e9bb67c1a04a1c04158a75fded20af4f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12

Workflow-enabled Internet Service Delivery for a Variety of Access Networks APNOMS 2003 Byung. Deok Chung*, Hoon Choi** , Seong. Beom Kim* Operations Support System Laboratory, KT* Department of Computer Engineering, CNU** Email: {bdchung, sbkimm}@kt. co. kr*, hchoi@ce. cnu. ac. kr Tel : 81 -42 -870 -8620
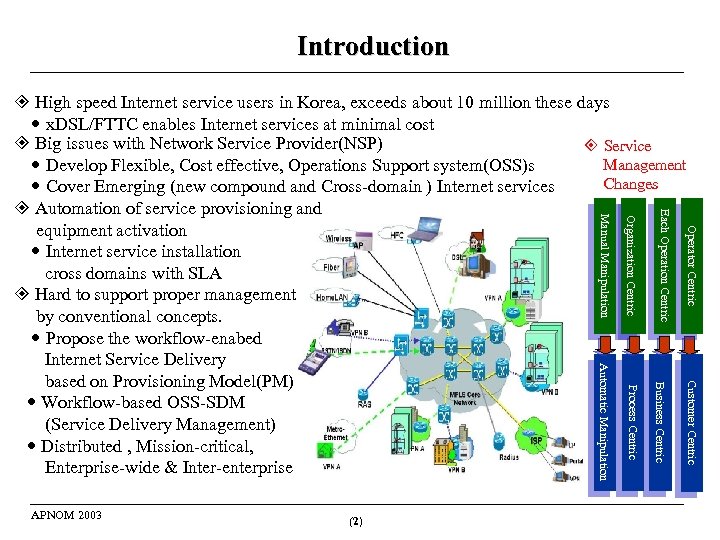
Introduction Operator Centric Customer Centric Business Centric Process Centric (2) Operator Centric Organization Centric Automatic Manipulation APNOM 2003 Each Operation Centric Manual Manipulation High speed Internet service users in Korea, exceeds about 10 million these days x. DSL/FTTC enables Internet services at minimal cost Big issues with Network Service Provider(NSP) Service Management Develop Flexible, Cost effective, Operations Support system(OSS)s Changes Cover Emerging (new compound and Cross-domain ) Internet services Automation of service provisioning and equipment activation Internet service installation cross domains with SLA Hard to support proper management by conventional concepts. Propose the workflow-enabed Internet Service Delivery based on Provisioning Model(PM) Workflow-based OSS-SDM (Service Delivery Management) Distributed , Mission-critical, Enterprise-wide & Inter-enterprise
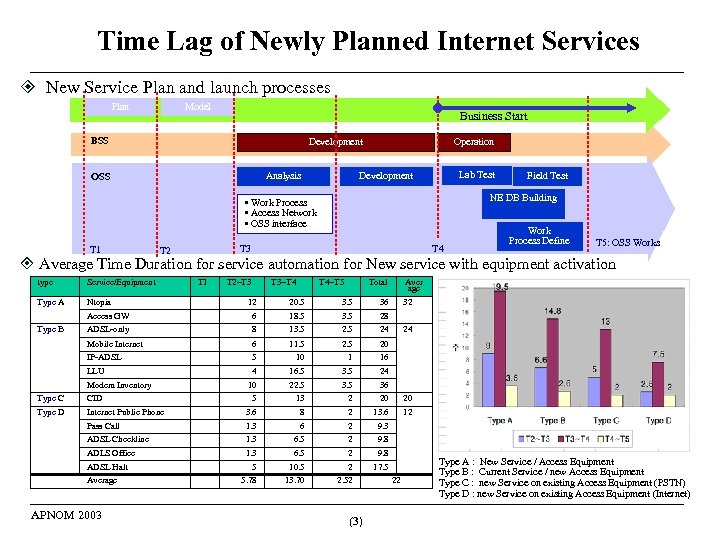
Time Lag of Newly Planned Internet Services New Service Plan and launch processes Plan Model Business Start BSS Development Analysis OSS Operation Lab Test Development NE DB Building • Work Process • Access Network • OSS interface T 1 T 3 T 2 Field Test T 4 Work Process Define T 5: OSS Works Average Time Duration for service automation for New service with equipment activation type Service/Equipment Type A Ntopia T 1 T 2~T 3 T 3~T 4 T 4~T 5 Total 20. 5 36 6 18. 5 3. 5 28 ADSL-only 8 13. 5 24 Mobile Internet 6 11. 5 20 IP-ADSL 5 10 1 16 LLU Type B 12 Access GW 4 16. 5 3. 5 24 10 22. 5 3. 5 Aver age 36 Modem Inventory 32 24 Type C CID 5 13 2 20 20 Type D Internet Public Phone 3. 6 8 2 13. 6 12 Pass Call 1. 3 6 2 9. 3 ADSL Checkline 1. 3 6. 5 2 9. 8 ADLS Office 1. 3 6. 5 2 9. 8 5 10. 5 2 17. 5 5. 78 13. 70 2. 52 ADSL Halt Average APNOM 2003 (3) 22 Type A : New Service / Access Equipment Type B : Current Service / new Access Equipment Type C : new Service on existing Access Equipment (PSTN) Type D : new Service on existing Access Equipment (Internet)
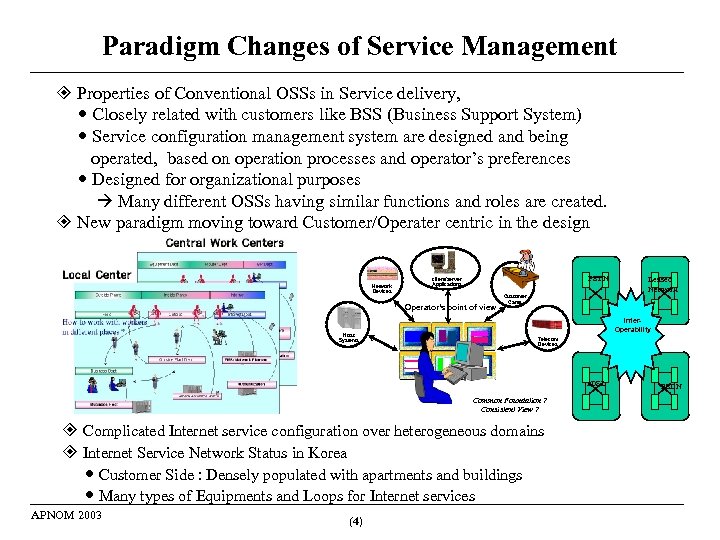
Paradigm Changes of Service Management Properties of Conventional OSSs in Service delivery, Closely related with customers like BSS (Business Support System) Service configuration management system are designed and being operated, based on operation processes and operator’s preferences Designed for organizational purposes Many different OSSs having similar functions and roles are created. New paradigm moving toward Customer/Operater centric in the design Network Devices PSTN client/server Applications Operator’s point of view Host Systems Customer Cares Inter. Operability Telecom Devices x. DSL Common Foundation ? Consistent View ? Complicated Internet service configuration over heterogeneous domains Internet Service Network Status in Korea Customer Side : Densely populated with apartments and buildings Many types of Equipments and Loops for Internet services APNOM 2003 (4) Leased Network PSDN
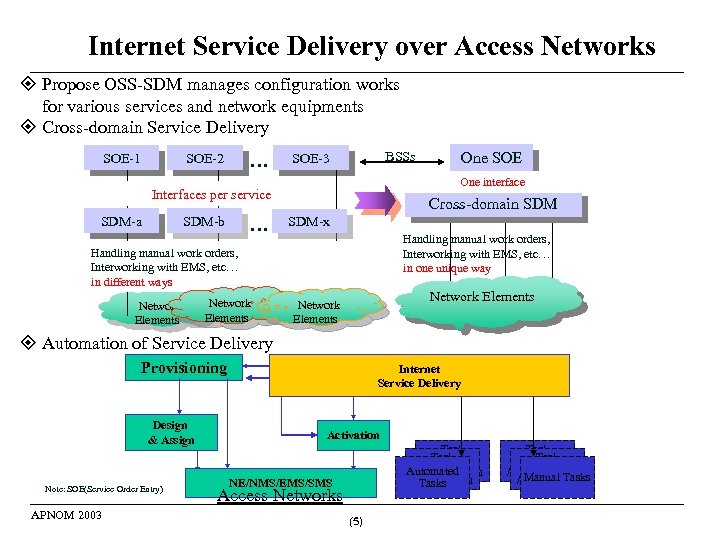
Internet Service Delivery over Access Networks Propose OSS-SDM manages configuration works for various services and network equipments Cross-domain Service Delivery SOE-1 … SOE-2 BSSs SOE-3 One interface Interfaces per service SDM-a SDM-b … Cross-domain SDM-x Handling manual work orders, Interworking with EMS, etc… in one unique way Handling manual work orders, Interworking with EMS, etc… in different ways Network Elements One SOE Network Elements Automation of Service Delivery Provisioning Design & Assign Note: SOE(Service Order Entry) APNOM 2003 Internet Service Delivery Activation Task generation Automated / distribution Tasks NE/NMS/EMS/SMS Access Networks (5) Task generation / distribution Manual Tasks / distribution
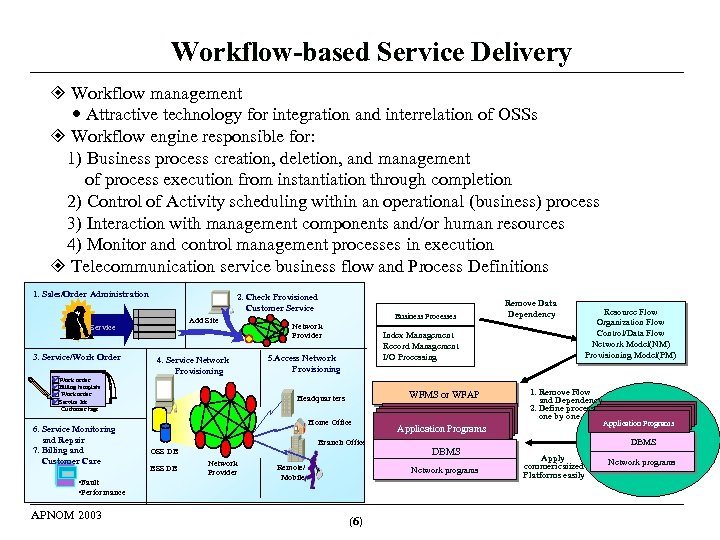
Workflow-based Service Delivery Workflow management Attractive technology for integration and interrelation of OSSs Workflow engine responsible for: 1) Business process creation, deletion, and management of process execution from instantiation through completion 2) Control of Activity scheduling within an operational (business) process 3) Interaction with management components and/or human resources 4) Monitor and control management processes in execution Telecommunication service business flow and Process Definitions 1. Sales/Order Administration 2. Check Provisioned Customer Service Add Site Service 3. Service/Work Order 4. Service Network Provisioning Work order Billing template Work order Service Ids Customer tags 6. Service Monitoring and Repair 7. Billing and Customer Care • Fault • Performance APNOM 2003 Business Processes Network Provider Index Management Record Management I/O Processing 5. Access Network Provisioning WFMS or WFAP Headquarters Home Office Branch Office OSS DB BSS DB Network Provider Remove Data Dependency Remote/ Mobile Network programs (6) 1. Remove Flow and Dependency 2. Define processes one by one Application Programs DBMS Resource Flow Organization Flow Control/Data Flow Network Model(NM) Provisioning Model(PM) Application Programs DBMS Apply commericaiized Platforms easily Network programs
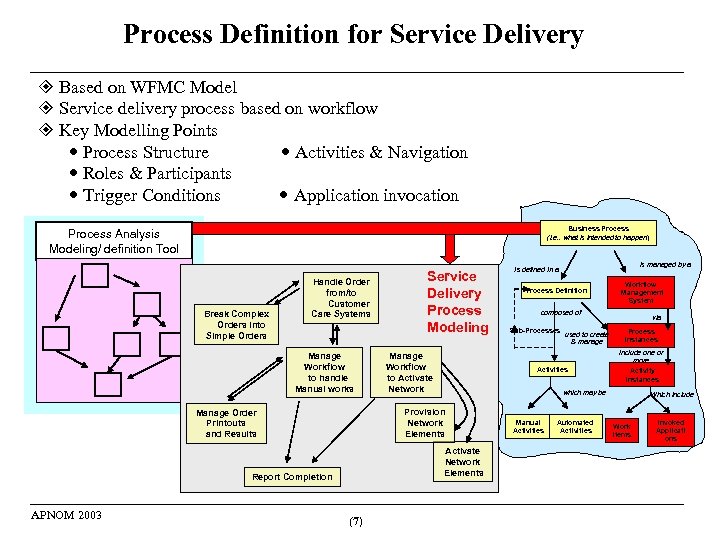
Process Definition for Service Delivery Based on WFMC Model Service delivery process based on workflow Key Modelling Points Process Structure Activities & Navigation Roles & Participants Trigger Conditions Application invocation Business Process (i. e. . what is intended to happen) Process Analysis Modeling/ definition Tool Break Complex Orders into Simple Orders Handle Order from/to Customer Care Systems Manage Workflow to handle Manual works Manage Workflow to Activate Network (7) Workflow Management System composed of Sub-Processes used to create & manage via Process Instances include one or more Activity Instances which may be Activate Network Elements Report Completion Process Definition Activities Provision Network Elements Manage Order Printouts and Results APNOM 2003 Service Delivery Process Modeling is managed by a is defined in a Manual Activities Automated Activities Which include Work Items Invoked Applicati ons
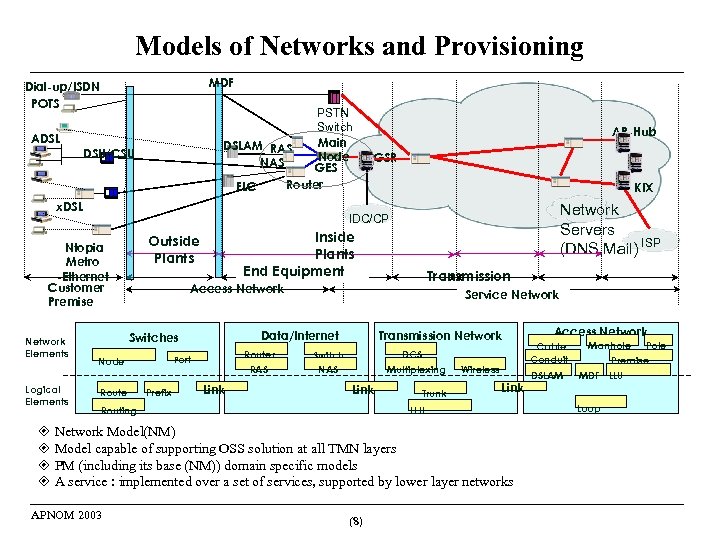
Models of Networks and Provisioning MDF Dial-up/ISDN POTS PSTN Switch Main DSLAM RAS Node NAS GES Router FLC ADSL DSU/CSU x. DSL Logical Elements GSR KIX Network Servers (DNS, Mail) ISP IDC/CP Inside Plants End Equipment Outside Plants Ntopia Metro -Ethernet Customer Premise Network Elements AP-Hub Transmission Access Network Data/Internet Switches Router RAS Port Node Prefix Service Network Link Transmission Network DCS Multiplexing Switch NAS Link Routing Trunk Wireless Link LLU Network Model(NM) Model capable of supporting OSS solution at all TMN layers PM (including its base (NM)) domain specific models A service : implemented over a set of services, supported by lower layer networks APNOM 2003 (8) Access Network Cable Conduit DSLAM Manhole Premise MDF LLU Loop
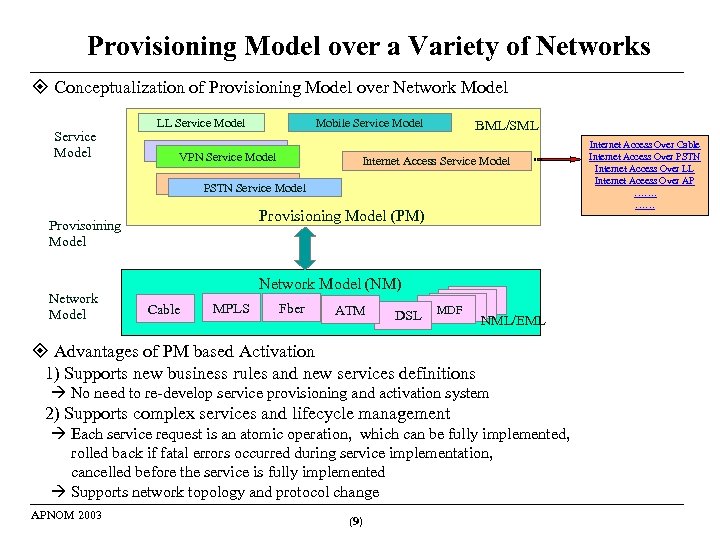
Provisioning Model over a Variety of Networks Conceptualization of Provisioning Model over Network Model Service Model LL Service Model Mobile Service Model VPN Service Model BML/SML Internet Access Service Model VPNPSTN Service Model Provisioning Model (PM) Provisoining Model Network Model (NM) Cable MPLS Fber ATM DSL MDF NML/EML Advantages of PM based Activation 1) Supports new business rules and new services definitions No need to re-develop service provisioning and activation system 2) Supports complex services and lifecycle management Each service request is an atomic operation, which can be fully implemented, rolled back if fatal errors occurred during service implementation, cancelled before the service is fully implemented Supports network topology and protocol change APNOM 2003 (9) Internet Access Over Cable Internet Access Over PSTN Internet Access Over LL Internet Aceess Over AP ……. ……
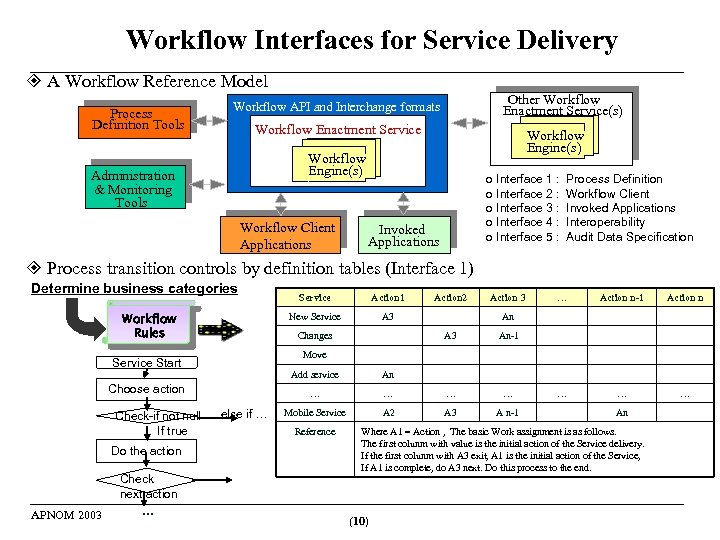
Workflow Interfaces for Service Delivery A Workflow Reference Model Process Definition Tools Other Workflow Enactment Service(s) Workflow API and Interchange formats Workflow Enactment Service Workflow Engine(s) Administration & Monitoring Tools Workflow Client Applications o Interface 1 : o Interface 2 : o Interface 3 : o Interface 4 : o Interface 5 : Invoked Applications Process Definition Workflow Client Invoked Applications Interoperability Audit Data Specification Process transition controls by definition tables (Interface 1) Determine business categories APNOM 2003 Check next action … Action 2 Action 3 … Action n-1 Action n … … … An A 3 An-1 Move Add service else if … An … Choose action Do the action A 3 Changes Service Start Check-if not null If true Action 1 New Service Workflow Rules Service … … … Mobile Service A 2 A 3 A n-1 Reference An Where A 1 = Action , The basic Work assignment is as follows. The first colunm with value is the initial action of the Service delivery. If the first colunm with A 3 exit, A 1 is the initial action of the Service, If A 1 is complete, do A 3 next. Do this process to the end. (10)
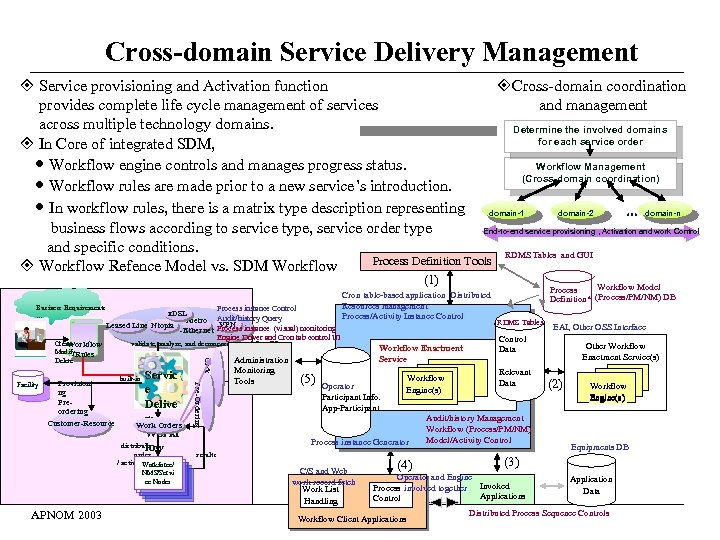
Cross-domain Service Delivery Management Service provisioning and Activation function Cross-domain coordination provides complete life cycle management of services and management across multiple technology domains. Determine the involved domains for each service order In Core of integrated SDM, Workflow engine controls and manages progress status. Workflow Management (Cross-domain coordination) Workflow rules are made prior to a new service’s introduction. In workflow rules, there is a matrix type description representing domain-1 domain-2 … domain-n business flows according to service type, service order type End-to-end service provisioning , Activation and work Control and specific conditions. RDMS Tables and GUI Process Definition Tools Workflow Refence Model vs. SDM Workflow (1) Order Tracking Pre-Ordering Workflow Model Process Cron table-based application Distributed Definition* (Process/PM/NM) DB Resources management Business Requirements Process instance Control x. DSL … Process/Activity Instance Control Metro Audit/history Query RDMS Tables VPN Leased Line Ntopia EAI, Other OSS Interface Process instance (visual) monitoring Workflow API and Interchange formats -Ethernet Engine Driver and Cron tab control UI Control validate, analyze, and decompose to workflow SO Create Workflow Other Workflow Enactment Service Data Workflow Enactment Modify. Rules Enactment Service(s) Service Delete Administration Monitoring Relevant built-in Servic Workflow (5) Operator Tools Provisioni Data Facility (2) Workflow Engine(s) e ng Participant Info. Engine(s) Pre. Delive App-Participant ordering Audit/history Management ry Customer-Resource Work Orders Workflow (Process/PM/NM) Workf (4) Model/Activity Control Process instance Generator distribute Equipments DB low order / activation Workforce/ NMS/Servi ce Nodes APNOM 2003 results C/S and Web work record fetch Work List Handling (4) (3) Operator and Engine Application Process involved together Invoked Process Data Applications Control Distributed Process Sequence Controls Workflow Client Applications (11)
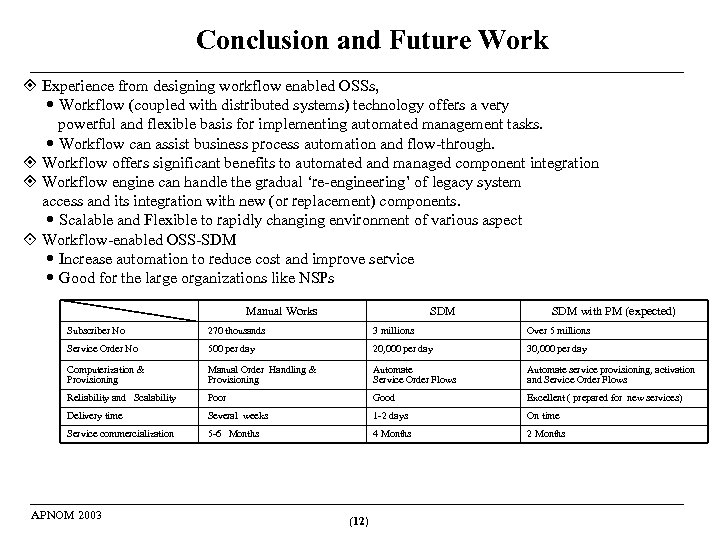
Conclusion and Future Work Experience from designing workflow enabled OSSs, Workflow (coupled with distributed systems) technology offers a very powerful and flexible basis for implementing automated management tasks. Workflow can assist business process automation and flow-through. Workflow offers significant benefits to automated and managed component integration Workflow engine can handle the gradual ‘re-engineering’ of legacy system access and its integration with new (or replacement) components. Scalable and Flexible to rapidly changing environment of various aspect Workflow-enabled OSS-SDM Increase automation to reduce cost and improve service Good for the large organizations like NSPs Manual Works SDM with PM (expected) Subscriber No 270 thousands 3 millions Over 5 millions Service Order No 500 per day 20, 000 per day 30, 000 per day Computerization & Provisioning Manual Order Handling & Provisioning Automate Service Order Flows Automate service provisioning, activation and Service Order Flows Reliability and Scalability Poor Good Excellent ( prepared for new services) Delivery time Several weeks 1 -2 days On time Service commercialization 5 -6 Months 4 Months 2 Months APNOM 2003 (12)
e9bb67c1a04a1c04158a75fded20af4f.ppt