years)(000’s) SEA Total Mean health expenditure (USS) person with diabetes 154 Bangladesh 93862. 1 21 Bhutan 413. 0 97 India 713498. 4 55 Maldives 186. 0 554 Mauritius 876. 7 254 Nepal 15556. 5 30 Sri Lanka 13339. 0 70 IDF Bulletin, 2011
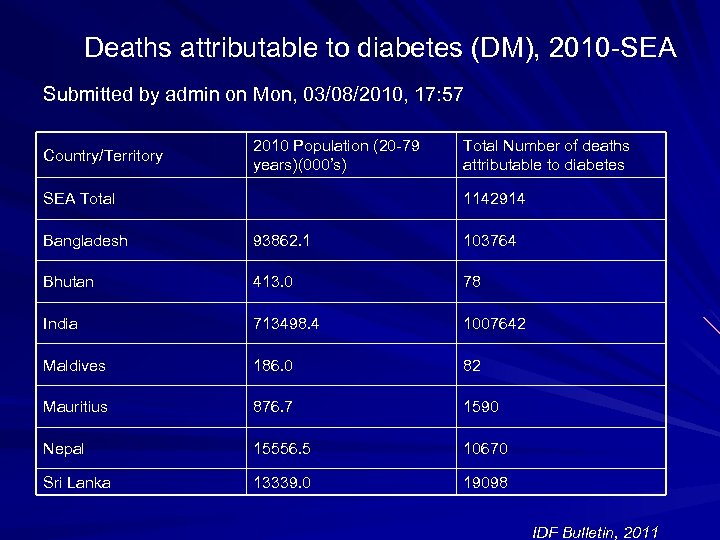
Deaths attributable to diabetes (DM), 2010 -SEA Submitted by admin on Mon, 03/08/2010, 17: 57 Country/Territory 2010 Population (20 -79 years)(000’s) SEA Total Number of deaths attributable to diabetes 1142914 Bangladesh 93862. 1 103764 Bhutan 413. 0 78 India 713498. 4 1007642 Maldives 186. 0 82 Mauritius 876. 7 1590 Nepal 15556. 5 10670 Sri Lanka 13339. 0 19098 IDF Bulletin, 2011


How is the day marked? Millions of people in over 160 countries. Walks and cycle rides Lighting buildings and monuments in blue. Radio & Television Program. Sports events. Free screenings for diabetes. Public information meetings.

How is the day marked? (Continued) Poster & leaflet campaigns. Diabetes workshop & exhibitions. Press conference. News paper & magazine articles. Events for children & adolescents. Activities & lessons in schools.

1991 World Diabetes Day begins The International Diabetes Federation and the World Health Organization created World Diabetes Day in response to diabetes epidemic 15

Every year on November 14, World Diabetes Day brings diabetes to the attention of the world.

November 14 is the birthday of Frederick Banting, one of the discoverers of insulin. (c) Banting House National Historic Site of Canada

The theme is set by the International Diabetes Federation and the World Health Organization.

In 2006, the United Nations passed resolution 61/225. It asks the world to observe November 14 as World Diabetes Day and to take action to address the diabetes threat.

. . . to become a truly global event.

The campaign evolved from one day in the year to a multi-year campaign 2002: Your Eyes and Diabetes 1991: Diabetes Goes Public 1992: Diabetes: A Problem of All Ages 2003: Diabetes and Kidneys in All Countries 2004: Diabetes and Obesity 1993: Growing Up with Diabetes 2005: Diabetes and Foot Care 1994: Diabetes and Growing Older 2006: Diabetes and the 1995: The Price of Ignorance Disadvantaged and Vulnerable 1996: Insulin for Life! 2007 -2008: Diabetes in Children and Adolescents 1997: Global Awareness: Our Key to a Better Life 2009 -2013: Diabetes Prevention and Education 1998: Diabetes and Human Rights 1999: The Costs of Diabetes 2000: Diabetes and Lifestyle in the New Millennium 2001: Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease

2009 -2013 Diabetes Education and Prevention The campaign slogan is: Let's Take Control of Diabetes. Now.

2009 -2013 Understand diabetes and take control

The global symbol for diabetes was developed during the Unite for Diabetes campaign. Why a circle? A positive symbol across cultures, the circle symbolizes life and health. Why blue? The colour blue reflects the sky that unites all nations. The blue border of the circle reflects the colour of the sky and the flag of the United Nations. The blue circle signifies the unity of the global diabetes community in response to the diabetes epidemic. http: //www. diabetesbluecircle. org

Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes § Obesity § Physical inactivity § Impaired fasting glucose levels Age Race/ethnicity Previous gestational diabetes (GDM) Family history of diabetes § Impaired glucose tolerance § Body fat distribution (IGT) Can be modified
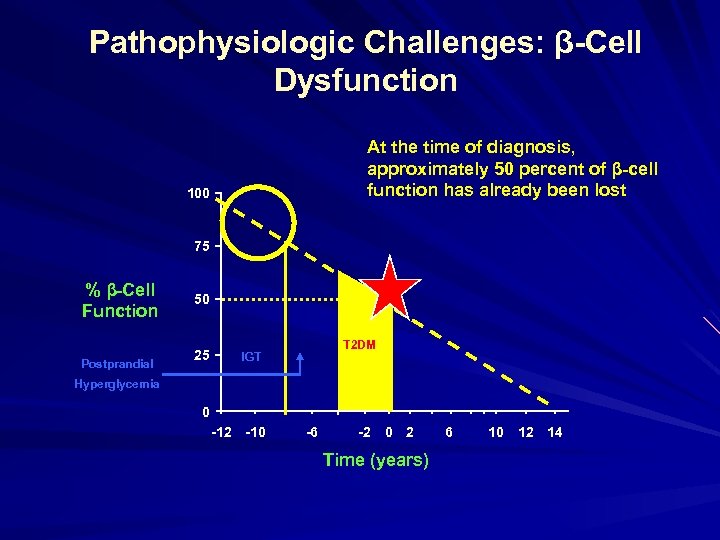
Pathophysiologic Challenges: β-Cell Dysfunction At the time of diagnosis, approximately 50 percent of β-cell function has already been lost 100 75 % β-Cell Function Postprandial 50 25 T 2 DM IGT Hyperglycemia 0 -12 -10 -6 -2 0 2 Time (years) 6 10 12 14
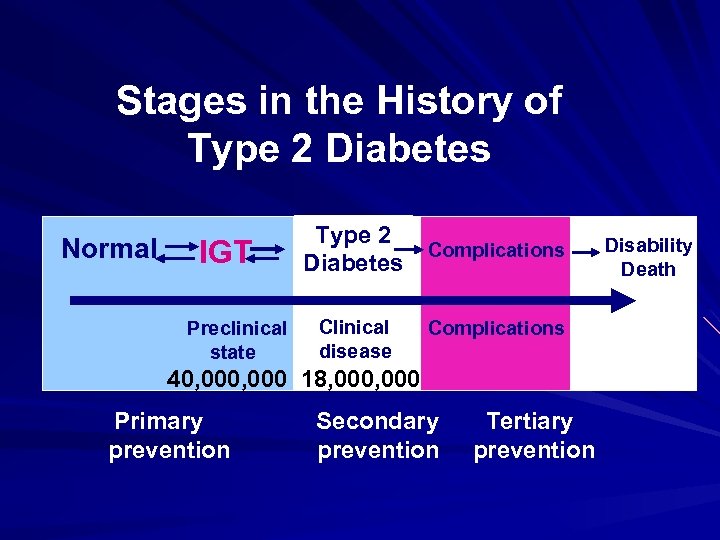
Stages in the History of Type 2 Diabetes Normal IGT Preclinical state Type 2 Diabetes Clinical disease Complications 40, 000 18, 000 Primary prevention Secondary prevention Tertiary prevention Disability Death

Building/Community Designs Discourage Walking
Something went wrong…………
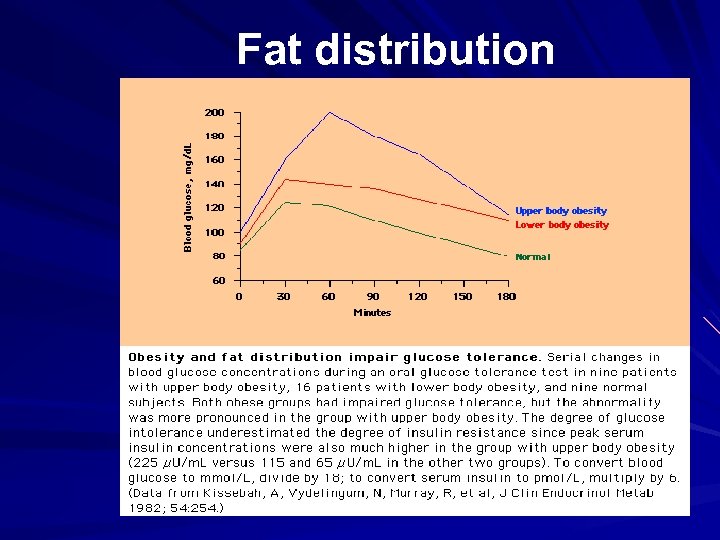
Fat distribution
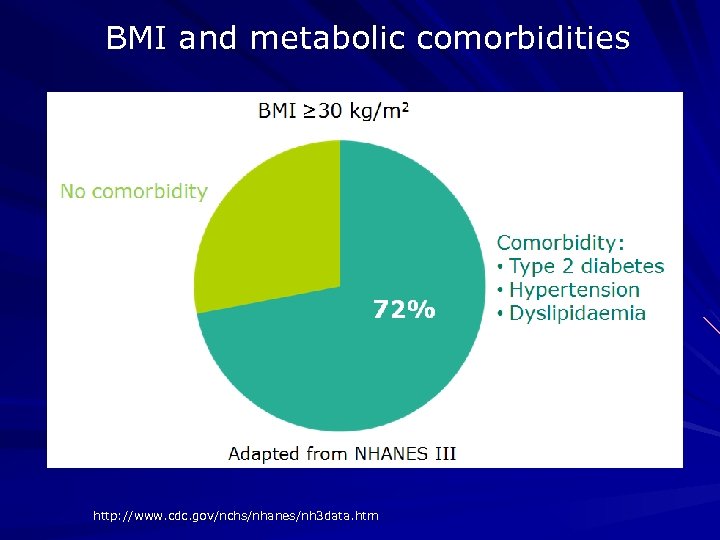
BMI and metabolic comorbidities http: //www. cdc. gov/nchs/nhanes/nh 3 data. htm
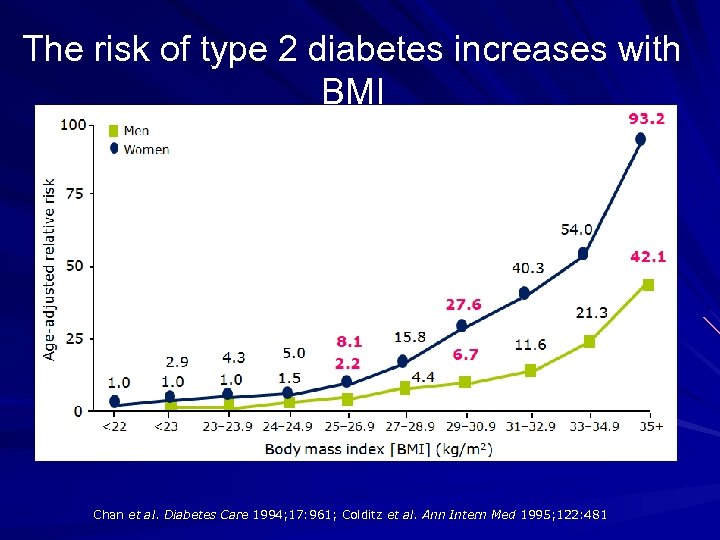
The risk of type 2 diabetes increases with BMI Chan et al. Diabetes Care 1994; 17: 961; Colditz et al. Ann Intern Med 1995; 122: 481
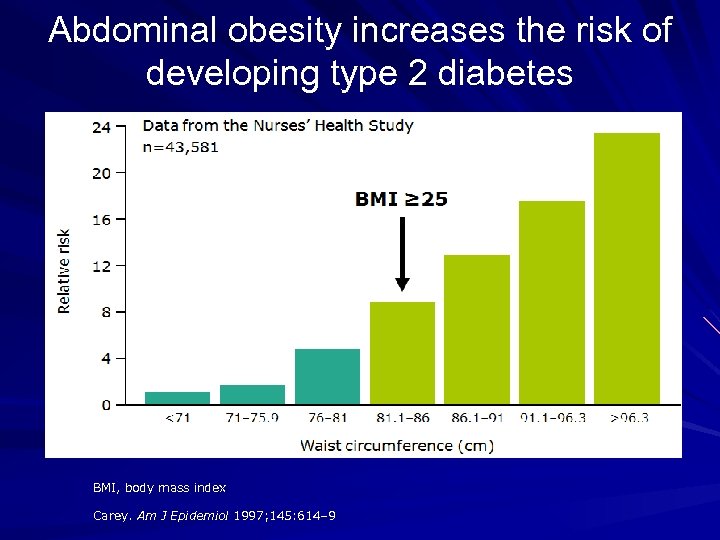
Abdominal obesity increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes BMI, body mass index Carey. Am J Epidemiol 1997; 145: 614– 9

SHOULD WE ATTEMPT TO PREVENT TYPE 2 DM? “ 5” Criteria should be full-field : 1. 2. 3. Important health problem. Early development, natural history, risk factor e. g. IFG; IGT; Age; F/H, Obesity; HTN, Dislipidemia etc. Test to detect predisease; Should be safe, acceptable & predictive FPG IFG OGTT IGT

Intervention criteria (Ctd) 4. Methods of intervention: Safe Effective Reliable DPP San Antonio STOP-NIDDM FINNS STUDY, Da Quiry Study etc. 5. Cost-effectiveness: Cost-effective. Affordable. Diabetes care 26(9): 2518 -2523: September 2003

International Bodies 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. IDF UN WHO ADA ACE AACE EASD etc.

The Science: Type 2 Diabetes Prevention

The Diabetes prevention program (DPP) One of the largest 27 -Centre trial. Started on 1996. Total participants : 3, 234. Three arms trial : Lifestyle intervention group. Metformin group Control group
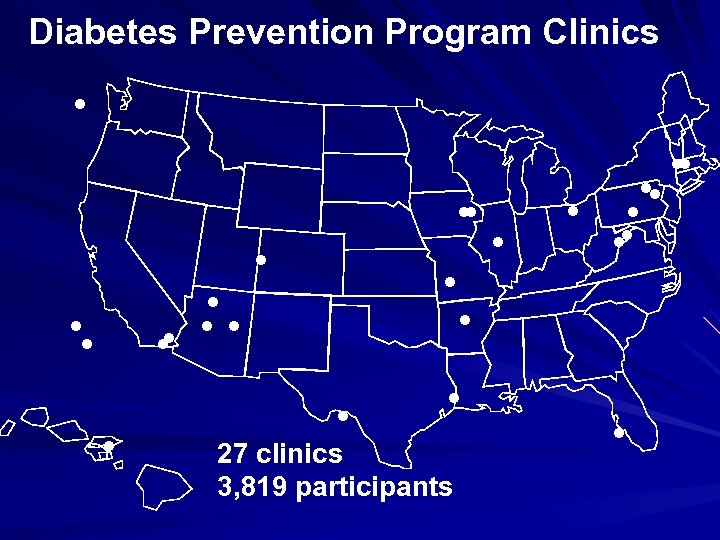
Diabetes Prevention Program Clinics . . 27 clinics 3, 819 participants

DPP Goals Primary To prevent or delay type 2 diabetes in people with impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) Secondary Reduce heart disease and stroke Reduce risk factors for heart disease and stroke
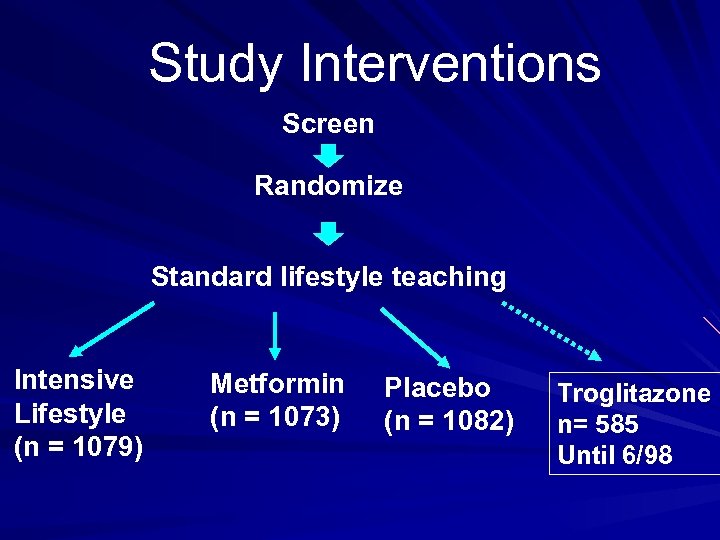
Study Interventions Screen Randomize Standard lifestyle teaching Intensive Lifestyle (n = 1079) Metformin (n = 1073) Placebo (n = 1082) Troglitazone n= 585 Until 6/98

LIFE STYLE BALANCE INTERVENTION WEIGHT LOSS GOAL. PHYSICAL ACTIVITY GOAL. DIETARY MODIFICATION.

Life style Intervention (Ctd) 7% loss of initial weight. In the first six month. Maximum wt. loss ; first 20 -24 weeks. 1 -2 lbs/week. Maintenance of wt. loss.

150 mins / week moderate exercise. Intensity to brisk walking. Minimum 3 times/week. Minimum 10 mins per session. Maximum 75 mins per session Evidence based, effective, feasible. Suitable for long term maintenance.

Double blind placebo control trial of Metformin. Both groups advised for lifestyle modification. Dose of Metformin : 850 mg/day orally – 1 st month. 850 mg twice daily subsequently. Average follow op period : 2. 8 years
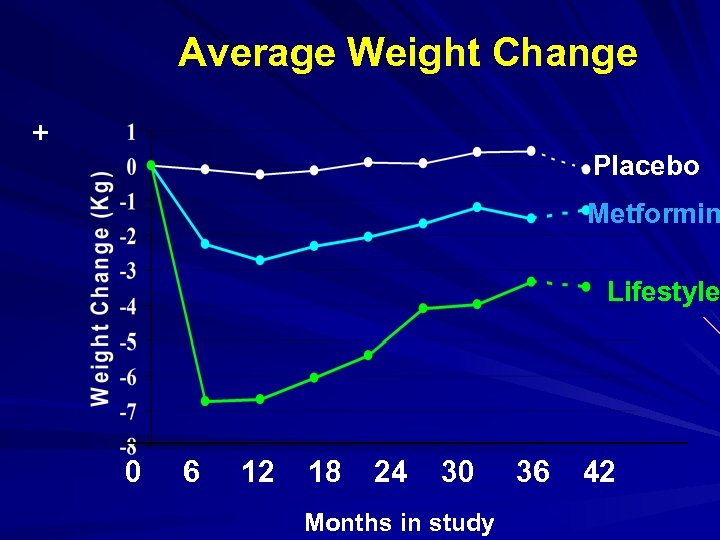
Average Weight Change + Placebo Metformin Lifestyle 0 6 12 18 24 30 Months in study 36 42
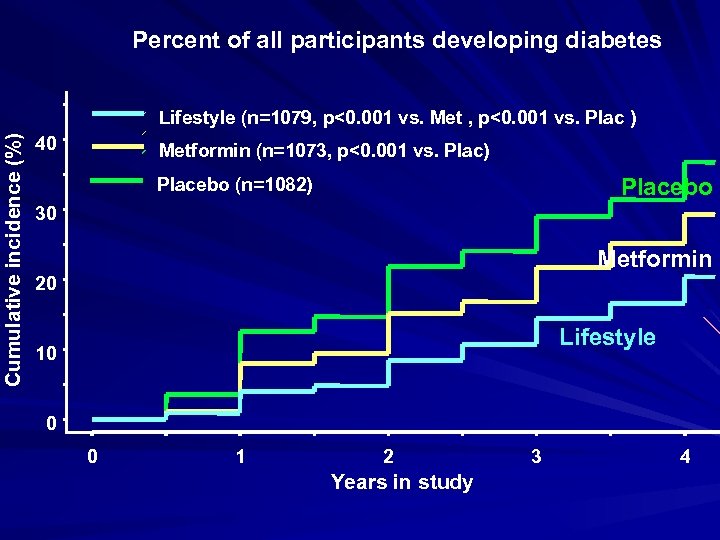
Percent of all participants developing diabetes Cumulative incidence (%) Lifestyle (n=1079, p<0. 001 vs. Met , p<0. 001 vs. Plac ) 40 Metformin (n=1073, p<0. 001 vs. Plac) Placebo (n=1082) 30 Metformin 20 Lifestyle 10 0 0 1 2 Years in study 3 4
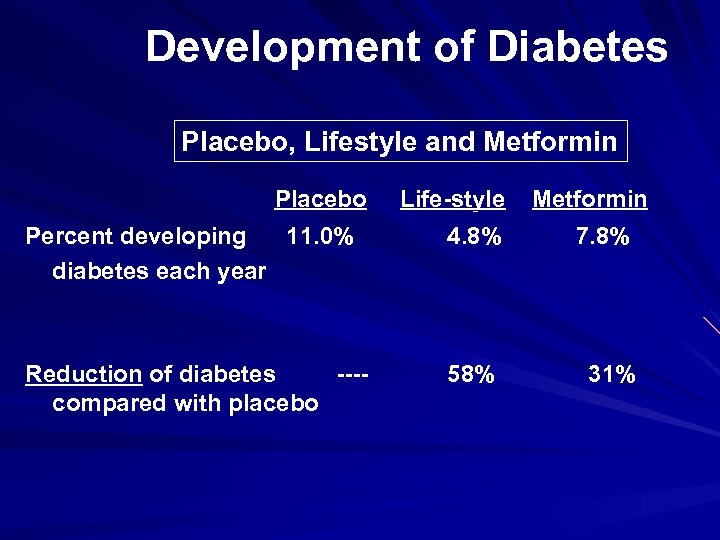
Development of Diabetes Placebo, Lifestyle and Metformin Placebo Life-style Metformin Percent developing 11. 0% diabetes each year 4. 8% 7. 8% Reduction of diabetes ---compared with placebo 58% 31%

4 -Major Intervention studies to reduce the incidence of type 2 diabetes

Weight loss improves glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes FPG, fasting plasma glucose Anderson et al. J Am Coll Nutr 2003; 22: 331– 9
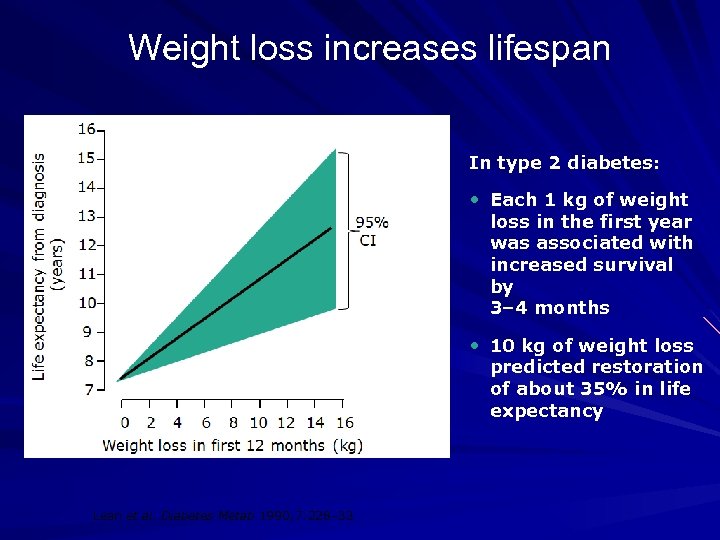
Weight loss increases lifespan In type 2 diabetes: • Each 1 kg of weight loss in the first year was associated with increased survival by 3– 4 months • 10 kg of weight loss predicted restoration of about 35% in life expectancy Lean et al. Diabetes Metab 1990; 7: 228– 33

Preferred food choices

Join World Diabetes Day: Go blue! Go round!

Summary To buildup awareness among the people Basic diabetic education Creation for facilities for recreation. Creation of health facilities.
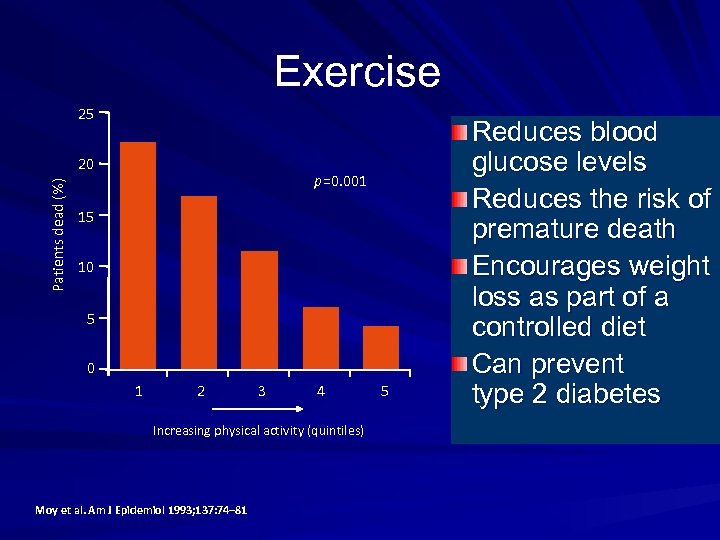
Exercise 25 Patients dead (%) 20 p=0. 001 15 10 5 0 1 2 3 4 Increasing physical activity (quintiles) Moy et al. Am J Epidemiol 1993; 137: 74– 81 5 Reduces blood glucose levels Reduces the risk of premature death Encourages weight loss as part of a controlled diet Can prevent type 2 diabetes

Benefits of modest weight loss in type 2 diabetes BP, blood pressure; CVD, cardiovascular disease; HDL-C, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol; TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglycerides 1. Anderson and Konz. Obes Res 2001; 9(Suppl. 4): 326 S– 34 S; 2. Anderson et al. J Am Coll Nutr 2003; 22: 331– 9
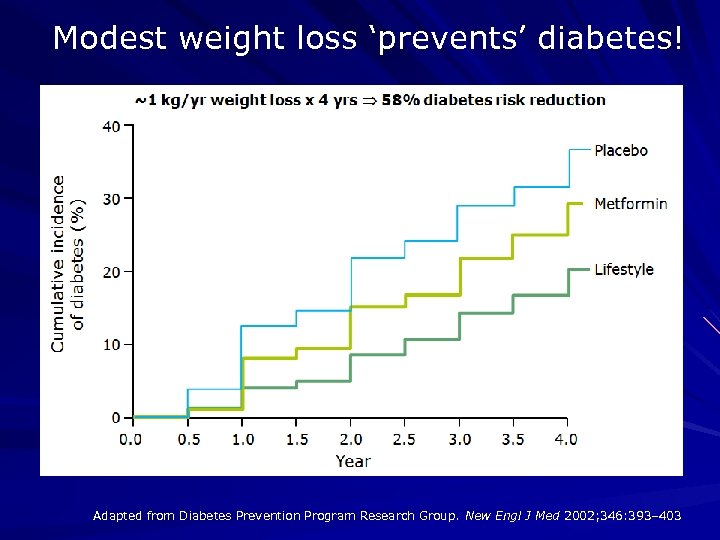
Modest weight loss ‘prevents’ diabetes! Adapted from Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. New Engl J Med 2002; 346: 393– 403

Prevention of DM Objective: l Is DM is preventable? l Types of prevention: – Primary –Secondary –Tertiary • Screening of high risk individuals • Life style modification

Prevention of DM Types of prevention: 1. Primary prevention: Measures to avoid the onset of the disease. 2. Secondary prevention: Early detection Prompt treatment. 3. Tertiary prevention: To prevent and or delay further progression of complications.

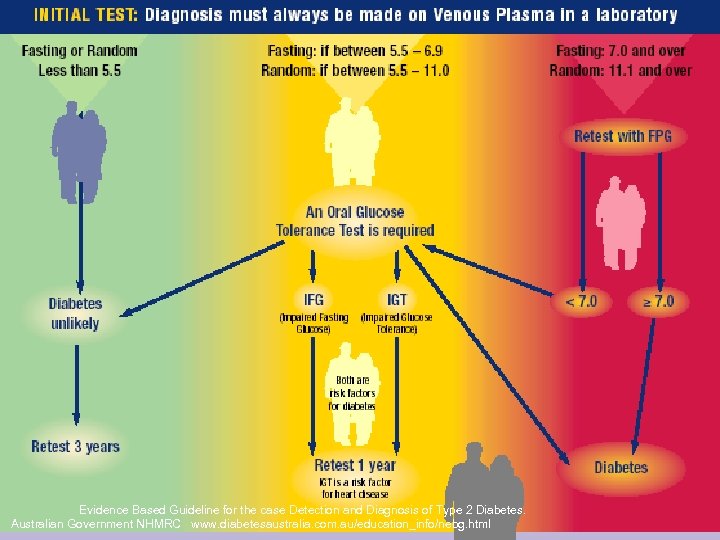
Evidence Based Guideline for the case Detection and Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes. Australian Government NHMRC www. diabetesaustralia. com. au/education_info/nebg. html

2010 State Tier III Priorities Other Relevant Diabetes Research, Prevention, and Discrimination Issues Smoke-Free Environment

2010 State Tier II Priorities Health Promotion School Based (health education, physical education, healthy foods) Menu Labeling State-Level Research Activities Diabetes-Specific and Stem Cell Research Protecting Stem Cell Research

2010 State Tier I Priorities Health Insurance Coverage/Protection Diabetes Cost Reduction Act (passage and preventing rollbacks) Medicaid Coverage Diabetes Prevention & Control Program Funding School Diabetes Care Private Driver’s Licenses Oppose Laws and/or State Action with Blanket Treatment of People with Diabetes
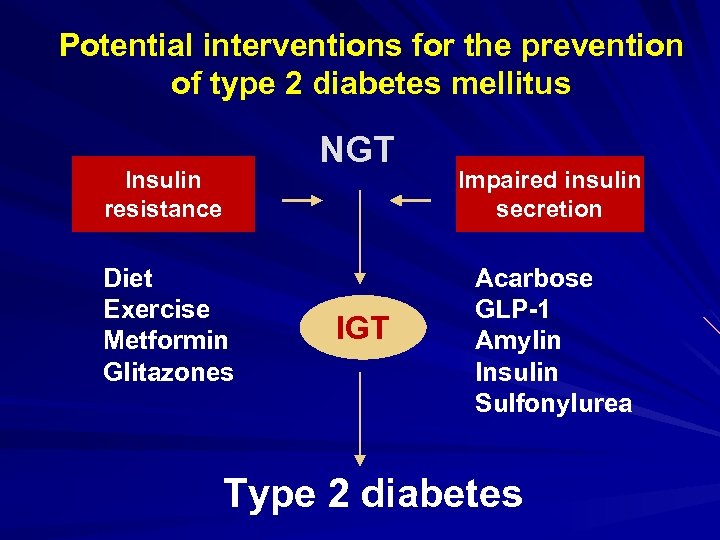
Potential interventions for the prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus NGT Insulin resistance Diet Exercise Metformin Glitazones IGT Impaired insulin secretion Acarbose GLP-1 Amylin Insulin Sulfonylurea Type 2 diabetes

Global Projections for the Diabetes Epidemic: 2003 -2025 NA EUR 23. 0 M 36. 2 M ↑ 57. 0% 48. 4 M 58. 6 M ↑ 21% EMME 19. 2 M 39. 4 M ↑ 105% AFR World 2003 = 194 M 2025 = 333 M ↑ 72% SACA 14. 2 M 26. 2 M ↑ 85% WP SEA 39. 3 M 81. 6 M ↑ 108% 7. 1 M 15. 0 M ↑ 111% M = million, AFR = Africa, NA = North America, EUR = Europe, SACA = South and Central America, EMME = Eastern Mediterranean and Middle East, SEA = South-East Asia, WP = Western Pacific Diabetes Atlas Committee. Diabetes Atlas 2 nd Edition: IDF 2003 2025 43. 0 M 75. 8 M ↑ 79%
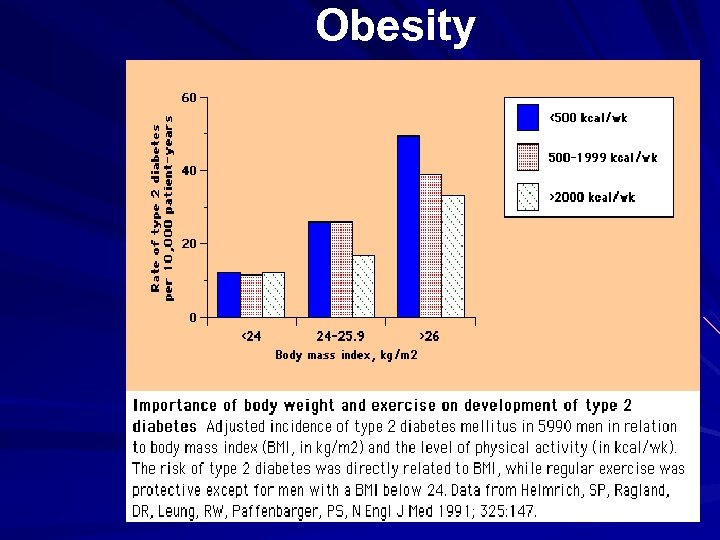
Obesity
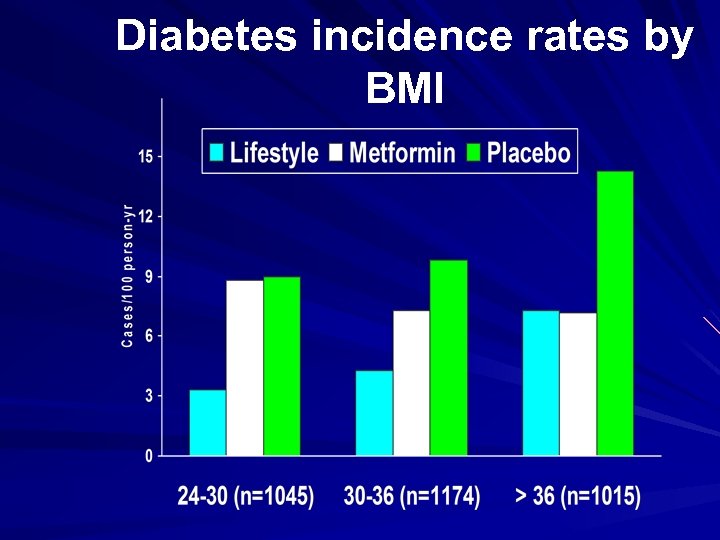
Diabetes incidence rates by BMI

The campaign has grown in strength from humble beginnings. . .

Poly Count grams of Saturated fat. <10 if you have heart disease; <20 g for others Sat Check food labels for hydrogenated oils and keep to a minimum. Avoid Fast Foods Trans Make this the main fat in you diet. Use olive oil, canola & peanut oil for cooking. Mono Omega 3: Fatty fish 2 times a week Omega 6: controversial, watch the science develop, minimal amount

Diabetes Prevention Studies Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study DPP Stop-NIDDM DREAM study

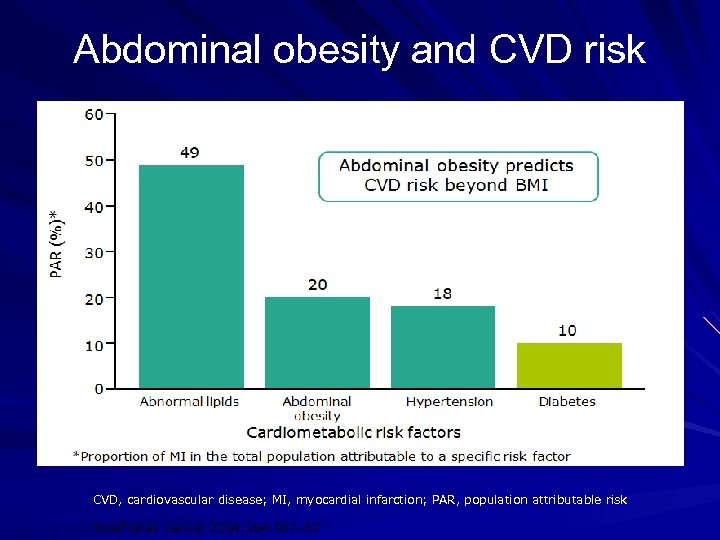
Abdominal obesity and CVD risk CVD, cardiovascular disease; MI, myocardial infarction; PAR, population attributable risk Yusuf et al. Lancet 2004; 364: 937– 52
63b9b00d20fc826dd7d0a0e797dd5371.ppt