4702395acf61b123d93b147f264935a3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12

Working Group: Can Six Blind Men Find Apples & Oranges? Measuring Variable Implementation of QI Interventions Using Multiple Data Sources

Presenters l l Alexander S. Young, MD, MSHS Elizabeth (Becky) Yano, Ph. D, MSPH Lisa V. Rubenstein, MD, MSPH Alison Hamilton, Ph. D

Overview l l 90 minutes: presentations 60 minutes: group discussion and breakout groups 30 minutes: group consensus on priorities, suggested next steps, directions Working group moves to plenary – 5 minute summary presented

Overview of Working Group l Presentations – – Introduction and overview (Alex) QUITS smoking cessation trial (Becky) TIDES depression collaborative care (Lisa) EQUIP evidence-based practice in schizophrenia (Alison)

Goal of Presentations l l Brief orientation to example QI intervention How context matters sets us up for variable QI intervention deployment Process for intentional adaptation of evidence into context of local practice Types of data sources brought to bear on measuring implementation – l including development of a fidelity score Triangulation of data sources to tell story

QI Intervention (QII) Examples l QUITS (Quality Improvement Trial for Smoking cessation) – – l evidence-based quality improvement to implement smoking cessation guidelines Scott Sherman MD & Becky Yano Ph. D (co-PIs) TIDES (Translating Interventions for Depression into Evidence-based Solutions) – – depression collaborative care model Lisa Rubenstein MD & Ed Chaney Ph. D (co-PIs)

QI Intervention Examples (cont’d) l EQUIP (Enhancing QUality of care In Psychosis) – – evidence-based quality improvement to implement effective treatments in schizophrenia Alex Young MD & Amy Cohen Ph. D (co-PIs)
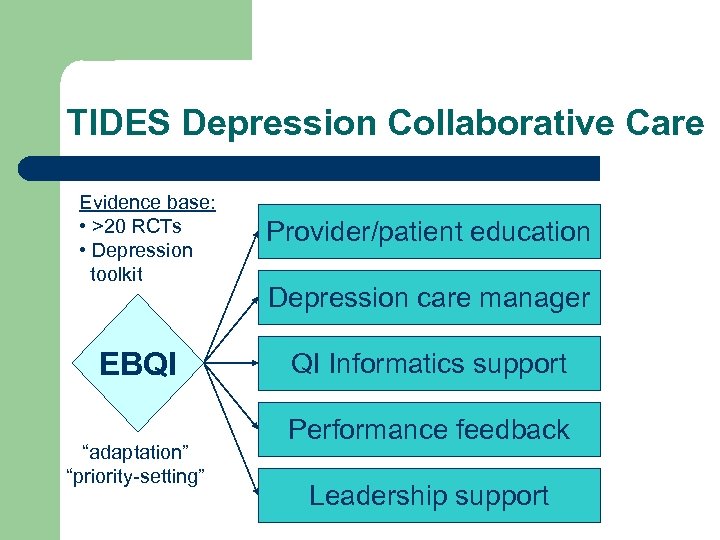
TIDES Depression Collaborative Care Evidence base: • >20 RCTs • Depression toolkit EBQI “adaptation” “priority-setting” Provider/patient education Depression care manager QI Informatics support Performance feedback Leadership support
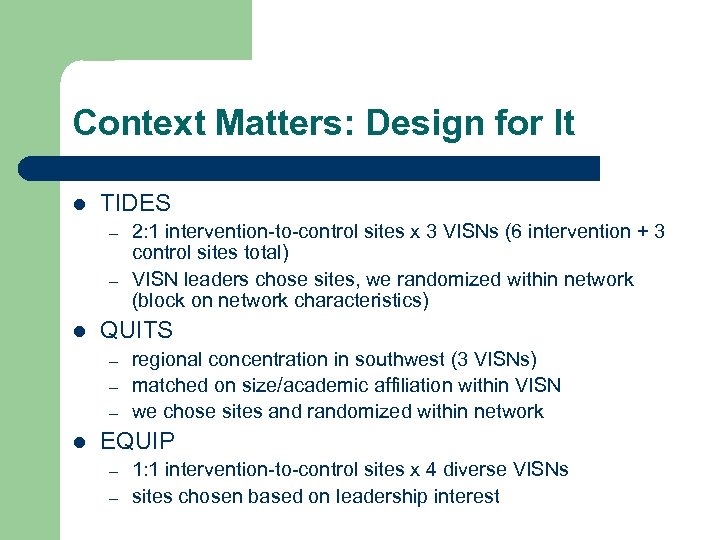
Context Matters: Design for It l TIDES – – l QUITS – – – l 2: 1 intervention-to-control sites x 3 VISNs (6 intervention + 3 control sites total) VISN leaders chose sites, we randomized within network (block on network characteristics) regional concentration in southwest (3 VISNs) matched on size/academic affiliation within VISN we chose sites and randomized within network EQUIP – – 1: 1 intervention-to-control sites x 4 diverse VISNs sites chosen based on leadership interest

Context Matters: Input from Sites l Attitudes / beliefs / experiences – – – l perceived need for the intervention competing demands staff openness to innovation Resources – – perceived time to use program and participate in implementation organizational structure, staffing, prior QI experience, informatics support Source: Kirchner JE, Parker LE, Yano EM, COVES evaluation (2007).
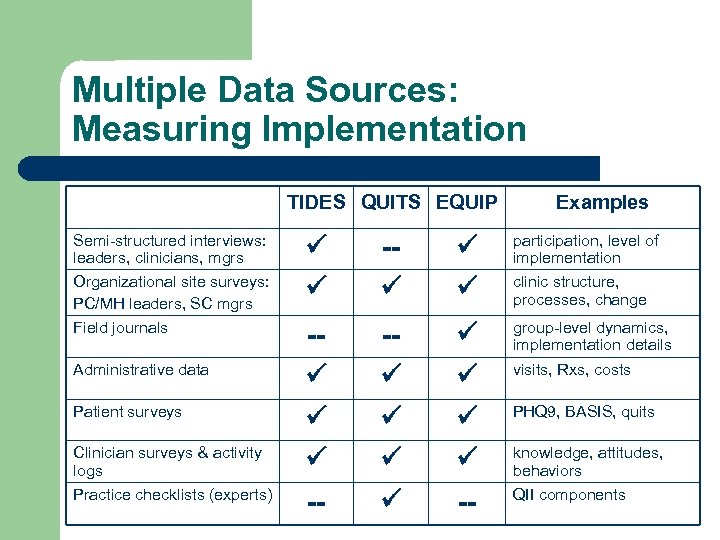
Multiple Data Sources: Measuring Implementation TIDES QUITS EQUIP Semi-structured interviews: leaders, clinicians, mgrs Organizational site surveys: PC/MH leaders, SC mgrs Field journals Administrative data Patient surveys Clinician surveys & activity logs Practice checklists (experts) Examples - participation, level of implementation - -- - -- group-level dynamics, implementation details clinic structure, processes, change visits, Rxs, costs PHQ 9, BASIS, quits knowledge, attitudes, behaviors QII components

Triangulation l Critical to collect information about implementation from multiple sources – – l be prepared for disagreement perspectives and opportunities for observation differ for managers, providers vs. patients Recognize differences between “exposed” sample and practice population – – does the “enrolled” group represent the practice? did the intervention penetrate among all providers?
4702395acf61b123d93b147f264935a3.ppt