f224f5d6f1ff1f4ffa2df7c826aaf8da.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Workshop on Implementing Electronic Government Procurement (e-GP) Delhi, India – May 18, 2006 The Role of e-GP in Improving Public Procurement Performance Knut Leipold The World Bank May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP
Workshop on Implementing Electronic Government Procurement (e-GP) Delhi, India – May 18, 2006 The Role of e-GP in Improving Public Procurement Performance Knut Leipold The World Bank May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP
 Voice of the Pros • “E-Procurement can protect life!” • “You loose some USD 450, 000 every day!” • “It allows for increased competition and less fraud. ” May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 2
Voice of the Pros • “E-Procurement can protect life!” • “You loose some USD 450, 000 every day!” • “It allows for increased competition and less fraud. ” May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 2
 Voice of the Cons • “Look at this! Not only that we have to use this E-Procurement system, we even have to pay USD 12, 000 for it this year!” • “We prefer the offline procurement process. ” • “We don’t like the e-Procurement system as it increases our workload. ” May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 3
Voice of the Cons • “Look at this! Not only that we have to use this E-Procurement system, we even have to pay USD 12, 000 for it this year!” • “We prefer the offline procurement process. ” • “We don’t like the e-Procurement system as it increases our workload. ” May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 3
 Objectives • Opportunities & Challenges of • e for GP e is a tool to improve GP • Encourage to use May 18, 2006 e for GP Workshop on Implementing e-GP 4
Objectives • Opportunities & Challenges of • e for GP e is a tool to improve GP • Encourage to use May 18, 2006 e for GP Workshop on Implementing e-GP 4
 Agenda 1. 2. Challenges 3. May 18, 2006 Opportunities Lessons Learned Workshop on Implementing e-GP 5
Agenda 1. 2. Challenges 3. May 18, 2006 Opportunities Lessons Learned Workshop on Implementing e-GP 5
 Agenda 1. 2. Challenges 3. May 18, 2006 Opportunities Lessons Learned Workshop on Implementing e-GP 6
Agenda 1. 2. Challenges 3. May 18, 2006 Opportunities Lessons Learned Workshop on Implementing e-GP 6
 Benefits of e-GP • Transparency • Efficiency • Economic Development May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 7
Benefits of e-GP • Transparency • Efficiency • Economic Development May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 7
 Transparency • Information on public procurement function • Information on procurement transactions • Compliance • Reduced corruption • Audit trails & institutional memory • Improved quality of public procurement reporting, monitoring, and management May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 8
Transparency • Information on public procurement function • Information on procurement transactions • Compliance • Reduced corruption • Audit trails & institutional memory • Improved quality of public procurement reporting, monitoring, and management May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 8
 Efficiency Ø Price decrease • Increased price transparency • Increased competition (!) • Aggregated demand • Lower transaction costs for suppliers • e-Reverse Auctions Ø Reduced transaction costs • staff, material, workflow • online vs. offline publication Ø Time is money! May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 9
Efficiency Ø Price decrease • Increased price transparency • Increased competition (!) • Aggregated demand • Lower transaction costs for suppliers • e-Reverse Auctions Ø Reduced transaction costs • staff, material, workflow • online vs. offline publication Ø Time is money! May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 9
 Economic Development Public Procurement • Government = single largest purchaser in a national economy • Value of public procurement: 10 -15% of GDP • Redistribution of taxpayers’ money GDP • Private business activation • Infrastructure development • Capacity building May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 10
Economic Development Public Procurement • Government = single largest purchaser in a national economy • Value of public procurement: 10 -15% of GDP • Redistribution of taxpayers’ money GDP • Private business activation • Infrastructure development • Capacity building May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 10
 Beneficiaries of e-GP • Transparency Government • Efficiency Suppliers • Economic Development Taxpayers May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 11
Beneficiaries of e-GP • Transparency Government • Efficiency Suppliers • Economic Development Taxpayers May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 11
 What is the Problem? Objectives of GP: Benefits of e-GP: • Open & fair competition • Efficiency • Transparency • Improved quality E-GP does not replace GP. It is a tool that can improve and reform GP. The challenge is successful e-GP implementation, as it addresses far more than just HW & SW. May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 12
What is the Problem? Objectives of GP: Benefits of e-GP: • Open & fair competition • Efficiency • Transparency • Improved quality E-GP does not replace GP. It is a tool that can improve and reform GP. The challenge is successful e-GP implementation, as it addresses far more than just HW & SW. May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 12
 Agenda 1. 2. Challenges 3. May 18, 2006 Opportunities Lessons Learned Workshop on Implementing e-GP 13
Agenda 1. 2. Challenges 3. May 18, 2006 Opportunities Lessons Learned Workshop on Implementing e-GP 13
 e-GP Implementation Understanding Technology Standards May 18, 2006 Management e-GP Infrastructure Policy Legislation Buyer & Supplier Activation Workshop on Implementing e-GP Buyer & Supplier Activation 14
e-GP Implementation Understanding Technology Standards May 18, 2006 Management e-GP Infrastructure Policy Legislation Buyer & Supplier Activation Workshop on Implementing e-GP Buyer & Supplier Activation 14
 Successful e-GP Adoption Understanding Technology Management e-GP Policy • Think Big, Start Small • Learn from Others Legislation • Assess the Current Situation • Develop a Strategy • Implement the Strategy Standards May 18, 2006 Infrastructure Buyer & Supplier Activation Workshop on Implementing e-GP 15
Successful e-GP Adoption Understanding Technology Management e-GP Policy • Think Big, Start Small • Learn from Others Legislation • Assess the Current Situation • Develop a Strategy • Implement the Strategy Standards May 18, 2006 Infrastructure Buyer & Supplier Activation Workshop on Implementing e-GP 15
 Agenda 1. 2. Challenges 3. May 18, 2006 Opportunities Lessons Learned Workshop on Implementing e-GP 16
Agenda 1. 2. Challenges 3. May 18, 2006 Opportunities Lessons Learned Workshop on Implementing e-GP 16
 Lessons Learned: Dos (I) • Have a vision and strategy • Get a Champion on high political level • Get stakeholder buy-in • Develop appropriate legal framework • Establish a Lead Agency • Run an awareness raising campaign • Build capacity May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 17
Lessons Learned: Dos (I) • Have a vision and strategy • Get a Champion on high political level • Get stakeholder buy-in • Develop appropriate legal framework • Establish a Lead Agency • Run an awareness raising campaign • Build capacity May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 17
 Lessons Learned: Dos (II) • Review procurement regulation and processes • Follow international standards • Phased implementation • Select a sustainable business model • Integration (link with other systems) • Strengthen international dialogue May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 18
Lessons Learned: Dos (II) • Review procurement regulation and processes • Follow international standards • Phased implementation • Select a sustainable business model • Integration (link with other systems) • Strengthen international dialogue May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 18
 Lessons Learned: Don’ts • • • There is no reason to wait! E-GP is far more than technology! E-GP does not solve all public procurement issues! • Decentralized public procurement does not require decentralized e-GP systems • Don’t mix digital with electronic signature! • Don’t forget the private sector! • Don’t set unnecessary barriers to the use of e-GP! May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 19
Lessons Learned: Don’ts • • • There is no reason to wait! E-GP is far more than technology! E-GP does not solve all public procurement issues! • Decentralized public procurement does not require decentralized e-GP systems • Don’t mix digital with electronic signature! • Don’t forget the private sector! • Don’t set unnecessary barriers to the use of e-GP! May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 19
 For More Information www. mdb-egp. org May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 20
For More Information www. mdb-egp. org May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 20
 Thank You! Kleipold@worldbank. org May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 21
Thank You! Kleipold@worldbank. org May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 21
 Back-up slides May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 22
Back-up slides May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 22
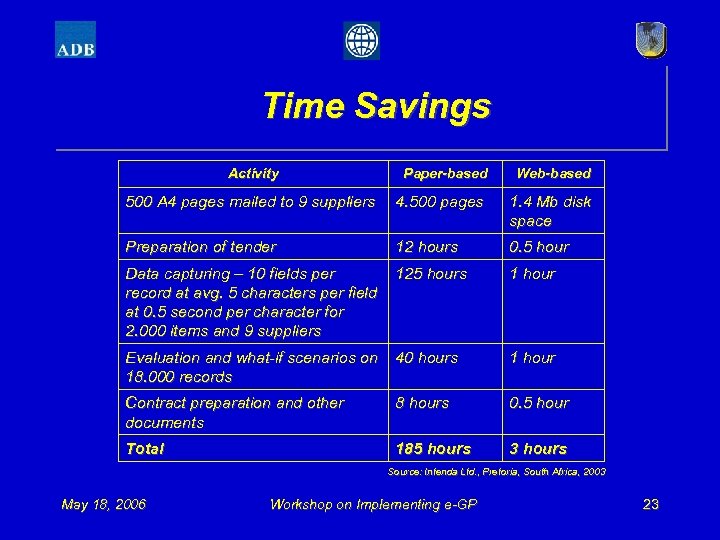 Time Savings Activity Paper-based Web-based 500 A 4 pages mailed to 9 suppliers 4. 500 pages 1. 4 Mb disk space Preparation of tender 12 hours 0. 5 hour Data capturing – 10 fields per record at avg. 5 characters per field at 0. 5 second per character for 2. 000 items and 9 suppliers 125 hours 1 hour Evaluation and what-if scenarios on 18. 000 records 40 hours 1 hour Contract preparation and other documents 8 hours 0. 5 hour Total 185 hours 3 hours Source: Intenda Ltd. , Pretoria, South Africa, 2003 May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 23
Time Savings Activity Paper-based Web-based 500 A 4 pages mailed to 9 suppliers 4. 500 pages 1. 4 Mb disk space Preparation of tender 12 hours 0. 5 hour Data capturing – 10 fields per record at avg. 5 characters per field at 0. 5 second per character for 2. 000 items and 9 suppliers 125 hours 1 hour Evaluation and what-if scenarios on 18. 000 records 40 hours 1 hour Contract preparation and other documents 8 hours 0. 5 hour Total 185 hours 3 hours Source: Intenda Ltd. , Pretoria, South Africa, 2003 May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 23
 Fighting Corruption with e-GP (I) Reducing fraud and corruption in public procurement: • online disclosure of procurement notices • online disclosure of awarded contracts • open and fair competition • increased compliance with procurement policy • less opportunity for corruptive, collusive, fraudulent, and coercive practices Potential for fraud and corruption: • inappropriate application of technology • e-Corruption May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 24
Fighting Corruption with e-GP (I) Reducing fraud and corruption in public procurement: • online disclosure of procurement notices • online disclosure of awarded contracts • open and fair competition • increased compliance with procurement policy • less opportunity for corruptive, collusive, fraudulent, and coercive practices Potential for fraud and corruption: • inappropriate application of technology • e-Corruption May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 24
 Fighting Corruption with e-GP (II) E-Procurement can reduce opportunity of fraud and corruption in the context of government procurement if • driven by political will • implemented appropriately. High level of transparency can be achieved at low costs and no need of major changes of the existing legal framework. May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 25
Fighting Corruption with e-GP (II) E-Procurement can reduce opportunity of fraud and corruption in the context of government procurement if • driven by political will • implemented appropriately. High level of transparency can be achieved at low costs and no need of major changes of the existing legal framework. May 18, 2006 Workshop on Implementing e-GP 25


