3e279fa3752ec694aa9346d33b42d1e7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 WORKSHOP PRIMARY CARE: Regional strategies to improve efficacy and equity while guarateeing economic sustainability e-Health in Primary Care contributing to economic sustainability in Andalusia Ana Carriazo Senior Advisor General Secretariat for Quality and Modernisation Regional Ministry of Health of Andalusia, Spain anam. carriazo@juntadeandalucia. es
WORKSHOP PRIMARY CARE: Regional strategies to improve efficacy and equity while guarateeing economic sustainability e-Health in Primary Care contributing to economic sustainability in Andalusia Ana Carriazo Senior Advisor General Secretariat for Quality and Modernisation Regional Ministry of Health of Andalusia, Spain anam. carriazo@juntadeandalucia. es
 Overview Diraya’s environment Diraya’s main features Facts and figures Costs and benefits Lessons learnt 13 June 2011
Overview Diraya’s environment Diraya’s main features Facts and figures Costs and benefits Lessons learnt 13 June 2011
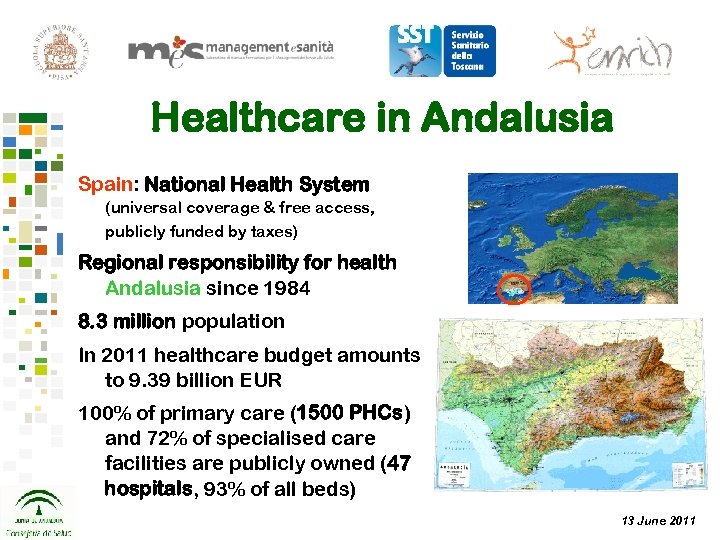 Healthcare in Andalusia Spain: National Health System (universal coverage & free access, publicly funded by taxes) Regional responsibility for health Andalusia since 1984 8. 3 million population In 2011 healthcare budget amounts to 9. 39 billion EUR 100% of primary care (1500 PHCs) and 72% of specialised care facilities are publicly owned (47 hospitals, 93% of all beds) 13 June 2011
Healthcare in Andalusia Spain: National Health System (universal coverage & free access, publicly funded by taxes) Regional responsibility for health Andalusia since 1984 8. 3 million population In 2011 healthcare budget amounts to 9. 39 billion EUR 100% of primary care (1500 PHCs) and 72% of specialised care facilities are publicly owned (47 hospitals, 93% of all beds) 13 June 2011
 Quality Plan e. Health Strategy 13 June 2011
Quality Plan e. Health Strategy 13 June 2011
 Diraya´s objective Integrate the healthcare information of every citizen SINGLE A HEALTH RECORD 13 June 2011
Diraya´s objective Integrate the healthcare information of every citizen SINGLE A HEALTH RECORD 13 June 2011
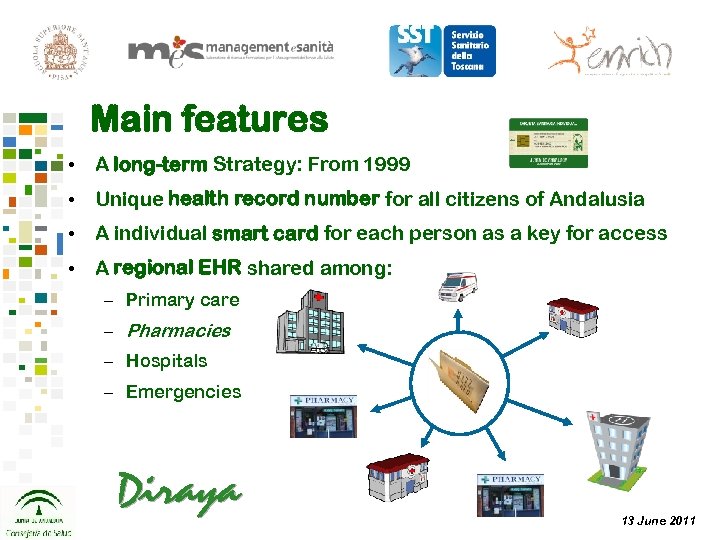 Main features • A long-term Strategy: From 1999 • Unique health record number for all citizens of Andalusia • A individual smart card for each person as a key for access • A regional EHR shared among: – Primary care – Pharmacies – Hospitals – Emergencies 13 June 2011
Main features • A long-term Strategy: From 1999 • Unique health record number for all citizens of Andalusia • A individual smart card for each person as a key for access • A regional EHR shared among: – Primary care – Pharmacies – Hospitals – Emergencies 13 June 2011
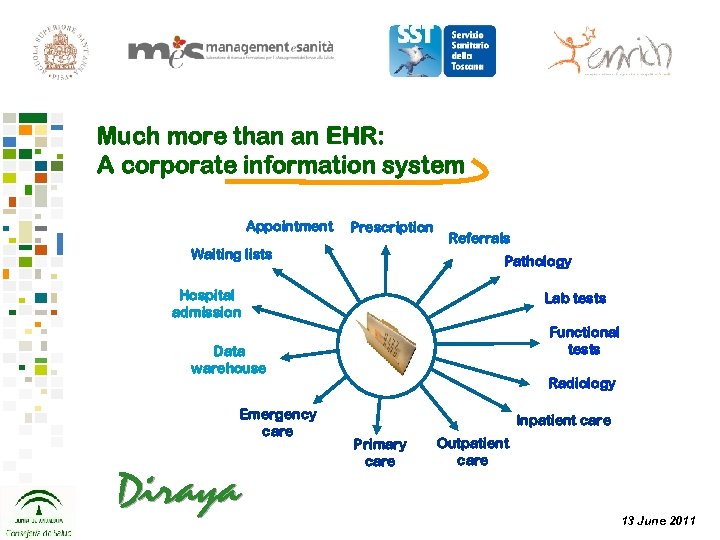 Much more than an EHR: A corporate information system Appointment Prescription Waiting lists Referrals Pathology Hospital admission Lab tests Functional tests Data warehouse Emergency care Radiology Inpatient care Primary care Outpatient care 13 June 2011
Much more than an EHR: A corporate information system Appointment Prescription Waiting lists Referrals Pathology Hospital admission Lab tests Functional tests Data warehouse Emergency care Radiology Inpatient care Primary care Outpatient care 13 June 2011
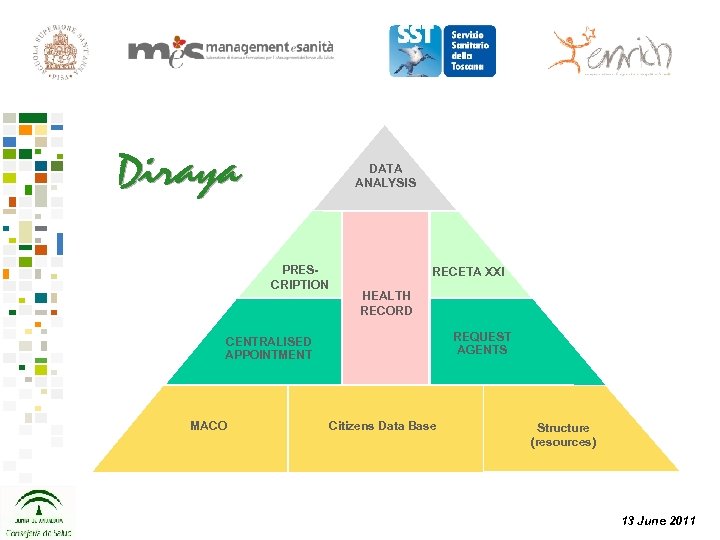 DATA ANALYSIS PRESCRIPTION RECETA XXI HEALTH RECORD REQUEST AGENTS CENTRALISED APPOINTMENT MACO Citizens Data Base Structure (resources) 13 June 2011
DATA ANALYSIS PRESCRIPTION RECETA XXI HEALTH RECORD REQUEST AGENTS CENTRALISED APPOINTMENT MACO Citizens Data Base Structure (resources) 13 June 2011
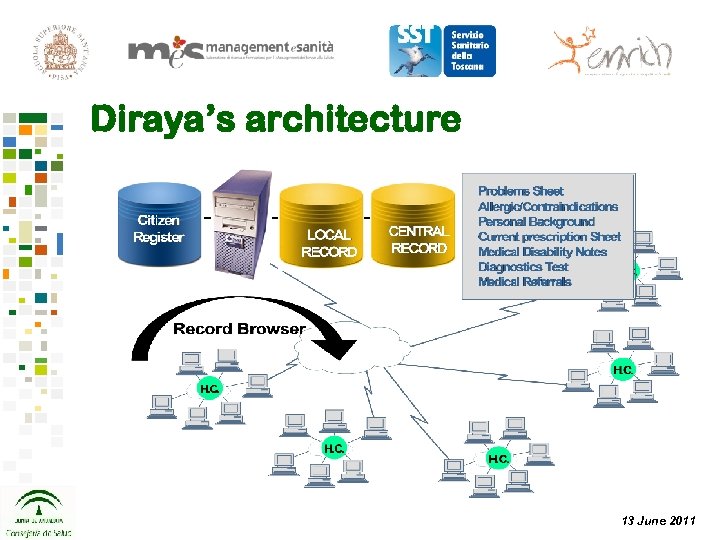 Diraya’s architecture 13 June 2011
Diraya’s architecture 13 June 2011
 Electronic health record 13 June 2011
Electronic health record 13 June 2011
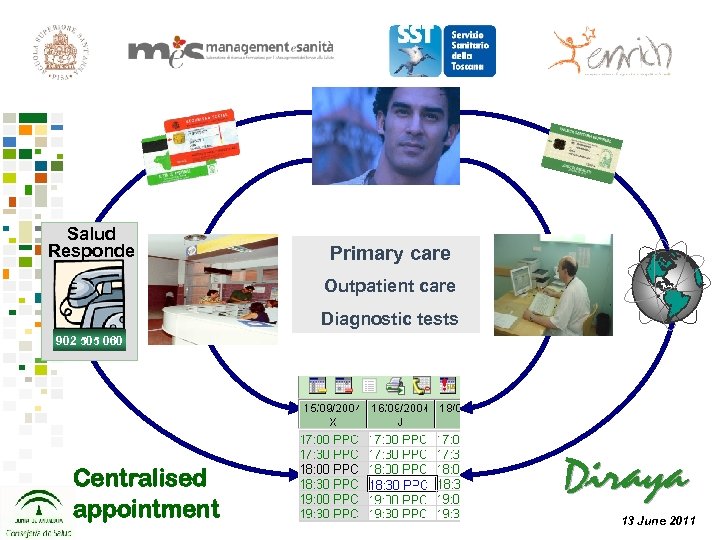 Salud Responde Primary care Outpatient care Diagnostic tests 902 505 060 Centralised appointment 13 June 2011
Salud Responde Primary care Outpatient care Diagnostic tests 902 505 060 Centralised appointment 13 June 2011
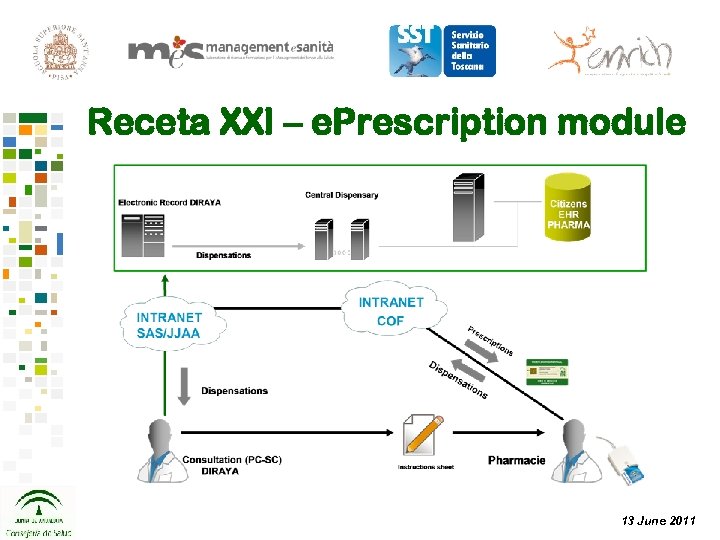 Receta XXI – e. Prescription module 13 June 2011
Receta XXI – e. Prescription module 13 June 2011
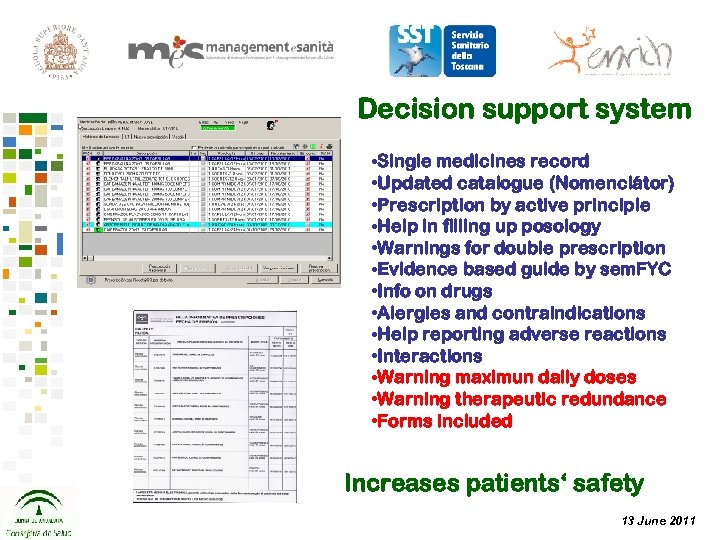 Decision support system • Single medicines record • Updated catalogue (Nomenclátor) • Prescription by active principle • Help in filling up posology • Warnings for double prescription • Evidence based guide by sem. FYC • Info on drugs • Alergies and contraindications • Help reporting adverse reactions • Interactions • Warning maximun daily doses • Warning therapeutic redundance • Forms included Increases patients‘ safety 13 June 2011
Decision support system • Single medicines record • Updated catalogue (Nomenclátor) • Prescription by active principle • Help in filling up posology • Warnings for double prescription • Evidence based guide by sem. FYC • Info on drugs • Alergies and contraindications • Help reporting adverse reactions • Interactions • Warning maximun daily doses • Warning therapeutic redundance • Forms included Increases patients‘ safety 13 June 2011
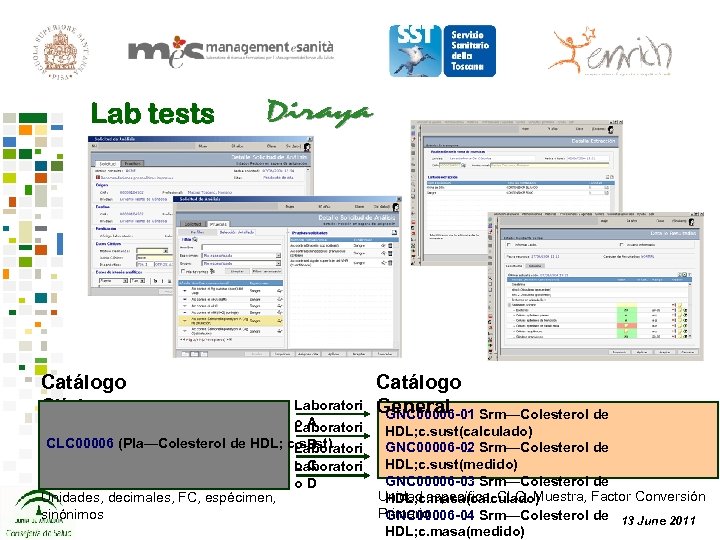 Lab tests Catálogo Clínico Laboratori o. A Laboratori CLC 00006 (Pla—Colesterol de HDL; c. sust) o. B Laboratori Unidades, decimales, FC, espécimen, sinónimos o. C Laboratori o. D Catálogo General Srm—Colesterol de GNC 00006 -01 HDL; c. sust(calculado) GNC 00006 -02 Srm—Colesterol de HDL; c. sust(medido) GNC 00006 -03 Srm—Colesterol de Unidad específica, CLC, Muestra, Factor Conversión HDL; c. masa(calculado) Primario GNC 00006 -04 Srm—Colesterol de 13 June 2011 HDL; c. masa(medido)
Lab tests Catálogo Clínico Laboratori o. A Laboratori CLC 00006 (Pla—Colesterol de HDL; c. sust) o. B Laboratori Unidades, decimales, FC, espécimen, sinónimos o. C Laboratori o. D Catálogo General Srm—Colesterol de GNC 00006 -01 HDL; c. sust(calculado) GNC 00006 -02 Srm—Colesterol de HDL; c. sust(medido) GNC 00006 -03 Srm—Colesterol de Unidad específica, CLC, Muestra, Factor Conversión HDL; c. masa(calculado) Primario GNC 00006 -04 Srm—Colesterol de 13 June 2011 HDL; c. masa(medido)
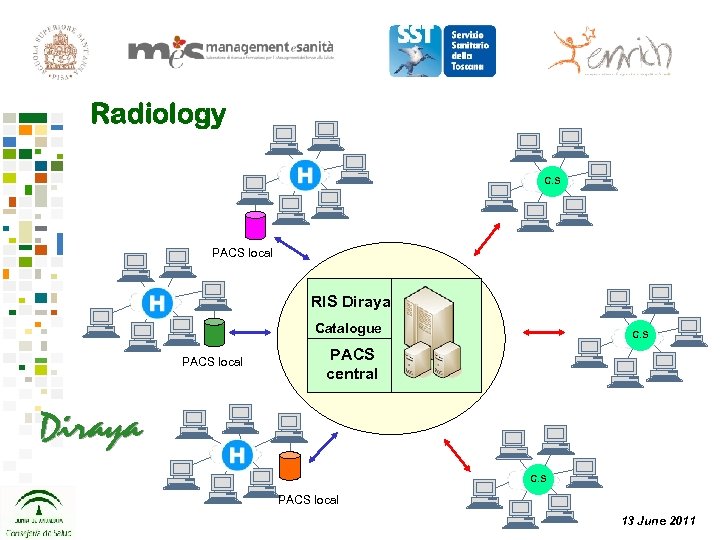 Radiology C. S PACS local RIS Diraya Catalogue PACS local C. S PACS central C. S PACS local 13 June 2011
Radiology C. S PACS local RIS Diraya Catalogue PACS local C. S PACS central C. S PACS local 13 June 2011
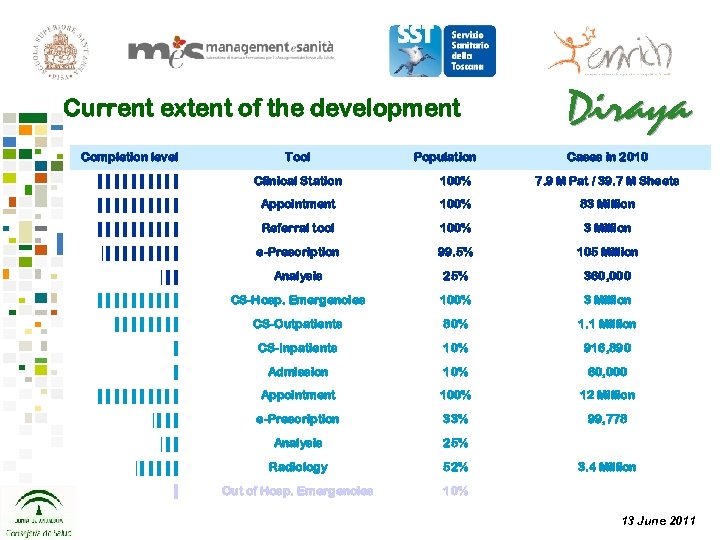 Current extent of the development Completion level Tool Population Cases in 2010 ▌▌▌▌▌ Clinical Station 100% 7. 9 M Pat / 39. 7 M Sheets ▌▌▌▌▌ Appointment 100% 83 Million ▌▌▌▌▌ Referral tool 100% 3 Million │▌▌▌▌▌ e-Prescription 99. 5% 105 Million Analysis 25% 360, 000 CS-Hosp. Emergencies 100% 3 Million CS-Outpatients 80% 1. 1 Million ▌ CS-Inpatients 10% 916, 890 ▌ Admission 10% 60, 000 Appointment 100% 12 Million e-Prescription 33% 99, 778 Analysis 25% Radiology 52% Out of Hosp. Emergencies 10% │▌▌ ▌▌▌▌▌▌▌▌ │▌▌▌▌▌ ▌ 3. 4 Million 13 June 2011
Current extent of the development Completion level Tool Population Cases in 2010 ▌▌▌▌▌ Clinical Station 100% 7. 9 M Pat / 39. 7 M Sheets ▌▌▌▌▌ Appointment 100% 83 Million ▌▌▌▌▌ Referral tool 100% 3 Million │▌▌▌▌▌ e-Prescription 99. 5% 105 Million Analysis 25% 360, 000 CS-Hosp. Emergencies 100% 3 Million CS-Outpatients 80% 1. 1 Million ▌ CS-Inpatients 10% 916, 890 ▌ Admission 10% 60, 000 Appointment 100% 12 Million e-Prescription 33% 99, 778 Analysis 25% Radiology 52% Out of Hosp. Emergencies 10% │▌▌ ▌▌▌▌▌▌▌▌ │▌▌▌▌▌ ▌ 3. 4 Million 13 June 2011
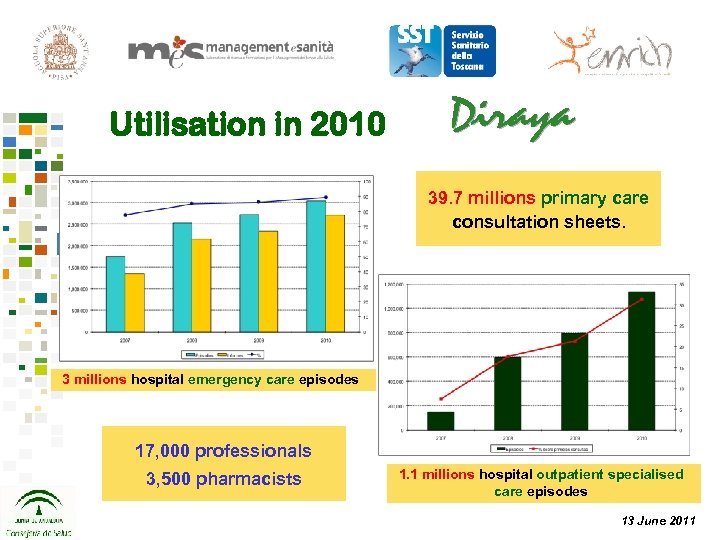 Utilisation in 2010 39. 7 millions primary care consultation sheets. 3 millions hospital emergency care episodes 17, 000 professionals 3, 500 pharmacists 1. 1 millions hospital outpatient specialised care episodes 13 June 2011
Utilisation in 2010 39. 7 millions primary care consultation sheets. 3 millions hospital emergency care episodes 17, 000 professionals 3, 500 pharmacists 1. 1 millions hospital outpatient specialised care episodes 13 June 2011
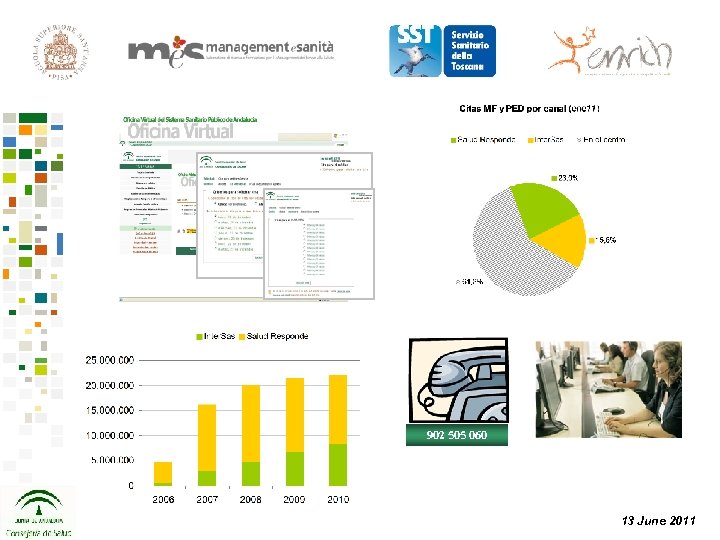 902 505 060 13 June 2011
902 505 060 13 June 2011
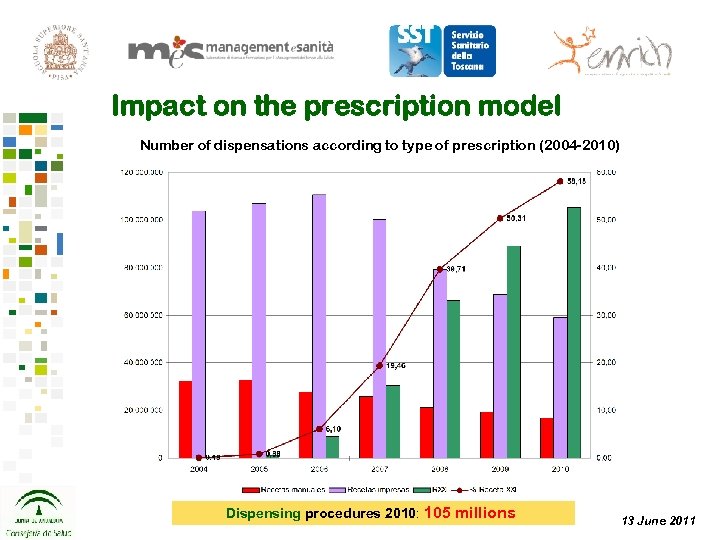 Impact on the prescription model Number of dispensations according to type of prescription (2004 -2010) Dispensing procedures 2010: 105 millions 13 June 2011
Impact on the prescription model Number of dispensations according to type of prescription (2004 -2010) Dispensing procedures 2010: 105 millions 13 June 2011
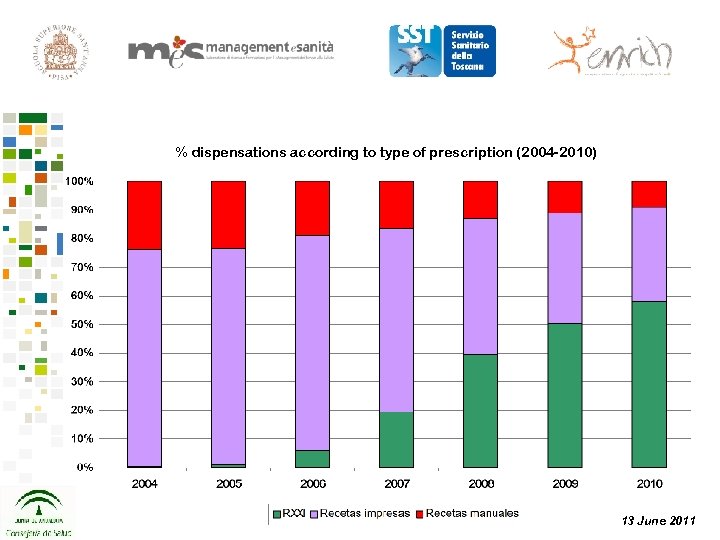 % dispensations according to type of prescription (2004 -2010) 13 June 2011
% dispensations according to type of prescription (2004 -2010) 13 June 2011
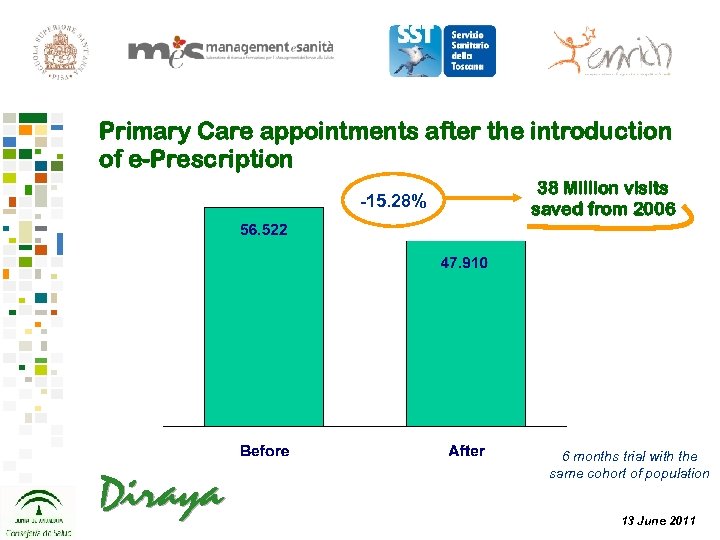 Primary Care appointments after the introduction of e-Prescription -15. 28% 38 Million visits saved from 2006 6 months trial with the same cohort of population 13 June 2011
Primary Care appointments after the introduction of e-Prescription -15. 28% 38 Million visits saved from 2006 6 months trial with the same cohort of population 13 June 2011
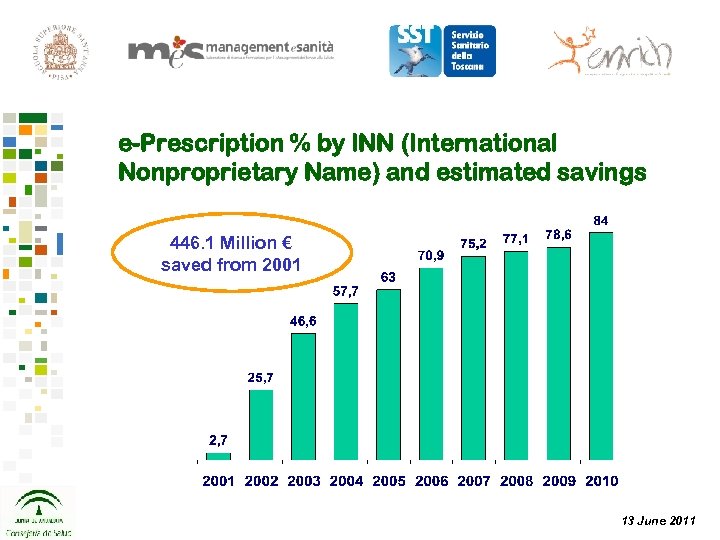 e-Prescription % by INN (International Nonproprietary Name) and estimated savings 446. 1 Million € saved from 2001 13 June 2011
e-Prescription % by INN (International Nonproprietary Name) and estimated savings 446. 1 Million € saved from 2001 13 June 2011
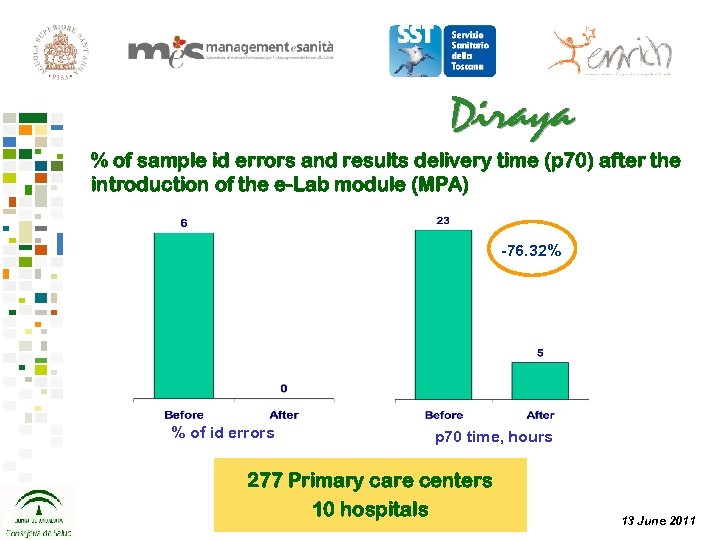 % of sample id errors and results delivery time (p 70) after the introduction of the e-Lab module (MPA) -76. 32% % of id errors p 70 time, hours 277 Primary care centers 10 hospitals 13 June 2011
% of sample id errors and results delivery time (p 70) after the introduction of the e-Lab module (MPA) -76. 32% % of id errors p 70 time, hours 277 Primary care centers 10 hospitals 13 June 2011
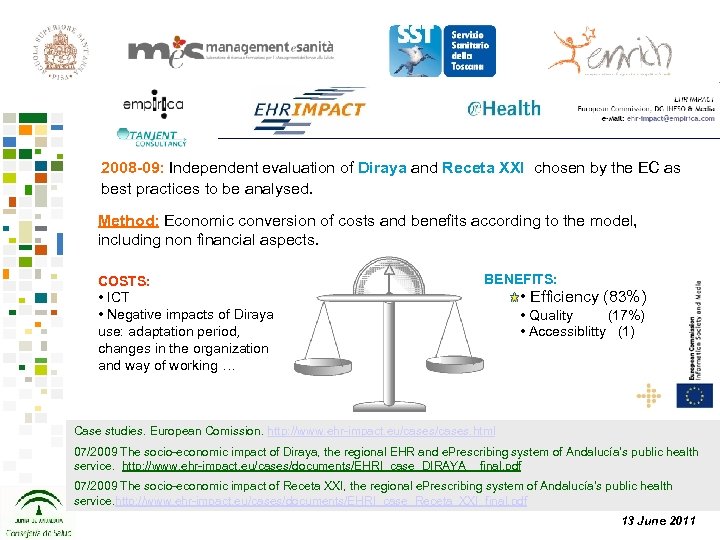 2008 -09: Independent evaluation of Diraya and Receta XXI chosen by the EC as best practices to be analysed. Method: Economic conversion of costs and benefits according to the model, including non financial aspects. COSTS: • ICT • Negative impacts of Diraya use: adaptation period, changes in the organization and way of working … BENEFITS: • Efficiency (83%) • Quality (17%) • Accessiblitty (1) Case studies. European Comission. http: //www. ehr-impact. eu/cases. html 07/2009 The socio-economic impact of Diraya, the regional EHR and e. Prescribing system of Andalucía’s public health service. http: //www. ehr-impact. eu/cases/documents/EHRI_case_DIRAYA__final. pdf 07/2009 The socio-economic impact of Receta XXI, the regional e. Prescribing system of Andalucía’s public health service. http: //www. ehr-impact. eu/cases/documents/EHRI_case_Receta_XXI_final. pdf 13 June 2011
2008 -09: Independent evaluation of Diraya and Receta XXI chosen by the EC as best practices to be analysed. Method: Economic conversion of costs and benefits according to the model, including non financial aspects. COSTS: • ICT • Negative impacts of Diraya use: adaptation period, changes in the organization and way of working … BENEFITS: • Efficiency (83%) • Quality (17%) • Accessiblitty (1) Case studies. European Comission. http: //www. ehr-impact. eu/cases. html 07/2009 The socio-economic impact of Diraya, the regional EHR and e. Prescribing system of Andalucía’s public health service. http: //www. ehr-impact. eu/cases/documents/EHRI_case_DIRAYA__final. pdf 07/2009 The socio-economic impact of Receta XXI, the regional e. Prescribing system of Andalucía’s public health service. http: //www. ehr-impact. eu/cases/documents/EHRI_case_Receta_XXI_final. pdf 13 June 2011
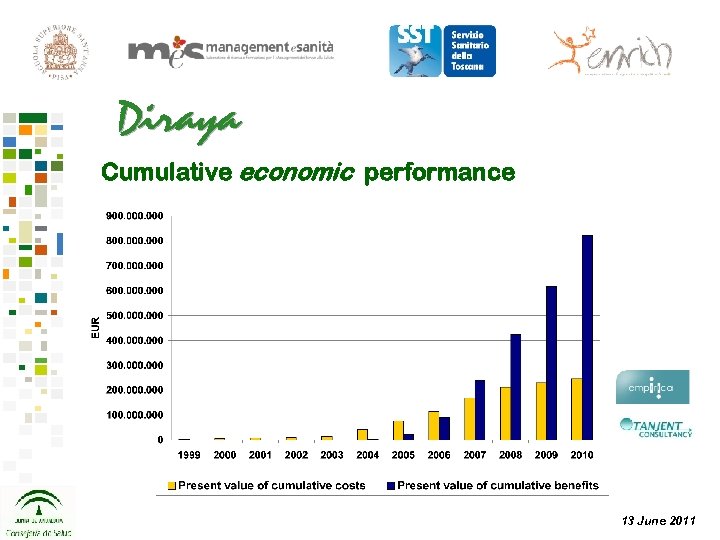 Cumulative economic performance 13 June 2011
Cumulative economic performance 13 June 2011
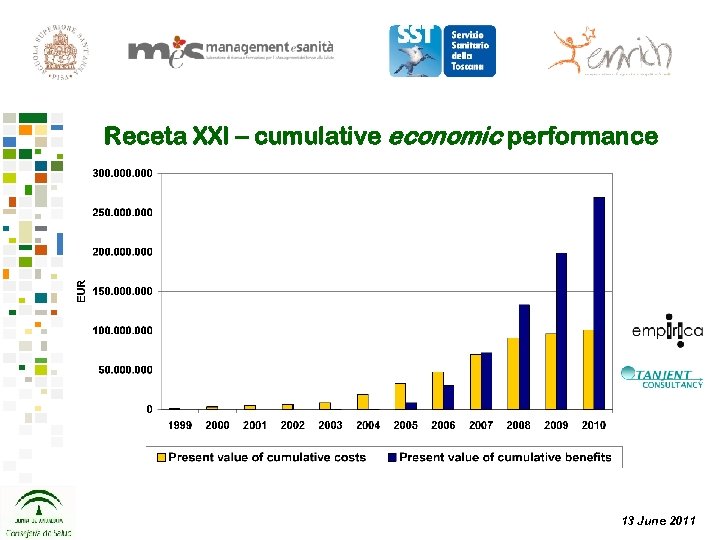 Receta XXI – cumulative economic performance 13 June 2011
Receta XXI – cumulative economic performance 13 June 2011
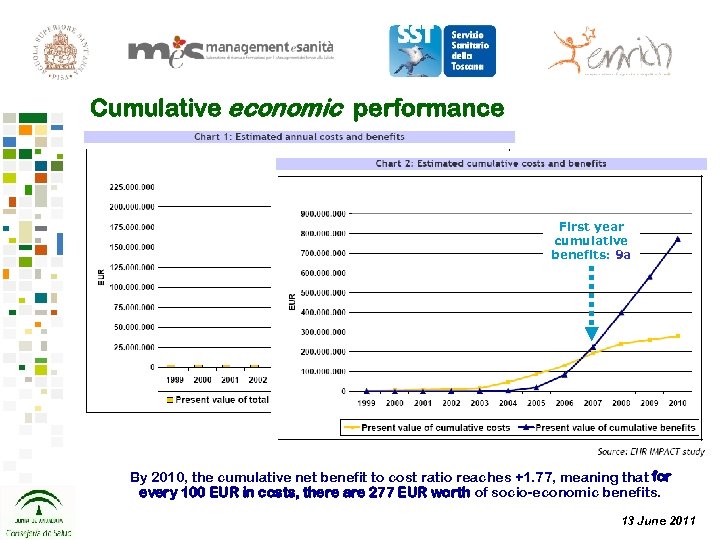 Cumulative economic performance First year cumulative benefits: 9 a By 2010, the cumulative net benefit to cost ratio reaches +1. 77, meaning that for every 100 EUR in costs, there are 277 EUR worth of socio-economic benefits. 13 June 2011
Cumulative economic performance First year cumulative benefits: 9 a By 2010, the cumulative net benefit to cost ratio reaches +1. 77, meaning that for every 100 EUR in costs, there are 277 EUR worth of socio-economic benefits. 13 June 2011
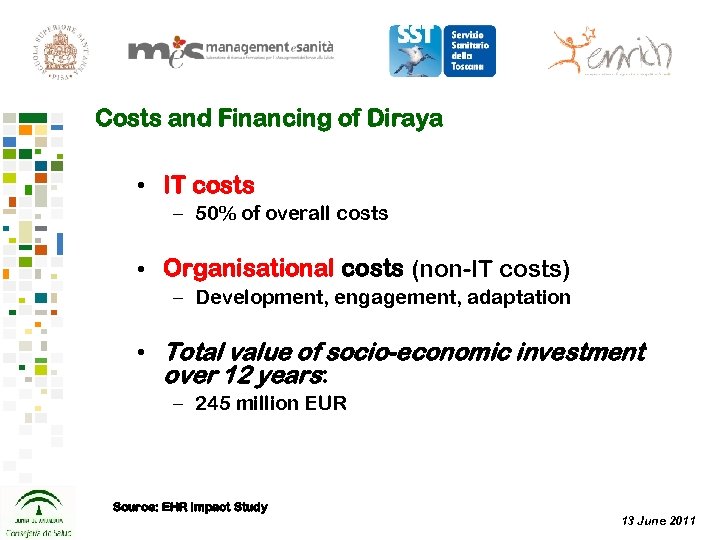 Costs and Financing of Diraya • IT costs – 50% of overall costs • Organisational costs (non-IT costs) – Development, engagement, adaptation • Total value of socio-economic investment over 12 years: – 245 million EUR Source: EHR Impact Study 13 June 2011
Costs and Financing of Diraya • IT costs – 50% of overall costs • Organisational costs (non-IT costs) – Development, engagement, adaptation • Total value of socio-economic investment over 12 years: – 245 million EUR Source: EHR Impact Study 13 June 2011
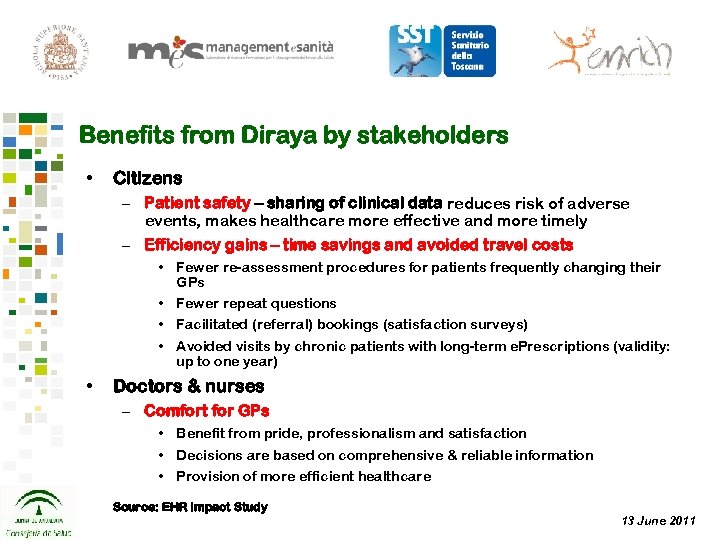 Benefits from Diraya by stakeholders • Citizens – Patient safety – sharing of clinical data reduces risk of adverse events, makes healthcare more effective and more timely – Efficiency gains – time savings and avoided travel costs • Fewer re-assessment procedures for patients frequently changing their GPs • Fewer repeat questions • Facilitated (referral) bookings (satisfaction surveys) • Avoided visits by chronic patients with long-term e. Prescriptions (validity: up to one year) • Doctors & nurses – Comfort for GPs • Benefit from pride, professionalism and satisfaction • Decisions are based on comprehensive & reliable information • Provision of more efficient healthcare Source: EHR Impact Study 13 June 2011
Benefits from Diraya by stakeholders • Citizens – Patient safety – sharing of clinical data reduces risk of adverse events, makes healthcare more effective and more timely – Efficiency gains – time savings and avoided travel costs • Fewer re-assessment procedures for patients frequently changing their GPs • Fewer repeat questions • Facilitated (referral) bookings (satisfaction surveys) • Avoided visits by chronic patients with long-term e. Prescriptions (validity: up to one year) • Doctors & nurses – Comfort for GPs • Benefit from pride, professionalism and satisfaction • Decisions are based on comprehensive & reliable information • Provision of more efficient healthcare Source: EHR Impact Study 13 June 2011
 Benefits from Diraya by stakeholders II • Benefits to the Andalusian health service – Reduction in exposure to risk due to better clinical governance • • – Time savings – redeployment of resources: • • • – • Assurance that medical information is recorded correctly and fully Assurance that advice is based on better information Fewer repeat questioning about medication and medical history Avoided visits for re-assessment and for renewal of prescriptions (reduced by ca. 15%) Better allocation of resources through e. Booking Cost savings from generic prescribing Cost avoidance through central server Regulation and standardization of procedures and tools Benefits to the regional Ministry of Health – – – Information from research feeds into evidence-based standards Dissemination of guidelines through Decision Support (DS) tools Support & integration of strategic initiatives (improved care processes) Source: EHR Impact Study 13 June 2011
Benefits from Diraya by stakeholders II • Benefits to the Andalusian health service – Reduction in exposure to risk due to better clinical governance • • – Time savings – redeployment of resources: • • • – • Assurance that medical information is recorded correctly and fully Assurance that advice is based on better information Fewer repeat questioning about medication and medical history Avoided visits for re-assessment and for renewal of prescriptions (reduced by ca. 15%) Better allocation of resources through e. Booking Cost savings from generic prescribing Cost avoidance through central server Regulation and standardization of procedures and tools Benefits to the regional Ministry of Health – – – Information from research feeds into evidence-based standards Dissemination of guidelines through Decision Support (DS) tools Support & integration of strategic initiatives (improved care processes) Source: EHR Impact Study 13 June 2011
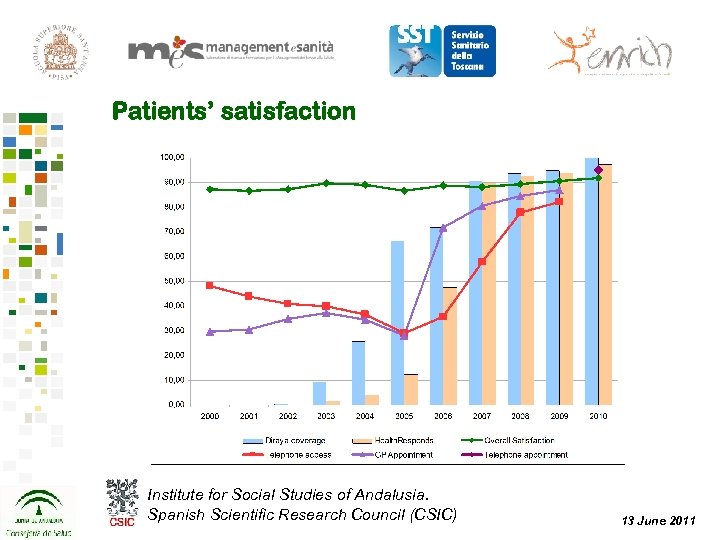 Patients’ satisfaction Institute for Social Studies of Andalusia. Spanish Scientific Research Council (CSIC) 13 June 2011
Patients’ satisfaction Institute for Social Studies of Andalusia. Spanish Scientific Research Council (CSIC) 13 June 2011
 Lessons learnt: risks • Unrealistic expectations • Technology fascination: e-health as an objective itself • Insufficient IT training of healthcare workers • Underestimate preparation for implementation • Inadequate IT infrastructure • Disappointing short-term results 13 June 2011
Lessons learnt: risks • Unrealistic expectations • Technology fascination: e-health as an objective itself • Insufficient IT training of healthcare workers • Underestimate preparation for implementation • Inadequate IT infrastructure • Disappointing short-term results 13 June 2011
 Lessons learnt: key factors for success • • • Align the EHR development with the regional government’s health strategy, supporting it Bottom-up approach: critical role of health care professionals in the design and development Integrate the projects needed for each module into a single project that delivers interoperable clinical and health information Step by step implementation assuring its use after a carefully designed piloting Ensure that the project horizon is long enough so that there is enough time to involve stakeholders and to adapt the system accordingly (collaborative model) Strong political support in the long run 13 June 2011
Lessons learnt: key factors for success • • • Align the EHR development with the regional government’s health strategy, supporting it Bottom-up approach: critical role of health care professionals in the design and development Integrate the projects needed for each module into a single project that delivers interoperable clinical and health information Step by step implementation assuring its use after a carefully designed piloting Ensure that the project horizon is long enough so that there is enough time to involve stakeholders and to adapt the system accordingly (collaborative model) Strong political support in the long run 13 June 2011
 Gracias Thanks Merci Grazie Gracias Merci Grazie Thanks Gracias Thanks Merci Grazie Gracias Thanks Grazie Thanks Merci Gracias Merci Grazie Thanks Gracias Thanks Merci Grazie Ana M. Carriazo Senior Advisor General Secretariat for Quality and Modernisation Regional Ministry of Health of Andalusia Av. de la Innovación s/n, Edificio Arena 1 41020 Sevilla (España) T: +34955006613 anam. carriazo@juntadeandalucia. es www. juntadeandalucia. es/salud 13 June 2011
Gracias Thanks Merci Grazie Gracias Merci Grazie Thanks Gracias Thanks Merci Grazie Gracias Thanks Grazie Thanks Merci Gracias Merci Grazie Thanks Gracias Thanks Merci Grazie Ana M. Carriazo Senior Advisor General Secretariat for Quality and Modernisation Regional Ministry of Health of Andalusia Av. de la Innovación s/n, Edificio Arena 1 41020 Sevilla (España) T: +34955006613 anam. carriazo@juntadeandalucia. es www. juntadeandalucia. es/salud 13 June 2011


