1dbf57a2000da31912ad3ce4458a0cbb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43
 Workshop on Advanced Technologies in Radiation Oncology Minesh Mehta
Workshop on Advanced Technologies in Radiation Oncology Minesh Mehta
 Principal “Dose-Limiting Toxicity” Brain Tumors Necrosis rates of ~5% starting at 60 Gy. 72 Gy with altered fractionation Visual damage of ~1 -3% starting at >54 Gy. Endocrine damage starts at ~45 Gy. Neurocognitive damage: Depends on what you measure, when, & age Cochlear dysfunction starts at >50 Gy
Principal “Dose-Limiting Toxicity” Brain Tumors Necrosis rates of ~5% starting at 60 Gy. 72 Gy with altered fractionation Visual damage of ~1 -3% starting at >54 Gy. Endocrine damage starts at ~45 Gy. Neurocognitive damage: Depends on what you measure, when, & age Cochlear dysfunction starts at >50 Gy
 Evidence Levels l Logically, few of the toxicity data come from phase III trials with toxicity endpoints. l Most come from phase I trials, or “institutional experiences” l Numerous variables need to be teased out separately, e. g. , age, volume, fractionation, comorbidities, otherapies, etc.
Evidence Levels l Logically, few of the toxicity data come from phase III trials with toxicity endpoints. l Most come from phase I trials, or “institutional experiences” l Numerous variables need to be teased out separately, e. g. , age, volume, fractionation, comorbidities, otherapies, etc.
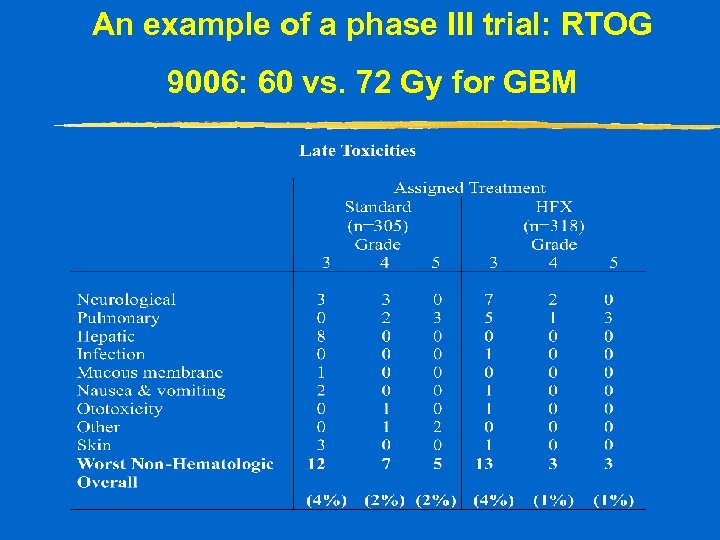 An example of a phase III trial: RTOG 9006: 60 vs. 72 Gy for GBM
An example of a phase III trial: RTOG 9006: 60 vs. 72 Gy for GBM
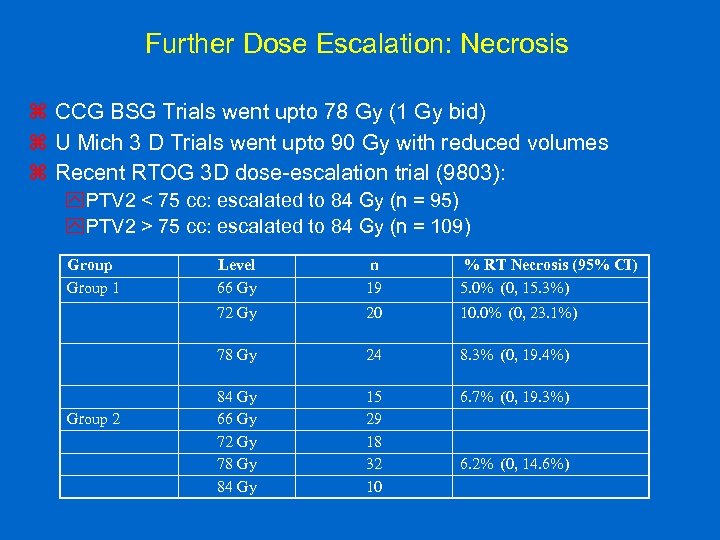 Further Dose Escalation: Necrosis z CCG BSG Trials went upto 78 Gy (1 Gy bid) z U Mich 3 D Trials went upto 90 Gy with reduced volumes z Recent RTOG 3 D dose-escalation trial (9803): y. PTV 2 < 75 cc: escalated to 84 Gy (n = 95) y. PTV 2 > 75 cc: escalated to 84 Gy (n = 109) Group 1 n 19 % RT Necrosis (95% CI) 5. 0% (0, 15. 3%) 72 Gy 20 10. 0% (0, 23. 1%) 78 Gy Group 2 Level 66 Gy 24 8. 3% (0, 19. 4%) 84 Gy 66 Gy 72 Gy 78 Gy 84 Gy 15 29 18 32 10 6. 7% (0, 19. 3%) 6. 2% (0, 14. 6%)
Further Dose Escalation: Necrosis z CCG BSG Trials went upto 78 Gy (1 Gy bid) z U Mich 3 D Trials went upto 90 Gy with reduced volumes z Recent RTOG 3 D dose-escalation trial (9803): y. PTV 2 < 75 cc: escalated to 84 Gy (n = 95) y. PTV 2 > 75 cc: escalated to 84 Gy (n = 109) Group 1 n 19 % RT Necrosis (95% CI) 5. 0% (0, 15. 3%) 72 Gy 20 10. 0% (0, 23. 1%) 78 Gy Group 2 Level 66 Gy 24 8. 3% (0, 19. 4%) 84 Gy 66 Gy 72 Gy 78 Gy 84 Gy 15 29 18 32 10 6. 7% (0, 19. 3%) 6. 2% (0, 14. 6%)
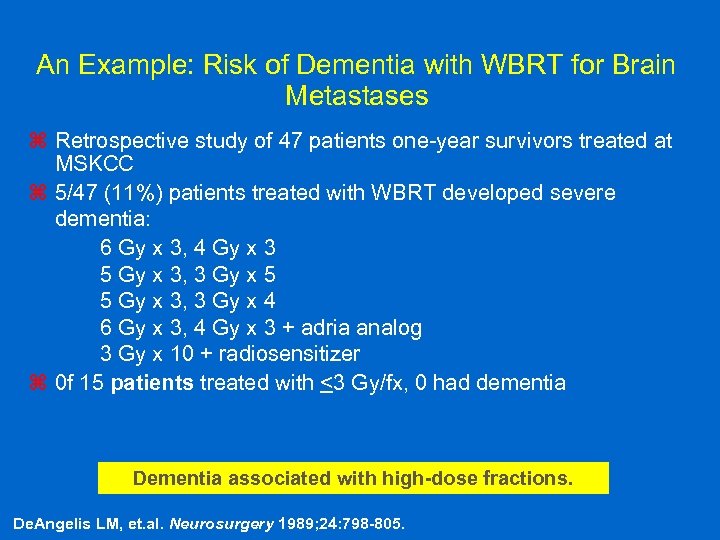 An Example: Risk of Dementia with WBRT for Brain Metastases z Retrospective study of 47 patients one-year survivors treated at MSKCC z 5/47 (11%) patients treated with WBRT developed severe dementia: 6 Gy x 3, 4 Gy x 3 5 Gy x 3, 3 Gy x 5 5 Gy x 3, 3 Gy x 4 6 Gy x 3, 4 Gy x 3 + adria analog 3 Gy x 10 + radiosensitizer z 0 f 15 patients treated with <3 Gy/fx, 0 had dementia Dementia associated with high-dose fractions. De. Angelis LM, et. al. Neurosurgery 1989; 24: 798 -805.
An Example: Risk of Dementia with WBRT for Brain Metastases z Retrospective study of 47 patients one-year survivors treated at MSKCC z 5/47 (11%) patients treated with WBRT developed severe dementia: 6 Gy x 3, 4 Gy x 3 5 Gy x 3, 3 Gy x 5 5 Gy x 3, 3 Gy x 4 6 Gy x 3, 4 Gy x 3 + adria analog 3 Gy x 10 + radiosensitizer z 0 f 15 patients treated with <3 Gy/fx, 0 had dementia Dementia associated with high-dose fractions. De. Angelis LM, et. al. Neurosurgery 1989; 24: 798 -805.
 Can SRS or SRT reduce toxicities? z Few direct comparisons exist z Significant dose-escalation can be achieved z In general, necrosis rates remain under 5% z However, only small volumes are generally treated z For long-term toxicity, benign tumors need to be studied and these are generally not included on any clinical trials, e. g. meningioma, vestibular schwannoma, etc.
Can SRS or SRT reduce toxicities? z Few direct comparisons exist z Significant dose-escalation can be achieved z In general, necrosis rates remain under 5% z However, only small volumes are generally treated z For long-term toxicity, benign tumors need to be studied and these are generally not included on any clinical trials, e. g. meningioma, vestibular schwannoma, etc.
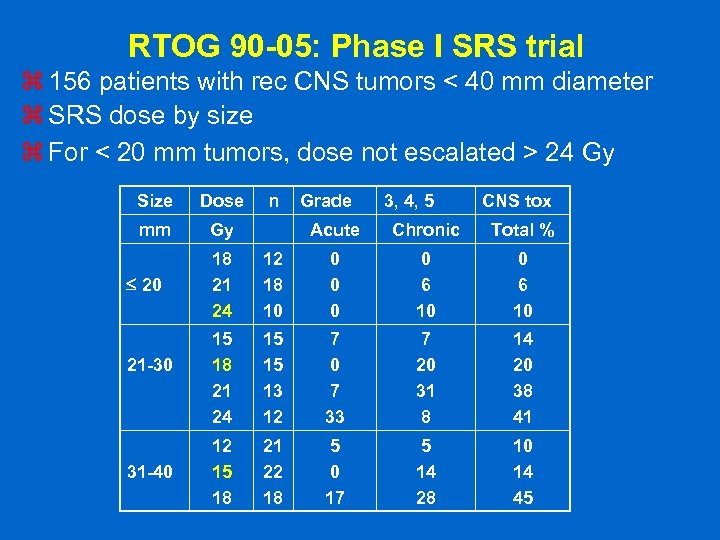 RTOG 90 -05: Phase I SRS trial z 156 patients with rec CNS tumors < 40 mm diameter z SRS dose by size z For < 20 mm tumors, dose not escalated > 24 Gy Size Dose mm Gy 20 21 -30 31 -40 n Grade 3, 4, 5 CNS tox Acute Chronic Total % 18 21 24 12 18 10 0 0 6 10 15 18 21 24 15 15 13 12 7 0 7 33 7 20 31 8 14 20 38 41 12 15 18 21 22 18 5 0 17 5 14 28 10 14 45
RTOG 90 -05: Phase I SRS trial z 156 patients with rec CNS tumors < 40 mm diameter z SRS dose by size z For < 20 mm tumors, dose not escalated > 24 Gy Size Dose mm Gy 20 21 -30 31 -40 n Grade 3, 4, 5 CNS tox Acute Chronic Total % 18 21 24 12 18 10 0 0 6 10 15 18 21 24 15 15 13 12 7 0 7 33 7 20 31 8 14 20 38 41 12 15 18 21 22 18 5 0 17 5 14 28 10 14 45
 An example of a phase III trial: RTOG 9305: SRS boost for GBM z 60 Gy + BCNU +/- SRS boost (15 -24 Gy) z 186 analyzable patients z 4 vs 0 G 3 late neuro toxicity in SRS arm z QOL comparable (Spitzer) z MMSE comparable z Quality-adjusted survival comparable
An example of a phase III trial: RTOG 9305: SRS boost for GBM z 60 Gy + BCNU +/- SRS boost (15 -24 Gy) z 186 analyzable patients z 4 vs 0 G 3 late neuro toxicity in SRS arm z QOL comparable (Spitzer) z MMSE comparable z Quality-adjusted survival comparable
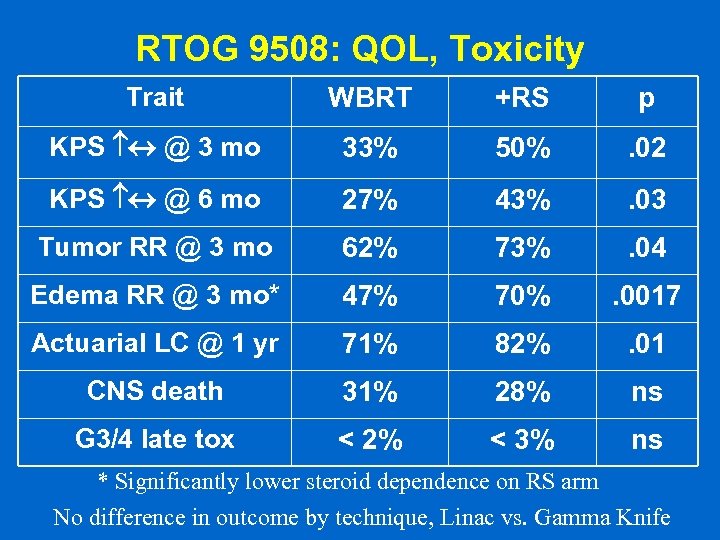 RTOG 9508: QOL, Toxicity Trait WBRT +RS p KPS @ 3 mo 33% 50% . 02 KPS @ 6 mo 27% 43% . 03 Tumor RR @ 3 mo 62% 73% . 04 Edema RR @ 3 mo* 47% 70% . 0017 Actuarial LC @ 1 yr 71% 82% . 01 CNS death 31% 28% ns G 3/4 late tox < 2% < 3% ns * Significantly lower steroid dependence on RS arm No difference in outcome by technique, Linac vs. Gamma Knife
RTOG 9508: QOL, Toxicity Trait WBRT +RS p KPS @ 3 mo 33% 50% . 02 KPS @ 6 mo 27% 43% . 03 Tumor RR @ 3 mo 62% 73% . 04 Edema RR @ 3 mo* 47% 70% . 0017 Actuarial LC @ 1 yr 71% 82% . 01 CNS death 31% 28% ns G 3/4 late tox < 2% < 3% ns * Significantly lower steroid dependence on RS arm No difference in outcome by technique, Linac vs. Gamma Knife
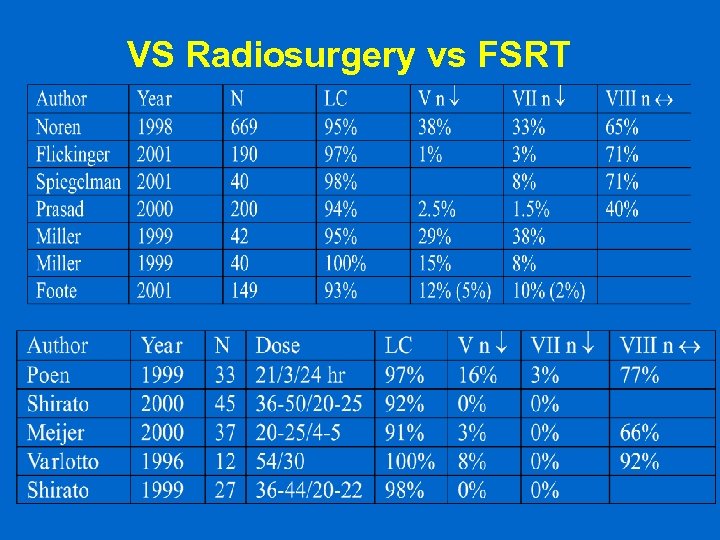 VS Radiosurgery vs FSRT
VS Radiosurgery vs FSRT
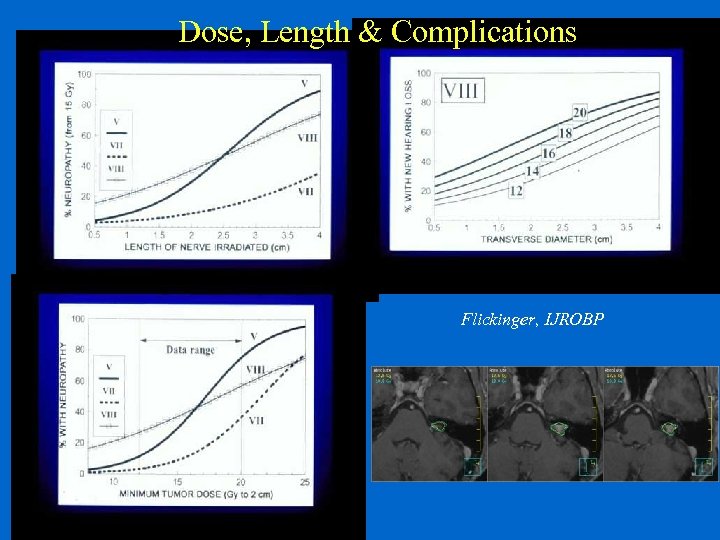 Dose, Length & Complications Flickinger, IJROBP
Dose, Length & Complications Flickinger, IJROBP
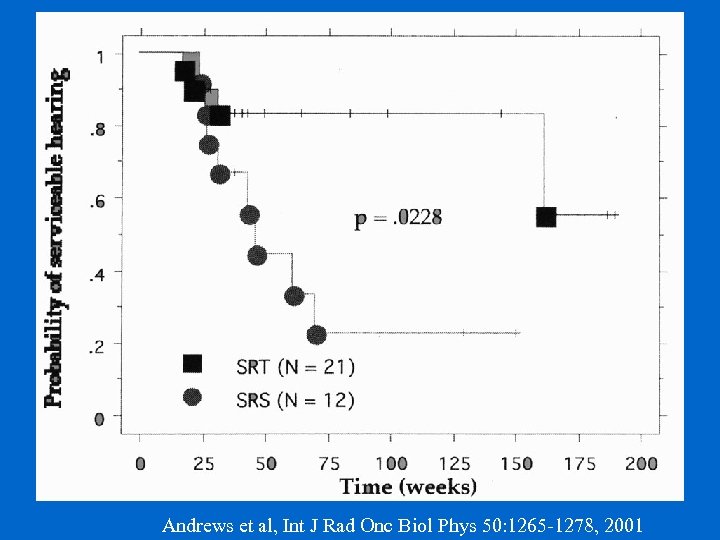 Probability of Serviceable Hearing Andrews et al, Int J Rad Onc Biol Phys 50: 1265 -1278, 2001
Probability of Serviceable Hearing Andrews et al, Int J Rad Onc Biol Phys 50: 1265 -1278, 2001
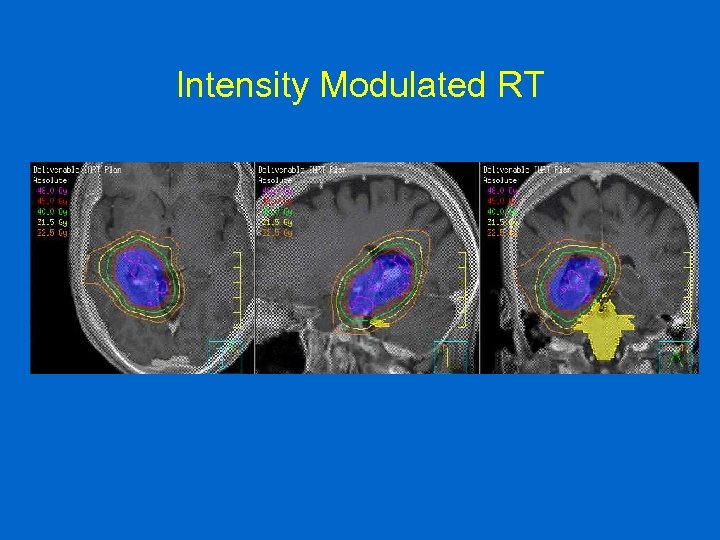 Intensity Modulated RT
Intensity Modulated RT
 INTENSITY MODULATED RADIATION THERAPY VERSUS THREE DIMENSIONAL CONFORMAL RADIATION THERAPY FOR THE TREATMENT OF HIGH GRADE GLIOMA: A DOSIMETRIC COMPARISON Shannon M Mac. Donald 1, Salahuddin Ahmad 2, Stefanos Kachris 3, Betty J Vogds 2, Melissa De. Rouen 3, Alicia E Gitttleman 3, Keith De. Wyngaert 3, Maria T Vlachaki 4 Massachusetts General Hospital University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center 3 New York University Medical Center 4 Wayne State University 1 2
INTENSITY MODULATED RADIATION THERAPY VERSUS THREE DIMENSIONAL CONFORMAL RADIATION THERAPY FOR THE TREATMENT OF HIGH GRADE GLIOMA: A DOSIMETRIC COMPARISON Shannon M Mac. Donald 1, Salahuddin Ahmad 2, Stefanos Kachris 3, Betty J Vogds 2, Melissa De. Rouen 3, Alicia E Gitttleman 3, Keith De. Wyngaert 3, Maria T Vlachaki 4 Massachusetts General Hospital University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center 3 New York University Medical Center 4 Wayne State University 1 2
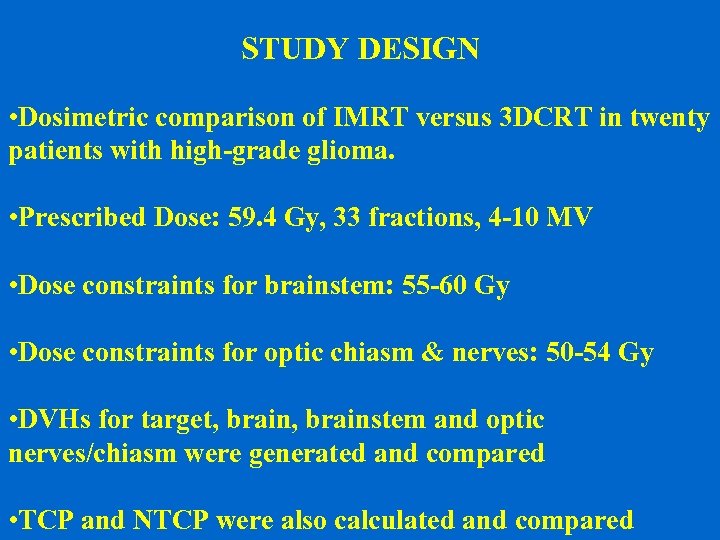 STUDY DESIGN • Dosimetric comparison of IMRT versus 3 DCRT in twenty patients with high-grade glioma. • Prescribed Dose: 59. 4 Gy, 33 fractions, 4 -10 MV • Dose constraints for brainstem: 55 -60 Gy • Dose constraints for optic chiasm & nerves: 50 -54 Gy • DVHs for target, brainstem and optic nerves/chiasm were generated and compared • TCP and NTCP were also calculated and compared
STUDY DESIGN • Dosimetric comparison of IMRT versus 3 DCRT in twenty patients with high-grade glioma. • Prescribed Dose: 59. 4 Gy, 33 fractions, 4 -10 MV • Dose constraints for brainstem: 55 -60 Gy • Dose constraints for optic chiasm & nerves: 50 -54 Gy • DVHs for target, brainstem and optic nerves/chiasm were generated and compared • TCP and NTCP were also calculated and compared
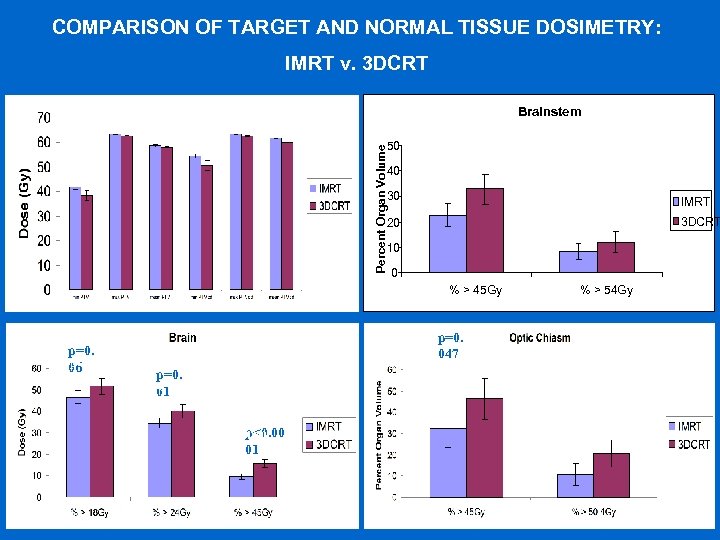 COMPARISON OF TARGET AND NORMALp=0. 0 TISSUE DOSIMETRY: IMRT v. 3 DCRT 04 Brainstem p=0. 023 p=0. 003 p≤ 0. 0001 p=0. 01 50 Percent Organ Volume p=0. 006 40 p=0. 004 30 IMRT 20 3 DCRT 10 0 % > 45 Gy p=0. 059 06 p=0. 047 p=0. 015 01 p<0. 00 p≤ 0. 0001 01 % > 54 Gy
COMPARISON OF TARGET AND NORMALp=0. 0 TISSUE DOSIMETRY: IMRT v. 3 DCRT 04 Brainstem p=0. 023 p=0. 003 p≤ 0. 0001 p=0. 01 50 Percent Organ Volume p=0. 006 40 p=0. 004 30 IMRT 20 3 DCRT 10 0 % > 45 Gy p=0. 059 06 p=0. 047 p=0. 015 01 p<0. 00 p≤ 0. 0001 01 % > 54 Gy
 So, Can IMRT further reduce toxicities? z Almost no direct comparisons exist z Significantly improved DVHs can be achieved z These may be meaningful for sites such as the chiasm, pit gland, hypothalamus, hippocampus, etc. z Limited data support that cochlear sparing in the pediatric population might preserve hearing
So, Can IMRT further reduce toxicities? z Almost no direct comparisons exist z Significantly improved DVHs can be achieved z These may be meaningful for sites such as the chiasm, pit gland, hypothalamus, hippocampus, etc. z Limited data support that cochlear sparing in the pediatric population might preserve hearing
 Compartmental Studies: Stem Cells z Subventricular zone stem cell compartment y. Remains mitotically active in adulthood y. Cells have self-renewal capacity xand differentiate into neurons or glia which xcan migrate over long distances in the brain xand are involved in repair processes after brain injury/toxicity y. In young rats, irradiation with 2 Gy produces apoptosis in the subependymal cell layer and also in the proliferating cellsin the hippocampus xwhich leads to prolonged impairment of repopulative capacity Doetsch, 1999; Hopewell, 1972; Bellinzona, 1996; Peissner, 1999; Tada, 1999
Compartmental Studies: Stem Cells z Subventricular zone stem cell compartment y. Remains mitotically active in adulthood y. Cells have self-renewal capacity xand differentiate into neurons or glia which xcan migrate over long distances in the brain xand are involved in repair processes after brain injury/toxicity y. In young rats, irradiation with 2 Gy produces apoptosis in the subependymal cell layer and also in the proliferating cellsin the hippocampus xwhich leads to prolonged impairment of repopulative capacity Doetsch, 1999; Hopewell, 1972; Bellinzona, 1996; Peissner, 1999; Tada, 1999
 The Role of the Hippocampus z Many patients exhibit learning/memory deficits with no pathologic changes, especially when the RT field involves the temporal lobes. z Recent work has shown that hippocampus-dependent learning and memory are strongly influenced by the activity of neural stem cells and their proliferative progeny. z The hippocampal granule cell layer undergoes continuous renewal and restructuring by the addition of new neurons. z Radiation at low doses affects the highly proliferative progenitors. A single low dose to the cranium of a mature rat is sufficient to ablate hippocampal neurogenesis. Monje ML: Radiation injury and neurogenesis. Current Opinion in Neurology. 16: 129 -34, 2003. ML
The Role of the Hippocampus z Many patients exhibit learning/memory deficits with no pathologic changes, especially when the RT field involves the temporal lobes. z Recent work has shown that hippocampus-dependent learning and memory are strongly influenced by the activity of neural stem cells and their proliferative progeny. z The hippocampal granule cell layer undergoes continuous renewal and restructuring by the addition of new neurons. z Radiation at low doses affects the highly proliferative progenitors. A single low dose to the cranium of a mature rat is sufficient to ablate hippocampal neurogenesis. Monje ML: Radiation injury and neurogenesis. Current Opinion in Neurology. 16: 129 -34, 2003. ML
 Hippocampus Avoidance Hypothesis z. The hippocampus plays a significant role in RT induced dementia z. Doses as low as 2 Gy cause significant toxicity to the hippocampus z. Conformal avoidance of the hippocampus may help reduce neurocognitive deficits
Hippocampus Avoidance Hypothesis z. The hippocampus plays a significant role in RT induced dementia z. Doses as low as 2 Gy cause significant toxicity to the hippocampus z. Conformal avoidance of the hippocampus may help reduce neurocognitive deficits
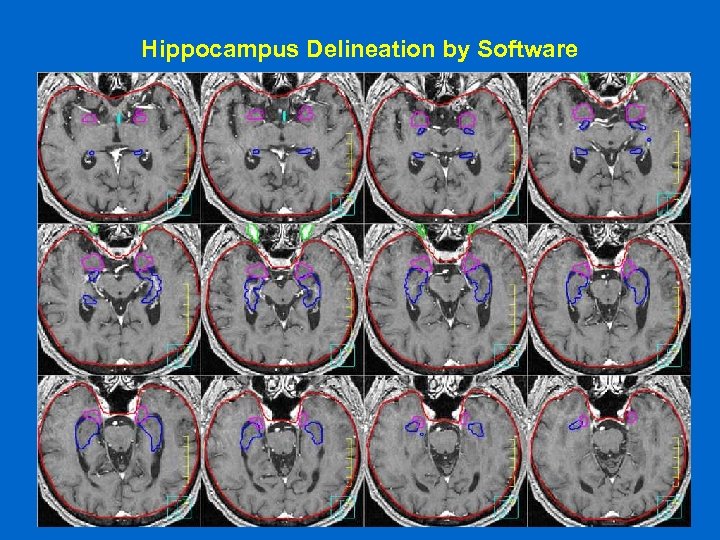 Hippocampus Delineation by Software
Hippocampus Delineation by Software
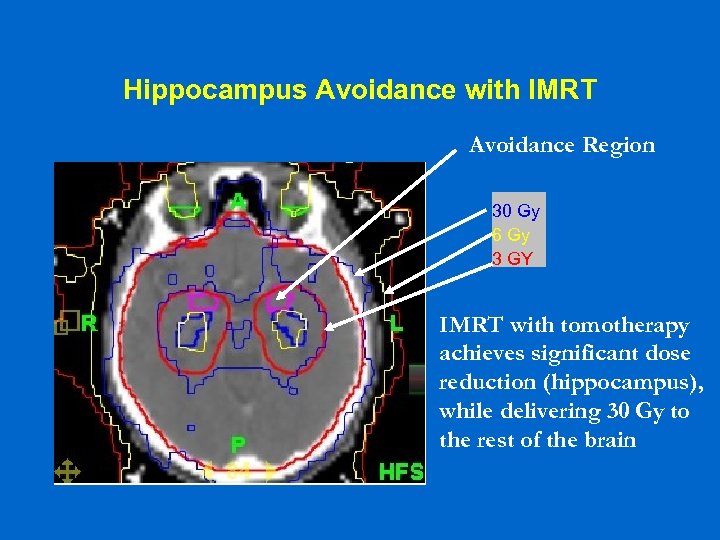 Hippocampus Avoidance with IMRT Avoidance Region 30 Gy 6 Gy 3 GY IMRT with tomotherapy achieves significant dose reduction (hippocampus), while delivering 30 Gy to the rest of the brain
Hippocampus Avoidance with IMRT Avoidance Region 30 Gy 6 Gy 3 GY IMRT with tomotherapy achieves significant dose reduction (hippocampus), while delivering 30 Gy to the rest of the brain
 Can IGRT further reduce toxicities? z Even in the head, positioning is a significant issue z IGRT reveals this dramatically z Application of IGRT might permit more accurate dose delivery z H/N serves as a good surrogate for the brain in this regard
Can IGRT further reduce toxicities? z Even in the head, positioning is a significant issue z IGRT reveals this dramatically z Application of IGRT might permit more accurate dose delivery z H/N serves as a good surrogate for the brain in this regard
 Study Design z Twenty patients analyzed z 10 conventional patients y Prospectively enrolled y Daily measurements (6 degrees of freedom) with optically guided patient localization system z 10 IMRT patients y Plans analyzed and selected analysis of impact daily set-up variation
Study Design z Twenty patients analyzed z 10 conventional patients y Prospectively enrolled y Daily measurements (6 degrees of freedom) with optically guided patient localization system z 10 IMRT patients y Plans analyzed and selected analysis of impact daily set-up variation
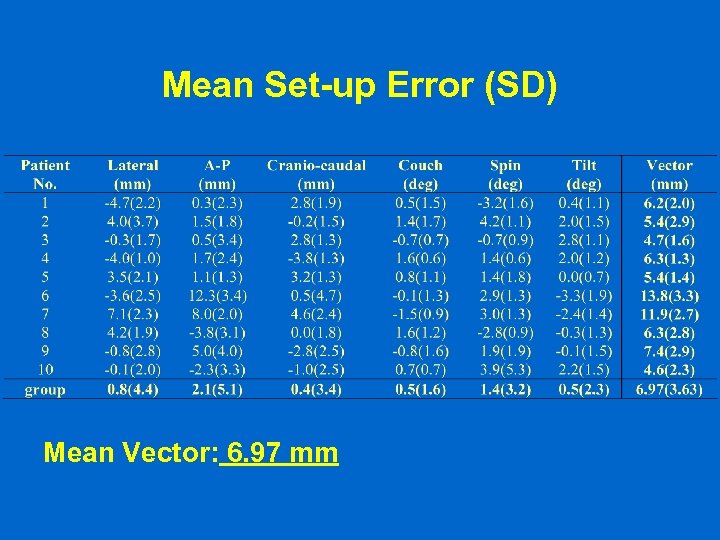 Mean Set-up Error (SD) Mean Vector: 6. 97 mm
Mean Set-up Error (SD) Mean Vector: 6. 97 mm
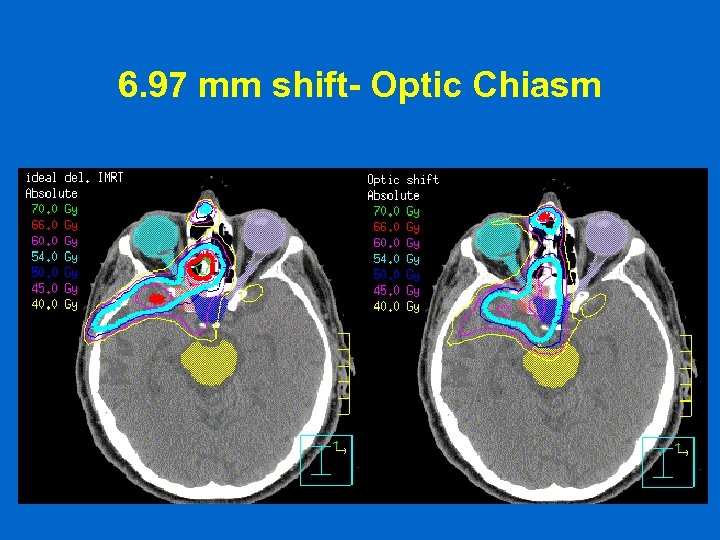 6. 97 mm shift- Optic Chiasm
6. 97 mm shift- Optic Chiasm
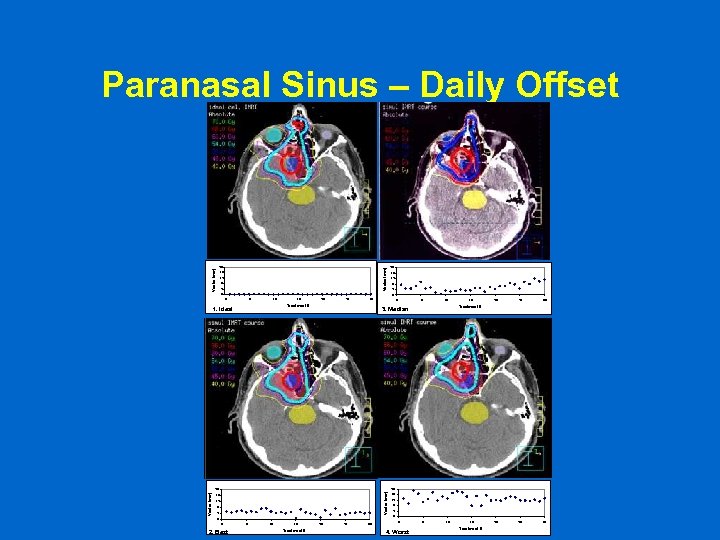 Paranasal Sinus – Daily Offset Vector (mm) 20 16 12 8 4 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 Treatment # 1. Ideal 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 Treatment # 3. Median 20 Vector (mm) 20 16 12 8 4 0 0 2. Best 5 10 15 Treatment # 20 25 30 16 12 8 4 0 0 4. Worst 5 10 15 Treatment #
Paranasal Sinus – Daily Offset Vector (mm) 20 16 12 8 4 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 Treatment # 1. Ideal 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 Treatment # 3. Median 20 Vector (mm) 20 16 12 8 4 0 0 2. Best 5 10 15 Treatment # 20 25 30 16 12 8 4 0 0 4. Worst 5 10 15 Treatment #
 CNS Tumors with a role for Radiotherapy
CNS Tumors with a role for Radiotherapy
 Roles of Radiotherapy z. Post-op adjunct to: y decrease local failure y delay progression/relapse y prolong survival, eg GBM, AA z. Primary curative therapy: y PNET, Germ Cell Tumors, Pilocytic astrocytoma z. To halt tumor growth: y Meningioma, Schwannoma z. To alter endocrine function z. To palliate
Roles of Radiotherapy z. Post-op adjunct to: y decrease local failure y delay progression/relapse y prolong survival, eg GBM, AA z. Primary curative therapy: y PNET, Germ Cell Tumors, Pilocytic astrocytoma z. To halt tumor growth: y Meningioma, Schwannoma z. To alter endocrine function z. To palliate
 Radiotherapy Improves Survival
Radiotherapy Improves Survival
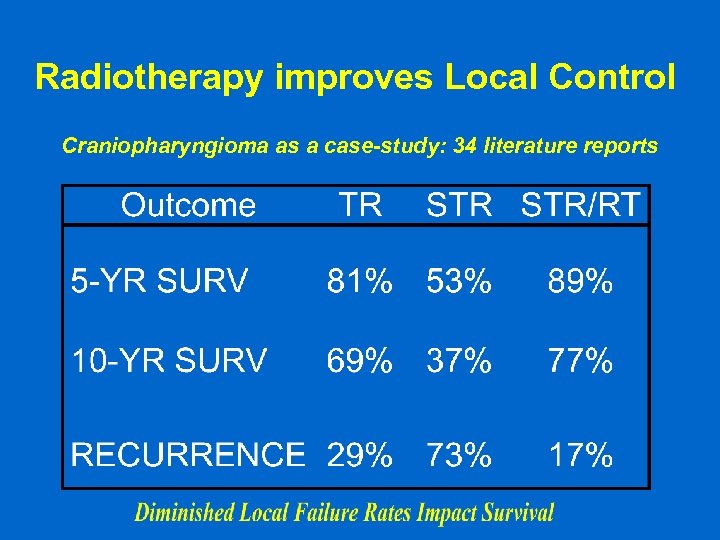 Radiotherapy improves Local Control Craniopharyngioma as a case-study: 34 literature reports
Radiotherapy improves Local Control Craniopharyngioma as a case-study: 34 literature reports
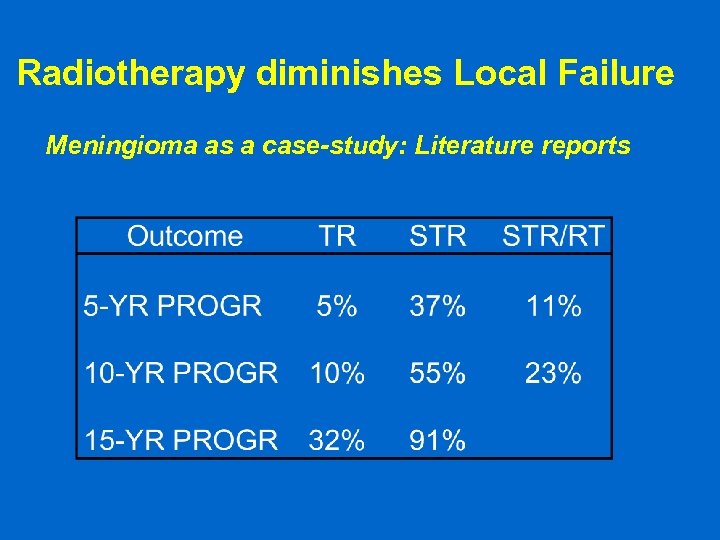 Radiotherapy diminishes Local Failure Meningioma as a case-study: Literature reports
Radiotherapy diminishes Local Failure Meningioma as a case-study: Literature reports
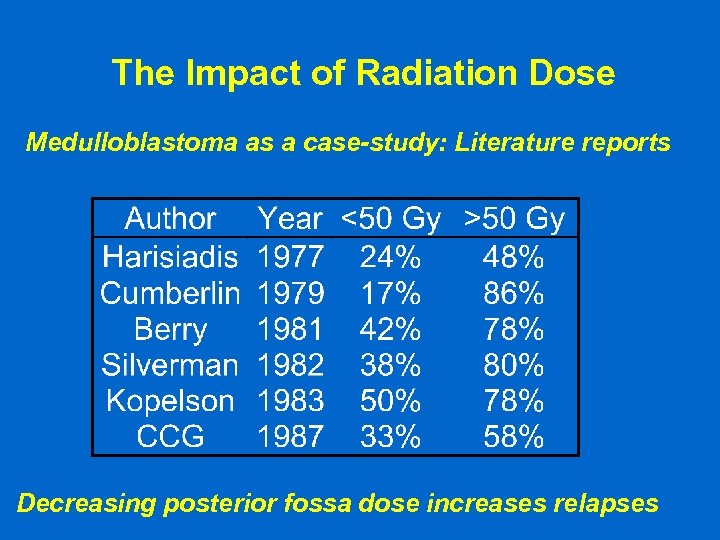 The Impact of Radiation Dose Medulloblastoma as a case-study: Literature reports Decreasing posterior fossa dose increases relapses
The Impact of Radiation Dose Medulloblastoma as a case-study: Literature reports Decreasing posterior fossa dose increases relapses
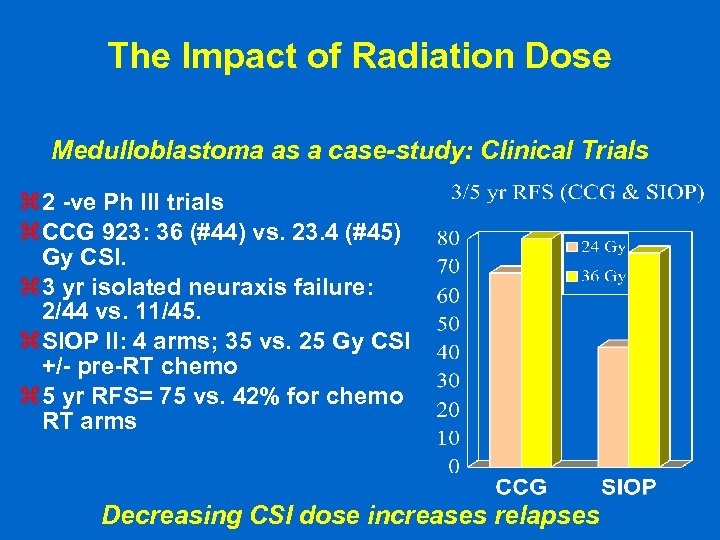 The Impact of Radiation Dose Medulloblastoma as a case-study: Clinical Trials z 2 -ve Ph III trials z CCG 923: 36 (#44) vs. 23. 4 (#45) Gy CSI. z 3 yr isolated neuraxis failure: 2/44 vs. 11/45. z SIOP II: 4 arms; 35 vs. 25 Gy CSI +/- pre-RT chemo z 5 yr RFS= 75 vs. 42% for chemo RT arms Decreasing CSI dose increases relapses
The Impact of Radiation Dose Medulloblastoma as a case-study: Clinical Trials z 2 -ve Ph III trials z CCG 923: 36 (#44) vs. 23. 4 (#45) Gy CSI. z 3 yr isolated neuraxis failure: 2/44 vs. 11/45. z SIOP II: 4 arms; 35 vs. 25 Gy CSI +/- pre-RT chemo z 5 yr RFS= 75 vs. 42% for chemo RT arms Decreasing CSI dose increases relapses
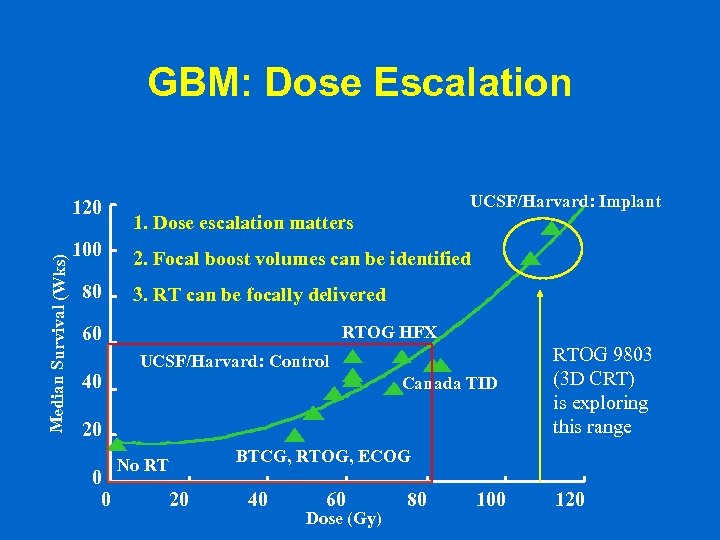 GBM: Dose Escalation Median Survival (Wks) 120 100 80 UCSF/Harvard: Implant 1. Dose escalation matters 2. Focal boost volumes can be identified 3. RT can be focally delivered RTOG HFX 60 40 UCSF/Harvard: Control Canada TID 20 0 0 No RT 20 RTOG 9803 (3 D CRT) is exploring this range BTCG, RTOG, ECOG 40 60 Dose (Gy) 80 100 120
GBM: Dose Escalation Median Survival (Wks) 120 100 80 UCSF/Harvard: Implant 1. Dose escalation matters 2. Focal boost volumes can be identified 3. RT can be focally delivered RTOG HFX 60 40 UCSF/Harvard: Control Canada TID 20 0 0 No RT 20 RTOG 9803 (3 D CRT) is exploring this range BTCG, RTOG, ECOG 40 60 Dose (Gy) 80 100 120
 RTOG 9305: GBM RS Ph III trial z 203 patients with GBM z 60 Gy + BCNU +/- RS boost (15 -24 Gy) z. Median f/u 44 months z. MS: 14. 1 vs 13. 7 months z 2 yr survival: 22 vs 18% z 3 yr survival: 16 vs 8% z. General QOL & cognitive function comparable RADIOSURGERY NOT PROVEN TO PROLONG SURVIVAL IN GBM Souhami, ASTRO 2002
RTOG 9305: GBM RS Ph III trial z 203 patients with GBM z 60 Gy + BCNU +/- RS boost (15 -24 Gy) z. Median f/u 44 months z. MS: 14. 1 vs 13. 7 months z 2 yr survival: 22 vs 18% z 3 yr survival: 16 vs 8% z. General QOL & cognitive function comparable RADIOSURGERY NOT PROVEN TO PROLONG SURVIVAL IN GBM Souhami, ASTRO 2002
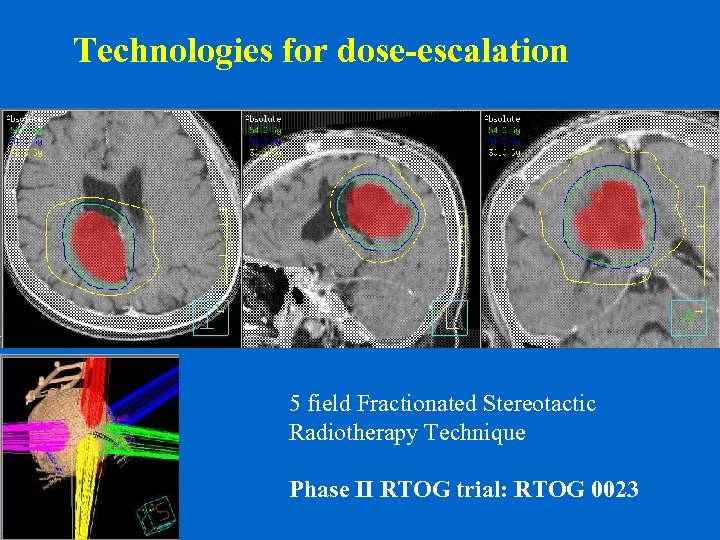 Technologies for dose-escalation 5 field Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy Technique Phase II RTOG trial: RTOG 0023
Technologies for dose-escalation 5 field Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy Technique Phase II RTOG trial: RTOG 0023
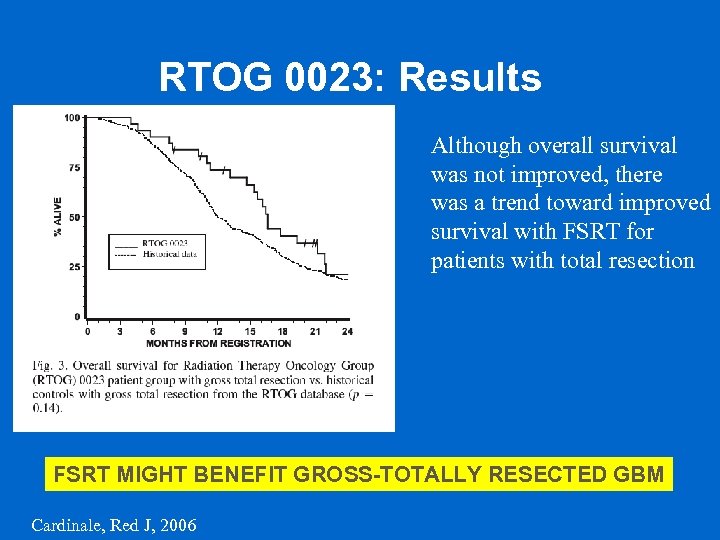 RTOG 0023: Results Although overall survival was not improved, there was a trend toward improved survival with FSRT for patients with total resection FSRT MIGHT BENEFIT GROSS-TOTALLY RESECTED GBM Cardinale, Red J, 2006
RTOG 0023: Results Although overall survival was not improved, there was a trend toward improved survival with FSRT for patients with total resection FSRT MIGHT BENEFIT GROSS-TOTALLY RESECTED GBM Cardinale, Red J, 2006
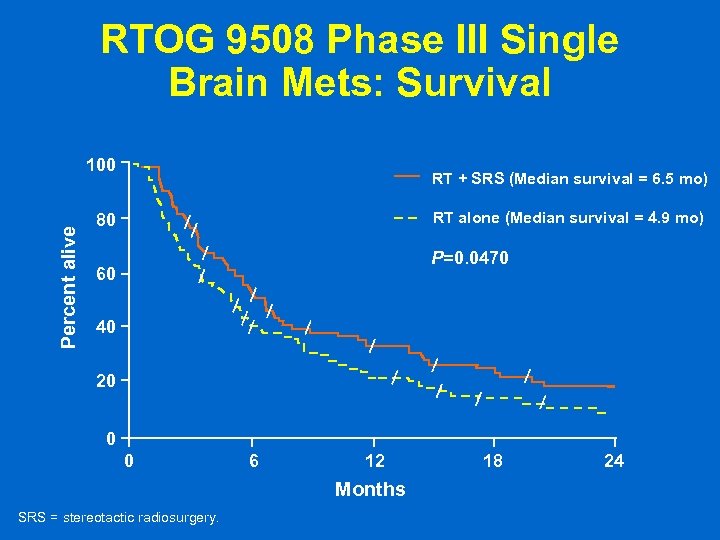 RTOG 9508 Phase III Single Brain Mets: Survival Percent alive 100 RT + SRS (Median survival = 6. 5 mo) RT alone (Median survival = 4. 9 mo) 80 P=0. 0470 60 40 20 0 0 6 12 Months SRS = stereotactic radiosurgery. 18 24
RTOG 9508 Phase III Single Brain Mets: Survival Percent alive 100 RT + SRS (Median survival = 6. 5 mo) RT alone (Median survival = 4. 9 mo) 80 P=0. 0470 60 40 20 0 0 6 12 Months SRS = stereotactic radiosurgery. 18 24
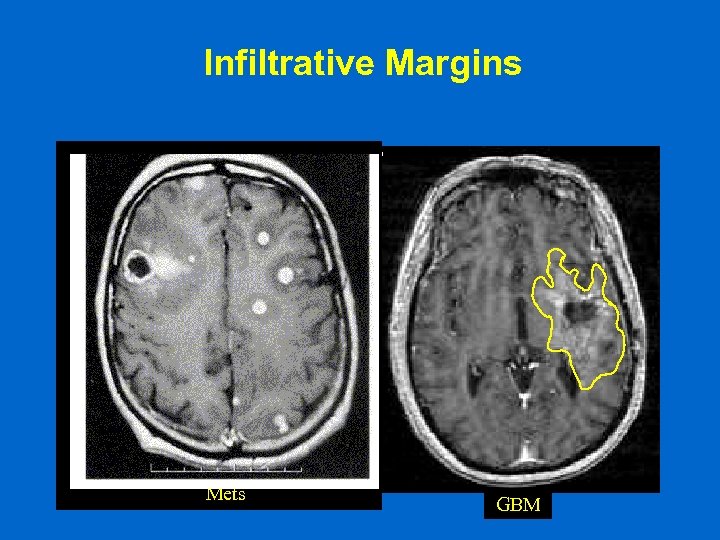 Infiltrative Margins A B Mets GBM
Infiltrative Margins A B Mets GBM
 MRSI for Treatment Planning z 34 pts (22 G 3, 12 G 4) evaluated with MRI/MRSI z MRI contours: T 2 for initial field; T 1 for boost z MRSI: Multivoxel technique: CNI (Choline/NAA Index) z Results: MRSI would change fields y. T 2 estimated microscopic region 50% larger than MRSI y. T 2 missed MRSI abnormality in 88% of pts (upto 28 mm) y. T 1 suggested lesser volume than MRSI y. T 1 suggested different location than MRSI Pirzkall A: IJROBP 2001 Mc. Knight: J Neurosurg, 2002: 90% sensitivity & 86% biopsy specificity for CNI >2. 5
MRSI for Treatment Planning z 34 pts (22 G 3, 12 G 4) evaluated with MRI/MRSI z MRI contours: T 2 for initial field; T 1 for boost z MRSI: Multivoxel technique: CNI (Choline/NAA Index) z Results: MRSI would change fields y. T 2 estimated microscopic region 50% larger than MRSI y. T 2 missed MRSI abnormality in 88% of pts (upto 28 mm) y. T 1 suggested lesser volume than MRSI y. T 1 suggested different location than MRSI Pirzkall A: IJROBP 2001 Mc. Knight: J Neurosurg, 2002: 90% sensitivity & 86% biopsy specificity for CNI >2. 5
 Conclusions z Radiotherapy plays a major role in the management of most primary brain tumors z Local failure is still paramount z Failed strategies: limited dose escalation, neutrons, brachytherapy, Imidazoles & BUd. R z Newer technologies may allow an improved therapeutic index
Conclusions z Radiotherapy plays a major role in the management of most primary brain tumors z Local failure is still paramount z Failed strategies: limited dose escalation, neutrons, brachytherapy, Imidazoles & BUd. R z Newer technologies may allow an improved therapeutic index


