d3218fae7a6c700a5fdddccc6b2a3055.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43
 World Class Performance – Turning Rhetoric into Reality?
World Class Performance – Turning Rhetoric into Reality?
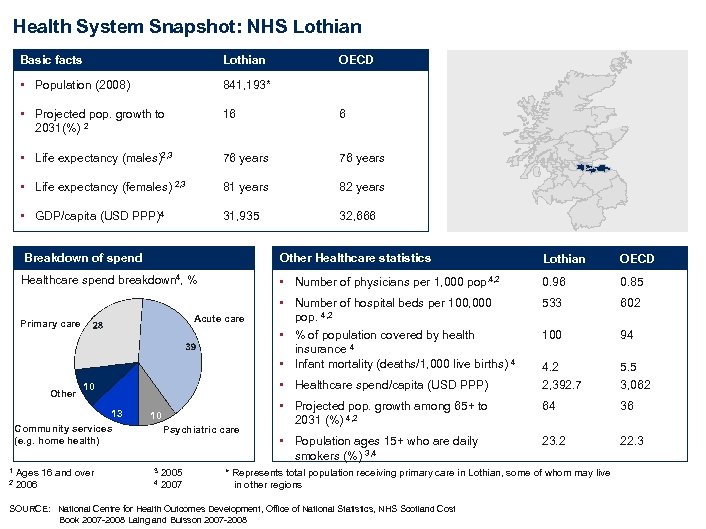 Health System Snapshot: NHS Lothian Basic facts Lothian • Population (2008) 841, 193* • Projected pop. growth to 16 6 • Life expectancy (males)2, 3 76 years • Life expectancy (females) 2, 3 81 years 82 years • GDP/capita (USD PPP)4 31, 935 32, 666 2031(%) OECD 2 Breakdown of spend Other Healthcare statistics Lothian OECD Healthcare spend breakdown 4, % • Number of physicians per 1, 000 pop. 4, 2 0. 96 0. 85 • Number of hospital beds per 100, 000 533 602 pop. • % of population covered by health insurance 4 • Infant mortality (deaths/1, 000 live births) 4 100 94 • Healthcare spend/capita (USD PPP) 4. 2 2, 392. 7 5. 5 3, 062 • Projected pop. growth among 65+ to 64 36 23. 2 22. 3 Acute care Primary care Other 10 13 10 Community services (e. g. home health) Psychiatric care 4, 2 2031 (%) 4, 2 • Population ages 15+ who are daily smokers (%) 1 2 Ages 16 and over 2006 3 4 2005 2007 3, 4 * Represents total population receiving primary care in Lothian, some of whom may live in other regions SOURCE: National Centre for Health Outcomes Development, Office of National Statistics, NHS Scotland Cost Book 2007 -2008 Laing and Buisson 2007 -2008
Health System Snapshot: NHS Lothian Basic facts Lothian • Population (2008) 841, 193* • Projected pop. growth to 16 6 • Life expectancy (males)2, 3 76 years • Life expectancy (females) 2, 3 81 years 82 years • GDP/capita (USD PPP)4 31, 935 32, 666 2031(%) OECD 2 Breakdown of spend Other Healthcare statistics Lothian OECD Healthcare spend breakdown 4, % • Number of physicians per 1, 000 pop. 4, 2 0. 96 0. 85 • Number of hospital beds per 100, 000 533 602 pop. • % of population covered by health insurance 4 • Infant mortality (deaths/1, 000 live births) 4 100 94 • Healthcare spend/capita (USD PPP) 4. 2 2, 392. 7 5. 5 3, 062 • Projected pop. growth among 65+ to 64 36 23. 2 22. 3 Acute care Primary care Other 10 13 10 Community services (e. g. home health) Psychiatric care 4, 2 2031 (%) 4, 2 • Population ages 15+ who are daily smokers (%) 1 2 Ages 16 and over 2006 3 4 2005 2007 3, 4 * Represents total population receiving primary care in Lothian, some of whom may live in other regions SOURCE: National Centre for Health Outcomes Development, Office of National Statistics, NHS Scotland Cost Book 2007 -2008 Laing and Buisson 2007 -2008
 Our Aspiration • NHS Lothian aspires to be at the level of Scotland’s best and a world top 25 health region in terms of outcomes and value.
Our Aspiration • NHS Lothian aspires to be at the level of Scotland’s best and a world top 25 health region in terms of outcomes and value.
 • To achieve this, NHS Lothian’s 5 -year strategic priorities are to: – Sustainably improve access to high quality care, increasing share of treatments ‘in the right setting at the right time’ and ‘shifting the balance of care’ towards self care and illness prevention – Improve health and reduce health inequalities in collaboration with social care providers and involve people in how they plan and deliver services, creating a ‘mutual NHS’ – Develop more robust information systems to support service delivery, and embrace technological advances that improves care and encourages self care – Develop a position at the forefront of R&D, in particular through the Bio. Quarter science park that is jointly established with academic, industry, and venture capital partners – Be an exemplar employer, thereby motivate and attract good staff and raise productivity
• To achieve this, NHS Lothian’s 5 -year strategic priorities are to: – Sustainably improve access to high quality care, increasing share of treatments ‘in the right setting at the right time’ and ‘shifting the balance of care’ towards self care and illness prevention – Improve health and reduce health inequalities in collaboration with social care providers and involve people in how they plan and deliver services, creating a ‘mutual NHS’ – Develop more robust information systems to support service delivery, and embrace technological advances that improves care and encourages self care – Develop a position at the forefront of R&D, in particular through the Bio. Quarter science park that is jointly established with academic, industry, and venture capital partners – Be an exemplar employer, thereby motivate and attract good staff and raise productivity
 To achieve this goal we need to answer 5 questions Key Strategy What value do we get for what we spend? How do we perform compared to world-class standards and our peers at a system and pathway level? What is the best way to improve our system? How can we learn from others? How do we build the capabilities we need to succeed?
To achieve this goal we need to answer 5 questions Key Strategy What value do we get for what we spend? How do we perform compared to world-class standards and our peers at a system and pathway level? What is the best way to improve our system? How can we learn from others? How do we build the capabilities we need to succeed?
 COST QUALITY
COST QUALITY
 Cost: Summary of aspirations, challenges, strategy and success stories Current strategy to address challenges • Regularly compare quality performance Aspirations to improve costs • Meet system aspirations of being recognized as on of the top 25 systems in the world in terms of value for money • Improve productivity and quality while reducing cost in the setting of economic uncertainty and non-monetary productivity metrics to benchmarks (though good benchmarks are lacking) • Pursue lean approaches throughout the system and especially in acute care setting • Fine-tune resources along the patient pathway to ensure system operates at optimal capacity Success Stories • Lothian has in partnership with GE Healthcare used Lean methodologies to achieve substantial improvements in efficiency of key services SOURCE: Lothian leadership team interviews
Cost: Summary of aspirations, challenges, strategy and success stories Current strategy to address challenges • Regularly compare quality performance Aspirations to improve costs • Meet system aspirations of being recognized as on of the top 25 systems in the world in terms of value for money • Improve productivity and quality while reducing cost in the setting of economic uncertainty and non-monetary productivity metrics to benchmarks (though good benchmarks are lacking) • Pursue lean approaches throughout the system and especially in acute care setting • Fine-tune resources along the patient pathway to ensure system operates at optimal capacity Success Stories • Lothian has in partnership with GE Healthcare used Lean methodologies to achieve substantial improvements in efficiency of key services SOURCE: Lothian leadership team interviews
 Quality: Summary of aspirations, challenges, strategy and success stories Current strategy to address challenges • Invest in Bioquarter Edinburgh to take Aspirations to achieve quality • Be recognized as region which is among the top 25 regions • • worldwide in terms of care outcomes Become a centre for medical innovation and commercialization Become national leader in patient safety Reduce inequalities in outcomes for disadvantaged population Improve outcomes for long term conditions research from ‘bench to bedside to business’ • Use promise of capital investment programs to motivate change among clinicians • Undertake large patient safety improvement project with Institute for Healthcare Improvement • Launch wellness programs to encourage patients to take ownership of their health • Improve systems for measuring outcomes – e. g. Eurocare, primary care data Success Stories • Lothian has exceeded all national targets for the reduction of hospital acquired infections • Keep Well campaign has significantly increased numbers of disadvantaged population having a PCP check up
Quality: Summary of aspirations, challenges, strategy and success stories Current strategy to address challenges • Invest in Bioquarter Edinburgh to take Aspirations to achieve quality • Be recognized as region which is among the top 25 regions • • worldwide in terms of care outcomes Become a centre for medical innovation and commercialization Become national leader in patient safety Reduce inequalities in outcomes for disadvantaged population Improve outcomes for long term conditions research from ‘bench to bedside to business’ • Use promise of capital investment programs to motivate change among clinicians • Undertake large patient safety improvement project with Institute for Healthcare Improvement • Launch wellness programs to encourage patients to take ownership of their health • Improve systems for measuring outcomes – e. g. Eurocare, primary care data Success Stories • Lothian has exceeded all national targets for the reduction of hospital acquired infections • Keep Well campaign has significantly increased numbers of disadvantaged population having a PCP check up
 The Lothian Way and Training Three themes People Centered - putting people at the heart of everything we do - being sensitive to individuals needs and providing the right service at the right time in the right place Partnership - working in partnership with staff, patients, the public and other agencies to provide the best possible service - being inclusive, involving patients and local people in decisions of their own healthcare Integrity - respecting people as individuals and treating them with courtesy and dignity - communicating openly and honestly; with each other and public
The Lothian Way and Training Three themes People Centered - putting people at the heart of everything we do - being sensitive to individuals needs and providing the right service at the right time in the right place Partnership - working in partnership with staff, patients, the public and other agencies to provide the best possible service - being inclusive, involving patients and local people in decisions of their own healthcare Integrity - respecting people as individuals and treating them with courtesy and dignity - communicating openly and honestly; with each other and public
 Re-Investment: Training & Development Additional £ 2. 7 million in staff training commitments Directly impact on 17, 500 staff Deals with the challenges emerging from the recent staff survey • Customer Care • Patient Experience • Health and Safety • Communications • Management of Change and Staff Engagement Priorities within key strategic themes as set out in our HR & OD Strategy • Living Values Engaging Leadership • Delivering Quality
Re-Investment: Training & Development Additional £ 2. 7 million in staff training commitments Directly impact on 17, 500 staff Deals with the challenges emerging from the recent staff survey • Customer Care • Patient Experience • Health and Safety • Communications • Management of Change and Staff Engagement Priorities within key strategic themes as set out in our HR & OD Strategy • Living Values Engaging Leadership • Delivering Quality
 Succession Planning and Development Importance of succession planning Designing a world class development programme in conjunction with the Edinburgh Institute of leadership & Management Practice (the Business Schools of Edinburgh and Edinburgh Napier Universities) and a world class university from USA. Launched in November 2009 20 places per annum on a 2 year – Masters level accredited bespoke programme Employees will be selected for the programme based on competency assessment and potential for senior management position.
Succession Planning and Development Importance of succession planning Designing a world class development programme in conjunction with the Edinburgh Institute of leadership & Management Practice (the Business Schools of Edinburgh and Edinburgh Napier Universities) and a world class university from USA. Launched in November 2009 20 places per annum on a 2 year – Masters level accredited bespoke programme Employees will be selected for the programme based on competency assessment and potential for senior management position.
 Lean in Lothian Benefit Highlights 2008/09 Patient Experience • Improved patient environments and information • New models for mental health older people • Urgent out-patient assessment slots, Same day triage, clinic outcomes recording (OPD 2) • Improved discharge planning–Liberton • 10% reduction in SAS A&E turnaround time • One stop wheelchair clinics introduced: 80% of adults same day provision (was 52 days) • Same day triage and appointing and improved theatre booking – potential 110 extra hand surgery cases pa • Pilot of 24/48 hour vetting and booking in MRI • Colorectal service achieving 98% cancer target Clinical/Corporate Governance • Increased use of Patient Management System (TRAK) to improve case management • Improved information transfer from SAS • Capacity and demand analysis to support delivery of 18 week RTT • Standardised admission, assessment and discharge processes improve reliability • 4 workstreams to improve unscheduled care identified and underway • Increased productivity, reduced duplication Overall anticipated cost saving/avoidance of £ 1. 4 million Skills Transfer • Lothian now self sufficient in lean, CAP and workout training • Integrated with workforce development • >120 delegates attended training • Lean leaders trained in advanced lean • >150 staff participated in events • Learning shared across NHS Scotland Process Culture • National recognition of lean project achievements -HSDU • Positive feedback from kaizen participants • More services taking forward further process improvements post-kaizen • Kaizens at St John’s and Astley Ainslie • Staff partnership support for all projects
Lean in Lothian Benefit Highlights 2008/09 Patient Experience • Improved patient environments and information • New models for mental health older people • Urgent out-patient assessment slots, Same day triage, clinic outcomes recording (OPD 2) • Improved discharge planning–Liberton • 10% reduction in SAS A&E turnaround time • One stop wheelchair clinics introduced: 80% of adults same day provision (was 52 days) • Same day triage and appointing and improved theatre booking – potential 110 extra hand surgery cases pa • Pilot of 24/48 hour vetting and booking in MRI • Colorectal service achieving 98% cancer target Clinical/Corporate Governance • Increased use of Patient Management System (TRAK) to improve case management • Improved information transfer from SAS • Capacity and demand analysis to support delivery of 18 week RTT • Standardised admission, assessment and discharge processes improve reliability • 4 workstreams to improve unscheduled care identified and underway • Increased productivity, reduced duplication Overall anticipated cost saving/avoidance of £ 1. 4 million Skills Transfer • Lothian now self sufficient in lean, CAP and workout training • Integrated with workforce development • >120 delegates attended training • Lean leaders trained in advanced lean • >150 staff participated in events • Learning shared across NHS Scotland Process Culture • National recognition of lean project achievements -HSDU • Positive feedback from kaizen participants • More services taking forward further process improvements post-kaizen • Kaizens at St John’s and Astley Ainslie • Staff partnership support for all projects
 Bio. Quarter
Bio. Quarter
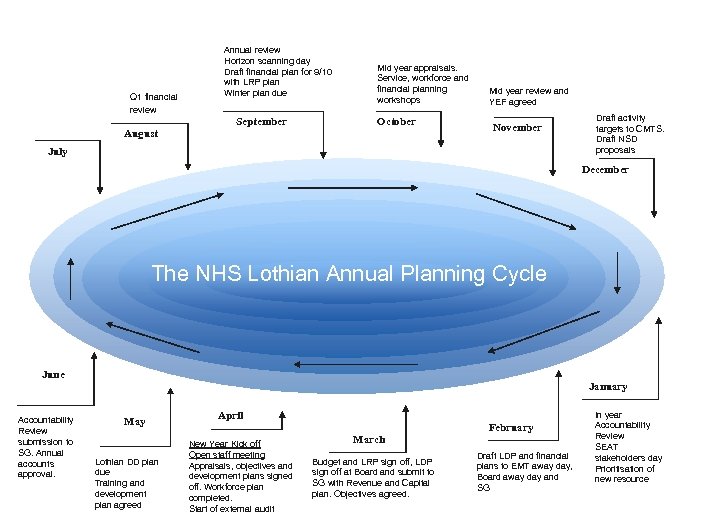 Q 1 financial review August Annual review Horizon scanning day Draft financial plan for 9/10 with LRP plan Winter plan due September Mid year appraisals. Service, workforce and financial planning workshops October Mid year review and YEF agreed November July Draft activity targets to CMTS. Draft NSD proposals December The NHS Lothian Annual Planning Cycle June Accountability Review submission to SG. Annual accounts approval. January May Lothian DD plan due Training and development plan agreed April New Year Kick off Open staff meeting Appraisals, objectives and development plans signed off. Workforce plan completed. Start of external audit March Budget and LRP sign off, LDP sign off at Board and submit to SG with Revenue and Capital plan. Objectives agreed. February Draft LDP and financial plans to EMT away day, Board away day and SG In year Accountability Review SEAT stakeholders day Prioritisation of new resource
Q 1 financial review August Annual review Horizon scanning day Draft financial plan for 9/10 with LRP plan Winter plan due September Mid year appraisals. Service, workforce and financial planning workshops October Mid year review and YEF agreed November July Draft activity targets to CMTS. Draft NSD proposals December The NHS Lothian Annual Planning Cycle June Accountability Review submission to SG. Annual accounts approval. January May Lothian DD plan due Training and development plan agreed April New Year Kick off Open staff meeting Appraisals, objectives and development plans signed off. Workforce plan completed. Start of external audit March Budget and LRP sign off, LDP sign off at Board and submit to SG with Revenue and Capital plan. Objectives agreed. February Draft LDP and financial plans to EMT away day, Board away day and SG In year Accountability Review SEAT stakeholders day Prioritisation of new resource
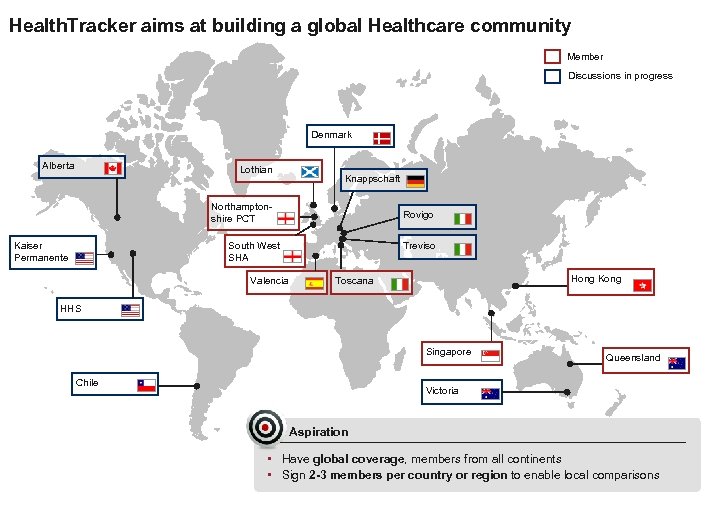 Health. Tracker aims at building a global Healthcare community Member Discussions in progress Denmark Alberta Lothian Knappschaft Northamptonshire PCT Rovigo South West SHA Kaiser Permanente Valencia Treviso Hong Kong Toscana HHS Singapore Chile Queensland Victoria Aspiration • Have global coverage, members from all continents • Sign 2 -3 members per country or region to enable local comparisons
Health. Tracker aims at building a global Healthcare community Member Discussions in progress Denmark Alberta Lothian Knappschaft Northamptonshire PCT Rovigo South West SHA Kaiser Permanente Valencia Treviso Hong Kong Toscana HHS Singapore Chile Queensland Victoria Aspiration • Have global coverage, members from all continents • Sign 2 -3 members per country or region to enable local comparisons
 Menu WELCOME to HEALTH TRACKER This is the prototype version of the upcoming new service from Mc. Kinsey & Company on health care management. Health. Tracker creates insights that deepen and advance health leaders’ ability to improve health system performance and make the most effective use of their healthcare budget. Please select one of the 5 resources section to start your journey with Health. Tracker. PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT CLINICAL HEALTH ECONOMICS IMPLEMENTATION KNOWLEDGE LEADERSHIP INSIGHTS BANK NETWORK Performance drivers Executive questions My dashboard My insights Mc. Kinsey research Clinical pathway Best practice insights Mc. Kinsey publications Expert-on-demand News Expert-on-demand My network Connect & collaborate Events You have mail: Soraya > Interesting article on region 3’s use of specialized care f… News: 4 th Paris international health care forum, Paris, April 23 rd, 2009 …go to inbox You are signed in as Alvin Bauer | Sign out © Copyright Mc. Kinsey 2009 | Privacy policy | Terms of use
Menu WELCOME to HEALTH TRACKER This is the prototype version of the upcoming new service from Mc. Kinsey & Company on health care management. Health. Tracker creates insights that deepen and advance health leaders’ ability to improve health system performance and make the most effective use of their healthcare budget. Please select one of the 5 resources section to start your journey with Health. Tracker. PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT CLINICAL HEALTH ECONOMICS IMPLEMENTATION KNOWLEDGE LEADERSHIP INSIGHTS BANK NETWORK Performance drivers Executive questions My dashboard My insights Mc. Kinsey research Clinical pathway Best practice insights Mc. Kinsey publications Expert-on-demand News Expert-on-demand My network Connect & collaborate Events You have mail: Soraya > Interesting article on region 3’s use of specialized care f… News: 4 th Paris international health care forum, Paris, April 23 rd, 2009 …go to inbox You are signed in as Alvin Bauer | Sign out © Copyright Mc. Kinsey 2009 | Privacy policy | Terms of use
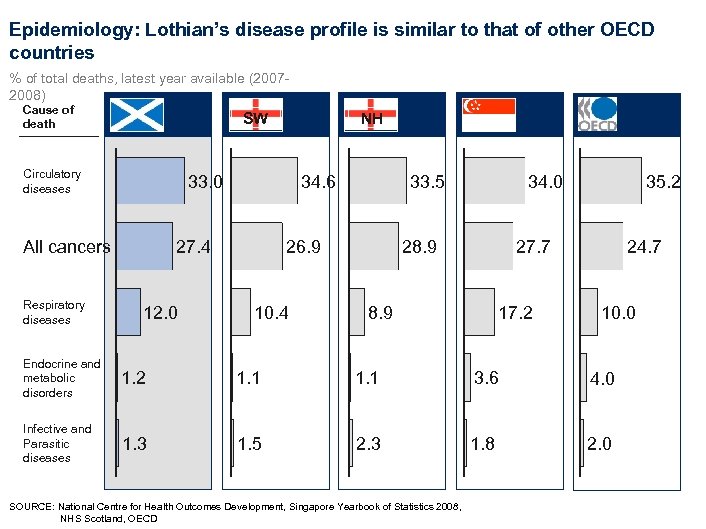 Epidemiology: Lothian’s disease profile is similar to that of other OECD countries % of total deaths, latest year available (20072008) Cause of death SW Circulatory diseases 33. 0 All cancers Respiratory diseases NH 34. 6 27. 4 12. 0 33. 5 26. 9 10. 4 34. 0 28. 9 35. 2 27. 7 8. 9 17. 2 24. 7 10. 0 Endocrine and metabolic disorders 1. 2 1. 1 3. 6 4. 0 Infective and Parasitic diseases 1. 3 1. 5 2. 3 1. 8 2. 0 SOURCE: National Centre for Health Outcomes Development, Singapore Yearbook of Statistics 2008, NHS Scotland, OECD
Epidemiology: Lothian’s disease profile is similar to that of other OECD countries % of total deaths, latest year available (20072008) Cause of death SW Circulatory diseases 33. 0 All cancers Respiratory diseases NH 34. 6 27. 4 12. 0 33. 5 26. 9 10. 4 34. 0 28. 9 35. 2 27. 7 8. 9 17. 2 24. 7 10. 0 Endocrine and metabolic disorders 1. 2 1. 1 3. 6 4. 0 Infective and Parasitic diseases 1. 3 1. 5 2. 3 1. 8 2. 0 SOURCE: National Centre for Health Outcomes Development, Singapore Yearbook of Statistics 2008, NHS Scotland, OECD
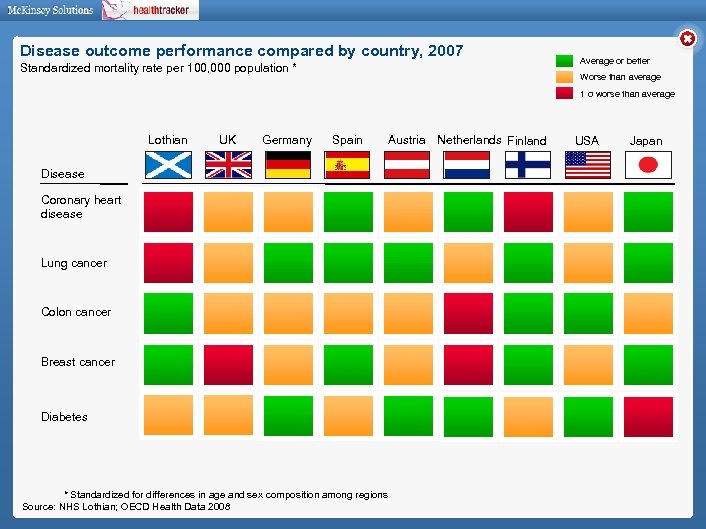 Disease outcome performance compared by country, 2007 Standardized mortality rate per 100, 000 population * Average or better Worse than average 1 σ worse than average Lothian UK Germany Spain Disease Coronary heart disease Lung cancer Colon cancer Breast cancer Diabetes * Standardized for differences in age and sex composition among regions Source: NHS Lothian; OECD Health Data 2008 Austria Netherlands Finland USA Japan
Disease outcome performance compared by country, 2007 Standardized mortality rate per 100, 000 population * Average or better Worse than average 1 σ worse than average Lothian UK Germany Spain Disease Coronary heart disease Lung cancer Colon cancer Breast cancer Diabetes * Standardized for differences in age and sex composition among regions Source: NHS Lothian; OECD Health Data 2008 Austria Netherlands Finland USA Japan
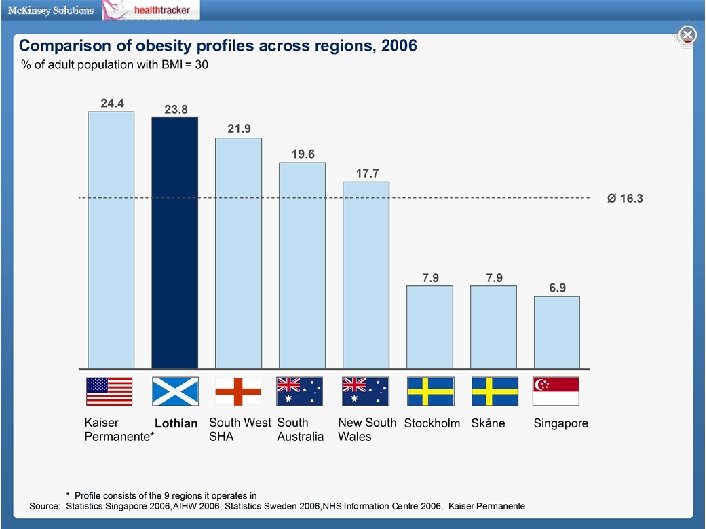
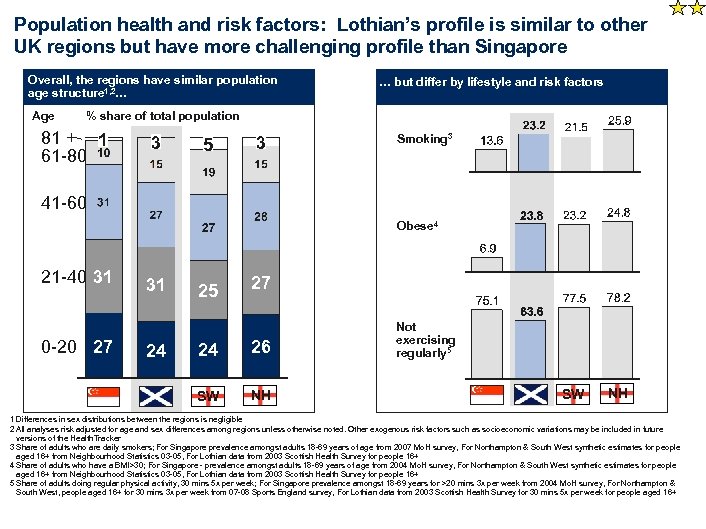 Population health and risk factors: Lothian’s profile is similar to other UK regions but have more challenging profile than Singapore Overall, the regions have similar population age structure 1, 2… Age … but differ by lifestyle and risk factors % share of total population 81 + 1 61 -80 3 5 3 Smoking 3 41 -60 Obese 4 21 -40 31 0 -20 27 31 25 27 24 26 SW 24 NH Not exercising regularly 5 SW NH 1 Differences in sex distributions between the regions is negligible 2 All analyses risk adjusted for age and sex differences among regions unless otherwise noted. Other exogenous risk factors such as socioeconomic variations may be included in future versions of the Health. Tracker 3 Share of adults who are daily smokers; For Singapore prevalence amongst adults 18 -69 years of age from 2007 Mo. H survey, For Northampton & South West synthetic estimates for people aged 16+ from Neighbourhood Statistics 03 -05, For Lothian data from 2003 Scottish Health Survey for people 16+ 4 Share of adults who have a BMI>30; For Singapore - prevalence amongst adults 18 -69 years of age from 2004 Mo. H survey, For Northampton & South West synthetic estimates for people aged 16+ from Neighbourhood Statistics 03 -05, For Lothian data from 2003 Scottish Health Survey for people 16+ 5 Share of adults doing regular physical activity, 30 mins 5 x per week; For Singapore prevalence amongst 18 -69 years for >20 mins 3 x per week from 2004 Mo. H survey, For Northampton & South West, people aged 16+ for 30 mins 3 x per week from 07 -08 Sports England survey, For Lothian data from 2003 Scottish Health Survey for 30 mins 5 x per week for people aged 16+
Population health and risk factors: Lothian’s profile is similar to other UK regions but have more challenging profile than Singapore Overall, the regions have similar population age structure 1, 2… Age … but differ by lifestyle and risk factors % share of total population 81 + 1 61 -80 3 5 3 Smoking 3 41 -60 Obese 4 21 -40 31 0 -20 27 31 25 27 24 26 SW 24 NH Not exercising regularly 5 SW NH 1 Differences in sex distributions between the regions is negligible 2 All analyses risk adjusted for age and sex differences among regions unless otherwise noted. Other exogenous risk factors such as socioeconomic variations may be included in future versions of the Health. Tracker 3 Share of adults who are daily smokers; For Singapore prevalence amongst adults 18 -69 years of age from 2007 Mo. H survey, For Northampton & South West synthetic estimates for people aged 16+ from Neighbourhood Statistics 03 -05, For Lothian data from 2003 Scottish Health Survey for people 16+ 4 Share of adults who have a BMI>30; For Singapore - prevalence amongst adults 18 -69 years of age from 2004 Mo. H survey, For Northampton & South West synthetic estimates for people aged 16+ from Neighbourhood Statistics 03 -05, For Lothian data from 2003 Scottish Health Survey for people 16+ 5 Share of adults doing regular physical activity, 30 mins 5 x per week; For Singapore prevalence amongst 18 -69 years for >20 mins 3 x per week from 2004 Mo. H survey, For Northampton & South West, people aged 16+ for 30 mins 3 x per week from 07 -08 Sports England survey, For Lothian data from 2003 Scottish Health Survey for 30 mins 5 x per week for people aged 16+
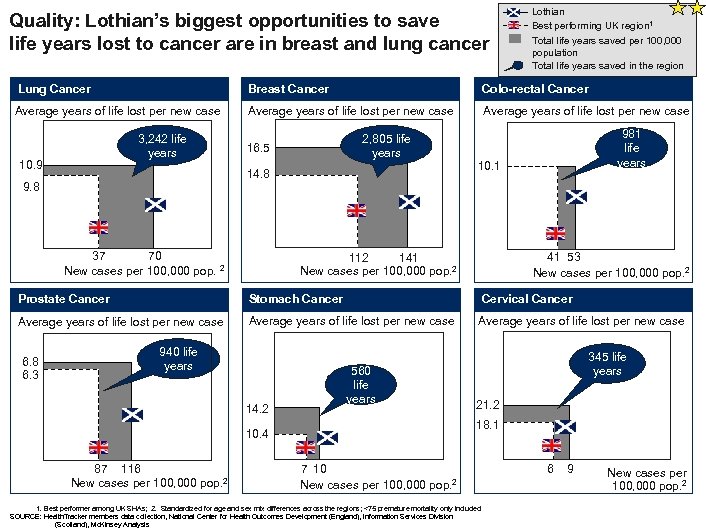 Quality: Lothian’s biggest opportunities to save life years lost to cancer are in breast and lung cancer Lothian Best performing UK region 1 Total life years saved per 100, 000 population Total life years saved in the region Lung Cancer Breast Cancer Colo-rectal Cancer Average years of life lost per new case 3, 242 life years 10. 9 2, 805 life years 16. 5 14. 8 9. 8 37 70 New cases per 100, 000 pop. 2 981 life years 10. 1 41 53 New cases per 100, 000 pop. 2 112 141 New cases per 100, 000 pop. 2 Prostate Cancer Stomach Cancer Cervical Cancer Average years of life lost per new case 6. 8 6. 3 940 life years 14. 2 560 life years 21. 2 18. 1 10. 4 87 116 New cases per 100, 000 pop. 2 345 life years 7 10 New cases per 100, 000 pop. 2 1. Best performer among UK SHAs; 2. Standardized for age and sex mix differences across the regions; <75 premature mortality only included SOURCE: Health. Tracker members data collection, National Center for Health Outcomes Development (England), Information Services Division (Scotland), Mc. Kinsey Analysis 6 9 New cases per 100, 000 pop. 2
Quality: Lothian’s biggest opportunities to save life years lost to cancer are in breast and lung cancer Lothian Best performing UK region 1 Total life years saved per 100, 000 population Total life years saved in the region Lung Cancer Breast Cancer Colo-rectal Cancer Average years of life lost per new case 3, 242 life years 10. 9 2, 805 life years 16. 5 14. 8 9. 8 37 70 New cases per 100, 000 pop. 2 981 life years 10. 1 41 53 New cases per 100, 000 pop. 2 112 141 New cases per 100, 000 pop. 2 Prostate Cancer Stomach Cancer Cervical Cancer Average years of life lost per new case 6. 8 6. 3 940 life years 14. 2 560 life years 21. 2 18. 1 10. 4 87 116 New cases per 100, 000 pop. 2 345 life years 7 10 New cases per 100, 000 pop. 2 1. Best performer among UK SHAs; 2. Standardized for age and sex mix differences across the regions; <75 premature mortality only included SOURCE: Health. Tracker members data collection, National Center for Health Outcomes Development (England), Information Services Division (Scotland), Mc. Kinsey Analysis 6 9 New cases per 100, 000 pop. 2
 Patient Safety • Reducing line infections (3 ITUs) – 60% in 1 y, >150 days with no infection • C. difficile – 80% reduction in pilot wards, 40% across others as spread • Leadership – Every board agenda, monthly at EMT, regular walkrounds, feedback and actions
Patient Safety • Reducing line infections (3 ITUs) – 60% in 1 y, >150 days with no infection • C. difficile – 80% reduction in pilot wards, 40% across others as spread • Leadership – Every board agenda, monthly at EMT, regular walkrounds, feedback and actions
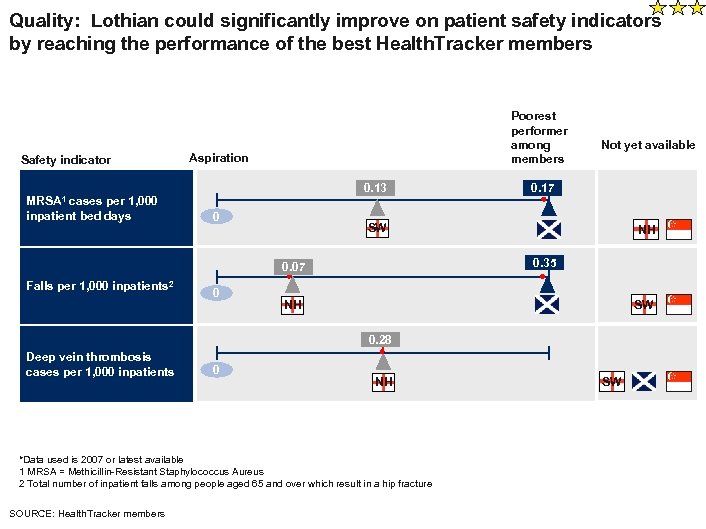 Quality: Lothian could significantly improve on patient safety indicators by reaching the performance of the best Health. Tracker members Safety indicator MRSA 1 cases per 1, 000 inpatient bed days Poorest performer among members Aspiration 0. 13 0 0 0. 17 SW NH 0. 35 0. 07 Falls per 1, 000 inpatients 2 Not yet available NH SW 0. 28 Deep vein thrombosis cases per 1, 000 inpatients 0 NH *Data used is 2007 or latest available 1 MRSA = Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus 2 Total number of inpatient falls among people aged 65 and over which result in a hip fracture SOURCE: Health. Tracker members SW
Quality: Lothian could significantly improve on patient safety indicators by reaching the performance of the best Health. Tracker members Safety indicator MRSA 1 cases per 1, 000 inpatient bed days Poorest performer among members Aspiration 0. 13 0 0 0. 17 SW NH 0. 35 0. 07 Falls per 1, 000 inpatients 2 Not yet available NH SW 0. 28 Deep vein thrombosis cases per 1, 000 inpatients 0 NH *Data used is 2007 or latest available 1 MRSA = Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus 2 Total number of inpatient falls among people aged 65 and over which result in a hip fracture SOURCE: Health. Tracker members SW
 e. Health Metrics • 23, 000 IT users • 12, 000 PCs • 279 sites • 10, 000 service desk calls per month • 95% customer satisfaction score • We spend 0. 86% of our budget on e. Health c. £ 11 m
e. Health Metrics • 23, 000 IT users • 12, 000 PCs • 279 sites • 10, 000 service desk calls per month • 95% customer satisfaction score • We spend 0. 86% of our budget on e. Health c. £ 11 m
 Big Ticket Deliverables Acute • Single PMS across all acute sites (2008) • Single PACS solution with Scotland-wide archive (2009) • Electronic ordering of laboratory and radiological investigations (2007 -09) • Call centre technology for Patient Appointments (2009 -) • Single regional laboratory system (2004 -09)
Big Ticket Deliverables Acute • Single PMS across all acute sites (2008) • Single PACS solution with Scotland-wide archive (2009) • Electronic ordering of laboratory and radiological investigations (2007 -09) • Call centre technology for Patient Appointments (2009 -) • Single regional laboratory system (2004 -09)
 Big Ticket Deliverables General Practice 2009 • 124 Practices • 85% using the same Practice System • Maturity of information system use allows very rich data mining activities to influence patient care • Electronic referrals to secondary care >95%
Big Ticket Deliverables General Practice 2009 • 124 Practices • 85% using the same Practice System • Maturity of information system use allows very rich data mining activities to influence patient care • Electronic referrals to secondary care >95%
 Big Ticket Deliverables Infrastructure • Upgraded Wide Area Network to 1 GB core with 100 MB to most medium sites and 10 MB to remainder. • Storage Area Networks at each main site with cross-site replication. • Server consolidation and virtualisation to reduce servers and use less energy • Single Active directory ( incl. GPs) to manage all users safely • Nearly universal use of CHI (>98% acute hospital and GP, >70% community, pharmacy etc)
Big Ticket Deliverables Infrastructure • Upgraded Wide Area Network to 1 GB core with 100 MB to most medium sites and 10 MB to remainder. • Storage Area Networks at each main site with cross-site replication. • Server consolidation and virtualisation to reduce servers and use less energy • Single Active directory ( incl. GPs) to manage all users safely • Nearly universal use of CHI (>98% acute hospital and GP, >70% community, pharmacy etc)
 Work in Progress Applications • Extend functionality in PMS to facilitate the eradication of home-grown audit/clinical databases • Modify PMS to fully support 18 Wks RTT and Cancer Tracking • Improve results reporting features to allow on-line signoff from multiple sites and locations • Implement Clinical Portal to enable clinicians to see all parts of record held on multiple, different systems including GP
Work in Progress Applications • Extend functionality in PMS to facilitate the eradication of home-grown audit/clinical databases • Modify PMS to fully support 18 Wks RTT and Cancer Tracking • Improve results reporting features to allow on-line signoff from multiple sites and locations • Implement Clinical Portal to enable clinicians to see all parts of record held on multiple, different systems including GP
 Work in Progress Infrastructure • Rollout of Microsoft OCS collaboration tools to 1000 people to facilitate smart working instead of travel to meetings • New hosting of external web site to develop patient feedback electronically and create community of users and consultees, and improve document workflow • Exploration of potential of Virtual Avatars in the clinical setting e. g. HIV drug compliance and sexual health history • Airline type check in booths • Digital telephony to confirm/change clinic appointments • Digital ECGs • Front sheet e-summary of all attendances and admissions
Work in Progress Infrastructure • Rollout of Microsoft OCS collaboration tools to 1000 people to facilitate smart working instead of travel to meetings • New hosting of external web site to develop patient feedback electronically and create community of users and consultees, and improve document workflow • Exploration of potential of Virtual Avatars in the clinical setting e. g. HIV drug compliance and sexual health history • Airline type check in booths • Digital telephony to confirm/change clinic appointments • Digital ECGs • Front sheet e-summary of all attendances and admissions
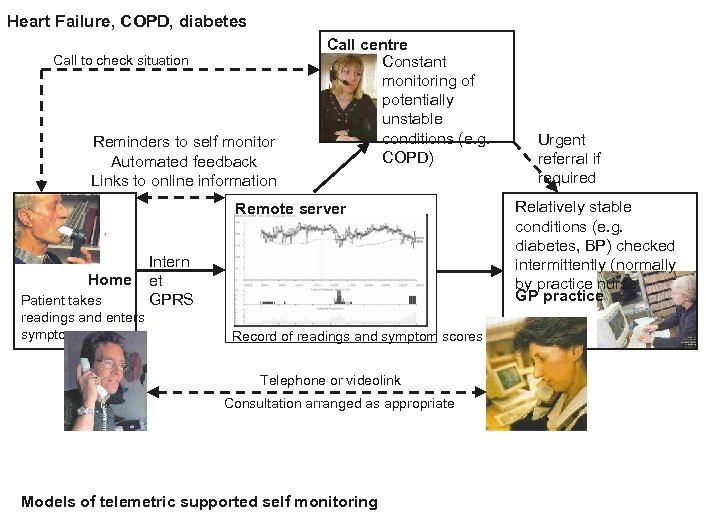 Heart Failure, COPD, diabetes Call to check situation Reminders to self monitor Automated feedback Links to online information Call centre Constant monitoring of potentially unstable conditions (e. g. COPD) Remote server Home Patient takes readings and enters symptom score Intern et GPRS Record of readings and symptom scores Telephone or videolink Consultation arranged as appropriate Models of telemetric supported self monitoring Urgent referral if required Relatively stable conditions (e. g. diabetes, BP) checked intermittently (normally by practice nurse GP practice
Heart Failure, COPD, diabetes Call to check situation Reminders to self monitor Automated feedback Links to online information Call centre Constant monitoring of potentially unstable conditions (e. g. COPD) Remote server Home Patient takes readings and enters symptom score Intern et GPRS Record of readings and symptom scores Telephone or videolink Consultation arranged as appropriate Models of telemetric supported self monitoring Urgent referral if required Relatively stable conditions (e. g. diabetes, BP) checked intermittently (normally by practice nurse GP practice
 Early Results COPD Complete questionnaire each day Physiological measures as needed Call centre monitors
Early Results COPD Complete questionnaire each day Physiological measures as needed Call centre monitors
 Do the patients like it? “I’ve never felt so well looked after in my life. I think it’s a godsend like. ” (Patient aged 58) “I don’t worry about him the same as I used tae. It’s all taken care of before it can get tae that level. That machine can tell Alec he’s ill even before he kens it hisself” (Spouse of patient aged 75) “There’s some times you phone them up for an appointment ye cannae get one. . . So I feel if I’ve got that (telehealth device) I’ve got a chance of a doctor anyway. ” (Patient age 75)
Do the patients like it? “I’ve never felt so well looked after in my life. I think it’s a godsend like. ” (Patient aged 58) “I don’t worry about him the same as I used tae. It’s all taken care of before it can get tae that level. That machine can tell Alec he’s ill even before he kens it hisself” (Spouse of patient aged 75) “There’s some times you phone them up for an appointment ye cannae get one. . . So I feel if I’ve got that (telehealth device) I’ve got a chance of a doctor anyway. ” (Patient age 75)
 Conclusions Patients like Telehealth It encourages evidence based practice and quality care Telehealth systems need robust underpinning structures to observe and manage the data provided Implementation needs to involve users early and must emphasise patient benefit They may not save time/resources in primary care We need rigorous research to discover where and how the systems are best applied
Conclusions Patients like Telehealth It encourages evidence based practice and quality care Telehealth systems need robust underpinning structures to observe and manage the data provided Implementation needs to involve users early and must emphasise patient benefit They may not save time/resources in primary care We need rigorous research to discover where and how the systems are best applied
 Implementation: what have we learned so far The infrastructure planning is more important than the device Clinicians need to believe there is a clear need for the device They will become involved if they believe patients will benefit Equipment should be easy to use and ideally, designed around the existing service
Implementation: what have we learned so far The infrastructure planning is more important than the device Clinicians need to believe there is a clear need for the device They will become involved if they believe patients will benefit Equipment should be easy to use and ideally, designed around the existing service
 Primary Aim in this Planning Window • Provide the right in information, at the right time in the right place, However : • 5 million casenote volumes • 37 linear kilometres of shelving • We therefore need to reduce our reliance on paper ASAP • Implementation of scanning solution in Health Records • Accelerate EPR solution
Primary Aim in this Planning Window • Provide the right in information, at the right time in the right place, However : • 5 million casenote volumes • 37 linear kilometres of shelving • We therefore need to reduce our reliance on paper ASAP • Implementation of scanning solution in Health Records • Accelerate EPR solution
 Primary Care IM&T Needs What is needed…. 78% of consultations are NOT about QOF – more info about managing demand Poorly performing doctors, & excellence…. Information by GP - not by practice Number of GPs - by hours worked Resource for analysing pt identifiable data
Primary Care IM&T Needs What is needed…. 78% of consultations are NOT about QOF – more info about managing demand Poorly performing doctors, & excellence…. Information by GP - not by practice Number of GPs - by hours worked Resource for analysing pt identifiable data

 5 Themes
5 Themes
 5 Themes 5 Teams
5 Themes 5 Teams
 5 Themes 5 Teams 5 People
5 Themes 5 Teams 5 People
 Themes of Lothian’s 5 x 5 x 5 programme I Patient Experience II Cost v Quality in a new economic context III Building community capacity to deliver Health Inequalities IV Worlds Best Clinical Quality V Demand Management, focusing on unscheduled care – with IM&T threading through all themes
Themes of Lothian’s 5 x 5 x 5 programme I Patient Experience II Cost v Quality in a new economic context III Building community capacity to deliver Health Inequalities IV Worlds Best Clinical Quality V Demand Management, focusing on unscheduled care – with IM&T threading through all themes




