f757cf96f7aba8016110967de0ce5bf0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 104
 Working Party State Supervision Meeting XIIIth AIDA World Congress Paris 18 May 2010
Working Party State Supervision Meeting XIIIth AIDA World Congress Paris 18 May 2010
 AGENDA I 1. Welcome and introduction to the topic: Impact of the financial crisis on the supervisory systems 2. Questionnaire: Impact of the financial crisis on the supervisory systems – Country Reports - Argentina - Australia - Denmark - France - Germany - Greece - Hungary - Ireland - Israel - Italy - Sweden - Switzerland
AGENDA I 1. Welcome and introduction to the topic: Impact of the financial crisis on the supervisory systems 2. Questionnaire: Impact of the financial crisis on the supervisory systems – Country Reports - Argentina - Australia - Denmark - France - Germany - Greece - Hungary - Ireland - Israel - Italy - Sweden - Switzerland
 AGENDA II 3. Panel discussion on the reports 4. Next Meeting 5. Any other business
AGENDA II 3. Panel discussion on the reports 4. Next Meeting 5. Any other business
 WORKING GROUP STATE SUPERVISION THE IMPACT OF THE FINANCIAL CRISIS ON THE INSURANCE SUPERVISORY AUTHORITIES ARGENTINA
WORKING GROUP STATE SUPERVISION THE IMPACT OF THE FINANCIAL CRISIS ON THE INSURANCE SUPERVISORY AUTHORITIES ARGENTINA
 PUBLIC ACT 20. 091 ON INSURERS AND THEIR CONTROL BROAD POWERS
PUBLIC ACT 20. 091 ON INSURERS AND THEIR CONTROL BROAD POWERS
 EFFECTS OF THE GLOBAL FINANCIAL CRISIS NO SIGNIFICANT EFFECTS • CAPITALIZATION OF A LOCAL BRANCH • INVESTMENTS ABROAD • ARGENTINE TREASURY BONDS
EFFECTS OF THE GLOBAL FINANCIAL CRISIS NO SIGNIFICANT EFFECTS • CAPITALIZATION OF A LOCAL BRANCH • INVESTMENTS ABROAD • ARGENTINE TREASURY BONDS
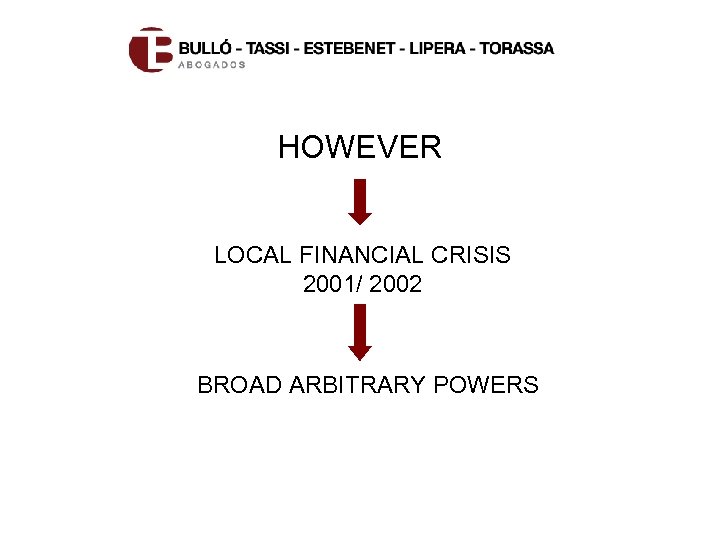 HOWEVER LOCAL FINANCIAL CRISIS 2001/ 2002 BROAD ARBITRARY POWERS
HOWEVER LOCAL FINANCIAL CRISIS 2001/ 2002 BROAD ARBITRARY POWERS
 MEASURES A) TECHNICAL RESULT B) RESERVES C) BOARD DIRECTOR´S RESPONSIBILITY D) SOLVENCY PARAMETERS FLEXIBILITY E) INVESTMENT ABROAD
MEASURES A) TECHNICAL RESULT B) RESERVES C) BOARD DIRECTOR´S RESPONSIBILITY D) SOLVENCY PARAMETERS FLEXIBILITY E) INVESTMENT ABROAD
 AMENDMENTS OF THE INSURANCE SUPERVISORY LAW 1 MODIFICATION TO ACT: REGULARIZATION AND FINANCIAL TURNAROUND OF ENTITIES, REORGANIZATIONS AND TEMPORARY EXCEPTIONS TO THE REQUEST SOLVENCY PARAMETERS 2 REGULATIONS ON INVESTMENT POLICY AND PROCEDURE 3 REGULATIONS ON MINIMUM CAPITALS 4 REGULATIONS ON ADMINISTRATIVE PROCESSES AND INTERNAL CONTROLS 5 REGULATION ON PREMIUMS AND POSITIVE TECHNICAL RESULT 6 REGULATIONS ON RESERVES
AMENDMENTS OF THE INSURANCE SUPERVISORY LAW 1 MODIFICATION TO ACT: REGULARIZATION AND FINANCIAL TURNAROUND OF ENTITIES, REORGANIZATIONS AND TEMPORARY EXCEPTIONS TO THE REQUEST SOLVENCY PARAMETERS 2 REGULATIONS ON INVESTMENT POLICY AND PROCEDURE 3 REGULATIONS ON MINIMUM CAPITALS 4 REGULATIONS ON ADMINISTRATIVE PROCESSES AND INTERNAL CONTROLS 5 REGULATION ON PREMIUMS AND POSITIVE TECHNICAL RESULT 6 REGULATIONS ON RESERVES
 FUTURE SOLVENCY II
FUTURE SOLVENCY II
 THANK YOU
THANK YOU
 WORKING GROUP STATE SUPERVISION EL IMPACTO DE LA CRISIS FINANCIERA EN LAS AUTORIDADES DE SUPERVISIÓN DE SEGUROS ARGENTINA
WORKING GROUP STATE SUPERVISION EL IMPACTO DE LA CRISIS FINANCIERA EN LAS AUTORIDADES DE SUPERVISIÓN DE SEGUROS ARGENTINA
 LEY 20. 091 DE LOS ASEGURADORES Y SU CONTROL AMPLIOS PODERES
LEY 20. 091 DE LOS ASEGURADORES Y SU CONTROL AMPLIOS PODERES
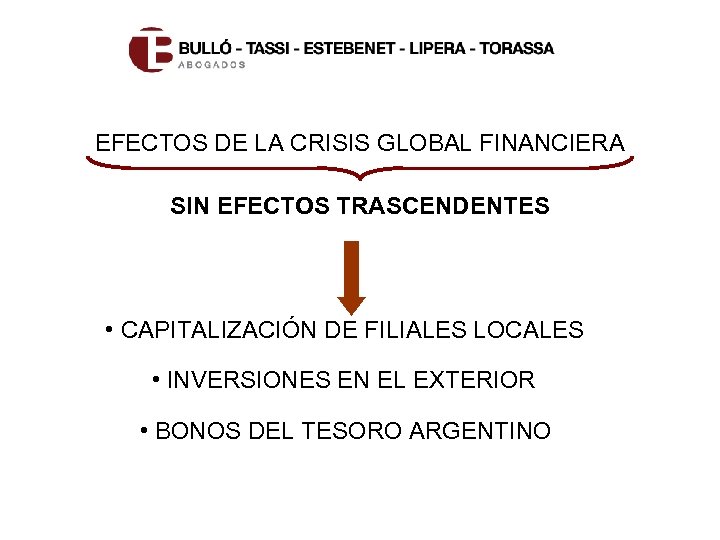 EFECTOS DE LA CRISIS GLOBAL FINANCIERA SIN EFECTOS TRASCENDENTES • CAPITALIZACIÓN DE FILIALES LOCALES • INVERSIONES EN EL EXTERIOR • BONOS DEL TESORO ARGENTINO
EFECTOS DE LA CRISIS GLOBAL FINANCIERA SIN EFECTOS TRASCENDENTES • CAPITALIZACIÓN DE FILIALES LOCALES • INVERSIONES EN EL EXTERIOR • BONOS DEL TESORO ARGENTINO
 PERO CRISIS FINANCIERA LOCAL 2001/ 2002 AMPLIOS PODERES DISCRECIONALES
PERO CRISIS FINANCIERA LOCAL 2001/ 2002 AMPLIOS PODERES DISCRECIONALES
 MEDIDAS A) RESULTADO TECNICO B) RESERVA C) RESPONSABILIDAD CONSEJOS DIRECTIVOS D) FLEXIBILIDAD EN PARAMETROS DE SOLVENCIA E) INVERSIONES EN EL EXTERIOR
MEDIDAS A) RESULTADO TECNICO B) RESERVA C) RESPONSABILIDAD CONSEJOS DIRECTIVOS D) FLEXIBILIDAD EN PARAMETROS DE SOLVENCIA E) INVERSIONES EN EL EXTERIOR
 MODIFICACIONES DE LA LEY DE SUPERVISIÓN DE SEGUROS 1 MODIFICACIÓN LEY: REGULARIZACIÓN Y SANEAMIENTO - REESTRUC TURACIÓN - EXCEPCIONES PARÁMETROS DE SOLVENCIA 2 NORMAS SOBRE POLITICA Y PROCEDIMIENTO DE INVERSIONES 3 NORMAS SOBRE CAPITALES MÍNIMOS 4 NORMAS SOBRE PROCESOS ADMINISTRATIVOS Y CONTROLES INTERNOS 5 NORMAS SOBRE PRIMAS Y RESULTADO TECNICO POSITIVO 6 NORMA SOBRE RESERVAS
MODIFICACIONES DE LA LEY DE SUPERVISIÓN DE SEGUROS 1 MODIFICACIÓN LEY: REGULARIZACIÓN Y SANEAMIENTO - REESTRUC TURACIÓN - EXCEPCIONES PARÁMETROS DE SOLVENCIA 2 NORMAS SOBRE POLITICA Y PROCEDIMIENTO DE INVERSIONES 3 NORMAS SOBRE CAPITALES MÍNIMOS 4 NORMAS SOBRE PROCESOS ADMINISTRATIVOS Y CONTROLES INTERNOS 5 NORMAS SOBRE PRIMAS Y RESULTADO TECNICO POSITIVO 6 NORMA SOBRE RESERVAS
 FUTURO SOLVENCIA II
FUTURO SOLVENCIA II
 GRACIAS
GRACIAS
 AIDA Working Group State Supervision Australian Response
AIDA Working Group State Supervision Australian Response
 1. 1 Can you give a short overview over the insurance supervisory framework (eg bodies, structures and law) in your country immediately before the GFC? The insurance supervisory framework in Australia is split between two key regulators: the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) - the prudential regulator responsible for solvency of authorised general and life insurers, and the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) - the regulator responsible for the main consumer protection legislation applying to insurers. Other regulators are responsible for other legislation impacting on insurers. 21
1. 1 Can you give a short overview over the insurance supervisory framework (eg bodies, structures and law) in your country immediately before the GFC? The insurance supervisory framework in Australia is split between two key regulators: the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) - the prudential regulator responsible for solvency of authorised general and life insurers, and the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) - the regulator responsible for the main consumer protection legislation applying to insurers. Other regulators are responsible for other legislation impacting on insurers. 21
 APRA oversees banks, credit unions, building societies, general insurance and reinsurance companies, life insurance, friendly societies, and most members of the superannuation industry. is funded largely by the industries that it supervises. was established on 1 July 1998. supervises institutions holding approximately $3. 6 trillion in assets for 22 million Australian depositors, policyholders and superannuation fund members. 22
APRA oversees banks, credit unions, building societies, general insurance and reinsurance companies, life insurance, friendly societies, and most members of the superannuation industry. is funded largely by the industries that it supervises. was established on 1 July 1998. supervises institutions holding approximately $3. 6 trillion in assets for 22 million Australian depositors, policyholders and superannuation fund members. 22
 Prudential regime re GFC Pre GFC regime was sophisticated because of failure of Australia's 2 nd largest general insurer, HIH in 2001. AUD$5. 3 billion in losses were borne by former policy holders. Primarily risk based, consultative and consistent with international best practice and has: – Preventive powers – Correction powers – Failure management powers – Data collection powers Funded by levies from industry 23
Prudential regime re GFC Pre GFC regime was sophisticated because of failure of Australia's 2 nd largest general insurer, HIH in 2001. AUD$5. 3 billion in losses were borne by former policy holders. Primarily risk based, consultative and consistent with international best practice and has: – Preventive powers – Correction powers – Failure management powers – Data collection powers Funded by levies from industry 23
 ASIC and Consumer Protection regime ASIC is Australia's corporate regulatory body and regulates the main insurance consumer protection legislation: the Corporations Act 2001 (Cth), in particular Chapter 7 (introduced in 2001) which imposes: – a licensing regime – consumer protection disclosure obligation and provisions compulsory binding external dispute resolution schemes the Insurance Contracts Act 1984 (Cth) (introduced in 1986) – amends common law and sets out rights and obligations of insurers and insureds aimed to provide fair balance Industry supervision - voluntary codes: – General Insurance Code of Practice – Insurance Brokers Code of Practice 24
ASIC and Consumer Protection regime ASIC is Australia's corporate regulatory body and regulates the main insurance consumer protection legislation: the Corporations Act 2001 (Cth), in particular Chapter 7 (introduced in 2001) which imposes: – a licensing regime – consumer protection disclosure obligation and provisions compulsory binding external dispute resolution schemes the Insurance Contracts Act 1984 (Cth) (introduced in 1986) – amends common law and sets out rights and obligations of insurers and insureds aimed to provide fair balance Industry supervision - voluntary codes: – General Insurance Code of Practice – Insurance Brokers Code of Practice 24
 2. 1 Please summarise how the GFC has affected – or been perceived as having affected – the insurance / reinsurance market in your country? General view: impact has not been as great as feared given the pre GFC failure of HIH as referred to above and Australia's relatively strong economy ample capacity generally and plenty of competition underwriting more and more targeted and accountable trade credit insurers have suffered in Australia workers compensation insurance rate increases private insurers, due to failures of builders, have withdrawn from the builders warranty market forcing the Government to take over GFC related claims against financial planners/mortgage brokers - withdrawal from the market of many PI insurers and cost increases, and reinsurance rates and appetite for unusual non traditional risk more limited. 25
2. 1 Please summarise how the GFC has affected – or been perceived as having affected – the insurance / reinsurance market in your country? General view: impact has not been as great as feared given the pre GFC failure of HIH as referred to above and Australia's relatively strong economy ample capacity generally and plenty of competition underwriting more and more targeted and accountable trade credit insurers have suffered in Australia workers compensation insurance rate increases private insurers, due to failures of builders, have withdrawn from the builders warranty market forcing the Government to take over GFC related claims against financial planners/mortgage brokers - withdrawal from the market of many PI insurers and cost increases, and reinsurance rates and appetite for unusual non traditional risk more limited. 25
 2. 3 Have there been any notable developments in the run-off or discontinuation of risk carrier or intermediary business, in particular, what particular classes of business have been affected? There have been no insurer failures in Australia since the GFC has also focussed many insurers on reviewing portfolios and running off/selling unprofitable ones and acquisitions are continuing in Australia where appropriate. 26
2. 3 Have there been any notable developments in the run-off or discontinuation of risk carrier or intermediary business, in particular, what particular classes of business have been affected? There have been no insurer failures in Australia since the GFC has also focussed many insurers on reviewing portfolios and running off/selling unprofitable ones and acquisitions are continuing in Australia where appropriate. 26
 3. 1 What examples are there during or since the GFC of the insurance supervisory authority of your country taking specific steps to influence, control or intervene in the conduct or operations of insurance / reinsurance risk carriers, or their directors and officers? No formal intervention occurred. APRA probably monitored entities impacted by foreign events pursuant to preventative powers. 27
3. 1 What examples are there during or since the GFC of the insurance supervisory authority of your country taking specific steps to influence, control or intervene in the conduct or operations of insurance / reinsurance risk carriers, or their directors and officers? No formal intervention occurred. APRA probably monitored entities impacted by foreign events pursuant to preventative powers. 27
 3. 2 Were the powers of intervention – existing before and during the GFC – of your country’s insurance supervisory authority sufficient? Regulation is one of most interventionist in western world. APRA's view is regime was sufficient but regulatory framework was in need of refinement. Since GFC various refinements have taken place to enhance and improve rights that already exist but which will have a significant impact on industry. 28
3. 2 Were the powers of intervention – existing before and during the GFC – of your country’s insurance supervisory authority sufficient? Regulation is one of most interventionist in western world. APRA's view is regime was sufficient but regulatory framework was in need of refinement. Since GFC various refinements have taken place to enhance and improve rights that already exist but which will have a significant impact on industry. 28
 3. 3 Have there been any examples during or since the GFC of the payment of insureds'/policyholders' claims being at risk from the potential insolvency of an insurance / reinsurance risk carrier or intermediary? No major Australian insurers or reinsurers have failed or were subject to regulatory intervention so as to put policyholder claims at risk. The number of claims being made has increased and will continue to be at a heightened level until effects of GFC are fully absorbed. The level has not been as high as anticipated. 29
3. 3 Have there been any examples during or since the GFC of the payment of insureds'/policyholders' claims being at risk from the potential insolvency of an insurance / reinsurance risk carrier or intermediary? No major Australian insurers or reinsurers have failed or were subject to regulatory intervention so as to put policyholder claims at risk. The number of claims being made has increased and will continue to be at a heightened level until effects of GFC are fully absorbed. The level has not been as high as anticipated. 29
 4. 1 In general terms, what (if any) changes have there been in the regulatory framework for the insurance or reinsurance industry since the onset of the GFC? In particular: Has there been an increase in funding or manpower for any supervisory authority? Has – in consequence of the GFC – the insurance supervisory/regulatory law and the powers of intervention been tightened in your country? No mass of new regulation/significantly tightened controls 2008: – extension of who must be authorised – approved capital requirements/reinsurance fine tuning – New Financial Claims Scheme 2009: – group supervision – new reporting requirements for intermediaries – executive remuneration – credit rating agencies licensing 30
4. 1 In general terms, what (if any) changes have there been in the regulatory framework for the insurance or reinsurance industry since the onset of the GFC? In particular: Has there been an increase in funding or manpower for any supervisory authority? Has – in consequence of the GFC – the insurance supervisory/regulatory law and the powers of intervention been tightened in your country? No mass of new regulation/significantly tightened controls 2008: – extension of who must be authorised – approved capital requirements/reinsurance fine tuning – New Financial Claims Scheme 2009: – group supervision – new reporting requirements for intermediaries – executive remuneration – credit rating agencies licensing 30
 4. 2 What (if any) changes are currently being discussed or proposed with respect to any part of the regulatory framework governing the insurance / reinsurance industry (eg further legislative proposals / draft bills / self regulation directives issued by the supervisory authority / increase in staff / more financial resources / modification of the authorities’ structures, eg merging of banking and insurance supervision)? Proposals to implement: changes to prudential reporting framework a capital review changes to national claims and policies database information on event reporting with ICA supervision of conglomerate groups improvements to preventative powers, correction powers, failure management powers, investigative powers and data collection powers, levy collection fine tuning re Auditor and actuary appointment FCS improvements 31
4. 2 What (if any) changes are currently being discussed or proposed with respect to any part of the regulatory framework governing the insurance / reinsurance industry (eg further legislative proposals / draft bills / self regulation directives issued by the supervisory authority / increase in staff / more financial resources / modification of the authorities’ structures, eg merging of banking and insurance supervision)? Proposals to implement: changes to prudential reporting framework a capital review changes to national claims and policies database information on event reporting with ICA supervision of conglomerate groups improvements to preventative powers, correction powers, failure management powers, investigative powers and data collection powers, levy collection fine tuning re Auditor and actuary appointment FCS improvements 31
 Working group state supervision: Denmark Presented by Åse Kogsbøll, Industriens Pension (as per 6 th of May 2010). 32
Working group state supervision: Denmark Presented by Åse Kogsbøll, Industriens Pension (as per 6 th of May 2010). 32
 About Industriens Pension • Founded 1992 • Labour Market Pension Fund, 2 nd pillar: DC • 400, 000 members (as of 1/7/2009: contributions are 12 per cent of the wages) • AUM DKK 75 bn. (EUR 10. 0 bn. ) • Benefits: retirement, disability, death and dread disease 33
About Industriens Pension • Founded 1992 • Labour Market Pension Fund, 2 nd pillar: DC • 400, 000 members (as of 1/7/2009: contributions are 12 per cent of the wages) • AUM DKK 75 bn. (EUR 10. 0 bn. ) • Benefits: retirement, disability, death and dread disease 33
 Industriens Pension – Annual return 34
Industriens Pension – Annual return 34
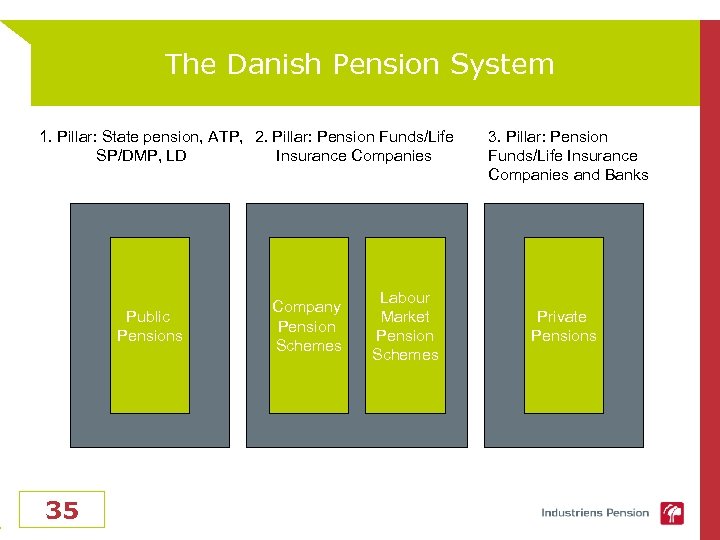 The Danish Pension System 1. Pillar: State pension, ATP, 2. Pillar: Pension Funds/Life SP/DMP, LD Insurance Companies Public Pensions 35 Labour Market Pension Schemes Company Pension Schemes 3. Pillar: Pension Funds/Life Insurance Companies and Banks Private Pensions
The Danish Pension System 1. Pillar: State pension, ATP, 2. Pillar: Pension Funds/Life SP/DMP, LD Insurance Companies Public Pensions 35 Labour Market Pension Schemes Company Pension Schemes 3. Pillar: Pension Funds/Life Insurance Companies and Banks Private Pensions
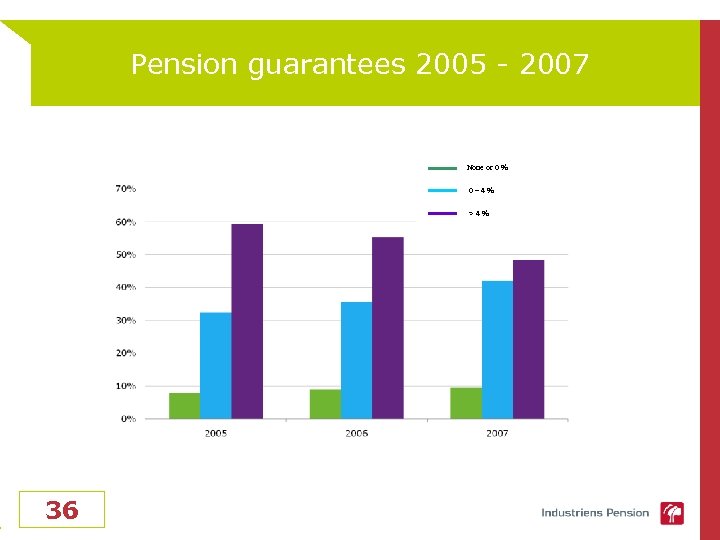 Pension guarantees 2005 - 2007 None or 0 % 0– 4% >4% 36
Pension guarantees 2005 - 2007 None or 0 % 0– 4% >4% 36
 The insurance supervisory framework • All financial institutions: Regulated by the Financial Business Act (438 articles) and the same supervision, the Danish FSA. • The act consists of general and sectorial articles • I 2007 before the crisis: – Insurance: Individual solvency requirements – In general: Risk based supervision 37
The insurance supervisory framework • All financial institutions: Regulated by the Financial Business Act (438 articles) and the same supervision, the Danish FSA. • The act consists of general and sectorial articles • I 2007 before the crisis: – Insurance: Individual solvency requirements – In general: Risk based supervision 37
 Effect on the insurance market? • Liability insurances • Increasing unemployment • Life insurances with or without guarantees 38
Effect on the insurance market? • Liability insurances • Increasing unemployment • Life insurances with or without guarantees 38
 Regulatory measures • In fall 2008: The stability agreement between DIA and the government: – Secure stabilitity for pension clients and the Danish credit-mortgage market. – Direct offshoot of the financial crisis – Temporary agreement. – Prolonged until dec. 2010 – Content: • A more favourable calculation of the reserves of the insurance companies • Caution and consolidation: A ceiling on the bonus policy 39
Regulatory measures • In fall 2008: The stability agreement between DIA and the government: – Secure stabilitity for pension clients and the Danish credit-mortgage market. – Direct offshoot of the financial crisis – Temporary agreement. – Prolonged until dec. 2010 – Content: • A more favourable calculation of the reserves of the insurance companies • Caution and consolidation: A ceiling on the bonus policy 39
 New regulatory measures • A new bill introduced on 26 th of March: – Partly adressed for banks, but several changes are adressed for all financial institutions including insurance companies – The Danish FSA’s supervision is strengthened (supervising the business models, secure financial stability, early action etc. ) – Focus on the governance of the institutions; new executive orders expected – Stricter rules of fit & proper – Renumeration policies with FSA supervision 40
New regulatory measures • A new bill introduced on 26 th of March: – Partly adressed for banks, but several changes are adressed for all financial institutions including insurance companies – The Danish FSA’s supervision is strengthened (supervising the business models, secure financial stability, early action etc. ) – Focus on the governance of the institutions; new executive orders expected – Stricter rules of fit & proper – Renumeration policies with FSA supervision 40
 Working Group on State Supervision Presentation to XIIIth AIDA World Congress 17 – 20 th May 2010 Yannis Samothrakis Dewey & Le. Boeuf LLP dl. com
Working Group on State Supervision Presentation to XIIIth AIDA World Congress 17 – 20 th May 2010 Yannis Samothrakis Dewey & Le. Boeuf LLP dl. com
 The impact of the financial crisis on the insurance supervisory authorities: crises of the supervisory bodies? Country report: France Dewey & Le. Boeuf LLP dl. com
The impact of the financial crisis on the insurance supervisory authorities: crises of the supervisory bodies? Country report: France Dewey & Le. Boeuf LLP dl. com
 Question 1 – Introductory questions ■ Supervisory bodies before the global financial crisis (GFC): 4 Until March 2010: ♦ ♦ Supervisor: Autorité de contrôle des assurances et des mutuelles (ACAM) Regulator: Comité des enterprises d'assurance (CEA) 4 In March 2010, replaced by the Autorité de contrôle prudentiel (ACP), following the merger of the ACAM, the CEA, the Banking Commission (Commission bancaire) and the Credit Institutions and Investment Firms Committee (Comité des Établissements de Crédit et des Entreprises d'Investissement) ■ Legal framework: 4 Insurance Code 4 Mutual Code 4 Social Security Code 4 Other legal provisions contained inter alia in the Civil Code, the Tax Code and other laws and regulations having an impact on insurance/reinsurance Dewey & Le. Boeuf LLP | 43
Question 1 – Introductory questions ■ Supervisory bodies before the global financial crisis (GFC): 4 Until March 2010: ♦ ♦ Supervisor: Autorité de contrôle des assurances et des mutuelles (ACAM) Regulator: Comité des enterprises d'assurance (CEA) 4 In March 2010, replaced by the Autorité de contrôle prudentiel (ACP), following the merger of the ACAM, the CEA, the Banking Commission (Commission bancaire) and the Credit Institutions and Investment Firms Committee (Comité des Établissements de Crédit et des Entreprises d'Investissement) ■ Legal framework: 4 Insurance Code 4 Mutual Code 4 Social Security Code 4 Other legal provisions contained inter alia in the Civil Code, the Tax Code and other laws and regulations having an impact on insurance/reinsurance Dewey & Le. Boeuf LLP | 43
 Question 2 – Effect of the GFC on the insurance/reinsurance market ■ General considerations: 4 Impact of the GFC felt on both sides of insurers’ balance sheet – in 2008, market value of insurers’ assets reduced by 5. 5% 4 Some specific lines of business particularly affected with a perceived reduced capacity - such as credit insurers ■ Life assurance 4 2008: ♦ ♦ significant drop in premiums of overall 11% drop of 41% for unit-linked contracts/funds 4 2009: ♦ trend was inverted, with premium collections for life assurance progressing by 12% back to 2007 levels ♦ life assurance accounted for about 55% of long-term savings according to the FFSA ■ Property insurance and liability insurance 4 1% increase in premium collection in 2009, down from 2. 5% increase in 2008 4 Professional risks were stable in 2009, as opposed to a 1. 9% increase in 2008 4 Non-professional risks saw an increase of 2% in 2009 Dewey & Le. Boeuf LLP | 44
Question 2 – Effect of the GFC on the insurance/reinsurance market ■ General considerations: 4 Impact of the GFC felt on both sides of insurers’ balance sheet – in 2008, market value of insurers’ assets reduced by 5. 5% 4 Some specific lines of business particularly affected with a perceived reduced capacity - such as credit insurers ■ Life assurance 4 2008: ♦ ♦ significant drop in premiums of overall 11% drop of 41% for unit-linked contracts/funds 4 2009: ♦ trend was inverted, with premium collections for life assurance progressing by 12% back to 2007 levels ♦ life assurance accounted for about 55% of long-term savings according to the FFSA ■ Property insurance and liability insurance 4 1% increase in premium collection in 2009, down from 2. 5% increase in 2008 4 Professional risks were stable in 2009, as opposed to a 1. 9% increase in 2008 4 Non-professional risks saw an increase of 2% in 2009 Dewey & Le. Boeuf LLP | 44
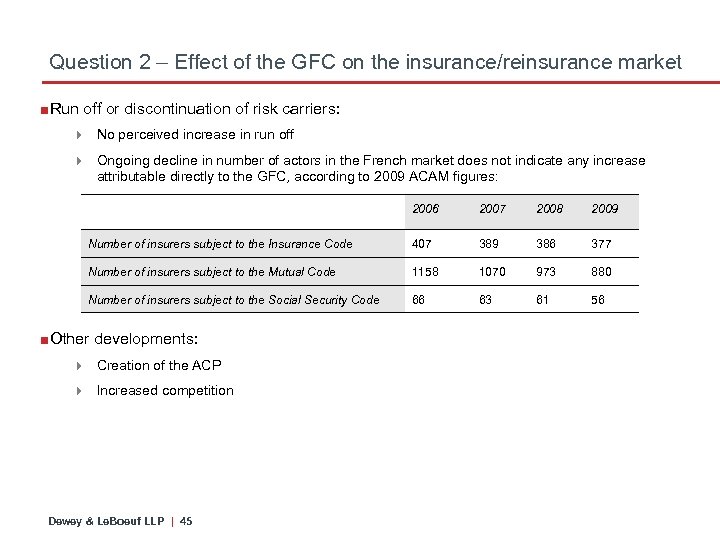 Question 2 – Effect of the GFC on the insurance/reinsurance market ■Run off or discontinuation of risk carriers: 4 No perceived increase in run off 4 Ongoing decline in number of actors in the French market does not indicate any increase attributable directly to the GFC, according to 2009 ACAM figures: 2006 2007 2008 2009 Number of insurers subject to the Insurance Code 407 389 386 377 Number of insurers subject to the Mutual Code 1158 1070 973 880 Number of insurers subject to the Social Security Code 66 63 61 56 ■Other developments: 4 Creation of the ACP 4 Increased competition Dewey & Le. Boeuf LLP | 45
Question 2 – Effect of the GFC on the insurance/reinsurance market ■Run off or discontinuation of risk carriers: 4 No perceived increase in run off 4 Ongoing decline in number of actors in the French market does not indicate any increase attributable directly to the GFC, according to 2009 ACAM figures: 2006 2007 2008 2009 Number of insurers subject to the Insurance Code 407 389 386 377 Number of insurers subject to the Mutual Code 1158 1070 973 880 Number of insurers subject to the Social Security Code 66 63 61 56 ■Other developments: 4 Creation of the ACP 4 Increased competition Dewey & Le. Boeuf LLP | 45
 Question 3 – Regulatory measures ■Supervisory intervention during the GFC: 4 Survey of ten largest life insurers’ investments 4 Additional stress tests 4 Sanctions for life insurers not complying with the legal cap on guaranteed rates of return for with-profits contracts/funds ■Impact of the GFC on the powers of supervisors: 4 Powers already wide-ranging before the crisis 4 ACP granted a new mission of safeguarding financial stability 4 ACP able to issue and enforce good practice Dewey & Le. Boeuf LLP | 46
Question 3 – Regulatory measures ■Supervisory intervention during the GFC: 4 Survey of ten largest life insurers’ investments 4 Additional stress tests 4 Sanctions for life insurers not complying with the legal cap on guaranteed rates of return for with-profits contracts/funds ■Impact of the GFC on the powers of supervisors: 4 Powers already wide-ranging before the crisis 4 ACP granted a new mission of safeguarding financial stability 4 ACP able to issue and enforce good practice Dewey & Le. Boeuf LLP | 46
 Question 4 – Amendments to legal framework of insurance supervision ■Resources of the ACP: 4 No specific increase 4 Provisional budget for 2010 consists in the sum of the respective budgets of the merged authorities (according to press documentation issued in March by the government) ■Impact of the GFC on the legal framework: 4 Except for the creation of the ACP, no other change attributed specifically to the GFC 4 Increase in taxes and levies on insurance and insurers since 2008 Dewey & Le. Boeuf LLP | 47
Question 4 – Amendments to legal framework of insurance supervision ■Resources of the ACP: 4 No specific increase 4 Provisional budget for 2010 consists in the sum of the respective budgets of the merged authorities (according to press documentation issued in March by the government) ■Impact of the GFC on the legal framework: 4 Except for the creation of the ACP, no other change attributed specifically to the GFC 4 Increase in taxes and levies on insurance and insurers since 2008 Dewey & Le. Boeuf LLP | 47
 Questions? Dewey & Le. Boeuf LLP | 48
Questions? Dewey & Le. Boeuf LLP | 48
 Contact ■Yannis Samothrakis ■Dewey & Le. Boeuf ■ 51, rue Pierre Charron ■ 75008 Paris ■ysamothrakis@dl. com Dewey & Le. Boeuf LLP dl. com ■+33 1 53 93 77 14
Contact ■Yannis Samothrakis ■Dewey & Le. Boeuf ■ 51, rue Pierre Charron ■ 75008 Paris ■ysamothrakis@dl. com Dewey & Le. Boeuf LLP dl. com ■+33 1 53 93 77 14
 Dewey & Le. Boeuf Worldwide Moscow San Francisco Silicon Valley Los Angeles Chicago Albany Boston Houston New York Washington, DC London Warsaw Brussels Frankfurt Paris Milan Rome Almaty Beijing Doha Riyadh Dubai Johannesburg Dewey & Le. Boeuf LLP | 50 Hong Kong
Dewey & Le. Boeuf Worldwide Moscow San Francisco Silicon Valley Los Angeles Chicago Albany Boston Houston New York Washington, DC London Warsaw Brussels Frankfurt Paris Milan Rome Almaty Beijing Doha Riyadh Dubai Johannesburg Dewey & Le. Boeuf LLP | 50 Hong Kong
 AIDA International – XIIIth AIDA World Congress 17 – 20 th May 2010 Working Party State Supervision 18 th May 2010 Gunne W. Bähr, Cologne, Germany
AIDA International – XIIIth AIDA World Congress 17 – 20 th May 2010 Working Party State Supervision 18 th May 2010 Gunne W. Bähr, Cologne, Germany
 Motive "Crisis is an efficient state. One has only to remove the taste of catastrophe. " Max Frisch
Motive "Crisis is an efficient state. One has only to remove the taste of catastrophe. " Max Frisch
 Content THE IMPACT OF THE FINANCIAL CRISIS ON THE INSURANCE SUPERVISORY AUTHORITIES: CRISES OF THE SUPERVISORY BODIES? - Country Report Germany -
Content THE IMPACT OF THE FINANCIAL CRISIS ON THE INSURANCE SUPERVISORY AUTHORITIES: CRISES OF THE SUPERVISORY BODIES? - Country Report Germany -
 Question 1 1. 1 Overview on the Insurance Supervisory Framework Gliederung § Federal Financial Service Authority (Bundesanstalt für Finanzdienstleistungsaufsicht, Ba. Fin) § Organisation of Ba. Fin laid down in the Financial Service Integration Act (Gesetz über die integrierte Finanzaufsicht, Fin. DAG) § Supervision of insurance companies is laid down in the German Insurance Supervisory Act (Versicherungsaufsichtsgesetz, VAG) § VAG contains in particular provisions securing the permanent satisfaction of obligations arising under insurance contracts and the protection of the insured § VAG and the Decree on Investment of Insurance Companies (Anlageverordnung, Anl. V) supplemented by orders of the Ba. Fin restrict the capital investment of insurance companies
Question 1 1. 1 Overview on the Insurance Supervisory Framework Gliederung § Federal Financial Service Authority (Bundesanstalt für Finanzdienstleistungsaufsicht, Ba. Fin) § Organisation of Ba. Fin laid down in the Financial Service Integration Act (Gesetz über die integrierte Finanzaufsicht, Fin. DAG) § Supervision of insurance companies is laid down in the German Insurance Supervisory Act (Versicherungsaufsichtsgesetz, VAG) § VAG contains in particular provisions securing the permanent satisfaction of obligations arising under insurance contracts and the protection of the insured § VAG and the Decree on Investment of Insurance Companies (Anlageverordnung, Anl. V) supplemented by orders of the Ba. Fin restrict the capital investment of insurance companies
 Question 1 1. 2 Combination with Supervision of other Financial Services Gliederung § Ba. Fin was formed on 1 May 2002 by Fin. DAG § Integrated financial supervisory authority § Merger of the three former supervisory authorities Ø Federal Banking Supervisory Office (Bundesaufsichtsamt für das Kreditwesen), Ø Federal Supervisory Office for Securities Trading (Bundesaufsichtsamt für den Wertpapierhandel), Ø Federal Insurance Supervisory Office (Bundesamt für das Versicherungswesen, BAV)
Question 1 1. 2 Combination with Supervision of other Financial Services Gliederung § Ba. Fin was formed on 1 May 2002 by Fin. DAG § Integrated financial supervisory authority § Merger of the three former supervisory authorities Ø Federal Banking Supervisory Office (Bundesaufsichtsamt für das Kreditwesen), Ø Federal Supervisory Office for Securities Trading (Bundesaufsichtsamt für den Wertpapierhandel), Ø Federal Insurance Supervisory Office (Bundesamt für das Versicherungswesen, BAV)
 Question 2 2. 1 Effect of the Global Financial Crisis § GFC is not regarded as an insurance crisis in Germany § Insurance companies – as important investors – are subject to the direct and indirect impact of the GFC § Due to the crisis, objections of potential policyholders against taking risks have increased (demand for insurance cover enlarges) § Crisis has shown need for a new solvency system based on a good risk management as laid down by the Solvency II Directive
Question 2 2. 1 Effect of the Global Financial Crisis § GFC is not regarded as an insurance crisis in Germany § Insurance companies – as important investors – are subject to the direct and indirect impact of the GFC § Due to the crisis, objections of potential policyholders against taking risks have increased (demand for insurance cover enlarges) § Crisis has shown need for a new solvency system based on a good risk management as laid down by the Solvency II Directive
 Question 2 2. 2 Effect on Availability and Pricing of Insurance § Credit insurance ØIn 2008, claim expenditure of German credit insurers significantly increased (53. 5%) ØInsurers adjusted their premium and underwriting policies § Life Insurance ØProfits of the insurance companies are relatively low in comparison to the guarantees issued ØNew business as well as profit participations for the year 2010 could by most insurance companies only be financed through consumption of own capital resources § Disaster/Catastrophe Bonds ØAffected rather heavily by the GFC ØHardly any new issues of bonds at the end of 2008, but the market rallied again
Question 2 2. 2 Effect on Availability and Pricing of Insurance § Credit insurance ØIn 2008, claim expenditure of German credit insurers significantly increased (53. 5%) ØInsurers adjusted their premium and underwriting policies § Life Insurance ØProfits of the insurance companies are relatively low in comparison to the guarantees issued ØNew business as well as profit participations for the year 2010 could by most insurance companies only be financed through consumption of own capital resources § Disaster/Catastrophe Bonds ØAffected rather heavily by the GFC ØHardly any new issues of bonds at the end of 2008, but the market rallied again
 Question 2 2. 3 Effect on Run-off § Discontinued business and run-off of risk carriers have already become an important issue before the GFC § GFC can be regarded as one factor of advancing run-off and discontinued business § In 2009, a German life insurer (“Victoria Lebensversicherung”) announced to pass on to run-off business § In respect of implementation of the Solvency II Directive, it is expected that run-off business will increase significantly § GFC had strong influence on intermediary business § In October 2009, one of the major financial intermediaries (MEG AG) applied for the institution of insolvency proceedings
Question 2 2. 3 Effect on Run-off § Discontinued business and run-off of risk carriers have already become an important issue before the GFC § GFC can be regarded as one factor of advancing run-off and discontinued business § In 2009, a German life insurer (“Victoria Lebensversicherung”) announced to pass on to run-off business § In respect of implementation of the Solvency II Directive, it is expected that run-off business will increase significantly § GFC had strong influence on intermediary business § In October 2009, one of the major financial intermediaries (MEG AG) applied for the institution of insolvency proceedings
 Question 2 2. 4 Other Developments § Increase in cost management § Measures to boost profitability § Higher number of aimed marketing measures § Reduction of personnel
Question 2 2. 4 Other Developments § Increase in cost management § Measures to boost profitability § Higher number of aimed marketing measures § Reduction of personnel
 Question 3 3. 1 Measures of Supervisory Authority (Ba. Fin) § Informal measures § Basic disapprovals § Formal admonishments § Dismissals of directors § Interdiction to act as director § Inception of a special commissioner § Withdrawal of authorisation from an insurance company
Question 3 3. 1 Measures of Supervisory Authority (Ba. Fin) § Informal measures § Basic disapprovals § Formal admonishments § Dismissals of directors § Interdiction to act as director § Inception of a special commissioner § Withdrawal of authorisation from an insurance company
 Question 3 3. 2 Sufficiency of Measures § No principle changes due to GFC § Requirements to take measures were partly eased § Supervisory powers were in some aspects expanded 3. 3 Risks for Policyholders § No risk for the payment obvious § No German insurance company obtained money from the state during the crisis § No insolvencies occurred
Question 3 3. 2 Sufficiency of Measures § No principle changes due to GFC § Requirements to take measures were partly eased § Supervisory powers were in some aspects expanded 3. 3 Risks for Policyholders § No risk for the payment obvious § No German insurance company obtained money from the state during the crisis § No insolvencies occurred
 Question 4 4. 1 Changes Regulatory Framework (I) § Legislator took various measures to tighten the insurance supervisory law § Financial Markets Stabilisation Act (Finanzmarktstabilisierungsgesetz) of 18 October 2008 ØFinancial market stabilisation fund ØSeries of further novelties: appointment of a special commissioner by Ba. Fin § Ba. Fin Circular 3/2009 entitled “Regulatory Minimum Requirements for Risk Management” (Aufsichtsrechtliche Mindestanforderungen an das Risikomanagement, Ma. Risk. VA)
Question 4 4. 1 Changes Regulatory Framework (I) § Legislator took various measures to tighten the insurance supervisory law § Financial Markets Stabilisation Act (Finanzmarktstabilisierungsgesetz) of 18 October 2008 ØFinancial market stabilisation fund ØSeries of further novelties: appointment of a special commissioner by Ba. Fin § Ba. Fin Circular 3/2009 entitled “Regulatory Minimum Requirements for Risk Management” (Aufsichtsrechtliche Mindestanforderungen an das Risikomanagement, Ma. Risk. VA)
 Question 4 4. 1 Changes Regulatory Framework (II) § Act to Strengthen the Financial Market and Insurance Supervision (Gesetz zur Stärkung der Finanzdienstleistungs- und der Versicherungsaufsicht) of 1 August 2009 ØIntensify the supervision of insurance holding companies ØProhibit the taking out of loans ØFix the number of management board and supervisory board appointments ØFix the reliability and qualification of members of supervisory boards of insurance companies ØStrengthen the position and function of the responsible actuary ØConcern the securitisation of insurance risks through special purpose insurance vehicles ØConcern the possibility of the imposition of payment prohibitions by the Ba. Fin ØConcern risk concentration in insurance groups
Question 4 4. 1 Changes Regulatory Framework (II) § Act to Strengthen the Financial Market and Insurance Supervision (Gesetz zur Stärkung der Finanzdienstleistungs- und der Versicherungsaufsicht) of 1 August 2009 ØIntensify the supervision of insurance holding companies ØProhibit the taking out of loans ØFix the number of management board and supervisory board appointments ØFix the reliability and qualification of members of supervisory boards of insurance companies ØStrengthen the position and function of the responsible actuary ØConcern the securitisation of insurance risks through special purpose insurance vehicles ØConcern the possibility of the imposition of payment prohibitions by the Ba. Fin ØConcern risk concentration in insurance groups
 Question 4 4. 2 Changes currently in Discussion § Draft Act concerning the implementation of special requirements as regards remuneration systems for insurance companies ØLaw will allow the supervisory authority to prohibit variable remuneration elements or alternatively to limit them to a certain part of the annual result § Rating agencies shall in future be supervised stronger ØDraft implementation law for the EU Rating Directive ØBa. Fin shall supervise rating agencies until a European Securities Regulatory Agency will be established in 2011 § Solvency II Directive
Question 4 4. 2 Changes currently in Discussion § Draft Act concerning the implementation of special requirements as regards remuneration systems for insurance companies ØLaw will allow the supervisory authority to prohibit variable remuneration elements or alternatively to limit them to a certain part of the annual result § Rating agencies shall in future be supervised stronger ØDraft implementation law for the EU Rating Directive ØBa. Fin shall supervise rating agencies until a European Securities Regulatory Agency will be established in 2011 § Solvency II Directive
 Thank you for your attention! Gunne W. Bähr, Cologne, Germany
Thank you for your attention! Gunne W. Bähr, Cologne, Germany
 FINANCIAL CRISIS IN INSURANCE - THE HUNGARIAN EXPERIENCE - Dr. Éva DÉRI insurance lawyer, Chairman of the Hungarian Chapter of the AIDA WP State Supervision
FINANCIAL CRISIS IN INSURANCE - THE HUNGARIAN EXPERIENCE - Dr. Éva DÉRI insurance lawyer, Chairman of the Hungarian Chapter of the AIDA WP State Supervision
 Market developments in Hungary (overwiew) 1. Suspension of investment funds’ bonds investing in real estates 2. Intermediaries’ desperate fight for clients 3. Changing supervision regime in
Market developments in Hungary (overwiew) 1. Suspension of investment funds’ bonds investing in real estates 2. Intermediaries’ desperate fight for clients 3. Changing supervision regime in
 1. Suspension of investment funds’ bonds investing in real estates HFSA, Securities Superv. : suspension for liquidity reasons (end 2008) Insurers : stop pay-outs to clients investing in such funds behind their unit linked contracts Standpoint of HFSA, Insurance Superv. : only if contract allows it
1. Suspension of investment funds’ bonds investing in real estates HFSA, Securities Superv. : suspension for liquidity reasons (end 2008) Insurers : stop pay-outs to clients investing in such funds behind their unit linked contracts Standpoint of HFSA, Insurance Superv. : only if contract allows it
 2. Intermediaries’ desperate fight for clients Intermediaries: re-partition of the market (since 2008) by transferring of „portfolio” by convincing clients to replace insurance (for commission) HFSA: increasing number of client complaints Standpoint of HFSA : portfolio transfer is not applicable!
2. Intermediaries’ desperate fight for clients Intermediaries: re-partition of the market (since 2008) by transferring of „portfolio” by convincing clients to replace insurance (for commission) HFSA: increasing number of client complaints Standpoint of HFSA : portfolio transfer is not applicable!
 3. Changing regime in supervision 3 a. New tools 3 b. New structure
3. Changing regime in supervision 3 a. New tools 3 b. New structure
 3 a. New tools for HFSA Ban activity for max. 90 days if market disorder discovered (Jan 2010) Maximum penalty increased form 75. 000, Eur to 7. 500. 000, -Eur (Jan 2010)
3 a. New tools for HFSA Ban activity for max. 90 days if market disorder discovered (Jan 2010) Maximum penalty increased form 75. 000, Eur to 7. 500. 000, -Eur (Jan 2010)
 3 b. New structure for HFSA: integrated authority (2000) Setting up of Financial Stability Board (Jan 2010) One-person leadership regime at the top again (Jan 2010) Merge with National Bank ?
3 b. New structure for HFSA: integrated authority (2000) Setting up of Financial Stability Board (Jan 2010) One-person leadership regime at the top again (Jan 2010) Merge with National Bank ?
 THANK YOU FOR THE ATTENTION ! deri. eva@pszaf. hu
THANK YOU FOR THE ATTENTION ! deri. eva@pszaf. hu
 AIDA International Association of Insurance Law Working Party 6 – State Supervision of Insurance Impact of Financial Crisis on Insurance Supervisory Regime Country Report: Ireland Tuesday, 18 May 2010
AIDA International Association of Insurance Law Working Party 6 – State Supervision of Insurance Impact of Financial Crisis on Insurance Supervisory Regime Country Report: Ireland Tuesday, 18 May 2010
 Question 1: the “old” framework - Combination of national and EU derived legislation - EU Framework Regulations: life, non-life and reinsurance - Central Bank and Financial Services Authority of Ireland (since 2003/04) - Financial Regulator: two directorates – prudential and consumer - all financial services activities (virtually) - “principles” based not “prescriptive”
Question 1: the “old” framework - Combination of national and EU derived legislation - EU Framework Regulations: life, non-life and reinsurance - Central Bank and Financial Services Authority of Ireland (since 2003/04) - Financial Regulator: two directorates – prudential and consumer - all financial services activities (virtually) - “principles” based not “prescriptive”
 Question 2: Global financial crisis (GFC) effects • Ireland - domestic and FOS/FOE international businesses – downward trend across all lines and products – balance sheets have generally held-up well (e. g. relative to credit institutions) although some overexposed • Run-offs / discontinuations – some levels – often more due to lack of critical mass or failed business plan in light of GFC – portfolio transfers out of the jurisdiction • GFC - capital efficiency / Solvency II drivers – Ireland as a hub – Zurich, Aviva, Others
Question 2: Global financial crisis (GFC) effects • Ireland - domestic and FOS/FOE international businesses – downward trend across all lines and products – balance sheets have generally held-up well (e. g. relative to credit institutions) although some overexposed • Run-offs / discontinuations – some levels – often more due to lack of critical mass or failed business plan in light of GFC – portfolio transfers out of the jurisdiction • GFC - capital efficiency / Solvency II drivers – Ireland as a hub – Zurich, Aviva, Others
 Question 3: recent measures • More “hands-on” Financial Regulator • Greater data flow • Movement away from “principles” basis to a proportionate risk based focus with “credible threat of enforcement” • High Court appointment of administrators – not seen since the 1980 s – two this year • Quinn Insurance – large domestic player now in administration – required to cease writing UK business
Question 3: recent measures • More “hands-on” Financial Regulator • Greater data flow • Movement away from “principles” basis to a proportionate risk based focus with “credible threat of enforcement” • High Court appointment of administrators – not seen since the 1980 s – two this year • Quinn Insurance – large domestic player now in administration – required to cease writing UK business
 Question 4: changes to regime • Credit institution regulatory inadequacies exposed • Perceived failures by the Financial Regulator leading to: – new Central Bank Commission – departures/key appointments – two new “directorates”: Patrick Honohan (World Bank) and Matthew Elderfield (Bermuda Monetary Authority) – increased staff levels: focus on enforcement and Solvency II
Question 4: changes to regime • Credit institution regulatory inadequacies exposed • Perceived failures by the Financial Regulator leading to: – new Central Bank Commission – departures/key appointments – two new “directorates”: Patrick Honohan (World Bank) and Matthew Elderfield (Bermuda Monetary Authority) – increased staff levels: focus on enforcement and Solvency II
 Question 4: changes to regime (cont) • Central Bank Bills – – potentially three enhanced accountability at all levels “patch work” of legislation to be codified consumer protection remit to move • Corporate Governance – consultation paper • “Fitness and probity” – directors / key functions • More to follow! 2415322 -v 1
Question 4: changes to regime (cont) • Central Bank Bills – – potentially three enhanced accountability at all levels “patch work” of legislation to be codified consumer protection remit to move • Corporate Governance – consultation paper • “Fitness and probity” – directors / key functions • More to follow! 2415322 -v 1
 AIDA International Association of Insurance Law Working Party 6 – State Supervision of Insurance Impact of Financial Crisis on Insurance Supervisory Regime Country Report: Ireland Tuesday, 18 May 2010
AIDA International Association of Insurance Law Working Party 6 – State Supervision of Insurance Impact of Financial Crisis on Insurance Supervisory Regime Country Report: Ireland Tuesday, 18 May 2010
 EOIN CAULFIELD Partner – Insurance TEL. +353 1 639 5000 MOBILE. +353 87 827 2222 E-MAIL. eoin. caulfield@williamfry. ie www. willamfry. ie
EOIN CAULFIELD Partner – Insurance TEL. +353 1 639 5000 MOBILE. +353 87 827 2222 E-MAIL. eoin. caulfield@williamfry. ie www. willamfry. ie
 WORKING GROUP STATE SUPERVISION The impact of the financial crisis on the insurance supervisory authorities: crises of the supervisory bodies? March 2010 Questionnaire, Italy DLA Piper May 2010
WORKING GROUP STATE SUPERVISION The impact of the financial crisis on the insurance supervisory authorities: crises of the supervisory bodies? March 2010 Questionnaire, Italy DLA Piper May 2010
 Question 1 (Introductory Questions)
Question 1 (Introductory Questions)
 Question 1 (Introductory Questions) § 1. 1 Can you give a short overview over the insurance supervisory framework (eg bodies, structures and law) in your country immediately before the GFC? § the Supervisory Authority for Private Insurance Undertakings and Insurance Undertakings of Public Interest (ISVAP) § the Supervisory Authority for Pension Funds (COVIP) § (the Bank of Italy) § (the National Commission for Listed Companies and the Stock Exchange CONSOB)
Question 1 (Introductory Questions) § 1. 1 Can you give a short overview over the insurance supervisory framework (eg bodies, structures and law) in your country immediately before the GFC? § the Supervisory Authority for Private Insurance Undertakings and Insurance Undertakings of Public Interest (ISVAP) § the Supervisory Authority for Pension Funds (COVIP) § (the Bank of Italy) § (the National Commission for Listed Companies and the Stock Exchange CONSOB)
 Question 1 (Introductory Questions) § 1. 1 Can you give a short overview over the insurance supervisory framework (eg bodies, structures and law) in your country immediately before the GFC? § ISVAP was established under Law no. 576 of 1982. It is mainly responsible for the stability, efficiency and the solvency of insurance undertakings, the consumers information and the protection of interests of policyholders and beneficiaries in general. § Law No. 576 has been consolidated with other insurance laws in the Insurance Code (Legislative Decree no. 209/2005) effective 1 January 2006. § The Insurance Code, the Civil Code and the ISVAP Regulations are presently the main sources of law in the matter of insurance and reinsurance. § The Insurance Code was amended (inter alia) by Legislative Decree no. 56 of 2008, implementing the EU Directive 2005/68 of 2005 on reinsurance and by Legislative Decree no. 173 of 2008, implementing the EU Directive 2006/46 on disclosure of information in the financial statements on the economic relationships with related parties.
Question 1 (Introductory Questions) § 1. 1 Can you give a short overview over the insurance supervisory framework (eg bodies, structures and law) in your country immediately before the GFC? § ISVAP was established under Law no. 576 of 1982. It is mainly responsible for the stability, efficiency and the solvency of insurance undertakings, the consumers information and the protection of interests of policyholders and beneficiaries in general. § Law No. 576 has been consolidated with other insurance laws in the Insurance Code (Legislative Decree no. 209/2005) effective 1 January 2006. § The Insurance Code, the Civil Code and the ISVAP Regulations are presently the main sources of law in the matter of insurance and reinsurance. § The Insurance Code was amended (inter alia) by Legislative Decree no. 56 of 2008, implementing the EU Directive 2005/68 of 2005 on reinsurance and by Legislative Decree no. 173 of 2008, implementing the EU Directive 2006/46 on disclosure of information in the financial statements on the economic relationships with related parties.
 Question 1 (Introductory Questions) § 1. 2 In particular, was the supervision of insurance combined in any way with the supervision of any other financial service (eg banking)? § ISVAP works in cooperation with the Bank of Italy, Consob and Covip as well as the Antitrust authority
Question 1 (Introductory Questions) § 1. 2 In particular, was the supervision of insurance combined in any way with the supervision of any other financial service (eg banking)? § ISVAP works in cooperation with the Bank of Italy, Consob and Covip as well as the Antitrust authority
 Question 2 (Effect of the GFC on the Insurance / Reinsurance Market)
Question 2 (Effect of the GFC on the Insurance / Reinsurance Market)
 Question 2 (Effect of the GFC on the Insurance / Reinsurance Market) § 2. 1 Please summarise how the GFC has affected – or been perceived as having affected – the insurance / reinsurance market in your country? § Based on the latest data published by ANIA (the Italian Association of Insurance Companies) it appears that motor liability insurance has been significantly affected by the crisis in 2009 § Also premiums in the property sector (fire and property insurance) were affected by the economic downturn § In 2009, premiums written in class III (linked policies) have been 80% lower that in 2008
Question 2 (Effect of the GFC on the Insurance / Reinsurance Market) § 2. 1 Please summarise how the GFC has affected – or been perceived as having affected – the insurance / reinsurance market in your country? § Based on the latest data published by ANIA (the Italian Association of Insurance Companies) it appears that motor liability insurance has been significantly affected by the crisis in 2009 § Also premiums in the property sector (fire and property insurance) were affected by the economic downturn § In 2009, premiums written in class III (linked policies) have been 80% lower that in 2008
 Question 3 (Regulatory Measures)
Question 3 (Regulatory Measures)
 Question 3 (Regulatory Measures) § 3. 1 What examples are there during or since the GFC of the insurance supervisory authority of your country taking specific steps to influence, control or intervene in the conduct or operations of insurance / reinsurance risk carriers, or their directors and officers? § (i) Bank of Italy - Consob - Isvap Documents no. 2 of 6 February 2009 and no. 4 of 3 March 2010 § Guidelines for the disclosure in the annual and half yearly financial statements on the going concern assumption, financial risks, test of assets for impairment and uncertainties in the use of estimations. § The purpose of the documents is to ensure that undertakings provide clear and accurate information on the effects of the crisis on profits and losses, assets and liabilities, strategic and operating decisions and any adjustments made to adapt the strategy to the altered environment.
Question 3 (Regulatory Measures) § 3. 1 What examples are there during or since the GFC of the insurance supervisory authority of your country taking specific steps to influence, control or intervene in the conduct or operations of insurance / reinsurance risk carriers, or their directors and officers? § (i) Bank of Italy - Consob - Isvap Documents no. 2 of 6 February 2009 and no. 4 of 3 March 2010 § Guidelines for the disclosure in the annual and half yearly financial statements on the going concern assumption, financial risks, test of assets for impairment and uncertainties in the use of estimations. § The purpose of the documents is to ensure that undertakings provide clear and accurate information on the effects of the crisis on profits and losses, assets and liabilities, strategic and operating decisions and any adjustments made to adapt the strategy to the altered environment.
 Question 3 (Regulatory Measures) § 3. 1 What examples are there during or since the GFC of the insurance supervisory authority of your country taking specific steps to influence, control or intervene in the conduct or operations of insurance / reinsurance risk carriers, or their directors and officers? § (ii) Isvap communications § By communications dated 1 July 2009, 20 February 2008, 6 August 2008, 29 September 2008, ISVAP invited all undertakings to carry out proper stress test in order to verify the potential impact of the prolonged crisis on the relevant solvency margins and notify ISVAP of the outcome of such tests § In particular, by communications of 29 September 2008 and 20 February 2008 respectively, ISVAP required specific information on investments made in Lehman Brothers' financial instruments and subprime collaterals
Question 3 (Regulatory Measures) § 3. 1 What examples are there during or since the GFC of the insurance supervisory authority of your country taking specific steps to influence, control or intervene in the conduct or operations of insurance / reinsurance risk carriers, or their directors and officers? § (ii) Isvap communications § By communications dated 1 July 2009, 20 February 2008, 6 August 2008, 29 September 2008, ISVAP invited all undertakings to carry out proper stress test in order to verify the potential impact of the prolonged crisis on the relevant solvency margins and notify ISVAP of the outcome of such tests § In particular, by communications of 29 September 2008 and 20 February 2008 respectively, ISVAP required specific information on investments made in Lehman Brothers' financial instruments and subprime collaterals
 Question 3 (Regulatory Measures) § 3. 2 Were the powers of intervention – existing before and during the FGC – of your country’s insurance supervisory authority sufficient? § Apparently yes, since no defaults of insurance undertakings occurred as a direct result of the crisis
Question 3 (Regulatory Measures) § 3. 2 Were the powers of intervention – existing before and during the FGC – of your country’s insurance supervisory authority sufficient? § Apparently yes, since no defaults of insurance undertakings occurred as a direct result of the crisis
 Question 3 (Regulatory Measures) § 3. 3 Have there been any examples during or since the GFC of the payment of insureds‘/policyholders' claims being at risk from the potential insolvency of an insurance / reinsurance risk carrier or intermediary? § Various retail banks and insurance companies have offered their customers index polices linked to bonds issued by Lehman Brothers over the 12 -24 months before the Lehman Brothers was adjudicated bankrupt. Further to the denial of repayment of premium opposed by some undertakings, many of such investors claimed that these policies were presented to them as “safe investments” fully warranted and sued the relevant undertakings in Court
Question 3 (Regulatory Measures) § 3. 3 Have there been any examples during or since the GFC of the payment of insureds‘/policyholders' claims being at risk from the potential insolvency of an insurance / reinsurance risk carrier or intermediary? § Various retail banks and insurance companies have offered their customers index polices linked to bonds issued by Lehman Brothers over the 12 -24 months before the Lehman Brothers was adjudicated bankrupt. Further to the denial of repayment of premium opposed by some undertakings, many of such investors claimed that these policies were presented to them as “safe investments” fully warranted and sued the relevant undertakings in Court
 Question 4 (Amendments of the Insurance Supervisory Law)
Question 4 (Amendments of the Insurance Supervisory Law)
 Question 4 (Amendments of the Insurance Supervisory Law) § 4. 1 In general terms, what (if any) changes have there been in the regulatory framework for the insurance or reinsurance industry since the onset of the GFC? § (i) Law No. 2 of 28 January 2009 and ISVAP Regulation no. 28 of 17 February 2009 § Legislative Decree on Anti-Financial Crisis Measures No. 185 (Now Law No. 2 of 28 January 2009) was approved with a view to reduce the impact of the financial global crisis. § In accordance with the guidelines set forth by Law No. 2 of 28 January 2009, ISVAP issued the Regulation no. 28 of 17 February 2009 containing the regulatory framework “for the implementation of provisions regarding criteria for the assessment of items listed under assets which are however not destined to remain as long-term company assets, introduced under Decree Law no. 185 of 29 November 2008” § The most significant innovation provided for under the new regulation consists in insurance companies being permitted not to align the budget value of short-term financial instruments to the price deducible from market trends at the end of the year.
Question 4 (Amendments of the Insurance Supervisory Law) § 4. 1 In general terms, what (if any) changes have there been in the regulatory framework for the insurance or reinsurance industry since the onset of the GFC? § (i) Law No. 2 of 28 January 2009 and ISVAP Regulation no. 28 of 17 February 2009 § Legislative Decree on Anti-Financial Crisis Measures No. 185 (Now Law No. 2 of 28 January 2009) was approved with a view to reduce the impact of the financial global crisis. § In accordance with the guidelines set forth by Law No. 2 of 28 January 2009, ISVAP issued the Regulation no. 28 of 17 February 2009 containing the regulatory framework “for the implementation of provisions regarding criteria for the assessment of items listed under assets which are however not destined to remain as long-term company assets, introduced under Decree Law no. 185 of 29 November 2008” § The most significant innovation provided for under the new regulation consists in insurance companies being permitted not to align the budget value of short-term financial instruments to the price deducible from market trends at the end of the year.
 Question 4 (Amendments of the Insurance Supervisory Law) § (ii) Isvap Regulation no. 32 of 11 June 2009 § On 11 June 2009 Isvap issued the Regulation No. 32 containing new rules applicable to insurance contracts in which the services provided are directly connected to a share index or other benchmark value. § Index-linked policies, which were regulated under ISVAP Circulars no. 332/1998 and no. 451/2001 – haven been reviewed in depth. § The most significant innovation is that the performance and the surrender values of index-linked contracts cannot be directly linked to specific assets held by the insurance company, but only to "official" share indexes, bond indexes and inflation-linked indexes (i. e. those calculated by third parties on the basis of objective and predefined criteria which are widely available and constructed on financial instruments traded on liquid and active regulated markets). § Solvency margins requested to the companies which intend to offer index-linked policies have been increased; from 1% to 4% of technical reserves. § Article 8 also defines the principles of diversification which the insurance companies must observe with reference to all index-linked products. Companies may not invest over 10% of their total technical reserves for such contracts in assets of the same issuer or group. § The index-linked policies are now obliged to guarantee in any case minimum performance in the event of the death of the policyholder, in proportion to the premium paid.
Question 4 (Amendments of the Insurance Supervisory Law) § (ii) Isvap Regulation no. 32 of 11 June 2009 § On 11 June 2009 Isvap issued the Regulation No. 32 containing new rules applicable to insurance contracts in which the services provided are directly connected to a share index or other benchmark value. § Index-linked policies, which were regulated under ISVAP Circulars no. 332/1998 and no. 451/2001 – haven been reviewed in depth. § The most significant innovation is that the performance and the surrender values of index-linked contracts cannot be directly linked to specific assets held by the insurance company, but only to "official" share indexes, bond indexes and inflation-linked indexes (i. e. those calculated by third parties on the basis of objective and predefined criteria which are widely available and constructed on financial instruments traded on liquid and active regulated markets). § Solvency margins requested to the companies which intend to offer index-linked policies have been increased; from 1% to 4% of technical reserves. § Article 8 also defines the principles of diversification which the insurance companies must observe with reference to all index-linked products. Companies may not invest over 10% of their total technical reserves for such contracts in assets of the same issuer or group. § The index-linked policies are now obliged to guarantee in any case minimum performance in the event of the death of the policyholder, in proportion to the premium paid.
 THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION
THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION
 Cliquez pour modifier le style du titre du masque AIDA International – XIIIth AIDA World Congress 17 – 20 th May 2010 Working Party State Supervision 18 May 2010 Christian Felderer, General Counsel SCOR Switzerland XIIIthe AIDA World Congress, Paris – Working Party State Supervision – Impact of the Financial Crisis on the Insurance Supervisory Authorities – COUNTRY REPORT SWITZERLAND Christian Felderer, General Counsel SCOR Switzerland
Cliquez pour modifier le style du titre du masque AIDA International – XIIIth AIDA World Congress 17 – 20 th May 2010 Working Party State Supervision 18 May 2010 Christian Felderer, General Counsel SCOR Switzerland XIIIthe AIDA World Congress, Paris – Working Party State Supervision – Impact of the Financial Crisis on the Insurance Supervisory Authorities – COUNTRY REPORT SWITZERLAND Christian Felderer, General Counsel SCOR Switzerland
 Impact of the financial crisis on the supervision systems – country reports Switzerland XIIIthe AIDA World Congress, Paris – Working Party State Supervision – Impact of the Financial Crisis on the Insurance Supervisory Authorities – COUNTRY REPORT SWITZERLAND Christian Felderer, General Counsel SCOR Switzerland
Impact of the financial crisis on the supervision systems – country reports Switzerland XIIIthe AIDA World Congress, Paris – Working Party State Supervision – Impact of the Financial Crisis on the Insurance Supervisory Authorities – COUNTRY REPORT SWITZERLAND Christian Felderer, General Counsel SCOR Switzerland
 Question 1 1. 1. Overview on the insurance supervisory framework Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority (FINMA) Revised Insurance Supervisory Act (ISA) of 22 June 2007 Financial Market Supervisory Act (FINMASA) of 22 June 2007 1. 2. Combination Transition from FOPI to FINMA. Combination of insurance and banking supervision under one federal authority: FINMA XIIIthe AIDA World Congress, Paris – Working Party State Supervision – Impact of the Financial Crisis on the Insurance Supervisory Authorities – COUNTRY REPORT SWITZERLAND Christian Felderer, General Counsel SCOR Switzerland
Question 1 1. 1. Overview on the insurance supervisory framework Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority (FINMA) Revised Insurance Supervisory Act (ISA) of 22 June 2007 Financial Market Supervisory Act (FINMASA) of 22 June 2007 1. 2. Combination Transition from FOPI to FINMA. Combination of insurance and banking supervision under one federal authority: FINMA XIIIthe AIDA World Congress, Paris – Working Party State Supervision – Impact of the Financial Crisis on the Insurance Supervisory Authorities – COUNTRY REPORT SWITZERLAND Christian Felderer, General Counsel SCOR Switzerland
 Question 2 2. 1. Effect of the Global Financial Crisis (GFC) Corporate governance and code of conduct Seven pieces of legislation under the Financial Market Supervisory Authority umbrella 2. 2. Effect on availability and pricing of insurance No Swiss specific effects 2. 3. Effect on run-off No Swiss specific effects XIIIthe AIDA World Congress, Paris – Working Party State Supervision – Impact of the Financial Crisis on the Insurance Supervisory Authorities – COUNTRY REPORT SWITZERLAND Christian Felderer, General Counsel SCOR Switzerland
Question 2 2. 1. Effect of the Global Financial Crisis (GFC) Corporate governance and code of conduct Seven pieces of legislation under the Financial Market Supervisory Authority umbrella 2. 2. Effect on availability and pricing of insurance No Swiss specific effects 2. 3. Effect on run-off No Swiss specific effects XIIIthe AIDA World Congress, Paris – Working Party State Supervision – Impact of the Financial Crisis on the Insurance Supervisory Authorities – COUNTRY REPORT SWITZERLAND Christian Felderer, General Counsel SCOR Switzerland
 Question 2 – cont’d 2. 4. Other developments No specific other developments XIIIthe AIDA World Congress, Paris – Working Party State Supervision – Impact of the Financial Crisis on the Insurance Supervisory Authorities – COUNTRY REPORT SWITZERLAND Christian Felderer, General Counsel SCOR Switzerland
Question 2 – cont’d 2. 4. Other developments No specific other developments XIIIthe AIDA World Congress, Paris – Working Party State Supervision – Impact of the Financial Crisis on the Insurance Supervisory Authorities – COUNTRY REPORT SWITZERLAND Christian Felderer, General Counsel SCOR Switzerland
 Question 3 3. 1. Specific steps taken by supervisory authority Specific issue and exposure related reporting Information meetings 3. 2. Powers of intervention No principle changes, due to revised prudential regulation implemented only in 2007 3. 3. Risks of insolvency due to GFC No materializing risk. However, closer individual monitoring. XIIIthe AIDA World Congress, Paris – Working Party State Supervision – Impact of the Financial Crisis on the Insurance Supervisory Authorities – COUNTRY REPORT SWITZERLAND Christian Felderer, General Counsel SCOR Switzerland
Question 3 3. 1. Specific steps taken by supervisory authority Specific issue and exposure related reporting Information meetings 3. 2. Powers of intervention No principle changes, due to revised prudential regulation implemented only in 2007 3. 3. Risks of insolvency due to GFC No materializing risk. However, closer individual monitoring. XIIIthe AIDA World Congress, Paris – Working Party State Supervision – Impact of the Financial Crisis on the Insurance Supervisory Authorities – COUNTRY REPORT SWITZERLAND Christian Felderer, General Counsel SCOR Switzerland
 Question 4 4. 1. Changes at supervisory level No notable increase in funding and manpower Involvement of outside special experts (e. g. review of financial modeling/SST Models, accounting, legal issues) 4. 2. Proposals for change Supervisory tools to address the too big to fail risk Limiting economic risks caused by large companies CEO of FINMA: “Radical changes are required…. . ” XIIIthe AIDA World Congress, Paris – Working Party State Supervision – Impact of the Financial Crisis on the Insurance Supervisory Authorities – COUNTRY REPORT SWITZERLAND Christian Felderer, General Counsel SCOR Switzerland
Question 4 4. 1. Changes at supervisory level No notable increase in funding and manpower Involvement of outside special experts (e. g. review of financial modeling/SST Models, accounting, legal issues) 4. 2. Proposals for change Supervisory tools to address the too big to fail risk Limiting economic risks caused by large companies CEO of FINMA: “Radical changes are required…. . ” XIIIthe AIDA World Congress, Paris – Working Party State Supervision – Impact of the Financial Crisis on the Insurance Supervisory Authorities – COUNTRY REPORT SWITZERLAND Christian Felderer, General Counsel SCOR Switzerland


